Rivastigmine Tartrate
Rivastigmine Tartrate Prescribing Information
Rivastigmine tartrate is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor indicated for treatment of:
• Mild-to-moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type (AD) (
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of mild-to-moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type (AD).
• Mild-to-moderate dementia associated with Parkinson's disease (PD) (
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of mild-to-moderate dementia associated with Parkinson's disease (PD).
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The recommended dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is 6 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 3 mg to 6 mg twice a day). There is evidence from the clinical trials that doses at the higher end of this range may be more beneficial.
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 2 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 2 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
•
•
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The recommended dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is 6 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 3 mg to 6 mg twice a day). There is evidence from the clinical trials that doses at the higher end of this range may be more beneficial.
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 2 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 2 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules shown to be effective in the single controlled clinical trial conducted in dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease is 3 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 1.5 mg to 6 mg twice a day).
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 4 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 4 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
• Initiate treatment with 1.5 mg twice a day
• After a minimum of 4 weeks, if tolerated, increase dose to 3 mg twice a day and further to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day if tolerated with a minimum of 4 weeks at each dose (
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules shown to be effective in the single controlled clinical trial conducted in dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease is 3 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 1.5 mg to 6 mg twice a day).
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 4 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 4 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening (
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The recommended dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is 6 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 3 mg to 6 mg twice a day). There is evidence from the clinical trials that doses at the higher end of this range may be more beneficial.
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 2 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 2 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules should be taken with meals in divided doses in the morning and evening.
The dosage of rivastigmine tartrate capsules shown to be effective in the single controlled clinical trial conducted in dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease is 3 mg to 12 mg per day, administered twice a day (daily doses of 1.5 mg to 6 mg twice a day).
Initiate treatment with the 1.5 mg twice a day with rivastigmine tartrate capsules.
After a minimum of 4 weeks and if well tolerated, increase the dose to 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg twice a day and 6 mg twice a day should be attempted after a minimum of 4 weeks at the previous dose and if well tolerated. The maximum dose is 6 mg twice a day (12 mg per day).
Rivastigmine tartrate oral solution and rivastigmine tartrate capsules may be interchanged at equal doses.
• Capsules: 1.5 mg, 3 mg, 4.5 mg, or 6 mg (
Capsules, containing rivastigmine tartrate equivalent to 1.5 mg, 3 mg, 4.5 mg, or 6 mg of rivastigmine base, are available as follows:
1.5 mg capsule - white to off white powder filled in size "2" hard gelatin capsules with yellow opaque color cap and yellow opaque color body imprinted "C 91".
3 mg capsule - white to off white powder filled in size "2" hard gelatin capsules with orange opaque color cap and orange opaque color body imprinted "C 92".
4.5 mg capsule - white to off white powder filled in size "2" hard gelatin capsules with red opaque color cap and red opaque color body imprinted "C 93".
6 mg capsule - white to off white powder filled in size "2" hard gelatin capsules with red opaque color cap and orange opaque color body imprinted "C 94".
There are no adequate data on the developmental risks associated with the use of rivastigmine tartrate in pregnant women. In animals, no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development were observed at oral doses 2-4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD)
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules are contraindicated in patients with:
• known hypersensitivity to rivastigmine, other carbamate derivatives or other components of the formulation
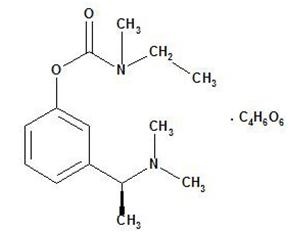
Rivastigmine tartrate is a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor and is known chemically as (S)-N-Ethyl-N-methyl-3-[1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-phenyl carbamate hydrogen-(2R,3R)-tartrate. Rivastigmine tartrate is commonly referred to in the pharmacological literature as SDZ ENA 713 or ENA 713. It has an empirical formula of C14H22N2O2• C4H6O6(hydrogen tartrate salt-hta salt) and a molecular weight of 400.43 g/mol (hta salt). Rivastigmine tartrate is a white to off-white, fine crystalline powder that is very soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and acetonitrile, slightly soluble in n-octanol and very slightly soluble in ethyl acetate.
The distribution coefficient at 37°C in n-octanol/phosphate buffer solution pH 7 is 3.0.
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules, USP contain rivastigmine tartrate, equivalent to 1.5 mg, 3 mg, 4.5 mg, and 6 mg of rivastigmine base for oral administration. Inactive ingredients are hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and colloidal silicon dioxide. Each hard-gelatin capsule contains gelatin, titanium dioxide and red and/or yellow iron oxides.

• a previous history of application site reaction with rivastigmine transdermal patch suggestive of allergic contact dermatitis, in the absence of negative allergy testing
There have been isolated postmarketing reports of patients experiencing disseminated allergic dermatitis when administered rivastigmine irrespective of the route of administration (oral or transdermal). Treatment should be discontinued if disseminated allergic dermatitis occurs
In patients who develop application site reactions, suggestive of allergic contact dermatitis to rivastigmine tartrate patch and who still require rivastigmine, treatment should be switched to oral rivastigmine only after negative allergy testing and under close medical supervision. It is possible that some patients sensitized to rivastigmine by exposure to rivastigmine patch may not be able to take rivastigmine in any form.
Isolated cases of generalized skin reactions have been described in postmarketing experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of rivastigmine tartrate capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
• Gastrointestinal adverse reactions may include significant nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia/decreased appetite, and weight loss, and may necessitate treatment interruption. Dehydration may result from prolonged vomiting or diarrhea and can be associated with serious outcomes. (
Rivastigmine tartrate can cause gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including significant nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia/decreased appetite, and weight loss. Dehydration may result from prolonged vomiting or diarrhea and can be associated with serious outcomes. The incidence and severity of these reactions are dose-related
If treatment is interrupted for longer than 3 days, treatment should be reinitiated with the lowest daily dose
Inform caregivers to monitor for gastrointestinal adverse reactions and to inform the physician if they occur. It is critical to inform caregivers that if therapy has been interrupted for more than 3 days because of intolerance, the next dose should not be administered without contacting the physician regarding proper retitration.
• Discontinue rivastigmine in case of disseminated allergic dermatitis, which may occur after oral or transdermal administration (
Rivastigmine tartrate capsules are contraindicated in patients with:
• known hypersensitivity to rivastigmine, other carbamate derivatives or other components of the formulation
• a previous history of application site reaction with rivastigmine transdermal patch suggestive of allergic contact dermatitis, in the absence of negative allergy testing
Isolated cases of generalized skin reactions have been described in postmarketing experience
• Known hypersensitivity to rivastigmine, other carbamate derivatives or other components of the formulation.
• History of application site reaction with rivastigmine transdermal patch suggestive of allergic contact dermatitis, in the absence of negative allergy testing.
There have been isolated postmarketing reports of patients experiencing disseminated allergic dermatitis when administered rivastigmine irrespective of the route of administration (oral or transdermal). Treatment should be discontinued if disseminated allergic dermatitis occurs
In patients who develop application site reactions, suggestive of allergic contact dermatitis to rivastigmine tartrate patch and who still require rivastigmine, treatment should be switched to oral rivastigmine only after negative allergy testing and under close medical supervision. It is possible that some patients sensitized to rivastigmine by exposure to rivastigmine patch may not be able to take rivastigmine in any form.