Scopolamine
Scopolamine Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions, Hyperthermia (Serious adverse reactions of hyperthermia have been reported postmarketing in adult and pediatric patients receiving transdermal scopolamine, including fatal cases. Anticholinergic agents, including scopolamine, can increase core body temperature and reduce sweating, which may cause further increases in body temperature. Hyperthermia may be exacerbated by exposure to external heat sources or high environmental temperature. Pediatric and geriatric patients may be more susceptible to these anticholinergic effects on thermoregulation. Advise patients if body temperature increases, or they are not sweating in warm environmental conditions, to remove the transdermal system and contact their healthcare provider. Symptoms may persist following removal of the used transdermal system as there may be continued systemic absorption of scopolamine through the skin. Scopolamine transdermal system is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5)] . | 4/2025 |
Scopolamine Transdermal System is indicated in adults for the prevention of:
- nausea and vomiting associated with motion sickness.
- post-operative nausea and vomiting (PONV) associated with recovery from anesthesia and/or opiate analgesia and surgery.
- Each scopolamine transdermal system is formulated to deliverin vivoapproximately 1 mg of scopolamine over 3 days.
- Only wear one transdermal system at any time.
- Do not cut the transdermal system.
- Apply the transdermal system to the skin in the postauricular area (hairless area behind one ear).
- After the transdermal system is applied on the dry skin behind the ear, wash hands thoroughly with soap and water and dry hands[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- If the transdermal system becomes displaced, discard the transdermal system, and apply a new transdermal system on the hairless area behind the other ear.
- Once the transdermal system has been affixed, avoid touching or applying pressure to the transdermal system while it is being worn, since pressure exerted on it may cause scopolamine to ooze out at the edge.
- Upon removal, fold the used transdermal system in half with the sticky side together, and discard in household trash in a manner that prevents accidental contact or ingestion by children, pets, or others.
- Wash the hands and application site with soap and water after transdermal system removal[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- Each scopolamine transdermal system delivers 1 mg of scopolamine over 3 days.
- Only wear one transdermal system at a time.
- Do not cut the transdermal system.
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after application.
- Avoid touching or applying pressure to the transdermal system once applied.
- Upon removal, fold used transdermal system in half with sticky side together, discard to prevent accidental contact or ingestion, and wash the hands and application site with soap and water.
- Motion Sickness: Apply one transdermal system to the hairless area behind one ear at least 4 hours before antiemetic effect is required for use up to 3 days. If therapy for more than 3 days is required, remove the first transdermal system and apply a new transdermal system behind the other ear. ()
2.2 Recommended Adult DosageMotion SicknessApply one scopolamine transdermal system to the hairless area behind one ear at least 4 hours before the antiemetic effect is required – for use up to 3 days. If therapy is required for longer than 3 days, remove the first transdermal system and apply a new scopolamine transdermal system behind the other ear.
PONVFor surgeries other than cesarean section: Apply one scopolamine transdermal system the evening before scheduled surgery. Remove the transdermal system 24 hours following surgery. - PONV: For surgeries other than cesarean section, apply one transdermal system behind the ear the evening before surgery and remove 24 hours following surgery. ()
2.2 Recommended Adult DosageMotion SicknessApply one scopolamine transdermal system to the hairless area behind one ear at least 4 hours before the antiemetic effect is required – for use up to 3 days. If therapy is required for longer than 3 days, remove the first transdermal system and apply a new scopolamine transdermal system behind the other ear.
PONVFor surgeries other than cesarean section: Apply one scopolamine transdermal system the evening before scheduled surgery. Remove the transdermal system 24 hours following surgery.
Transdermal system: 1 mg/3 days (
Transdermal system: 1 mg/3 days
Transdermal system: round patch with a tan coloured backing layer placed on a squarish release liner. The release liner is dimpled. The backing has an imprint of "Scopolamine 1 mg/3 days". The matrix is dispersed white and may contain light spots and is free of visible crystals.
- Geriatric Patients: Consider more frequent monitoring during treatment due to increased risk of CNS adverse reactions. (,
5.2 Neuropsychiatric Adverse ReactionsPsychiatric Adverse ReactionsScopolamine has been reported to exacerbate psychosis. Other psychiatric reactions have also been reported, including acute toxic psychosis, agitation, speech disorder, hallucinations, paranoia, and delusions
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Monitor patients for new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system. Also, monitor patients for new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during concomitant treatment with other drugs that are associated with similar psychiatric effects[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. In cases of psychiatric reactions occurring, scopolamine transdermal system should be removed at once. If, despite this, the symptoms persist in a severe form, instruct patients to seek medical attention.SeizuresSeizures and seizure-like activity have been reported in patients receiving scopolamine. Weigh this potential risk against the benefits before prescribing scopolamine transdermal system to patients with a history of seizures, including those receiving anti-epileptic medication or who have risk factors that can lower the seizure threshold.
Cognitive Adverse ReactionsScopolamine can cause drowsiness, disorientation, and confusion. Discontinue scopolamine transdermal system if signs or symptoms of cognitive impairment develop. If, despite this, the symptoms persist in a severe form, instruct patients to seek medical attention. Elderly and pediatric patients may be more sensitive to the neurological and psychiatric effects of scopolamine transdermal system. Consider more frequent monitoring during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system in elderly patients
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Scopolamine transdermal system is not approved for use in pediatric patients[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].Hazardous ActivitiesScopolamine transdermal system may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle, operating machinery, or participating in underwater sports. Concomitant use of other drugs that cause central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions (e.g., alcohol, sedatives, hypnotics, opiates, and anxiolytics) or have anticholinergic properties (e.g., other belladonna alkaloids, sedating antihistamines, meclizine, tricyclic antidepressants, and muscle relaxants) may increase this effect
[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery or participate in underwater sports until they are reasonably certain that scopolamine transdermal system does not affect them adversely.)8.5 Geriatric UseClinical trials of scopolamine transdermal system did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 years and older to determine if they respond differently from younger subjects. In other clinical experience, elderly patients had an increased risk of neurologic and psychiatric adverse reactions, such as hallucinations, confusion, dizziness, and drug withdrawal syndrome
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6)].Consider more frequent monitoring for CNS adverse reactions during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system in geriatric patients[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Serious adverse reactions of hyperthermia have been reported postmarketing in geriatric patients receiving transdermal scopolamine, including a fatal case. Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to the anticholinergic effects of disruption in thermoregulation. Advise patients if body temperature increases, or they are not sweating in warm environmental conditions, to remove the transdermal system and contact their healthcare provider
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. - Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Consider more frequent monitoring during treatment due to increased risk of CNS adverse reactions. (,
5.2 Neuropsychiatric Adverse ReactionsPsychiatric Adverse ReactionsScopolamine has been reported to exacerbate psychosis. Other psychiatric reactions have also been reported, including acute toxic psychosis, agitation, speech disorder, hallucinations, paranoia, and delusions
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Monitor patients for new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system. Also, monitor patients for new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during concomitant treatment with other drugs that are associated with similar psychiatric effects[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. In cases of psychiatric reactions occurring, scopolamine transdermal system should be removed at once. If, despite this, the symptoms persist in a severe form, instruct patients to seek medical attention.SeizuresSeizures and seizure-like activity have been reported in patients receiving scopolamine. Weigh this potential risk against the benefits before prescribing scopolamine transdermal system to patients with a history of seizures, including those receiving anti-epileptic medication or who have risk factors that can lower the seizure threshold.
Cognitive Adverse ReactionsScopolamine can cause drowsiness, disorientation, and confusion. Discontinue scopolamine transdermal system if signs or symptoms of cognitive impairment develop. If, despite this, the symptoms persist in a severe form, instruct patients to seek medical attention. Elderly and pediatric patients may be more sensitive to the neurological and psychiatric effects of scopolamine transdermal system. Consider more frequent monitoring during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system in elderly patients
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Scopolamine transdermal system is not approved for use in pediatric patients[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].Hazardous ActivitiesScopolamine transdermal system may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle, operating machinery, or participating in underwater sports. Concomitant use of other drugs that cause central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions (e.g., alcohol, sedatives, hypnotics, opiates, and anxiolytics) or have anticholinergic properties (e.g., other belladonna alkaloids, sedating antihistamines, meclizine, tricyclic antidepressants, and muscle relaxants) may increase this effect
[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery or participate in underwater sports until they are reasonably certain that scopolamine transdermal system does not affect them adversely.)8.6 Renal or Hepatic ImpairmentScopolamine transdermal system has not been studied in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Consider more frequent monitoring during treatment with scopolamine transdermal system in patients with renal or hepatic impairment because of the increased risk of CNS adverse reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Scopolamine transdermal system is contraindicated in patients with:
- angle closure glaucoma [see.]
5.1 Acute Angle Closure GlaucomaThe mydriatic effect of scopolamine may cause an increase in intraocular pressure resulting in acute angle closure glaucoma. Monitor intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma and adjust glaucoma therapy during scopolamine transdermal system use, as needed. Advise patients to immediately remove the transdermal system and contact their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of acute angle closure glaucoma (e.g., eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos or colored images in association with red eyes from conjunctival congestion and corneal edema).
- hypersensitivity to scopolamine or other belladonna alkaloids or to any ingredient or component in the formulation or delivery system. Reactions have included rash generalized and erythema [see.,
6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of scopolamine transdermal system. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Psychiatric disorders: acute psychosis including: disorientation, hallucinations, and paranoiaNervous system disorders: amnesia, coordination abnormalities, disturbance in attention, headache, restlessness, speech disorderGeneral disorders and administration site conditions: application site reactions (including blistering, burning, pruritus, and rash), and hyperthermiaEye disorders: amblyopia, angle closure glaucoma, dry eyes, eyelid irritation, eye pruritusSkin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: erythema, rash generalized, skin irritationRenal and urinary disorders: dysuriaEar and labyrinth disorders: vertigo]11 DESCRIPTIONScopolamine transdermal system is designed for continuous release of scopolamine following application to an area of intact skin on the head, behind the ear. Each system contains 1.3 mg of scopolamine base. Scopolamine is (9-methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo [3.3.1.02,4]nonan-7-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate. The empirical formula is C17H21NO4and its structural formula is:
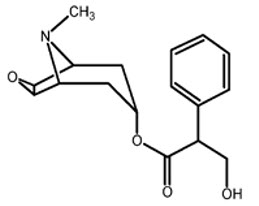
Scopolamine has a molecular weight of 303.35 and a pKa of 7.55 to 7.81. The scopolamine transdermal system is a circular, 0.28 mm thick, 2.5 cm2film with four layers. Proceeding from the visible surface towards the surface attached to the skin, these layers are: (1) a backing membrane of tan-colored, aluminized, polyester film; (2) a drug layer of scopolamine, light mineral oil, isopropyl palmitate, crospovidone, and polyisobutylene; (3) a microporous polypropylene membrane that controls the rate of delivery of scopolamine from the system to the skin surface; and (4) a contact layer formulation of mineral oil, polyisobutylene, isopropyl palmitate, crospovidone, and scopolamine. A release liner of siliconized polyester, which covers the adhesive layer, is removed before the system is used.
Cross section of the system:


Chemical Structure 
Image