Sevoflurane
Sevoflurane Prescribing Information
Sevoflurane is indicated for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia in adult and pediatric patients for inpatient and outpatient surgery.
Sevoflurane should be administered only by persons trained in the administration of general anesthesia. Facilities for maintenance of a patent airway, artificial ventilation, oxygen enrichment, and circulatory resuscitation must be immediately available. Since level of anesthesia may be altered rapidly, only vaporizers producing predictable concentrations of sevoflurane should be used.
The concentration of sevoflurane being delivered from a vaporizer should be known. This may be accomplished by using a vaporizer calibrated specifically for sevoflurane. The administration of general anesthesia must be individualized based on the patient's response.
- Known or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. (see WARNINGS- Malignant Hyperthermia, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY – Pharmacogenomics).
- Known or suspected sensitivity to sevoflurane or to other halogenated inhalational anesthetics.
Adverse events are derived from controlled clinical studies conducted in the United States, Canada, and Europe. The reference drugs were isoflurane, enflurane, and propofol in adults and halothane in pediatric patients. The studies were conducted using a variety of premedications, other anesthetics, and surgical procedures of varying length. Most adverse events reported were mild and transient, and may reflect the surgical procedures, patient characteristics (including disease) and/or medications administered.
Of the 5182 patients enrolled in the clinical studies, 2906 were exposed to sevoflurane, including 118 adults and 507 pediatric patients who underwent mask induction. Each patient was counted once for each type of adverse event. Adverse events reported in patients in clinical studies and considered to be possibly or probably related to sevoflurane are presented within each body system in order of decreasing frequency in the following listings. One case of malignant hyperthermia was reported in pre-registration clinical studies.
In clinical studies, no significant adverse reactions occurred with other drugs commonly used in the perioperative period, including: central nervous system depressants, autonomic drugs, skeletal muscle relaxants, anti-infective agents, hormones and synthetic substitutes, blood derivatives, and cardiovascular drugs.
Epinephrine administered with sevoflurane may increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. Monitor the electrocardiogram and blood pressure and ensure emergency medications to treat ventricular arrhythmias are readily available.
Sevoflurane may lead to marked hypotension in patients treated with calcium antagonists. Blood pressure should be closely monitored and emergency medications to treat hypotension should be readily available when calcium antagonists are used concomitantly with sevoflurane.
In animals, impairment of atrioventricular conduction has been observed when verapamil and sevoflurane are administered concomitantly.
See
Concomitant use of MAO inhibitors and inhalational anesthetics may increase the risk of hemodynamic instability during surgery or medical procedures.
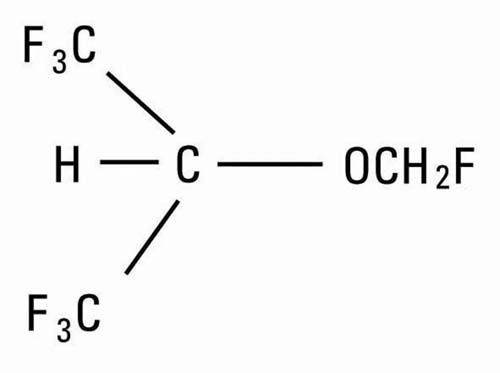
Sevoflurane USP, volatile liquid for inhalation, a nonflammable and nonexplosive liquid administered by vaporization, is a halogenated general inhalation anesthetic drug. Sevoflurane is fluoromethyl 2,2,2,-trifluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl) ethyl ether and its structural formula is: