Smoflipid
Smoflipid Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions (
SMOFlipid is indicated in adult and pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates, as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
• For intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein. ()2.1 Important Administration Instructions• SMOFlipid is prepared and administered by a healthcare provider in the inpatient setting. Patients and caregivers may prepare and administer SMOFlipid for home use after appropriate training by a trained healthcare provider.• SMOFlipid is for intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein.• Do not exceed the recommended maximum infusion rate in Table 1[see Dosage and Administration and Warnings and Precautions ].• SMOFlipid admixtures with osmolarityͦ Greater than or equal to 900 mOsm/L must be infused through a central vein.ͦ Less than 900 mOsm/L may be administered either through a central or peripheral vein.
• Use a 1.2 micron in-line filter during administration.• Use a dedicated infusion line without any connections. Do not connect multiple medications in series.• To prevent air embolism, use a nonvented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set and fully evacuate residual gas in the bag prior to administration.• Do not pressurize the flexible bag to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off the pump before the bag runs dry.• Do not use infusion sets and lines that contain di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), including infusion sets that contain polyvinyl chloride (PVC) components, because they contain DEHP as a plasticizer.• SMOFlipid can be infused concurrently into the same vein as dextrose-amino acid solutions (as part of PN) by a Y-connector located near the infusion site; flow rates of each solution should be controlled separately by infusion pumps.• After connecting the infusion set, start infusion of SMOFlipid immediately. Complete the infusion within 12 hours when using a Y-connector and within 24 hours when used as part of an admixture.
• SMOFlipid Pharmacy Bulk Package is only indicated for use in pharmacy admixture programs for the preparation of three-in-one or total nutrition admixtures. ()2.2 Preparation InstructionsUse the following instructions to prepare single-dose SMOFlipid 100 mL, 250 mL, and 500 mL Flexible Containers for administration:
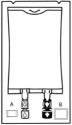
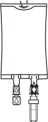
1.000000000000000e+00 Inspect Bag• Inspect the integrity indicator (Oxalert®) (A) before removing the overpouch.• Discard the product if the indicator is black, overpouch is opened or damaged, emulsion color is not white, or seals of bag are broken.
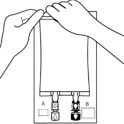
2.000000000000000e+00 Remove Overpouch• Place the bag on a clean, flat surface.• Tear overpouch at notch and pull down.• Discard the Oxalert sachet (A) and the oxygen absorber (B).• Visually inspect the bag and contents for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The lipid emulsion should be a homogenous liquid with a milky white appearance. If the mixture is not white or the emulsion has separated (noted by discoloration, phase separation, or oily droplets), or if particulates and/or leakage are observed, discard the bag.
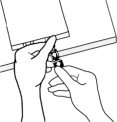
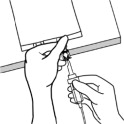
3.000000000000000e+00 Spike Bag• Identify the infusion port (bluecap with the arrow pointing away from the bag).• Immediately before inserting the infusion set, break off theblueinfusion port cap.• Use infusion sets according to ISO Number 8536-4 with an external spike diameter of 5.5 to 5.7 mm and use a nonvented infusion set or close the air-inlet on a vented set.• Use a 1.2 micron in-line filter for administration.• Hold the base of the infusion port.• Insert the spike through the infusion port by rotating your wrist slightly until the spike is inserted.• Do not pierce the infusion port more than once.
4.000000000000000e+00 Hang the bag• On the hanger cut and start infusion.• Discard unused portion.
SMOFlipid 100 mL, 250 mL and 500 mL single-dose Flexible Containers• After removing the overpouch, infuse immediately. If not used immediately, the product should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no longer than 24 hours. After removal from storage, infuse within 12 hours when using a Y-connector and within 24 hours when used as part of an admixture.
SMOFlipid 1000 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package• For admixing use only and not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, transfer to a separate PN container for individual patient use.• Transfer the contents through the blue infusion port using a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set. Discard any unused contents.• Use the Pharmacy Bulk Package immediately for admixing after removal from overpouch. If not used immediately, the product can be stored for no longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). After removal from storage, and once the closure is penetrated, use Pharmacy Bulk Package contents within 4 hours.
Admixing Instructions• Prepare the admixture in PN containers using strict aseptic techniques to avoid microbial contamination.• Do not add SMOFlipid to the PN container first; destabilization of the lipid may occur. The prime destabilizers of emulsions are excessive acidity (such as a pH <5) and inappropriate electrolyte content. Amino acid solutions exert buffering effects that protect the emulsion from destabilization. Give careful consideration to the addition of divalent cations (Ca++and Mg++), which have been shown to cause emulsion instability.• Do not inject additives directly into SMOFlipid.• SMOFlipid may be mixed with amino acid and dextrose injections to produce “all-in-one” PN admixtures. The mixing sequence below must be followed for manual compounding to minimize pH-related problems by ensuring that typically acidic dextrose injections are not mixed with lipid emulsions alone; shake bags gently after each addition.ͦ Transfer dextrose injection to the PN container.ͦ Transfer amino acid injection.ͦ Transfer SMOFlipid.
• Simultaneous transfer of amino acid injection, dextrose injection, and SMOFlipid to the PN container is also permitted; follow automated compounding device instructions as indicated. Use gentle agitation during admixing to minimize localized concentration effects.• Additions to the PN admixtures should be evaluated by a pharmacist for compatibility. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC.• Inspect the admixture to ensure that precipitates have not formed during preparation of the admixture and the emulsion has not separated. Discard the admixture if any of the above are observed.• Infuse admixtures containing SMOFlipid immediately. If not used immediately, store admixtures under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no longer than 24 hours. Infusion must be complete within 24 hours after removal from refrigeration. Discard any remaining admixture.• Protect the admixed PN solution from light.

smofl-img-01.jpg 
smofl-img-02.jpg 
smofl-img-03.jpg 
smofl-img-04.jpg 
smofl-img-05.jpg • Protect the admixed PN solution from light. ()2.2 Preparation InstructionsUse the following instructions to prepare single-dose SMOFlipid 100 mL, 250 mL, and 500 mL Flexible Containers for administration:





1.000000000000000e+00 Inspect Bag• Inspect the integrity indicator (Oxalert®) (A) before removing the overpouch.• Discard the product if the indicator is black, overpouch is opened or damaged, emulsion color is not white, or seals of bag are broken.
2.000000000000000e+00 Remove Overpouch• Place the bag on a clean, flat surface.• Tear overpouch at notch and pull down.• Discard the Oxalert sachet (A) and the oxygen absorber (B).• Visually inspect the bag and contents for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The lipid emulsion should be a homogenous liquid with a milky white appearance. If the mixture is not white or the emulsion has separated (noted by discoloration, phase separation, or oily droplets), or if particulates and/or leakage are observed, discard the bag.
3.000000000000000e+00 Spike Bag• Identify the infusion port (bluecap with the arrow pointing away from the bag).• Immediately before inserting the infusion set, break off theblueinfusion port cap.• Use infusion sets according to ISO Number 8536-4 with an external spike diameter of 5.5 to 5.7 mm and use a nonvented infusion set or close the air-inlet on a vented set.• Use a 1.2 micron in-line filter for administration.• Hold the base of the infusion port.• Insert the spike through the infusion port by rotating your wrist slightly until the spike is inserted.• Do not pierce the infusion port more than once.
4.000000000000000e+00 Hang the bag• On the hanger cut and start infusion.• Discard unused portion.
SMOFlipid 100 mL, 250 mL and 500 mL single-dose Flexible Containers• After removing the overpouch, infuse immediately. If not used immediately, the product should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no longer than 24 hours. After removal from storage, infuse within 12 hours when using a Y-connector and within 24 hours when used as part of an admixture.
SMOFlipid 1000 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package• For admixing use only and not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, transfer to a separate PN container for individual patient use.• Transfer the contents through the blue infusion port using a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set. Discard any unused contents.• Use the Pharmacy Bulk Package immediately for admixing after removal from overpouch. If not used immediately, the product can be stored for no longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). After removal from storage, and once the closure is penetrated, use Pharmacy Bulk Package contents within 4 hours.
Admixing Instructions• Prepare the admixture in PN containers using strict aseptic techniques to avoid microbial contamination.• Do not add SMOFlipid to the PN container first; destabilization of the lipid may occur. The prime destabilizers of emulsions are excessive acidity (such as a pH <5) and inappropriate electrolyte content. Amino acid solutions exert buffering effects that protect the emulsion from destabilization. Give careful consideration to the addition of divalent cations (Ca++and Mg++), which have been shown to cause emulsion instability.• Do not inject additives directly into SMOFlipid.• SMOFlipid may be mixed with amino acid and dextrose injections to produce “all-in-one” PN admixtures. The mixing sequence below must be followed for manual compounding to minimize pH-related problems by ensuring that typically acidic dextrose injections are not mixed with lipid emulsions alone; shake bags gently after each addition.ͦ Transfer dextrose injection to the PN container.ͦ Transfer amino acid injection.ͦ Transfer SMOFlipid.
• Simultaneous transfer of amino acid injection, dextrose injection, and SMOFlipid to the PN container is also permitted; follow automated compounding device instructions as indicated. Use gentle agitation during admixing to minimize localized concentration effects.• Additions to the PN admixtures should be evaluated by a pharmacist for compatibility. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC.• Inspect the admixture to ensure that precipitates have not formed during preparation of the admixture and the emulsion has not separated. Discard the admixture if any of the above are observed.• Infuse admixtures containing SMOFlipid immediately. If not used immediately, store admixtures under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no longer than 24 hours. Infusion must be complete within 24 hours after removal from refrigeration. Discard any remaining admixture.• Protect the admixed PN solution from light.

smofl-img-01.jpg 
smofl-img-02.jpg 
smofl-img-03.jpg 
smofl-img-04.jpg 
smofl-img-05.jpg • Recommended dosage depends on age, energy expenditure, clinical status, body weight, tolerance, ability to metabolize and eliminate lipids, and consideration of additional energy given to the patient. ()2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration• The recommended nutritional requirements of lipid and recommended dosages of SMOFlipid to be administered to meet those requirements for pediatric and adult patients are provided in Table 1, along with recommendations for the initial and maximum infusion rates.• The recommended duration of infusion for SMOFlipid will vary depending on the clinical situation. Adjust the administration flow rate by taking into account the dose being administered, the daily volume/intake, and the duration of the infusion[see Overdosage ].• When determining dose, energy supplied by dextrose and amino acids from PN, as well as energy from oral or enteral nutrition, has to be taken into account. Energy and lipid provided from lipid-based medications should also be taken into account (e.g., propofol).• Prior to administration of SMOFlipid, correct severe fluid and electrolyte disorders and measure serum triglyceride levels to establish a baseline value. In patients with elevated triglyceride levels, initiate SMOFlipid at a lower dosage and titrate in smaller increments, monitoring the triglyceride levels with each adjustment[see Warnings and Precautions ].• SMOFlipid contains 0.162 to 0.225 mg/mL of all-rac-alpha-tocopherol. Take into account the amount of all-rac-alpha-tocopherol in SMOFlipid when determining the need for additional supplementation.
Table 1: Recommended Pediatric and Adult Dosage and Infusion Rate *The neonatal period is defined as including term, post-term, and preterm newborn infants. The neonatal period for term and post-term infants is the day of birth plus 27 days. For preterm infants, the neonatal period is defined as the day of birth through the expected age of delivery plus 27 days (i.e., 44 weeks post-menstrual age). ** Daily dosage should also not exceed a maximum of 60% of total energy requirements [see Overdosage ].AgeNutritional RequirementsDirect Infusion RateRecommended Initial Dosage and Maximum Dosage
Initial
MaximumBirth to 2 years of age (including preterm and term neonates*)
[see Warnings and Precautions ]
Initial 0.5 to 1 g/kg/day not to exceed 3 g/kg/day**
0.1 to 0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age
Initial 1 to 2 g/kg/day
not to exceed 3 g/kg/day**
0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age
Initial 1 g/kg/day
not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day**0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Adults
1 to 2 g/kg/day
not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day**0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.5 mL/kg/hour• For information on the age-appropriate infusion rate, see the full prescribing information (,2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration• The recommended nutritional requirements of lipid and recommended dosages of SMOFlipid to be administered to meet those requirements for pediatric and adult patients are provided in Table 1, along with recommendations for the initial and maximum infusion rates.• The recommended duration of infusion for SMOFlipid will vary depending on the clinical situation. Adjust the administration flow rate by taking into account the dose being administered, the daily volume/intake, and the duration of the infusion[see Overdosage ].• When determining dose, energy supplied by dextrose and amino acids from PN, as well as energy from oral or enteral nutrition, has to be taken into account. Energy and lipid provided from lipid-based medications should also be taken into account (e.g., propofol).• Prior to administration of SMOFlipid, correct severe fluid and electrolyte disorders and measure serum triglyceride levels to establish a baseline value. In patients with elevated triglyceride levels, initiate SMOFlipid at a lower dosage and titrate in smaller increments, monitoring the triglyceride levels with each adjustment[see Warnings and Precautions ].• SMOFlipid contains 0.162 to 0.225 mg/mL of all-rac-alpha-tocopherol. Take into account the amount of all-rac-alpha-tocopherol in SMOFlipid when determining the need for additional supplementation.
Table 1: Recommended Pediatric and Adult Dosage and Infusion Rate *The neonatal period is defined as including term, post-term, and preterm newborn infants. The neonatal period for term and post-term infants is the day of birth plus 27 days. For preterm infants, the neonatal period is defined as the day of birth through the expected age of delivery plus 27 days (i.e., 44 weeks post-menstrual age). ** Daily dosage should also not exceed a maximum of 60% of total energy requirements [see Overdosage ].AgeNutritional RequirementsDirect Infusion RateRecommended Initial Dosage and Maximum Dosage
Initial
MaximumBirth to 2 years of age (including preterm and term neonates*)
[see Warnings and Precautions ]
Initial 0.5 to 1 g/kg/day not to exceed 3 g/kg/day**
0.1 to 0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age
Initial 1 to 2 g/kg/day
not to exceed 3 g/kg/day**
0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age
Initial 1 g/kg/day
not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day**0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.75 mL/kg/hour
Adults
1 to 2 g/kg/day
not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day**0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes
0.5 mL/kg/hour)5.1 Clinical Decompensation with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and InfantsIn the postmarketing setting, serious adverse reactions including acute respiratory distress, metabolic acidosis, and death have been reported in neonates and infants after rapid infusion of intravenous lipid emulsions. Hypertriglyceridemia was commonly reported.
Strictly adhere to the recommended total daily dosage; the hourly infusion rate should not exceed 0.75 mL/kg/hour
[see Dosage and Administration ].Preterm and small for gestational age infants have poor clearance of intravenous lipid emulsion and increased free fatty acid plasma levels following lipid emulsion infusion.
Carefully monitor the infant's ability to eliminate the infused lipids from the circulation (e.g., measure serum triglycerides and/or plasma free fatty acid levels). If signs of poor clearance of lipids from the circulation occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation
[see Warnings and Precautions and Overdosage ].
Age | Nutritional Requirements | |
Initial Recommended Dosage |
| |
Birth to 2 years of age (including preterm and term neonates) | 0.5 to 1 g/kg/day | 3 g/kg/day |
Pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age | 1 to 2 g/kg/day | 3 g/kg/day |
Pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age | 1 g/kg/day | 2.5 g/kg/day |
Adults | 1 to 2 g/kg/day | 2.5 g/kg/day |
SMOFlipid is a sterile, homogenous lipid injectable emulsion in Flexible Containers supplied as:
• 20 g of lipid/100 mL in 100 mL single-dose Flexible Container• 50 g of lipid/250 mL in 250 mL single-dose Flexible Container• 100 g of lipid/500 mL in 500 mL single-dose Flexible Container• 200 g of lipid/1000 mL in 1000 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package
Administration of the recommended dose of SMOFlipid is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. No animal reproduction studies have been conducted with SMOFlipid. There are risks to the fetus associated with severe malnutrition during pregnancy (
Severe malnutrition in pregnant women is associated with preterm delivery, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malformations, and perinatal mortality. Parenteral nutrition should be considered if the pregnant woman's nutritional requirements cannot be fulfilled by oral or enteral intake.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Use of SMOFlipid is contraindicated in patients with:
• Known hypersensitivity to fish, egg, soybean, peanut or any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid[see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.3 Hypersensitivity ReactionsSMOFlipid contains soybean oil, fish oil, and egg phospholipids, which may cause hypersensitivity reactions. Cross reactions have been observed between soybean and peanut. In postmarketing experience, anaphylaxis has been reported following SMOFlipid administration[see Adverse Reactions ].SMOFlipid is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to fish, egg, soybean, peanut or any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid[see Contraindications ]. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, stop infusion of SMOFlipid immediately and initiate appropriate treatment and supportive measures.• Severe disorders of lipid metabolism characterized by hypertriglyceridemia (serum triglyceride >1,000 mg/dL)[see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.7 HypertriglyceridemiaThe use of SMOFlipid is contraindicated in patients with hypertriglyceridemia with serum triglyceride concentrations >1,000 mg/dL.
Patients with conditions such as inherited lipid disorders, obesity, diabetes mellitus, or metabolic syndromes have a higher risk of developing hypertriglyceridemia with the use of SMOFlipid. In addition, patients with hypertriglyceridemia may have worsening of their hypertriglyceridemia with administration of SMOFlipid. Excessive dextrose administration may further increase such risk.
Evaluate patients' capacity to metabolize and eliminate the infused lipid emulsion by measuring serum triglycerides before the start of infusion (baseline value) and regularly throughout treatment. If triglyceride levels are above 400 mg/dL in adults, stop the SMOFlipid infusion and monitor serum triglyceride levels to avoid clinical consequences of hypertriglyceridemia such as pancreatitis. In pediatric patients with hypertriglyceridemia, lower triglyceride levels (i.e., below 400 mg/dL) may be associated with adverse reactions. Monitor serum triglyceride levels to avoid potential complications with hypertriglyceridemia such as pancreatitis, lipid pneumonitis, and neurologic changes, including kernicterus.
To minimize the risk of new or worsening of hypertriglyceridemia, assess high-risk patients for their overall energy intake including other sources of lipids and dextrose, as well as concomitant drugs that may affect lipid and dextrose metabolism.