Sorafenib
Sorafenib Prescribing Information
Tablets: 200 mg sorafenib, round, biconvex, pink film-coated tablets debossed with “TV” on one side and “S3” on the other side.
- Sorafenib tablets are contraindicated in patients with known severe hypersensitivity to sorafenib or any other component of sorafenib tablets.
- Sorafenib in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel is contraindicated in patients with squamous cell lung cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (.)]
5.8 Increased Mortality
Observed with Sorafenib Administered in Combination with Carboplatin/Paclitaxel
and Gemcitabine/Cisplatin in Squamous Cell Lung CancerIn a subset analysis of two randomized controlled trials in chemo-naive patients with Stage IIIB-IV non-small cell lung cancer, patients with squamous cell carcinoma experienced higher mortality with the addition of sorafenib compared to those treated with carboplatin/paclitaxel alone (HR 1.81; 95% CI 1.19, 2.74) and gemcitabine/cisplatin alone (HR 1.22; 95% CI 0.82, 1.80). The use of sorafenib in combination with carboplatin/paclitaxel is contraindicated in patients with squamous cell lung cancer. Sorafenib in combination with gemcitabine/cisplatin is not recommended in patients with squamous cell lung cancer. The safety and effectiveness of sorafenib has not been established in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular events [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Cardiovascular EventsIn the SHARP (HCC) study, the incidence of cardiac ischemia/infarction was 2.7% in sorafenib-treated patients compared with 1.3% in those receiving placebo; in the TARGET (RCC) study, the incidence of cardiac ischemia/infarction was higher in the sorafenib-treated group (2.9%) compared with patients receiving placebo (0.4%), and in the DECISION (DTC) study, the incidence of cardiac ischemia/infarction was 1.9% in the sorafenib-treated group compared with 0% in patients receiving placebo. Patients with unstable coronary artery disease or recent myocardial infarction were excluded from this study. In multiple clinical trials, congestive heart failure has been reported in 1.9% of sorafenib-treated patients (N=2276)
[see Adverse Reactions ].Consider temporary or permanent discontinuation of sorafenib in patients who develop cardiovascular events
[see Dosage and Administration ]. - Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.2 HemorrhageAn increased risk of bleeding may occur following sorafenib administration. In the SHARP (HCC) study, the rates of bleeding from esophageal varices (2.4% and 4%) and of bleeding with a fatal outcome from any site (2.4% and 4%) were similar in sorafenib-treated patients and those receiving placebo, respectively. In the TARGET (RCC) study, bleeding was reported in 15.3% of patients in the sorafenib-treated group and 8.2% of patients receiving placebo. The incidence of Grade 3 and 4 bleeding was 2% and 0%, respectively, in sorafenib-treated patients, and 1.3% and 0.2%, respectively, in those receiving placebo. There was one fatal hemorrhage in each treatment group in the TARGET (RCC) study. In the DECISION (DTC) study, bleeding was reported in 17.4% of sorafenib-treated patients and 9.6% of those receiving placebo; however, the incidence of Grade 3 bleeding was similar (1% and 1.4%) in sorafenib-treated patients and in those receiving placebo.
If any bleeding necessitates medical intervention, consider permanent discontinuation of sorafenib
[see Dosage and Administration ]. Due to the potential risk of bleeding, treat tracheal, bronchial, and esophageal infiltration with local therapy prior to administering sorafenib in patients with DTC. - Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.3 HypertensionIn the SHARP (HCC) study, hypertension was reported in 9.4% of sorafenib-treated patients and 4.3% of patients receiving placebo. In the TARGET (RCC) study, hypertension was reported in 16.9% of sorafenib-treated patients and 1.8% of patients receiving placebo. In the DECISION (DTC) study, hypertension was reported in 40.6% of sorafenib-treated patients and 12.4% of patients receiving placebo. Hypertension was usually mild to moderate, occurred early in the course of treatment, and was managed with standard antihypertensive therapy. Permanent discontinuation due to hypertension occurred in 1 of 297 sorafenib-treated patients in the SHARP (HCC) study, 1 of 451 sorafenib-treated patients in the TARGET (RCC) study, and 1 of 207 sorafenib-treated patients in the DECISION (DTC) study.
Monitor blood pressure weekly during the first 6 weeks of sorafenib. Thereafter, monitor blood pressure and treat hypertension, if required, in accordance with standard medical practice. In cases of severe or persistent hypertension despite institution of antihypertensive therapy, consider temporary or permanent discontinuation of sorafenib
[see Dosage and Administration ]. - Dermatologic toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.4 Dermatologic ToxicitiesHand-foot skin reaction and rash represent the most common adverse reactions attributed to sorafenib. Rash and hand-foot skin reaction are usually Grade 1 and 2 and generally appear during the first six weeks of treatment with sorafenib. Permanent discontinuation of therapy due to hand-foot skin reaction occurred in 4 (1.3%) of 297 sorafenib-treated patients with HCC, 3 (0.7%) of 451 sorafenib-treated patients with RCC, and 11 (5.3%) of 207 sorafenib-treated patients with DTC.
Management of dermatologic toxicities may include topical therapies for symptomatic relief, temporary treatment interruption and/or dose reduction of sorafenib, or in severe or persistent cases, permanent discontinuation of sorafenib
[see Dosage and Administration ].There have been reports of severe dermatologic toxicities, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). These cases may be life-threatening. Discontinue sorafenib if SJS or TEN are suspected.
- Gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.5 Gastrointestinal
PerforationGastrointestinal perforation has been reported in less than 1% of patients taking sorafenib. In some cases this was not associated with apparent intra-abdominal tumor. In the event of a gastrointestinal perforation, permanently discontinue sorafenib.
- QT interval prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions () and Clinical Pharmacology (
5.9 QT Interval ProlongationSorafenib can prolong the QT/QTc interval. QT/QTc interval prolongation increases the risk for ventricular arrhythmias.
Avoid sorafenib in patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Monitor electrolytes and electrocardiograms in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, drugs known to prolong the QT interval, including Class Ia and III antiarrhythmics. Correct electrolyte abnormalities (magnesium, potassium, calcium). Interrupt sorafenib if QTc interval is greater than 500 milliseconds or for an increase from baseline of 60 milliseconds or greater
[see Clinical Pharmacology ].]12.2 PharmacodynamicsCardiac ElectrophysiologyThe effect of sorafenib 400 mg twice daily on the QTc interval was evaluated in a multi-center, open-label, non-randomized trial in 53 patients with advanced cancer. No large changes in the mean QTc intervals (that is, >20 ms) from baseline were detected in the trial. After one 28-day treatment cycle, the largest mean QTc interval change of 8.5 ms (upper bound of two-sided 90% confidence interval, 13.3 ms) was observed at 6 hours post-dose on day 1 of cycle 2
[see Warnings and Precautions , Drug Interactions ]. - Drug-induced liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.10 Drug-Induced Liver InjurySorafenib-induced hepatitis is characterized by a hepatocellular pattern of liver damage with significant increases of transaminases which may result in hepatic failure and death. Increases in bilirubin and INR may also occur. The incidence of severe drug-induced liver injury, defined as elevated transaminase levels above
20 times the upper limit of normal or transaminase elevations with significant clinical sequelae (for example, elevated INR, ascites, fatal, or transplantation), was two of 3,357 patients (0.06%) in a global monotherapy database.Monitor liver function tests regularly. In case of significantly increased transaminases without alternative explanation, such as viral hepatitis or progressing underlying malignancy, discontinue sorafenib
[see Dosage and Administration ]. - Impairment of TSH suppression in DTC [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.12 Impairment of
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression in Differentiated Thyroid CarcinomaSorafenib impairs exogenous thyroid suppression. In the DECISION (DTC) study, 99% of patients had a baseline thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level less than 0.5 mU/L. Elevation of TSH level above 0.5 mU/L was observed in 41% of sorafenib-treated patients as compared with 16% of those receiving placebo patients. For patients with impaired TSH suppression while receiving sorafenib, the median maximal TSH was 1.6 mU/L and 25% had TSH levels greater than 4.4 mU/L.
Monitor TSH levels monthly and adjust thyroid replacement medication as needed in patients with DTC.
Sorafenib, a kinase inhibitor, is the tosylate salt of sorafenib. Sorafenib tosylate, USP has the chemical name 4-(4-{3-[4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ureido}phenoxy)N2-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide 4-methylbenzene sulfonate. The molecular formula of sorafenib tosylate, USP is C21H16ClF3N4O3 x C7H8O3S and the molecular weight of sorafenib tosylate, USP is 637.03 g/mole. Its structural formula is:
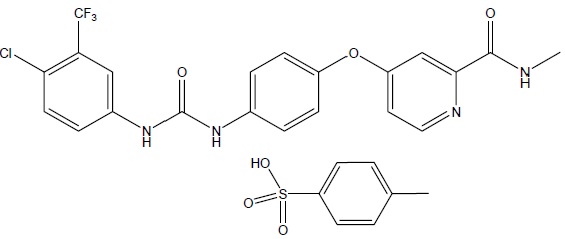
Sorafenib tosylate, USP is a white to yellowish or brownish solid. Sorafenib tosylate, USP is practically insoluble in aqueous media, slightly soluble in ethanol and soluble in PEG 400.
Sorafenib tablets, USP for oral use is supplied as film-coated tablets containing 200 mg sorafenib equivalent to 274 mg sorafenib tosylate, USP and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 400, sodium lauryl sulfate, and titanium dioxide.
Sorafenib tablets, USP are supplied as round, biconvex, pink film-coated tablets, debossed with “TV” on one side and “S3” on the other side, each containing 200 mg of sorafenib equivalent to 274 mg of sorafenib tosylate, USP.
Bottles of 120 tablets (NDC 0480-5425-89)
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in a dry place.
Sorafenib is a kinase inhibitor that decreases tumor cell proliferation