Strensiq prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Strensiq patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP (2.2 )
- Recommended dosage regimen is 2 mg/kg administered subcutaneously three times per week, or 1 mg/kg administered six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen.
- The dose may be increased to 3 mg/kg three times per week for insufficient efficacy.
Juvenile-Onset HPP (2.3 )
- Recommended dosage regimen is 2 mg/kg administered subcutaneously three times per week, or 1 mg/kg administered six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen.
Preparation and Weight-Based Dosing (2.4 ):
- Caution: Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg because the systemic asfotase alfa exposure achieved with the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial (higher concentration) is lower than that achieved with the other strength vials (lower concentration). A lower exposure may not be adequate for this subgroup of patients.
- See full prescribing information for tables of weight-based dosing by treatment regimen.
Administration (2.5 ):
- For subcutaneous injection only.
- Rotate injection sites. Do not administer to areas that are reddened, inflamed or swollen.
Recommendations Prior to STRENSIQ Treatment
Initiate STRENSIQ under the supervision of a healthcare provider with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Dosage for Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of perinatal/infantile-onset HPP is 6 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as either:
- 2 mg/kg three times per week, or
- 1 mg/kg six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
The dose of STRENSIQ may be increased for lack of efficacy (e.g., no improvement in respiratory status, growth, or radiographic findings) up to 9 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as 3 mg/kg three times per week.
Dosage for Juvenile-Onset HPP
The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of juvenile-onset HPP is 6 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as either:
- 2 mg/kg three times per week, or
- 1 mg/kg six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Preparation and Weight-Based Dosing Tables
Caution: Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg because the systemic exposure of asfotase alfa achieved with the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial (higher concentration) is lower than that achieved with the other strength vials (lower concentration). A lower exposure may not be adequate for this subgroup of patients [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Determine the total weekly volume needed for the prescribed dosage based on the patient's weight and recommended dosage. Follow these steps to determine the patient dose.
- Total weekly dose (mg) = patient's weight (kg) × prescribed dose (mg/kg/week)
- Total injection volume (mL) per week = Total dose (mg/week) divided by the STRENSIQ concentration (40 mg/mL or 100 mg/mL). Note product concentrations are: 40 mg/mL (vial strengths 18 mg/0.45 mL, 28 mg/0.7 mL, 40 mg/mL) or 100 mg/mL (vial strength 80 mg/0.8 mL).
- Round total injection volume to the nearest hundredth of a mL
- Total number of vials per week = Total injection volume divided by vial volume (mL)
- Determine the number of injection days per week (three or six per week).
- Determine dose per injection day. Patient weights should be rounded to the nearest kilogram when determining dose. Use the following tables for guidance, for patients administering 2 mg/kg three times per week (Table 1), 1 mg/kg six times per week (Table 2) and for dose escalations to 3 mg/kg three times per week, recommended only for patients with perinatal/infantile-onset HPP [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] (Table 3).
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 6 mg | 0.15 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 8 mg | 0.2 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 10 mg | 0.25 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 12 mg | 0.3 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 14 mg | 0.35 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 8 | 16 mg | 0.4 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 9 | 18 mg | 0.45 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 10 | 20 mg | 0.5 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 15 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 20 | 40 mg | 1 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 25 | 50 mg | 1.25 mL | Two 28 mg/0.7 mL vials |
| 30 | 60 mg | 1.5 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 35 | 70 mg | 1.75 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 40 | 80 mg | 0.8 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 50 | 100 mg | 1 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 60 | 120 mg | 1.2 mL When preparing a volume for injection greater than 1 mL, split the volume equally between two syringes, and administer two injections. When administering the two injections, use two separate injection sites. | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 70 | 140 mg | 1.4 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 80 | 160 mg | 1.6 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 mg | 0.08 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 4 mg | 0.1 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 5 mg | 0.13 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 6 mg | 0.15 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 7 mg | 0.18 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 8 | 8 mg | 0.2 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 9 | 9 mg | 0.23 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 10 | 10 mg | 0.25 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 15 | 15 mg | 0.38 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 20 | 20 mg | 0.5 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 25 | 25 mg | 0.63 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 30 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 35 | 35 mg | 0.88 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 40 | 40 mg | 1 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 50 | 50 mg | 0.5 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 60 | 60 mg | 0.6 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 70 | 70 mg | 0.7 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 80 | 80 mg | 0.8 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 90 | 90 mg | 0.9 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 100 | 100 mg | 1 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 9 mg | 0.23 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 12 mg | 0.3 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 15 mg | 0.38 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 18 mg | 0.45 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 21 mg | 0.53 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 8 | 24 mg | 0.6 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 9 | 27 mg | 0.68 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 10 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 15 | 45 mg | 1.13 mL When preparing a volume for injection greater than 1 mL, split the volume equally between two syringes, and administer two injections. When administering the two injections, use two separate injection sites. | Two 28 mg/0.7 mL vials |
| 20 | 60 mg | 1.5 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 25 | 75 mg | 1.88 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
- Take the unopened STRENSIQ vial(s) out of the refrigerator 15 to 30 minutes before injecting to allow the liquid to reach room temperature.
Do not warm STRENSIQ in any other way (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water). - Inspect the solution in the vial(s) for particulate matter and discoloration. STRENSIQ is supplied as a clear, slightly opalescent or opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution; a few small translucent or white particles may be present. Discard any vial(s) not consistent with this appearance.
- Assemble injection supplies. Administer STRENSIQ using sterile disposable 1 mL syringes and ½ inch injection needles, between 25 to 29 gauge are recommended. The use of two different gauge needles is recommended, a larger bore needle (e.g. 25 gauge) for withdrawal of the medication, and a smaller bore needle (e.g. 29 gauge) for the injection. For doses greater than 1 mL, the injection volume should be split equally between two 1 mL syringes. Always use a new syringe and needle for each injection.
- Remove vial cap, aseptically prepare the vial and insert the syringe into the vial to withdraw the prescribed dose for administration. Do not shake.
- Remove any air bubbles in the syringe and verify the correct dose.
- STRENSIQ vials are for one time use only. Discard any unused product.
Administration
STRENSIQ is for subcutaneous injection only.
- When administering two injections, use two separate injection sites.
- Administer STRENSIQ within 3 hours upon removal of the vial(s) from refrigeration.
- Rotate the injection from among the following sites to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy: abdominal area, thigh, deltoid, or buttocks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
- Do NOT administer injections in areas that are reddened, inflamed, or swollen.
- Inject STRENSIQ subcutaneously into the determined site and properly dispose of the syringe and the needle.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Strensiq prescribing information
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate STRENSIQ under the supervision of a healthcare provider with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue STRENSIQ and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
| Boxed Warning | 7/2024 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.1 ) | 7/2024 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) | 7/2024 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
STRENSIQ ® is indicated for the treatment of patients with perinatal/infantile- and juvenile-onset hypophosphatasia (HPP).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP (2.2 )
- Recommended dosage regimen is 2 mg/kg administered subcutaneously three times per week, or 1 mg/kg administered six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen.
- The dose may be increased to 3 mg/kg three times per week for insufficient efficacy.
Juvenile-Onset HPP (2.3 )
- Recommended dosage regimen is 2 mg/kg administered subcutaneously three times per week, or 1 mg/kg administered six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen.
Preparation and Weight-Based Dosing (2.4 ):
- Caution: Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg because the systemic asfotase alfa exposure achieved with the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial (higher concentration) is lower than that achieved with the other strength vials (lower concentration). A lower exposure may not be adequate for this subgroup of patients.
- See full prescribing information for tables of weight-based dosing by treatment regimen.
Administration (2.5 ):
- For subcutaneous injection only.
- Rotate injection sites. Do not administer to areas that are reddened, inflamed or swollen.
Recommendations Prior to STRENSIQ Treatment
Initiate STRENSIQ under the supervision of a healthcare provider with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Dosage for Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of perinatal/infantile-onset HPP is 6 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as either:
- 2 mg/kg three times per week, or
- 1 mg/kg six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
The dose of STRENSIQ may be increased for lack of efficacy (e.g., no improvement in respiratory status, growth, or radiographic findings) up to 9 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as 3 mg/kg three times per week.
Dosage for Juvenile-Onset HPP
The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of juvenile-onset HPP is 6 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as either:
- 2 mg/kg three times per week, or
- 1 mg/kg six times per week. Injection site reactions may limit the tolerability of the six times per week regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Preparation and Weight-Based Dosing Tables
Caution: Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg because the systemic exposure of asfotase alfa achieved with the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial (higher concentration) is lower than that achieved with the other strength vials (lower concentration). A lower exposure may not be adequate for this subgroup of patients [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Determine the total weekly volume needed for the prescribed dosage based on the patient's weight and recommended dosage. Follow these steps to determine the patient dose.
- Total weekly dose (mg) = patient's weight (kg) × prescribed dose (mg/kg/week)
- Total injection volume (mL) per week = Total dose (mg/week) divided by the STRENSIQ concentration (40 mg/mL or 100 mg/mL). Note product concentrations are: 40 mg/mL (vial strengths 18 mg/0.45 mL, 28 mg/0.7 mL, 40 mg/mL) or 100 mg/mL (vial strength 80 mg/0.8 mL).
- Round total injection volume to the nearest hundredth of a mL
- Total number of vials per week = Total injection volume divided by vial volume (mL)
- Determine the number of injection days per week (three or six per week).
- Determine dose per injection day. Patient weights should be rounded to the nearest kilogram when determining dose. Use the following tables for guidance, for patients administering 2 mg/kg three times per week (Table 1), 1 mg/kg six times per week (Table 2) and for dose escalations to 3 mg/kg three times per week, recommended only for patients with perinatal/infantile-onset HPP [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] (Table 3).
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 6 mg | 0.15 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 8 mg | 0.2 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 10 mg | 0.25 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 12 mg | 0.3 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 14 mg | 0.35 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 8 | 16 mg | 0.4 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 9 | 18 mg | 0.45 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 10 | 20 mg | 0.5 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 15 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 20 | 40 mg | 1 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 25 | 50 mg | 1.25 mL | Two 28 mg/0.7 mL vials |
| 30 | 60 mg | 1.5 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 35 | 70 mg | 1.75 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 40 | 80 mg | 0.8 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 50 | 100 mg | 1 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 60 | 120 mg | 1.2 mL When preparing a volume for injection greater than 1 mL, split the volume equally between two syringes, and administer two injections. When administering the two injections, use two separate injection sites. | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 70 | 140 mg | 1.4 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 80 | 160 mg | 1.6 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 mg | 0.08 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 4 mg | 0.1 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 5 mg | 0.13 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 6 mg | 0.15 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 7 mg | 0.18 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 8 | 8 mg | 0.2 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 9 | 9 mg | 0.23 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 10 | 10 mg | 0.25 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 15 | 15 mg | 0.38 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 20 | 20 mg | 0.5 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 25 | 25 mg | 0.63 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 30 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 35 | 35 mg | 0.88 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 40 | 40 mg | 1 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 50 | 50 mg | 0.5 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 60 | 60 mg | 0.6 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 70 | 70 mg | 0.7 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 80 | 80 mg | 0.8 mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| 90 | 90 mg | 0.9 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| 100 | 100 mg | 1 mL | Two 80 mg/0.8 mL vials |
| Body Weight (kg) Do not use the 80 mg/0.8 mL vial of STRENSIQ in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | Dose to Inject | Volume to Inject | Vial Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 9 mg | 0.23 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 4 | 12 mg | 0.3 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 5 | 15 mg | 0.38 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 6 | 18 mg | 0.45 mL | 18 mg/0.45 mL |
| 7 | 21 mg | 0.53 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 8 | 24 mg | 0.6 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 9 | 27 mg | 0.68 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL |
| 10 | 30 mg | 0.75 mL | 40 mg/1 mL |
| 15 | 45 mg | 1.13 mL When preparing a volume for injection greater than 1 mL, split the volume equally between two syringes, and administer two injections. When administering the two injections, use two separate injection sites. | Two 28 mg/0.7 mL vials |
| 20 | 60 mg | 1.5 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
| 25 | 75 mg | 1.88 mL | Two 40 mg/1 mL vials |
- Take the unopened STRENSIQ vial(s) out of the refrigerator 15 to 30 minutes before injecting to allow the liquid to reach room temperature. Do not warm STRENSIQ in any other way (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water).
- Inspect the solution in the vial(s) for particulate matter and discoloration. STRENSIQ is supplied as a clear, slightly opalescent or opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution; a few small translucent or white particles may be present. Discard any vial(s) not consistent with this appearance.
- Assemble injection supplies. Administer STRENSIQ using sterile disposable 1 mL syringes and ½ inch injection needles, between 25 to 29 gauge are recommended. The use of two different gauge needles is recommended, a larger bore needle (e.g. 25 gauge) for withdrawal of the medication, and a smaller bore needle (e.g. 29 gauge) for the injection. For doses greater than 1 mL, the injection volume should be split equally between two 1 mL syringes. Always use a new syringe and needle for each injection.
- Remove vial cap, aseptically prepare the vial and insert the syringe into the vial to withdraw the prescribed dose for administration. Do not shake.
- Remove any air bubbles in the syringe and verify the correct dose.
- STRENSIQ vials are for one time use only. Discard any unused product.
Administration
STRENSIQ is for subcutaneous injection only.
- When administering two injections, use two separate injection sites.
- Administer STRENSIQ within 3 hours upon removal of the vial(s) from refrigeration.
- Rotate the injection from among the following sites to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy: abdominal area, thigh, deltoid, or buttocks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
- Do NOT administer injections in areas that are reddened, inflamed, or swollen.
- Inject STRENSIQ subcutaneously into the determined site and properly dispose of the syringe and the needle.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
STRENSIQ is a clear, slightly opalescent or opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution; few small translucent or white particles may be present. The product is available as:
- Injection: 18 mg/0.45 mL, 28 mg/0.7 mL, 40 mg/mL, or 80 mg/0.8 mL solution in single-dose vials
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on STRENSIQ use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, asfotase alfa administered intravenously to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis showed no evidence of fetotoxicity, embryolethality or teratogenicity at doses causing plasma exposures up to 21 and 24 times, respectively, the exposure at the recommended human dose (see Data ) .
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Asfotase alfa administered during the period of organogenesis to rats (from gestation Day 6 to Day 19 post-partum) and rabbits (on gestation days 7 to 19) at intravenous doses up to 50 mg/kg/day, approximately 21 and 24 times the human AUC of 65486 ng.h/mL at 2 mg/kg dose administered three times weekly for a 50 kg individual, respectively did not cause any adverse effects on embryofetal development. A pre- and post-natal development study in pregnant rats showed no evidence of adverse effects on pre- and post-natal development at intravenous doses (from Day 6 of gestation to Day 19 postpartum) of asfotase alfa up to 50 mg/kg/day approximately 21 times the human AUC of 65486 ng.h/mL at 2 mg/kg dose administered three times weekly for a 50 kg individual.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of asfotase alfa in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for STRENSIQ and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from asfotase alfa or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of STRENSIQ for the treatment of perinatal/infantile- and juvenile-onset HPP have been established in pediatric patients. Use of STRENSIQ for this indication is based on 4 prospective, open-label clinical trials conducted in 89 pediatric patients with perinatal/infantile-onset or juvenile-onset HPP [see Clinical Studies (14) ].
Geriatric Use
No patients with perinatal/infantile- or juvenile-onset HPP aged 65 years were enrolled in clinical trials of STRENSIQ. Therefore, there is no information available to determine whether patients aged 65 years and over respond differently from younger patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Lipodystrophy: Localized reactions were reported after several months of treatment; follow proper injection technique and rotate injection sites. (5.2 )
- Ectopic Calcifications (eye and kidneys): Monitor using ophthalmologic examinations and renal ultrasounds at baseline and periodically during treatment. (5.3 )
- Possible Immune-Mediated Clinical Effects: Evaluate patients for antibody formation if clinically indicated. (5.4 )
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
Life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies, including STRENSIQ. Signs and symptoms consistent with anaphylaxis included difficulty breathing, choking sensation, nausea, periorbital edema, and dizziness. These reactions have occurred within minutes after subcutaneous administration of STRENSIQ and have been observed more than 1 year after treatment initiation. Other hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported in STRENSIQ-treated patients, including vomiting, fever, headache, flushing, irritability, chills, erythema, rash, pruritus and oral hypoesthesia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy. Initiate STRENSIQ under the supervision of a healthcare provider with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue STRENSIQ and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Consider the risks and benefits of re-administering STRENSIQ to individual patients following a severe reaction. If the decision is made to re-administer the product, monitor patients for a reoccurrence of signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
Lipodystrophy
Localized lipodystrophy, including lipoatrophy and lipohypertrophy, has been reported at injection sites after several months in patients treated with STRENSIQ in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Advise patients to follow proper injection technique and to rotate injection sites [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Ectopic Calcifications
Patients with HPP are at increased risk for developing ectopic calcifications. Events of ectopic calcification, including ophthalmic (conjunctival and corneal) and renal (nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis), have been reported in the clinical trial experience with STRENSIQ. There was insufficient information to determine whether or not the reported events were consistent with the disease or due to STRENSIQ. No visual changes or changes in renal function were reported resulting from the occurrence of ectopic calcifications.
Ophthalmology examinations and renal ultrasounds are recommended at baseline and periodically during treatment with STRENSIQ to monitor for signs and symptoms of ophthalmic and renal ectopic calcifications and for changes in vision or renal function.
Possible Immune-Mediated Clinical Effects
In clinical trials, most STRENSIQ-treated patients developed anti-asfotase alfa antibodies and neutralizing antibodies which resulted in reduced systemic exposure of asfotase alfa [see Immunogenicity (6.2) ]. In postmarketing reports, some STRENSIQ-treated patients with initial therapeutic response subsequently developed recurrence and worsening in disease-associated laboratory and radiographic biomarkers (some in association with neutralizing antibodies) suggesting possible immune-mediated effects on STRENSIQ's pharmacologic action resulting in disease progression [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) ] . The effect of anti-asfotase alfa antibody formation on the long-term efficacy of STRENSIQ is unknown. There are no marketed anti-asfotase alfa antibody tests. If patients experience progression of HPP symptoms or worsening of disease-associated laboratory and imaging biomarkers after a period of initial therapeutic response to STRENSIQ, consider obtaining anti-asfotase alfa antibody testing by contacting STRENSIQ Medical Information at Alexion at 1-888-765-4747 or by email at medinfo@alexion.com. Close clinical follow up is recommended.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Lipodystrophy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Ectopic Calcifications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Possible Immune-Mediated Clinical Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to STRENSIQ in 99 patients with perinatal/infantile- or juvenile onset HPP (age 1 day to 58 years) treated with STRENSIQ, most for more than 2 years (range 1 day to 312 weeks [78 months]): 51 patients received at least 96 weeks (24 months) of treatment and 39 patients received 168 weeks (42 months) or more of treatment [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Common Adverse Reactions
Overall, the most common adverse reactions reported were injection site reactions (63%) . Other common adverse reactions included lipodystrophy (28%), ectopic calcifications (14%), and hypersensitivity reactions (12%).
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 10% in clinical trials following subcutaneous injection of STRENSIQ by patient population and STRENSIQ dosage regimen.
The frequency of injection site reactions, lipodystrophy and ectopic calcification were higher in patients with juvenile-onset HPP as compared to perinatal/infantile-onset HPP patients.
The majority of injection site reactions resolved within a week. Two patients experienced injection site reactions that led to reductions of their STRENSIQ dose. One patient switched from six times per week dosing to 3 times per week dosing as a result of injection site reactions. One other patient experienced a severe injection site reaction of injection site discoloration and withdrew from the trial.
| Perinatal/Infantile-onset HPP | Juvenile-onset HPP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Category or Term | STRENSIQ less than or equal to 6 mg/kg per week (N=66) n (%) | STRENSIQ more than 6 mg/kg/week Adverse reactions are from the combined period of 6 mg/kg and above (i.e. total drug exposure regardless of starting dose and intermediary doses as long as the patient reached doses > 6 mg/kg) (N=13) n (%) | Total (N=79) n (%) | STRENSIQ (N=20) n (%) |
| Injection site reactions | 38 (58) | 6 (46) | 44 (56) | 18 (90) |
| Erythema | 29 (44) | 3 (23) | 32 (41) | 15 (75) |
| Discoloration/ Hypopigmentation | 11 (17) | 1 (8) | 12 (15) | 8 (40) |
| Pain/ Tenderness | 10 (15) | 1 (8) | 11 (14) | 8 (40) |
| Pruritus/ Itching | 10 (15) | 0 (0) | 10 (13) | 7 (35) |
| Swelling | 8 (12) | 0 (0) | 8 (10) | 6 (30) |
| Induration | 9 (14) | 1 (8) | 10 (13) | 3 (15) |
| Macule | 4 (6) | 0 (0) | 4 (5) | 7 (35) |
| Reaction, not otherwise specified | 6 (9) | 1 (8) | 7 (9) | 4 (20) |
| Bruising | 6 (9) | 0 (0) | 6 (8) | 4 (20) |
| Nodule | 2 (3) | 0 (0) | 2 (3) | 2 (10) |
| Other injection site reactions Other injection site reactions include injection site rash, inflammation, papule, hemorrhage, hematoma, urticaria, warmth, calcification, mass, scar and cellulitis. | 10 (15) | 3 (23) | 13 (17) | 4 (20) |
| Ectopic calcifications | 3 (5) | 0 (0) | 3 (4) | 11 (55) |
| Lipodystrophy | 12 (18) | 2 (15) | 14 (18) | 14 (70) |
| Injection site atrophy | 4 (6) | 2 (15) | 6 (8) | 8 (40) |
| Injection site hypertrophy | 5 (8) | 0 (0) | 5 (6) | 6 (30) |
| Other lipodystrophy Other lipodystrophy includes lipohypertrophy. | 4 (6) | 0 (0) | 4 (5) | 1 (5) |
| Hypersensitivity reactions | 7 (11) | 3 (23) | 10 (13) | 2 (10) |
| Vomiting/emesis | 2 (3) | 2 (15) | 4 (5) | 2 (10) |
| Other hypersensitivity reactions Other hypersensitivity reactions include erythema/redness, pyrexia/fever, irritability, nausea, pain, rigor/chills, hypoesthesia oral, headache, flushing, and anaphylaxis. | 6 (9) | 2 (15) | 8 (10) | 2 (10) |
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions that occurred at rates less than 1% included:
- Hypocalcemia
- Renal Stones
- Chronic hepatitis
- Decreased vitamin B6
Long-Term Safety
In long-term extension trials reflecting a median exposure to STRENSIQ of 142 weeks (range 0.1 weeks to 392 weeks) in 112 patients with perinatal/infantile- (n = 89), juvenile- (n = 22), and adult-onset (n = 1) HPP (age at enrollment = 1 day to 66.5 years), the most common adverse reactions were similar to those reported in Table 4.
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of the antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other asfotase alfa products may be misleading.
During clinical trials, anti-asfotase alfa antibodies have been detected in patients receiving treatment with STRENSIQ using an electrochemiluminescent (ECL) immunoassay. Antibody positive samples were tested to determine the presence of neutralizing antibodies based on in vitro inhibition of the catalytic activity of STRENSIQ.
Among STRENSIQ-treated patients with hypophosphatasia (HPP) in clinical studies who had post-baseline antibody data available, 97/109 (89%) tested positive for anti-asfotase alfa antibodies at some time point during STRENSIQ treatment. Among those 97 patients, 55 (57%) also tested positive for neutralizing antibodies at some time point during STRENSIQ treatment. No correlation was observed between the anti-asfotase alfa antibody titers and the neutralizing antibody (% inhibition) values. Formation of anti-asfotase alfa antibody resulted in a reduced systemic exposure of asfotase alfa [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of STRENSIQ. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Some STRENSIQ-treated patients with initial therapeutic response to STRENSIQ subsequently developed worsening in disease-associated laboratory and radiographic biomarkers (some in association with neutralizing antibodies) suggesting possible immune-mediated effects on STRENSIQ's pharmacologic action resulting in disease progression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drug Interference with Laboratory Tests: Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) is used as a detection reagent in many laboratory tests and the presence of asfotase alfa in clinical laboratory samples could result in erroneous test results. Inform laboratory personnel and discuss use of an alternative testing platform for patients on treatment. (7.1 )
- Serum Alkaline Phosphatase : Serum ALP measurements are expected to be elevated during treatment and may be unreliable for clinical decision making. (7.1 )
Drug Interference with Laboratory Tests
Laboratory Tests Utilizing Alkaline Phosphatase as a Detection Reagent
Studies have shown that there is analytical interference between asfotase alfa and laboratory tests that utilize an alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-conjugated test system, rendering erroneous test results in patients treated with STRENSIQ. ALP-conjugated test systems are utilized to measure substances such as hormones, bacterial antigens and antibodies. Therefore, it is recommended that laboratory assays which do not have ALP-conjugate technology be used when testing samples from patients who are receiving STRENSIQ.
To avoid erroneous test results for patients treated with STRENSIQ, inform laboratory personnel that the patient is being treated with STRENSIQ and discuss the use of a testing platform which does not utilize an ALP-conjugated test system.
Serum Alkaline Phosphatase
High serum ALP measurements detected through clinical laboratory testing are expected in patients receiving STRENSIQ and reflect circulating concentrations of asfotase alfa .
Do not rely on serum ALP measurements for clinical decision making in patients treated with STRENSIQ.
DESCRIPTION
Asfotase alfa is a tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) produced by recombinant DNA technology in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Asfotase alfa is a soluble glycoprotein composed of two identical polypeptide chains. Each chain contains 726 amino acids with a theoretical mass of 161 kDa. Each chain consists of the catalytic domain of human TNSALP, the human immunoglobulin G 1 Fc domain and a deca-aspartate peptide used as a bone targeting domain. The two polypeptide chains are covalently linked by two disulfide bonds.
STRENSIQ (asfotase alfa) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, nonpyrogenic, clear, slightly opalescent or opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow, with few small translucent or white particles, aqueous solution for subcutaneous administration. STRENSIQ is supplied in glass single-dose vials containing asfotase alfa; dibasic sodium phosphate, heptahydrate; monobasic sodium phosphate, monohydrate; and sodium chloride at a pH between 7.2 and 7.6. Table 5 describes the content of STRENSIQ vial presentations.
| Ingredient | Quantity per Vial | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asfotase Alfa | 18 mg/0.45 mL | 28 mg/0.7 mL | 40 mg/mL | 80 mg/0.8 mL |
| Dibasic sodium phosphate, heptahydrate | 2.48 mg | 3.85 mg | 5.5 mg | 4.4 mg |
| Monobasic sodium phosphate, monohydrate | 0.28 mg | 0.43 mg | 0.62 mg | 0.5 mg |
| Sodium chloride | 3.94 mg | 6.13 mg | 8.76 mg | 7.01 mg |
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
HPP is caused by a deficiency in TNSALP enzyme activity, which leads to elevations in several TNSALP substrates, including inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). TNSALP is a metallo-enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphomonoesters with release of inorganic phosphate and alcohol. Elevated extracellular levels of PPi block hydroxyapatite crystal growth which inhibits bone mineralization and causes an accumulation of unmineralized bone matrix which manifests as rickets and bone deformation in infants and children and as osteomalacia (softening of bones) once growth plates close, along with muscle weakness. Replacement of the TNSALP enzyme upon STRENSIQ treatment reduces the enzyme substrate levels.
Pharmacodynamics
Perinatal/infantile- and juvenile-onset HPP patients treated with STRENSIQ had reductions in plasma TNSALP substrates, PPi and pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) within 6 to 12 weeks of treatment. Reductions in plasma PPi and PLP levels did not correlate with clinical outcomes.
Bone biopsy data from perinatal/infantile-onset and juvenile-onset HPP patients treated with STRENSIQ demonstrated decreases in osteoid volume and thickness indicating improved bone mineralization.
Pharmacokinetics
Based on data in 38 HPP patients, the pharmacokinetics of asfotase alfa exhibit dose proportionality across the dose range of 0.3 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg once every other day (three times a week) and appear to be time-independent. Steady state exposure was achieved as early as three weeks after the administration of the first dose. The elimination half-life following subcutaneous administration was approximately 5 days.
Table 6 summarizes the pharmacokinetic parameters following multiple doses in 20 HPP patients after subcutaneous administration of STRENSIQ at 2 mg/kg three times per week in Study 2 (age of less than or equal to 5 years) and Study 3 (age of greater than 5 to 12 years), indicating the pharmacokinetics were similar between patients in the two age groups.
| Study 2 | Study 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (range). Study 3 includes patients with perinatal/infantile- or juvenile-onset of disease. t last , time of last concentration; t max , time of maximal concentration; C max , maximal concentration; AUC t , area under the concentration-time curves over a dosing interval of 48 hours | ||
| N | 14 | 6 |
| Age (year) | 3.4 ± 2.1 (0.2, 6.2) | 8.6 ± 2.2 (6.1, 12.6) |
| Weight at baseline (kg) | 11.2 ± 5.0 (2.9, 17.1) | 21.2 ± 7.9 (11.4, 35.4) |
| t last (h) | 48.1 ± 0.1 (47.9, 48.3) | 48.0 ± 0.1 (48.0, 48.1) |
| t max (h) | 14.9 ± 10.4 (0, 32.2) | 20.8 ± 10.0 (11.9, 32.2) |
| C max (ng/mL) | 1794 ± 690 (856, 3510) | 2108 ± 788 (905, 3390) |
| AUC t (h•ng/mL) | 66042 ± 25758 (27770, 119122) | 89877 ± 33248 (37364, 142265) |
| Accumulation Ratio Ratio values reflect the fold increase of AUC t from Week 1 based on mean AUC t, values. | 1.5 | 3.9 |
Population PK analysis of asfotase alfa concentrations supports weight-based dosing because body weight is a major covariate of asfotase alfa clearance. The formulation concentration had an impact on the systemic exposure of asfotase alfa in HPP patients. The higher concentration formulation (80 mg/0.8 mL vial) achieved an approximately 25% lower systemic asfotase alfa exposure (i.e., concentrations and AUC) compared to the lower concentration formulations (18 mg/0.45 mL, 28 mg/0.7 mL or 40 mg/mL vials) at the same dose of STRENSIQ [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Anti-Drug Antibody Effects on Pharmacokinetics
Formation of anti-drug antibodies resulted in reduced systemic exposure of asfotase alfa.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential or studies to evaluate mutagenic potential have not been performed with asfotase alfa. Asfotase alfa at intravenous doses up to 50 mg/kg/day administered daily in pregnant rats (approximately 21 times the human AUC of 65486 ng.h/mL at 2 mg/kg dose administered three times weekly for a 50 kg individual) was found to have no adverse effect on fertility and reproductive performance of male and female rats.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
Study 1 was a 24-week prospective single-arm trial in 11 patients with severe perinatal/infantile-onset HPP. In this study, 7/11 (64%) were female and 10/11 (91%) patients were white, and age ranged from 3 weeks to 39.5 months. Severe perinatal/infantile-onset HPP was defined as biochemical, medical history and radiographic evidence of HPP as well as the presence of any of the following: rachitic chest deformity, vitamin B6-dependent seizures, or failure to thrive. Ten of 11 patients completed the 24-week trial and continued treatment in the extension phase. Nine patients have been treated for at least 216 weeks (54 months) and 4 patients have been treated for over 240 weeks (60 months). Patients received subcutaneous STRENSIQ 3 mg/kg per week for the first month; subsequently, dose increases up to 9 mg/kg per week were allowed for changes in weight and/or for lack of efficacy. All 10 patients required dose increases up to 6 mg/kg per week or higher; 9 patients increased between 4 and 24 weeks after starting treatment and 1 patient increased after 70 weeks due to suboptimal clinical response. One patient's dose was decreased from 9 mg/kg per week to 6 mg/kg per week based on PK data.
Study 2 was a prospective open-label study in 59 patients with perinatal/infantile-onset HPP. In this study, 32/59 (54%) were female, 46/59 (78%) were white, and age ranged from 1 day to 78 months. Patients received subcutaneous STRENSIQ at 6 mg/kg per week for the first 4 weeks. Ten patients received dose increases higher than 6 mg/kg per week due to suboptimal clinical response, with dose increases occurring between 8 and 24 weeks after starting treatment. The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of perinatal/infantile-onset HPP is up to 9 mg/kg per week administered subcutaneously as 3 mg/kg three times per week [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Forty-one patients were treated for at least 24 weeks (6 months) and 15 patients were treated for at least 96 weeks (24 months).
Survival and Ventilation-Free Survival in Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
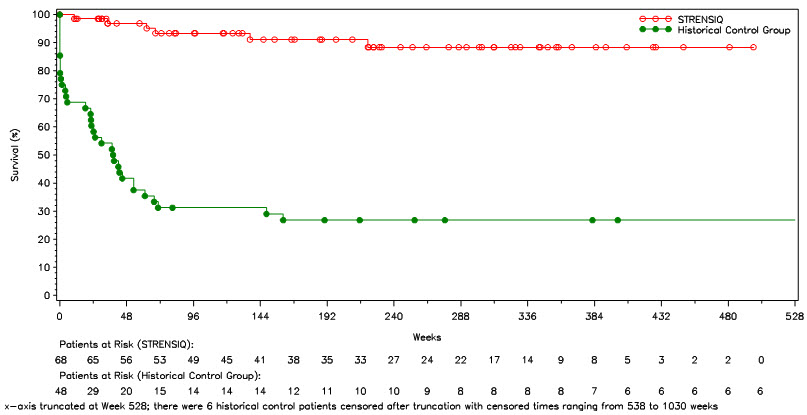
Survival and invasive ventilation-free survival were compared in STRENSIQ-treated patients (Studies 1 and 2) with a historical cohort of untreated patients with similar clinical characteristics (Table 7 and Figure 1).
| STRENSIQ-Treated | Historical Controls | |
|---|---|---|
| Survival | n = 68 | n = 48 |
| Alive at Point of Last Contact (%) | 91 | 27 |
| Hazard Ratio (STRENSIQ/Historical Control), 95% Confidence Interval Adjusted for year of diagnosis. | 0.14 (0.05, 0.39) | |
| Kaplan-Meier Estimate and Alive at Age 1 Year (Week 48) (%) | 97 | 42 |
| Invasive Ventilation-Free Survival Alive and not initiating invasive ventilation after start of STRENSIQ treatment. STRENSIQ-treated patients on invasive ventilation at baseline were excluded from this analysis. | n = 54 | n = 48 |
| Alive and Not on Ventilation at Point of Last Contact (%) | 85 | 25 |
| Hazard Ratio (STRENSIQ/Historical Control), 95% Confidence Interval | 0.21 (0.09, 0.51) | |
| Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Alive and Not on Ventilation at Age 1 Year (Week 48) (%) | 96 | 31 |
In patients who required any form of respiratory support, 21 of 26 (81%) of the treated patients survived through their last assessment (median age at last assessment was 3.2 years of age), versus 1 of 20 (5%) of historical controls.
Figure 1: Overall Survival in STRENSIQ-Treated versus Historical Control Patients with Perinatal/ Infantile-Onset HPP (Pooled Studies 1 and 2)
Skeletal Manifestations in Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
Radiographs from 68 STRENSIQ-treated perinatal/infantile-onset HPP patients, including 64 patients in Studies 1 and 2, and 4 patients in Study 3 [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] , were examined to assess HPP-related rickets using the 7-point Radiographic Global Impression of Change (RGI-C) scale. Patients with a minimum RGI-C score of +2 were defined as "responders". Radiologic improvements could be seen by Month 24; at last assessment, 50/68 [74%] treated patients were rated as RGI-C responders. No comparative data were available from historical controls. The mean time interval between the baseline and last RGI-C assessment was 24 months (range was 1 month to 67 months).
Eighteen perinatal/infantile-onset HPP patients experienced fractures during the course of treatment. There were insufficient data to determine the effect of STRENSIQ on fractures.
Growth in Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
Height and weight measurements (as measured by Z-scores) were available post-treatment for 72 perinatal/infantile-onset HPP patients, including 68 patients enrolled in Studies 1 and 2, and 4 patients enrolled in Study 3 (Table 8).
| Height Z-score | Weight Z-score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Last Assessment | Baseline | Last Assessment | |||||
| Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | |
| Studies 1 and 2 The mean time interval between baseline and last assessment was 21 months (range was 1 month to 72 months). (N=68) | -3.3 | -10.1, 0.9 | -2.9 | -10.6, 0.4 | -3.2 | -23.8, 0 | -2.4 | -20.9. 1.1 |
| Study 3 (N=4) The mean time between baseline and last assessment was 56 months (range was 53 months to 60 months). | -2.6 | -6.6, -0.7 | -1.5 | -5.8, 0.4 | -2.5 | -8.2, -1.0 | -1.5 | -5.4, 0.5 |
Long-Term Extension Trials in Perinatal/Infantile-Onset HPP
Long-term data were collected in 68 STRENSIQ-treated patients with perinatal/infantile onset HPP in Studies 1 and 2 and an additional 10 patients enrolled in Study 2. The longest duration of follow-up in the 78 patients was 7 years (84 months). At point of last contact, 69/78 (88%) STRENSIQ-treated patients had survived.
Juvenile-Onset HPP
Study 3 was a prospective open-label 24-week trial that included 8 juvenile-onset HPP patients and 5 perinatal/ infantile-onset HPP patients; 11/13 (85%) were male and 12/13 (92%) were white [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . On study entry, patients were 6 to 12 years of age. All 8 juvenile-onset patients entered the extension study and were treated for at least 48 months. At trial entry, patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous STRENSIQ 6 mg/kg per week or 9 mg/kg per week. Two patients received dose reductions during the primary treatment period, including one patient who experienced a decrease in vitamin B6 levels and one patient who experienced recurrent injection site reactions. During the extension phase, the dosing regimen for all patients was initially changed to 3 mg/kg per week. Dosing was subsequently increased to 6 mg/kg per week, with no patients requiring doses higher than 6 mg/kg per week. The recommended dosage regimen of STRENSIQ for the treatment of juvenile-onset HPP is 6 mg/kg per week [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Growth in Juvenile-Onset HPP
Height and weight measurements (as measured by Z-scores) in 8 STRENSIQ-treated juvenile-onset HPP patients were compared with a historical cohort of 32 untreated patients with similar clinical characteristics (Table 9). Height and weight data for historical patients were collected from medical records.
| Height Z-score | Weight Z-score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Last Assessment | Baseline | Last Assessment | |||||
| Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | Mean | Min, Max | |
| STRENSIQ (N=8) The mean time interval between baseline and last assessment was 55 months (range was 53 months to 60 months). | -1.5 | -3.8, 0 | -0.9 | -2, 0 | -1.1 | -3.5, 2.3 | 0 | -1.3, 2.2 |
| Control (N=32) The mean time interval between baseline and last assessment was 61 months (range was 19 months to 109 months). | -1.1 | -4.9, 2.6 | -1.1 | -4.9, 1.8 | -1.2 | -5, 2.1 | -1 | -5.7, 2.1 |
Skeletal Manifestations in Juvenile-Onset HPP
Radiographs from 8 STRENSIQ-treated juvenile-onset HPP patients and 32 historical controls were compared to assess HPP-related rickets using the 7-point RGI-C (Radiographic Global Impression of Change) scale. Patients who achieved a RGI-C score of 2 or higher (corresponding to substantial healing of rickets) were classified as being responders to treatment. All 8 treated patients were rated as responders by Month 54 of treatment. The mean duration between the baseline and last RGI-C assessments for control patients was 56 months (range was 8 to 95 months). At last assessment, 2/32 (6%) of control patients were rated as responders.
Eight of 20 (40%) patients with juvenile-onset HPP experienced new fractures during the course of treatment. There were insufficient data to assess the effect of STRENSIQ on fractures.
Gait/Mobility in Juvenile-Onset HPP
Gait was assessed using a modified Performance Oriented Mobility Assessment-Gait (MPOMA-G) scale in 8 STRENSIQ-treated juvenile-onset HPP patients at 6-month intervals out to 36 months. Mobility was also assessed using the 6 Minute Walk Test (6MWT) in 7 of the 8 patients. Step length improved by at least 1 point in either foot in 6/8 patients compared to 1/6 (17%) control patients. The proportion of patients who had 6MWT percent predicted values within the normal range for age, sex, and height-matched peers increased from 0/8 patients at baseline to 6/6 patients (100%) by Month 48 and all 6 were also able to walk longer distances at this time point compared to baseline.
Long-Term Extension Trials in Juvenile-Onset HPP
Long-term data were collected in 8 patients with juvenile-onset HPP treated with STRENSIQ for at least 6 years (72 months). At last assessment, 7 patients with available 6MWT results had maintained improvements in gait/mobility.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
STRENSIQ is supplied as a sterile, nonpyrogenic, preservative-free, clear, slightly opalescent or opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution; a few small translucent or white particles may be present. The product is available as single-dose vials in a carton of one (1) or twelve (12) vials at the following strengths:
| Strength | National Drug Code (NDC) | Quantity of Vials in Carton |
|---|---|---|
| 18 mg/0.45 mL | NDC 25682-010-01 | 1 |
| NDC 25682-010-12 | 12 | |
| 28 mg/0.7 mL | NDC 25682-013-01 | 1 |
| NDC 25682-013-12 | 12 | |
| 40 mg/mL | NDC-25682-016-01 | 1 |
| NDC-25682-016-12 | 12 | |
| For pediatric patients 40 kg and greater | ||
| 80 mg/0.8 mL | NDC 25682-019-01 | 1 |
| NDC 25682-019-12 | 12 | |
STRENSIQ vials must be stored in the original carton until the time of use under refrigerated conditions at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and protected from light.
Once removed from refrigeration, STRENSIQ should be administered within 3 hours.
Do not use beyond the expiration date stamped on the carton.
DO NOT FREEZE OR SHAKE.
Vials are for one time use only. Discard any unused product.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE STRENSIQ ® [stren' sik] (asfotase alfa) injection, for subcutaneous use vial
Read this "Instructions for Use" before you start using STRENSIQ and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Do not share your syringes or needles with anyone else. You may give an infection to them or get an infection from them.
Supplies needed to give your STRENSIQ injection (See Figure A ):
- 1 or 2 STRENSIQ vial(s).
- 1 or 2 sterile disposable 1 mL syringes for injection with 25 to 29 gauge (G), ½ inch needles.
- The use of two different gauge needles is recommended, a larger bore needle (e.g. 25 gauge) for withdrawal of the medication, and a smaller bore needle (e.g. 29 gauge) for the injection.
- Always use a new syringe and needle for each injection.
- 2 alcohol wipes
- 1 gauze or cotton ball
- a clean flat surface, like a table
- 1 sharps container for throwing away used needles and syringes. See " Disposing of used needles and syringes " at the end of these instructions.
| Figure A |
 |
Storing your STRENSIQ dose:
- Store STRENSIQ in the original carton in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until you are ready to use it.
- Do not freeze your STRENSIQ vials. Do not use STRENSIQ if it has been frozen.
- Do not shake your STRENSIQ vials.
- Protect STRENSIQ from light until you are ready to use it.
- Do not use STRENSIQ after the expiration date printed on the carton.
- STRENSIQ vials are for 1 time use only. Throw away any unused STRENSIQ left in the vial.
Preparing your STRENSIQ dose and giving your STRENSIQ injection:
- Prepare a clean flat surface, like a table or counter top.
- Remove the unopened STRENSIQ vial(s) out of the refrigerator and allow it to sit at room temperature for at least 15 to 30 minutes. Injecting STRENSIQ when cold can make the injection feel uncomfortable.
- Do not warm STRENSIQ in any way other than letting it sit at room temperature (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water).
- Gather all the supplies you will need to give your STRENSIQ injection.
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Utilize STRENSIQ within 3 hours after removing it from the refrigerator.
- Inject STRENSIQ exactly as your healthcare provider has shown you.
| Step 1: | Check the liquid in the STRENSIQ vial. STRENSIQ liquid should look clear or slightly yellow and may have a few small white particles in it. Do not use it if the liquid is discolored or contains any lumps or large particles in it. Throw it away and get a new vial. | |
| Step 2: | Using your thumb, flip the plastic cap off the STRENSIQ vial. |  |
| Step 3: | Remove the larger bore needle (e.g., 25 G) from the package. Pick up the syringe and place the needle on the tip of the syringe. Push down and twist the needle onto the syringe until it is tight. | |
| Step 4: | Hold the syringe with the needle pointing up and pull back the plunger until the top of the plunger reaches the line for your prescribed dose. | |
| Step 5: | Pull the cap straight off of the needle.
|  |
| Step 6: | Hold the STRENSIQ vial firmly on a flat surface, then push the needle through the rubber stopper of the STRENSIQ vial. |  |
| Step 7: | Keeping the needle in the STRENSIQ vial, lift the vial and turn it upside down with the needle pointing toward the ceiling. Slowly push the plunger all the way in. | |
| Step 8: | With the needle tip still in the liquid, slowly pull back the plunger until the top of the plunger reaches the line slightly past the line for your prescribed dose. Do not pull the needle out of the STRENSIQ vial. Slowly push the plunger up until the top of the plunger reaches the line for your prescribed dose.
|  |
| Step 9: | Turn the STRENSIQ vial upright and pull the syringe straight out of the vial's rubber stopper.
|  |
| Step 10: | Hold the syringe with the needle pointing up and tap the barrel of the syringe with your finger to remove any air bubbles. |  |
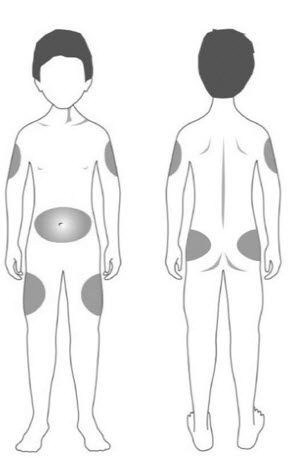
| Step 11: | Choose your injection site. STRENSIQ is injected under the skin (subcutaneously) of your stomach-area (abdomen), upper arms, upper legs, or buttocks.
|  |
| Step 12: | Pinch the skin. Hold the syringe at a 90° angle (straight up and down) and insert the needle into your skin. For patients with little fat, hold the syringe at a 45° angle and insert the needle into your skin. | 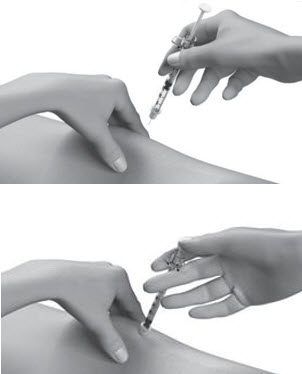 |
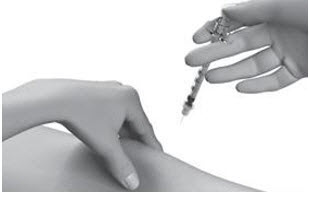
| Step 13: | Push the plunger slowly and steadily all the way in to give your dose. | 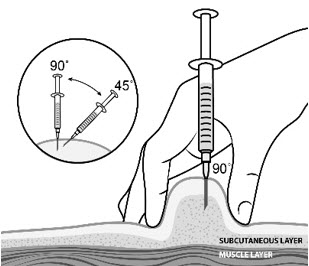 |
| Step 14: | Pull the needle out of your skin.
|  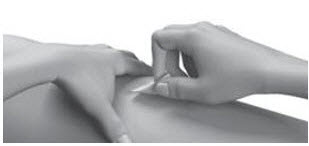 |
Disposing of used needles and syringes:
- Put your used needles in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid,
- without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal .
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Keep STRENSIQ and all medicines, needles and syringes out of the reach of children.
This "Instructions for Use" has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Boston, MA 02210 USA U.S. License Number: 1743
Approved: 6/2020
© 2020 Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Printed in USA
Mechanism of Action
HPP is caused by a deficiency in TNSALP enzyme activity, which leads to elevations in several TNSALP substrates, including inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). TNSALP is a metallo-enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphomonoesters with release of inorganic phosphate and alcohol. Elevated extracellular levels of PPi block hydroxyapatite crystal growth which inhibits bone mineralization and causes an accumulation of unmineralized bone matrix which manifests as rickets and bone deformation in infants and children and as osteomalacia (softening of bones) once growth plates close, along with muscle weakness. Replacement of the TNSALP enzyme upon STRENSIQ treatment reduces the enzyme substrate levels.