Get your patient on Tavaborole - Tavaborole Topical Solution, 5% solution (Tavaborole Topical Solution, 5%)
Tavaborole - Tavaborole Topical Solution, 5% solution prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tavaborole topical solution, 5% is an oxaborole antifungal indicated for the treatment of onychomycosis of the toenails due to Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton mentagrophyte.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply tavaborole topical solution to affected toenails once daily for 48 weeks.
Tavaborole topical solution should be applied to the entire toenail surface and under the tip of each toenail being treated.
Tavaborole topical solution is for topical use only and not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tavaborole topical solution, 5% is a clear, colorless alcohol-based solution. Each milliliter of solution contains 43.5 mg (5% w/w) of tavaborole
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary There are no available data on tavaborole topical solution use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In oral animal reproductive studies, administration of tavaborole during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryofetal toxicity and malformations at 570 times the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) based on Area Under the Curve (AUC) comparisons in rats and embryofetal toxicity at 155 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons in rabbits. Embryofetal toxicity was noted following dermal administration in rabbits up to 36 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons [ see Data ]. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies carry some risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects in the U.S. general population is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. Data Animal Data Oral Administration: In an oral embryofetal development study in rats, oral doses of 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day tavaborole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-19) to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (increased embryofetal resorption and/or deaths) and drug-related skeletal malformations and variations suggestive of delayed development (i.e., a delay in ossification) were noted in fetuses at 300 mg/kg/day tavaborole [570 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons]. No developmental toxicity was noted in rats at 100 mg/kg/day tavaborole (26 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). In an oral embryofetal development study in rabbits, oral doses of 15, 50, and 150 mg/kg/day tavaborole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 7-19) to pregnant female rabbits. In the presence of maternal toxicity, excessive embryofetal mortality due to post-implantation loss was noted at 150 mg/kg/day tavaborole. No drug related malformations were noted in rabbits at 150 mg/kg/day tavaborole (155 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No embryofetal mortality was noted in rabbits at 50 mg/kg/day tavaborole (16 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). In an oral pre-and post-natal development study in rats, oral doses of 15, 60, and 100 mg/kg/day tavaborole were administered from the beginning of organogenesis (gestation day 6) through the end of lactation (lactation day 20). In the presence of minimal maternal toxicity, no embryofetal toxicity or effects on postnatal development were noted at 100 mg/kg/day (29 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). Topical administration: In a dermal embryofetal development study in rabbits, topical doses of 1%, 5%, and 10% tavaborole solution were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-28) to pregnant female rabbits. A dose dependent increase in dermal irritation at the treatment site was noted at 5% and 10% tavaborole solution. A decrease in fetal bodyweight was noted at 10% tavaborole solution. No drug related malformations were noted in rabbits at 10% tavaborole solution (36 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No embryofetal toxicity was noted in rabbits at 5% tavaborole solution (26 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of tavaborole in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production after topical application of tavaborole topical solution to women who are breastfeeding. tavaborole topical solution is systemically absorbed. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of tavaborole topical solution to a breastfed infant. Therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for tavaborole topical solution and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from tavaborole topical solution or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of tavaborole topical solution were established in patients 6 years of age and older. Use of tavaborole topical solution in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of tavaborole topical solution in adults with additional data from an open-label pharmacokinetics study of tavaborole in subjects 12 years to less than 17 years old [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Geriatric Use
In clinical trials of 791 subjects who were exposed to tavaborole topical solution, 19% were 65 years of age and over, while 4% were 75 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% in subjects treated with tavaborole topical solution included application site exfoliation, ingrown toenail, application site erythema, and application site dermatitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Encube Ethicals Private Limited at 1-833-285-4151 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two clinical trials, 791 subjects were treated with Tavaborole topical solution. The most commonly reported adverse reactions are listed below (Table 1).
| Table 1 : Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥1% of Tavaborole topical solution, 5%-Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than Observed with Vehicle | ||
| Preferred Term | Tavaborole topical solution N= 791 n(%) | Vehicle N= 395 n(%) |
| Application site exfoliation | 21 (2.7%) | 1 (0.3%) |
| Ingrown toenail | 20 (2.5%) | 1 (0.3%) |
| Application site erythema | 13 (1.6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Application site dermatitis | 10 (1.3%) | 0 (0%) |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of Tavaborole topical solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug product exposure:
Hypersensitivity; contact allergy
DESCRIPTION
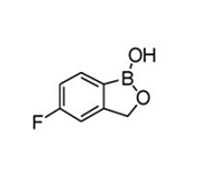
Tavaborole topical solution, 5% contains tavaborole, 5% (w/w) in a clear, colorless alcohol-based solution for topical use. The active ingredient, tavaborole, is an oxaborole antifungal with the chemical name of 5-fluoro-1,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborole. The chemical formula is C 7 H 6 BFO 2 , the molecular weight is 151.93 and the structural formula is:
Tavaborole is a white to off-white powder. It is slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in ethanol and propylene glycol.
Each mL of tavaborole topical solution contains 43.5 mg of tavaborole. Inactive ingredients include alcohol USP (87.43% v/v), propylene glycol USP, and edetate calcium disodium USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Tavaborole topical solution is an oxaborole antifungal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4 ) ].
Pharmacodynamics
At therapeutic doses, tavaborole topical solution is not expected to prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
Tavaborole undergoes extensive metabolism. Renal excretion is the major route of elimination of the metabolites.
In a clinical pharmacology trial of six healthy adult male volunteers who received a single topical application of 5% 14 C-tavaborole solution, tavaborole conjugates and metabolites were shown to be excreted primarily in the urine.
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of tavaborole was investigated in 24 adult subjects with distal subungual onychomycosis involving at least 4 toenails (including at least 1 great toenail) following a single dose and a 2-week daily topical application of 200 μL of a 5% solution of tavaborole to all ten toenails and 2 mm of skin surrounding each toenail. Steady state was achieved after 14 days of dosing. After a single dose, the mean (± standard deviation) peak concentration (Cₘₐₓ) of tavaborole was 3.5 ± 2.3 ng/mL (n=21 with measurable concentrations, range 0.618-10.2 ng/mL, LLOQ=0.5 ng/mL), and the mean AUC last ± SD was 44.4 ± 25.5 ng•hr/mL (n=21). After 2 weeks of daily dosing, the mean Cₘₐₓ± SD was 5.2 ± 3.5 ng/mL (n=24, range 1.5-12.8 ng/mL), and the mean AUCτ ± SD was 75.8 ± 44.5 ng•hr/mL.
In another study PK of tavaborole was investigated in 22 subjects aged 12 years to less than 17 years with distal subungual onychomycosis involving at least 4 toenails (including at least 1 great toenail with at least 20% involvement) following once daily application of 5% solution of tavaborole to all ten toenails and 2 mm of skin surrounding each toenail for 29 days. On Day 29, the mean ± SD C max was 5.9 ± 4.9 ng/mL (n=21 with measurable concentrations, range 1.0 -16.4 ng/mL, LLOQ=0.5 ng/mL), and the mean ± SD AUC 0-24 was 76.0 ± 62.5 ng•hr/mL.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
In vitro studies have shown that tavaborole, at therapeutic concentrations, neither inhibits nor induces cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of tavaborole is inhibition of fungal protein synthesis. Tavaborole inhibits protein synthesis by inhibition of an aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) synthetase (AARS).
Activity in vitro and in clinical infections
Tavaborole has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1) ]:
Trichophyton rubrum
Trichophyton mentagrophytes Mechanism of Resistance
Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton rubrum strains from isolates collected in the clinical trials have not demonstrated resistance following repeated exposure to tavaborole.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, oral doses of 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg/day tavaborole were administered to rats once daily for 104 weeks. No drug related neoplastic findings were noted at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day tavaborole (14 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
In a dermal carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, topical doses of 5%, 10%, and 15% tavaborole solution were administered to mice once daily for 104 weeks. No drug related neoplastic findings were noted at topical doses up to 15% tavaborole solution (89 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Tavaborole revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay and Human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (rat micronucleus assay).
No effects on fertility were observed in male and female rats that were administered oral doses up to 300 mg/kg/day tavaborole (107 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons) prior to and during early pregnancy.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of tavaborole topical solution was evaluated in two multicenter, double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled trials. Tavaborole topical solution or vehicle was applied once daily for 48 weeks in subjects with 20% to 60% clinical involvement of the target toenail, without dermatophytomas or lunula (matrix) involvement.
A total of 1194 subjects (795 tavaborole topical solution, 399 Vehicle) 18 to 88 years of age, 82% male, 84% white, participated in these two trials. Efficacy assessments were made at 52 weeks following a 48-week treatment period.
The Complete Cure efficacy endpoint included negative mycology (negative KOH wet mount and negative fungal culture) and Completely Clear Nail (no clinical evidence of onychomycosis as evidenced by a normal toenail plate, no onycholysis, and no subungual hyperkeratosis). Efficacy results from the two trials are summarized in Table 2 .
| Table 2 : Efficacy Outcomes | ||||
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
| Efficacy Variable | Tavaborole topical solution N= 399 n(%) | Vehicle N= 194 n(%) | Tavaborole topical solution N= 396 n(%) | Vehicle N= 205 n(%) |
| Complete Cure • | 26 (6.5%) | 1 (0.5%) | 36 (9.1%) | 3 (1.5%) |
| Complete or Almost Complete Cure † | 61 (15.3%) | 3 (1.5%) | 71 (17.9%) | 8 (3.9%) |
| Mycologic Cure ‡ | 124 (31.1%) | 14 (7.2%) | 142 (35.9%) | 25 (12.2%) |
• Complete cure defined as 0% clinical involvement of the target toenail plus negative KOH and negative culture. † Complete or almost complete cure defined as ≤10% affected target toenail area involved and negative KOH and culture. ‡ Mycologic cure defined as negative KOH and negative culture.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Tavaborole topical solution, 5% is a clear, colorless solution supplied in an amber glass bottle with a screw cap. At initial use, the screw cap is replaced with the dropper assembly.
Tavaborole topical solution, 5% is supplied in the following presentations:
NDC 21922- 020 -12: One bottle containing 10 mL of solution with one glass pointed-tip dropper. The Packaging of This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber.
Storage and Handling
Store at 20–25°C (68–77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
CAUTION: Flammable. Keep away from heat and flame.
Discard product within 3 months after insertion of the dropper. Keep bottle tightly closed. Keep out of reach of children.
Instructions for Use
Tavaborole (ta va bor ole) topical solution, 5%
Important information: Tavaborole topical solution is for use on toenails only. Do not use tavaborole topical solution in your mouth, eyes, or vagina.
Read the Instructions for Use that comes with tavaborole topical solution before you start using it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
How to apply tavaborole topical solution: Your toenails should be clean and dry before you apply tavaborole topical solution.
Step 1: Before you apply tavaborole topical solution to your affected toenail for the first time, remove the cap from the tavaborole topical solution bottle. ( See Figure A ) Throw away the cap.
Step 2: Remove the wrapping from the dropper that comes with tavaborole topical solution. insert the dropper into the tavaborole topical solution bottle. ( See Figure B )
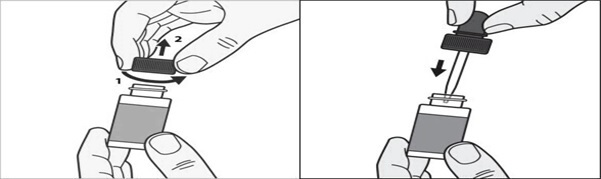
Figure A Figure B
Only apply tavaborole topical solution using the provided dropper. Do not use the dropper for any other purpose .
Step 3: With the dropper inserted into the tavaborole topical solution, squeeze the bulb and then release the bulb to draw tavaborole topical solution into the dropper.
Step 4: Remove the dropper from the bottle and hold the dropper tip over your affected toenail. Slowly squeeze the bulb to apply tavaborole topical solution to your toenail. Apply enough solution to completely cover your toenail. You may need to use more than one drop. ( See Figure C )
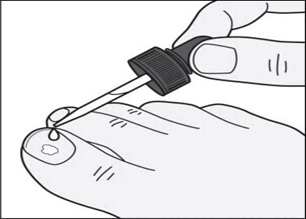
Figure C
Step 6: Use the dropper tip to gently spread tavaborole topical solution to cover the entire toenail up to the edges of the toenail. ( See Figure D )
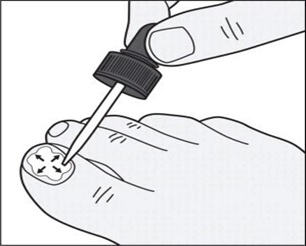
Figure D
Step 7: In addition to the top of the toenail, also apply tavaborole topical solution under the tip of the toenail. Use the dropper tip to gently spread tavaborole topical solution under the entire tip of the toenail. ( See Figures E and F )
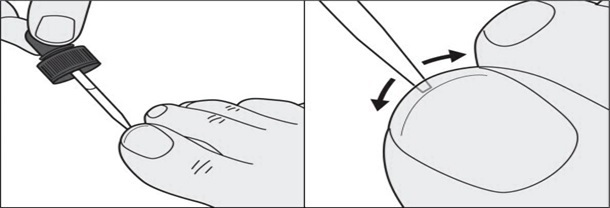
Figure E Figure F
Step 8: Repeat Steps 3 to 7 to apply tavaborole topical solution to each affected toenail.
Step 9: Let the tavaborole topical solution dry completely. This may take a couple of minutes. Avoid getting tavaborole topical solution on skin that is not surrounding skin, use a tissue to wipe any excess solution from the surrounding skin. Do not wipe tavaborole topical solution off of your toenails.
Step 10: After applying tavaborole topical solution to your toenails, insert the dropper back into the bottle and screw it on tightly.
Step 11: Wash your hands with soap and water after applying tavaborole topical solution.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by: Encube Ethicals Pvt. Ltd. Plot No. C-1, Madkaim Industrial Estate, Madkaim, Post: Mardol, Ponda, Goa - 403 404, India.
Distributed by: Encube Ethicals, Inc . 200 Meredith Drive, Suite 202 Durham, NC 27713 USA
Rev.07/24
Mechanism of Action
Tavaborole topical solution is an oxaborole antifungal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4 ) ].