Tazarotene
Tazarotene Prescribing Information
Tazarotene gel is for topical use only. Tazarotene gel is not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use. Avoid accidental transfer of tazarotene gel into eyes, mouth, or other mucous membranes. If contact with mucous membranes occurs, rinse thoroughly with water
Application of tazarotene gel may cause excessive irritation in the skin of certain sensitive individuals. Local reactions (including blistering and skin desquamation, pruritus, burning, erythema) and hypersensitivity adverse reactions (including urticaria) have been observed with topical tazarotene.
If these adverse reactions occur, consider discontinuing the medication or reducing the dosing frequency, as appropriate, until the integrity of the skin is restored. Alternatively, patients with psoriasis who are being treated with the 0.1% concentration can be switched to the lower concentration. Frequency of application should be closely monitored by careful observation of the clinical therapeutic response and skin tolerance. Therapy can be resumed, or the drug concentration or frequency of application can be increased as the patient becomes able to tolerate treatment.
Concomitant topical medications and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect should be avoided. It is also advisable to "rest" a patient's skin until the effects of such preparations subside before treatment with tazarotene gel is initiated.
Tazarotene gel, should not be used on eczematous skin, as it may cause severe irritation. Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, may be more irritating to patients using tazarotene gel.
Wash hands thoroughly after application.
Gel, 0.05%, in 30 g and 100 g tubes. Each gram of tazarotene gel, 0.05% contains 0.5 mg of tazarotene in a clear to yellow translucent, aqueous gel.
Tazarotene gel is contraindicated in:
- Pregnancy. Retinoids may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female[see Warnings and Precautions (), Use in Specific Populations (
5.1 Embryofetal ToxicityBased on data from animal reproduction studies, retinoid pharmacology and the potential for systemic absorption, tazarotene gel may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Tazarotene elicits malformations and developmental effects associated with retinoids after topical and oral administration to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis.
Systemic exposure to tazarotenic acid is dependent upon the extent of the body surface area treated. In patients treated topically over sufficient body surface area, exposure could be in the same order of magnitude as in orally treated animals.
Tazarotene is a teratogenic substance and causes fetal malformations in animals, and it is not known what level of exposure is required for teratogenicity in humans
[see Clinical Pharmacology ].There were thirteen reported pregnancies in subjects who participated in the clinical trials for topical tazarotene. Nine of the subjects had been treated with topical tazarotene, and the other four had been treated with vehicle. One of the subjects who was treated with tazarotene cream elected to terminate the pregnancy for non-medical reasons unrelated to treatment. The other eight pregnant women who were inadvertently exposed to topical tazarotene during the clinical trials subsequently delivered apparently healthy babies. As the exact timing and extent of exposure in relation to the gestation times are not certain, the significance of these findings is unknown.
Females of Child-bearing PotentialFemales of child-bearing potential should be warned of the potential risk and use adequate birth-control measures when tazarotene gel is used. The possibility that a female of child-bearing potential is pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered.
A negative result for pregnancy test should be obtained within 2 weeks prior to tazarotene gel therapy. Tazarotene gel therapy should begin during a normal menstrual period
[see Use in Specific Populations ].,8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryBased on data from animal reproduction studies, retinoid pharmacology, and the potential for systemic absorption, tazarotene gel may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Safety in pregnant females has not been established. The potential risk to the fetus outweighs the potential benefit to the mother from tazarotene gel during pregnancy; therefore, tazarotene gel should be discontinued as soon as pregnancy is recognized
[see Contraindications , Warnings and Precautions , Clinical Pharmacology ]. Limited case reports of pregnancy in females enrolled in clinical trials for tazarotene gel have not established a clear association with tazarotene and major birth defects or miscarriage risk. Because the exact timing and extent of exposure in relation to the gestational age are not certain, the significance of these findings is unknown.In animal reproduction studies with pregnant rats, tazarotene dosed topically during organogenesis at 0.5 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of tazarotene gel, 0.1% resulted in reduced fetal body weights and reduced skeletal ossification. In animal reproduction studies with pregnant rabbits dosed topically with tazarotene gel at 7 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%, there were single incidences of known retinoid malformations, including spina bifida, hydrocephaly, and heart anomalies.
In animal reproduction studies with pregnant rats and rabbits, tazarotene dosed orally during organogenesis at 0.5 and 13 times, respectively, the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1% resulted in malformations, fetal toxicity, developmental delays, and/or behavioral delays. In pregnant rats, tazarotene dosed orally prior to mating through early gestation resulted in decreased litter size, decreased numbers of live fetuses, decreased fetal body weights, and increased malformations at doses approximately 2 times higher than the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%
[see Data].The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. Adverse outcomes in pregnancy occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
DataAnimal DataIn rats, a tazarotene gel, 0.05% formulation dosed topically during gestation days 6 through 17 at 0.25 mg/kg/day, which represented 0.5 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1% (i.e., 2 mg/cm2over a 20% body surface area), resulted in reduced fetal body weights and reduced skeletal ossification. Rabbits dosed topically with 0.25 mg/kg/day tazarotene gel, which represented 7 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%, during gestation days 6 through 18 were noted with single incidences of known retinoid malformations, including spina bifida, hydrocephaly, and heart anomalies.
When tazarotene was given orally to animals, developmental delays were seen in rats, and malformations and post-implantation loss were observed in rats and rabbits at doses producing 0.5 and 13 times, respectively, the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%.
In female rats orally administered 2 mg/kg/day of tazarotene from 15 days before mating through gestation day 7, which represented 2 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%, classic developmental effects of retinoids were observed including decreased number of implantation sites, decreased litter size, decreased numbers of live fetuses, and decreased fetal body weights. A low incidence of retinoid-related malformations was observed at that dose.
In a pre- and postnatal development toxicity study, topical administration of tazarotene gel (0.125 mg/kg/day) to pregnant female rats from gestation day 16 through lactation day 20 reduced pup survival, but did not affect the reproductive capacity of the offspring. Based on data from another study, the maximum systemic exposure in the rat would be 0.3 times the maximum systemic exposure in subjects treated with the MRHD of tazarotene gel, 0.1%.
)].8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive PotentialPregnancy TestingPregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential within 2 weeks prior to initiating tazarotene gel therapy which should begin during a menstrual period.
ContraceptionFemalesBased on animal studies, tazarotene gel may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman
[see Use in Specific Populations ]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with tazarotene gel. - Individuals who have known hypersensitivity to any of its components[see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.2 Local Irritation and Hypersensitivity ReactionsApplication of tazarotene gel may cause excessive irritation in the skin of certain sensitive individuals. Local reactions (including blistering and skin desquamation, pruritus, burning, erythema) and hypersensitivity adverse reactions (including urticaria) have been observed with topical tazarotene.
If these adverse reactions occur, consider discontinuing the medication or reducing the dosing frequency, as appropriate, until the integrity of the skin is restored. Alternatively, patients with psoriasis who are being treated with the 0.1% concentration can be switched to the lower concentration. Frequency of application should be closely monitored by careful observation of the clinical therapeutic response and skin tolerance. Therapy can be resumed, or the drug concentration or frequency of application can be increased as the patient becomes able to tolerate treatment.
Concomitant topical medications and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect should be avoided. It is also advisable to "rest" a patient's skin until the effects of such preparations subside before treatment with tazarotene gel is initiated.
Tazarotene gel, should not be used on eczematous skin, as it may cause severe irritation. Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, may be more irritating to patients using tazarotene gel.
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Embryofetal toxicity[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Embryofetal ToxicityBased on data from animal reproduction studies, retinoid pharmacology and the potential for systemic absorption, tazarotene gel may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Tazarotene elicits malformations and developmental effects associated with retinoids after topical and oral administration to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis.
Systemic exposure to tazarotenic acid is dependent upon the extent of the body surface area treated. In patients treated topically over sufficient body surface area, exposure could be in the same order of magnitude as in orally treated animals.
Tazarotene is a teratogenic substance and causes fetal malformations in animals, and it is not known what level of exposure is required for teratogenicity in humans
[see Clinical Pharmacology ].There were thirteen reported pregnancies in subjects who participated in the clinical trials for topical tazarotene. Nine of the subjects had been treated with topical tazarotene, and the other four had been treated with vehicle. One of the subjects who was treated with tazarotene cream elected to terminate the pregnancy for non-medical reasons unrelated to treatment. The other eight pregnant women who were inadvertently exposed to topical tazarotene during the clinical trials subsequently delivered apparently healthy babies. As the exact timing and extent of exposure in relation to the gestation times are not certain, the significance of these findings is unknown.
Females of Child-bearing PotentialFemales of child-bearing potential should be warned of the potential risk and use adequate birth-control measures when tazarotene gel is used. The possibility that a female of child-bearing potential is pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered.
A negative result for pregnancy test should be obtained within 2 weeks prior to tazarotene gel therapy. Tazarotene gel therapy should begin during a normal menstrual period
[see Use in Specific Populations ]. - Photosensitivity and Risk of Sunburn[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.3 Photosensitivity and Risk for SunburnBecause of heightened burning susceptibility, exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) should be avoided unless deemed medically necessary, and in such cases, exposure should be minimized during the use of tazarotene gel. Patients must be warned to use sunscreens and protective clothing when using tazarotene gel. Patients with sunburn should be advised not to use tazarotene gel until fully recovered. Patients who may have considerable sun exposure due to their occupation and those patients with inherent sensitivity to sunlight should exercise particular caution when using tazarotene gel.
Tazarotene gel should be administered with caution if the patient is also taking drugs known to be photosensitizers (e.g., thiazides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, phenothiazines, sulfonamides) because of the increased possibility of augmented photosensitivity.
No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with tazarotene gel.
In a trial of 27 healthy female subjects between the ages of 20–55 years receiving a combination oral contraceptive tablet containing 1 mg norethindrone and 35 mcg ethinyl estradiol, concomitant use of tazarotene administered as 1.1 mg orally (mean ± SD C
maxand AUC
0-24of tazarotenic acid were 28.9 ± 9.4 ng/mL and 120.6 ± 28.5 ng•hr/mL, respectively) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol over a complete cycle.
The impact of tazarotene on the pharmacokinetics of progestin only oral contraceptives (i.e., minipills) has not been evaluated.
Tazarotene gel, 0.05% is for topical use and contains the active ingredient, tazarotene. Each gram of tazarotene gel, 0.05% contains 0.5 mg of tazarotene in a clear to yellow translucent, aqueous gel.
Tazarotene is a member of the acetylenic class of retinoids. Chemically, tazarotene is ethyl 6-[(4,4- dimethylthiochroman-6-yl)ethynyl]nicotinate. The compound has an empirical formula of C
21H
21NO
2S and molecular weight of 351.46. The structural formula is shown below:
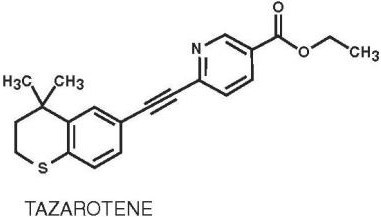
Tazarotene gel contains the following inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol 1%; ascorbic acid; butylated hydroxyanisole; butylated hydroxytoluene; carbomer homopolymer type B; edetate disodium; hexylene glycol; poloxamer 407; polyethylene glycol 400; polysorbate 40; purified water; and tromethamine.