Testosterone Prescribing Information
- Virilization has been reported in children who were secondarily exposed to testosterone gel[see Warnings and Precautions (.) and Adverse Reactions (5.2 Potential for Secondary Exposure to Testosterone
Cases of secondary exposure resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms have included enlargement of the penis or clitoris, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases, these signs and symptoms regressed with removal of the exposure to testosterone gel. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age-appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. The risk of transfer was increased in some of these cases by not adhering to precautions for the appropriate use of the topical testosterone product. Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using testosterone gel 1.62%
[seeDosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Inappropriate changes in genital size or development of pubic hair or libido in children, or changes in body hair distribution, significant increase in acne, or other signs of virilization in adult women should be brought to the attention of a physician and the possibility of secondary exposure to testosterone gel should also be brought to the attention of a physician. Testosterone gel should be promptly discontinued until the cause of virilization has been identified.
)]6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of testosterone gel 1%. Because the reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure (Table 5).
Table 5: Adverse Reactions from Post Approval Experience of Testosterone Gel 1% by System Organ ClassSystem Organ ClassAdverse ReactionBlood and lymphatic system disorders:Elevated hemoglobin or hematocrit, polycythemia, anemia Cardiovascular disorders:Myocardial infarction, stroke Endocrine disorders:Hirsutism Gastrointestinal disorders:Nausea General disorders:Asthenia, edema, malaise Genitourinary disorders:Impaired urination* Hepatobiliary disorders:Abnormal liver function tests Investigations:Lab test abnormal**, elevated PSA, electrolyte changes (nitrogen, calcium, potassium [includes hypokalemia] ,phosphorus, sodium), impaired glucose tolerance, hyperlipidemia, HDL, fluctuating testosterone levels, weight increaseNeoplasms:Prostate cancer Nervous system disorders:Dizziness, headache, insomnia, sleep apnea Psychiatric disorders:Amnesia, anxiety, depression, hostility, emotional lability, decreased libido, nervousness Reproductive system and breast disorders:Gynecomastia, mastodynia, oligospermia, priapism (frequent or prolonged erections), prostate enlargement, BPH, testis disorder*** Respiratory disorders:Dyspnea Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:Acne, alopecia, application site reaction (discolored hair, dry skin, erythema, paresthesia, pruritus, rash), skin dry, pruritus, sweating Vascular disorders:Hypertension, vasodilation (hot flushes), venous thromboembolism *Impaired urination includesnocturia, urinary hesitancy, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, urinary urgency and weak urinary stream**Lab test abnormal includeselevated AST, elevated ALT, elevated testosterone, elevated hemoglobin or hematocrit, elevated cholesterol, elevated cholesterol/LDL ratio, elevated triglycerides, or elevated serum creatinine***Testis disorder includesatrophy or non-palpable testis, varicocele, testis sensitivity or tendernessSecondary Exposure to Testosterone in ChildrenCases of secondary exposure to testosterone resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms of these reported cases have included enlargement of the clitoris (with surgical intervention) or the penis, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases with a reported outcome, these signs and symptoms were reported to have regressed with removal of the testosterone gel exposure. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. In some of the cases, direct contact with the sites of application on the skin of men using testosterone gel was reported. In at least one reported case, the reporter considered the possibility of secondary exposure from items such as the testosterone gel user's shirts and/or other fabric, such as towels and sheets[seeWarnings and Precautions]. - Children should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using testosterone gel[see Dosage and Administration (.) and Warnings and Precautions (
2.2 Administration InstructionsTestosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to clean, dry, intact skin of the upper arms and shoulders. Do not apply testosterone gel 1.62% to any other parts of the body, including the abdomen, genitals, chest, armpits (axillae), or knees
[seeClinical Pharmacology]. Area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by the patient's short sleeve t-shirt. Patients should be instructed to use the palm of the hand to apply testosterone gel 1.62% and spread across the maximum surface area as directed in Table 2 (for pump) and in Figure 1.Table 2: Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%, PumpTotal Dose of
TestosteroneTotal Pump
ActuationsPump Actuations Per Upper Arm and ShoulderUpper Arm and
Shoulder #1Upper Arm and
Shoulder #220.25 mg 1 1 0 40.5 mg 2 1 1 60.75 mg 3 2 1 81 mg 4 2 2 The prescribed daily dose of testosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to the right and left upper arms and shoulders as shown in the shaded areas in Figure 1.
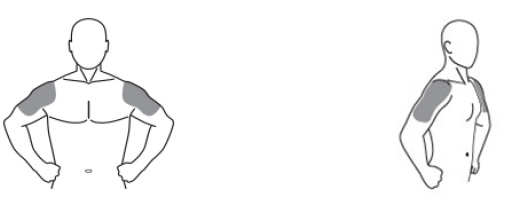 Figure 1. Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%
Figure 1. Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%Once the application site is dry, the site should be covered with clothing
[seeClinical Pharmacology]. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid fire, flames or smoking until the gel has dried since alcohol based products, including testosterone gel 1.62%, are flammable.The patient should avoid swimming or showering or washing the administration site for a minimum of 2 hours after application
[seeClinical Pharmacology].To obtain a full first dose, it is necessary to prime the canister pump. To do so, with the canister in the upright position, slowly and fully depress the actuator three times. Safely discard the gel from the first three actuations. It is only necessary to prime the pump before the first dose.
After the priming procedure, fully depress the actuator once for every 20.25 mg of testosterone gel 1.62%. Testosterone gel 1.62% should be delivered directly into the palm of the hand and then applied to the application sites.
Strict adherence to the following precautions is advised in order to minimize the potential for secondary exposure to testosterone fromtestosterone gel 1.62%-treated skin:- Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application site(s) of men using testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Testosterone gel 1.62% should only be applied to the upper arms and shoulders. The area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by a short sleeve t-shirt.
- Patients should wash their hands with soap and water immediately after applying testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Patients should cover the application site(s) with clothing (e.g., a t-shirt) after the gel has dried.
- Prior to situations in which direct skin-to-skin contact is anticipated, patients should wash the application site(s) thoroughly with soap and water to remove any testosterone residue.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which testosterone gel 1.62% has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible.
)]5.2 Potential for Secondary Exposure to TestosteroneCases of secondary exposure resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms have included enlargement of the penis or clitoris, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases, these signs and symptoms regressed with removal of the exposure to testosterone gel. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age-appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. The risk of transfer was increased in some of these cases by not adhering to precautions for the appropriate use of the topical testosterone product. Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using testosterone gel 1.62%
[seeDosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Inappropriate changes in genital size or development of pubic hair or libido in children, or changes in body hair distribution, significant increase in acne, or other signs of virilization in adult women should be brought to the attention of a physician and the possibility of secondary exposure to testosterone gel should also be brought to the attention of a physician. Testosterone gel should be promptly discontinued until the cause of virilization has been identified.
- Healthcare providers should advise patients to strictly adhere to recommended instructions for use[see Dosage and Administration (), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
2.2 Administration InstructionsTestosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to clean, dry, intact skin of the upper arms and shoulders. Do not apply testosterone gel 1.62% to any other parts of the body, including the abdomen, genitals, chest, armpits (axillae), or knees
[seeClinical Pharmacology]. Area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by the patient's short sleeve t-shirt. Patients should be instructed to use the palm of the hand to apply testosterone gel 1.62% and spread across the maximum surface area as directed in Table 2 (for pump) and in Figure 1.Table 2: Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%, PumpTotal Dose of
TestosteroneTotal Pump
ActuationsPump Actuations Per Upper Arm and ShoulderUpper Arm and
Shoulder #1Upper Arm and
Shoulder #220.25 mg 1 1 0 40.5 mg 2 1 1 60.75 mg 3 2 1 81 mg 4 2 2 The prescribed daily dose of testosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to the right and left upper arms and shoulders as shown in the shaded areas in Figure 1.
 Figure 1. Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%
Figure 1. Application Sites for Testosterone Gel 1.62%Once the application site is dry, the site should be covered with clothing
[seeClinical Pharmacology]. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid fire, flames or smoking until the gel has dried since alcohol based products, including testosterone gel 1.62%, are flammable.The patient should avoid swimming or showering or washing the administration site for a minimum of 2 hours after application
[seeClinical Pharmacology].To obtain a full first dose, it is necessary to prime the canister pump. To do so, with the canister in the upright position, slowly and fully depress the actuator three times. Safely discard the gel from the first three actuations. It is only necessary to prime the pump before the first dose.
After the priming procedure, fully depress the actuator once for every 20.25 mg of testosterone gel 1.62%. Testosterone gel 1.62% should be delivered directly into the palm of the hand and then applied to the application sites.
Strict adherence to the following precautions is advised in order to minimize the potential for secondary exposure to testosterone fromtestosterone gel 1.62%-treated skin:- Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application site(s) of men using testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Testosterone gel 1.62% should only be applied to the upper arms and shoulders. The area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by a short sleeve t-shirt.
- Patients should wash their hands with soap and water immediately after applying testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Patients should cover the application site(s) with clothing (e.g., a t-shirt) after the gel has dried.
- Prior to situations in which direct skin-to-skin contact is anticipated, patients should wash the application site(s) thoroughly with soap and water to remove any testosterone residue.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which testosterone gel 1.62% has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible.
Testosterone gel 1.62% is indicated for replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH], luteinizing hormone [LH]) above the normal range.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations, but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range.
Limitations of use:
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in men with “age-related hypogonadism” (also referred to as “late-onset hypogonadism”) have not been established.
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in males less than 18 years old have not been established [seeUse in Specific Populations (
8.4 Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of testosterone gel 1.62% in pediatric patients less than 18 years old has not been established. Improper use may result in acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses.
)]. - Topical testosterone products may have different doses, strengths, or application instructions that may result in different systemic exposure [seeIndications and Usage (
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGETestosterone gel 1.62% is indicated for replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH], luteinizing hormone [LH]) above the normal range.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations, but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range.
Limitations of use:
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in men with “age-related hypogonadism” (also referred to as “late-onset hypogonadism”) have not been established.
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in males less than 18 years old have not been established[seeUse in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Topical testosterone products may have different doses, strengths, or application instructions that may result in different systemic exposure[seeIndications and Usage (1),andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Testosterone gel 1.62% is indicated for replacement therapy in males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)
Limitations of use:
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in men with “age-related hypogonadism” have not been established.
- Safety and efficacy of testosterone gel 1.62% in males less than 18 years old have not been established.
- Topical testosterone products may have different doses, strengths, or application instructions that may result in different systemic exposure.
),andClinical Pharmacology (12.3 PharmacokineticsAbsorptionTestosterone gel 1.62% delivers physiologic amounts of testosterone, producing circulating testosterone concentrations that approximate normal levels (300 – 1000 ng/dL) seen in healthy men. Testosterone gel 1.62% provides continuous transdermal delivery of testosterone for 24 hours following once daily application to clean, dry, intact skin of the shoulders and upper arms. Average serum testosterone concentrations over 24 hours (Cavg) observed when testosterone gel 1.62% was applied to the upper arms/shoulders were comparable to average serum testosterone concentrations (Cavg) when testosterone gel 1.62% was applied using a rotation method utilizing the abdomen and upper arms/shoulders. The rotation of abdomen and upper arms/shoulders was a method used in the pivotal clinical trial
[seeClinical Studies (14.1)].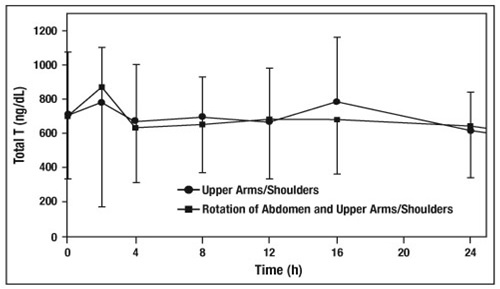 Figure 2: Mean (±SD) Serum Total Testosterone Concentrations on Day 7 in Patients Following Testosterone Gel1.62% Once-Daily Application of 81 mg of Testosterone (N=33) for 7 DaysDistribution
Figure 2: Mean (±SD) Serum Total Testosterone Concentrations on Day 7 in Patients Following Testosterone Gel1.62% Once-Daily Application of 81 mg of Testosterone (N=33) for 7 DaysDistributionCirculating testosterone is primarily bound in the serum to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. Approximately 40% of testosterone in plasma is bound to SHBG, 2% remains unbound (free) and the rest is loosely bound to albumin and other proteins.
MetabolismTestosterone is metabolized to various 17-keto steroids through two different pathways. The major active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and DHT.
ExcretionThere is considerable variation in the half-life of testosterone concentration as reported in the literature, ranging from 10 to 100 minutes. About 90% of a dose of testosterone given intramuscularly is excreted in the urine as glucuronic acid and sulfuric acid conjugates of testosterone and its metabolites. About 6% of a dose is excreted in the feces, mostly in the unconjugated form. Inactivation of testosterone occurs primarily in the liver.
When testosterone gel 1.62% treatment is discontinued, serum testosterone concentrations return to approximately baseline concentrations within 48 to 72 hours after administration of the last dose.
Potential for testosterone transferThe potential for testosterone transfer following administration of testosterone gel 1.62% when it was applied only to upper arms/shoulders was evaluated in two clinical studies of males dosed with testosterone gel 1.62% and their untreated female partners. In one study, 8 male subjects applied a single dose of testosterone gel 1.62% 81 mg to their shoulders and upper arms. Two (2) hours after application, female subjects rubbed their hands, wrists, arms, and shoulders to the application site of the male subjects for 15 minutes. Serum concentrations of testosterone were monitored in female subjects for 24 hours after contact occurred. After direct skin-to-skin contact with the site of application, mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxin female subjects increased by 280% and 267%, respectively, compared to mean baseline testosterone concentrations. In a second study evaluating transfer of testosterone, 12 male subjects applied a single dose of testosterone gel 1.62% 81 mg to their shoulders and upper arms. Two (2) hours after application, female subjects rubbed their hands, wrists, arms, and shoulders to the application site of the male subjects for 15 minutes while the site of application was covered by a t-shirt. When a t-shirt was used to cover the site of application, mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxin female subjects increased by 6% and 11%, respectively, compared to mean baseline testosterone concentrations.
A separate study was conducted to evaluate the potential for testosterone transfer from 16 males dosed with testosterone gel 1.62% 81 mg when it was applied to abdomen only for 7 days, a site of application not approved for testosterone gel 1.62%. Two (2) hours after application to the males on each day, the female subjects rubbed their abdomens for 15 minutes to the abdomen of the males. The males had covered the application area with a T-shirt. The mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxin female subjects on day 1 increased by 43% and 47%, respectively, compared to mean baseline testosterone concentrations. The mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxin female subjects on day 7 increased by 60% and 58%, respectively, compared to mean baseline testosterone concentrations.
Effect of showeringIn a randomized, 3-way (3 treatment periods without washout period) crossover study in 24 hypogonadal men, the effect of showering on testosterone exposure was assessed after once daily application of testosterone gel 1.62% 81 mg to upper arms/shoulders for 7 days in each treatment period. On the 7th day of each treatment period, hypogonadal men took a shower with soap and water at either 2, 6, or 10 hours after drug application. The effect of showering at 2 or 6 hours post-dose on Day 7 resulted in 13% and 12% decreases in mean Cavg, respectively, compared to Day 6 when no shower was taken after drug application. Showering at 10 hours after drug application had no effect on bioavailability. The amount of testosterone remaining in the outer layers of the skin at the application site on the 7th day was assessed using a tape stripping procedure and was reduced by at least 80% after showering 2 to 10 hours post-dose compared to on the 6th day when no shower was taken after drug application.
Effect of hand washingIn a randomized, open-label, single-dose, 2-way crossover study in 16 healthy male subjects, the effect of hand washing on the amount of residual testosterone on the hands was evaluated. Subjects used their hands to apply the maximum dose (81 mg testosterone) of testosterone gel 1.62% to their upper arms and shoulders. Within 1 minute of applying the gel, subjects either washed or did not wash their hands prior to study personnel wiping the subjects’ hands with ethanol dampened gauze pads. The gauze pads were then analyzed for residual testosterone content. A mean (SD) of 0.1 (0.04) mg of residual testosterone (0.12% of the actual applied dose of testosterone, and a 96% reduction compared to when hands were not washed) was recovered after washing hands with water and soap.
Effect of sunscreen or moisturizing lotion on absorption of testosteroneIn a randomized, 3-way (3 treatment periods without washout period) crossover study in 18 hypogonadal males, the effect of applying a moisturizing lotion or a sunscreen on the absorption of testosterone was evaluated with the upper arms/shoulders as application sites. For 7 days, moisturizing lotion or sunscreen (SPF 50) was applied daily to the testosterone gel 1.62% application site 1 hour after the application of testosterone gel 1.62% 40.5 mg.
Application of moisturizing lotion increased mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxby 14% and 17%, respectively, compared to testosterone gel 1.62% administered alone. Application of sunscreen increased mean testosterone Cavgand Cmaxby 8% and 13%, respectively, compared to testosterone gel 1.62% applied alone.
)].
Prior to initiating testosterone gel 1.62%, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
- Dosage and Administration fortestosterone gel 1.62% differs from testosterone gel 1%. For dosage and administration of testosterone gel 1% refer to its full prescribing information. (2)
- Prior to initiating testosterone gel 1.62%, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone has been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these concentrations are below the normal range .
- Starting dose of testosterone gel 1.62% is 40.5 mg of testosterone (2 pump actuations), applied topically once daily in the morning.
- Apply to clean, dry, intact skin of the shoulders and upper arms. Do not apply testosterone gel 1.62% to any other parts of the body including the abdomen, genitals, chest, armpits (axillae), or knees.
- Dose adjustment: testosterone gel 1.62% can be dose adjusted between a minimum of 20.25 mg of testosterone (1 pump actuation) and a maximum of 81 mg of testosterone (4 pump actuations). The dose should be titrated based on the pre-dose morning serum testosterone concentration at approximately 14 days and 28 days after starting treatment or following dose adjustment. Additionally, serum testosterone concentration should be assessed periodically thereafter.
- Patients should wash hands immediately with soap and water after applying testosterone gel 1.62% and cover the application site(s) with clothing after the gel has dried. Wash the application site thoroughly with soap and water prior to any situation where skin-to-skin contact of the application site with another person is anticipated.
The recommended starting dose of testosterone gel 1.62% is 40.5 mg of testosterone (2 pump actuations) applied topically once daily in the morning to the shoulders and upper arms.
The dose can be adjusted between a minimum of 20.25 mg of testosterone (1 pump actuation) and a maximum of 81 mg of testosterone (4 pump actuations). To ensure proper dosing, the dose should be titrated based on the pre-dose morning serum testosterone concentration from a single blood draw at approximately 14 days and 28 days after starting treatment or following dose adjustment. In addition, serum testosterone concentration should be assessed periodically thereafter. Table 1 describes the dose adjustments required at each titration step.
Pre-Dose Morning Total Serum Testosterone Concentration | Dose Titration |
| Greater than 750 ng/dL | Decrease daily dose by 20.25 mg (1 pump actuation) |
| Equal to or greater than 350 and equal to or less than 750 ng/dL | No change: continue on current dose |
| Less than 350 ng/dL | Increase daily dose by 20.25 mg (1 pump actuation) |
The application site and dose of testosterone gel 1.62% are not interchangeable with other topical testosterone products.
Testosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to clean, dry, intact skin of the upper arms and shoulders. Do not apply testosterone gel 1.62% to any other parts of the body, including the abdomen, genitals, chest, armpits (axillae), or knees
Total Dose of Testosterone | Total Pump Actuations | Pump Actuations Per Upper Arm and Shoulder | |
Upper Arm and Shoulder #1 | Upper Arm and Shoulder #2 | ||
| 20.25 mg | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 40.5 mg | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 60.75 mg | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 81 mg | 4 | 2 | 2 |
The prescribed daily dose of testosterone gel 1.62% should be applied to the right and left upper arms and shoulders as shown in the shaded areas in Figure 1.

Once the application site is dry, the site should be covered with clothing
The patient should avoid swimming or showering or washing the administration site for a minimum of 2 hours after application
To obtain a full first dose, it is necessary to prime the canister pump. To do so, with the canister in the upright position, slowly and fully depress the actuator three times. Safely discard the gel from the first three actuations. It is only necessary to prime the pump before the first dose.
After the priming procedure, fully depress the actuator once for every 20.25 mg of testosterone gel 1.62%. Testosterone gel 1.62% should be delivered directly into the palm of the hand and then applied to the application sites.
- Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application site(s) of men using testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Testosterone gel 1.62% should only be applied to the upper arms and shoulders. The area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by a short sleeve t-shirt.
- Patients should wash their hands with soap and water immediately after applying testosterone gel 1.62%.
- Patients should cover the application site(s) with clothing (e.g., a t-shirt) after the gel has dried.
- Prior to situations in which direct skin-to-skin contact is anticipated, patients should wash the application site(s) thoroughly with soap and water to remove any testosterone residue.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which testosterone gel 1.62% has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible.
Prior to initiating testosterone gel 1.62%, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
Testosterone gel 1.62% for topical use only, is available as follows:
- A metered-dose pump. Each pump actuation delivers 20.25 mg of testosterone in 1.25 g of gel.
- Testosterone gel 1.62% is contraindicated in men with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate [seeWarnings and Precautions ()
5.1 Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer- Patients with BPH treated with androgens are at an increased risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
- Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluation of patients for prostate cancer prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens is appropriate[seeContraindications (4)].
andAdverse Reactions (.)]6.1 Clinical Trial ExperienceBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Testosterone gel 1.62% was evaluated in a two-phase, 364-day, controlled clinical study.
The first phase was a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled period of 182 days, in which 234 hypogonadal men were treated with testosterone gel 1.62% and 40 received placebo. Patients could continue in an open-label, non-comparative, maintenance period for an additional 182 days
[seeClinical Studies].The most common adverse reaction reported in the double-blind period was increased prostate specific antigen (PSA) reported in 26 testosterone gel 1.62%-treated patients (11.1%). In 17 patients, increased PSA was considered an adverse event by meeting one of the two pre-specified criteria for abnormal PSA values, defined as (1) average serum PSA >4 ng/mL based on two separate determinations, or (2) an average change from baseline in serum PSA of greater than 0.75 ng/mL on two determinations.
During the 182-day, double-blind period of the clinical trial, the mean change in serum PSA value was 0.14 ng/mL for patients receiving testosterone gel 1.62% and -0.12 ng/mL for the patients in the placebo group. During the double-blind period, seven patients had a PSA value >4 ng/mL, four of these seven patients had PSA less than or equal to 4 ng/mL upon repeat testing. The other three patients did not undergo repeat PSA testing.
During the 182-day, open-label period of the study, the mean change in serum PSA values was 0.10 ng/mL for both patients continuing on active therapy and patients transitioning onto active from placebo. During the open-label period, three patients had a serum PSA value > 4 ng/mL, two of whom had a serum PSA less than or equal to 4 ng/mL upon repeated testing. The other patient did not undergo repeat PSA testing. Among previous placebo patients, 3 of 28 (10.7%), had increased PSA as an adverse event in the open-label period.
Table 4 shows adverse reactions reported by >2% of patients in the 182-day, double-blind period of the testosterone gel 1.62% clinical trial and more frequent in the testosterone gel 1.62% treated group versus placebo.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions Reported in >2% of Patients in the 182-Day, Double-Blind Period of Testosterone Gel 1.62% Clinical Trial
*Number (%) of PatientsAdverse ReactionTestosterone gel1.62%
N=234Placebo
N= 40PSA increased* 26 (11.1%) 0% Emotional lability** 6 (2.6%) 0% Hypertension 5 (2.1%) 0% Hematocrit or hemoglobin increased 5 (2.1%) 0% Contact dermatitis*** 5 (2.1%) 0% PSA increasedincludes: PSA values that met pre-specified criteria for abnormal PSA values (an average change from baseline > 0.75 ng/mL and/or an average PSA value >4 ng/mL based on two measurements) as well as those reported as adverse events.**
Emotional labilityincludes: mood swings, affective disorder, impatience, anger, and aggression.***
Contact dermatitisincludes: 4 patients with dermatitis at non-application sites.Other adverse reactions occurring in less than or equal to 2% of testosterone gel 1.62%-treated patients and more frequently than placebo included: frequent urination, and hyperlipidemia.
In the open-label period of the study (N=191), the most commonly reported adverse reaction (experienced by greater than 2% of patients) was increased PSA (n=13; 6.2%) and sinusitis. Other adverse reactions reported by less than or equal to 2% of patients included increased hemoglobin or hematocrit, hypertension, acne, libido decreased, insomnia, and benign prostatic hypertrophy.
During the 182-day, double-blind period of the clinical trial, 25 testosterone gel 1.62%-treated patients (10.7%) discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions. These adverse reactions included 17 patients with PSA increased and 1 report each of: hematocrit increased, blood pressure increased, frequent urination, diarrhea, fatigue, pituitary tumor, dizziness, skin erythema and skin nodule (same patient – neither at application site), vasovagal syncope, and diabetes mellitus. During the 182-day, open-label period, 9 patients discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions. These adverse reactions included 6 reports of PSA increased, 2 of hematocrit increased, and 1 each of triglycerides increased and prostate cancer.
Application Site ReactionsIn the 182-day double-blind period of the study, application site reactions were reported in two (2/234; 0.9%) patients receiving testosterone gel 1.62%, both of which resolved. Neither of these patients discontinued the study due to application site adverse reactions. In the open-label period of the study, application site reactions were reported in three (3/219; 1.4%) additional patients that were treated with testosterone gel 1.62%. None of these subjects were discontinued from the study due to application site reactions.
- Testosterone gel 1.62% is contraindicated in women who are pregnant. Testosterone gel 1.62% can cause virilization of the female fetus when administered to a pregnant woman. Pregnant women need to be aware of the potential for transfer of testosterone from men treated with testosterone gel 1.62%. If a pregnant woman is exposed to testosterone gel 1.62%, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [seeWarnings and Precautions ()5.2 Potential for Secondary Exposure to Testosterone
Cases of secondary exposure resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms have included enlargement of the penis or clitoris, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases, these signs and symptoms regressed with removal of the exposure to testosterone gel. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age-appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. The risk of transfer was increased in some of these cases by not adhering to precautions for the appropriate use of the topical testosterone product. Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using testosterone gel 1.62%
[seeDosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Inappropriate changes in genital size or development of pubic hair or libido in children, or changes in body hair distribution, significant increase in acne, or other signs of virilization in adult women should be brought to the attention of a physician and the possibility of secondary exposure to testosterone gel should also be brought to the attention of a physician. Testosterone gel should be promptly discontinued until the cause of virilization has been identified.
andUse in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Testosterone gel 1.62% for topical use is a clear, colorless to light yellow gel containing testosterone. Testosterone is an androgen. Testosterone gel 1.62% is available in a metered-dose pump.
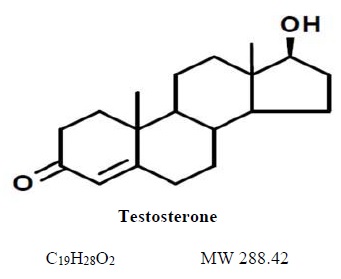
The active pharmacologic ingredient in testosterone gel 1.62% is testosterone. Testosterone USP is a white or slightly creamy white powder chemically described as 17-beta hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one. The structural formula is:
The inactive ingredients in testosterone gel 1.62% are: carbopol 980, ethyl alcohol, isopropyl myristate, purified water, and sodium hydroxide.