Valganciclovir Prescribing Information
- Hematologic Toxicity: Severe leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and bone marrow failure including aplastic anemia have been reported in patients treated with valganciclovir[see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.1 Hematologic ToxicitySevere leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and bone marrow failure including aplastic anemia have been reported in patients treated with valganciclovir or ganciclovir. Valganciclovir should be avoided if the absolute neutrophil count is less than 500 cells/μL, the platelet count is less than 25,000/μL, or the hemoglobin is less than 8 g/dL. Valganciclovir should also be used with caution in patients with pre-existing cytopenias and in patients receiving myelosuppressive drugs or irradiation. Cytopenia may occur at any time during treatment and may worsen with continued dosing. Cell counts usually begin to recover within 3 days to 7 days after discontinuing drug. In patients with severe leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia and/or thrombocytopenia, treatment with hematopoietic growth factors may be considered.
Due to the frequency of neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia in patients receiving valganciclovir
[see Adverse Reactions ], complete blood counts with differential and platelet counts should be performed frequently, especially in infants, in patients with renal impairment, and in patients in whom ganciclovir or other nucleoside analogues have previously resulted in leukopenia, or in whom neutrophil counts are less than 1,000 cells/μL at the beginning of treatment. Increased monitoring for cytopenias may be warranted if therapy with oral ganciclovir is changed to valganciclovir , because of increased plasma concentrations of ganciclovir after valganciclovir administration[see Clinical Pharmacology ]. - Impairment of Fertility: Based on animal data and limited human data, valganciclovir may cause temporary or permanent inhibition of spermatogenesis in males and suppression of fertility in females [see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.3 Impairment of FertilityBased on animal data and limited human data, valganciclovir at the recommended human doses may cause temporary or permanent inhibition of spermatogenesis in males, and may cause suppression of fertility in females. Advise patients that fertility may be impaired with use of valganciclovir
[see Use in Specific Populations , Nonclinical Toxicology ]. - Fetal Toxicity: Based on animal data, valganciclovir has the potential to cause birth defects in humans [see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.4 Fetal ToxicityGanciclovir may cause fetal toxicity when administered to pregnant women based on findings in animal studies. When given to pregnant rabbits at dosages resulting in 2 times the human exposure (based on AUC), ganciclovir caused malformations in multiple organs of the fetuses. Maternal and fetal toxicity were also observed in pregnant mice and rabbits. Therefore, valganciclovir has the potential to cause birth defects. Pregnancy should be avoided in female patients taking valganciclovir and in females with male partners taking valganciclovir. Females of reproductive potential should be advised to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 30 days following treatment with valganciclovir because of the potential risk to the fetus. Similarly, males should be advised to use condoms during and for at least 90 days following treatment with valganciclovir
[see Dosage and Administration , Use in Specific Populations , Nonclinical Toxicology ]. - Mutagenesis and Carcinogenesis: Based on animal data, valganciclovir has the potential to cause cancers in humans[see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.5 Mutagenesis and CarcinogenesisAnimal data indicate that ganciclovir is mutagenic and carcinogenic. Valganciclovir should therefore be considered a potential carcinogen in humans
[see Dosage and Administration , Nonclinical Toxicology ].
Valganciclovir is a deoxynucleoside analogue cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA polymerase inhibitor indicated for:
- Treatment of CMV retinitis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
- Prevention of CMV disease in kidney, heart, and kidney-pancreas transplant patients at high risk.
- Prevention of CMV disease in kidney and heart transplant patients at high risk.
Adult Dosage ( For dosage recommendations in adult patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration ] .Treatment of CMV Retinitis:
Prevention of CMV Disease:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment of CMV retinitis | Induction: 900 mg (two 450 mg tablets) twice a day for 21 days Maintenance: 900 mg (two 450 mg tablets) once a day | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prevention of CMV disease in heart or kidney-pancreas transplant patients | 900 mg (two 450 mg tablets) once a day within 10 days of transplantation until 100 days post-transplantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prevention of CMV disease in kidney transplant patients | 900 mg (two 450 mg tablets) once a day within 10 days of transplantation until 200 days post-transplantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pediatric Dosage ( Prevention of CMV Disease in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Patients: For pediatric kidney transplant patients 4 months to 16 years of age, the recommended once daily mg dose (7 x BSA x CrCl) should start within 10 days of post-transplantation until 200 days post-transplantation.Prevention of CMV Disease in Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients : For pediatric heart transplant patients 1 month to 16 years of age, the recommended once daily mg dose (7 x BSA x CrCl) should start within 10 days of transplantation until 100 days post-transplantation.The recommended once daily dosage of valganciclovir tablets is based on body surface area (BSA) and creatinine clearance (CrCl) derived from a modified Schwartz formula, and is calculated using the equation below: Pediatric Dose (mg) = 7 x BSA x CrCl (calculated using a modified Schwartz formula). If the calculated Schwartz creatinine clearance exceeds 150 mL/min/1.73m2, then a maximum value of 150 mL/min/1.73m2should be used in the equation. The k values used in the modified Schwartz formula are based on pediatric patient age, as shown in Table 1. 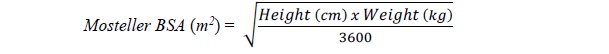 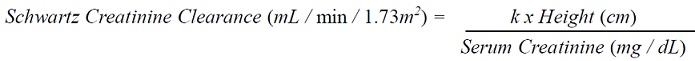 Table 1: k Values According to Pediatric Patient Age*
Monitor serum creatinine levels regularly and consider changes in height and body weight and adapt the dose as appropriate during prophylaxis period. All calculated doses should be rounded to the nearest 25 mg increment for the actual deliverable dose. If the calculated dose exceeds 900 mg, a maximum dose of 900 mg should be administered. Valganciclovir for oral solution is the preferred formulation since it provides the ability to administer a dose calculated according to the formula above; however, valganciclovir tablets may be used if the calculated doses are within 10% of available tablet strength (450 mg). For example, if the calculated dose is between 405 mg and 495 mg, one 450 mg tablet may be taken. Before prescribing valganciclovir tablets, pediatric patients should be assessed for the ability to swallow tablets. 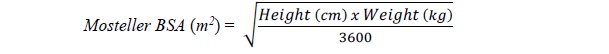 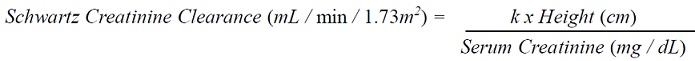 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prevention of CMV disease in kidney transplant patients 4 months to 16 years of age | Dose once a day within 10 days of transplantation until 200 days post-transplantation according to dosage algorithm (note the calculation of creatinine clearance using a modified Schwartz formula in children) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prevention of CMV disease in heart transplant patients 1 month to 16 years of age | Dose once a day within 10 days of transplantation until 100 days post-transplantation according to dosage algorithm (note the calculation of creatinine clearance using a modified Schwartz formula in children) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Valganciclovir tablets should be taken with food. (,
2.1 General Dosing Information- Adult patients should use valganciclovir tablets, not valganciclovir for oral solution.
- Valganciclovir tablets should be taken with food[see Clinical Pharmacology ].
)12.3 PharmacokineticsValganciclovir is a prodrug of ganciclovir. Valganciclovir Cmaxand AUC are approximately 1% and 3% of those of ganciclovir, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics in Adults:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir after administration of valganciclovir tablets have been evaluated in HIV-and CMV-seropositive patients, patients with AIDS and CMV retinitis, and in solid organ transplant patients (Table 10).Table 10: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics* in Healthy Volunteers and HIV-positive/CMV-positive Adults AdministeredValganciclovirTablets 900 mg Once Daily with Food*Data were obtained from single and multiple dose studies in healthy volunteers, HIV-positive patients, and HIV-positive/CMV-positive patients with and without retinitis. Patients with CMV retinitis tended to have higher ganciclovir plasma concentrations than patients without CMV retinitis. PK parameterNValue (Mean±SD)AUC0-24h(mcg ∙h/mL)57 29.1 ± 9.7 Cmax(mcg/mL) 58 5.61 ± 1.52 Absolute oral bioavailability (%) 32 59.4 ± 6.1 Elimination half-life (hr) 73 4.08 ± 0.76 Renal clearance (mL/min/kg) 20 3.21 ± 0.75
(1 study, n=20)The systemic ganciclovir exposures attained following administration of 900 mg valganciclovir tablets once daily were comparable across kidney, heart and liver transplant recipients (Table 11).
Table 11: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients AdministeredValganciclovirTablets 900 mg Once Daily with Food* Includes kidney-pancreas ParameterValue (Mean±SD)Heart Transplant Recipients(N=17)Liver Transplant Recipients(N=75)Kidney Transplant Recipients*(N=68)AUC0-24h(mcg ∙h/mL)40.2 ± 11.8 46.0 ± 16.1 48.2 ± 14.6 Cmax(mcg/mL) 4.9 ± 1.1 5.4 ± 1.5 5.3 ± 1.5 Elimination half-life (hr) 6.58 ± 1.50 6.18 ± 1.42 6.77 ± 1.25 The pharmacokinetic parameters of ganciclovir following 200 days of valganciclovir administration in high-risk kidney transplant patients were similar to those in solid organ transplant patients who received valganciclovir for 100 days.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and ExcretionThe pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of valganciclovir are provided in Table 12.
Table 12: Pharmacokinetic Properties of Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir Associated withValganciclovir TabletsaSteady state ganciclovir PK was assessed after administration of valganciclovir tablets (875 mg once daily) with a high fat meal containing approximately 600 total calories (31.1 g fat, 51.6 g carbohydrates and 22.2 g protein) to 16 HIV-positive subjects. ValganciclovirGanciclovirAbsorptionTmax(h)
median (min-max) (fed conditions)2.18
1.7 h to 3.0 hFood effect (high fat meal/fasting): PK parameter ratio and 90% confidence intervala Cmax:
1.14 (0.95, 1.36)
AUC:
1.30 (1.07, 1.51)a
Tmax: ↔Distribution% Bound to human plasma proteins (ex vivo) Unknown 1% to 2% over 0.5 mcg/mL to 51 mcg/mL Cerebrospinal fluid penetration Unknown Yes MetabolismHydrolyzed by intestinal and liver esterases No significant metabolism EliminationDose proportionality AUC was dose proportional under fed conditions across a valganciclovir dose range of 450 mg to 2,625 mg Major route of elimination Metabolism to ganciclovir Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion t1/2(h) See Tables 10 and 11 % Of dose excreted in urine Unknown % Of dose excreted in feces Unknown Specific Populations:Renal Impairment:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir from a single oral dose of 900 mg valganciclovir tablets were evaluated in 24 otherwise healthy individuals with renal impairment. Decreased renal function results in decreased clearance of ganciclovir and increased terminal half-life (Table 13).Table 13: Pharmacokinetics of Ganciclovir from a Single Oral Dose of 900 mg Valganciclovir Tablets*Creatinine clearance calculated from 24-hour urine collection. EstimatedCreatinine Clearance*
(mL/min)NApparent Clearance
(mL/min)Mean±SDAUClast(mcg∙h/mL)Mean±SDHalf-life(hours)Mean±SD51-70
21-50
11-20
≤ 106
6
6
6249 ± 99
136 ± 64
45 ± 11
12.8 ± 849.5 ± 22.4
91.9 ± 43.9
223 ± 46
366 ± 664.85 ± 1.4
10.2 ± 4.4
21.8 ± 5.2
67.5 ± 34Hemodialysis reduces plasma concentrations of ganciclovir by about 50% following valganciclovir administration. Adult patients receiving hemodialysis (CrCl less than 10 mL/min) cannot use valganciclovir tablets because the daily dose of valganciclovir tablets required for these patients is less than 450 mg
[see Dosage and Administration and Use in Specific Populations ].Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Patients:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir were evaluated following the administration of valganciclovir in 63 pediatric solid organ transplant patients aged 4 months to 16 years, and in 16 pediatric heart transplant patients less than 4 months of age. In these studies, patients received oral doses of valganciclovir (either valganciclovir for oral solution or tablets) to produce exposure equivalent to an adult 900 mg dose[see Dosage and Administration , Adverse Reactions , Use in Specific Populations , Clinical Studies ].In studies using the pediatric valganciclovir dosing algorithm, the pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir were similar across organ types and age ranges (Table 14). Relative to adult transplant patients (Table 11), AUC values in pediatric patients were somewhat increased, but were within the range considered safe and effective in adults.
Table 14: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics by Age in Pediatric Solid Organ Transplant Patients Administered ValgancicloviraN= number of patients, NA=not applicable
aAges ranged from 26 days to 124 days.Age GroupOrganPK Parameter mean (SD)< 4 months4 months to≤ 2 years> 2 years to < 12 years≥ 12 years
Heart(N=26)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)14a
66.3 (20.5)
10.8 (3.30)
3.5 (0.87)6
55.4 (22.8)
8.2 (2.5)
3.8 (1.7)2
59.6 (21.0)
12.5 (1.2)
2.8 (0.9)4
60.6 (25.0)
9.5 (3.3)
4.9 (0.8)
Kidney(N=31)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)
NA2
67.6 (13.0)
10.4 (0.4)
4.5 (1.5)10
55.9 (12.1)
8.7 (2.1)
4.8 (1.0)19
47.8 (12.4)
7.7 (2.1)
6.0 (1.3)
Liver(N=17)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)NA 9
69.9 (37.0)
11.9 (3.7)
2.8 (1.5)6
59.4 (8.1)
9.5 (2.3)
3.8 (0.7)2
35.4 (2.8)
5.5 (1.1)
4.4 (0.2)Pharmacokinetics in Geriatric Patients:The pharmacokinetic characteristics of valganciclovir in elderly patients have not been established.In vivo drug-drug interaction studies were not conducted with valganciclovir. However, because valganciclovir is rapidly and extensively converted to ganciclovir, interactions associated with ganciclovir will be expected for valganciclovir
Drug Interactions:[see Drug Interactions ].Table 15 and Table 16 provide a listing of established drug interaction studies with ganciclovir. Table 15 provides the effects of coadministered drug on ganciclovir plasma pharmacokinetic parameters, whereas Table 16 provides the effects of ganciclovir on plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of coadministered drug.
Table 15: Results of Drug Interaction Studies with Ganciclovir: Effects of Coadministered Drug on Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetic ParametersCoadministered DrugGanciclovir DosageNGanciclovir Pharmacokinetic (PK) ParameterMycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1.5 g single dose 5 mg/kg IV single dose 12 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed (patients with normal renal function) Trimethoprim 200 mg once daily 1,000 mg every 8 hours 12 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours simultaneously administered with ganciclovir 5 mg/kg IV twice daily 11 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed 5 mg/kg IV once daily 11 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed Probenecid 500 mg every 6 hours 1,000 mg every 8 hours 10 AUC ↑ 53 ± 91%
(range: -14% to 299%)
Ganciclovir renal clearance ↓
22 ± 20%
(range: -54% to -4%)Table 16: Results of Drug Interaction Studies with Ganciclovir: Effects of Ganciclovir on Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered DrugCoadministered DrugGanciclovir DosageNCoadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic (PK) ParameterOral cyclosporine at therapeutic doses 5 mg/kg infused over 1 hour every 12 hours 93 In a retrospective analysis of liver allograft recipients, there was no evidence of an effect on cyclosporine whole blood concentrations. Mycophenolate mofetil
(MMF) 1.5 g single dose5 mg/kg IV single dose 12 No PK interaction observed (patients with normal renal function) Trimethoprim 200 mg once daily 1,000 mg every 8 hours 12 No effect on trimethoprim PK parameters observed Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours 5 mg/kg IV twice daily 11 AUC0-12↑70 ± 40%
(range: 3% to 121%)
Cmax↑49 ± 48%
(range: -28% to 125%)Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours 5 mg/kg IV once daily 11 AUC0-12↑50 ± 26%
(range: 22% to 110%)
Cmax↑36 ± 36%
(range: -27% to 94%) - Valganciclovir tablets should not be broken or crushed. ()
2.6 Handling and DisposalCaution should be exercised in the handling of valganciclovir tablets. Tablets should not be broken or crushed. Because valganciclovir is considered a potential teratogen and carcinogen in humans, caution should be observed in handling broken tablets
[see Warnings and Precautions ]. Avoid direct contact with broken or crushed tablets with skin or mucous membranes. If such contact occurs, wash thoroughly with soap and water, and rinse eyes thoroughly with plain water.Handle and dispose valganciclovir according to guidelines for antineoplastic drugs because ganciclovir shares some of the properties of antitumor agents (i.e., carcinogenicity and mutagenicity).2
- Adult patients should use valganciclovir tablets, not valganciclovir for oral solution. ()
2.1 General Dosing Information- Adult patients should use valganciclovir tablets, not valganciclovir for oral solution.
- Valganciclovir tablets should be taken with food[see Clinical Pharmacology ].
- Adults with renal impairment: Adjust dose based on creatinine clearance. For adult patients receiving hemodialysis a dose recommendation cannot be given. (,
2.5 Dosage Recommendation for Adult Patients with Renal ImpairmentSerum creatinine levels or estimated creatinine clearance should be monitored regularly during treatment. Dosage recommendations for adult patients with reduced renal function are provided in Table 2. For adult patients on hemodialysis (CrCl less than 10 mL/min), a dose recommendation for valganciclovir tablets cannot be given
[see Use in Specific Populations , Clinical Pharmacology ].Table 2: Dosage Recommendations for Adult Patients with Impaired Renal Function*An estimated creatinine clearance in adults is calculated from serum creatinine by the following formulas:
(140 – age [years]) x (body weight [kg])
For males = ——————————————
(72) x (serum creatinine [mg/dL])
For females = 0.85 x male valueValganciclovir 450 mg TabletsCrCl* (mL/min)Induction DoseMaintenance/Prevention Dose≥ 60 900 mg twice daily 900 mg once daily 40 – 59 450 mg twice daily 450 mg once daily 25 – 39 450 mg once daily 450 mg every 2 days 10 – 24 450 mg every 2 days 450 mg twice weekly < 10
(on hemodialysis)not recommended not recommended Dosing in pediatric patients with renal impairment can be done using the recommended equations because CrCl is a component in the calculation
[see Dosage and Administration ].,8.6 Renal ImpairmentDose reduction is recommended when administering valganciclovir to patients with renal impairment
[see Dosage and Administration , Warnings and Precautions , Clinical Pharmacology ].For adult patients on hemodialysis (CrCl less than 10 mL/min), valganciclovir tablets should not be used. Adult hemodialysis patients should use ganciclovir in accordance with the dose-reduction algorithm cited in the CYTOVENE®-IV complete product information section on DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration and Clinical Pharmacology ].)12.3 PharmacokineticsValganciclovir is a prodrug of ganciclovir. Valganciclovir Cmaxand AUC are approximately 1% and 3% of those of ganciclovir, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics in Adults:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir after administration of valganciclovir tablets have been evaluated in HIV-and CMV-seropositive patients, patients with AIDS and CMV retinitis, and in solid organ transplant patients (Table 10).Table 10: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics* in Healthy Volunteers and HIV-positive/CMV-positive Adults AdministeredValganciclovirTablets 900 mg Once Daily with Food*Data were obtained from single and multiple dose studies in healthy volunteers, HIV-positive patients, and HIV-positive/CMV-positive patients with and without retinitis. Patients with CMV retinitis tended to have higher ganciclovir plasma concentrations than patients without CMV retinitis. PK parameterNValue (Mean±SD)AUC0-24h(mcg ∙h/mL)57 29.1 ± 9.7 Cmax(mcg/mL) 58 5.61 ± 1.52 Absolute oral bioavailability (%) 32 59.4 ± 6.1 Elimination half-life (hr) 73 4.08 ± 0.76 Renal clearance (mL/min/kg) 20 3.21 ± 0.75
(1 study, n=20)The systemic ganciclovir exposures attained following administration of 900 mg valganciclovir tablets once daily were comparable across kidney, heart and liver transplant recipients (Table 11).
Table 11: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients AdministeredValganciclovirTablets 900 mg Once Daily with Food* Includes kidney-pancreas ParameterValue (Mean±SD)Heart Transplant Recipients(N=17)Liver Transplant Recipients(N=75)Kidney Transplant Recipients*(N=68)AUC0-24h(mcg ∙h/mL)40.2 ± 11.8 46.0 ± 16.1 48.2 ± 14.6 Cmax(mcg/mL) 4.9 ± 1.1 5.4 ± 1.5 5.3 ± 1.5 Elimination half-life (hr) 6.58 ± 1.50 6.18 ± 1.42 6.77 ± 1.25 The pharmacokinetic parameters of ganciclovir following 200 days of valganciclovir administration in high-risk kidney transplant patients were similar to those in solid organ transplant patients who received valganciclovir for 100 days.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and ExcretionThe pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of valganciclovir are provided in Table 12.
Table 12: Pharmacokinetic Properties of Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir Associated withValganciclovir TabletsaSteady state ganciclovir PK was assessed after administration of valganciclovir tablets (875 mg once daily) with a high fat meal containing approximately 600 total calories (31.1 g fat, 51.6 g carbohydrates and 22.2 g protein) to 16 HIV-positive subjects. ValganciclovirGanciclovirAbsorptionTmax(h)
median (min-max) (fed conditions)2.18
1.7 h to 3.0 hFood effect (high fat meal/fasting): PK parameter ratio and 90% confidence intervala Cmax:
1.14 (0.95, 1.36)
AUC:
1.30 (1.07, 1.51)a
Tmax: ↔Distribution% Bound to human plasma proteins (ex vivo) Unknown 1% to 2% over 0.5 mcg/mL to 51 mcg/mL Cerebrospinal fluid penetration Unknown Yes MetabolismHydrolyzed by intestinal and liver esterases No significant metabolism EliminationDose proportionality AUC was dose proportional under fed conditions across a valganciclovir dose range of 450 mg to 2,625 mg Major route of elimination Metabolism to ganciclovir Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion t1/2(h) See Tables 10 and 11 % Of dose excreted in urine Unknown % Of dose excreted in feces Unknown Specific Populations:Renal Impairment:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir from a single oral dose of 900 mg valganciclovir tablets were evaluated in 24 otherwise healthy individuals with renal impairment. Decreased renal function results in decreased clearance of ganciclovir and increased terminal half-life (Table 13).Table 13: Pharmacokinetics of Ganciclovir from a Single Oral Dose of 900 mg Valganciclovir Tablets*Creatinine clearance calculated from 24-hour urine collection. EstimatedCreatinine Clearance*
(mL/min)NApparent Clearance
(mL/min)Mean±SDAUClast(mcg∙h/mL)Mean±SDHalf-life(hours)Mean±SD51-70
21-50
11-20
≤ 106
6
6
6249 ± 99
136 ± 64
45 ± 11
12.8 ± 849.5 ± 22.4
91.9 ± 43.9
223 ± 46
366 ± 664.85 ± 1.4
10.2 ± 4.4
21.8 ± 5.2
67.5 ± 34Hemodialysis reduces plasma concentrations of ganciclovir by about 50% following valganciclovir administration. Adult patients receiving hemodialysis (CrCl less than 10 mL/min) cannot use valganciclovir tablets because the daily dose of valganciclovir tablets required for these patients is less than 450 mg
[see Dosage and Administration and Use in Specific Populations ].Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Patients:The pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir were evaluated following the administration of valganciclovir in 63 pediatric solid organ transplant patients aged 4 months to 16 years, and in 16 pediatric heart transplant patients less than 4 months of age. In these studies, patients received oral doses of valganciclovir (either valganciclovir for oral solution or tablets) to produce exposure equivalent to an adult 900 mg dose[see Dosage and Administration , Adverse Reactions , Use in Specific Populations , Clinical Studies ].In studies using the pediatric valganciclovir dosing algorithm, the pharmacokinetics of ganciclovir were similar across organ types and age ranges (Table 14). Relative to adult transplant patients (Table 11), AUC values in pediatric patients were somewhat increased, but were within the range considered safe and effective in adults.
Table 14: Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetics by Age in Pediatric Solid Organ Transplant Patients Administered ValgancicloviraN= number of patients, NA=not applicable
aAges ranged from 26 days to 124 days.Age GroupOrganPK Parameter mean (SD)< 4 months4 months to≤ 2 years> 2 years to < 12 years≥ 12 years
Heart(N=26)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)14a
66.3 (20.5)
10.8 (3.30)
3.5 (0.87)6
55.4 (22.8)
8.2 (2.5)
3.8 (1.7)2
59.6 (21.0)
12.5 (1.2)
2.8 (0.9)4
60.6 (25.0)
9.5 (3.3)
4.9 (0.8)
Kidney(N=31)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)
NA2
67.6 (13.0)
10.4 (0.4)
4.5 (1.5)10
55.9 (12.1)
8.7 (2.1)
4.8 (1.0)19
47.8 (12.4)
7.7 (2.1)
6.0 (1.3)
Liver(N=17)N
AUC0-24h(mcg∙h/mL)
Cmax(mcg/mL)
t1/2(h)NA 9
69.9 (37.0)
11.9 (3.7)
2.8 (1.5)6
59.4 (8.1)
9.5 (2.3)
3.8 (0.7)2
35.4 (2.8)
5.5 (1.1)
4.4 (0.2)Pharmacokinetics in Geriatric Patients:The pharmacokinetic characteristics of valganciclovir in elderly patients have not been established.In vivo drug-drug interaction studies were not conducted with valganciclovir. However, because valganciclovir is rapidly and extensively converted to ganciclovir, interactions associated with ganciclovir will be expected for valganciclovir
Drug Interactions:[see Drug Interactions ].Table 15 and Table 16 provide a listing of established drug interaction studies with ganciclovir. Table 15 provides the effects of coadministered drug on ganciclovir plasma pharmacokinetic parameters, whereas Table 16 provides the effects of ganciclovir on plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of coadministered drug.
Table 15: Results of Drug Interaction Studies with Ganciclovir: Effects of Coadministered Drug on Ganciclovir Pharmacokinetic ParametersCoadministered DrugGanciclovir DosageNGanciclovir Pharmacokinetic (PK) ParameterMycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1.5 g single dose 5 mg/kg IV single dose 12 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed (patients with normal renal function) Trimethoprim 200 mg once daily 1,000 mg every 8 hours 12 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours simultaneously administered with ganciclovir 5 mg/kg IV twice daily 11 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed 5 mg/kg IV once daily 11 No effect on ganciclovir PK parameters observed Probenecid 500 mg every 6 hours 1,000 mg every 8 hours 10 AUC ↑ 53 ± 91%
(range: -14% to 299%)
Ganciclovir renal clearance ↓
22 ± 20%
(range: -54% to -4%)Table 16: Results of Drug Interaction Studies with Ganciclovir: Effects of Ganciclovir on Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered DrugCoadministered DrugGanciclovir DosageNCoadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic (PK) ParameterOral cyclosporine at therapeutic doses 5 mg/kg infused over 1 hour every 12 hours 93 In a retrospective analysis of liver allograft recipients, there was no evidence of an effect on cyclosporine whole blood concentrations. Mycophenolate mofetil
(MMF) 1.5 g single dose5 mg/kg IV single dose 12 No PK interaction observed (patients with normal renal function) Trimethoprim 200 mg once daily 1,000 mg every 8 hours 12 No effect on trimethoprim PK parameters observed Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours 5 mg/kg IV twice daily 11 AUC0-12↑70 ± 40%
(range: 3% to 121%)
Cmax↑49 ± 48%
(range: -28% to 125%)Didanosine 200 mg every 12 hours 5 mg/kg IV once daily 11 AUC0-12↑50 ± 26%
(range: 22% to 110%)
Cmax↑36 ± 36%
(range: -27% to 94%)
- Valganciclovir tablets, USP: 450 mg, pink, film-coated biconvex oval tablets debossed with “VL” on one side and “450” on the other side.
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended with use of valganciclovir. ()
8.2 LactationRisk SummaryNo data are available regarding the presence of valganciclovir (prodrug) or ganciclovir (active drug) in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Animal data indicate that ganciclovir is excreted in the milk of lactating rats. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. Advise nursing mothers that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with valganciclovir because of the potential for serious adverse events in nursing infants and because of the potential for transmission of HIV
[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions , Nonclinical Toxicology ].
Valganciclovir tablets are contraindicated in patients who have had a demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to valganciclovir, ganciclovir, or any component of the formulation
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
Valganciclovir, a prodrug of ganciclovir, is rapidly converted to ganciclovir after oral administration. Adverse reactions known to be associated with ganciclovir usage can therefore be expected to occur with valganciclovir.
Adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities are available for 370 patients who received maintenance therapy with valganciclovir tablets 900 mg once daily in two open-label clinical trials. Approximately 252 (68%) of these patients received valganciclovir tablets for more than nine months (maximum duration was 36 months). Table 3 and Table 4 show pooled selected adverse reactions and abnormal laboratory values from these patients.
Patients with CMV Retinitis | |
Adverse Reactions according to Body System | Valganciclovir Tablets (N=370) % |
Gastrointestinal system Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Abdominal pain | 41 30 21 15 |
General disorders and administrative site conditions Pyrexia | 31 |
Nervous system disorders Headache Insomnia Neuropathy peripheral Paresthesia | 22 16 9 8 |
Eye disorders Retinal detachment | 15 |
Patients with CMV Retinitis | |
Laboratory Abnormalities | Valganciclovir Tablets (N=370) % |
| Neutropenia: ANC/μL < 500 500 – < 750 750 – < 1,000 | 19 17 17 |
| Anemia: Hemoglobin g/dL < 6.5 6.5 – < 8.0 8.0 – < 9.5 | 7 13 16 |
| Thrombocytopenia: Platelets/μL < 25,000 25,000 – < 50,000 50,000 – < 100,000 | 4 6 22 |
| Serum Creatinine: mg/dL > 2.5 > 1.5 – 2.5 | 3 12 |
Adverse Reactions | Valganciclovir Tablets (N=244) % | Oral Ganciclovir (N=126) % |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 30 | 29 |
| Nausea | 23 | 23 |
| Vomiting | 16 | 14 |
Nervous system disorders | ||
| Tremors | 28 | 25 |
| Headache | 22 | 27 |
| Insomnia | 20 | 16 |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Pyrexia | 13 | 14 |
Table 6 shows selected adverse reactions regardless of severity with an incidence of greater than or equal to 5% from another clinical trial where kidney transplant patients received either valganciclovir once daily starting within 10 days post-transplant until Day 100 post-transplant followed by 100 days of placebo or valganciclovir once daily until Day 200 post-transplant. The overall safety profile of valganciclovir
did not change with the extension of prophylaxis until Day 200 post-transplant in high risk kidney transplant patients.Adverse Reactions | Valganciclovir Tablets Day 100 Post-transplant (N=164) % | Valganciclovir Tablets Day 200 Post-transplant (N=156) % |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 26 | 31 |
| Nausea | 11 | 11 |
| Vomiting | 3 | 6 |
Nervous system disorders | ||
| Tremors | 12 | 17 |
| Headache | 10 | 6 |
| Insomnia | 7 | 6 |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Pyrexia | 12 | 9 |
Table 7 and Table 8 show selected laboratory abnormalities reported with valganciclovir tablets in two trials in solid organ transplant patients.
| *Laboratory abnormalities are those reported by investigators. | ||||||||||||||
Laboratory Abnormalities | Valganciclovir Tablets (N=244) % | Ganciclovir Capsules (N=126) % | ||||||||||||
| Neutropenia: ANC/μL < 500 500 – < 750 750 – < 1,000 | 5 3 5 | 3 2 2 | ||||||||||||
| Anemia: Hemoglobin g/dL < 6.5 6.5 – < 8.0 8.0 – < 9.5 | 1 5 31 | 2 7 25 | ||||||||||||
| Thrombocytopenia: Platelets/μL < 25,000 25,000 – < 50,000 50,000 – < 100,000 | 0 1 18 | 2 3 21 | ||||||||||||
| Serum Creatinine: mg/dL > 2.5 > 1.5 – 2.5 | 14 45 | 21 47 | ||||||||||||
| *Laboratory abnormalities are those reported by investigators. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Laboratory Abnormalities | Valganciclovir Tablets Day 100 Post-transplant (N=164) % | Valganciclovir Tablets Day 200 Post-transplant (N=156) % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neutropenia: ANC/μL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 500 | 9 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 500 – < 750 | 6 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 750 – < 1,000 | 7 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anemia: Hemoglobin g/dL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 6.5 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.5 – < 8.0 | 5 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.0 – < 9.5 | 17 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thrombocytopenia: Platelets/μL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 25,000 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 – < 50,000 | 1 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50,000 – < 100,000 | 7 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum Creatinine: mg/dL > 2.5 > 1.5 – 2.5 | 17 50 | 14 48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other adverse drug reactions with valganciclovir in clinical trials in either patients with CMV retinitis or solid organ transplant patients that occurred in at least 5% of patients are listed below.
Other adverse reactions with valganciclovir in clinical trials in either patients with CMV retinitis or solid organ transplant patients that occurred in less than 5% of patients are listed below.
Valganciclovir for oral solution and tablets have been studied in 179 pediatric solid organ transplant patients who were at risk for developing CMV disease (aged 3 weeks to 16 years) and in 24 neonates with symptomatic congenital CMV disease (aged 8 days to 34 days), with duration of ganciclovir exposure ranging from 2 days to 200 days
In general, the safety profile was similar in pediatric patients compared to that observed in adult patients. However, the rates of certain adverse reactions, and laboratory abnormalities, such as upper respiratory tract infection, pyrexia, nasopharyngitis, anemia, and abdominal pain were reported more frequently in pediatric patients than in adults
The overall safety profile of valganciclovir was similar with the extension of prophylaxis until Day 200 post-transplant in high risk pediatric kidney transplant patients. However, the incidence of severe neutropenia (ANC < 500/μL) was higher in pediatric kidney transplant patients treated with valganciclovir until Day 200 (17/57, 30%) compared to pediatric kidney transplant patients treated until Day 100 (3/63, 5%). There were no differences in the incidence of severe (Grade 4) anemia or thrombocytopenia in patients treated 100 days or 200 days with valganciclovir.