Vecamyl
(Mecamylamine Hydrochloride)Vecamyl Prescribing Information
For the management of moderately severe to severe essential hypertension and in uncomplicated cases of malignant hypertension.
Therapy is usually started with one 2.5 mg tablet of Mecamylamine HCl twice a day. This initial dosage should be modified by increments of one 2.5 mg tablet at intervals of not less than 2 days until the desired blood pressure response occurs (the criterion being a dosage just under that which causes signs of mild postural hypotension).
The average total daily dosage of Mecamylamine HCl is 25 mg, usually in three divided doses. However, as little as 2.5 mg daily may be sufficient to control hypertension in some patients. A range of two to four or even more doses may be required in severe cases when smooth control is difficult to obtain. In severe or urgent cases, larger increments at smaller intervals may be needed. Partial tolerance may develop in certain patients, requiring an increase in the daily dosage of Mecamylamine HCl.
Administration of Mecamylamine HCl after meals may cause a more gradual absorption and smoother control of excessively high blood pressure. The timing of doses in relation to meals should be consistent. Since the blood pressure response to antihypertensive drugs is increased in the early morning, the larger dose should be given at noontime and perhaps in the evening. The morning dose, as a rule, should be relatively small and in some instances may even be omitted.
The initial regulation of dosage should be determined by blood pressure readings in the erect position at the time of maximal effect of the drug, as well as by other signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. The effective maintenance dosage should be regulated by blood pressure readings in the erect position and by limitation of dosage to that which causes slight faintness or dizziness in this position. If the patient or a relative can use a sphygmomanometer, instructions may be given to reduce or omit a dose if readings fall below a designated level or if faintness or lightheadedness occurs. However, no change should be instituted without the knowledge of the physician.
Close supervision and education of the patient, as well as critical adjustment of dosage, are essential to successful therapy.
When Mecamylamine HCl is given with other antihypertensive drugs, the dosage of these other agents, as well as that of Mecamylamine HCl, should be reduced to avoid excessive hypotension. However, thiazides should be continued in their usual dosage, while that of Mecamylamine HCl is decreased by at least 50 percent.
Mecamylamine HCl should not be used in mild, moderate, labile hypertension and may prove unsuitable in uncooperative patients. It is contraindicated in coronary insufficiency or recent myocardial infarction. Mecamylamine HCl should be given with great discretion, if at all, when renal insufficiency is manifested by a rising or elevated BUN. The drug is contraindicated in uremia. Patients receiving antibiotics and sulfonamides should generally not be treated with ganglion blockers. Other contraindications are glaucoma, organic pyloric stenosis or hypersensitivity to the product.
The following adverse reactions have been reported and within each category are listed in order of decreasing severity.
Mecamylamine, a secondary amine, readily penetrates into the brain and thus may produce central nervous system effects. Tremor, choreiform movements, mental aberrations, and convulsions may occur rarely. These have occurred most often when large doses of Mecamylamine HCl were used, especially in patients with cerebral or renal insufficiency.
When ganglion blockers or other potent antihypertensive drugs are discontinued suddenly, hypertensive levels return. In patients with malignant hypertension and others, this may occur abruptly and may cause fatal cerebral vascular accidents or acute congestive heart failure. When Mecamylamine HCl is withdrawn, this should be done gradually and other antihypertensive therapy usually must be substituted. On the other hand, the effects of Mecamylamine HCl sometimes may last from hours to days after therapy is discontinued.
Patients receiving antibiotics and sulfonamides generally should not be treated with ganglion blockers. The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by anesthesia, other antihypertensive drugs and alcohol.
Mecamylamine HCl is a potent, oral antihypertension agent and ganglion blocker, and is a secondary amine. It is N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan- 2 -amine hydrochloride. Its empirical formula is C11H21N • HCl and its structural formula is:
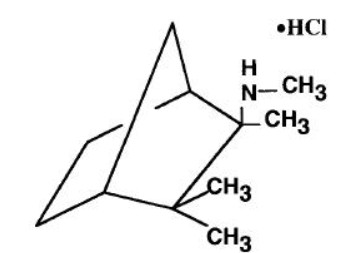
It is a white, odorless, or practically odorless, crystalline powder, is highly stable, soluble in water and has a molecular weight of 203.75.
Mecamylamine HCl is supplied as tablets for oral use, each containing 2.5 mg mecamylamine HCl. Inactive ingredients are calcium phosphate, D&C Yellow 10, FD&C Yellow 6, lactose, magnesium stearate, cornstarch, and talc.