Xeomin Prescribing Information
Postmarketing safety data from XEOMIN and other approved botulinum toxins suggest that botulinum toxin effects may, in some cases, be observed beyond the site of local injection. The symptoms are consistent with the mechanism of action of botulinum toxin and may include asthenia, generalized muscle weakness, diplopia, blurred vision, ptosis, dysphagia, dysphonia, dysarthria, urinary incontinence, and breathing difficulties. These symptoms have been reported hours to weeks after injection. Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of death related to the spread of toxin effects. The risk of symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity but symptoms can occur in adults treated for spasticity and other conditions, and particularly in those patients who have underlying conditions that would predispose them to these symptoms. In unapproved uses, including lower limb spasticity in children, and in approved indications, symptoms consistent with spread of toxin effect have been reported at doses comparable to or lower than doses used to treat cervical dystonia.
Patients or caregivers should be advised to seek immediate medical care if swallowing, speech, or respiratory disorders occur.
Indications and Usage (XEOMIN is indicated in adult patients for the temporary improvement in the appearance of upper facial lines:
| 7/2024 |
Dosage and Administration (Reconstituted XEOMIN is intended for intramuscular or intra-salivary gland injection only. If proposed injection sites are marked with a pen, DO NOT inject XEOMIN through the pen marks; otherwise a permanent tattooing effect may occur. For intramuscular injections, the number of injection sites is dependent upon the size of the muscle to be treated and the volume of reconstituted XEOMIN injected. Inject XEOMIN carefully when injected at sites close to sensitive structures, such as the carotid artery, lung apices, and esophagus. Before administering XEOMIN, the healthcare provider should be familiar with the patient's anatomy and any anatomic alterations, e.g., due to prior surgical procedures. Chronic Sialorrhea Chronic Sialorrhea in Adult Patients Use a sterile needle (e.g., 27-30 gauge (0.30-0.40 mm diameter), 12.5 mm length) for intra-salivary gland administration for the treatment of chronic sialorrhea. Inject XEOMIN close to the center of the gland. The salivary glands can be located using ultrasound imaging or surface anatomical landmarks [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients Use a sterile needle (e.g., 27-30 gauge (0.30-0.40 mm diameter), 12.5 mm length) for intra-salivary gland administration for the treatment of chronic sialorrhea. Inject XEOMIN close to the center of the gland. Ultrasound guidance is recommended for the localization of the involved salivary glands [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] .Upper Limb Spasticity Upper Limb Spasticity in Adult Patients Use a sterile needle (e.g., 26-gauge (0.45 mm diameter), 37 mm length for superficial muscles; or 22-gauge (0.70 mm diameter), 75 mm length for deeper musculature) in the intramuscular administration in the treatment of upper limb spasticity in adults. Localization of the involved muscles with electromyographic guidance, nerve stimulation, or ultrasound techniques is recommended. Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral Palsy Use a sterile needle (e.g., 30-gauge (0.30 mm diameter), 25 mm length for superficial muscles; or 27-gauge (0.40 mm diameter), 37 mm length for deeper musculature) in the intramuscular administration in the treatment of upper limb spasticity in pediatric patients. Localization of the involved muscles with techniques such as electromyographic guidance, nerve stimulation, or ultrasound is recommended. Cervical Dystonia Use a sterile needle (e.g., 26-gauge (0.45 mm diameter), 37 mm length for superficial muscles; or 22-gauge (0.70 mm diameter), 75 mm length for deeper musculature) in the intramuscular administration in the treatment of cervical dystonia. Localization of the involved muscles with electromyographic guidance, ultrasound, or nerve stimulation techniques may be useful. Blepharospasm Use a sterile needle (e.g., 30-gauge (0.40 mm diameter), 12.5 mm length) in the intramuscular administration in the treatment of blepharospasm. Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Horizontal Forehead Lines, and Lateral Canthal Lines) Use a sterile needle [e.g., 30-33 gauge (0.3-0.2 mm diameter)], 13 mm length) for the intramuscular administration in the treatment of upper facial lines. | 7/2024 |
Warnings and Precautions (Use caution when XEOMIN is used where the targeted muscle shows excessive weakness or atrophy. Use caution when XEOMIN is used in patients who have marked facial asymmetry, with surgical alterations to the facial anatomy, pre-existing eyelid or eyebrow ptosis, when excessive weakness or atrophy is present in the target muscles, excessive dermatochalasis, deep dermal scarring, thick sebaceous skin (e.g., the inability to substantially lessen glabellar lines even by physically spreading them apart). | 9/2023 |
XEOMIN is an acetylcholine release inhibitor and neuromuscular blocking agent indicated for the treatment or improvement of:
- Chronic sialorrhea in patients 2 years of age and older ()
1.1 Chronic SialorrheaXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of chronic sialorrhea in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Upper limb spasticity in adults ()
1.2 Upper Limb SpasticityUpper Limb Spasticity in Adult PatientsXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of upper limb spasticity in adult patients.
Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral PalsyXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of upper limb spasticity in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy.
- Upper limb spasticity in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy ()
1.2 Upper Limb SpasticityUpper Limb Spasticity in Adult PatientsXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of upper limb spasticity in adult patients.
Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral PalsyXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of upper limb spasticity in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy.
- Cervical dystonia in adults ()
1.3 Cervical DystoniaXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of cervical dystonia in adult patients.
- Blepharospasm in adults ()
1.4 BlepharospasmXEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of blepharospasm in adult patients.
- the appearance of upper facial lines in adults:
- moderate to severe glabellar lines associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity ()
1.5 Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Horizontal Forehead Lines, and Lateral Canthal Lines)XEOMIN is indicated in adult patients for the temporary improvement in the appearance of upper facial lines:- moderate to severe glabellar lines (GL) associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity
- moderate to severe horizontal forehead lines (HFL) associated with frontalis muscle activity
- moderate to severe lateral canthal lines (LCL) associated with orbicularis oculi muscle activity.
- moderate to severe horizontal forehead lines associated with frontalis muscle activity ()
1.5 Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Horizontal Forehead Lines, and Lateral Canthal Lines)XEOMIN is indicated in adult patients for the temporary improvement in the appearance of upper facial lines:- moderate to severe glabellar lines (GL) associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity
- moderate to severe horizontal forehead lines (HFL) associated with frontalis muscle activity
- moderate to severe lateral canthal lines (LCL) associated with orbicularis oculi muscle activity.
- moderate to severe lateral canthal lines associated with orbicularis oculi muscle activity ()
1.5 Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Horizontal Forehead Lines, and Lateral Canthal Lines)XEOMIN is indicated in adult patients for the temporary improvement in the appearance of upper facial lines:- moderate to severe glabellar lines (GL) associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity
- moderate to severe horizontal forehead lines (HFL) associated with frontalis muscle activity
- moderate to severe lateral canthal lines (LCL) associated with orbicularis oculi muscle activity.
- moderate to severe glabellar lines associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity (
- Chronic Sialorrhea in Adults: the recommended total dose is 100 Units per treatment session consisting of 30 Units per parotid gland and 20 Units per submandibular gland, no sooner than every 16 weeks ()
2.2 Recommended Dose for Chronic SialorrheaChronic Sialorrhea in Adult PatientsThe recommended total dose per treatment session is 100 Units. XEOMIN is injected into the parotid and submandibular glands on both sides (i.e., 4 injection sites per treatment session). The recommended total dose per treatment session is 100 Units. The dose is divided with a ratio of 3:2 between the parotid and submandibular glands (Table 1).
Figure 1: Glands for Injection in Chronic Sialorrhea in Adult Patients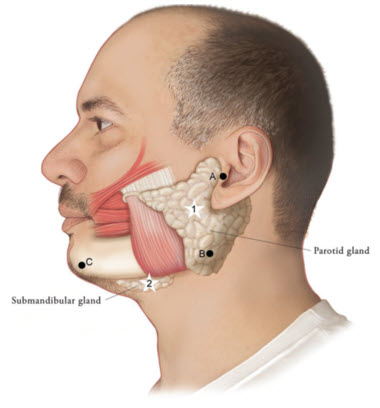
Use the following guidelines if locating salivary glands using anatomic landmarks:
1) To inject theparotidgland, find the midpoint on the line connecting the tragus and mandible angle (Site A and B, respectively, Figure 1), approximately at the height of the ear lobe. Deliver the injection one finger breadth anterior to this site (Star 1, Figure 1).2) To inject thesubmandibulargland, find the midpoint between the angle of the mandible and the tip of the chin (Site B and C, respectively, Figure 1). Deliver the injection one finger breadth medial to the inferior surface of the mandible at this site (Star 2, Figure 1).
Table 1: Dosing by Gland for Treatment of Chronic Sialorrhea in Adult Patients Gland(s) Units Per Side Total Parotid gland(s) 30 Units 60 Units Submandibular gland(s) 20 Units 40 Units Both Glands50 Units 100 UnitsThe concentration used in the clinical study after reconstitution was 5 Units/0.1mL. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient, and no sooner than every 16 weeks.

Figure 1 Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric PatientsXEOMIN is injected into the parotid and submandibular glands on both sides (i.e., 4 injection sites per treatment session). Ultrasound imaging is recommended to guide needle placement into the salivary glands. The body-weight adjusted dose is divided with a ratio of 3:2 between the parotid and submandibular glands (Table 2). XEOMIN has not been studied in children weighing less than 12 kg
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)].Figure 2: Glands for Injection in Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients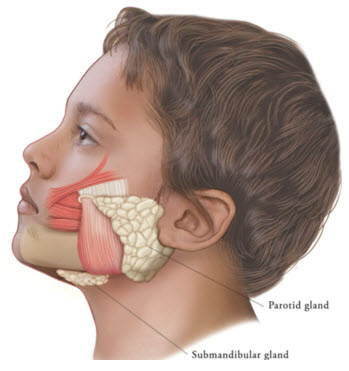
Table 2: Dosing by Body Weight Class for Treatment of Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients Body weight Parotid gland, each side Submandibular gland, each side Total dose, both glands, both sides Dose per gland Volume per injection Dose per gland Volume per injection 12 kg or more to less than 15 kg 6 Units 0.24 mL 4 Units 0.16 mL 20 Units 15 kg or more to less than 19 kg 9 Units 0.36 mL 6 Units 0.24 mL 30 Units 19 kg or more to less than 23 kg 12 Units 0.48 mL 8 Units 0.32 mL 40 Units 23 kg or more to less than 27 kg 15 Units 0.6 mL 10 Units 0.4 mL 50 Units 27 kg or more to less than 30 kg 18 Units 0.72 mL 12 Units 0.48 mL 60 Units 30 kg or more 22.5 Units 0.9 mL 15 Units 0.6 mL 75 Units The concentration used in the clinical study after reconstitution was 2.5 Units/0.1 mL. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient, and no sooner than every 16 weeks.

Figure 2 - Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients: the recommended dose is based on body weight administered in a 3:2 dose ratio into the parotid and submandibular glands, respectively, no sooner than every 16 weeks; ultrasound guidance recommended ()
2.2 Recommended Dose for Chronic SialorrheaChronic Sialorrhea in Adult PatientsThe recommended total dose per treatment session is 100 Units. XEOMIN is injected into the parotid and submandibular glands on both sides (i.e., 4 injection sites per treatment session). The recommended total dose per treatment session is 100 Units. The dose is divided with a ratio of 3:2 between the parotid and submandibular glands (Table 1).
Figure 1: Glands for Injection in Chronic Sialorrhea in Adult Patients
Use the following guidelines if locating salivary glands using anatomic landmarks:
1) To inject theparotidgland, find the midpoint on the line connecting the tragus and mandible angle (Site A and B, respectively, Figure 1), approximately at the height of the ear lobe. Deliver the injection one finger breadth anterior to this site (Star 1, Figure 1).2) To inject thesubmandibulargland, find the midpoint between the angle of the mandible and the tip of the chin (Site B and C, respectively, Figure 1). Deliver the injection one finger breadth medial to the inferior surface of the mandible at this site (Star 2, Figure 1).
Table 1: Dosing by Gland for Treatment of Chronic Sialorrhea in Adult Patients Gland(s) Units Per Side Total Parotid gland(s) 30 Units 60 Units Submandibular gland(s) 20 Units 40 Units Both Glands50 Units 100 UnitsThe concentration used in the clinical study after reconstitution was 5 Units/0.1mL. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient, and no sooner than every 16 weeks.

Figure 1 Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric PatientsXEOMIN is injected into the parotid and submandibular glands on both sides (i.e., 4 injection sites per treatment session). Ultrasound imaging is recommended to guide needle placement into the salivary glands. The body-weight adjusted dose is divided with a ratio of 3:2 between the parotid and submandibular glands (Table 2). XEOMIN has not been studied in children weighing less than 12 kg
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)].Figure 2: Glands for Injection in Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients
Table 2: Dosing by Body Weight Class for Treatment of Chronic Sialorrhea in Pediatric Patients Body weight Parotid gland, each side Submandibular gland, each side Total dose, both glands, both sides Dose per gland Volume per injection Dose per gland Volume per injection 12 kg or more to less than 15 kg 6 Units 0.24 mL 4 Units 0.16 mL 20 Units 15 kg or more to less than 19 kg 9 Units 0.36 mL 6 Units 0.24 mL 30 Units 19 kg or more to less than 23 kg 12 Units 0.48 mL 8 Units 0.32 mL 40 Units 23 kg or more to less than 27 kg 15 Units 0.6 mL 10 Units 0.4 mL 50 Units 27 kg or more to less than 30 kg 18 Units 0.72 mL 12 Units 0.48 mL 60 Units 30 kg or more 22.5 Units 0.9 mL 15 Units 0.6 mL 75 Units The concentration used in the clinical study after reconstitution was 2.5 Units/0.1 mL. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient, and no sooner than every 16 weeks.

Figure 2
- Upper Limb Spasticity in Adults: the recommended total dose is up to 400 Units, divided among affected muscles ()
2.3 Recommended Dose for Upper Limb SpasticityUpper Limb Spasticity in Adult PatientsTailor the dosage, frequency, and number of injection sites to the individual patient based on the size, number, and location of muscles to be treated, severity of spasticity, presence of local muscle weakness, patient's response to previous treatment, and adverse event history with XEOMIN. Administer repeat XEOMIN treatments no sooner than every 12 weeks. In patients not previously treated with a botulinum toxin, begin initial dosing at the low end of the recommended dosing range and titrate as clinically necessary. Most patients in clinical studies were retreated between 12 and 14 weeks.
Table 3: XEOMIN Dosing by Muscle for Treatment of Adult Upper Limb Spasticity Clinical Pattern MuscleUnits (Range) Number of injection sites per muscle Clenched FistFlexor digitorum superficialis25 Units-100 Units 2 Flexor digitorum profundus25 Units-100 Units 2 Flexed WristFlexor carpi radialis25 Units-100 Units 1-2 Flexor carpi ulnaris20 Units-100 Units 1-2 Flexed ElbowBrachioradialis25 Units-100 Units 1-3 Biceps50 Units-200 Units 1-4 Brachialis25 Units-100 Units 1-2 Pronated ForearmPronator quadratus10 Units-50 Units 1 Pronator teres25 Units-75 Units 1-2 Thumb-in-PalmFlexor pollicis longus10 Units-50 Units 1 Adductor pollicis5 Units-30 Units 1 Flexor pollicis brevis/Opponens pollicis5 Units-30 Units 1 Figure 3: Muscles Involved In Adult Upper Limb Spasticity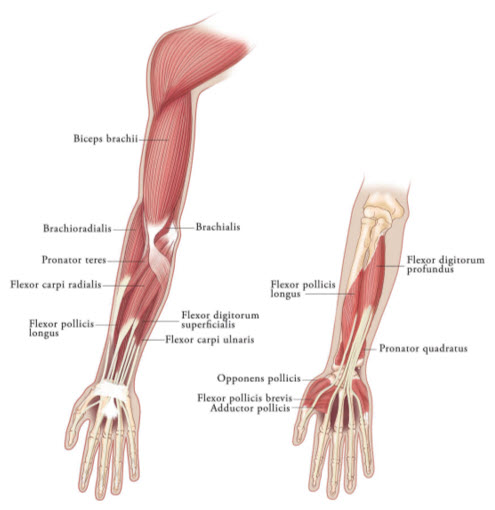

Figure 3 Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral PalsyTailor the exact dosage, frequency, and number of injection sites to the individual patient based on size, number and localization of involved muscles; the severity of spasticity; and the presence of local muscle weakness.
The maximum recommended dose is 8 Units/kg, divided among affected muscles, up to a maximum dose of 200 Units per single upper limb. If both upper limbs are treated, do not exceed a total XEOMIN dosage of 16 Units/kg, up to a maximum of 400 Units.
Based on the selected dose, a reconstituted solution at a concentration between 1.25 Units/0.1 mL and 5 Units/0.1 mL is recommended
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the clinical need of the patient; administer repeat treatments no sooner than every 12 weeks. Most patients in clinical studies were retreated between 12 and 16 weeks.Table 4 includes the recommended dose ranges for the treatment of the clinical patterns of flexed elbow, flexed wrist, pronated forearm, clenched fist, and thumb-in-palm.
Table 4: XEOMIN Dosing by Muscle for Treatment of Pediatric Upper Limb Spasticity, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral Palsy Clinical Pattern MuscleDosage Number of Injection Sites per Muscle Range
(Units/kg)Maximum
(Units)Flexed ElbowBrachioradialis1-2 50 1-2 Biceps2-3 75 1-3 Brachialis1-2 50 1-2 Flexed WristFlexor carpi radialis1 25 1 Flexor carpi ulnaris1 25 1 Pronated ForearmPronator quadratus0.5 12.5 1 Pronator teres1-2 50 1-2 Clenched FistFlexor digitorum superficialis1 25 1 Flexor digitorum profundus1 25 1 Thumb-in-PalmFlexor pollicis longus1 25 1 Adductor pollicis0.5 12.5 1 Flexor pollicis brevis/ opponens pollicis0.5 12.5 1 Figure 4: Muscles Injected for Pediatric Upper Limb Spasticity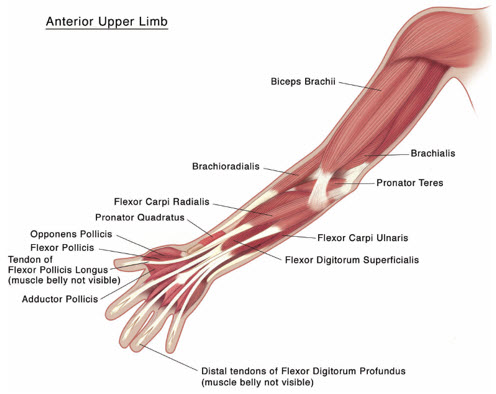

Figure 4 - Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy: the recommended total dose is 8 Units/kg (maximum 200 Units) per single upper limb or 16 Units/kg (maximum 400 U) in both upper limbs, divided among affected muscles ()
2.3 Recommended Dose for Upper Limb SpasticityUpper Limb Spasticity in Adult PatientsTailor the dosage, frequency, and number of injection sites to the individual patient based on the size, number, and location of muscles to be treated, severity of spasticity, presence of local muscle weakness, patient's response to previous treatment, and adverse event history with XEOMIN. Administer repeat XEOMIN treatments no sooner than every 12 weeks. In patients not previously treated with a botulinum toxin, begin initial dosing at the low end of the recommended dosing range and titrate as clinically necessary. Most patients in clinical studies were retreated between 12 and 14 weeks.
Table 3: XEOMIN Dosing by Muscle for Treatment of Adult Upper Limb Spasticity Clinical Pattern MuscleUnits (Range) Number of injection sites per muscle Clenched FistFlexor digitorum superficialis25 Units-100 Units 2 Flexor digitorum profundus25 Units-100 Units 2 Flexed WristFlexor carpi radialis25 Units-100 Units 1-2 Flexor carpi ulnaris20 Units-100 Units 1-2 Flexed ElbowBrachioradialis25 Units-100 Units 1-3 Biceps50 Units-200 Units 1-4 Brachialis25 Units-100 Units 1-2 Pronated ForearmPronator quadratus10 Units-50 Units 1 Pronator teres25 Units-75 Units 1-2 Thumb-in-PalmFlexor pollicis longus10 Units-50 Units 1 Adductor pollicis5 Units-30 Units 1 Flexor pollicis brevis/Opponens pollicis5 Units-30 Units 1 Figure 3: Muscles Involved In Adult Upper Limb Spasticity

Figure 3 Upper Limb Spasticity in Pediatric Patients, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral PalsyTailor the exact dosage, frequency, and number of injection sites to the individual patient based on size, number and localization of involved muscles; the severity of spasticity; and the presence of local muscle weakness.
The maximum recommended dose is 8 Units/kg, divided among affected muscles, up to a maximum dose of 200 Units per single upper limb. If both upper limbs are treated, do not exceed a total XEOMIN dosage of 16 Units/kg, up to a maximum of 400 Units.
Based on the selected dose, a reconstituted solution at a concentration between 1.25 Units/0.1 mL and 5 Units/0.1 mL is recommended
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Determine the timing for repeat treatment based on the clinical need of the patient; administer repeat treatments no sooner than every 12 weeks. Most patients in clinical studies were retreated between 12 and 16 weeks.Table 4 includes the recommended dose ranges for the treatment of the clinical patterns of flexed elbow, flexed wrist, pronated forearm, clenched fist, and thumb-in-palm.
Table 4: XEOMIN Dosing by Muscle for Treatment of Pediatric Upper Limb Spasticity, Excluding Spasticity Caused by Cerebral Palsy Clinical Pattern MuscleDosage Number of Injection Sites per Muscle Range
(Units/kg)Maximum
(Units)Flexed ElbowBrachioradialis1-2 50 1-2 Biceps2-3 75 1-3 Brachialis1-2 50 1-2 Flexed WristFlexor carpi radialis1 25 1 Flexor carpi ulnaris1 25 1 Pronated ForearmPronator quadratus0.5 12.5 1 Pronator teres1-2 50 1-2 Clenched FistFlexor digitorum superficialis1 25 1 Flexor digitorum profundus1 25 1 Thumb-in-PalmFlexor pollicis longus1 25 1 Adductor pollicis0.5 12.5 1 Flexor pollicis brevis/ opponens pollicis0.5 12.5 1 Figure 4: Muscles Injected for Pediatric Upper Limb Spasticity

Figure 4 - Cervical Dystonia: the recommended initial dose is 120 Units per treatment session ()
2.4 Recommended Dose for Cervical DystoniaThe recommended initial dose of XEOMIN for cervical dystonia is 120 Units. In a placebo-controlled trial utilizing initial XEOMIN doses of 120 Units and 240 Units, no meaningful difference in effectiveness was demonstrated between the doses [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. In previously treated patients, their past dose, response to treatment, duration of effect, and adverse event history should be taken into consideration when determining the XEOMIN dose.
In the treatment of cervical dystonia, XEOMIN is usually injected into the sternocleidomastoid, levator scapulae, splenius capitis, scalenus, and/or the trapezius muscle(s) (see Figure 5). This list is not exhaustive, as any of the muscles responsible for controlling head position may require treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. The dose and number of injection sites in each treated muscle should be individualized based on the number and location of the muscle(s) to be treated, the degree of spasticity/dystonia, muscle mass, body weight, and response to any previous botulinum toxin injections.
The frequency of XEOMIN repeat treatments should be determined by clinical response, but should generally be no more frequent than every 12 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Figure 5: Muscles Involved in Cervical Dsytonia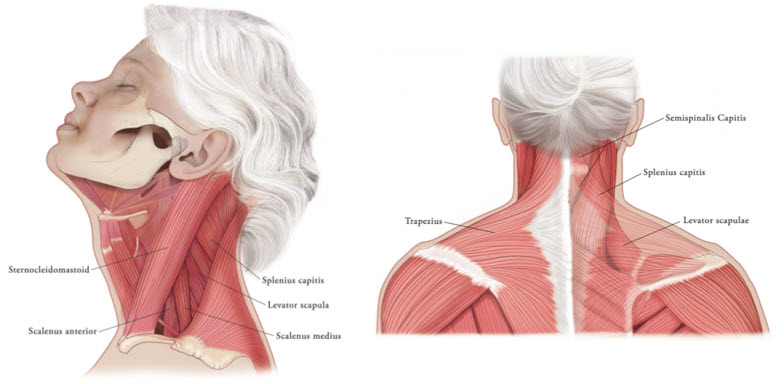

Figure 5 - Blepharospasm: the recommended initial dose is 50 Units (25 Units per eye) ()
2.5 Recommended Dose for BlepharospasmIn treatment-naïve patients, the recommended initial dose of XEOMIN is 50 Units (25 Units per eye). In patients previously treated with a botulinum toxin A, consider their past dose, response to treatment, duration of effect, and adverse event history when determining the XEOMIN dose.
Do not exceed a total XEOMIN dose of 100 Units per treatment session (50 Units per eye).
Inject XEOMIN into the lateral and medial orbicularis oculi muscle of the upper lid; lateral canthus and the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle of the lower lid; and the corrugator muscle, if necessary (see Figure 6). The number and location of injections may be changed in response to adverse reactions or based on the patient's response to treatment, but do not exceed a total dose of 50 Units per eye.
Figure 6: Injection Sites for Blepharospasm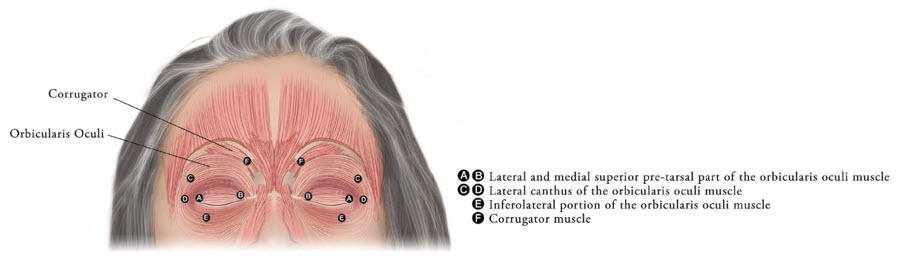
Determine the frequency of XEOMIN repeat treatments by clinical response but administer repeat treatments no more frequent than every 12 weeks
[see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Figure 6
The maximum recommended dose of XEOMIN for simultaneous treatment of upper facial lines [i.e., glabellar lines (GL), horizontal forehead lines (HFL) and lateral canthal lines (LCL)] in adult patients is 64 Units, comprised of 20 Units for GL, 20 Units for HFL, and 24 Units for LCL.
Administer retreatment with XEOMIN no more frequently than every three months.
When not treating upper facial lines (GL, HFL, and LCL) simultaneously in adult patients, refer to the following instructions:
Equally distribute GL treatment to five equal intramuscular injections of 4 Units each. Inject 4 Units of reconstituted XEOMIN intramuscularly into each of 5 sites, 2 in each corrugator muscle and 1 in the procerus muscle for a maximum recommended dose of 20 Units (see Figure 7).
To reduce the complication of ptosis take the following steps:
- Avoid injection near the levator palpebrae superioris, particularly in patients with larger brow depressor complexes.
- Place corrugator injections at least 1 cm above the bony supraorbital ridge.
Treat HFL in conjunction with GL to minimize the potential for brow ptosis. The maximum recommended dose for treatment of HFL (20 Units) in conjunction with GL (20 Units) is 40 Units.
Equally distribute HFL treatment to 5 horizontally orientated intramuscular injection sites (4 Units each) into the frontalis muscle, at least 2 cm above the orbital rim (see Figure 7).
Inject 4 Units of reconstituted XEOMIN into 3 sites per side (6 total injection sites) in the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle for a total of 12 Units per side (24 Units overall). Place one injection in the horizontal extension of the lateral canthus approximately 1 cm lateral from the bony orbital rim. Place the other two injections approximately 1 cm above and below the area of the first injection (see Figure 7). Give injections with the needle bevel tip up and oriented away from the eye. Avoid injections too close to the zygomaticus major muscle to prevent lip ptosis.
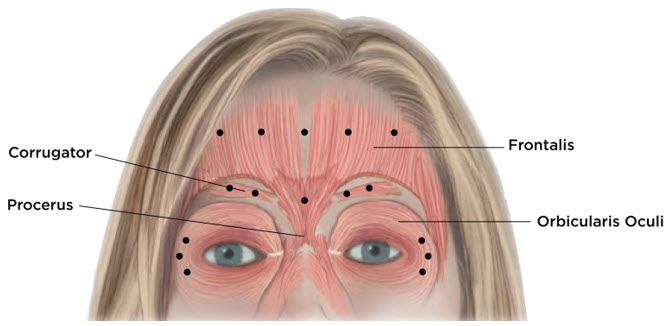

- Glabellar Lines:four Units into each of five sites, for a maximum dose of 20 Units
- Horizontal Forehead Linestreated simultaneously with Glabellar Lines:for HFL four Units into each of five sites (20 Units) and four Units into each of five GL sites (20 Units), for a maximum dose of 40 Units
- Lateral Canthal Lines:four Units into each of three sites per side (six injection sites in total), for a maximum dose of 12 Units per side (24 Units in total)
Administer retreatment with XEOMIN no more frequently than every three months.
- Is intended for intramuscular or intraglandular injection in the parotid and submandibular glands only ()
2.7 Preparation and Reconstitution TechniquePrior to injection, reconstitute each vial of XEOMIN with sterile, preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
[see Dosage Form and Strengths (3)]. A 20-27 gauge short bevel needle is recommended for reconstitution. Draw up an appropriate amount of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP into a syringe (see Table 5). Clean the exposed portion of the rubber stopper of the vial with alcohol (70%) prior to insertion of the needle. After vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper, the vacuum will draw the saline into the vial. Gently inject any remaining saline into the vial to avoid foam formation. If the vacuum does not pull the saline into the vial, then XEOMIN must be discarded. Remove the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the saline by carefully swirling and inverting/flipping the vial – do not shake vigorously. Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear, colorless solution free of particulate matter. Do not use XEOMIN if the reconstituted solution has a cloudy appearance or contains floccular or particulate matter.After reconstitution, use XEOMIN for only one injection session and for only one patient. Administer reconstituted XEOMIN within 24 hours after dilution. During this time period, store unused reconstituted XEOMIN in the original container in a refrigerator 2°C -8°C (36°F -46°F) for up to 24 hours until time of use. XEOMIN vials are for single-dose only. Discard any unused portion.
Diluent volumes for reconstitution of XEOMIN are indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Diluent Volumes for Reconstitution of XEOMIN Volume of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP50 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL100 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL200 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL0.25 mL 20 Units - - 0.5 mL 10 Units 20 Units 40 Units 1 mL 5 Units 10 Units 20 Units 1.25 mL 4 Units 8 Units 16 Units 2 mL 2.5 Units 5 Units 10 Units 2.5 mL 2 Units 4 Units 8 Units 4 mL 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 5 Units 5 mL 1 Unit 2 Units 4 Units 8 mLWhen using 8 mL of diluent for a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 8 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 16 mLWhen using 16 mL of diluent for a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 12 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 16 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- - 1.25 Units - Use for only one injection session and for only one patient ()
2.7 Preparation and Reconstitution TechniquePrior to injection, reconstitute each vial of XEOMIN with sterile, preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
[see Dosage Form and Strengths (3)]. A 20-27 gauge short bevel needle is recommended for reconstitution. Draw up an appropriate amount of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP into a syringe (see Table 5). Clean the exposed portion of the rubber stopper of the vial with alcohol (70%) prior to insertion of the needle. After vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper, the vacuum will draw the saline into the vial. Gently inject any remaining saline into the vial to avoid foam formation. If the vacuum does not pull the saline into the vial, then XEOMIN must be discarded. Remove the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the saline by carefully swirling and inverting/flipping the vial – do not shake vigorously. Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear, colorless solution free of particulate matter. Do not use XEOMIN if the reconstituted solution has a cloudy appearance or contains floccular or particulate matter.After reconstitution, use XEOMIN for only one injection session and for only one patient. Administer reconstituted XEOMIN within 24 hours after dilution. During this time period, store unused reconstituted XEOMIN in the original container in a refrigerator 2°C -8°C (36°F -46°F) for up to 24 hours until time of use. XEOMIN vials are for single-dose only. Discard any unused portion.
Diluent volumes for reconstitution of XEOMIN are indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Diluent Volumes for Reconstitution of XEOMIN Volume of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP50 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL100 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL200 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL0.25 mL 20 Units - - 0.5 mL 10 Units 20 Units 40 Units 1 mL 5 Units 10 Units 20 Units 1.25 mL 4 Units 8 Units 16 Units 2 mL 2.5 Units 5 Units 10 Units 2.5 mL 2 Units 4 Units 8 Units 4 mL 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 5 Units 5 mL 1 Unit 2 Units 4 Units 8 mLWhen using 8 mL of diluent for a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 8 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 16 mLWhen using 16 mL of diluent for a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 12 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 16 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- - 1.25 Units - Instructions are specific for 50 Unit, 100 Unit, and 200 Unit vials ()
2.7 Preparation and Reconstitution TechniquePrior to injection, reconstitute each vial of XEOMIN with sterile, preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
[see Dosage Form and Strengths (3)]. A 20-27 gauge short bevel needle is recommended for reconstitution. Draw up an appropriate amount of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP into a syringe (see Table 5). Clean the exposed portion of the rubber stopper of the vial with alcohol (70%) prior to insertion of the needle. After vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper, the vacuum will draw the saline into the vial. Gently inject any remaining saline into the vial to avoid foam formation. If the vacuum does not pull the saline into the vial, then XEOMIN must be discarded. Remove the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the saline by carefully swirling and inverting/flipping the vial – do not shake vigorously. Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear, colorless solution free of particulate matter. Do not use XEOMIN if the reconstituted solution has a cloudy appearance or contains floccular or particulate matter.After reconstitution, use XEOMIN for only one injection session and for only one patient. Administer reconstituted XEOMIN within 24 hours after dilution. During this time period, store unused reconstituted XEOMIN in the original container in a refrigerator 2°C -8°C (36°F -46°F) for up to 24 hours until time of use. XEOMIN vials are for single-dose only. Discard any unused portion.
Diluent volumes for reconstitution of XEOMIN are indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Diluent Volumes for Reconstitution of XEOMIN Volume of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP50 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL100 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL200 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL0.25 mL 20 Units - - 0.5 mL 10 Units 20 Units 40 Units 1 mL 5 Units 10 Units 20 Units 1.25 mL 4 Units 8 Units 16 Units 2 mL 2.5 Units 5 Units 10 Units 2.5 mL 2 Units 4 Units 8 Units 4 mL 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 5 Units 5 mL 1 Unit 2 Units 4 Units 8 mLWhen using 8 mL of diluent for a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 8 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 16 mLWhen using 16 mL of diluent for a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 12 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 16 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- - 1.25 Units - Store in a refrigerator (2°C to 8°C) and use within 24 hours ()
2.7 Preparation and Reconstitution TechniquePrior to injection, reconstitute each vial of XEOMIN with sterile, preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
[see Dosage Form and Strengths (3)]. A 20-27 gauge short bevel needle is recommended for reconstitution. Draw up an appropriate amount of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP into a syringe (see Table 5). Clean the exposed portion of the rubber stopper of the vial with alcohol (70%) prior to insertion of the needle. After vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper, the vacuum will draw the saline into the vial. Gently inject any remaining saline into the vial to avoid foam formation. If the vacuum does not pull the saline into the vial, then XEOMIN must be discarded. Remove the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the saline by carefully swirling and inverting/flipping the vial – do not shake vigorously. Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear, colorless solution free of particulate matter. Do not use XEOMIN if the reconstituted solution has a cloudy appearance or contains floccular or particulate matter.After reconstitution, use XEOMIN for only one injection session and for only one patient. Administer reconstituted XEOMIN within 24 hours after dilution. During this time period, store unused reconstituted XEOMIN in the original container in a refrigerator 2°C -8°C (36°F -46°F) for up to 24 hours until time of use. XEOMIN vials are for single-dose only. Discard any unused portion.
Diluent volumes for reconstitution of XEOMIN are indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Diluent Volumes for Reconstitution of XEOMIN Volume of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP50 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL100 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL200 Unit Vial:
Resulting dose in Units per 0.1 mL0.25 mL 20 Units - - 0.5 mL 10 Units 20 Units 40 Units 1 mL 5 Units 10 Units 20 Units 1.25 mL 4 Units 8 Units 16 Units 2 mL 2.5 Units 5 Units 10 Units 2.5 mL 2 Units 4 Units 8 Units 4 mL 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 5 Units 5 mL 1 Unit 2 Units 4 Units 8 mLWhen using 8 mL of diluent for a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 100 Unit or 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 8 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- 1.25 Units 2.5 Units 16 mLWhen using 16 mL of diluent for a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN, complete the following steps: - Reconstitute a 200 Unit vial of XEOMIN with 4 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, following instructions above.
- Withdraw 12 mL of preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, into an appropriately sized syringe for 16 mL in total.
- Using the same syringe, draw up the 4 mL of XEOMIN solution from the reconstituted vial and mix gently.
- - 1.25 Units
For injection: 50 Units, 100 Units, or 200 Units lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution only with preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Pregnancy: based on animal data, may cause fetal harm ()
8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryThere are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of XEOMIN in pregnant women. XEOMIN should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. XEOMIN was embryotoxic in rats and increased abortions in rabbits when given at doses higher than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for cervical dystonia (120 Units), on a body weight basis.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
DataAnimal DataWhen XEOMIN was administered intramuscularly to pregnant rats during organogenesis (3 Units/kg, 10 Units/kg, or 30 Units/kg on gestational days [GDs] 6, 12, and 19; or 7 Units/kg on GDs 6 to 19; or 2 Units/kg, 6 Units/kg, or 18 Units/kg on GDs 6, 9, 12, 16, and 19), decreases in fetal body weight and skeletal ossification were observed at doses that were also maternally toxic. The no-effect level for embryotoxicity in rats was 6 Units/kg (3 times the MRHD for cervical dystonia on a body weight basis). Intramuscular administration to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis (1.25 Units/kg, 2.5 Units/kg, or 5.0 Units/kg on GDs 6, 18, and 28) resulted in an increased rate of abortion at the highest dose, which was also maternally toxic. In rabbits, the no-effect level for increased abortion was 2.5 Units/kg (similar to the MRHD for cervical dystonia on a body weight basis).