Get your patient on Acthar (Repository Corticotropin)
Acthar prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Acthar patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Acthar Gel vial is for either intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. (2.1 )
- Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector:
- Infantile spasms: doses must be administered intramuscularly using the Acthar gel vial. The recommended dose is 150 U/m 2 divided into twice daily injections of 75 U/m 2 . After 2 weeks of treatment dosing should be gradually tapered and discontinued over a 2-week period. Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is not to be used for the treatment of infantile spasms (2.2 )
- Acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis: daily intramuscular or subcutaneous doses of 80 to 120 units for 2-3 weeks may be administered. It may be necessary to taper the dose. (2.3 )
- Other disorders and diseases: individualize dosing depending on the disease and patient. The usual dose is 40 to 80 units given intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 24 to 72 hours. It may be necessary to taper the dose. (2.4 )
Important Information
Acthar Gel vial is intended for either intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is for subcutaneous administration by adults (18 years of age and older) only. The single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector should only be used to administer single doses of either 40 units or 80 units. For administration of doses other than 40 units or 80 units, use the Acthar Gel multi-dose vial.
Recommended Dosage for Infantile Spasms in Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age
In the treatment of infantile spasms, Acthar Gel must be administered intramuscularly using the Acthar gel vial. Do not use the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector for the treatment of infantile spasms. The recommended regimen is a daily dose of 150 U/m 2 (divided into twice daily intramuscular (IM) injections of 75 U/m 2 ) administered over a 2-week period. Dosing with Acthar Gel should then be gradually tapered over a 2-week period to avoid adrenal insufficiency. The following is one suggested tapering schedule: 30 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; 15 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; 10 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; and 10 U/m 2 every other morning for 6 days.
Acthar Gel is typically dosed based on body surface area (BSA). For calculation of body surface area, use the following formula:

Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbations in Adults with Multiple Sclerosis
The recommended dose is daily intramuscular or subcutaneous doses of 80 to 120 units for 2-3 weeks for acute exacerbations.
Dosage should be individualized according to the medical condition of each patient. Frequency and dose of the drug should be determined by considering the severity of the disease and the initial response of the patient.
Although drug dependence does not occur, sudden withdrawal of Acthar Gel after prolonged use may lead to adrenal insufficiency or recurrent symptoms which make it difficult to stop the treatment. It may be necessary to taper the dose and increase the injection interval to gradually discontinue the medication.
Recommended Dosage for Other Indications for Adults and Children Over 2 Years of Age
Dosage should be individualized according to the disease under treatment and the general medical condition of each patient. Frequency and dose of the drug should be determined by considering severity of the disease and the initial response of the patient.
The usual dose of Acthar Gel is 40 to 80 units given intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 24 to 72 hours.
Although drug dependence does not occur, sudden withdrawal of Acthar Gel after prolonged use may lead to adrenal insufficiency or recurrent symptoms which make it difficult to stop the treatment. It may be necessary to taper the dose and increase the injection interval to gradually discontinue the medication.
Preparation and Administration
Visually inspect the liquid for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Acthar Gel must not be injected if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter.
Acthar Gel Multi-Dose Vial
- Warm to room temperature before using.
- Take caution to not over-pressurize the vial prior to withdrawing the product.
Acthar Gel Single-Dose Pre-filled SelfJect Injector
Preparation
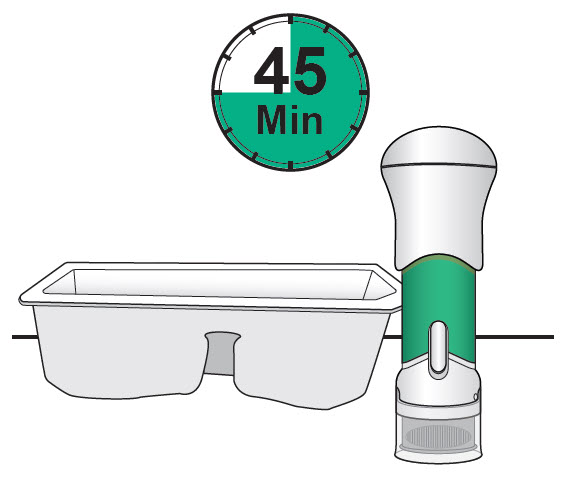
- Prior to injection, remove from the refrigerator and sealed tray and allow to sit for 45 minutes to warm to room temperature.
Administration
- Read the FDA-approved Instructions for Use carefully before administering.
- Administer by subcutaneous injection only. Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is not for intramuscular injection.
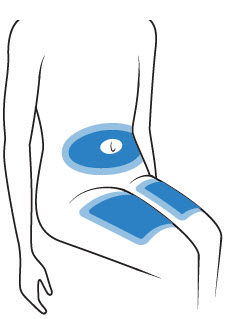
- Inject in the upper thigh, abdomen, or back of arm. Avoid injecting within 1 inch of navel, knee, or groin area.
- Avoid areas with scars, tattoos, warts, birthmarks, or stretch marks, or where the skin is irritated.
- Rotate injection sites. Do not use the same site more than one time per week.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Acthar prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Acthar Gel is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of infantile spasms in infants and children under 2 years of age. (1.1 )
- Acthar Gel is indicated for the treatment of exacerbations of multiple sclerosis in adults. (1.2 )
- Acthar Gel may be used for the following disorders and diseases: rheumatic (1.3 ); collagen (1.4 ); dermatologic (1.5 ); allergic states (1.6 ); ophthalmic (1.7 ); respiratory (1.8 ); and edematous state. (1.9 )
Infantile Spasms
Acthar Gel is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of infantile spasms in infants and children under 2 years of age.
Multiple Sclerosis
Acthar Gel is indicated for the treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis in adults. Controlled clinical trials have shown Acthar Gel to be effective in speeding the resolution of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis. However, there is no evidence that it affects the ultimate outcome or natural history of the disease.
Rheumatic Disorders
As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in: Psoriatic arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy); Ankylosing spondylitis.
Collagen Diseases
During an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of: systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis).
Dermatologic Diseases
Severe erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Allergic States
Serum sickness.
Ophthalmic Diseases
Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa such as: keratitis; iritis, iridocyclitis, diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis, optic neuritis, chorioretinitis; anterior segment inflammation.
Respiratory Diseases
Symptomatic sarcoidosis.
Edematous State
To induce a diuresis or a remission of proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome without uremia of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Acthar Gel vial is for either intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. (2.1 )
- Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector:
- Infantile spasms: doses must be administered intramuscularly using the Acthar gel vial. The recommended dose is 150 U/m 2 divided into twice daily injections of 75 U/m 2 . After 2 weeks of treatment dosing should be gradually tapered and discontinued over a 2-week period. Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is not to be used for the treatment of infantile spasms (2.2 )
- Acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis: daily intramuscular or subcutaneous doses of 80 to 120 units for 2-3 weeks may be administered. It may be necessary to taper the dose. (2.3 )
- Other disorders and diseases: individualize dosing depending on the disease and patient. The usual dose is 40 to 80 units given intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 24 to 72 hours. It may be necessary to taper the dose. (2.4 )
Important Information
Acthar Gel vial is intended for either intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is for subcutaneous administration by adults (18 years of age and older) only. The single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector should only be used to administer single doses of either 40 units or 80 units. For administration of doses other than 40 units or 80 units, use the Acthar Gel multi-dose vial.
Recommended Dosage for Infantile Spasms in Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age
In the treatment of infantile spasms, Acthar Gel must be administered intramuscularly using the Acthar gel vial. Do not use the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector for the treatment of infantile spasms. The recommended regimen is a daily dose of 150 U/m 2 (divided into twice daily intramuscular (IM) injections of 75 U/m 2 ) administered over a 2-week period. Dosing with Acthar Gel should then be gradually tapered over a 2-week period to avoid adrenal insufficiency. The following is one suggested tapering schedule: 30 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; 15 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; 10 U/m 2 in the morning for 3 days; and 10 U/m 2 every other morning for 6 days.
Acthar Gel is typically dosed based on body surface area (BSA). For calculation of body surface area, use the following formula:

Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbations in Adults with Multiple Sclerosis
The recommended dose is daily intramuscular or subcutaneous doses of 80 to 120 units for 2-3 weeks for acute exacerbations.
Dosage should be individualized according to the medical condition of each patient. Frequency and dose of the drug should be determined by considering the severity of the disease and the initial response of the patient.
Although drug dependence does not occur, sudden withdrawal of Acthar Gel after prolonged use may lead to adrenal insufficiency or recurrent symptoms which make it difficult to stop the treatment. It may be necessary to taper the dose and increase the injection interval to gradually discontinue the medication.
Recommended Dosage for Other Indications for Adults and Children Over 2 Years of Age
Dosage should be individualized according to the disease under treatment and the general medical condition of each patient. Frequency and dose of the drug should be determined by considering severity of the disease and the initial response of the patient.
The usual dose of Acthar Gel is 40 to 80 units given intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 24 to 72 hours.
Although drug dependence does not occur, sudden withdrawal of Acthar Gel after prolonged use may lead to adrenal insufficiency or recurrent symptoms which make it difficult to stop the treatment. It may be necessary to taper the dose and increase the injection interval to gradually discontinue the medication.
Preparation and Administration
Visually inspect the liquid for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Acthar Gel must not be injected if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter.
Acthar Gel Multi-Dose Vial
- Warm to room temperature before using.
- Take caution to not over-pressurize the vial prior to withdrawing the product.
Acthar Gel Single-Dose Pre-filled SelfJect Injector
Preparation
- Prior to injection, remove from the refrigerator and sealed tray and allow to sit for 45 minutes to warm to room temperature.
Administration
- Read the FDA-approved Instructions for Use carefully before administering.
- Administer by subcutaneous injection only. Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector is not for intramuscular injection.
- Inject in the upper thigh, abdomen, or back of arm. Avoid injecting within 1 inch of navel, knee, or groin area.
- Avoid areas with scars, tattoos, warts, birthmarks, or stretch marks, or where the skin is irritated.
- Rotate injection sites. Do not use the same site more than one time per week.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection available as:
400 USP Units/5 mL (80 USP Units/mL) in a multi-dose vial for subcutaneous or intramuscular injection.
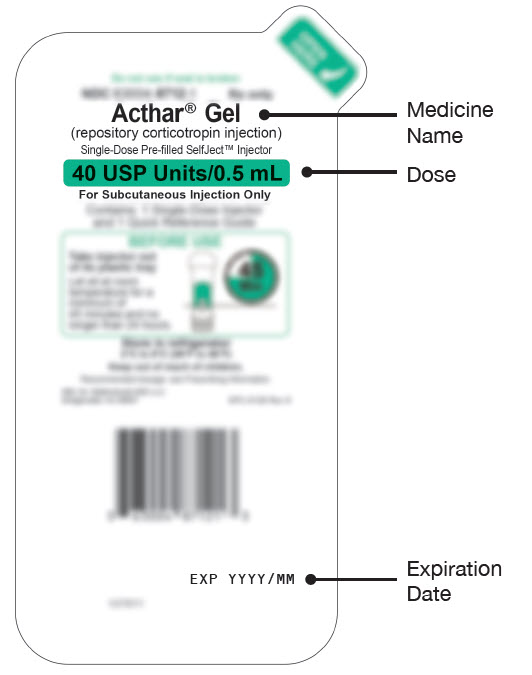
40 USP Units/0.5 mL in a single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector for subcutaneous injection.
80 USP Units/mL in a single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector for subcutaneous injection.
Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) is a clear light amber solution mobile at room temperature.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on Acthar Gel's pharmacological effect of stimulating an endogenous steroid response [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.1) ] , Acthar Gel may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. The published literature on systemic corticosteroid use during pregnancy, which may be relevant, suggests potential concerns. Intrauterine growth restriction, decreased birth weight, and preterm birth have been reported with maternal use of corticosteroids; however, the underlying maternal condition may also contribute to these risks. Hypoadrenalism has also been reported in infants after high-dose and/or long-term use of corticosteroids during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ) . The potential adverse developmental effects of Acthar Gel have not been adequately assessed in animals.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal-Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Hypoadrenalism has been reported in infants born to mothers treated with systemic corticosteroids during pregnancy. Infants born to mothers treated with Acthar Gel should be carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism, such as poor feeding, irritability, weakness, and vomiting, and managed accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the presence of corticotropin in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Acthar Gel and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Acthar Gel or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Acthar Gel is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of infantile spasms in infants and children less than 2 years of age. Both serious and other adverse reactions can occur in this population [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
The efficacy of Acthar Gel for the treatment of infantile spasms in infants and children less than 2 years of age was evaluated in a randomized, single blinded (video EEG interpreter blinded) clinical trial and an additional active control supportive trial [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . A responding patient was defined as having both complete cessation of spasms and elimination of hypsarrhythmia.
Safety in the pediatric population for infantile spasms was evaluated by retrospective chart reviews and data from non-sponsor conducted clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . While the types of adverse reactions seen in infants and children under 2 years of age treated for infantile spasms are similar to those seen in older patients, their frequency and severity may be different due to the very young age of the infant, the underlying disorder, the duration of therapy and the dosage regimen. Effects on growth are of particular concern [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ] . Serious adverse reactions observed in adults may also occur in children [see Warnings and Precautions (5) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Acthar Gel is contraindicated:
- for intravenous administration.
- in infants under 2 years of age who have suspected congenital infections.
- with concomitant administration of live or live attenuated vaccines in patients receiving immunosuppressive doses of Acthar Gel.
- in patients with scleroderma, osteoporosis, systemic fungal infections, ocular herpes simplex, recent surgery, history of or the presence of a peptic ulcer, congestive heart failure, uncontrolled hypertension, primary adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenocortical hyperfunction, or sensitivity to proteins of porcine origin.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
The adverse effects of Acthar Gel are related primarily to its steroidogenic effects. Not all of the adverse events described below have been seen after treatment with Acthar Gel, but they might be expected to occur because they are steroidogenic effects [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) ] .
Infections
Acthar Gel may increase the risks related to infections with any pathogen, including viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan or helminthic infections. Patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity should be observed closely, and if therapy is prolonged, chemoprophylaxis should be instituted.
Cushing's Syndrome and Adrenal Insufficiency Upon Withdrawal
Treatment with Acthar Gel can cause hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression and Cushing's syndrome. These conditions should be monitored especially with chronic use.
Suppression of the HPA may occur following prolonged therapy with the potential for adrenal insufficiency after withdrawal of the medication. Patients should be monitored for signs of insufficiency such as weakness, hyperpigmentation, weight loss, hypotension and abdominal pain.
The symptoms of adrenal insufficiency in infants treated for infantile spasms can be difficult to identify. The symptoms are non-specific and may include anorexia, fatigue, lethargy, weakness, excessive weight loss, hypotension and abdominal pain. It is critical that parents and caregivers be made aware of the possibility of adrenal insufficiency when discontinuing Acthar Gel and should be instructed to observe for, and be able to recognize, these symptoms [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
The recovery of the adrenal gland may take from days to months so patients should be protected from the stress (e.g., trauma or surgery) by the use of corticosteroids during the period of stress.
The adrenal insufficiency may be minimized by tapering of the dose when discontinuing treatment.
Signs or symptoms of Cushing's syndrome may occur during therapy but generally resolve after therapy is stopped. Patients should be monitored for these signs and symptoms such as deposition of adipose tissue in characteristics sites (e.g., moon face, truncal obesity), cutaneous striae, easy bruisability, decreased bone mineralization, weight gain, muscle weakness, hyperglycemia, and hypertension.
Elevated Blood Pressure, Salt and Water Retention, and Hypokalemia
Acthar Gel can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium and calcium. Dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. Caution should be used in the treatment of patients with hypertension or renal insufficiency. Acthar Gel is contraindicated in patients with congestive heart failure [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Vaccination
Administration of live or live attenuated vaccines is contraindicated in patients receiving immunosuppressive doses of Acthar Gel. Killed or inactivated vaccines may be administered; however, the response to such vaccines can not be predicted. Other immunization procedures should be undertaken with caution in patients who are receiving Acthar Gel, especially when high doses are administered, because of the possible hazards of neurological complications and lack of antibody response.
Masking Symptoms of Other Diseases
Acthar Gel often acts by masking symptoms of other diseases/disorders without altering the course of the other disease/disorder. Patients should be monitored carefully during and for a period following discontinuation of therapy for signs of infection, abnormal cardiac function, hypertension, hyperglycemia, change in body weight and fecal blood loss.
Gastrointestinal Perforation and Bleeding
Acthar Gel can cause GI bleeding and gastric ulcer. There is also an increased risk for perforation in patients with certain gastrointestinal disorders. Signs of gastrointestinal perforation, such as peritoneal irritation, may be masked by the therapy. Use caution where there is the possibility of impending perforation, abscess or other pyogenic infections, diverticulitis, fresh intestinal anastomoses, and active or latent peptic ulcer.
Behavioral and Mood Disturbances
Use of Acthar Gel may be associated with central nervous system effects ranging from euphoria, insomnia, irritability (especially in infants), mood swings, personality changes, and severe depression, to frank psychotic manifestations. Also, existing emotional instability or psychotic tendencies may be aggravated. These effects are reversible once Acthar Gel therapy is stopped.
Comorbid Diseases
Patients with a comorbid disease may have that disease worsened. Caution should be used when prescribing Acthar Gel in patients with diabetes and myasthenia gravis.
Ophthalmic Effects
Prolonged use of Acthar Gel may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi and viruses.
Immunogenicity Potential
Acthar Gel is immunogenic. Limited available data suggest that a patient may develop antibodies to Acthar Gel after chronic administration and loss of endogenous ACTH and Acthar Gel activity. Prolonged administration of Acthar Gel may increase the risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Cases of anaphylaxis have been reported in the postmarketing setting. Use in patients with sensitivity to porcine protein is contraindicated, and the possibility of sensitivity should be considered during the course of treatment should symptoms arise.
Use in Patients with Hypothyroidism or Liver Cirrhosis
There is an enhanced effect in patients with hypothyroidism and in those with cirrhosis of the liver.
Negative Effects on Growth and Physical Development
Long-term use of Acthar Gel may have negative effects on growth and physical development in pediatric patients. Changes in appetite are seen with Acthar Gel therapy, with the effects becoming more frequent as the dose or treatment period increases. These effects are reversible once Acthar Gel therapy is stopped. Growth and physical development of pediatric patients on prolonged therapy should be carefully monitored.
Decrease in Bone Density
Decrease in bone formation and an increase in bone resorption both through an effect on calcium regulation (i.e., decreasing absorption and increasing excretion) and inhibition of osteoblast function may occur. These, together with a decrease in the protein matrix of the bone (secondary to an increase in protein catabolism) and reduced sex hormone production, may lead to inhibition of bone growth in children and adolescents and to the development of osteoporosis at any age. Special consideration should be given to patients at increased risk of osteoporosis (i.e., postmenopausal women) before initiating therapy, and bone density should be monitored in patients on long term therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Cushing's Syndrome and Adrenal Insufficiency Upon Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Elevated Blood Pressure, Salt and Water Retention, and Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Masking Symptoms of Other Diseases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Behavioral and Mood Disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Ophthalmic Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Immunogenicity Potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Negative Effects on Growth and Physical Development [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
- Decrease in Bone Density [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age
While the types of adverse reactions seen in infants and children under age 2 treated for infantile spasms are similar to those seen in older patients, their frequency and severity may be different due to the very young age of the infant, the underlying disorder, the duration of therapy and the dosage regimen. Below is a summary of adverse reactions specifically tabulated from source data derived from retrospective chart reviews and clinical trials in children under 2 years of age treated for infantile spasms. The number of patients in controlled trials at the recommended dose was too few to provide meaningful incidence rates or to permit a meaningful comparison to the control groups. The most common adverse reactions (5% or greater in the recommended twice daily dosing group) for the treatment of infantile spasms are increased risk of infections, convulsions, hypertension, irritability, and pyrexia.
| Adverse Reactions | Recommended 75 U/m 2 twice daily n=122, (%) | 150 U/m 2 once daily n=37 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac disorders | ||
| Cardiac Hypertrophy | 3 | 0 |
| Endocrine disorders | ||
| Cushingoid | 3 | 22 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 3 | 14 |
| Vomiting | 3 | 5 |
| Constipation | 0 | 5 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Irritability | 7 | 19 |
| Pyrexia | 5 | 8 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Infection Specific infections that occurred at ≥2% were candidiasis, otitis media, pneumonia and upper respiratory tract infections. | 20 | 46 |
| Investigations | ||
| Weight gain | 1 | 3 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Increased appetite | 0 | 5 |
| Decreased appetite | 3 | 3 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Convulsion In the treatment of infantile spasms, other types of seizures/convulsions may occur because some patients with infantile spasms progress to other forms of seizures (for example, Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome). Additionally, the spasms sometimes mask other seizures and once the spasms resolve after treatment, the other seizures may become visible. | 12 | 3 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Nasal Congestion | 1 | 5 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Acne | 0 | 14 |
| Rash | 0 | 8 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 11 | 19 |
These adverse reactions may also be seen in adults and children over 2 years of age when treated for other purposes and with different doses and regimens.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Acthar Gel.
Because adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic responses have presented as dizziness, nausea, and anaphylaxis (anaphylactic shock, hypotension, respiratory compromise, urticaria, edema).
Cardiovascular
Necrotizing angitis (adults only), congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and palpitations.
Dermatologic
Skin thinning (adults only), facial erythema, and increased sweating (adults only).
Endocrine
Decreased carbohydrate tolerance (infants only), hirsutism, and menstrual irregularities.
Gastrointestinal
Pancreatitis (adults only), abdominal distention, and ulcerative esophagitis.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Injection site reaction and asthenic conditions (including fatigue, malaise, asthenia, and lethargy).
Infections and Infestations
Abscess.
Investigations
Blood glucose increased.
Metabolic
Hypokalemic alkalosis (infants only) and fluid retention (including peripheral swelling).
Musculoskeletal
Muscle weakness and vertebral compression fractures (infants only).
Neurological
Headache (adults only), vertigo (adults only), subdural hematoma, intracranial hemorrhage (adults only), and reversible brain shrinkage (usually secondary to hypertension) (infants only).
Psychiatric Disorders
Insomnia.
Possible Additional Steroidogenic Effects
Based on steroidogenic effects of Acthar Gel certain adverse events may be expected due to the pharmacological effects of corticosteroids. The adverse events that may occur but have not been reported for Acthar Gel are:
Dermatologic
Impaired wound healing, petechiae and ecchymoses, and suppression of skin test reactions.
Metabolic
Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism and alteration in glucose tolerance.
Musculoskeletal
Loss of muscle mass and aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads.
Neurological
Increased intracranial pressure with papilledema, (pseudo-tumor cerebri) usually after treatment, and subdural effusion.
Ophthalmic
Exophthalmos.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Formal drug-drug interaction studies have not been performed.
Acthar Gel may accentuate the electrolyte loss associated with diuretic therapy.
DESCRIPTION
Acthar Gel is a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and other pituitary peptides. The Acthar Gel manufacturing process converts the initial porcine pituitary extract with low ACTH content into a mixture having modified porcine ACTH and other related peptide analogs solubilized in gelatin. A major component in the formulated complex mixture is N-25 deamidated porcine ACTH (1-39).
Acthar Gel is supplied as a sterile preparation in 16% gelatin to provide a prolonged release after intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. Acthar Gel also contains 0.5% phenol, not more than 0.1% cysteine (added), sodium hydroxide and/or acetic acid to adjust pH and Water for Injection.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Acthar Gel in the treatment of infantile spasms is unknown.
Acthar Gel and endogenous ACTH stimulate the adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, and a number of weakly androgenic substances. Prolonged administration of large doses of Acthar Gel induces hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the adrenal cortex and continuous high output of cortisol, corticosterone and weak androgens. The release of endogenous ACTH is under the influence of the nervous system via the regulatory hormone released from the hypothalamus and by a negative corticosteroid feedback mechanism. Elevated plasma cortisol suppresses ACTH release.
Acthar Gel is also reported to bind to melanocortin receptors.
The trophic effects of endogenous ACTH and Acthar Gel on the adrenal cortex are not well understood beyond the fact that they appear to be mediated by cyclic AMP.
Pharmacokinetics
ACTH rapidly disappears from the circulation following its intravenous administration; in people, the plasma half-life is about 15 minutes. The pharmacokinetics of Acthar Gel have not been adequately characterized.
The maximal effects of a trophic hormone on a target organ are achieved when optimal amounts of hormone are acting continuously. Thus, a fixed dose of Acthar Gel will demonstrate a linear increase in adrenocortical secretion with increasing duration for the infusion.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Adequate studies of the carcinogenic potential of Acthar Gel have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
The genotoxic potential of Acthar Gel has not been adequately evaluated.
Impairment of Fertility
The potential effects of Acthar Gel on fertility have not been adequately assessed in animals.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of Acthar Gel as a treatment for infantile spasms was demonstrated in a single blinded (video EEG interpreter blinded) clinical trial in which patients were randomized to receive either a 2-week course of treatment with Acthar Gel (75 U/m 2 intramuscular twice daily) or prednisone (1 mg/kg by mouth twice daily). The primary outcome was a comparison of the number of patients in each group who were treatment responders, defined as a patient having complete suppression of both clinical spasms and hypsarrhythmia on a full sleep cycle video EEG performed 2 weeks following treatment initiation, rated by an investigator blinded to treatment. Thirteen of 15 patients (86.7%) responded to Acthar Gel as compared to 4 of 14 patients (28.6%) given prednisone (p<0.002). The 2-week treatment was followed by a 2-week period of taper. Nonresponders to the prednisone treatment were eligible to receive Acthar Gel treatment. Seven of 8 patients (87.5%) responded to Acthar Gel after not responding to prednisone. Similarly, the 2 nonresponder patients from the Acthar Gel treatment were eligible to receive treatment with prednisone. One of the 2 patients (50%) responded to the prednisone treatment after not responding to Acthar Gel.
A supportive single-blind, randomized clinical trial comparing high-dose, long-duration treatment (150 U/m 2 once daily for 3 weeks, n=30) of Acthar Gel with low-dose, short-duration treatment (20 U once daily for 2 weeks, n=29) for the treatment of infantile spasms was also evaluated in infants and children less than 2 years of age. Nonresponders (defined as in the previously described study) in the low-dose group received a dose escalation at 2 weeks to 30 U once daily. Nominal statistical superiority of the high dose treatment, as compared to the low dose treatment, was observed for cessation of spasms but not for the resolution of hypsarrhythmia.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) is a clear light amber solution mobile at room temperature. Acthar Gel is supplied in the following configurations:
| Strength | Package size | NDC number |
|---|---|---|
| 80 USP Units/mL | 5 mL multi-dose vial (1 count) | 63004-8710-1 |
| 40 USP Units/0.5 mL | Single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector (4 count) | 63004-8712-4 |
| 80 USP Units/mL | Single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector (4 count) | 63004-8711-4 |
Storage and Handling
Store Acthar Gel vial and Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector under refrigeration between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the carton to protect from light.
After removing the single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector from the refrigerator, it can be stored at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 24 hours. Do not heat, freeze, or put the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector into direct sunlight.
Dispense single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injectors in the original sealed carton with the enclosed Instructions for Use.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ACTHAR ® GEL [AK-thar jel] (repository corticotropin injection) for subcutaneous use only Single-Dose Pre-filled SelfJect™ Injector
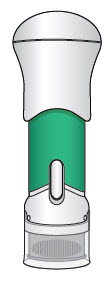 |
| Green Body Injector: 40 USP Units/0.5 mL of Acthar Gel |
Step 1: Read These Instructions
- Carefully read, understand, and follow this Instructions for Use before you use the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector.
- Contact your healthcare provider if you are unsure of how to give the injection.
Important Information
|
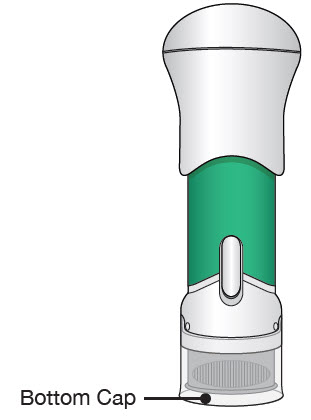
| The parts of the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector are shown below: | |
| Before Use | After the Injection is Complete |
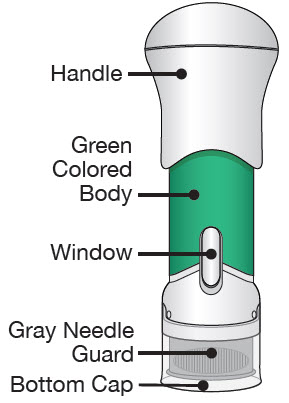 |  |
Storing Your Injector
|
Step 2: Prepare to Use the Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
Step 3: Choose and Clean the Injection Site
|
|
| |
|
|
Step 4: Inspect and Uncap 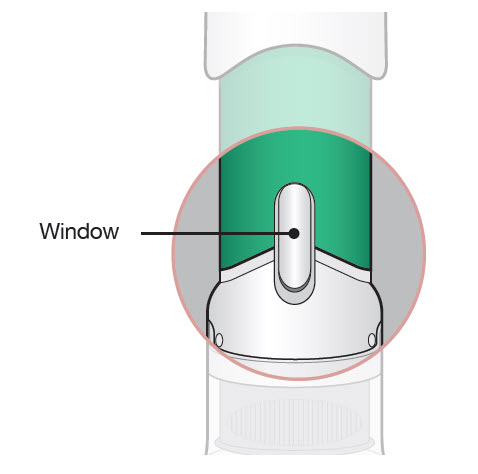
|
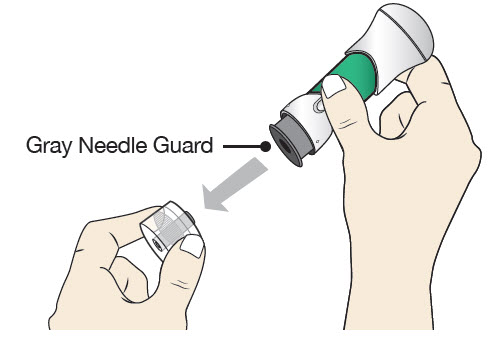 |
|
Step 5: Inject
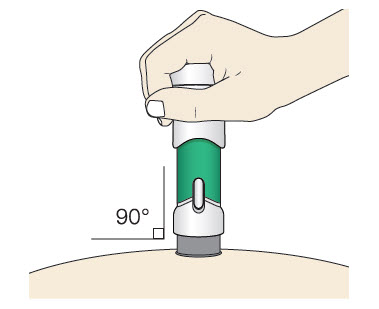 |
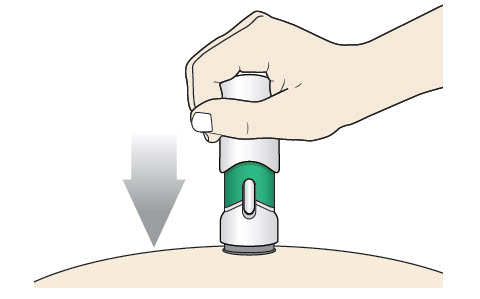 |
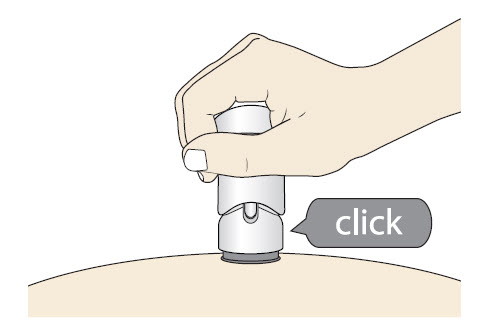 |
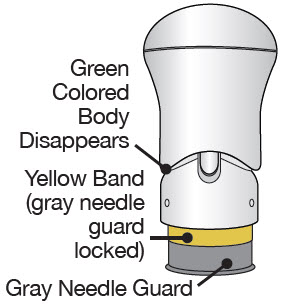
| Before you lift the injector up, check to make sure that no part of the Green Colored Body remains visible. If you see color, continue pushing down on the Handle until the Green Colored Body disappears completely. |
Step 6: Lift
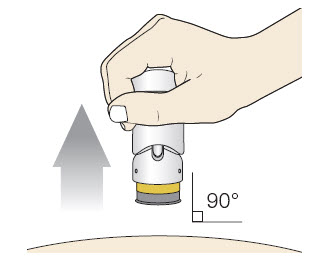 |
After the injection is complete, the injector should look like this: 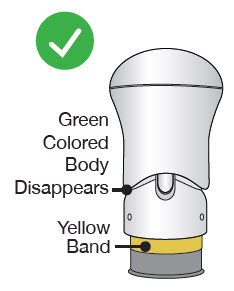 | After use, the injector should not look like this : 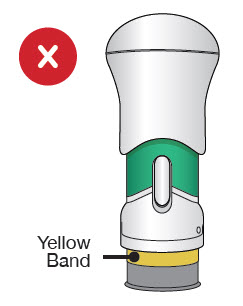 |
| If you see the Green Colored Body and the Yellow Band at the same time, then you did not give the full dose. Do not try to inject with this injector again. Do not use another injector. Contact your healthcare provider. | |
|
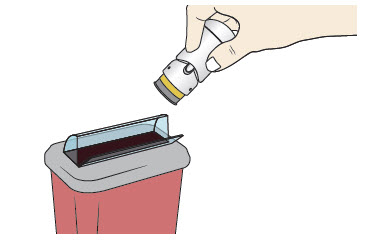
Step 7: Throw Away (Dispose of) your Used Acthar Gel single-dose pre-filled SelfJect injector
|
|
Manufactured for: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807
SPC-0204 Rev 8
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 08/2024
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Acthar Gel in the treatment of infantile spasms is unknown.
Acthar Gel and endogenous ACTH stimulate the adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, and a number of weakly androgenic substances. Prolonged administration of large doses of Acthar Gel induces hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the adrenal cortex and continuous high output of cortisol, corticosterone and weak androgens. The release of endogenous ACTH is under the influence of the nervous system via the regulatory hormone released from the hypothalamus and by a negative corticosteroid feedback mechanism. Elevated plasma cortisol suppresses ACTH release.
Acthar Gel is also reported to bind to melanocortin receptors.
The trophic effects of endogenous ACTH and Acthar Gel on the adrenal cortex are not well understood beyond the fact that they appear to be mediated by cyclic AMP.