Get your patient on Adbry (Tralokinumab-Ldrm)
Adbry prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Patient support program
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Financial assistance & copay programs
Specialty pharmacy coordination
Legal resources
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to ADBRY initiation, complete all age appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines (2.1 )
- Administer ADBRY by subcutaneous injection. (2.2 )
- In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, it is recommended that ADBRY be given by or under supervision of an adult. (2.2 )
- The recommended dosage of ADBRY (2.3 )
Dosage in Adults
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) every other week |
| Autoinjector | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every other week |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) | 150 mg (one 150 mg injection) every other week |
- A dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks may be considered for adult patients below 100 kg who achieve clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. (2.3 )
Vaccination Prior to Treatment
Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with ADBRY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Important Administration Instructions
- ADBRY is administered by subcutaneous injection.
- ADBRY is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of ADBRY prior to use according to the "Instructions for Use" [see Instructions for Use ] .
Use of the Autoinjector
- The ADBRY autoinjector is for use in adults only.
- A caregiver or adult patient may inject ADBRY using the autoinjector.
Use of the Prefilled Syringe
- The ADBRY prefilled syringe is for use in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older.
- A caregiver or patient 12 years of age and older may inject ADBRY using the prefilled syringe. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer ADBRY under the supervision of an adult.
Administration Instructions
- Administer subcutaneous injection into the thigh or abdomen, except for the 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel. The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver administers the injection.
- DO NOT inject ADBRY into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised, or scarred.
- For adults taking the initial loading dose of 600 mg, administer each of the injections (four ADBRY 150 mg injections using prefilled syringes or two ADBRY 300 mg injections using autoinjectors) at different injection sites within the same body area.
- For the subsequent 300 mg doses using the prefilled syringe , administer the two ADBRY 150 mg injections at different injection sites within the same body area, rotating the body area with each subsequent set of injections.
- For the subsequent 300 mg doses using the autoinjector , administer one ADBRY 300 mg injection, rotating the body area with each subsequent injection
- For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older taking the initial loading dose of 300 mg, use prefilled syringes to administer the two ADBRY 150 mg injections at different injection sites within the same body area.
- For the subsequent 150 mg doses, use a prefilled syringe to administer one ADBRY 150 mg injection, rotating the body area with each subsequent injection.
- The ADBRY "Instructions for Use" contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of ADBRY [see Instructions for Use ] .
Recommended Dosage
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage for adults is:
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) every other week |
| Autoinjector | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every other week |
After 16 weeks of treatment, for adult patients with body weight below 100 kg who achieve clear or almost clear skin, a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks may be considered.
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage for pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is:
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) | 150 mg (one 150 mg injection) every other week |
Concomitant Topical Therapies
ADBRY can be used with or without topical corticosteroids. Topical calcineurin inhibitors may be used, but should be reserved for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
Preparation for Use
- Before injection, remove ADBRY prefilled syringes or autoinjectors from the refrigerator and allow to reach room temperature (at least 30 minutes for the prefilled syringes and at least 45 minutes for the autoinjectors) without removing the needle cover or cap, respectively.
- After removal from the refrigerator, ADBRY may be kept at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) and must be used within 14 days or discarded.
- Inspect ADBRY visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. ADBRY injection is a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particulate matter, is discolored or cloudy (other than clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow).
- ADBRY does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Adbry prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ADBRY is indicated for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. ADBRY can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to ADBRY initiation, complete all age appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines (2.1 )
- Administer ADBRY by subcutaneous injection. (2.2 )
- In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, it is recommended that ADBRY be given by or under supervision of an adult. (2.2 )
- The recommended dosage of ADBRY (2.3 )
Dosage in Adults
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) every other week |
| Autoinjector | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every other week |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) | 150 mg (one 150 mg injection) every other week |
- A dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks may be considered for adult patients below 100 kg who achieve clear or almost clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment. (2.3 )
Vaccination Prior to Treatment
Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with ADBRY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Important Administration Instructions
- ADBRY is administered by subcutaneous injection.
- ADBRY is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of ADBRY prior to use according to the "Instructions for Use" [see Instructions for Use ] .
Use of the Autoinjector
- The ADBRY autoinjector is for use in adults only.
- A caregiver or adult patient may inject ADBRY using the autoinjector.
Use of the Prefilled Syringe
- The ADBRY prefilled syringe is for use in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older.
- A caregiver or patient 12 years of age and older may inject ADBRY using the prefilled syringe. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer ADBRY under the supervision of an adult.
Administration Instructions
- Administer subcutaneous injection into the thigh or abdomen, except for the 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel. The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver administers the injection.
- DO NOT inject ADBRY into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised, or scarred.
- For adults taking the initial loading dose of 600 mg, administer each of the injections (four ADBRY 150 mg injections using prefilled syringes or two ADBRY 300 mg injections using autoinjectors) at different injection sites within the same body area.
- For the subsequent 300 mg doses using the prefilled syringe , administer the two ADBRY 150 mg injections at different injection sites within the same body area, rotating the body area with each subsequent set of injections.
- For the subsequent 300 mg doses using the autoinjector , administer one ADBRY 300 mg injection, rotating the body area with each subsequent injection
- For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older taking the initial loading dose of 300 mg, use prefilled syringes to administer the two ADBRY 150 mg injections at different injection sites within the same body area.
- For the subsequent 150 mg doses, use a prefilled syringe to administer one ADBRY 150 mg injection, rotating the body area with each subsequent injection.
- The ADBRY "Instructions for Use" contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of ADBRY [see Instructions for Use ] .
Recommended Dosage
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage for adults is:
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) every other week |
| Autoinjector | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every other week |
After 16 weeks of treatment, for adult patients with body weight below 100 kg who achieve clear or almost clear skin, a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks may be considered.
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage for pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is:
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage | |
|---|---|---|
| Prefilled syringe | 300 mg (two 150 mg injections) | 150 mg (one 150 mg injection) every other week |
Concomitant Topical Therapies
ADBRY can be used with or without topical corticosteroids. Topical calcineurin inhibitors may be used, but should be reserved for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
Preparation for Use
- Before injection, remove ADBRY prefilled syringes or autoinjectors from the refrigerator and allow to reach room temperature (at least 30 minutes for the prefilled syringes and at least 45 minutes for the autoinjectors) without removing the needle cover or cap, respectively.
- After removal from the refrigerator, ADBRY may be kept at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) and must be used within 14 days or discarded.
- Inspect ADBRY visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. ADBRY injection is a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particulate matter, is discolored or cloudy (other than clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow).
- ADBRY does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ADBRY is a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution available as:
- Injection: 150 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle guard
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL solution in a single-dose autoinjector
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ADBRY during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register pregnant patients, or pregnant women may enroll themselves in the registry by calling 1-877-311-8972 or visiting https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/adbry-tralokinumab/.
Risk Summary
There are limited data from the use of ADBRY in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. Monoclonal antibodies are actively transported across the placenta (see Clinical Considerations ) .
In an enhanced pre-and post-natal developmental study, no adverse developmental effects were observed in offspring born to pregnant monkeys after intravenous administration of tralokinumab-ldrm during organogenesis through parturition at doses up to 10 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses and peaks during the third trimester. Therefore, ADBRY may be present in infants exposed in utero . The potential clinical impact of tralokinumab-ldrm exposure in infants exposed in utero should be considered.
Data
Animal Data
In a pre- and post-natal development study, intravenous doses up to 100 mg/kg tralokinumab-ldrm were administered to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys once every week from gestation day 20 to parturition. No maternal or developmental toxicity was observed at doses up to 100 mg/kg/week (10 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis of 10 mg/kg/week).
In an enhanced pre- and post-natal development study, intravenous doses up to 100 mg/kg tralokinumab-ldrm (10 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis of 10 mg/kg/week) were administered to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys once every week from the beginning of organogenesis to parturition. No treatment-related adverse effects on embryofetal toxicity or malformations, or on morphological, functional, or immunological development were observed in the infants from birth through 6 months of age.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tralokinumab-ldrm in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is present in breast milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure to ADBRY on the breastfed infant are unknown. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ADBRY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from ADBRY or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ADBRY have been established for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable.
Use of ADBRY in this age group is supported by a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (ECZTRA 6) in 289 subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Of the 289 subjects, 195 were treated with ADBRY and 94 were treated with matching placebo. The safety and effectiveness were consistent between subjects 12 to 17 years of age and adult subjects [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of ADBRY have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age.
Geriatric Use
Of the 1605 subjects exposed to ADBRY in 5 atopic dermatitis trials in the initial treatment period of up to 16 weeks, 77 subjects were 65 years or older. Clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADBRY is contraindicated in patients who have known hypersensitivity to tralokinumab-ldrm or any excipients in ADBRY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and angioedema have occurred after administration of ADBRY. Discontinue ADBRY in the event of a hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1 )
- Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Patients should report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider. (5.2 )
- Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating treatment with ADBRY. If patients become infected while receiving ADBRY and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with ADBRY until the infection resolves. (5.3 )
- Risk of Infection with Live Vaccines: Avoid use of live vaccines. (5.4 )
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with use of ADBRY.
If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue ADBRY immediately and initiate appropriate therapy.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in atopic dermatitis subjects who received ADBRY. Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. Most subjects with conjunctivitis or keratitis recovered or were recovering during the treatment period [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Advise patients to report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections
Patients with known helminth infections were excluded from participation in clinical studies. It is unknown if ADBRY will influence the immune response against helminth infections by inhibiting IL-13 signaling.
Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating treatment with ADBRY. If patients become infected while receiving ADBRY and do not respond to antihelminth treatment, discontinue treatment with ADBRY until the infection resolves.
Risk of Infection with Live Vaccines
ADBRY may alter a patient's immunity and increase the risk of infection following administration of live vaccines. Prior to initiating therapy with ADBRY, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with ADBRY. Limited data are available regarding coadministration of ADBRY with non-live vaccines [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Conjunctivitis and Keratitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials in Adults
The safety of ADBRY was evaluated in a pool of 5 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in subjects with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis including three phase 3 Eczema Tralokinumab trials (ECZTRA 1, ECZTRA 2, and ECZTRA 3), a dose-finding trial, and a vaccine response trial. The safety population had a mean age of 37 years; 43% of subjects were female, 67% were White, 21% were Asian, and 9% were Black. In terms of co-morbid conditions, 39% of the subjects had asthma, 49% had hay fever, 36% had food allergy, and 21% had allergic conjunctivitis at baseline.
In these 5 atopic dermatitis trials, 1964 subjects were treated with subcutaneous injections of ADBRY, with or without concomitant topical corticosteroids (TCS). A total of 807 subjects were treated with ADBRY for at least 1 year.
ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2 compared the safety of ADBRY monotherapy to placebo through Week 52. ECZTRA 3 compared the safety of ADBRY + TCS to placebo + TCS through Week 32.
Weeks 0 to 16 (ECZTRA 1, ECZTRA 2, and ECZTRA 3):
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions identified in the pool of 3 trials (ECZTRA 1, ECZTRA 2, and ECZTRA 3) and that occurred at a rate of at least 1% in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week monotherapy group, and in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week + TCS trial, all at a higher rate than placebo during the first 16 weeks of treatment.
| Adverse Reaction | ADBRY Monotherapy Pooled analysis of ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2. | ADBRY + TCS Analysis of ECZTRA 3 where subjects were on background TCS therapy. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADBRY 300 mg Q2W ADBRY 600 mg at Week 0, followed by 300 mg every other week. | PLACEBO | ADBRY 300 mg Q2W+ TCS | PLACEBO + TCS | |
| N=1180 n (%) | N=388 n (%) | N=243 n (%) | N=123 n (%) | |
| Upper respiratory tract infections Upper respiratory tract infections cluster includes upper respiratory tract infection, viral upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, and nasopharyngitis; mainly reported as common cold. | 281 (23.8) | 79 (20.4) | 73 (30.0) | 19 (15.4) |
| Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis cluster includes conjunctivitis and allergic conjunctivitis. | 88 (7.5) | 12 (3.1) | 33 (13.6) | 6 (4.9) |
| Injection site reactions Injection site reactions cluster includes pain, erythema, and swelling. | 87 (7.4) | 16 (4.1) | 27 (11.1) | 1 (0.8) |
| Eosinophilia Eosinophilia cluster includes eosinophilia and eosinophil count increased. | 17 (1.4) | 2 (0.5) | 3 (1.2) | 0 |
In the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) through Week 16, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 0.7% in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week group and 0% of the placebo group. In the concomitant TCS trial (ECZTRA 3) through Week 16, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 0.8% in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week +TCS group and 0% of the placebo + TCS group. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in the ADBRY group compared to the placebo group were injection site reaction (0.3% v. 0) and eosinophilia (0.3% v. 0) in ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2; and injection site reaction (0.4% v. 0) and conjunctivitis (0.4% v. 0) in ECZTRA 3.
Weeks 16-52 (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) and Weeks 16-32 (ECZTRA 3):
The safety profile of ADBRY 300 mg every other week with or without TCS during maintenance treatment was consistent with that in the initial 16-week treatment period. In addition, the frequency of adverse reactions with ADBRY 300 mg every other week and every 4 weeks in ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2 was 44% and 34%, respectively, and 43% and 26% with ADBRY 300 mg + TCS every other week and every 4 weeks in ECZTRA 3, respectively.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials in Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older
The safety of tralokinumab was assessed in a trial of 289 subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (ECZTRA 6). Of the 289 subjects, 195 were treated with ADBRY and 94 were treated with matching placebo. The safety profile of ADBRY in these subjects, assessed through the initial treatment period of 16 weeks and the long-term period of 52 weeks, was comparable to the safety profile from trials in adults with atopic dermatitis.
Safety through 268 weeks (ECZTEND)
ECZTEND was an open-label, multicenter, long-term extension trial that further assessed the safety of ADBRY for up to 5 years of treatment in adults and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis who had previously participated in ADBRY trials. The safety data in ECZTEND reflect exposure to ADBRY in 1672 subjects who received 300 mg of ADBRY every two weeks (Q2W), including 1422 exposed for at least 52 weeks, 1184 exposed for at least 104 weeks, 701 exposed for at least 156 weeks, and 33 exposed for at least 264 weeks.
The long-term safety profile was consistent with the safety profile observed up to week 16.
Specific Adverse Reactions
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
Conjunctivitis, including allergic conjunctivitis, was reported in 7.5% of subjects treated with ADBRY 300 mg every other week (29 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) and in 3.1% of subjects treated with placebo (12 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) in the initial treatment period of up to 16 weeks in the pool of 5 trials. In the ADBRY group, 126 subjects reported 145 events of conjunctivitis, with 114 events resolved at the end of initial treatment period. Conjunctivitis led to discontinuation of treatment in 2 subjects.
During the initial treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2), conjunctivitis was reported in 7.7% of subjects treated with ADBRY 300 mg every other week (30 events per 100 subject-years of exposure).
During the maintenance treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) from 16 to 52 weeks, conjunctivitis was reported in 14 (8.9%) subjects treated with ADBRY 300 mg every other week (20 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) and in 10 (6.3%) subjects treated with ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks (14 events per 100 subject-years of exposure); and included no serious events, 1 severe event, and 1 event that led to discontinuation. A comparable pattern was seen during the continuation treatment period of an additional 16 weeks in the ADBRY combination trial ECZTRA 3.
Keratoconjunctivitis (including 1 atopic keratoconjunctivitis (0.1%)) was reported in 5 (0.3%) subjects (1.2 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) treated with ADBRY and 0% of subjects treated with placebo during the initial treatment period of up to 16 weeks in the pool of 5 trials. Keratoconjunctivitis was reported as resolved in 2 out of 5 subjects by the end of trials.
Keratitis (including 1 ulcerative keratitis (0.1%)) was reported in 4 (0.2%) subjects treated with ADBRY (0.9 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) and 1 (0.2%) subject (viral keratitis) treated with placebo (0.6 events per 100 subject-years of exposure) during the initial treatment period of up to 16 weeks in the pool of 5 trials. Keratitis was reported as resolved in all but 1 subject by the end of trials. None of the events were serious or led to treatment discontinuation.
During the initial treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2), keratitis event rate of 2 per 100 subject-years was reported for ADBRY 300 mg every other week.
During the maintenance treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) from 16 to 52 weeks in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week group, keratitis was reported in 1 (0.6%) subject (ulcerative, severe, resolved after discontinuation) at an exposure-adjusted event rate of 1.2 per 100 subject-years, and keratoconjunctivitis (not serious or severe, resolved, not led to discontinuation) was reported in 3 (1.9%) subjects (3.6 events per 100 subject-years of exposure). No events of keratitis or keratoconjunctivitis was reported in ADBRY every 4 weeks or placebo groups. In the continuation treatment period of ECZTRA 3 (from 16 to 32 weeks), there were no additional events of keratitis reported for subjects randomized to ADBRY 300 mg + TCS.
Eosinophil Counts
ADBRY-treated subjects had a greater mean initial increase from baseline in eosinophil count compared to subjects treated with placebo. The mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 4 were 190 and 100 cells/mcL, respectively. The increase in the ADBRY-treated subjects declined to baseline level with continued treatment. Eosinophilia (> 5000 cells/mcL) in the initial treatment period of up to 16 weeks was reported in 1.2% in the ADBRY-treated subjects and 0.3% in the placebo-treated subjects. The safety profile for subjects with eosinophilia was comparable to the safety profile for all subjects included in the pool of 5 atopic dermatitis trials.
DESCRIPTION
Tralokinumab-ldrm, an interleukin-13 antagonist, is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody. Tralokinumab-ldrm is produced in mouse myeloma cells by recombinant DNA technology, consists of 1326 amino acids, and has a molecular weight of approximately 147 kilodaltons.
ADBRY (tralokinumab-ldrm) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution for subcutaneous use supplied as either a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle guard in a siliconized Type-1 clear glass syringe or a single-dose autoinjector with a siliconized Type-1 clear glass syringe inside. None of the components of the prefilled syringe, autoinjector or the needle guard are made with natural rubber latex.
Each prefilled syringe delivers 150 mg tralokinumab-ldrm in 1 mL and the inactive ingredients: acetic acid (0.3 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.1 mg), sodium acetate trihydrate (6 mg), sodium chloride (5 mg), and Water for Injection, at an approximate pH of 5.5.
Each autoinjector delivers 300 mg tralokinumab-ldrm in 2 mL and the inactive ingredients: acetic acid (0.6 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.2 mg), sodium acetate trihydrate (12 mg), sodium chloride (10 mg), and Water for Injection, at an approximate pH of 5.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Tralokinumab-ldrm is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to human interleukin-13 (IL-13) and inhibits its interaction with the IL-13 receptor α1 and α2 subunits (IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2). IL-13 is a naturally occurring cytokine of the Type 2 immune response. Tralokinumab-ldrm inhibits the bioactivity of IL-13 by blocking IL-13 interaction with IL-13Rα1/IL-4Rα receptor complex. Tralokinumab-ldrm inhibits IL-13-induced responses including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and IgE.
Pharmacodynamics
ADBRY was associated with decreased concentrations of Th2 and Th22 immunity biomarkers in the blood, such as thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17), periostin, IL-22, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and serum IgE. ADBRY decreased expression of keratin 16 and Ki-67 in AD skin, and upregulated protein expression of loricrin. ADBRY suppressed expression of genes in the Th2 pathway, including CCL17, CCL18 and CCL26 as well as markers of Th17- and Th22-regulated genes in lesional skin. The clinical relevance of these is not fully understood.
Immune Response to Non-live Vaccines during Treatment
Immune responses to non-live vaccines were assessed in a trial in which adult subjects with atopic dermatitis were treated with an initial dose of 600 mg (four 150 mg injections) followed by 300 mg every other week administered as subcutaneous injection. After 12 weeks of ADBRY administration, subjects were vaccinated with a combined tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccine, and a meningococcal vaccine. Antibody responses were assessed 4 weeks later. Antibody response to tetanus, diphtheria, acellular pertussis, and a meningococcal vaccine was similar in tralokinumab-ldrm treated and placebo treated subjects. Immune responses to other vaccines were not assessed.
Pharmacokinetics
In adults, the mean (SD) steady-state trough concentration of tralokinumab-ldrm ranged from 98.0 (41.1) mcg/mL to 101.4 (42.7) mcg/mL following administration of ADBRY at 300 mg every other week. Tralokinumab-ldrm exposure increased proportionally over a dosage range up to 2100 mg for a 70 kg subject (30 mg/kg IV) (3.5 times the maximum approved recommended dosage). Steady-state tralokinumab-ldrm concentrations were achieved by week 16 following a 600 mg starting dose and 300 mg every other week.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of tralokinumab-ldrm was estimated to be 76%. The time to maximum tralokinumab-ldrm concentrations (t max ) was 5 to 8 days after administration.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of tralokinumab-ldrm was estimated to be approximately 4.2 L.
Elimination
The half-life of tralokinumab-ldrm was 3 weeks and systemic clearance was estimated to be 0.149 L/day.
Metabolism
Tralokinumab-ldrm is expected to be metabolized into small peptides by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients, Patients with Renal and Hepatic Impairment
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of tralokinumab-ldrm were observed based on age (ranged from 18 – 92 years), sex, mild to moderate renal impairment, or mild hepatic impairment. The effect of severe renal impairment or moderate to severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tralokinumab-ldrm is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
In subjects 12 to 17 years of age with atopic dermatitis, the mean (SD) steady-state trough concentration of tralokinumab-ldrm was 59.6 mcg/mL (19.4) and 112.8 mcg/mL (39.2) following administration of ADBRY at 150 mg and 300 mg every other week, respectively.
Body Weight
The exposure of tralokinumab-ldrm decreases with increasing body weight. After 300 mg dose every 4 weeks, the median tralokinumab-ldrm exposure (AUC) of subjects with body weight of above 100 kg is expected to be 1.46-fold lower than that of subjects weighing below 100 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Drug Interaction Studies
Cytochrome P450 Substrates
The effects of tralokinumab on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate), warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate), omeprazole (CYP2C19 substrate), metoprolol (CYP2D6 substrate), and caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate) were evaluated in a clinical trial in 18-20 subjects with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis receiving an initial SC dose of 600 mg followed by 300 mg SC every other week for 14 weeks. No clinically significant changes in the exposure (AUC or Cmax) of the CYP450 substrates after multiple tralokinumab administrations were observed compared to that when administered alone.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the trials described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other trials, including those of ADBRY or of other tralokinumab products.
In ECZTRA 1, ECZTRA 2, and ECZTRA 3, and the vaccine-response trial, the incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) during the initial 16-week treatment period was 1.4% for subjects treated with ADBRY 300 mg every other week and in 1.3% for subjects treated with placebo; neutralizing antibodies were seen in 0.1% of subjects treated with ADBRY and 0.2% of subjects treated with placebo.
Across all trial periods, the ADA incidence for subjects who received ADBRY was 4.6%; 0.9% had persistent ADA and 1.0% had neutralizing antibodies.
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics, safety, or efficacy of tralokinumab-ldrm were observed in patients who tested positive for anti-tralokinumab-ldrm antibody (including neutralizing antibodies).
In the open-label long-term extension trial (ECZTEND), anti-drug-antibody (ADA) responses were assessed up to 248 weeks and were not associated with any impact on tralokinumab exposure or safety.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential for tralokinumab-ldrm.
No effects on fertility parameters such as reproductive organs, menstrual cycle and sperm analysis were observed in male or female sexually mature cynomolgus monkeys that were subcutaneously administered tralokinumab-ldrm at doses up to 350 mg/animal (10 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis of 10 mg/kg/week) in females once a week for three consecutive menstrual cycles (maximum of 15 doses) or 600 mg/animal (10 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis of 10 mg/kg/week) in males once a week for 13 weeks. The monkeys were not mated to evaluate fertility.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adults
The efficacy of ADBRY was assessed in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials [ECZTRA 1 (NCT03131648), ECZTRA 2 (NCT03160885), and ECZTRA 3 (NCT03363854)]. Efficacy was assessed in a total of 1934 subjects 18 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) not adequately controlled by topical medication(s). Disease severity was defined by an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥ 3 in the overall assessment of AD lesions on a severity scale of 0 to 4, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 72, and a minimum body surface area (BSA) involvement of ≥10%. At baseline, 58% of subjects were male, 69% of subjects were White, 50% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), and 50% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 4 (severe AD). The baseline mean EASI score was 32 and the baseline weekly averaged Worst Daily Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) was 8 on a scale of 0-10.
In all three trials, subjects received subcutaneous injections of ADBRY 600 mg or placebo on Day 0, followed by 300 mg every other week or placebo for 16 weeks. Responders were defined as achieving an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear") or EASI-75 (improvement of at least 75% in EASI score from baseline) at Week 16.
To evaluate maintenance of response in the monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2), subjects responding to initial treatment with ADBRY 300 mg every other week were re-randomized to ADBRY 300 mg every other week, ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks or placebo every other week for another 36 weeks following first dose administration. Subjects randomized to placebo in the initial treatment period who achieved a clinical response at Week 16 continued to receive placebo every other week for another 36 weeks. Non-responders at Week 16, and subjects who lost clinical response during the maintenance period were placed on open-label treatment with ADBRY 300 mg every other week and optional use of TCS.
In the combination therapy trial (ECZTRA 3), subjects received either ADBRY 300 mg every other week with TCS or placebo with TCS and as needed topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) until Week 16. Subjects in the ADBRY 300 mg with TCS group who achieved clinical response at Week 16 were re-randomized to ADBRY 300 mg every other week with TCS or ADBRY every 4 weeks with TCS for another 16 weeks following first dose administration. Subjects in the placebo with TCS group who achieved clinical response at Week 16 continued on placebo with TCS for another 16 weeks. Subjects who did not achieve clinical response at Week 16 received ADBRY 300 mg every other week for another 16 weeks. A mid-potency TCS (i.e., mometasone furoate 0.1% cream) was dispensed at each dosing visit. Subjects were instructed to apply a thin film of the dispensed TCS as needed once daily to active lesions from Week 0 to Week 32 and were to discontinue treatment with TCS when control was achieved. An additional, lower potency TCS or TCI could be used at the investigator's discretion on areas of the body where use of the supplied TCS was not advisable, such as areas of thin skin.
All three trials assessed the primary endpoints of the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 or 1 at Week 16 and the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 at Week 16. Secondary endpoints included the reduction of Worst Daily Pruritus NRS (weekly average) of at least 4 points on the 11-point itch NRS from baseline to Week 16 .
Clinical Response at Week 16 (ECZTRA 1, ECZTRA 2, and ECZTRA 3)
The results of the ADBRY monotherapy trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) and the ADBRY with TCS trial (ECZTRA 3) are presented in Table 2 .
| ECZTRA 1 | ECZTRA 2 | ECZTRA 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADBRY 300 mg every other week | Placebo | ADBRY 300 mg every other week | Placebo | ADBRY 300 mg every other week + TCS | Placebo + TCS | |
| Abbreviations: AD = Atopic Dermatitis CI = Confidence Interval. Note: Difference and 95% CI are based on the CMH test stratified by region and baseline IGA score. | ||||||
| Number of subjects randomized and dosed (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized and dosed. | 601 | 197 | 577 | 193 | 243 | 123 |
| IGA 0 or 1 Responders was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear"). , Subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered as non-responders. | 16% | 7% | 21% | 9% | 38% | 27% |
| Difference from Placebo | 9% | 12% | 11% | |||
| (95% CI) | (4%, 13%) | (7%, 17%) | (1%, 21%) | |||
| EASI-75 | 25% | 13% | 33% | 10% | 56% | 37% |
| Difference from Placebo | 12% | 22% | 20% | |||
| (95% CI) | (6%, 18%) | (17%, 28%) | (9%, 30%) | |||
| Number of subjects with baseline Worst Daily Pruritus NRS (weekly average) score ≥4 | 594 | 194 | 563 | 192 | 240 | 123 |
| Worst Daily Pruritus NRS (≥4 point reduction) | 20% | 10% | 25% | 9% | 46% | 35% |
| Difference from Placebo | 10% | 16% | 11% | |||
| (95% CI) | (4%, 15%) | (11%, 21%) | (1%, 22%) | |||
A higher proportion of subjects in the ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm achieved EASI-90 compared to placebo in the three pivotal trials.
Examination of age, gender, race, body weight, and previous treatment, including immunosuppressants, did not identify differences in response to ADBRY 300 mg every other week among these subgroups.
Monotherapy Trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2) – Maintenance Period (Week 16-52 )
In ECZTRA 1, 179 ADBRY 300 mg every other week responders (IGA 0/1 or EASI-75) were re-randomized (and dosed) at Week 16 to ADBRY 300 mg every other week (68 subjects), ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks (76 subjects) or placebo (35 subjects). Among these subjects, 39 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm, 36 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks arm and 19 subjects in placebo arm were IGA 0/1 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of IGA 0/1 response at Week 52 was as follows: 20 subjects (51%) in every other week arm, 14 subjects (39%) in every 4 weeks arm and 9 subjects (47%) in the placebo arm. Among the re-randomized subjects, 47 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm, 57 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks arm and 30 subjects in placebo arm were EASI-75 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of EASI-75 response at Week 52 was as follows: 28 subjects (60%) in every other week arm, 28 subjects (49%) in every 4 weeks arm and 10 subjects (33%) in the placebo arm.
In ECZTRA 2, 218 ADBRY 300 mg every other week responders (IGA 0/1 or EASI-75) were re-randomized (and dosed) at Week 16 to ADBRY 300 mg every other week (90 subjects), ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks (84 subjects) or placebo (44 subjects). Among these subjects, 53 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm, 44 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks arm and 26 subjects in placebo arm were IGA 0/1 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of IGA 0/1 response at Week 52 was as follows: 32 subjects (60%) in every other week arm, 22 subjects (50%) in every 4 weeks arm and 6 subjects (23%) in the placebo arm. Among the re-randomized subjects, 76 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm, 69 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks arm and 40 subjects in placebo arm were EASI-75 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of EASI-75 response at Week 52 was as follows: 43 subjects (57%) in every other week arm, 38 subjects (55%) in every 4 weeks arm and 8 subjects (20%) in the placebo arm.
Concomitant TCS Trial (ECZTRA 3) – Maintenance Period (Week 16-32)
In ECZTRA 3, 131 ADBRY 300 mg every other week + TCS responders (IGA 0/1 or EASI-75) were re-randomized (and dosed) at Week 16 to ADBRY 300 mg every other week + TCS (65 subjects) or ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks + TCS (66 subjects). Among these subjects, 45 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week + TCS arm and 46 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks + TCS arm were IGA 0/1 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of IGA 0/1 response at Week 32 was as follows: 40 subjects (89%) in every other week arm and 35 subjects (76%) in every 4 weeks arm. Among the re-randomized subjects, 65 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every other week arm and 62 subjects in ADBRY 300 mg every 4 weeks arm were EASI-75 responders at Week 16. Maintenance of EASI-75 response at Week 32 was as follows: 60 subjects (92%) in every other week arm and 56 subjects (90%) in every 4 weeks arm.
Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older
The efficacy of ADBRY monotherapy in pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older was assessed in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (ECZTRA 6; NCT03526861) in 289 subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate-to-severe AD defined by IGA score ≥ 3 in the overall assessment of AD lesions on a severity scale of 0 to 4, an EASI score ≥ 16 at baseline, and a minimum BSA involvement of ≥10%. Eligible subjects enrolled into this trial had previous inadequate response to topical medication.
A total of 98 subjects received an initial dose of ADBRY 300 mg followed by 150 mg every other week up to Week 16. Subjects who met the clinical response criteria (IGA of 0 or 1 or EASI-75) at Week 16 without the use of rescue medication were re-randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either ADBRY every other week or every 4 weeks up to Week 52, receiving the same dose as during the initial 16-week treatment period. Subjects who did not meet the clinical response criteria at Week 16 or did not maintain the response during the maintenance treatment period, or used rescue medication during the initial treatment period were transferred to open-label treatment with ADBRY 300 mg every other week with optional use of topical corticosteroids. Subjects randomized to placebo in the initial treatment period who achieved a clinical response at Week 16 continued to receive placebo every other week in the maintenance treatment period.
In this trial, the mean subject age was 14.6 years (range: 12 to 17 years), the mean weight was 61.5 kg, 48% of subjects were female, 57% were White, 25% were Asian, and 11% were Black. For ethnicity, 91.3% of subjects identified as non-Hispanic/Latino and 8.7% identified as Hispanic/Latino. At baseline, 53% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), 47% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 4 (severe AD), the mean BSA involvement was 51%, and 21% of subjects had received prior systemic immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine and mycophenolate). Also, at baseline the mean EASI score was 32, the baseline Adolescent Worst Pruritus NRS score was 8. Overall, 84% of subjects had at least one co-morbid allergic condition; 68% had allergic rhinitis, 51% had asthma, and 57% had food allergies.
The primary endpoints were the proportion of subjects with IGA 0 or 1 at Week 16 ("clear" or "almost clear") and the proportion of patients with EASI-75 (improvement of at least 75% in EASI from baseline) at Week 16. Secondary endpoints included the reduction in itch, as measured by the proportion of subjects with ≥4 point improvement in Adolescent Worst Pruritus NRS from baseline.
The efficacy results at Week 16 for subjects 12 to 17 years of age are presented in Table 3.
| ADBRY 150 mg every other week | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: AD = Atopic Dermatitis, CI = Confidence Interval | ||
| Number of subjects randomized and dosed (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized and dosed. | 98 | 94 |
| IGA 0 or 1 Subjects who received rescue treatment from week 2 to week 16 or had missing data were considered non-responders. , Responder was defined as a subject with IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear" on a 0-4 IGA scale). | 21% | 4% |
| Difference from Placebo | 18% | |
| (95% CI) | (8%, 27%) | |
| EASI-75 | 29% | 6% |
| Difference from Placebo | 23% | |
| (95% CI) | (12%, 33%) | |
| Number of subjects with baseline Worst Daily Pruritus NRS (weekly average) score ≥4 | 95 | 90 |
| Worst Daily Pruritus NRS( ≥4 point reduction) , The percentage is calculated relative to the number of subjects with a baseline value ≥4. | 23% | 3% |
| Difference from Placebo | 20% | |
| (95% CI) | (11%, 29%) | |
In ECZTRA 6, a higher proportion of subjects in the ADBRY 150 mg every other week group achieved EASI-90 compared to placebo.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
ADBRY (tralokinumab-ldrm) injection is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution, supplied in a single-dose prefilled syringe with a 27-gauge, ½ inch needle and a needle guard, or a single-dose autoinjector with a 27-gauge, ½ inch needle.
Each prefilled syringe delivers 150 mg of ADBRY in 1 mL solution (NDC 50222-346-01).
Each autoinjector delivers 300 mg of ADBRY in 2 mL solution (NDC 50222-350-00).
ADBRY is available in pack sizes containing either 2 or 4 prefilled syringes with needle guard or 1 or 2 autoinjectors.
| 150 mg in a 1 mL prefilled syringe – Pack Size | NDC # |
|---|---|
| Two cartons (multipack) containing 4 prefilled syringes | NDC 50222-346-04 |
| One carton containing 2 prefilled syringes | NDC 50222-346-02 |
| 300 mg in a 2 mL autoinjector – Pack Size | NDC # |
|---|---|
| One carton containing 2 autoinjectors | NDC 50222-350-02 |
| One carton containing 1 autoinjector | NDC 50222-350-01 |
Storage and Handling
ADBRY does not contain preservatives. Discard any unused portion.
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light.
If necessary, ADBRY may be kept at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for a maximum of 14 days in the original carton. Do not store above 30°C (86°F). Do not put ADBRY back in the refrigerator after reaching room temperature. If the carton needs to be removed permanently from refrigerator, the date of removal may be recorded on the outer carton in the space provided. After removal from the refrigerator, ADBRY must be used within 14 days or discarded.
Do not expose ADBRY to heat or direct sunlight.
Do not freeze. Do not shake.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ADBRY ® [ad'-bree] (tralokinumab-ldrm) injection, for subcutaneous use
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject ADBRY.
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using the ADBRY prefilled syringe and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Keep this Instructions for Use and refer to it as needed.
Each single-dose prefilled syringe contains 150 mg of ADBRY. The ADBRY prefilled syringes are for one time use only.
Important Information You Need to Know Before Injecting ADBRY:
- Your healthcare provider should show you or your caregiver how to prepare and inject a dose of ADBRY using the prefilled syringe before you inject ADBRY for the first time. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions about how to inject ADBRY the right way.
- ADBRY is given as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
- Do not inject yourself or someone else until you have been shown how to inject ADBRY the right way.
- In children 12 years of age and older, it is recommended that ADBRY be given by or under supervision of an adult.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your prescribed dose before injecting ADBRY.
- Rotate the injection site each time you give an injection.
- The ADBRY prefilled syringe has a needle guard that will be activated to cover the needle after the injection is finished.
- Do not remove the needle cover until just before you give the injection.
- Do not share or reuse your ADBRY prefilled syringe.
- Do not inject through clothes.
| Storing ADBRY | |
|---|---|
|
|
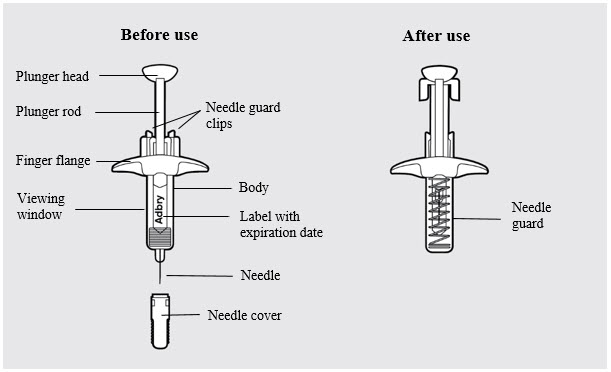
ADBRY prefilled syringe parts (see Figure A ):
Figure A
Step 1: Setting up ADBRY injection
Figure B
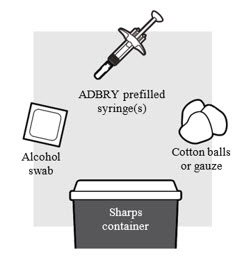
1a: Gather the supplies needed for your injection. For each ADBRY dose you will need (see Figure B ):
- A clean, flat, well-lit work surface, like a table
- Prescribed number of ADBRY prefilled syringe(s)
- An alcohol swab (not included in the carton)
- Clean cotton balls or gauze pads (not included in the carton)
- A puncture-resistant sharps disposal container (not included in the carton). See Step 5 "Disposing of ADBRY" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Figure C
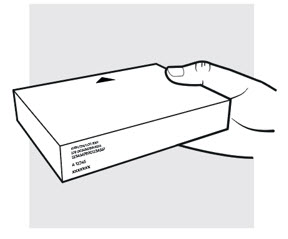
1b: Take the ADBRY prefilled syringe carton out of the refrigerator
- Check the expiration date (EXP) on the carton (see Figure C ). Do not use if the expiration date on the carton has passed.
- When using the first prefilled syringe, check to make sure the seal on the ADBRY carton is intact.
- Do not use the ADBRY prefilled syringes if the seal on the carton is broken.
Figure D
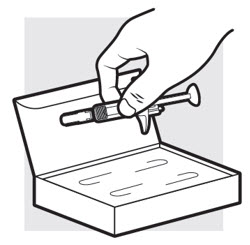
1c: Determine how many ADBRY prefilled syringes you need for your dose
If you have been prescribed a 300 mg dose, you will need 2 syringes.
If you have been prescribed a 150 mg dose, you will only need 1 syringe and the remaining syringe should be returned to the refrigerator in its carton.
- Remove the ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) by grasping the body (not the plunger rod) of the ADBRY prefilled syringe ( see Figure D ).
- Do not touch the needle guard clips to keep from activating the safety device (needle guard) too soon.
- Do not remove the needle cover on the prefilled syringe until you have reached Step 3 and are ready to inject.
Figure E

1d: Let the ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) warm up to room temperature (see Figure E )
Place the ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) on the flat surface and wait 30 minutes before you inject ADBRY to let the prefilled syringe(s) warm up to room temperature 68°F to 86°F (20°C to 30°C). This will help to reduce discomfort.
- Do not microwave the prefilled syringes, run hot water over them, or leave them in direct sunlight.
- Do not shake the syringes.
- Do not remove the needle cover on the prefilled syringes until you have reached Step 3 and are ready to inject.
- Do not put the syringes back in the refrigerator after they have reached room temperature.
Figure F
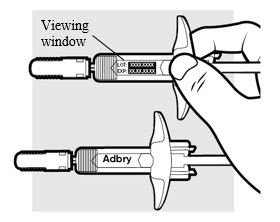
1e: Inspect the ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) (see Figure F )
- Make sure ADBRY appears on the label.
- Check the expiration date printed on the syringe.
- Check the medicine through the viewing window. The medicine inside should be clear to slightly pearly and colorless to pale yellow.
- Do not use the ADBRY prefilled syringe, throw away and get a new one if:
- the expiration date printed on the syringe has passed
- the medicine is cloudy, discolored, or has particles in it
- looks damaged or has been dropped
- You may see small air bubbles in the liquid. This is normal. You do not need to do anything about it.
Step 2: Choosing and preparing injection area
Figure G
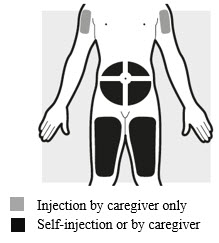
2a: Choose the area for your injection (see Figure G )
- You may inject into your thighs or your stomach area (abdomen), but not within 2 inches (5 cm) of your belly button (navel).
- The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver gives the injection.
- Inject your dose into a different body area each time you inject ADBRY.
- If you need more than 1 injection for your dose, inject into the same body area, but at least 1 inch (3 cm) apart from each other.
- Do not inject where the skin is tender, damaged, bruised or scarred.
Figure H
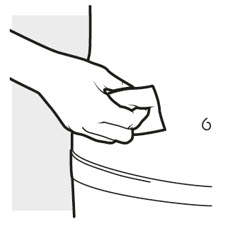
2b: Wash your hands and prepare your skin
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Clean the injection area with an alcohol swab using a circular motion ( see Figure H ).
- Let the area dry completely.
- Do not blow or touch the cleaned area before injecting.
Step 3: Injecting ADBRY
Figure I
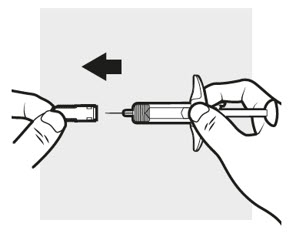
3a: Pull off the ADBRY needle cover
Hold the ADBRY prefilled syringe body with one hand, pull the needle cover straight off with your other hand ( see Figure I ) and throw it away in the sharps container.
- Do not try to recap the ADBRY prefilled syringe.
- Do not hold the plunger rod or plunger head while removing the needle cover.
- You may see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle. This is normal.
- Do not touch the needle, or let it touch any surface. If either of these occur, throw away the syringe and get a new one.
Figure J
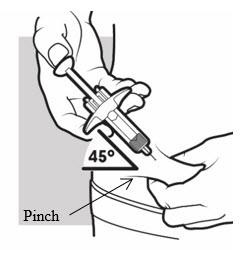
3b: Insert the needle
With one hand, gently pinch and hold a fold of skin where you cleaned the injection area. With the other hand, insert the needle completely at about a 45-degree angle into your skin ( see Figure J ).
Figure K
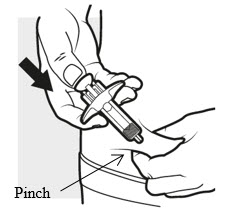
3c: Inject the medicine
Use your thumb to firmly push down the plunger head all the way down ( see Figure K ). All the medicine is injected when you cannot push the plunger head any further.
Figure L
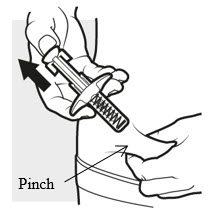
3d: Release and remove
Lift your thumb off the plunger head. The needle will automatically move back inside the syringe body and lock into place ( see Figure L ).
- Place a dry cotton ball or gauze pad over the injection site for a few seconds. Do not rub the injection site. If needed, cover the injection site with a small bandage.
- There may be a small amount of blood or liquid where you injected. This is normal.
Throw away the used ADBRY prefilled syringe in the sharps disposal container. See Step 5 "Disposing of ADBRY" .
Step 4: Repeating for multiple injections
Figure M

If you need to give multiple injections for your prescribed dose, repeat step 3. The other injection(s) should be given into the same body area, but at least 1 inch (3 cm) away from each other.
Step 5: Disposing of ADBRY syringe(s)
Figure N
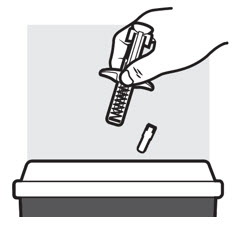
- Put the used ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use ( see Figure N ). Do not throw away the ADBRY prefilled syringe(s) in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
For more information go to www.ADBRY.com or call 1-844-692-3279. If you still have questions, call your healthcare provider.
Manufactured by: LEO Pharma A/S Industriparken 55, DK-2750 Ballerup, Denmark Distributed by: LEO Pharma Inc., Madison, NJ 07940, USA U.S. License No. 2169 ADBRY ® is a registered trademark of LEO Pharma A/S. © 2023 LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised 12/2023
Mechanism of Action
Tralokinumab-ldrm is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to human interleukin-13 (IL-13) and inhibits its interaction with the IL-13 receptor α1 and α2 subunits (IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2). IL-13 is a naturally occurring cytokine of the Type 2 immune response. Tralokinumab-ldrm inhibits the bioactivity of IL-13 by blocking IL-13 interaction with IL-13Rα1/IL-4Rα receptor complex. Tralokinumab-ldrm inhibits IL-13-induced responses including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and IgE.