Addyi prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Addyi patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dosage is 100 mg taken once daily at bedtime (2.1)
- ADDYI is dosed at bedtime because administration during waking hours increases risks of hypotension, syncope, accidental injury, and central nervous system (CNS) depression (2.1)
- Discontinue ADDYI treatment after 8 weeks if no improvement (2.3)
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ADDYI is 100 mg administered orally once per day at bedtime. ADDYI is dosed at bedtime because administration during waking hours increases the risks of hypotension, syncope, accidental injury, and central nervous system (CNS) depression (such as somnolence and sedation) .
Missed Dose
If a dose of ADDYI is missed at bedtime, instruct the patient to take the next dose at bedtime on the next day. Instruct the patient to not double the next dose.
Discontinuation of ADDYI
Discontinue ADDYI after 8 weeks if the patient does not report an improvement in her HSDD symptoms.
Initiation of ADDYI Following Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor Use
If initiating ADDYI following moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor use, start ADDYI 2 weeks after the last dose of the CYP3A4 inhibitor.
If initiating a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor following ADDYI use, start the moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor 2 days after the last dose of ADDYI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Addyi prescribing information
WARNING: HYPOTENSION and SYNCOPE IN CERTAIN SETTINGS
Interaction with Alcohol
The use of ADDYI and alcohol together close in time increases the risk of severe hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]. Counsel patients to wait at least two hours after consuming one or two standard alcoholic drinks before taking ADDYI at bedtime or to skip their ADDYI dose if they have consumed three or more standard alcoholic drinks that evening.
Contraindicated with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
The concomitant use of ADDYI and moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increases flibanserin concentrations, which can cause severe hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . Therefore, the use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated in patients taking ADDYI [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Contraindicated in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The use of ADDYI in patients with hepatic impairment increases flibanserin concentrations, which can cause severe hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] . Therefore, ADDYI is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4) ] .
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
Indications and Usage (1) | 12/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ADDYI is indicated for the treatment of women less than 65 years of age with acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) as characterized by low sexual desire that causes marked distress or interpersonal difficulty and is not due to:
- A co-existing medical or psychiatric condition,
- Problems within the relationship, or
- The effects of a medication or other drug substance.
Acquired HSDD refers to HSDD that develops in a patient who previously had no problems with sexual desire. Generalized HSDD refers to HSDD that occurs regardless of the type of stimulation, situation or partner.
Limitations of Use
- ADDYI is not indicated in men.
- ADDYI is not indicated to enhance sexual performance.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dosage is 100 mg taken once daily at bedtime (2.1)
- ADDYI is dosed at bedtime because administration during waking hours increases risks of hypotension, syncope, accidental injury, and central nervous system (CNS) depression (2.1)
- Discontinue ADDYI treatment after 8 weeks if no improvement (2.3)
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ADDYI is 100 mg administered orally once per day at bedtime. ADDYI is dosed at bedtime because administration during waking hours increases the risks of hypotension, syncope, accidental injury, and central nervous system (CNS) depression (such as somnolence and sedation) .
Missed Dose
If a dose of ADDYI is missed at bedtime, instruct the patient to take the next dose at bedtime on the next day. Instruct the patient to not double the next dose.
Discontinuation of ADDYI
Discontinue ADDYI after 8 weeks if the patient does not report an improvement in her HSDD symptoms.
Initiation of ADDYI Following Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor Use
If initiating ADDYI following moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor use, start ADDYI 2 weeks after the last dose of the CYP3A4 inhibitor.
If initiating a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor following ADDYI use, start the moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor 2 days after the last dose of ADDYI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 100 mg, oval, pink, debossed on one side with "f100" and blank on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary There are no studies of ADDYI in pregnant women to inform whether there is a drug-associated risk in humans. In animals, fetal toxicity only occurred in the presence of significant maternal toxicity including reductions in weight gain and sedation. In pregnant rats and rabbits, adverse reproductive and developmental effects consisted of decreased fetal weight, structural anomalies and increases in fetal loss at exposures greater than 15 times exposures achieved with the recommended human dosage [see Data ] . Animal studies cannot rule out the potential for fetal harm.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data Animal Data Pregnant rats were administered flibanserin at doses of 0, 20, 80 and 400 mg/kg/day (3, 15 and 41 times clinical exposures at the recommended human dose based on AUC) during organogenesis. The highest dose was associated with significant maternal toxicity as evidenced by severe clinical signs and marked reductions in weight gain during dosing. In the litters of high-dose dams, there were decreased fetal weights, decreased ossification of the forelimbs and increased number of lumbar ribs, and two fetuses with anophthalmia secondary to severe maternal toxicity. The no adverse effect level for embryofetal toxicity was 80 mg/kg/day (15 times clinical exposure based on AUC).
Pregnant rabbits were administered flibanserin at doses of 0, 20, 40 and 80 mg/kg/day (4, 8 and 16 times the clinical exposure at the recommended human dose) during organogenesis. Marked decreases in maternal body weight gain (>75%), abortion and complete litter resorption were observed at 40 and 80 mg/kg/day indicating significant maternal toxicity at these doses. Increases in resorptions and decreased fetal weights were observed at ≥ 40 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related teratogenic effects were observed in fetuses at any dose level. The no adverse effect level for maternal and embryofetal effects was 20 mg/kg/day (3-4 times clinical exposure based on AUC).
Pregnant rats were administered flibanserin at doses of 0, 20, 80 and 200 mg/kg/day (3, 15 and ~ 20 times clinical exposures at the recommended human dose) from day 6 of pregnancy until day 21 of lactation to assess for effects on peri- and postnatal development. The highest dose was associated with clinical signs of toxicity in pregnant and lactating rats. All doses resulted in sedation and decreases in body weight gain during pregnancy. Flibanserin prolonged gestation in some dams in all dose groups and decreased implantations, number of fetuses and fetal weights at 200 mg/kg/day. Dosing dams with 200 mg/kg also decreased pup weight gain and viability during the lactation period and delayed opening of the vagina and auditory canals. Flibanserin had no effects on learning, reflexes, fertility or reproductive capacity of the F1 generation. The no adverse effect level for maternal toxicity and peri/postnatal effects was 20 mg/kg/day [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ].
Lactation
Risk Summary Flibanserin is excreted in rat milk. It is unknown whether flibanserin is present in human milk, whether ADDYI has effects on the breastfed infant, or whether ADDYI affects milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions including sedation in a breastfed infant, ADDYI is not recommended in breastfeeding women.
Pediatric Use
ADDYI is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
ADDYI is not indicated for the treatment of HSDD in geriatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 . 5.2 , and 5.4 )] . Safety and effectiveness of ADDYI for the treatment of HSDD have not been established in geriatric patients.
Hepatic Impairment
ADDYI is contraindicated for use in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment. Flibanserin exposure increased 4.5-fold in patients with hepatic impairment, compared to those with normal hepatic function, increasing the risk of hypotension, syncope, and CNS depression [see Boxed Warning , Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.5) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizers
CYP2C19 poor metabolizers had increased flibanserin exposures compared to CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers. Additionally, syncope occurred in a subject who was a CYP2C19 poor metabolizer [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.5) ]. Therefore, increase monitoring for adverse reactions (e.g., hypotension) in patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers. The frequencies of poor CYP2C19 metabolizers are approximately 2–5% among Caucasians and Africans and approximately 2–15% among Asians.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADDYI is contraindicated in patients:
- Using concomitant moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- With hepatic impairment [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
- With known hypersensitivity to ADDYI or any of its components. Reactions, including anaphylaxis, reactions consistent with angioedema (e.g., swelling of the face, lips, and mouth), pruritus, and urticaria have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypotension and Syncope due to an Interaction with Alcohol : After taking ADDYI at bedtime, advise patients to avoid alcohol until the following day. (5.1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Depression (e.g., Somnolence, Sedation) : Can occur with ADDYI alone. Exacerbated by other CNS depressants, and in settings where flibanserin concentrations are increased. Patients should avoid activities requiring full alertness (e.g., driving or operating machinery) until at least six hours after each dose and until they know how ADDYI affects them. (5.3)
- Hypotension and Syncope with ADDYI Alone : Patients with pre-syncope should immediately lie supine and promptly seek medical help if symptoms do not resolve. (5.4)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, pruritus, urticaria : Avoid in women with known hypersensitivity to ADDYI or any of its components (5.6 )
Hypotension and Syncope due to an Interaction with Alcohol
Taking ADDYI within two hours after consuming alcohol increases the risk of severe hypotension and syncope. To reduce this risk, counsel patients to wait at least two hours after drinking one or two standard alcoholic drinks before taking ADDYI at bedtime [see Boxed Warning and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Patients who drink three or more standard alcoholic drinks should skip their ADDYI dose that evening. One standard alcoholic drink contains 14 grams of pure alcohol and is equivalent to one 12-ounce regular beer (5% alcohol), 5-ounces wine (12% alcohol), or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits/shot (40% alcohol).
After taking ADDYI at bedtime, advise patients to not use alcohol until the following day.
Hypotension and Syncope with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
The concomitant use of ADDYI with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors significantly increases flibanserin concentrations, which can lead to hypotension and syncope [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. The concomitant use of ADDYI with a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is contraindicated. If the patient requires a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, discontinue ADDYI at least 2 days prior to starting the moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. In cases where the benefit of initiating a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor within 2 days of stopping ADDYI clearly outweighs the risk of flibanserin exposure related hypotension and syncope, monitor the patient for signs of hypotension and syncope. Discontinue the moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor for 2 weeks before restarting ADDYI [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Multiple Concomitant Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors Concomitant use of multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors that may include herbal supplements (e.g., ginkgo, resveratrol) or non-prescription drugs (e.g., cimetidine) could also lead to clinically relevant increases in flibanserin concentrations that may increase the risk of hypotension and syncope [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Central Nervous System Depression
ADDYI can cause CNS depression (e.g., somnolence, sedation). In five 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials of premenopausal women with HSDD, the incidence of somnolence, sedation or fatigue was 21% and 8% in patients treated with 100 mg ADDYI once daily at bedtime and placebo, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . In two similarly designed trials in naturally postmenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD, the incidence of somnolence, sedation or fatigue was 10% and 6% in patients less than 65 years of age treated with 100 mg ADDYI once daily at bedtime and placebo, respectively. The risk of CNS depression is increased if ADDYI is taken during waking hours, or if ADDYI is taken with alcohol or other CNS depressants, or with medications that increase flibanserin concentrations, such as CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Drug Interactions (7) ].
Patients should avoid activities requiring full alertness (e.g., driving or operating machinery) until at least 6 hours after taking ADDYI and until they know how ADDYI affects them [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
Hypotension and Syncope with ADDYI Alone
The use of ADDYI − without other concomitant medications known to cause hypotension or syncope − can cause hypotension and syncope. In five 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials of premenopausal women with HSDD, hypotension was reported in 0.2% and <0.1% of ADDYI-treated patients and placebo-treated patients, respectively; syncope was reported in 0.4% and 0.2% of ADDYI‑treated patients and placebo-treated patients, respectively. In two similarly designed trials in naturally postmenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD, there was no difference in the incidence of hypotension between ADDYI-treated patients and placebo-treated patients. One case of syncope was reported in the ADDYI treatment group.
The risk of hypotension and syncope is increased if ADDYI is taken during waking hours or if higher than the recommended dose is taken [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Drug Interactions (7) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ].
Consider the benefits of ADDYI and the risks of hypotension and syncope in patients with pre-existing conditions that predispose to hypotension. Patients who experience pre-syncope should immediately lie supine and promptly seek medical help if the symptoms do not resolve. Prompt medical attention should also be obtained for patients who experience syncope.
Syncope and Hypotension in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The use of ADDYI in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment significantly increases flibanserin concentrations, which can lead to hypotension and syncope. Therefore, the use of ADDYI is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, reactions consistent with angioedema (e.g., swelling of the face, lips, and mouth), pruritus, and urticaria have been reported with ADDYI. ADDYI is contraindicated in women with known hypersensitivity to ADDYI or any of its components [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . Immediately discontinue ADDYI and initiate appropriate treatment if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
Mammary Tumors in Female Mice
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in mice, there was a statistically significant and dose-related increase in the incidence of malignant mammary tumors in female mice at flibanserin exposures 3 and 10 times the recommended clinical dose of ADDYI. No such increases were seen in male mice or in male or female rats [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)] . The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.5) ]
- CNS depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The approved 100 mg ADDYI dosage at bedtime was administered to 2,997 premenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD in clinical trials, of whom 1,672 received treatment for at least 6 months, 850 received treatment for at least 12 months, and 88 received treatment for at least 18 months [see Clinical Studies (14) ].
In clinical trials, ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime was administered to 801 postmenopausal women less than 65 years of age with acquired, generalized HSDD, of whom 460 received ADDYI treatment for at least 6 months, and 23 received ADDYI treatment for longer than 6 months.
Premenopausal Women
The data presented below in Table 1 and Table 2 (left columns) are derived from five 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in premenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD. In these trials, the frequency and quantity of alcohol use was not recorded. Three of these trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) also provided efficacy data [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. One trial (Study 5) did not evaluate the 100 mg bedtime dose.
In four trials in premenopausal women (Studies 1 through 4), 100 mg ADDYI at bedtime was administered to 1543 premenopausal women with HSDD, of whom 1060 completed 24 weeks of treatment. The age range of women enrolled was 18-56 years old with a mean age of 36 years old, and 88% were Caucasian and 9% were Black.
In Studies 1 through 4 in premenopausal women, serious adverse reactions were reported in 0.9% and 0.5% of ADDYI-treated patients and placebo-treated patients, respectively.
Postmenopausal Women
The data presented below in Table 1 and Table 2 (right columns) are derived from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials intended to be of 24-week duration in naturally postmenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD (Studies 6 and 7). One trial (Study 7) was discontinued prematurely. In these trials, 100 mg ADDYI at bedtime was administered to 801 postmenopausal women less than 65 years of age with HSDD, of whom 460 completed 24 weeks of treatment. The age range of women enrolled was 34-80 years old with a mean age of 56 years old, and 91% were Caucasian, 7% were Black and 94% were less than 65 years of age. The clinical trial population had no significant comorbid medical conditions and were not taking concomitant medications. Serious adverse reactions were reported in 1.5% and 0.7% of ADDYI-treated patients and placebo-treated patients less than 65 years of age, respectively.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation Table 1 displays the most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in six trials of women less than 65 years of age with HSDD that evaluated the ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime dosage by population studied.
Adverse Reaction | Trials in Premenopausal Women Includes Studies 1-4 | Trials in Postmenopausal Women Includes Studies 6 and 7 | ||
Placebo (N=1556) | ADDYI (N=1543) | Placebo (N=797) | ADDYI (N=801) | |
Overall | 6% | 13% | 5% | 9% |
Dizziness | 0.1% | 1.7% | 0.3% | 0.9% |
Nausea | 0.1% | 1.2% | 0.3% | 0.5% |
Insomnia | 0.2% | 1.1% | 0.5% | 1.4% |
Somnolence | 0.3% | 1.1% | 0.1% | 0.6% |
Anxiety | 0.3% | 1% | 0.6% | 1.2% |
Most Common Adverse Reactions Table 2 summarizes the most common adverse reactions reported in six trials of women less than 65 years of age with HSDD. This table shows adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients treated with ADDYI and at a higher incidence than with placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]. The majority of these adverse reactions began within the first 14 days of treatment.
Trials in Premenopausal Women | Trials in Postmenopausal Women | |||
Adverse Reaction | Placebo (N=1556) | ADDYI (N=1543) | Placebo (N=797) | ADDYI (N=801) |
Dizziness | 2.2% | 11.4% | 3.3% | 7.9% |
Somnolence | 2.9% | 11.2% | 1.8% | 7.7% |
Nausea | 3.9% | 10.4% | 3.9% | 6.6% |
Fatigue | 5.5% | 9.2% | 3.9% | 3.0% |
Insomnia | 2.8% | 4.9% | 3.4% | 5.7% |
Dry mouth | 1.0% | 2.4% | 1.3% | 2.4% |
Urinary tract infection | 2.4% | 2.3% | 3.0% | 3.2% |
Anxiety | 1.0% | 1.8% | 1.6% | 2.6% |
Sinusitis | 3.5% | 2.9% | 2.1% | 2.5% |
Constipation | 0.4% | 1.6% | 1.8% | 2.5% |
Less Common Adverse Reactions In six trials in women less than 65 years of age with HSDD treated with ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime, less common adverse reactions (reported in ≥1% but <2% of ADDYI-treated patients and at a higher incidence than with placebo) in the premenopausal population included: abdominal pain, metrorrhagia, rash, sedation, vertigo. In the postmenopausal population, less common adverse reactions included: sleep disorder, bronchitis, edema peripheral, cough, vertigo, palpitations, rash, abnormal dreams.
Appendicitis In the five trials of premenopausal women with HSDD, appendicitis was reported in 6/3973 (0.2%) flibanserin-treated patients, while there were no reports of appendicitis in the 1905 placebo-treated patients. Appendicitis was not reported in trials of postmenopausal women.
Accidental Injury In five trials of premenopausal women with HSDD, accidental injury was reported in 42/1543 (2.7%) ADDYI-treated patients and 47/1905 (2.5%) placebo-treated patients. Among these 89 patients who experienced injuries, 9/42 (21%) ADDYI-treated patients and 3/47 (6%) placebo-treated patients reported adverse reactions consistent with CNS depression (e.g., somnolence, fatigue, or sedation) within the preceding day. In two trials of postmenopausal women less than 65 years of age with HSDD, accidental injury was reported in 33/801 (4.1%) ADDYI-treated patients and 28/797 (3.5%) placebo-treated patients. Among these 61 patients who experienced injuries, 1/33 (3.0%) ADDYI-treated patients and 3/28 (10.7%) placebo-treated patients reported adverse reactions consistent with CNS depression (e.g., somnolence, fatigue, or sedation) the preceding day.
Adverse Reactions in Patients Who Reported Hormonal Contraceptive Use In four trials of premenopausal women with HSDD, 1466 patients (43%) reported concomitant use of hormonal contraceptives (HC) at study enrollment. These trials were not prospectively designed to assess an interaction between ADDYI and HC. ADDYI-treated patients who reported HC use had a greater incidence of dizziness, somnolence, and fatigue compared to ADDYI-treated patients who did not report HC use (dizziness 9.9% in HC non-users, 13.4% in HC users; somnolence 10.6% in HC non-users, 12.3% in HC users; fatigue 7.5% in HC non-users, 11.4% in HC users). There were no meaningful differences in the incidence of these adverse reactions in placebo-treated patients who reported or did not report HC use [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Data from Other Trials One death occurred in a 54 year-old postmenopausal woman treated with 100 mg ADDYI taken at bedtime. This patient had a history of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia and baseline alcohol consumption of 1-3 drinks daily. She died of acute alcohol intoxication 14 days after starting ADDYI. Blood alcohol concentration on autopsy was 0.289 g/dL. The autopsy report also noted coronary artery disease. A relationship between this patient’s death and use of ADDYI is unknown [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Hypotension, Syncope, and CNS Depression in Studies of Healthy Subjects
Hypotension, Syncope, and CNS Depression with Alcohol
Alcohol and ADDYI Administration at the Same Time The first alcohol interaction study was conducted in 25 healthy subjects (23 men and 2 premenopausal women). The study excluded subjects who drank fewer than five alcoholic drinks per week and those with a history of orthostatic hypotension, or syncope. A single dose of 100 mg ADDYI was administered concurrently with 0.4 g/kg or 0.8 g/kg alcohol in the morning; alcohol was consumed over 10 minutes. Hypotension or syncope requiring therapeutic intervention (ammonia salts and/or placement in supine or Trendelenburg position) occurred in 4 (17%) of the 23 subjects co-administered 100 mg ADDYI and 0.4 g/kg alcohol (equivalent to two 12 ounce cans of beer containing 5% alcohol content, two 5 ounce glasses of wine containing 12% alcohol content, or two 1.5 ounce shots of 80-proof spirit in a 70 kg person). In these four subjects, all of whom were men, the magnitude of the systolic blood pressure reductions ranged from 28 to 54 mmHg and the magnitude of the diastolic blood pressure reductions ranged from 24 to 46 mmHg. In addition, 6 (25%) of the 24 subjects co-administered 100 mg ADDYI and 0.8 g/kg alcohol (equivalent to four 12 ounce cans of beer containing 5% alcohol content, four 5 ounce glasses of wine containing 12% alcohol content, or four 1.5 ounce shots of 80-proof spirit in a 70 kg person) experienced orthostatic hypotension when standing from a sitting position. The magnitude of the systolic blood pressure reduction in these 6 subjects ranged from 22 to 48 mmHg, and the diastolic blood pressure reductions ranged from 0 to 27 mmHg. One of these subjects required therapeutic intervention (ammonia salts and placement supine with the foot of the bed elevated). There were no events requiring therapeutic interventions when ADDYI or alcohol were administered alone.
In this study, somnolence was reported in 67%, 74%, and 92% of subjects who received ADDYI alone, ADDYI in combination with 0.4 g/kg alcohol, and ADDYI in combination with 0.8 g/kg alcohol, respectively. [ see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3 and 5.4) ].
In the second alcohol interaction study, 96 healthy premenopausal women received a single dose of 100 mg ADDYI concurrently with 0.2 g/kg, 0.4 g/kg, or 0.6 g/kg alcohol (equivalent to one, two or three alcoholic drinks in a 70 kg person, respectively) in the morning. The study excluded subjects with a history of syncope, orthostatic hypotension, hypotensive events, and dizziness, and those with a resting systolic blood pressure less than 110 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure less than 60 mmHg.
In this study, no subjects experienced syncope or hypotension requiring therapeutic intervention. However, subjects who were already hypotensive (blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg) or symptomatic (e.g., dizzy) while in the semi-recumbent position were not permitted to stand for orthostatic measurements, and those with blood pressures below 90/40 mmHg while in the semi-recumbent position had blood pressures repeated until it was deemed safe for them to change position. More subjects had missing or delayed orthostatic measurements (in general, due to hypotension or dizziness) when receiving ADDYI and alcohol, compared to those who received alcohol alone or ADDYI alone. This pattern of missing or delayed orthostatic measurements is concerning for a risk of hypotension and syncope if those subjects had been allowed to stand.
In this study, somnolence was reported in 81-89% of subjects administered ADDYI with alcohol, compared to 25-41% of subjects administered alcohol alone and 84% of subjects taking ADDYI alone. Dizziness was reported in 27-40% of subjects administered ADDYI with alcohol, compared to 6-20% of subjects administered alcohol alone and 31% of subjects taking ADDYI alone. [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.3 , 5.4) ].
Alcohol Use at Various Time Intervals Before ADDYI Administration In a third alcohol interaction study, 64 healthy premenopausal women consumed 0.4 g/kg alcohol (equivalent to 2 alcoholic drinks in a 70 kg person) two, four or six hours prior to receiving ADDYI 100 mg or placebo in the afternoon. The study excluded subjects with a history or presence of orthostatic hypotension, history of hypotension, syncope, or dizziness. Prior to receiving alcohol, the subjects in the ADDYI arm had taken ADDYI for three days to achieve steady state. Syncope occurred in one subject who received alcohol alone. The incidences of orthostatic hypotension and hypotension (blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg) at all time points were similar among subjects administered alcohol before ADDYI, subjects administered alcohol alone, and subjects administered ADDYI alone. Three subjects were unable to stand due to feeling dizzy or hypotension; two following alcohol and ADDYI separated by 2 and 6 hours, and one subject who received ADDYI alone.
In this study, somnolence was reported in 35-53% of subjects administered ADDYI and alcohol, compared to 5-8% of subjects taking alcohol alone and 50% of subjects taking ADDYI alone. Dizziness was reported in 5-13% of subjects administered ADDYI and alcohol, compared to 0-3% of subjects taking alcohol alone and 12% of subjects taking ADDYI alone.
Alcohol Use in the Evening Before Bedtime ADDYI Administration In another alcohol interaction study, 24 premenopausal women consumed 0.4 g/kg alcohol (equivalent to 2 alcoholic drinks in a 70 kg person) during the evening meal two and a half to four hours prior to taking ADDYI 100 mg at bedtime. There were no cases of syncope. Upon rising the following morning, the incidence of hypotension was 23% among subjects administered ADDYI after alcohol, 23% among subjects administered alcohol alone and 36% with ADDYI alone. No cases of somnolence or dizziness were reported in this study. Conclusions are limited because blood pressure and orthostatic measurements were not taken after ADDYI administration until the following morning.
Dedicated alcohol-interaction studies were not conducted in postmenopausal women.
Hypotension and Syncope with Fluconazole In a pharmacokinetic drug interaction study of 100 mg ADDYI and 200 mg fluconazole (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, moderate CYP2C9 inhibitor, and a strong CYP2C19 inhibitor) in healthy subjects, hypotension or syncope requiring placement supine with legs elevated occurred in 3/15 (20%) subjects treated with concomitant ADDYI and fluconazole compared to no such adverse reactions in subjects treated with ADDYI alone or fluconazole alone. One of these 3 subjects became unresponsive with a blood pressure of 64/41 mm Hg and required transportation to the hospital emergency department where she required intravenous saline. Due to these adverse reactions, the study was stopped. In this study, the concomitant use of ADDYI and fluconazole increased flibanserin exposure 7-fold [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Syncope with Ketoconazole In a pharmacokinetic drug interaction study of 50 mg flibanserin and 400 mg ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, syncope occurred in 1/24 (4%) healthy subjects treated with concomitant flibanserin and ketoconazole, 1/24 (4%) receiving flibanserin alone, and no subjects receiving ketoconazole alone. In this study, the concomitant use of flibanserin and ketoconazole increased flibanserin exposure 4.5-fold [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Syncope in Poor CYP2C19 Metabolizers In a pharmacogenomic study of 100 mg ADDYI in subjects who were poor or extensive CYP2C19 metabolizers, syncope occurred in 1/9 (11%) subjects who were CYP2C19 poor metabolizers (this subject had a 3.2 fold higher flibanserin exposure compared to CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers) compared to no such adverse reactions in subjects who were CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers [see Drug Interactions (7) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.5) ].
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ADDYI. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, reactions consistent with angioedema (e.g., swelling of the face, lips, and mouth), pruritus, and urticaria.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting
- General disorders and administration site conditions: asthenia, feeling abnormal, feeling drunk, malaise
- Nervous system disorders: headache, presyncope, gait disturbance, vision blurred
- Psychiatric disorders: brain fog
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 3 contains clinically significant drug interactions (DI) with ADDYI.
Alcohol | |
Clinical Implications | The coadministration of ADDYI with alcohol increased the risk of hypotension, syncope, and CNS depression compared to the use of ADDYI alone or alcohol alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ]. |
Preventing or Managing DI | Counsel patients to wait at least two hours after consuming one or two standard alcoholic drinks before taking ADDYI at bedtime or to skip their ADDYI dose if they have consumed three or more alcoholic drinks that evening. [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . |
Other CNS Depressants | |
Examples | Diphenhydramine, opioids, hypnotics, benzodiazepines |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with CNS depressants may increase the risk of CNS depression (e.g., somnolence) compared to the use of ADDYI alone. |
Preventing or Managing DI | Discuss the concomitant use of other CNS depressants with the patient when prescribing ADDYI. |
Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
Examples of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors | Ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, clarithromycin, nefazodone, ritonavir, saquinavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, boceprevir, telaprevir, telithromycin and conivaptan |
Examples of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors | Amprenavir, atazanavir, ciprofloxacin, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, fosamprenavir, verapamil, and grapefruit juice |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increases flibanserin exposure compared to the use of ADDYI alone. The risk of hypotension and syncope is increased with concomitant use of ADDYI and moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. |
Preventing or Managing DI | The concomitant use of ADDYI with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated . |
Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
Examples | Oral contraceptives, cimetidine, fluoxetine, ginkgo, ranitidine |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase the risk of adverse reactions. |
Preventing or Managing DI | Discuss the use of multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors with the patient when prescribing ADDYI. |
Strong CYP2C19 Inhibitors | |
Examples | Proton pump inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, benzodiazepines, antifungals |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with strong CYP2C19 inhibitors may increase flibanserin exposure which may increase the risk of hypotension, syncope, and CNS depression. |
Preventing or Managing DI | Discuss the use of a strong CYP2C19 inhibitor with the patient when prescribing ADDYI. |
CYP3A4 Inducers | |
Examples | Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapetine, St. John's Wort |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with CYP3A4 inducers substantially decreases flibanserin exposure compared to the use of ADDYI alone. |
Preventing or Managing DI | The concomitant use of ADDYI with CYP3A4 inducers is not recommended. |
Digoxin or Other P-glycoprotein Substrates | |
Examples | Digoxin, sirolimus |
Clinical Implications | The concomitant use of ADDYI with digoxin, a drug that is transported by P-glycoprotein (P-gp), increases the digoxin concentration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . This may lead to digoxin toxicity. |
Preventing or Managing DI | Increase monitoring of concentrations of drugs transported by P-gp that have a narrow therapeutic index (e.g., digoxin). |
DESCRIPTION
The chemical name of flibanserin is 2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-1-[2-[4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]. Its empirical formula is C 20 H 21 F 3 N 4 O and its molecular weight is 390.41.
The structural formula is:

Flibanserin is a white to off-white powder, insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetonitrile and toluene, soluble in acetone, freely soluble in chloroform, and very soluble in methylene chloride.
ADDYI (flibanserin) tablets are for oral administration. Each ADDYI tablet contains 100 mg of flibanserin. Inactive ingredients consist of lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, talc, macrogol, and the coloring agents, titanium dioxide and iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ADDYI in the treatment of women less than 65 years of age with acquired, generalized HSDD as characterized by low sexual desire that causes marked distress or interpersonal difficulty (not due a co-existing medical or psychiatric condition, problems within the relationship, or the effects of a medication or other drug substance) is not known.
Pharmacodynamics
Receptor Binding: In vitro, flibanserin demonstrated high affinity for the following serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) receptors: agonist activity at 5-HT 1A and antagonist activity at 5-HT 2A . Flibanserin also has moderate antagonist activities at the 5-HT 2B , 5-HT 2C , and dopamine D 4 receptors.
Alcohol Interaction See Clinical Trials Experience (6.1)
Cardiac Electrophysiology The effect of ADDYI on the QT interval was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active- (single dose moxifloxacin) controlled crossover study in 56 healthy men and women. Subjects in the ADDYI groups received either 50 mg twice a day (equivalent to the daily recommended dosage) or 100 mg three times a day (3 times the daily recommended dosage) administered for 5 days. The time frame for electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements covered maximum plasma concentrations of flibanserin and relevant metabolites. In this study, ADDYI did not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent. The mean increase in heart rate associated with the 100 mg three times a day dose of ADDYI compared to placebo ranged from 1.7 to 3.2 beats per minute.
Pharmacokinetics
Flibanserin showed dose-proportional pharmacokinetics for Cmax after single oral doses of 100 mg to 250 mg (the recommended and 2.5 times the recommended dosage, respectively) in healthy female subjects. Steady state was achieved after 3 days of dosing. The extent of exposure (AUC 0-∞ ) with once-daily dosing of 100 mg of flibanserin was increased 1.4-fold as compared to a single dose.
Figure 1 Mean + SD Plasma Flibanserin Concentration-Time Profiles in Healthy Female Subjects Following a Single Oral Dose of 100 mg of Flibanserin (Linear Scale)
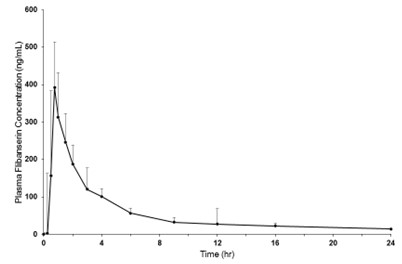
Absorption Following oral administration of a single 100 mg dose of flibanserin in healthy premenopausal women (N=8), mean (SD) Cmax was 419 (206) ng/mL and mean (SD) AUC 0-inf was 1543 (511) ng•hr/mL. Median (range) time to reach Cmax was 0.75 (0.75 to 4.0) hours. Absolute bioavailability of flibanserin following oral dosing is 33%.
Effect of Food Food increased the extent of absorption and slowed the rate of absorption of a 50 mg dose of flibanserin (one half the recommended dosage). Low-, moderate-, and high-fat meals increased flibanserin AUC 0-inf by 1.18-, 1.43-, and 1.56-fold; increased Cmax by 1.02-, 1.13-, and 1.15-fold; and prolonged median Tmax to 1.5, 0.9, 1.8 hours from 0.8 hours under fasted conditions, respectively.
Distribution Approximately 98% of flibanserin is bound to human serum proteins, mainly to albumin.
Elimination Metabolism Flibanserin is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP2C19. Based on in vitro and/or in vivo data, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2D6 contribute minimally to the metabolism of flibanserin. After a single oral solution dose of 50 mg 14 C-radiolabeled flibanserin, 44% of the total 14 C-flibanserin related radioactivity was recovered in urine, and 51% was recovered in feces. Flibanserin is extensively metabolized to at least 35 metabolites, most of them occurring in low concentrations in plasma. Two metabolites could be characterized that showed plasma concentrations similar to that achieved with flibanserin: 6,21-dihydroxy-flibanserin-6,21-disulfate and 6-hydroxy-flibanserin-6-sulfate. These two metabolites are inactive.
Excretion Flibanserin has a mean terminal half-life of approximately 11 hours.
Specific Populations Hepatic Impairment Single 50 mg oral doses of flibanserin were administered to 10 patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 6 points), 4 patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 8-9 points), and 14 healthy subjects matched by age, weight, and gender. Systemic flibanserin exposure (AUC 0-inf ) increased 4.5-fold in patients with mild hepatic impairment, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, and t 1/2 was longer (26 hours compared to 10 hours in matching healthy controls). Due to the small number of patients (n=4) with moderate hepatic impairment enrolled in the study, it is not possible to make conclusions about the quantitative effect of moderate hepatic impairment on flibanserin exposure. ADDYI is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Renal Impairment Single 50 mg oral doses of flibanserin were administered to 7 patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (GFR 30 to 80 mL/min), 9 patients with severe renal impairment (GFR <30 mL/min, not on dialysis), and 16 healthy subjects matched by age, weight, and gender. Flibanserin exposure (AUC 0-inf ) increased 1.1-fold in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment and 1.2-fold in patients with severe renal impairment, compared to the healthy control subjects.
Race/Ethnicity A cross-study comparison between healthy Japanese women and Caucasian women with HSDD showed that flibanserin exposure was approximately 1.4-fold higher in Japanese women. When the mean flibanserin exposure in Japanese women was adjusted for weight, the AUC tau,ss in Japanese women was 2246 ng•hr/mL, which is comparable to 2080 ng•hr/mL in Caucasian women. The similarity in weight-adjusted AUC tau,ss suggests that weight, not race, is the factor contributing to the observed difference in flibanserin exposure between Japanese and Caucasian women.
Age No formal study has been conducted to study the effect of age on flibanserin exposures.
Drug Interaction Studies
Drugs that Increase Flibanserin Exposure The effects of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics of flibanserin are presented in Table 4 as change relative to flibanserin administered alone (test/reference).
Moderate CYP3A4/Moderate CYP2C9/Strong CYP2C19 Inhibitor (Fluconazole) In a study of 15 healthy female subjects, a fluconazole 400 mg loading dose followed by 200 mg administered once daily for 5 days increased flibanserin 100 mg single dose exposure (AUC 0-inf ) 7-fold and Cmax 2.2-fold compared to flibanserin 100 mg alone. Three of 15 subjects (20%) experienced hypotension or syncope from concomitant use of fluconazole and flibanserin; therefore, the study was stopped early [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor (Ketoconazole) In a study of 24 healthy female subjects, ketoconazole 400 mg administered once daily for 5 days following a light breakfast increased flibanserin 50 mg single-dose exposure (AUC 0-inf ) 4.5-fold and Cmax 1.8-fold compared to flibanserin 50 mg alone [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor (Itraconazole) In a study of 12 healthy male and female subjects, itraconazole 200 mg administered once daily for 4 days following a loading dose of 400 mg increased flibanserin 50 mg single dose exposure (AUC 0-inf ) 2.6-fold and Cmax 1.7-fold when flibanserin was given 2 hours after itraconazole on Day 5, compared to exposures with flibanserin 50 mg alone. The 200 mg itraconazole dose does not maximally inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitor (Grapefruit Juice) In a study of 26 healthy female subjects, grapefruit juice (240 mL) increased flibanserin 100 mg single dose exposure (AUC 0-inf ) by 1.4-fold and Cmax 1.1-fold compared to flibanserin 100 mg alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitor (Oral Contraceptives) In a meta-analysis of 17 oral contraceptive users and 91 non-users in Phase 1 studies, the oral contraceptive users had a 1.4-fold higher flibanserin AUC and 1.3‑fold higher Cmax compared to the non-users [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitor (Paroxetine) Paroxetine is a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor. In a study of 19 healthy male and female subjects, flibanserin exposure decreased by approximately 4% when flibanserin 50 mg twice daily was given with paroxetine compared to flibanserin alone. Paroxetine was dosed at 20 mg once daily for 3 days followed by 40 mg once daily for 7 days.
Drugs that Decrease Flibanserin Exposure Strong CYP3A4 Inducer (Rifampin) In a study of 24 healthy female subjects, rifampin 600 mg given once daily for 7 days prior to administration of 100 mg flibanserin significantly decreased flibanserin exposure by 95% [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Moderate CYP3A4 Inducer (Etravirine) Steady state etravirine, a moderate CYP3A4 inducer, decreased flibanserin exposures by approximately 21% [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of ADDYI | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% Confidence Interval) of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Flibanserin with/without Coadministered Drug No Effect =1.00 | |
Cmax | AUC 0-inf | |||
Fluconazole 200 mg | 100 mg | 15 | 2.2 (1.8 – 2.8) | 7.0 (6.0 – 8.2) |
Ketoconazole 400 mg | 50 mg | 24 | 1.8 (1.7 – 2.1) | 4.5 (4.0 – 5.1) |
Itraconazole 200 mg itraconazole dose was not optimal for maximal inhibition of CYP3A4 enzyme. | 50 mg | 12 | 1.7 (1.4 – 2.0) | 2.6 (2.1 – 3.0) |
Oral Contraceptives | 50 mg | 39 | 1.3 (1.1 – 1.6) | 1.4 (1.2 – 1.7) |
Paroxetine 40 mg | 50 mg twice daily | 19 | 1.0 (0.9 – 1.2) | 1.0 (0.9 – 1.0) |
Effects of Flibanserin on Other Drugs The effects of flibanserin on the pharmacokinetics of other drugs are presented in Table 5 as change relative to the other drug administered alone (test/reference).
Digoxin and P-glycoprotein Substrates A single center, open-label, randomized, two-way crossover study in 24 healthy men and women evaluated the effect of flibanserin on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Flibanserin 100 mg was administered once daily over 5 days followed by a single dose of 0.5 mg digoxin, a P-gp substrate. Flibanserin increased digoxin AUC 0-inf by 2.0-fold and Cmax by 1.5-fold, compared to digoxin alone [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4 (Simvastatin) An open-label, randomized, crossover study in 12 healthy men and women evaluated the effect of flibanserin 50 mg twice daily for 4 days on the pharmacokinetics of simvastatin 40 mg once daily. Flibanserin increased the AUC 0-inf of simvastatin, a substrate of CYP3A4, 1.3‑fold and Cmax by 1.2-fold. Flibanserin co-administered with simvastatin increased simvastatin acid AUC 0-inf by 1.5-fold and Cmax by 1.4-fold.
Oral Contraceptives A study in 24 healthy women evaluated the effect of 100 mg flibanserin once daily for 2 weeks on the pharmacokinetics of a single-dose of ethinyl estradiol (EE) 30 mcg/levonorgestrel (LNG) 150 mcg. Flibanserin increased the EE AUC 0-inf by 1.09-fold and the EE Cmax by 1.1-fold. Flibanserin decreased the LNG AUC 0-inf by 1.06-fold and did not change the LNG Cmax. [see Adverse Events (6.1), Drug Interactions (7) ].
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2B6 (Bupropion) An open-label, randomized, two-period crossover study in 28 healthy women evaluated the effect of flibanserin on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion. Flibanserin 50 mg twice daily was administered for 2 days followed by 100 mg once daily for 13 days. Bupropion 150 mg twice daily was given for 8 days beginning on Day 6 of flibanserin treatment. Flibanserin did not change bupropion AUC t,ss (1.0-fold change) and Cmax (1.0-fold change) but hydroxybupropion AUC t,ss decreased by 9% and Cmax by 11%.
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of ADDYI | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% Confidence Interval) of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered Drug with/without Flibanserin No Effect =1.00 | |
Cmax | AUC 0-inf | |||
Simvastatin 40 mg | 50 mg twice daily | 12 | 1.7 (1.4 – 2.0) | 2.6 (2.1 – 3.1) |
Digoxin 0.5 mg | 100 mg | 24 | 1.5 (1.3 – 1.6) | 2.0 (1.5 – 2.5) |
Ethinyl estradiol 30 mcg/ Levonorgestrel 150 mcg | 100 mg | 24 | 1.1 (1.0 – 1.1) 1.0 (0.9 – 1.0) | 1.1 (1.0 – 1.2) 1.0 (0.9 – 1.1) |
Bupropion 150 mg | 100 mg | 28 | 1.0 (0.9 – 1.1) | 1.0 (1.0 – 1.1) |
Pharmacogenomics
Patients who are poor metabolizers of CYP2D6, CYP2C9 or CYP2C19 are deficient in CYP2D6, CYP2C9 or CYP2C19 enzyme activity, respectively. Extensive metabolizers have normal functioning CYP enzymes.
CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizers A study comparing flibanserin exposure in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers to CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers was conducted in lieu of a drug interaction study with ADDYI and a strong CYP2C19 inhibitor. In 9 women who were poor metabolizers of CYP2C19, Cmax and AUC 0-inf of flibanserin 100 mg once daily increased 1.5-fold (1.1-2.1) and 1.3-fold (0.9-2.1), compared to exposures among 8 extensive metabolizers of CYP2C19. Flibanserin half-life was increased from 11.1 hours in the extensive metabolizers of CYP2C19 to 13.5 hours in the poor metabolizers of CYP2C19 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
The frequencies of poor metabolizers of CYP2C19 are approximately 2–5% among Caucasians and Africans and approximately 2–15% among Asians.
CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers A study comparing flibanserin exposure in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers to CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers was conducted in addition to a drug interaction study with paroxetine, a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor. In 12 poor metabolizers of CYP2D6, steady state Cmax and AUC of flibanserin 50 mg twice daily was decreased by 4% and increased by 18%, respectively, compared to exposures among 19 extensive metabolizers, intermediate metabolizers and ultra rapid metabolizers of CYP2D6 .
CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizers A study comparing flibanserin exposure in CYP2C9 poor metabolizers to CYP2C9 extensive metabolizers was conducted in lieu of a drug interaction study with ADDYI and a strong CYP2C9 inhibitor. In 8 women who were poor metabolizers of CYP2C9, Cmax and AUC 0-inf of flibanserin 100 mg once daily decreased 23% and 18%, compared to exposures among 8 extensive metabolizers of CYP2C9 .
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in CD-1 mice with dietary administration of 0, 10, 80, 200 and 1000/1200 mg/kg/day of flibanserin. Statistically significant increases in combined mammary tumors (adenoacanthomas and adenocarcinomas) were observed in female mice administered flibanserin at doses of 200 and 1200 mg/kg/day (exposures, based on AUC, were 3 and 10 times the clinical exposures at the recommended clinical dose). No increases in mammary tumors were observed in male mice. Statistically significant increases were also seen for combined hepatocellular adenomas/carcinomas in female mice treated with flibanserin 1200 mg/kg/day and for hepatocellular carcinomas in male mice treated with flibanserin 1000 mg/kg/day (exposures, based on AUC, were 8 times the clinical exposure at the recommended clinical dose).
There were no significant increases in tumor incidence in a two year carcinogenicity study conducted in Wistar rats with dietary administration of 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg/day flibanserin (up to 5-8 times human exposure at the recommended clinical dose).
Mutagenesis Flibanserin was negative for mutagenesis in vitro in Salmonella typhimurium (Ames test) and in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Flibanserin was positive for chromosomal aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes but negative for chromosomal aberrations in vivo in the rat bone marrow micronucleus assay and negative for DNA damage in rat liver in the Comet assay.
Impairment of Fertility Female and male rats were administered flibanserin 14 and 28 days before mating, respectively, to assess for potential effects on fertility and early reproductive performance. Flibanserin slightly increased the duration of the estrus cycle but had no adverse effects on fertility or early embryonic development at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (~20 times human exposure at the recommended clinical dose).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Trials in Premenopausal Patients with HSDD
The efficacy of ADDYI for the treatment of acquired, generalized HSDD in premenopausal women [ see Indications and Usage (1) ] was established in three 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Study 1, NCT00360529; Study 2, NCT00360555; and Study 3, NCT00996164). The clinical trials enrolled premenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD of at least 6 months duration as evidenced by low sexual desire that caused marked distress or interpersonal difficulty and was not due to: a co-existing medical or psychiatric condition, problems with the relationship, or the effects of a medication or other drug substance. Acquired HSDD was defined as HSDD that developed in patients who previously had no problems with sexual desire. Generalized HSDD was defined as HSDD that was not limited to certain types of stimulation, situations or partners.
The patients were treated with ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime (n = 1187) or placebo (n = 1188). Most of the trial participants were Caucasian (88.6%); the remainder were Black (9.6%) and Asian (1.5%). The mean age of study participants was 36 years old (range 19 to 55 years old); the mean duration in the monogamous, heterosexual relationship was 11 years, and the mean duration of HSDD was approximately 5 years. The completion rate across these three trials was 69% and 78% for the ADDYI and placebo groups, respectively.
These trials each had two co-primary efficacy endpoints, one for satisfying sexual events (SSEs) and the other for sexual desire:
- The change from baseline to Week 24 in the number of monthly SSEs (i.e., sexual intercourse, oral sex, masturbation, or genital stimulation by the partner). The SSEs were based on patient responses to the following questions: “Did you have a sexual event?” and “Was the sex satisfying for you?”
- Studies 1 and 2 had a different sexual desire endpoint than Studies 3:
- In Studies 1 and 2, the sexual desire co-primary endpoint was the change from baseline to Week 24 in the calculated monthly sexual desire score and was based on patient responses to the question: “Indicate your most intense level of sexual desire.” Every day, patients rated their sexual desire level from 0 (no desire) to 3 (strong desire) and recorded their response in an electronic Diary (eDiary). These responses were summed over a 28-day period to yield the calculated monthly sexual desire score, which ranged from 0 to 84.
- In Study 3, the desire domain of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI Desire) was the sexual desire co-primary endpoint. The desire domain of the FSFI has two questions. The first question asks patients “Over the past 4 weeks, how often did you feel sexual desire or interest?”, with responses ranging from 1 (almost never or never) to 5 (almost always or always). The second question asks patients “Over the past 4 weeks, how would you rate your level (degree) of sexual desire or interest?”, with responses ranging from 1 (very low or none at all) to 5 (very high). The FSFI Desire score was calculated by adding the patient’s responses to these two questions then multiplying that sum by 0.6. The FSFI Desire domain score ranged from 1.2 to 6.
The desire domain of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI Desire) was also used as a secondary endpoint in Studies 1 and 2.
The three trials had a secondary endpoint that measured bother (a component of distress) related to sexual desire using Question 13 of the Female Sexual Distress Scale-Revised (FSDS-R). This question asks “How often did you feel: Bothered by low sexual desire?” Patients assessed their sexual distress over a 7-day recall period and responded on a scale of 0 (never) to 4 (always).
The efficacy results from Studies 1, 2, and 3 are summarized in Table 6 . In the three trials, ADDYI resulted in statistically significant improvement compared to placebo in the change from baseline in monthly SSEs at Week 24. In Study 1 and 2, there were no statistically significant differences between ADDYI and placebo for the eDiary sexual desire endpoint (change in baseline to Week 24). In contrast, in Study 3 there was statistically significant improvement in the change from baseline to Week 24 in sexual desire (using the FSFI Desire Domain) with ADDYI compared to placebo. The FSFI Desire Domain findings were consistent across all three trials as were the findings for the secondary endpoint that assessed distress using Question 13 of the FSDS-R.
| Study 1 | Study 2 Excludes subjects from two study sites that had data integrity issues | Study 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADDYI | Placebo | ADDYI | Placebo | ADDYI | Placebo | |
| Full Analysis Set | n=280 | n=290 | n=365 | n=372 | n=532 | n=536 |
| CI = Confidence Interval; NS = not statistically significant; N/A = not applicable Shaded cells show the results for the co-primary efficacy endpoints for each trial. e-Diary desire was evaluated as a co-primary endpoint in Studies 1 and 2; FSFI desire was evaluated as a co-primary endpoint in Study 3. The efficacy results are based on the full analysis set comprised of all randomized patients who took at least one dose of study medication and had at least one on-treatment efficacy assessment. Missing values were imputed using last-observation-carried-forward. The unadjusted means are presented for the baseline values. For satisfying sexual events, p-values are based on the Wilcoxon rank sum test stratified by pooled center. Median change from baseline is shown because the data are not normally distributed. For FSFI-desire, e-Diary desire, and FSDS-R Question 13, reported p-values are based on an ANCOVA model using baseline as a covariate with treatment and pooled center as main effect terms. For the change from baseline, the adjusted least squares mean (standard error) are presented. | ||||||
Number of satisfying sexual events (per 28 days) | ||||||
Baseline (Mean) | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
Change from baseline (Mean) | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
Treatment diff. (95% CI) | 0.9 (0.3, 1.4) | 0.0 | 0.6 (-0.03, 1.2) | 0.5 | 1.0 (0.4, 1.5) | 0.5 |
Change from baseline (Median) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
Median treatment difference | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |||
p-value vs placebo | p<0.01 | p<0.01 | p<0.0001 | |||
e-Diary Desire | ||||||
Baseline (Mean) | 12.9 | 11.8 | 12.1 | 10.2 | Not Used | Not Used |
Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) | 9.1 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 6.7 | ||
Treatment diff. (95% CI) | 2.3 (-0.1, 4.7) | 1.7 (-0.5, 4.0) | ||||
p-value vs placebo | NS | NS | ||||
FSFI Desire | ||||||
Baseline (Mean) | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
Treatment diff. (95% CI) | 0.4 (0.2, 0.5) | 0.3 (0.2, 0.5) | 0.3 (0.2, 0.4) | |||
p-value vs placebo | N/A p-value not reported for secondary endpoints because the trial failed on the eDiary Desire co-primary efficacy endpoint | N/A | p<0.0001 | |||
FSDS-R Question 13 A decrease in score represents improvement | ||||||
Baseline (Mean) | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.4 |
Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) | -0.8 | -0.5 | -0.8 | -0.5 | -1.0 | -0.7 |
Treatment diff. (95% CI) | -0.4 (-0.5, -0.2) | -0.3 (-0.4, -0.1) | -0.3 (-0.4, -0.1) | |||
p-value vs placebo | N/A | N/A | p=0.0001 | |||
Exploratory analyses were conducted to assess whether the treatment effects varied depending on baseline number of SSEs, FSFI desire score, and FSDS-R Question 13 distress score. No notable differences were identified among these subgroups.
Supportive analyses were conducted to help interpret the clinical meaningfulness of the observed treatment effects. These analyses defined responders for each efficacy endpoint by anchoring change from baseline to end of treatment with the Patient's Global Impression of Improvement (PGI‑I). The first analysis considered responders to be those who reported being “much improved” or “very much improved.” In this analysis, the absolute difference in the percentage of responders with ADDYI and the percentage of responders with placebo across the three trials in premenopausal women was 8-9% for SSEs (29-39% for ADDYI; 21-31% for placebo), 10-13% for FSFI desire domain (43-48% for ADDYI; 31-38% for placebo), and 7-13% for FSDS-R Question 13 (21-34% for ADDYI; 14-25% for placebo). The second analysis considered responders to be those who reported being at least "minimally improved". The absolute difference in the percentage of responders with ADDYI and the percentage of responders with placebo across the three trials in premenopausal women was 10-15% for SSEs (44-48% for ADDYI; 33-36% for placebo), 12-13% for FSFI desire domain (43-51% for ADDYI; 31-39% for placebo), and 9-12% for FSDS-R Question 13 (50-60% for ADDYI; 41-48% for placebo).
Trials in Postmenopausal Patients with HSDD (< 65 Years of Age)
The efficacy of ADDYI for the treatment of acquired, generalized HSDD in naturally postmenopausal women less than 65 years of age [see Indications and Usage (1) ] was established in a single 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Study 6, NCT00996372). The trial included postmenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD of at least 6 months duration.
In Study 6, 447 postmenopausal patients less than 65 years of age received ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime and 455 received placebo. Most of the trial participants less than 65 years of age were White (92%); the remainder were Black (7%) and Asian (1%). The mean age of study participants less than 65 years of age was 55 years (range 39 to 64 years); the mean duration in the monogamous, heterosexual relationship was 21 years, and the mean duration of HSDD was approximately 5 years. The study completion rate for the ADDYI and placebo groups less than 65 years of age was 79% and 83%, respectively. In this trial, postmenopausal patients with significant comorbidities such as uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (Hgb A1C > 7%), cardiovascular disease, uncorrected thyroid disorders, psychiatric disorders, etc., were excluded.
The trial had two co-primary efficacy endpoints - one for SSEs counts and one for desire domain of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI Desire) (similar to Study 3) - and a secondary endpoint that measured bother (a component of distress) related to sexual desire using Question 13 FSDS-R. These endpoints are defined in Section 14.1.
The efficacy results for patients less than 65 years of age from Study 6 are summarized in Table 7 . ADDYI resulted in statistically significant improvement compared to placebo in the co-primary and secondary endpoints.
| Full Analysis Set <65 years of age | ADDYI n=430 | Placebo n=451 |
|---|---|---|
| CI = Confidence Interval | ||
| The efficacy results are based on the full analysis set <65 years of age comprised of all randomized patients <65 years of age who took at least one dose of study medication and had at least one post-baseline efficacy assessment. Missing values were imputed using last-observation-carried-forward. | ||
| For satisfying sexual events, p-values are based on the Wilcoxon rank sum test. For FSFI-desire and FSDS-R Question 13, reported p-values are based on an ANCOVA model using baseline as a covariate with treatment and pooled center as main effect terms. | ||
| The unadjusted means are presented for the baseline values. For the change from baseline, the adjusted least squares means are presented. | ||
Number of satisfying sexual events (count) per 28 days | ||
Baseline (Mean) Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) Treatment difference (95% CI) | 2.0 0.9 0.4 (-0.0, 0.8) p < 0.025 | 2.0 0.6 |
FSFI Desire | ||
Baseline (Mean) Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) Treatment difference (95% CI) | 1.8 0.7 0.3 (0.2, 0.5) p < 0.0001 | 1.8 0.4 |
FSDS-R Question 13 A decreased in scope represents improvement | ||
Baseline (Mean) Change from baseline at Week 24 (Mean) Treatment difference (95% CI) | 3.3 -0.8 -0.2 (-0.4, -0.1) p < 0.01 | 3.3 -0.6 |
Effects on Driving
In a randomized, placebo-controlled, 4-way crossover study in 83 healthy premenopausal female subjects, no adverse effect was detected on measures of driving performance itself or psychomotor performance thought to be important for driving performance when assessed 9 hours following single and multiple doses of ADDYI 100 mg once daily at bedtime or single doses of ADDYI 200 mg at bedtime (two times the maximum recommended dosage) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
The effect of ADDYI on driving performance in postmenopausal women was not evaluated.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ADDYI is available as a 100 mg oval, pink, film-coated tablet debossed on one side with “f100” and blank on the other side. Available in bottles of 30 tablets. (NDC 58604-214-30)
Storage Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP controlled room temperature].
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ADDYI in the treatment of women less than 65 years of age with acquired, generalized HSDD as characterized by low sexual desire that causes marked distress or interpersonal difficulty (not due a co-existing medical or psychiatric condition, problems within the relationship, or the effects of a medication or other drug substance) is not known.