Admelog prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Administration guides
Patient education materials
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Financial assistance & copay programs
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- See Full Prescribing Information for important preparation and administration instructions. (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. (2.2 )
- Subcutaneous injection (2.2 ):
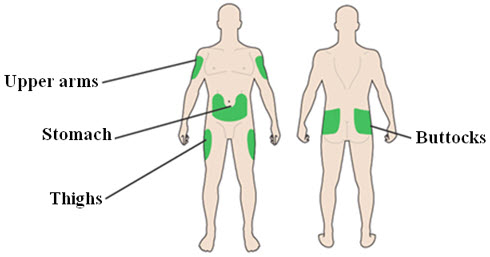
- Administer ADMELOG by subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks within 15 minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal.
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Continuous subcutaneous infusion (Insulin Pump) (2.2 ):
- Refer to the insulin infusion pump user manual to see if ADMELOG can be used. Use in accordance with the insulin pump instructions for use.
- Administer ADMELOG by continuous subcutaneous infusion using an insulin pump in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer.
- Rotate infusion sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Do not mix with other insulins or diluents in the pump.
- Intravenous Infusion: Administer ADMELOG by intravenous infusion ONLY after dilution and under medical supervision. (2.2 )
- The dosage of ADMELOG must be individualized based on the route of administration and the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal. (2.3 )
Important Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Always check insulin labels before administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
- Inspect ADMELOG visually before use. It should appear clear and colorless. Do not use ADMELOG if particulate matter or coloration is seen.
- Use ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen with caution in patients with visual impairment who may rely on audible clicks to dial their dose.
- Do NOT mix ADMELOG with other insulins when administering using a continuous subcutaneous infusion pump.
Preparation and Administration Instructions for the Approved Routes of Administration
Subcutaneous Injection
- Administer the dose of ADMELOG subcutaneously within fifteen minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal into the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks.
- Rotate injection site within the same region from one injection to the next to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- ADMELOG administered by subcutaneous injection should generally be used in regimens with intermediate or long-acting insulin.
- The ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen dials in 1-unit increments.
- Prior to subcutaneous use, ADMELOG may be diluted with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection. Dilute one-part ADMELOG to one-part 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to yield a concentration one-half that of ADMELOG (equivalent to U-50). If diluted ADMELOG is not used immediately, refrigerate at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours or store at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for 4 hours. Discard the unused diluted ADEMLOG after 24 hours if refrigerated or after 4 hours if stored at room temperature.
Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion (Insulin Pump)
- Refer to the continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump user manual to see if ADMELOG can be used with the insulin pump. Use ADMELOG in accordance with the insulin pump system's instructions for use.
- Administer ADMELOG by continuous subcutaneous infusion in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer. Rotate infusion sites within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
- Train patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy available in case of insulin pump failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ].
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- Change ADMELOG in the pump reservoir at least every 7 days or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter.
- Change the infusion sets and the infusion set insertion site according to the manufacturer's user manual.
- Do NOT dilute or mix ADMELOG when administering by continuous subcutaneous infusion.
- Do NOT expose ADMELOG in the pump reservoir to temperatures greater than 98.6°F (37°C).
Intravenous Administration
- Administer ADMELOG intravenously ONLY under medical supervision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.6) ] .
- Dilute ADMELOG to concentrations from 0.1 unit/mL to 1 unit/mL using 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2) ] .
- Closely monitor of blood glucose and potassium levels to avoid hypoglycemia and hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.6) ].
Dosage Recommendations
- Individualize and adjust the dosage of ADMELOG based on the route of administration, the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal.
- Dosage modifications may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function, or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] .
- When switching from another insulin lispro product to ADMELOG, the dose of ADMELOG should be the same as the other insulin lispro product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
- When switching from other insulins to ADMELOG, the ADMELOG dosage may need to be adjusted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Dosage Adjustment for Drug Interactions
- Dosage modification may be needed when ADMELOG is coadministered with certain drugs [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
- Do NOT mix ADMELOG with any other insulin.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Admelog prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ADMELOG is indicated to improve glycemic control in adult and pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- See Full Prescribing Information for important preparation and administration instructions. (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. (2.2 )
- Subcutaneous injection (2.2 ):
- Administer ADMELOG by subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks within 15 minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal.
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Continuous subcutaneous infusion (Insulin Pump) (2.2 ):
- Refer to the insulin infusion pump user manual to see if ADMELOG can be used. Use in accordance with the insulin pump instructions for use.
- Administer ADMELOG by continuous subcutaneous infusion using an insulin pump in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer.
- Rotate infusion sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Do not mix with other insulins or diluents in the pump.
- Intravenous Infusion: Administer ADMELOG by intravenous infusion ONLY after dilution and under medical supervision. (2.2 )
- The dosage of ADMELOG must be individualized based on the route of administration and the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal. (2.3 )
Important Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Always check insulin labels before administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
- Inspect ADMELOG visually before use. It should appear clear and colorless. Do not use ADMELOG if particulate matter or coloration is seen.
- Use ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen with caution in patients with visual impairment who may rely on audible clicks to dial their dose.
- Do NOT mix ADMELOG with other insulins when administering using a continuous subcutaneous infusion pump.
Preparation and Administration Instructions for the Approved Routes of Administration
Subcutaneous Injection
- Administer the dose of ADMELOG subcutaneously within fifteen minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal into the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks.
- Rotate injection site within the same region from one injection to the next to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- ADMELOG administered by subcutaneous injection should generally be used in regimens with intermediate or long-acting insulin.
- The ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen dials in 1-unit increments.
- Prior to subcutaneous use, ADMELOG may be diluted with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection. Dilute one-part ADMELOG to one-part 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to yield a concentration one-half that of ADMELOG (equivalent to U-50). If diluted ADMELOG is not used immediately, refrigerate at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours or store at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for 4 hours. Discard the unused diluted ADEMLOG after 24 hours if refrigerated or after 4 hours if stored at room temperature.
Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion (Insulin Pump)
- Refer to the continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump user manual to see if ADMELOG can be used with the insulin pump. Use ADMELOG in accordance with the insulin pump system's instructions for use.
- Administer ADMELOG by continuous subcutaneous infusion in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer. Rotate infusion sites within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
- Train patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy available in case of insulin pump failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ].
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- Change ADMELOG in the pump reservoir at least every 7 days or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter.
- Change the infusion sets and the infusion set insertion site according to the manufacturer's user manual.
- Do NOT dilute or mix ADMELOG when administering by continuous subcutaneous infusion.
- Do NOT expose ADMELOG in the pump reservoir to temperatures greater than 98.6°F (37°C).
Intravenous Administration
- Administer ADMELOG intravenously ONLY under medical supervision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.6) ] .
- Dilute ADMELOG to concentrations from 0.1 unit/mL to 1 unit/mL using 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2) ] .
- Closely monitor of blood glucose and potassium levels to avoid hypoglycemia and hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.6) ].
Dosage Recommendations
- Individualize and adjust the dosage of ADMELOG based on the route of administration, the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal.
- Dosage modifications may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function, or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] .
- When switching from another insulin lispro product to ADMELOG, the dose of ADMELOG should be the same as the other insulin lispro product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
- When switching from other insulins to ADMELOG, the ADMELOG dosage may need to be adjusted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Dosage Adjustment for Drug Interactions
- Dosage modification may be needed when ADMELOG is coadministered with certain drugs [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
- Do NOT mix ADMELOG with any other insulin.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 100 units/mL (U-100) is a clear and colorless solution available as:
- 10 mL multiple-dose vials
- 3 mL multiple-dose vials
- 3 mL single-patient-use SoloStar prefilled pens
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published studies with another insulin lispro product used during pregnancy have not reported an association between insulin lispro and the induction of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes [see Data ] . There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy [see Clinical Considerations ] .
Pregnant rats and rabbits were exposed to another insulin lispro product in animal reproduction studies during organogenesis. Fetal growth retardation was observed in offspring of rats exposed to insulin lispro at a dose approximately 3 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 unit/kg/day. No adverse effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in offspring of rabbits exposed to insulin lispro at doses up to approximately 0.24 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 unit/kg/day [see Data ] .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6%–10% in women with pregestational diabetes with a HbA1c >7% and has been reported to be as high as 20%–25% in women with a HbA1c >10%. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%–4% and 15%–20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo-fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, preeclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Human data
Published data from retrospective studies and meta-analyses do not report an association with another insulin lispro product and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when insulin lispro is used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish or exclude the absence of any risk because of methodological limitations including small sample size, selection bias, confounding by unmeasured factors, and some lacking comparator groups.
Animal data
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study with another insulin lispro product, female rats were given subcutaneous insulin lispro injections of 5 and 20 units/kg/day (0.8 and 3 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1 unit/kg/day, based on units/body surface area, respectively) from 2 weeks prior to cohabitation through Gestation Day 19. There were no adverse effects on female fertility, implantation, or fetal viability and morphology. However, fetal growth retardation was observed at the 20 units/kg/day dose as indicated by decreased fetal weight and an increased incidence of fetal runts/litter.
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits with another insulin lispro product, insulin lispro doses of 0.1, 0.25, and 0.75 unit/kg/day (0.03, 0.08, and 0.24 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1 unit/kg/day, based on units/body surface area, respectively) were injected subcutaneously on Gestation Days 7 through 19. There were no adverse effects on fetal viability, weight, and morphology at any dose.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Available data from published literature suggest that exogenous human insulin products, including insulin lispro, are transferred into human milk. There are no adverse reactions reported in breastfed infants in the literature. There are no data on the effects of exogenous human insulin products, including insulin lispro, on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ADMELOG and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from ADMELOG or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ADMELOG to improve glycemic control have been established in pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus. Use of ADMELOG for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study with another insulin lispro product, 100 units/ml, in 60 pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with type 1 diabetes mellitus and studies in adult patients with diabetes mellitus [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients (n=2,834) in eight clinical studies of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, 12% (n=338) were 65 years of age or over. The majority of these patients had type 2 diabetes. HbA1c values and hypoglycemia rates did not differ by age.
Of the total number of patients (n=1,011) in clinical studies of ADMELOG or another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, 26.5% (n=268) were 65 years of age or over. The majority of these patients had type 2 diabetes. HbA1c values and hypoglycemia rates did not differ by age.
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies to assess the effect of age on the onset of ADMELOG action have not been performed.
Renal Impairment
Patients with renal impairment may be at increased risk of hypoglycemia and may require more frequent ADMELOG dose adjustment and more frequent blood glucose monitoring [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment may be at increased risk of hypoglycemia and may require more frequent ADMELOG dose adjustment and more frequent blood glucose monitoring [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADMELOG is contraindicated:
- during episodes of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
- in patients who are hypersensitive to insulin lispro or to any of the excipients in ADMELOG [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Never share an ADMELOG SoloStar disposable prefilled pen or syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed. (5.1 )
- Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen: Make changes to a patient's insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. (5.2 )
- Hypoglycemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor blood glucose and increase monitoring frequency with changes to insulin dosage, use of glucose lowering medications, meal pattern, physical activity; in patients with renal or hepatic impairment; and in patients with hypoglycemia unawareness. (5.3 , 6 , 7 , 8.6 , 8.7 )
- Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors: Accidental mix-ups between insulin products can occur. Instruct patients to check insulin labels before injection. (5.4 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: May be life-threatening. Discontinue ADMELOG, monitor and treat if indicated. (5.5 )
- Hypokalemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia and treat if indicated. (5.6 )
- Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure; consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs. (5.7 )
- Hyperglycemia and Ketoacidosis Due to Insulin Pump Device Malfunction: Monitor glucose and administer ADMELOG by subcutaneous injection if pump malfunction occurs. (5.8 )
Never Share an ADMELOG SoloStar Pen or Syringe Between Patients
ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Patients using ADMELOG vials must never share needles or syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen
Changes in an insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] or hyperglycemia. Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis have been reported to result in hyperglycemia; and a sudden change in the injection site (to unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Make any changes to a patient's insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. Advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including ADMELOG.
Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place an individual and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery).
Hypoglycemia can happen suddenly, and symptoms may differ in each individual and change over time in the same individual. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic nerve disease, in patients using medications that block the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., beta-blockers) [see Drug Interactions (7) ] , or in patients who experience recurrent hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia after an injection is related to the duration of action of the insulin and, in general, is highest when the glucose lowering effect of the insulin is maximal. As with all insulins, the glucose lowering effect time course of ADMELOG may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and depends on many conditions, including the area of injection as well as the injection site blood supply and temperature [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to co-administered medication [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] .
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors
Accidental mix-ups between insulin products have been reported. To avoid medication errors between ADMELOG and other insulins, instruct patients to always check the insulin label before each injection.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulins, including ADMELOG. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue ADMELOG; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . ADMELOG is contraindicated in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to insulin lispro or any of the excipients in ADMELOG [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Hypokalemia
All insulins, including ADMELOG, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia if indicated (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations).
Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin, including ADMELOG, and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR-gamma agonist must be considered.
Hyperglycemia and Ketoacidosis Due to Insulin Pump Device Malfunction
Malfunction of the insulin pump or insulin infusion set or insulin degradation can rapidly lead to hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis. Prompt identification and correction of the cause of hyperglycemia or ketosis is necessary. Interim subcutaneous injections with ADMELOG may be required. Patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy must be trained to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy available in case of pump failure [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere:
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions with Subcutaneous Injections of ADMELOG
Two clinical trials with ADMELOG were conducted: one in patients with type 1 diabetes and one in patients with type 2 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
- The data in Table 1 reflect the exposure of 252 patients with type 1 diabetes to ADMELOG with mean exposure duration of 49 weeks. The type 1 diabetes population had the following characteristics: Mean age was 43 years and mean duration of diabetes was 20 years. Fifty-nine percent were male, 80% were White, 6% were Black or African American and 7% were Hispanic. At baseline, the mean eGFR was 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 and 49% of patients had eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean BMI was 26 kg/m 2 . The mean HbA1c at baseline was 8.07%.
- Two hundred fifty-three patients with type 2 diabetes were exposed to ADMELOG with mean exposure duration of 25 weeks. The type 2 diabetes population had the following characteristics: Mean age was 62 years and mean duration of diabetes was 17 years. Fifty-four percent were male, 90% were White, 6% were Black or African American and 17% were Hispanic. At baseline, the mean eGFR was 77 mL/min/1.73 m 2 and 27% of patients had eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean BMI was 32 kg/m 2 . The mean HbA1c at baseline was 7.99%.
Common adverse reactions were defined as reactions that occurred in ≥5% of the population studied.
Common adverse reactions (other than hypoglycemia) during a clinical trial in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus are listed in Table 1. In a 26-week clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, no adverse reactions (other than hypoglycemia) occurred in ≥5% of ADMELOG-treated patients (n=253) were observed.
| ADMELOG + Insulin Glargine (100 units/mL), % (n=252) | |
|---|---|
| Nasopharyngitis | 13% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 6% |
Severe Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most commonly observed adverse reaction in patients using insulin, including ADMELOG [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . The rates of reported hypoglycemia depend on the definition of hypoglycemia used, diabetes type, insulin dose, intensity of glucose control, background therapies, and other intrinsic and extrinsic patient factors. For these reasons, comparing rates of hypoglycemia in clinical trials for ADMELOG with the incidence of hypoglycemia for other products may be misleading and also, may not be representative of hypoglycemia rates that will occur in clinical practice.
In the ADMELOG trials, severe hypoglycemia was defined as an event requiring assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate, glucagon, or other resuscitative actions. The incidence of severe hypoglycemia in patients receiving ADMELOG with type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus was 13.5% at 52 weeks and 2.4% at 26 weeks, respectively [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Adverse Reactions Associated with Insulin Initiation and Intensification of Glucose Control
Intensification or rapid improvement in glucose control has been associated with a transitory, reversible ophthalmologic refraction disorder, worsening of diabetic retinopathy, and acute painful peripheral neuropathy. However, long-term glycemic control decreases the risk of diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy.
Lipodystrophy
Long-term use of insulin, including ADMELOG, can cause lipodystrophy at the site of repeated insulin injections or infusion. Lipodystrophy includes lipohypertrophy (thickening of adipose tissue) and lipoatrophy (thinning of adipose tissue) and may affect insulin absorption [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Weight Gain
Weight gain can occur with insulins, including ADMELOG, and has been attributed to the anabolic effects of insulin and the decrease in glucosuria.
Peripheral Edema
Insulins, including ADMELOG, may cause sodium retention and edema, particularly if previously poor metabolic control is improved by intensified insulin therapy.
Adverse Reactions with Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) of ADMELOG
In a randomized, open-label crossover study in adult patients with type 1 diabetes treated over two 4-week periods, the incidence of infusion set occlusions (defined as failure to correct hyperglycemia [plasma glucose ≥300 mg/dL] by insulin bolus via insulin pump) in ADMELOG-treated patients (n=25) was evaluated. Infusion set occlusions were reported by 24% of patients.
In a randomized, 16-week, open-label, parallel design study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes, adverse reactions related to infusion site-related reactions for another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, occurred in 21% of patients. The most frequently reported infusion site-related reactions were infusion site erythema and infusion site reaction.
Allergic Reactions
Local Allergy
As with any insulin therapy, patients taking ADMELOG may experience redness, swelling, or itching at the site of the injection. These minor reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks, but in some occasions may require discontinuation of ADMELOG. In some instances, these reactions may be related to factors other than insulin, such as irritants in a skin cleansing agent or poor injection technique.
Systemic Allergy
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, may occur with any insulin, including ADMELOG. Generalized allergy to insulin may cause whole body rash (including pruritus), dyspnea, wheezing, hypotension, tachycardia, or diaphoresis.
Localized reactions and generalized myalgias have been reported with injected metacresol, which is an excipient in ADMELOG [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medication, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to ADMELOG in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other insulin products may be misleading.
In a 52-week study of ADMELOG in type 1 diabetes patients, 49.4% were positive at baseline and 22.6% had treatment-emergent ADA (i.e., either new ADA, or increase in titer of at least 4-fold).
In a 26-week study of ADMELOG in type 2 diabetes patients, 26.4% were positive at baseline and 18.8% had treatment-emergent ADA (i.e., either new ADA, or increase in titer of at least 4-fold).
Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Medication errors in which other insulins have been accidentally substituted for another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, have been identified during post approval use.
Localized cutaneous amyloidosis at the injection site has occurred. Hyperglycemia has been reported with repeated insulin injections into areas of localized cutaneous amyloidosis; hypoglycemia has been reported with a sudden change to an unaffected injection site.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 2 presents clinically significant drug interactions with ADMELOG.
| Drugs That May Increase the Risk of Hypoglycemia | |
| Drugs: | Antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics. |
| Intervention: | Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when ADMELOG is concomitantly administered with these drugs. |
| Drugs That May Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of ADMELOG | |
| Drugs: | Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones. |
| Intervention: | Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when ADMELOG is concomitantly administered with these drugs. |
| Drugs That May Increase or Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of ADMELOG | |
| Drugs: | Alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia. |
| Intervention: | Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when ADMELOG is concomitantly administered with these drugs. |
| Drugs That May Blunt Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia | |
| Drugs: | Beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine and reserpine. |
| Intervention: | Increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when ADMELOG is concomitantly administered with these drugs. |
DESCRIPTION
Insulin lispro is a rapid-acting human insulin analog produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a non-pathogenic laboratory strain of Escherichia coli . Insulin lispro differs from human insulin in that the amino acid proline at position B28 is replaced by lysine and the lysine in position B29 is replaced by proline. Insulin lispro has a molecular weight of 5808 Da, identical to that of human insulin.
ADMELOG (insulin lispro) injection is a sterile, aqueous, clear, and colorless solution for subcutaneous or intravenous use. Each mL of ADMELOG contains 100 units of insulin lispro, and the inactive ingredients: dibasic sodium phosphate (1.88 mg), glycerin (16 mg), metacresol (3.15 mg), zinc oxide (content adjusted to provide 0.0197 mg zinc ion), and Water for Injection, USP. Insulin lispro has a pH of 7.0 to 7.8. The pH is adjusted by addition of aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide. ADMELOG is latex free.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Regulation of glucose metabolism is the primary activity of insulins and insulin analogs, including insulin lispro products. Insulins lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulins inhibit lipolysis and proteolysis and enhance protein synthesis.
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of ADMELOG After Subcutaneous Injection
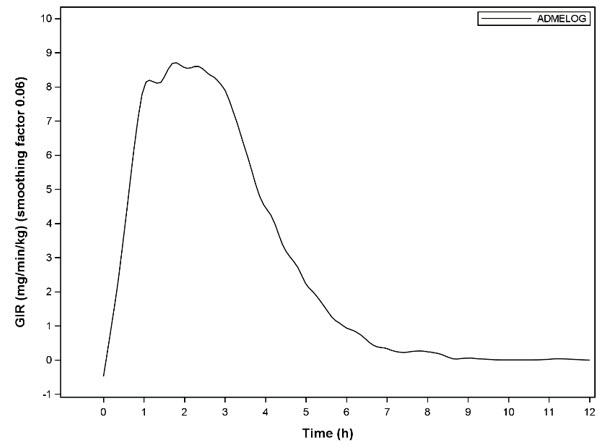
The pharmacodynamic profile of a single 0.3 unit/kg dose of ADMELOG administered subcutaneously was evaluated in a euglycemic clamp study enrolling 30 patients with type 1 diabetes. In this study, the mean (SD) time to maximum effect of ADMELOG (measured by the peak rate of glucose infusion) was approximately 2.1 (0.8) hours. The mean (SD) area under the glucose infusion rate curves (measure of overall pharmacodynamic effect) and mean (SD) maximum glucose infusion rate were 1953.5 (547.3) mg/kg and 9.97 (2.37) mg/min/kg, respectively (see Figure 1 ).
Figure 1: Mean Smoothed Glucose Infusion Rate Body Weight Standardized after Subcutaneous Injection of ADMELOG (0.3 unit/kg) in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes |
|
The time course of action of insulin and insulin analogs, including insulin lispro products, may vary considerably in different individuals or within the same individual. The rate of insulin absorption and, consequently, the onset of activity are known to be affected by the site of injection, exercise, and other variables [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Pharmacodynamics of AMELOG after Intravenous Administration
The glucose lowering effect of intravenous administration of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, was tested in 21 patients with type 1 diabetes. For the study, the patients' usual doses of insulin were held, and blood glucose concentrations were allowed to reach a stable range of 200 to 260 mg/dL during a one to three-hour run-in phase. The run-in phase was followed by a 6-hour assessment phase. During the assessment phase, patients received intravenous infusion of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, at an initial infusion rate of 0.5 units/hour. The infusion rate could be adjusted at regular timed intervals to achieve and maintain blood glucose concentrations between 100 to 160 mg/dL.
The mean blood glucose levels during the assessment phase for patients on another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, therapy are summarized below in Table 3. All patients achieved the targeted glucose range at some point during the 6-hour assessment phase. At the endpoint, blood glucose was within the target range (100 to 160 mg/dL) for 17 of 20 patients treated with another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL. The average time (±SE) required to attain near normoglycemia was 129 ± 14 minutes for another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL.
| Time from Start of Infusion (minutes) | Mean Blood Glucose (mg/dL) Intravenous Results shown as mean ± SD. |
|---|---|
| 0 | 224 ± 16 |
| 30 | 205 ± 21 |
| 60 | 195 ± 20 |
| 120 | 165 ± 26 |
| 180 | 140 ± 26 |
| 240 | 123 ± 20 |
| 300 | 120 ± 27 |
| 360 | 122 ± 25 |
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
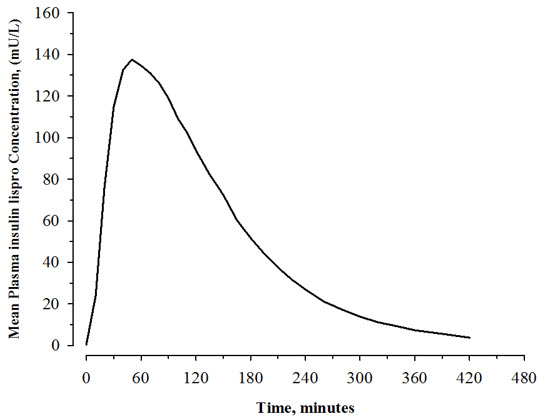
The pharmacokinetic profile of a single 0.3 unit/kg dose of ADMELOG administered subcutaneously was evaluated in a study enrolling 30 patients with type 1 diabetes. In this study, the mean observed area under the plasma insulin lispro concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity and peak plasma insulin lispro concentration were 12800 pg∙hr/mL and 5070 pg/mL, respectively. The median time to maximum plasma insulin lispro concentration was 0.83 hours after injection (see Figure 2 ).
Figure 2: Mean Plasma Concentrations of ADMELOG after a Single Subcutaneous Administration of ADMELOG (0.3 unit/kg) in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
The absolute bioavailability of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, after subcutaneous injection ranges from 55% to 77% with doses between 0.1 to 0.2 unit/kg, inclusive.
Distribution
When administered intravenously as bolus injections of 0.1 and 0.2 unit/kg dose in two separate groups of healthy subjects, the mean volume of distribution of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, appeared to decrease with increase in dose (1.55 and 0.72 L/kg, respectively).
Elimination
Metabolism
Human metabolism studies have not been conducted. However, animal studies indicate that the metabolism of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, is identical to that of regular human insulin.
Excretion
When administered intravenously, another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL demonstrated dose-dependent clearance, with a mean clearance of 21.0 mL/min/kg (0.1 unit/kg dose), and 9.6 mL/min/kg (0.2 unit/kg dose). Another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, demonstrated a mean t 1/2 of 0.85 hours (51 minutes) and 0.92 hours (55 minutes), respectively for 0.1 unit/kg and 0.2 unit/kg doses.
Specific Populations
The effects of age, gender, race, obesity, pregnancy, or smoking on the pharmacokinetics of ADMELOG have not been studied.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Type 2 diabetic patients with varying degrees of renal impairment showed no difference in pharmacokinetics of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL. However, the sensitivity of the patients to insulin did change, with an increased response to insulin as the renal function declined. Some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Type 2 diabetic patients with impaired hepatic function showed no effect on the pharmacokinetics of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, as compared to patients with no hepatic dysfunction. However, some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with liver failure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Standard 2-year carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed. In Fischer 344 rats, a 12-month repeat-dose toxicity study was conducted with insulin lispro at subcutaneous doses of 20 and 200 units/kg/day (approximately 3 and 32 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1 unit/kg/day, based on units/body surface area). Insulin lispro did not produce important target organ toxicity including mammary tumors at any dose.
Insulin lispro was not mutagenic in the following genetic toxicity assays: bacterial mutation, unscheduled DNA synthesis, mouse lymphoma, chromosomal aberration, and micronucleus assays.
Male fertility was not compromised when male rats given subcutaneous insulin lispro injections of 5 and 20 units/kg/day (0.8 and 3 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1 unit/kg/day, based on units/body surface area) for 6 months were mated with untreated female rats. In a combined fertility, perinatal, and postnatal study in male and female rats given 1, 5, and 20 units/kg/day subcutaneously (0.16, 0.8, and 3 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1 unit/kg/day, based on units/body surface area), mating and fertility were not adversely affected in either gender at any dose.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Overview of Clinical Studies
The safety and effectiveness of ADMELOG to improve glycemic control in adult and pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus have been established based on adequate and well-controlled studies of ADMELOG in adult patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, and based on adequate and well-controlled studies of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, in adult and pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with type 1 diabetes mellitus and adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The safety and effectiveness of:
- ADMELOG were studied in 507 adult patients with type 1 diabetes and 505 adult patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, were studied in 1,087 adult and pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes and in 722 adult patients with type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – Subcutaneous Injection
ADMELOG: Study in Adult Patients
A 26-week open-label, active-controlled study (NCT02273180) evaluated the glucose lowering effect of ADMELOG plus insulin glargine, 100 units/mL, compared to that of Comparator (another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, or a non–U.S.-licensed insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL), plus insulin glargine, 100 units/mL. A total of 507 patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin glargine 100 units/mL and rapid-acting mealtime insulin analogs participated in the study. Patients were randomized to ADMELOG (n=253) or Comparator (n=254). ADMELOG or Comparator was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately prior to meals.
The mean age of these patients was 43 years old, and 60% were male. The population was 82% White, 5% Black or African American and 5% were Hispanic. The population had type 1 diabetes mellitus for a mean duration of 19 years. The mean eGFR was 90.6 mL/min/1.73 m 2 and 48.7% of patients had GFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean BMI was approximately 26 kg/m 2 . At baseline, 61%, 38% and 2% of the patients were using other insulin lispro products, 100 units/mL, insulin aspart, 100 units/mL, or both, respectively.
At week 26, treatment with ADMELOG provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that was non-inferior to that achieved with the Comparator (see Table 4 ).
| ADMELOG + Insulin Glargine | Comparator + Insulin Glargine | |
|---|---|---|
| N ITT: Intent-to-treat; all randomized patients. | 253 | 254 |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.08 | 7.99 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline Estimated using a multiple imputation method that models a "return to baseline" for patients having missing data who discontinued treatment. ANCOVA was used with treatment and stratification groups as fixed factors and baseline HbA1c as a covariate. | -0.40 | -0.46 |
| Adjusted mean difference Treatment difference: ADMELOG - Comparator. (95% CI) | 0.06 (-0.086 to 0.201) | |
Another Insulin Lispro Product, 100 units/mL: Study in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
A 12-month, randomized, parallel, open-label, active-controlled study was conducted in 167 patients with type 1 diabetes to assess the safety and efficacy of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL (n=81), compared with regular human insulin, 100 units/mL (n=86). This other insulin lispro product was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately prior to meals and regular human insulin was administered 30 to 45 minutes before meals. Human insulin extended zinc suspension was administered once or twice daily as the basal insulin in both treatment groups. There was a 2 to 4-week run-in period with regular human insulin and human insulin extended zinc suspension before randomization.
The mean age of these patients was 31 years (range 12 to 70 years), and 47% were male. The population was 97% White.
| Another Insulin Lispro Product + Human Insulin Extended Zinc | Regular Human Insulin + Human Insulin Extended Zinc | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 81 | 86 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) Values are Mean ± SD. | 8.2 ± 1.4 | 8.3 ± 1.7 |
| Change from baseline HbA1c (%) | -0.1 ± 0.9 | 0.1 ± 1.1 |
| Treatment difference in HbA1c mean (95% confidence interval) | 0.4 (0.0; 0.8) | |
Another Insulin Lispro Product, 100 units/mL: Studies in Pediatric Patients 3 Years of Age and Older
An 8-month, crossover study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes (n=463), aged 9 to 19 years, compared two subcutaneous multiple-dose treatment regimens: another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, or regular human insulin, 100 units/mL, both administered with NPH human insulin isophane suspension as the basal insulin. Insulin lispro achieved glycemic control comparable to regular human insulin, as measured by HbA1c (see Table 6 ).
| Baseline | Another Insulin Lispro Product + NPH | Regular Human Insulin + NPH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) Values are Mean ± SD. | 8.6 ± 1.5 | 8.7 ± 1.5 | 8.7 ± 1.6 |
| Change from baseline HbA1c (%) | - | 0.1 ± 1.1 | 0.1 ± 1.3 |
In a 9-month, crossover study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (n=60), aged 3 to 11 years, compared three subcutaneous injection regimens: another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, administered immediately before meals, this same insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, administered immediately after meals and regular human insulin, 100 units/mL administered 30 minutes before meals resulted in similar glycemic control, as measured by HbA1c, regardless of treatment group.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion
Another Insulin Lispro Product, 100 units/mL: Studies in Adult and Pediatric Patients 15 Years of Age and Older
To evaluate the administration of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, as a subcutaneous infusion via external insulin pumps, two open-label, crossover studies were performed in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- One study involved 39 patients, ages 19 to 58 years, treated for 24 weeks with another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, or regular human insulin 100 units/mL. After 12 weeks of treatment, the mean HbA1c values decreased from 7.8% to 7.2% in patients treated with another insulin lispro, and from 7.8% to 7.5% in the regular human insulin-treated patients.
- Another study involved 60 patients (mean age 39, range 15 to 58 years) treated for 24 weeks with either another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, or buffered regular human insulin, 100 units/mL. After 12 weeks of treatment, the mean HbA1c values decreased from 7.7% to 7.4% in patients treated with insulin lispro and remained unchanged from 7.7% in the buffered regular human insulin-treated patients.
Another Insulin Lispro Product, 100 units/mL: Study in Pediatric Patients 4 Years of Age and Older
A randomized, 16-week, open-label, parallel design, study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (n=298), aged 4 to 18 years, compared two subcutaneous continuous infusion regimens administered via an external insulin pump: insulin aspart, 100 units/mL (n=198), or another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL (n=100). These two treatments resulted in comparable changes from baseline in HbA1c after 16 weeks of treatment (see Table 7 ).
| Another Insulin Lispro Product | Insulin Aspart | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 100 | 198 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) Values are Mean ± SD. | 8.2 ± 0.8 | 8.0 ± 0.9 |
| Change from Baseline HbA1c (%) | -0.1 ± 0.7 | -0.1 ± 0.8 |
| Treatment Difference in HbA1c, Mean (95% confidence interval) | 0.1 (-0.3, 0.1) | |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
ADMELOG: Study in Adult Patients
A 26-week open-label, active-controlled study (NCT02294474) evaluated the glucose lowering effect of ADMELOG plus insulin glargine, 100 units/mL, compared to that of Comparator (another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, or a non–U.S.-licensed insulin lispro, 100 units/mL) plus insulin glargine, 100 units/mL. A total of 505 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin glargine, 100 units/mL, and rapid-acting mealtime insulin analogs participated in the study. Patients were randomized to ADMELOG, 100 units/mL (n=253) or Comparator (n=252). ADMELOG or Comparator, was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately prior to meals.
The mean age of these patients was 63 years, and 53% were male. The population was 88% White, 6% Black or African American and 18% were Hispanic. The population had type 2 diabetes mellitus for a mean duration of 17 years. The mean eGFR was 77.9 mL/min/1.73 m 2 and 26.9% of patients had GFR >90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean BMI was approximately 32.2 kg/m 2 . At baseline, 51%, 48%, and 0.4% of the patients were using other insulin lispro products, 100 units/mL, insulin aspart, 100 units/mL, or both, respectively.
At week 26, treatment with ADMELOG provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that was non-inferior to that achieved with the Comparator (see Table 8 ).
| ADMELOG + Insulin Glargine | Comparator + Insulin Glargine | |
|---|---|---|
| N ITT: Intent-to-treat; all randomized patients. | 253 | 252 |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline (mean) | 8.00 | 8.03 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline Estimated using a multiple imputation method that models a "return-to-baseline" for patients having missing data who discontinued treatment. ANCOVA was used with treatment and stratification groups as fixed factors and baseline HbA1c as a covariate. | -0.86 | -0.80 |
| Adjusted mean difference Treatment difference: ADMELOG – Comparator. (95% CI) | -0.06 (-0.209 to 0.091) | |
Another Insulin Lispro Product, 100 units/mL: Study in Adult Patients
A 6-month randomized, crossover, open-label, active-controlled study was conducted in 722 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin to assess the safety and efficacy of another insulin lispro product, 100 units/mL, for 3 months followed by regular human insulin, 100 units/mL, for 3 months or the reverse sequence. This other insulin lispro product was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately before meals and regular human insulin was administered 30 to 45 minutes before meals. NPH human insulin isophane suspension or human insulin extended zinc suspension was administered once or twice daily as the basal insulin in both treatment groups. All patients participated in a 2 to 4-week run-in period with regular human insulin and NPH human insulin isophane suspension or human insulin extended zinc suspension.
Most of the patients were White (88%), and the numbers of males and females in each group were approximately equal. The mean age was 59 years (range 24 to 85 years). The average body mass index (BMI) was 28.2 kg/m 2 . During the study, the majority of patients used NPH human insulin isophane suspension (84%) compared with human insulin extended zinc suspension (16%) as their basal insulin. The reductions from baseline in HbA1c were similar between the two treatments from the combined groups (see Table 9 ).
| Baseline | Another Insulin Lispro Product + Basal Insulin | Regular Human Insulin + Basal Insulin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) Values are Mean ± SD. | 8.9 ± 1.7 | 8.2 ± 1.3 | 8.2 ± 1.4 |
| Change from baseline HbA1c (%) | - | -0.7 ± 1.4 | -0.7 ± 1.3 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
ADMELOG (insulin lispro) injection 100 units/mL (U-100) is available as a clear and colorless solution in:
| Dosage Unit | Package Size | NDC # |
|---|---|---|
| 10 mL multiple-dose vials | Carton of 1 | 0024-5924-10 |
| 3 mL multiple-dose vials | Carton of 1 | 0024-5926-05 |
| 3 mL single-patient-use SoloStar prefilled pen | Carton of 5 | 0024-5925-05 |
Each prefilled SoloStar pen is for use by a single patient.
The ADMELOG SoloStar prefilled pen dials in 1-unit increments.
Storage and Handling
Dispense in the original sealed carton with the enclosed Instructions for Use.
Store ADMELOG according to the table below. Do not freeze and do not use ADMELOG if it has been frozen. Protect from direct heat and light.
In-use (opened) ADMELOG vials and ADMELOG SoloStar pens must be used within 28 days or be discarded, even if they still contain ADMELOG.
| ADMELOG | Not In-Use (Unopened) Room Temperature (Up to 86°F [30°C]) | Not In-Use (Unopened) Refrigerated (36°F–46°F [2°C–8°C]) | In-Use (Opened) Room Temperature (Up to 86°F [30°C]) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mL multiple-dose vial | 28 days | Until expiration date | 28 days refrigerated/room temperature |
| 3 mL multiple-dose vial | 28 days | Until expiration date | 28 days refrigerated/room temperature |
| 3 mL single-patient-use SoloStar prefilled pen | 28 days | Until expiration date | 28 days Do not refrigerate. |
Use in an External Insulin Pump
Change the ADMELOG in the pump reservoir at least every 7 days or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter, or after exposure to temperatures that exceed 98.6°F (37°C).
Diluted ADMELOG for Subcutaneous Injection
Diluted ADMELOG may remain in patient use for up to 24 hours when stored in a refrigerator (36°F–46°F [2°C–8°C]) or for up to 4 hours when stored at room temperature (86°F [30°C]). Do not dilute ADMELOG used in an external insulin pump.
Admixture for Intravenous Administration
Infusion bags prepared with ADMELOG are stable when stored in a refrigerator (36°F–46°F [2°C–8°C]) for 24 hours or may be used at room temperature for up to 4 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ADMELOG ® [ad-mah-log] (insulin lispro) injection, for subcutaneous use 10 mL or 3 mL Vial (100 units/mL, U-100)
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using ADMELOG and each time you get a new ADMELOG vial. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Do not share your ADMELOG syringes with other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
Supplies needed to give your injection
- an ADMELOG 10 mL or 3 mL vial
- a U-100 insulin syringe and needle
- 2 alcohol swabs
- 1 sharps container for throwing away used needles and syringes. See " Disposing of used needles and syringes " at the end of these instructions.
Preparing your ADMELOG dose
- Wash your hands with soap and water or with alcohol.
- Check the ADMELOG label to make sure you are taking the right type of insulin. This is especially important if you use more than 1 type of insulin.
- Check the insulin to make sure it is clear and colorless. Do not use ADMELOG if it is colored or cloudy, or if you see particles in the solution.
- Do not use ADMELOG after the expiration date stamped on the label or 28 days after you first use it.
- Always use a syringe that is marked for U-100 insulin. If you use a syringe other than a U-100 insulin syringe, you may get the wrong dose of insulin.
- Always use a new syringe or needle for each injection to help ensure sterility and prevent blocked needles. Do not reuse or share your syringes or needles with other people. You may give other people a serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
Step 1:
If you are using a new vial, remove the protective cap. Do not remove the stopper.
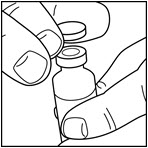
Step 2:
Wipe the top of the vial with an alcohol swab. You do not have to shake the vial of ADMELOG before use.
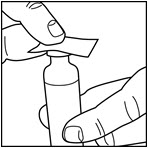
Step 3:
Draw air into the syringe equal to your insulin dose. Put the needle through the rubber top of the vial and push the plunger to inject the air into the vial.
|
|
Step 4:
Leave the syringe in the vial and turn both upside down. Hold the syringe and vial firmly in one hand. Make sure the tip of the needle is in the insulin. With your free hand, pull the plunger to withdraw the correct dose into the syringe.
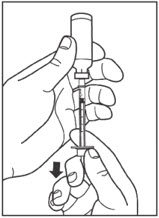
Step 5:
Before you take the needle out of the vial, check the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are in the syringe, hold the syringe straight up and tap the side of the syringe until the bubbles float to the top. Push the bubbles out with the plunger and draw insulin back in until you have the correct dose.
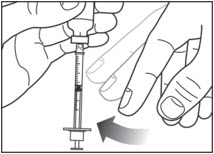
Step 6:
Remove the needle from the vial. Do not let the needle touch anything. You are now ready to inject.
Giving your ADMELOG injection with a syringe
- Inject your insulin exactly as your healthcare provider has shown you.
- ADMELOG starts acting fast, so give your injection within 15 minutes before or right after you eat a meal.
Step 7:
- Choose your injection site: ADMELOG is injected under the skin (subcutaneously) of your upper arms, thighs, buttocks, or stomach area (abdomen).
- Change (rotate) your injection sites within the area you choose for each dose to reduce your risk of getting pits in the skin or thickened skin (lipodystrophy) and skin with lumps (localized cutaneous amyloidosis) at the injection sites.
- Do not inject where the skin has pits, is thickened, or has lumps.
- Do not inject where the skin is tender, bruised, scaly or hard, or into scars or damaged skin.
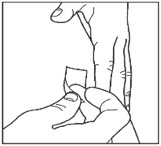
- Wipe the skin with an alcohol swab to clean the injection site. Let the injection site dry before you inject your dose.
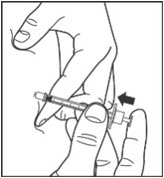
Step 8:
- Pinch the skin.
- Insert the needle in the way your healthcare provider showed you.
- Release the skin.
- Slowly push in the plunger of the syringe all the way, making sure you have injected all the insulin.
- Leave the needle in the skin for about 10 seconds.
Step 9:
- Pull the needle straight out of your skin.
- Gently press the injection site for several seconds. Do not rub the area.
- Do not recap the used needle. Recapping the needle can lead to a needle-stick injury.
Giving your ADMELOG using an insulin pump
- If you have been prescribed an insulin pump, check the pump manufacturer's user manual to see if ADMELOG can be used with the pump.
- ADMELOG should be given into an area of your body recommended in the instructions that come with your insulin pump.
- Change your insertion site according to the manufacturer's user manual.
- Change (rotate) your insertion sites within the area you choose for each insertion to reduce your risk of getting pits in skin or thickened skin (lipodystrophy) and skin with lumps (localized cutaneous amyloidosis) at the injection sites. Do not insert into the exact same spot for each injection. Do not insert where the skin has pits, is thickened, or has lumps. Do not insert where the skin is tender, bruised, scaly or hard, or into scars or damaged skin.
- Call your healthcare provider and choose a new infusion site if the skin at the infusion site becomes red, itchy, or thickened.
- Your healthcare provider should provide recommendations for appropriate pump basal and meal-time infusion rates. Call your healthcare provider if you have any questions about using the insulin pump.
- Change the insulin in the reservoir at least every 7 days or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter, even if you have not used all of the insulin.
- Do not dilute or mix ADMELOG with any other type of insulin in your insulin pump.
- You should be trained on how to give insulin by injection and have an alternative insulin delivery system in case of pump failure.
- When you start using ADMELOG by infusion pump, your insulin dose may need to be changed. Check with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your insulin dose.
Disposing of used needles and syringes
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
How should I store ADMELOG?
Unopened (not in-use) ADMELOG vials
- Store unused ADMELOG vials in the refrigerator from 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze ADMELOG.
- Keep ADMELOG away from direct heat and light.
- If a vial has been frozen or overheated, throw it away.
- Unopened vials can be used until the expiration date on the carton and label if they have been stored in the refrigerator.
- Unopened vials should be thrown away after 28 days if they are stored at room temperature.
After ADMELOG vials have been opened (in-use)
- Store in-use (opened) ADMELOG vials in a refrigerator from 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) or at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C) for up to 28 days .
- Do not freeze ADMELOG.
- Keep ADMELOG out of direct heat and light.
- If a vial has been frozen, throw it away.
- The ADMELOG vial you are using should be thrown away after 28 days, even if it still has insulin left in it.
ADMELOG in an insulin pump
- Throw away ADMELOG in the pump reservoir if it has been exposed to temperatures higher than 98.6°F (37°C). This may happen if the pump housing, cover, tubing, or sport case is exposed to sunlight or direct heat.
Keep ADMELOG vials, syringes, needles and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC Morristown, NJ 07960 A SANOFI COMPANY U.S. License No. 1752
ADMELOG is a registered trademark of sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. ©2025 sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: May 2025
Mechanism of Action
Regulation of glucose metabolism is the primary activity of insulins and insulin analogs, including insulin lispro products. Insulins lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulins inhibit lipolysis and proteolysis and enhance protein synthesis.