Afrezza prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Administration guides
Patient education materials
Treatment initiation and patient onboarding
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Only administer via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA inhaler (2.2 )
- Administer at the beginning of each meal (2.2 )
- See full prescribing information for the recommended starting mealtime dosage in insulin-naïve patients and patients who are using subcutaneous mealtime insulin, or pre-mixed insulin (2.3 )
- Modify the mealtime AFREZZA dosage based on the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal (2.4 )
If blood glucose control is not achieved with increased AFREZZA dosages, consider discontinuing AFREZZA (2.4 )
Lung Function Assessment Prior to Administration
AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease because of the risk of acute bronchospasm in these patients. Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a medical history, physical examination and spirometry (FEV 1 ) in all patients to identify potential lung disease [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
Important Administration Information
Refer patients to the Instructions for Use for detailed instructions and visuals on how to prepare, administer, and store AFREZZA; use the AFREZZA cartridges; and use the AFREZZA inhaler.
- Only administer AFREZZA via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA Inhaler.
- Administer AFREZZA at the beginning of each meal.
- Administer AFREZZA using a single inhalation per cartridge (if the dose is greater than the contents of a single cartridge, more than one cartridge is needed) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )].
- To administer AFREZZA:
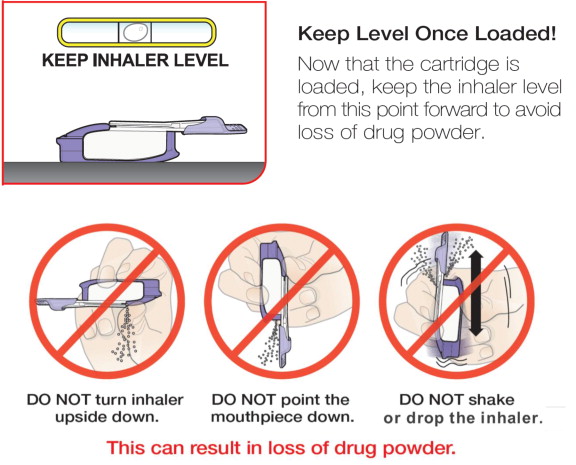
- Keep the inhaler level with the white mouthpiece on top and purple base on the bottom after a cartridge has been inserted into the inhaler. Loss of drug effect can occur if the inhaler is turned upside down, held with the mouthpiece pointing down, shaken, or dropped after the cartridge has been inserted but before the dose has been administered. If any of the above occur, replace the cartridge before use.
- Hold the inhaler away from the mouth and fully exhale.
- After the inhaler is placed in the mouth and the lips form a seal, tilt the inhaler down towards the chin while keeping the head level.
- With the mouth closed around the mouthpiece, inhale deeply through the inhaler.
- Hold the breath for as long as comfortable and at the same time remove the inhaler from the mouth.
- After holding the breath, exhale and continue to breathe normally.
- The AFREZZA Inhaler can be used for up to 15 days from the date of first use. After 15 days of use, discard the inhaler and replace it with a new inhaler.
Recommended Starting Mealtime Dosage of AFREZZA
Insulin naïve patients
The initial dosage of AFREZZA is 4 units inhaled at the beginning of each meal.
Switching from Other Mealtime (prandial) Insulin Regimens to AFREZZA
When switching from another insulin to AFREZZA, a different insulin dosage may be needed and increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring and monitoring for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia may be needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 , 12.3 )].
Subcutaneous, Mealtime (prandial) Insulin:
Follow the recommendations in Table 1 to convert each injected mealtime insulin dosage (or bolus dosage for patients using insulin pumps) to the recommended mealtime dosage of AFREZZA.
Subcutaneous, Pre-Mixed Insulin:
- Refer to the prescribing information for the pre-mixed insulin to estimate the mealtime subcutaneous insulin dosage based on the product's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.
- Follow the recommendations in Table 1 to convert each estimated injected mealtime dosage to an AFREZZA mealtime dose.
- If basal insulin is clinically indicated, refer to the prescribing information for the chosen basal insulin for dosage recommendations.
• For AFREZZA doses exceeding the contents of a single cartridge at mealtime, use more than one cartridge. To achieve the required total mealtime dosage, use a combination of 4 unit, 8 unit, and 12 unit cartridges. When titrating dosages above 16 units after the initial conversion dosage, use combinations of different cartridges [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ), Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 ), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )] . | |
| Current Subcutaneous Mealtime Insulin Dosage | Starting Dosage of AFREZZA |
| Up to 3 units | 4 units |
| 4 to 5 units | 8 units |
| 6 to 7 units | 12 units |
| 8 or more units | 16 units |
Mealtime AFREZZA Dosage Modification
- Modify the mealtime AFREZZA dosage based on the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal.
- Dosage modifications may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )].
- Increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring during titration of AFREZZA. If blood glucose control is not achieved with increased AFREZZA dosages, consider discontinuing AFREZZA.
Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Dosage modification may be needed when:

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Afrezza prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE BRONCHOSPASM IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
- Acute bronchospasm has been observed in AFREZZA-treated patients with asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma or COPD [see Contraindications (4 )].
- Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a detailed medical history, physical examination, and spirometry (FEV 1 ) to identify potential lung disease in all patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
Dosage and Administration, Recommended Starting Mealtime Dosage of AFREZZA (2.3 ) 1/2026
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AFREZZA ® is indicated to improve glycemic control in adult patients with diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use:
- AFREZZA is not recommended for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) [see Warning and Precautions (5.6 )] .
- The safety and effectiveness of AFREZZA in patients who smoke have not been established. The use of AFREZZA is not recommended in patients who smoke or who have recently stopped smoking.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Only administer via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA inhaler (2.2 )
- Administer at the beginning of each meal (2.2 )
- See full prescribing information for the recommended starting mealtime dosage in insulin-naïve patients and patients who are using subcutaneous mealtime insulin, or pre-mixed insulin (2.3 )
- Modify the mealtime AFREZZA dosage based on the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal (2.4 ) If blood glucose control is not achieved with increased AFREZZA dosages, consider discontinuing AFREZZA (2.4 )
Lung Function Assessment Prior to Administration
AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease because of the risk of acute bronchospasm in these patients. Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a medical history, physical examination and spirometry (FEV 1 ) in all patients to identify potential lung disease [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
Important Administration Information
Refer patients to the Instructions for Use for detailed instructions and visuals on how to prepare, administer, and store AFREZZA; use the AFREZZA cartridges; and use the AFREZZA inhaler.
- Only administer AFREZZA via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA Inhaler.
- Administer AFREZZA at the beginning of each meal.
- Administer AFREZZA using a single inhalation per cartridge (if the dose is greater than the contents of a single cartridge, more than one cartridge is needed) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )].
- To administer AFREZZA:
- Keep the inhaler level with the white mouthpiece on top and purple base on the bottom after a cartridge has been inserted into the inhaler. Loss of drug effect can occur if the inhaler is turned upside down, held with the mouthpiece pointing down, shaken, or dropped after the cartridge has been inserted but before the dose has been administered. If any of the above occur, replace the cartridge before use.
- Hold the inhaler away from the mouth and fully exhale.
- After the inhaler is placed in the mouth and the lips form a seal, tilt the inhaler down towards the chin while keeping the head level.
- With the mouth closed around the mouthpiece, inhale deeply through the inhaler.
- Hold the breath for as long as comfortable and at the same time remove the inhaler from the mouth.
- After holding the breath, exhale and continue to breathe normally.
- The AFREZZA Inhaler can be used for up to 15 days from the date of first use. After 15 days of use, discard the inhaler and replace it with a new inhaler.
Recommended Starting Mealtime Dosage of AFREZZA
Insulin naïve patients
The initial dosage of AFREZZA is 4 units inhaled at the beginning of each meal.
Switching from Other Mealtime (prandial) Insulin Regimens to AFREZZA
When switching from another insulin to AFREZZA, a different insulin dosage may be needed and increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring and monitoring for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia may be needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 , 12.3 )].
Subcutaneous, Mealtime (prandial) Insulin:
Follow the recommendations in Table 1 to convert each injected mealtime insulin dosage (or bolus dosage for patients using insulin pumps) to the recommended mealtime dosage of AFREZZA.
Subcutaneous, Pre-Mixed Insulin:
- Refer to the prescribing information for the pre-mixed insulin to estimate the mealtime subcutaneous insulin dosage based on the product's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.
- Follow the recommendations in Table 1 to convert each estimated injected mealtime dosage to an AFREZZA mealtime dose.
- If basal insulin is clinically indicated, refer to the prescribing information for the chosen basal insulin for dosage recommendations.
• For AFREZZA doses exceeding the contents of a single cartridge at mealtime, use more than one cartridge. To achieve the required total mealtime dosage, use a combination of 4 unit, 8 unit, and 12 unit cartridges. When titrating dosages above 16 units after the initial conversion dosage, use combinations of different cartridges [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ), Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 ), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )] . | |
| Current Subcutaneous Mealtime Insulin Dosage | Starting Dosage of AFREZZA |
| Up to 3 units | 4 units |
| 4 to 5 units | 8 units |
| 6 to 7 units | 12 units |
| 8 or more units | 16 units |
Mealtime AFREZZA Dosage Modification
- Modify the mealtime AFREZZA dosage based on the patient's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results, and glycemic control goal.
- Dosage modifications may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )].
- Increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring during titration of AFREZZA. If blood glucose control is not achieved with increased AFREZZA dosages, consider discontinuing AFREZZA.
Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Dosage modification may be needed when:
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Inhalation Powder: single-use cartridges containing 4 units, 8 units or 12 units of insulin human as white powder.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited available data with AFREZZA use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine drug-associated risks for adverse developmental outcomes. Available information from published studies with human insulin use during pregnancy has not reported a clear association with human insulin and adverse developmental outcomes ( see Data ). There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy ( see Clinical Considerations ). In animal reproduction studies, there were no adverse developmental outcomes with subcutaneous administration of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) to pregnant rats during organogenesis at doses 21 times the human daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA, based on AUC (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6-10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20-25% in women with HbA1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for DKA, pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, stillbirth, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia- related morbidity.
Data
Human Data
There are limited data with AFREZZA use in pregnant women. Published data do not report a clear association with human insulin and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when human insulin is used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish the absence of any risk because of methodological limitations including small sample size and lack of blinding.
Animal Data
In pregnant rats given subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 6 through 17 (organogenesis), no major malformations were observed at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (21 times the human systemic exposure at a daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA, based on AUC).
In pregnant rabbits given subcutaneous doses of 2, 10, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 7 through 19 (organogenesis), adverse maternal effects were observed in all dose groups (at human systemic exposure following a daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA, based on AUC).
In pregnant rats given subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 7 through lactation day 20 (weaning), decreased epididymis and testes weights were observed in F1 male offspring, however, no decrease in fertility was noted, and impaired learning were observed in F1 pups at ³ 30 mg/kg/day (6 times the human systemic exposure at a daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA, based on AUC).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of AFREZZA in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. One small published study reported that exogenous subcutaneous insulin was present in human milk. No adverse effects in infants were noted. The carrier particles are present in rat milk ( see Data ). Potential adverse reactions that are related to inhalational administration of AFREZZA are unlikely to be associated with potential exposure of AFREZZA through breast milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for AFREZZA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from AFREZZA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Subcutaneous administration of the carrier particle in lactating rats resulted in excretion of the carrier particle in rat milk at levels that were approximately 10% of the maternal exposure. Given the results of the rat study, it is highly likely that the insulin and carrier in AFREZZA are excreted in human milk.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of AFREZZA to improve glycemic control in pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus have not been established.
Geriatric Use
In the AFREZZA clinical studies , 671 (12%) patients were 65 years of age or older, of which 42 (0.8%) were 75 years of age or older. In these studies, 381 (13%) of AFREZZA-treated patients were 65 years of age or older, of which 20 (0.7%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in effectiveness of AFREZZA have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . Clinical studies of AFREZZA did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether there were differences in safety between these patients and younger adult patients.
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies to assess the effect of age on pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics on insulin human, respectively, have not been conducted.
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of AFREZZA has not been studied. Frequent glucose monitoring and a lower dosage may be necessary in AFREZZA-treated patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of AFREZZA has not been studied. Some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with renal failure. Frequent glucose monitoring and a lower dosage may be necessary in AFREZZA-treated patients with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
AFREZZA is contraindicated:
- During episodes of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
- In patients with chronic lung disease, such as asthma or COPD, because of the risk of acute bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- In patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to any regular human insulin product or any of the inactive ingredients in AFREZZA. Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with AFREZZA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypoglycemia or Hyperglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen : Make necessary changes to a patient's insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. For patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, oral antidiabetic treatment dosage modifications may be needed. (5.2 )
- Hypoglycemia (may be life-threatening): Increase frequency of glucose monitoring in patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and those who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia. (5.3 )
- Decline in Pulmonary Function : Assess pulmonary function (e.g., spirometry (FEV 1 )) at baseline, after 6 months of therapy, and annually, even in the absence of pulmonary symptoms. In patients who have a decline of ≥ 20% in FEV 1 from baseline, consider discontinuing AFREZZA. Consider more frequent monitoring of pulmonary function in patients with pulmonary symptoms (5.4 )
- Lung Cancer : In patients with active lung cancer, a prior history of lung cancer, or in patients at risk for lung cancer, consider whether the benefits of AFREZZA use outweigh this potential risk. (5.5 )
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis : In patients at risk for DKA, increase the frequency of glucose monitoring and consider changing to alternate route of insulin delivery. (5.6 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions : Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with AFREZZA. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue AFREZZA, treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve. (5.7 )
- Hypokalemia (may be life-threatening): Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia. (5.8 )
- Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma Agonists: Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure; consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs. (5.9 )
Acute Bronchospasm in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease
Because of the risk of acute bronchospasm, AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma or COPD [see Contraindications (4 )] . Before initiating therapy with AFREZZA, evaluate patients with a medical history, physical examination, and spirometry (FEV 1 ) to identify potential underlying lung disease.
Acute bronchospasm has been observed in AFREZZA-treated patients with asthma and COPD. In a study of patients with asthma whose bronchodilators were temporarily withheld for assessment, bronchoconstriction and wheezing following AFREZZA dosing was reported in 29% (5/17) and 0% (0/13) of patients with and without a diagnosis of asthma, respectively. In this study, a mean decline in FEV 1 of 400 mL was observed 15 minutes after a single AFREZZA dose in patients with asthma. In a subset study of 8 patients with COPD, a mean decline in FEV 1 of 200 mL was observed 18 minutes after a single AFREZZA dose.
Hypoglycemia or Hyperglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen
Changes in an insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, injection site or type, or method of administration) may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] or hyperglycemia. If clinically indicated, make any necessary changes to a patient's insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage modifications of concomitant oral antidiabetic treatment may be needed [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , and 7.3 )] .
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including AFREZZA. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place an individual and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery).
AFREZZA's time action profile impacts the timing of hypoglycemia following inhalation of the drug product [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Hypoglycemia can occur suddenly, and symptoms may differ across patients and change over time in the same patient. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic nerve disease, in patients using medications that block the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., beta-blockers) [see Drug Interactions (7 )], or in patients who experience recurrent hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia after use of AFREZZA is related to the duration of action of the insulin and, in general, is highest when the glucose lowering effect of the insulin is maximal [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . The glucose lowering effect time course of AFREZZA may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and depends on many conditions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )] . Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to concomitantly administered medication [see Drug Interactions (7 )]. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )]. Advise patients to recognize and manage hypoglycemia and self-monitor glucose. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of glucose monitoring is recommended.
Decline in Pulmonary Function
AFREZZA causes a decline in pulmonary function over time as measured by FEV 1 . In clinical trials excluding patients with chronic lung disease and lasting up to 2 years, AFREZZA-treated patients experienced a small [40 mL (95% CI: -80, -1)] but greater FEV 1 decline than comparator-treated patients. The FEV 1 decline was noted within the first 3 months, and persisted for the entire duration of therapy (up to 2 years of observation). In this population, the annual rate of FEV 1 decline did not appear to worsen with increased duration of use. The effects of AFREZZA on pulmonary function for treatment duration longer than 2 years has not been established. There are insufficient data in long term studies to draw conclusions regarding reversal of the effect on FEV 1 after discontinuation of AFREZZA. The observed changes in FEV 1 were similar in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Assess pulmonary function (e.g., spirometry) at baseline, after the first 6 months of therapy, and annually thereafter, even in the absence of pulmonary symptoms. In patients who have a decline of ≥ 20% in FEV 1 from baseline, consider discontinuing AFREZZA. Consider more frequent monitoring of pulmonary function in patients with pulmonary symptoms such as wheezing, bronchospasm, breathing difficulties, or persistent or recurring cough. If symptoms persist, discontinue AFREZZA [see Adverse Reactions (6 )] .
Lung Cancer
In clinical trials, two cases of lung cancer, one in controlled trials and one in uncontrolled trials (2 cases in 2,750 patient-years of exposure), were observed in patients exposed to AFREZZA while no cases of lung cancer were observed in patients exposed to comparators (0 cases in 2,169 patient-years of exposure). In both cases, a prior history of heavy tobacco use was identified as a risk factor for lung cancer. Two additional cases of lung cancer (squamous cell and lung blastoma) occurred in non-smokers exposed to AFREZZA and were reported by investigators after clinical trial completion. These data are insufficient to determine whether AFREZZA has an effect on lung or respiratory tract tumors.
In patients with active lung cancer, a prior history of lung cancer, or in patients at risk for lung cancer, consider whether the benefits of AFREZZA use outweigh this potential risk.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
In clinical trials enrolling patients with type 1 diabetes, DKA was more common in AFREZZA-treated patients (0.43%; n=13) than in comparator-treated patients (0.14%; n=3). Patients with type 1 diabetes should always use AFREZZA concomitantly with basal insulin. In patients at risk for DKA, such as those with an acute illness or infection, increase the frequency of glucose monitoring and consider discontinuing AFREZZA and giving insulin using an alternate route of administration.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with AFREZZA.
If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue AFREZZA, treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve [see Adverse Reactions (6 )] . AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to any regular human insulin product or any of the inactive ingredients in AFREZZA [see Contraindications (4 )] .
Hypokalemia
All insulin products, including AFREZZA, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death.
Monitor potassium levels in AFREZZA-treated patients at risk for hypokalemia (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations and patients receiving intravenously administered insulin).
Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure.
Patients treated with insulin, including AFREZZA, and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR-gamma agonist should be considered.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Acute bronchospasm in patients with chronic lung disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Decline in pulmonary function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Lung cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure of 3,017 patients to AFREZZA and include 1,026 patients with type 1 diabetes and 1,991 patients with type 2 diabetes. The mean exposure duration was 8.2 months for patients with type 1 diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes. In the overall population:
- 1,874 patients were exposed to AFREZZA for 6 months and 724 patients for greater than one year.
- 620 and 1,254 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, were exposed to AFREZZA for up to 6 months.
- 238 and 486 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, were exposed to AFREZZA for greater than one year (median exposure was 1.8 years).
AFREZZA was studied in placebo and active-controlled trials (n = 3 and n = 10, respectively).
The mean age of the population was 50 years and 20 patients were older than 75 years of age; 51% of the population were males; 83% were White, 5% were Black or African American, and 2% were Asian; 10% were Hispanic. At baseline, the type 1 diabetes population had diabetes for an average of 17 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.3%, and the type 2 diabetes population had diabetes for an average of 11 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.8%. At baseline, 33% of the population reported peripheral neuropathy, 32% reported retinopathy and 20% had a history of cardiovascular disease.
Table 2 shows the frequency of common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of AFREZZA in the pool of controlled trials in type 2 diabetes patients that occurred more commonly on AFREZZA than on placebo and/or comparator and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with AFREZZA.
•Carrier particle without insulin was used as placebo [see Description (11.1 )] . | |||
| AFREZZA (n = 1,991) % | Placebo• (n = 290) % | Non-placebo comparators (n=1,363) % | |
| Cough | 26 4 3 3 2 2 2 | 20 4 3 1 1 1 0.3 | 5 1 2 2 1 1 1 |
| Throat pain or irritation | |||
| Headache | |||
| Diarrhea | |||
| Productive cough | |||
| Fatigue | |||
| Nausea | |||
Table 3 shows the frequency of common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of AFREZZA in the pool of active-controlled trials in type 1 diabetes patients. These adverse reactions were not present at baseline, occurred more commonly on AFREZZA than on comparator, and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with AFREZZA.
| AFREZZA (n=1,026) | Subcutaneous Insulin (n = 835) | |
| Cough | 29 | 5 |
| Throat pain or irritation | 6 | 2 |
| Headache | 5 | 3 |
| Pulmonary function test decreased | 3 | 1 |
| Bronchitis | 3 | 2 |
| Urinary tract infection | 2 | 2 |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most commonly observed adverse reaction in patients using insulin, including AFREZZA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] . The incidence of severe and non-severe hypoglycemia in AFREZZA-treated patients versus placebo-treated patients with type 2 diabetes is shown in Table 4 . A hypoglycemic episode was recorded if a patient reported symptoms of hypoglycemia with or without a blood glucose value consistent with hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia was defined as an event with symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia requiring the assistance of another person and associated with either a blood glucose value consistent with hypoglycemia or prompt recovery after treatment for hypoglycemia.
| AFREZZA (N=177) | Placebo (N=176) | |
| Severe Hypoglycemia | 5% | 2% |
| Non-Severe Hypoglycemia | 67% | 30% |
Cough
Approximately 27% of patients treated with AFREZZA reported cough, compared to approximately 5% of patients treated with comparator. In clinical trials, cough was the most common reason for discontinuation of AFREZZA therapy (3% of AFREZZA-treated patients).
Pulmonary Function Decline
In clinical trials lasting up to 2 years, excluding patients with chronic lung disease, patients treated with AFREZZA had a 40 mL (95% CI: -80, -1) greater decline from baseline in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV 1 ) compared to patients treated with comparator anti-diabetes treatments. The decline occurred during the first 3 months of therapy and persisted over 2 years (Figure 1 ). A decline in FEV 1 of ≥ 15% occurred in 6% of AFREZZA-treated patients compared to 3% of comparator-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )].
Figure 1. Mean (+/-SE) Change in FEV 1 (Liters) from Baseline for Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Patients
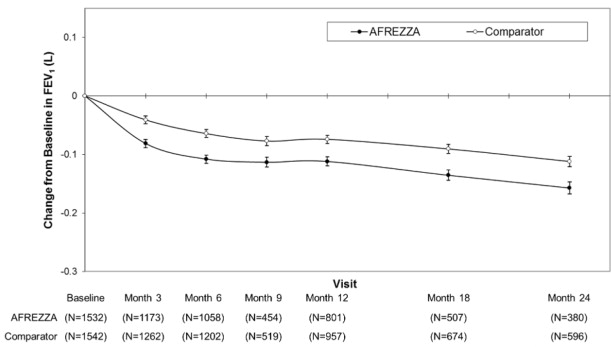
Weight Gain
Weight gain has occurred with some insulin therapies, including AFREZZA. Weight gain has been attributed to the anabolic effects of insulin and the decrease in glycosuria. In a clinical trial of patients with type 2 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14.3 )] , there was a mean 0.49 kg weight gain among AFREZZA-treated patients compared with a mean 1.13 kg weight loss among placebo-treated patients.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reaction has been identified during post approval use of AFREZZA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: bronchospasm.
Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Dosage modification may be needed when:
DESCRIPTION
AFREZZA Cartridges
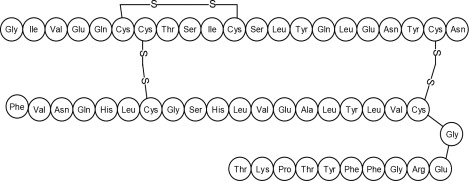
Human insulin is a rapid acting human insulin produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a non-pathogenic laboratory strain of Escherichia coli (K12). Chemically, human insulin has the empirical formula C 257 H 383 N 65 O 77 S 6 and a molecular weight of 5808. Human insulin has the following primary amino acid sequence:
AFREZZA (human insulin) inhalation powder is available in single-use plastic cartridges filled with a white powder containing insulin (human), which is administered via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA Inhaler only.
Insulin is adsorbed onto carrier particles consisting of fumaryl diketopiperazine (FDKP) and polysorbate 80.
AFREZZA Inhalation Powder is a dry powder supplied as 4 unit, 8 unit or 12 unit cartridges.
AFREZZA Inhaler
The AFREZZA Inhaler is breath-powered by the patient. When the patient inhales through the device, the powder is aerosolized and delivered to the lung. The amount of AFREZZA delivered to the lung will depend on individual patient factors.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels in adult patients with diabetes mellitus by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes, inhibits proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis.
Pharmacodynamics
The time course of insulin action (i.e., glucose lowering) may vary considerably in different patients or within the same patient, or when switching from subcutaneous mealtime insulin to AFREZZA. The average pharmacodynamic profile [i.e., glucose lowering effect measured by glucose infusion rate (GIR) over time in a euglycemic clamp study] after administration of a single AFREZZA dose of 4, 12, and 48 units in 30 patients with type 1 diabetes is shown in Figure 2(A) , and key characteristics regarding the timing of the effects are described in Table 5 :
| Parameter for Insulin Effect | AFREZZA 4 units | AFREZZA 12 units | AFREZZA 48 units |
| Time to first measurable effect | ~12 minutes | ~12 minutes | ~12 minutes |
| Time to peak effect | ~35 minutes | ~45 minutes | ~55 minutes |
| Time for effect to return to baseline | ~90 minutes | ~180 minutes | ~270 minutes |
Figure 2. Results After Administration of AFREZZA 4, 12, and 48 Units in Patients with T1DM (N=30)
A) Mean Insulin Effect (Baseline-Corrected Glucose Infusion Rate); and
B) Pharmacokinetic (Baseline-Corrected Serum Insulin Concentration Profiles)
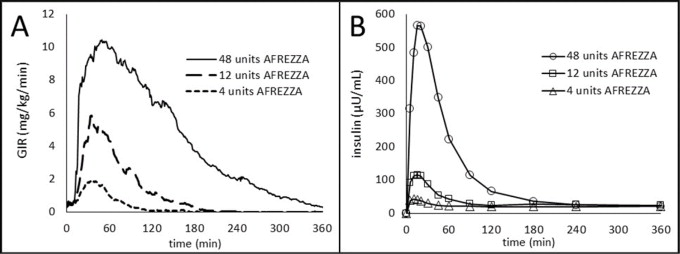
On average, the pharmacodynamics effect of AFREZZA, measured as area under the glucose infusion rate – time curve (AUC GIR) increased linearly with doses up to 48 units (106, 387, and 1581 mg/kg for 4, 12, and 48 units doses, respectively).
Intrapatient variability in AUC GIR and GIR max was approximately 28% (95% CI 21-42%) and 27% (95% CI 20-40%), respectively.
Pharmacokinetics
The area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC) of insulin increased dose proportionally up to 48 units. Intrapatient variability of AUC and peak concentration (C max ) of insulin was approximately 16% (95% CI 12-23%) and 21% (95% CI 16-30%), respectively.
Absorption
The pharmacokinetic profiles for orally inhaled AFREZZA 4, 12, and 48 units from a study in 30 patients with type 1 diabetes are shown in Figure 2(B) . A higher maximum plasma insulin concentration was achieved at an earlier timepoint in this study when patients were switched from subcutaneous mealtime insulin to AFREZZA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )]. The time to maximum serum insulin concentration (t max ) ranged from 10-20 minutes after oral inhalation of 4 to 48 units of AFREZZA.
Elimination
The apparent terminal half-life ranged from 120 to 206 minutes. Serum insulin concentrations declined to baseline by approximately 60 to 240 minutes.
Metabolism and Excretion
The metabolism and excretion of AFREZZA are comparable to regular human insulin.
Carrier Particles
Clinical pharmacology studies showed that carrier particles [see Description (11.1 )] are not metabolized and are eliminated unchanged in the urine following the lung absorption. Following oral inhalation of AFREZZA, a mean of 39% of the inhaled dose of carrier particles was distributed to the lungs and a mean of 7% of the dose was swallowed. The swallowed fraction was not absorbed from the GI tract and was eliminated unchanged in the feces.
Drug Interaction Studies
Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids
Albuterol increased the AUC insulin after AFREZZA administration by 25% in patients with asthma [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )]. AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with asthma.
In a study in healthy volunteers no significant change in insulin exposure was observed when fluticasone was administered following AFREZZA administration.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of insulin human or of other insulin human products.
Increases in anti-insulin antibody concentrations were observed in patients treated with AFREZZA. Increases in anti-insulin antibodies were observed more frequently in patients treated with AFREZZA than in patients treated with subcutaneously injected mealtime insulin. There was no clinically significant effect of anti-drug antibodies on safety or effectiveness (as measured by HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose) of AFREZZA over the treatment duration of the studies which spanned 3 to 24 months.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis
In a 104 week carcinogenicity study, rats were given doses up to 46 mg/kg/day of the carrier and up to 1.23 mg/kg/day of insulin, by nose-only inhalation. No increased incidence of tumors was observed at systemic exposures equivalent to the insulin at a daily AFREZZA dose of 99 mg, based on a comparison of relative body surface areas across species.
Mutagenesis
No increased incidence of tumors was observed in a 26 week carcinogenicity study in transgenic mice (Tg-ras-H2) given doses up to 75 mg/kg/day of carrier and up to 5 mg/kg/day of AFREZZA.
AFREZZA was not genotoxic in Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay and in the chromosome aberration assay, using human peripheral lymphocytes with or without metabolic activation. The carrier alone was not genotoxic in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In fertility study in male and female rats at subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier (vehicle without insulin), there were no adverse effects on male fertility at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day. In female rats dosed 2 weeks prior to mating until gestation day 7, there was increased pre- and post-implantation loss at 100 mg/kg/day but not at 30 mg/kg/day (21 times and 6 times, respectively the human systemic exposure at a daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA, based on AUC).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Overview of Clinical Studies of AFREZZA in Adults for Diabetes Mellitus
AFREZZA has been studied in adults with type 1 diabetes in combination with basal insulin. The efficacy of AFREZZA, in combination with basal insulin, in type 1 diabetes patients was compared to insulin aspart in combination with basal insulin.
AFREZZA has been studied in adults with type 2 diabetes in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs. The efficacy of AFREZZA in type 2 diabetes patients was compared to placebo inhalation.
Adults with Type 1 Diabetes
Patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes participated in a 24-week, open-label, active-controlled study to evaluate the glucose lowering effect of mealtime AFREZZA used in combination with a basal insulin. Following a 4-week basal insulin optimization period, 344 patients were randomized to AFREZZA by oral inhalation (n=174) or insulin aspart given subcutaneously (n=170) at each meal of the day. All patients received basal insulin. Mealtime insulin doses were titrated to glycemic goals for the first 12 weeks and kept stable for the last 12 weeks of the study.
Results
At Week 24, treatment with mealtime AFREZZA and basal insulin provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that met the pre-specified non-inferiority margin of 0.4%. AFREZZA and basal insulin provided less HbA1c reduction than insulin aspart and basal insulin, and the difference was statistically significant. More patients in the insulin aspart and basal insulin group achieved the HbA1c target of ≤7% (Table 6 ).
a Adjusted mean was obtained using a Mixed Model Repeated Measures (MMRM) approach with HbA1c or FPG as the dependent variable and treatment, visit, region, basal insulin stratum, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed factors, and corresponding baseline as a covariate. An autoregression (1) [AR(1)] covariance structure was used. | ||
b Data at 24 weeks were available from 131 (75%) and 150 (88%) patients randomized to the AFREZZA and insulin aspart groups, respectively. | ||
c The percentage was calculated based on the number of patients randomized to the trial. | ||
| Efficacy Parameter | AFREZZA + Basal Insulin (N=174) | Insulin Aspart + Basal Insulin (N=170) |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline (adjusted mean a ) | 7.94 | 7.92 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean a,b ) | -0.21 | -0.40 |
| Difference from insulin aspart (adjusted mean a,b ) (95% CI) | 0.19 (0.02, 0.36) | |
| Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c ≤ 7% c | 14% | 27% |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| Baseline (adjusted mean a ) | 153.9 | 151.6 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean a, b ) | -25.3 | 10.2 |
| Difference from insulin aspart (adjusted mean a, b ) (95% CI) | -35.4 (-56.3, -14.6) | |
Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
A total of 479 adult patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on optimal/maximally tolerated doses of metformin only, or 2 or more oral antidiabetic (OAD) agents participated in a 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Following a 6-week run-in period, 353 patients were randomized to AFREZZA by oral inhalation (n=177) or an inhaled placebo powder without insulin (n=176). Insulin doses were titrated for the first 12 weeks and kept stable for the last 12 weeks of the study. OADs doses were kept stable in the study.
Results
At Week 24, treatment with AFREZZA plus OADs provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that was statistically significantly greater compared to the HbA1c reduction observed in the placebo plus OADs group (Table 7 ).
a Adjusted mean was obtained using a Mixed Model Repeated Measures (MMRM) approach with HbA1c or FPG as the dependent variable and treatment, visit, region, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed factors, and corresponding baseline as a covariate. An autoregression (1) [AR(1)] covariance structure was used. | ||
b Data at 24 weeks without rescue therapy were available from 139 (79%) and 129 (73%) patients randomized to the AFREZZA and placebo groups, respectively. | ||
c The percentage was calculated based on the number of patients randomized to the trial. | ||
| Efficacy Parameter | AFREZZA + Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents (N=177) | Placebo + Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents (N=176) |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline (adjusted mean a ) | 8.25 | 8.27 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean a,b ) | -0.82 | -0.42 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean a,b ) (95% CI) | -0.40 (-0.57, -0.23) | |
| Percentage (%) of patients achieving HbA1C ≤7% c | 32% | 15% |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| Baseline (adjusted mean a ) | 175.9 | 175.2 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean a,b ) | -11.2 | -3.8 |
| Difference from placebo (adjusted mean a,b ) (95% CI) | -7.4 (-18.0, 3.2) | |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
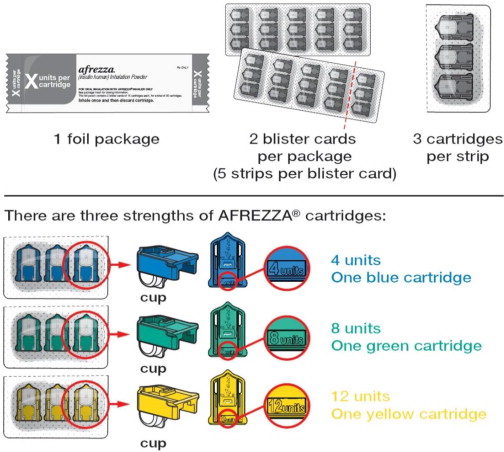
AFREZZA (insulin human) Inhalation Powder is available as 4 unit, 8 unit and 12 unit single-use cartridges. Three cartridges are contained in a single cavity of a blister strip. Each card contains 5 blister strips (each containing three cartridges) separated by perforations for a total of 15 cartridges. Two cards of the same cartridge strength are packaged in a foil laminate overwrap (30 cartridges per foil package).
The cartridges are color-coded, blue for 4 units, green for 8 units and yellow for 12 units. Each cartridge is marked with “afrezza” and “4 units”, “8 units” or “12 units”.
The AFREZZA Inhaler is individually packaged in a clear overwrap. The inhaler is fully assembled with a removable mouthpiece cover. The AFREZZA Inhaler can be used for up to 15 days from the date of first use. After 15 days of use, the inhaler must be discarded and replaced with a new inhaler.
AFREZZA (insulin human) Inhalation Powder is available in the following configurations:
| NDC | Cartridge Strength | Quantity of Cartridges per Strength | Total Quantity of Cartridges per Kit | Total Units in Kit | Number of Inhalers |
| 47918-874-90 | 4 units | 90 | 90 | 360 Units | 2 |
| 47918-878-90 | 8 units | 90 | 90 | 720 Units | 2 |
| 47918-891-90 | 12 units | 90 | 90 | 1,080 Units | 2 |
| 47918-898-18 | 8 units, 12 units | 90 | 180 | 1,800 Units | 2 |
| 47918-880-18 (Titration Pack) | 4 units, 8 units | 90 | 180 | 1,080 Units | 2 |
| 47918-902-18 (Titration Pack) | 4 units, 8 units, 12 units | 60 | 180 | 1,440 Units | 2 |
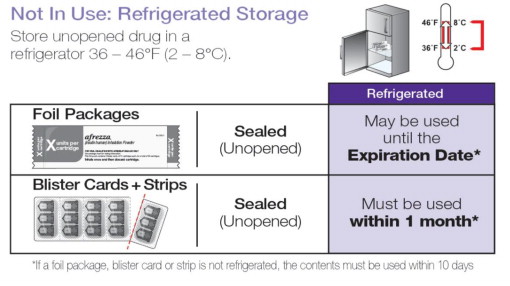
Storage :
Not in Use: Refrigerated Storage 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF)
• If a foil package, blister card or strip is not refrigerated, the contents must be used within 10 days. | |
| Sealed (Unopened) Foil Package | May be stored until the Expiration Date• |
| Sealed (Unopened) Blister Cards and Strips | Must be used within 1 month• |
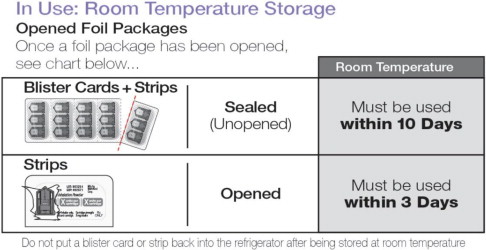
In Use: Room Temperature Storage 25ºC (77ºF), excursions permitted 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF)
| Sealed (Unopened) Blister Cards and Strips | Must be used within 10 days |
| Opened Strips | Must be used within 3 days |
Do not put a blister card or strip back into the refrigerator after being stored at room temperature.
Inhaler Storage :
Store refrigerated or at room temperature 2ºC to 25ºC (36ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted. Inhaler may be stored refrigerated, but should be at room temperature before use.
Handling :
Before use, cartridges should be at room temperature for 10 minutes.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
AFREZZA® (uh-FREZZ-uh)
(insulin human)
inhalation powder, for oral inhalation use
This “Instructions for Use” contains information on how to use AFREZZA ® (insulin human) Inhalation Powder.
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using AFREZZA and each time you get a new AFREZZA Inhaler. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Your healthcare provider should show you how to use your AFREZZA Inhaler the right way before you use it for the first time.
Important information about AFREZZA:
- AFREZZA starts acting fast, so take your medicine right before you eat a meal.
- AFREZZA comes in 3 strengths (see Figure A ):
- 4 units (blue cartridge)
- 8 units (green cartridge)
- 12 units (yellow cartridge)

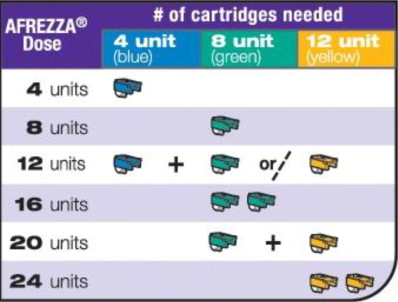
- If your prescribed AFREZZA dose is higher than 12 units, you will need to use more than 1 cartridge.
- If you need to use more than 1 cartridge for your dose, throw away the used cartridge before getting a new one. You can tell when a cartridge has been used, because the cup has moved to the center.
- Do not try to open the AFREZZA cartridges. The AFREZZA Inhaler opens the cartridge automatically during use.
- AFREZZA cartridges should only be used with the AFREZZA Inhaler. Do not try to breathe in the AFREZZA insulin powder in any other way. Do not put cartridges in your mouth and do not swallow cartridges.
- Use only 1 AFREZZA Inhaler at a time. The same inhaler should be used for the 4 unit, 8 unit or 12 unit cartridges.
- Store the inhaler in a clean, dry place with the mouthpiece cover on until your next dose.
- Throw away your AFREZZA Inhaler after 15 days and get a new one.
If you are having problems with your AFREZZA Inhaler or if it breaks and you need a new one, call 1-877-323-8505.
Know your AFREZZA Inhaler:
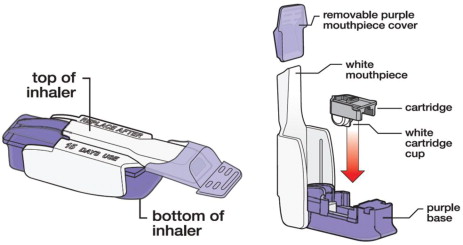
Know your AFREZZA cartridges:
| How to take your dose of AFREZZA: Always be sure you have the right number of AFREZZA cartridges for your dose available before you start. AFREZZA cartridges must only be used with the AFREZZA Inhaler. | |
| Step 1: Select the AFREZZA cartridges for your dose | |
| Use the figure below (Figure B ) to select the AFREZZA cartridges for your dose. Note: If your prescribed AFREZZA dose is higher than 12 units, you will need to use more than 1 cartridge. If you have any questions about which cartridges you should use to administer your prescribed AFREZZA dose, talk with your prescribing health care provider. | |
 | |
 | Open Packages Remove a blister card from the foil package. Tear along perforation to remove one strip. |
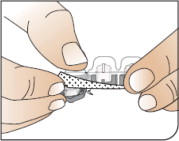 | Push Cartridges to Remove Remove a cartridge from the strip by pressing on the clear side to push the cartridge out. Remove the right number of cartridges for your dose. Pushing on the cup will not damage the cartridge. AFREZZA cartridges left over in an opened strip must be used within 3 days. |
 | |
| Before Proceeding: Check that you have the right AFREZZA cartridge(s) for your dose. Use only 1 inhaler for multiple cartridges. Throw away your AFREZZA Inhaler after 15 days and get a new one. | |
| Step 2: Loading a cartridge | |||
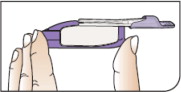 | Hold Inhaler Hold the inhaler level in one (1) hand with the white mouthpiece on the top and purple base on the bottom. | ||
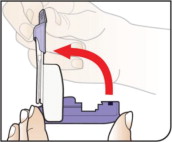 | Open Inhaler Open the inhaler by lifting the white mouthpiece to a vertical position. Before you put the AFREZZA cartridge in your inhaler, make sure it has been at room temperature for 10 minutes . | ||
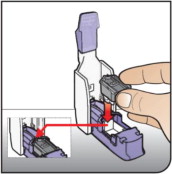 | Place Cartridge Hold the cartridge with the cup facing down. Line up the cartridge with the opening in the inhaler. The pointed end of the cartridge should line up with the pointed end in the inhaler. Place the cartridge into the inhaler. Be sure that the cartridge lies flat in the inhaler. | ||
 If any of these occur, throw away the cartridge and load a new cartridge. If any of these occur, throw away the cartridge and load a new cartridge. | |||
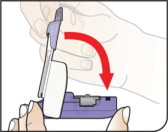 | Close Inhaler Lower the mouthpiece to close the inhaler (this will open the drug cartridge). You should feel a snap when the inhaler is closed. | ||
| Step 3: Inhaling AFREZZA | |||
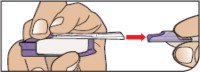 | Remove the Mouthpiece Cover Important: Keep the inhaler level during and after removal of the purple mouthpiece cover. | ||
 | |||
 | Exhale Hold the inhaler away from your mouth and fully blow out (exhale). | ||
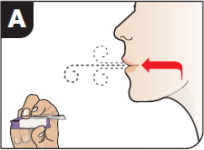
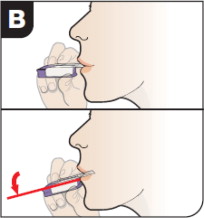 | Position Inhaler in Mouth Keeping your head level, place the mouthpiece in your mouth and tilt the inhaler down towards your chin, as shown. Close your lips around the mouthpiece to form a seal. Tilt the inhaler downward while keeping your head level. | ||
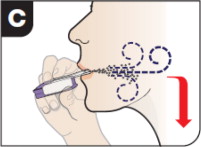 | Inhale Deeply and Hold Breath With your mouth closed around the mouthpiece, inhale deeply through the inhaler . Hold your breath for as long as comfortable and at the same time remove the inhaler from your mouth. After holding your breath, exhale and continue to breathe normally. | ||
| Step 4: Removing a used cartridge | |
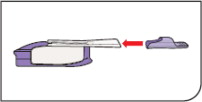 | Replace Mouthpiece Cover Place the purple mouthpiece cover back onto the inhaler. |
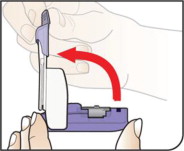 | Open Inhaler Open the inhaler by lifting up the white mouthpiece. |
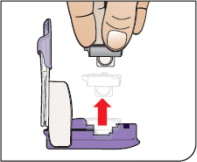 | Remove Cartridge Remove the cartridge from the purple base. |
 | Throw away (or recycle) the Cartridge Throw away the used cartridge in your regular household trash. Alternatively, the used cartridge (composed of HDPE, assigned recycling number 2) can be recycled. |
| Multiple cartridge dosing | |
| If you need more than one (1) AFREZZA cartridge for your dose, see the AFREZZA dosage chart above (Figure B ). | 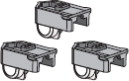 |
| Repeat steps 2 through 4 for each AFREZZA cartridge you need for your prescribed AFREZZA dose. | |
 | |
| How should I store AFREZZA? |
 |
 |
 |
| Caring for your AFREZZA Inhaler: |
|
|
|
Manufactured by: MannKind Corporation Danbury, CT 06810 US License No. #2190 © 2016 – 2024 MannKind Corporation
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 01/2026
AFREZZA is a registered trademark of MannKind Corporation Patent: www.mannkindcorp.com/patent-notices
Mechanism of Action
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels in adult patients with diabetes mellitus by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes, inhibits proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis.


