Apretude prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Apretude patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HIV-1 Screening: Screen all individuals for HIV-1 infection immediately prior to initiating APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP and prior to each injection while taking APRETUDE. (2.2 )
- Prior to initiating APRETUDE, an oral lead-in dosing may be used for approximately 1 month with the recommended dosage to assess the tolerability of APRETUDE. (2.4 )
- For gluteal intramuscular injection only. (2.5 , 2.7 )
- Recommended Dosing Schedule: Initiate APRETUDE with a single 600-mg (3-mL) injection given 1 month apart for 2 consecutive months on the last day of an oral lead-in if used or within 3 days and continue with the injections every 2 months thereafter. (2.5 )
Dosage and Administration Overview
- APRETUDE contains cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension in a single-dose vial [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )] .
- APRETUDE must be administered by a healthcare provider by gluteal intramuscular injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.7 )] .
- APRETUDE may be initiated with oral cabotegravir prior to the intramuscular injections or the patient may proceed directly to injection of APRETUDE without an oral lead-in [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] .
HIV-1 Screening for Individuals Receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis
Individuals must be tested for HIV-1 infection prior to initiating APRETUDE or oral cabotegravir, and with each subsequent injection of APRETUDE, using a test approved or cleared by the FDA for the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection. If an antigen/antibody-specific test is used and provides negative results, then such negative results should be confirmed using an RNA-specific assay, even if the results of the RNA-assay are available after APRETUDE or oral cabotegravir administration [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Adherence to APRETUDE
Prior to starting APRETUDE, healthcare providers should carefully select individuals who agree to the required injection dosing and testing schedule and counsel individuals about the importance of adherence to scheduled dosing visits to help reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection and development of resistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.3 ), Microbiology (12.4 )] .
Optional Oral Lead-In Dosing to Assess Tolerability of APRETUDE
The healthcare provider and individual may decide to use an oral lead-in with oral cabotegravir prior to the initiation of APRETUDE to assess the tolerability of cabotegravir or the healthcare provider and individual may proceed directly to injection of APRETUDE without the use of an oral lead-in [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] .
No safety and efficacy data are available for use of APRETUDE without an oral lead-in [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )]. However, in HIV-1 treatment clinical trials, data show that an oral lead-in is not needed to ensure adequate plasma cabotegravir exposure upon initiation of injections and that the safety and efficacy results of CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension) were similar when administered with and without an oral lead-in.
Gluteal Intramuscular Injection Dosing with APRETUDE
Initiation Injections
If an oral lead-in is used, initiation injections should be administered on the last day of oral lead‑in or within 3 days thereafter. The recommended initiation injection doses of APRETUDE in individuals is a single 600‑mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE given 1 month apart for 2 consecutive months (Table 1 and Table 2 ). Individuals may be given the second APRETUDE initiation injection up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections.
Continuation Injections
After the 2 initiation injection doses given consecutively 1 month apart, the recommended continuation injection dose of APRETUDE is a single 600-mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE every 2 months (Table 2 ). Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections.
| a Should be administered on the last day of oral lead-in or within 3 days thereafter. | ||
| b Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections. | ||
Oral Lead-In (Month Prior | Intramuscular (Gluteal) | Intramuscular (Gluteal) Continuation Injection |
Oral cabotegravir 30 mg by mouth once daily for 28 days | APRETUDE a 600-mg (3 mL) | APRETUDE b 600-mg (3 mL) |
| a Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections. | |
Intramuscular (Gluteal) | Intramuscular (Gluteal) |
APRETUDE a | APRETUDE a |
600-mg (3 mL) | 600-mg (3 mL) |
Recommended Dosing Schedule for Missed Injections
Adherence to the injection dosing schedule is strongly recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] . Individuals who miss a scheduled injection visit should be clinically reassessed to ensure resumption of APRETUDE remains appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 )] . Refer to Table 3 for dosing recommendations after missed injections.
Planned Missed Injections
If an individual plans to miss a scheduled every-2-month continuation injection visit by more than 7 days, take daily oral cabotegravir for up to 2 months to replace 1 missed scheduled every-2-month injection. The recommended oral daily dose is one 30-mg tablet of oral cabotegravir. The first dose of oral cabotegravir (or alternative oral PrEP regimen) should be taken approximately 2 months after the last injection dose of APRETUDE. Restart injection with APRETUDE on the day oral cabotegravir dosing completes or within 3 days, thereafter, as recommended in Table 3 . For oral PrEP durations greater than 2 months, an alternative regimen to oral cabotegravir is recommended.
Unplanned Missed Injections
If a scheduled injection visit is missed or delayed by more than 7 days and oral dosing has not been taken in the interim, clinically reassess the individual to determine if resumption of injection dosing remains appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . If the injection dosing schedule will be continued, see Table 3 for dosing recommendations.
Time since Last Injection | Recommendation |
If second injection is missed and time since first injection is: | |
Less than or equal to 2 months | Administer 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE as soon as possible, then continue to follow the every-2-month injection dosing schedule. |
Greater than 2 months | Restart with 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE, followed by a second 600-mg (3-mL) initiation injection dose 1 month later. Then continue to follow the every-2-month injection dosing schedule thereafter. |
If third or subsequent injection is missed and time since prior injection is: | |
Less than or equal to 3 months | Administer 600-mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE as soon as possible, then continue with the every-2-month injection dosing schedule. |
Greater than 3 months | Restart with 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE, followed by the second 600-mg (3-mL) initiation injection dose 1 month later. Then continue with the every-2-month injection dosing schedule thereafter. |
Administration Instructions
Refer to the Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations. Carefully follow these instructions and ensure that the vial adaptor is used correctly when preparing the suspension for injection to avoid leakage.
APRETUDE is a suspension for gluteal intramuscular injection that does not need further dilution or reconstitution.
The ventrogluteal site is recommended for injection. A dorsogluteal approach (upper outer quadrant) is acceptable, if preferred by the healthcare professional. Do not administer by any other route or anatomical site. Consider the body mass index (BMI) of the individual to ensure that the needle length is sufficient to reach the gluteus muscle. Longer needle lengths (not included in the dosing kit) may be required for individuals with higher BMI (e.g., >30 kg/m 2 ) to ensure that the injection is administered intramuscularly as opposed to subcutaneously.
If the pack has been stored in the refrigerator, the vial should be brought to room temperature prior to administration (not to exceed 30°C [86°F]).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. The APRETUDE vial has a brown tint to the glass that may limit visual inspection. Discard the vial if the medicine exhibits particulate matter or discoloration.
Shake the vial vigorously so that the suspension looks uniform before injecting. Small air bubbles are expected and acceptable.
Once the suspension has been drawn into the syringe, the injection should be administered as soon as possible, but may remain in the syringe for up to 2 hours. The filled syringe should not be placed in the refrigerator. If the medicine remains in the syringe for more than 2 hours, the filled syringe and needle must be discarded [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )].

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Apretude prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF DRUG RESISTANCE WITH USE OF APRETUDE FOR HIV-1 PRE‑EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS (PrEP) IN UNDIAGNOSED HIV-1 INFECTION
Individuals must be tested for HIV-1 infection prior to initiating APRETUDE or oral cabotegravir, and with each subsequent injection of APRETUDE, using a test approved or cleared by the FDA for the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection. Drug-resistant HIV-1 variants have been identified with use of APRETUDE by individuals with undiagnosed HIV-1 infection. Do not initiate APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP unless negative infection status is confirmed. Individuals who acquire HIV-1 while receiving APRETUDE for PrEP must transition to a complete HIV-1 treatment regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Warnings and Precautions, Hypersensitivity Reactions (5.4 ) | 4/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
APRETUDE is indicated for pre‑exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to reduce the risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents weighing at least 35 kg who are at risk for HIV-1 acquisition. Individuals must have a negative HIV-1 test prior to initiating APRETUDE (with or without an oral lead-in with oral cabotegravir) for HIV-1 PrEP [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.4 ), Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HIV-1 Screening: Screen all individuals for HIV-1 infection immediately prior to initiating APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP and prior to each injection while taking APRETUDE. (2.2 )
- Prior to initiating APRETUDE, an oral lead-in dosing may be used for approximately 1 month with the recommended dosage to assess the tolerability of APRETUDE. (2.4 )
- For gluteal intramuscular injection only. (2.5 , 2.7 )
- Recommended Dosing Schedule: Initiate APRETUDE with a single 600-mg (3-mL) injection given 1 month apart for 2 consecutive months on the last day of an oral lead-in if used or within 3 days and continue with the injections every 2 months thereafter. (2.5 )
Dosage and Administration Overview
- APRETUDE contains cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension in a single-dose vial [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )] .
- APRETUDE must be administered by a healthcare provider by gluteal intramuscular injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.7 )] .
- APRETUDE may be initiated with oral cabotegravir prior to the intramuscular injections or the patient may proceed directly to injection of APRETUDE without an oral lead-in [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] .
HIV-1 Screening for Individuals Receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis
Individuals must be tested for HIV-1 infection prior to initiating APRETUDE or oral cabotegravir, and with each subsequent injection of APRETUDE, using a test approved or cleared by the FDA for the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection. If an antigen/antibody-specific test is used and provides negative results, then such negative results should be confirmed using an RNA-specific assay, even if the results of the RNA-assay are available after APRETUDE or oral cabotegravir administration [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Adherence to APRETUDE
Prior to starting APRETUDE, healthcare providers should carefully select individuals who agree to the required injection dosing and testing schedule and counsel individuals about the importance of adherence to scheduled dosing visits to help reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection and development of resistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.3 ), Microbiology (12.4 )] .
Optional Oral Lead-In Dosing to Assess Tolerability of APRETUDE
The healthcare provider and individual may decide to use an oral lead-in with oral cabotegravir prior to the initiation of APRETUDE to assess the tolerability of cabotegravir or the healthcare provider and individual may proceed directly to injection of APRETUDE without the use of an oral lead-in [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] .
No safety and efficacy data are available for use of APRETUDE without an oral lead-in [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )]. However, in HIV-1 treatment clinical trials, data show that an oral lead-in is not needed to ensure adequate plasma cabotegravir exposure upon initiation of injections and that the safety and efficacy results of CABENUVA (cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended-release injectable suspension) were similar when administered with and without an oral lead-in.
Gluteal Intramuscular Injection Dosing with APRETUDE
Initiation Injections
If an oral lead-in is used, initiation injections should be administered on the last day of oral lead‑in or within 3 days thereafter. The recommended initiation injection doses of APRETUDE in individuals is a single 600‑mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE given 1 month apart for 2 consecutive months (Table 1 and Table 2 ). Individuals may be given the second APRETUDE initiation injection up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections.
Continuation Injections
After the 2 initiation injection doses given consecutively 1 month apart, the recommended continuation injection dose of APRETUDE is a single 600-mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE every 2 months (Table 2 ). Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections.
| a Should be administered on the last day of oral lead-in or within 3 days thereafter. | ||
| b Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections. | ||
Oral Lead-In (at Least 28 Days) (Month Prior to Starting Injections) | Intramuscular (Gluteal) Initiation Injection (Month 1 and Month 2) | Intramuscular (Gluteal) Continuation Injection (Month 4 and Every 2 Months Onwards) |
Oral cabotegravir 30 mg by mouth once daily for 28 days | APRETUDE a 600-mg (3 mL) | APRETUDE b 600-mg (3 mL) |
| a Individuals may be given APRETUDE up to 7 days before or after the date the individual is scheduled to receive the injections. | |
Intramuscular (Gluteal) Initiation Injection (Month 1 and Month 2) | Intramuscular (Gluteal) Continuation Injection (Month 4 and Every 2 Months Onwards) |
APRETUDE a | APRETUDE a |
600-mg (3 mL) | 600-mg (3 mL) |
Recommended Dosing Schedule for Missed Injections
Adherence to the injection dosing schedule is strongly recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] . Individuals who miss a scheduled injection visit should be clinically reassessed to ensure resumption of APRETUDE remains appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 )] . Refer to Table 3 for dosing recommendations after missed injections.
Planned Missed Injections
If an individual plans to miss a scheduled every-2-month continuation injection visit by more than 7 days, take daily oral cabotegravir for up to 2 months to replace 1 missed scheduled every-2-month injection. The recommended oral daily dose is one 30-mg tablet of oral cabotegravir. The first dose of oral cabotegravir (or alternative oral PrEP regimen) should be taken approximately 2 months after the last injection dose of APRETUDE. Restart injection with APRETUDE on the day oral cabotegravir dosing completes or within 3 days, thereafter, as recommended in Table 3 . For oral PrEP durations greater than 2 months, an alternative regimen to oral cabotegravir is recommended.
Unplanned Missed Injections
If a scheduled injection visit is missed or delayed by more than 7 days and oral dosing has not been taken in the interim, clinically reassess the individual to determine if resumption of injection dosing remains appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . If the injection dosing schedule will be continued, see Table 3 for dosing recommendations.
Time since Last Injection | Recommendation |
If second injection is missed and time since first injection is: | |
Less than or equal to 2 months | Administer 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE as soon as possible, then continue to follow the every-2-month injection dosing schedule. |
Greater than 2 months | Restart with 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE, followed by a second 600-mg (3-mL) initiation injection dose 1 month later. Then continue to follow the every-2-month injection dosing schedule thereafter. |
If third or subsequent injection is missed and time since prior injection is: | |
Less than or equal to 3 months | Administer 600-mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection of APRETUDE as soon as possible, then continue with the every-2-month injection dosing schedule. |
Greater than 3 months | Restart with 600-mg (3-mL) gluteal intramuscular injection of APRETUDE, followed by the second 600-mg (3-mL) initiation injection dose 1 month later. Then continue with the every-2-month injection dosing schedule thereafter. |
Administration Instructions
Refer to the Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations. Carefully follow these instructions and ensure that the vial adaptor is used correctly when preparing the suspension for injection to avoid leakage.
APRETUDE is a suspension for gluteal intramuscular injection that does not need further dilution or reconstitution.
The ventrogluteal site is recommended for injection. A dorsogluteal approach (upper outer quadrant) is acceptable, if preferred by the healthcare professional. Do not administer by any other route or anatomical site. Consider the body mass index (BMI) of the individual to ensure that the needle length is sufficient to reach the gluteus muscle. Longer needle lengths (not included in the dosing kit) may be required for individuals with higher BMI (e.g., >30 kg/m 2 ) to ensure that the injection is administered intramuscularly as opposed to subcutaneously.
If the pack has been stored in the refrigerator, the vial should be brought to room temperature prior to administration (not to exceed 30°C [86°F]).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. The APRETUDE vial has a brown tint to the glass that may limit visual inspection. Discard the vial if the medicine exhibits particulate matter or discoloration.
Shake the vial vigorously so that the suspension looks uniform before injecting. Small air bubbles are expected and acceptable.
Once the suspension has been drawn into the syringe, the injection should be administered as soon as possible, but may remain in the syringe for up to 2 hours. The filled syringe should not be placed in the refrigerator. If the medicine remains in the syringe for more than 2 hours, the filled syringe and needle must be discarded [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )].
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: Single-dose vial containing 600 mg/3 mL (200 mg/mL) of cabotegravir extended‑release injectable suspension.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Assess the benefit-risk of using APRETUDE to the infant while breastfeeding due to the potential for adverse reactions and residual concentrations in the systemic circulation for up to 12 months or longer after discontinuation. (8.2 )
- Pediatrics: Not recommended in individuals weighing <35 kg. (8.4 )
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to APRETUDE during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register individuals by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
There are insufficient human data on the use of APRETUDE during pregnancy to adequately assess a drug-associated risk of birth defects and miscarriage. Discuss the benefit-risk of using APRETUDE with individuals of childbearing potential or during pregnancy.
Cabotegravir use in pregnant individuals has not been evaluated. APRETUDE should be used during pregnancy only if the expected benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
The APR has been established to monitor for birth defects following prenatal exposure to antiretrovirals. The rate of miscarriage is not reported in the APR. The background rate for major birth defects in a U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) is 2.7%. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15% to 20%. The APR uses the MACDP as the U.S. reference population for birth defects in the general population. The MACDP evaluates mothers and infants from a limited geographic area and does not include outcomes for births that occurred at <20 weeks’ gestation.
In animal reproduction studies with oral cabotegravir, a delay in the onset of parturition and increased stillbirths and neonatal deaths were observed in a rat pre- and postnatal development study at >28 times the exposure at the recommended human dose (RHD). No evidence of adverse developmental outcomes was observed with oral cabotegravir in rats or rabbits (>28 times or similar to the exposure at the RHD, respectively) given during organogenesis (see Data) .
Clinical Considerations
Cabotegravir is detected in systemic circulation for up to 12 months or longer after discontinuing injections of APRETUDE; therefore, consideration should be given to the potential for fetal exposure during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Data
Animal Data: Cabotegravir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 0.5, 5, or 1,000 mg/kg/day from 15 days before cohabitation, during cohabitation, and from Gestation Days 0 to 17. There were no effects on fetal viability when fetuses were delivered by caesarean, although a minor decrease in fetal body weight was observed at 1,000 mg/kg/day (>28 times the exposure in humans at the RHD). No drug-related fetal toxicities were observed at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 13 times the exposure in humans at the RHD), and no drug-related fetal malformations were observed at any dose.
Cabotegravir was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at 0, 30, 500, or 2,000 mg/kg/day from Gestation Days 7 to 19. No drug-related fetal toxicities were observed at 2,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.7 times the exposure in humans at the RHD).
In a rat pre- and postnatal development study, cabotegravir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 0.5, 5, or 1,000 mg/kg/day from Gestation Day 6 to Lactation Day 21. A delay in the onset of parturition and increases in the number of stillbirths and neonatal deaths by Lactation Day 4 were observed at 1,000 mg/kg/day (>28 times the exposure in humans at the RHD); there were no alterations to growth and development of surviving offspring. In a cross-fostering study, similar incidences of stillbirths and early postnatal deaths were observed when rat pups born to cabotegravir-treated mothers were nursed from birth by control mothers. There was no effect on neonatal survival of control pups nursed from birth by cabotegravir-treated mothers. A lower dose of 5 mg/kg/day (13 times the exposure at the RHD) was not associated with delayed parturition or neonatal mortality in rats. Studies in pregnant rats showed that cabotegravir crosses the placenta and can be detected in fetal tissue.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of cabotegravir in human milk. Cabotegravir is present in animal milk (see Data) . When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. It is not known if cabotegravir affects human milk production, or has effects on the breastfed infant. If cabotegravir is present in human milk, residual exposures may remain for 12 months or longer after the last injections have been administered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Cabotegravir concentrations may be detectable in systemic circulation for up to 12 months or longer after discontinuing injections of APRETUDE. Breastfeeding should only be considered if the expected benefit justifies the potential risk to the infant, including the potential risk for adverse reaction in the breastfed child, along with the risk of HIV-1 acquisition due to nonadherence and subsequent vertical transmission to the child. Breastfeeding is not recommended if acute HIV-1 infection is suspected to avoid the risk of postnatal transmission of HIV-1 infection.
Data
Animal lactation studies with cabotegravir have not been conducted. However, cabotegravir was detected in the plasma of nursing pups on Lactation Day 10 in the rat pre- and postnatal development study.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP in adolescents weighing at least 35 kg who are at risk for HIV-1 acquisition is supported by data from 2 adequate and well-controlled trials of APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP in adults with additional safety and pharmacokinetic data from studies in adults with HIV-1 who were administered CABENUVA, and in adolescent participants with HIV-1 who were administered separate components of CABENUVA in addition to their current antiretroviral therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ), Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP was evaluated in 2 open-label multicenter clinical trials, HPTN 083-01 and HPTN 084-01, in adolescent individuals 12 to less than 18 years of age weighing at least 35 kg who are at risk for HIV-1 acquisition. Sixty-four adolescents were enrolled. Of these, 62 adolescent participants received one or more injections. In adolescents receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP, the safety data were comparable to the safety data reported in adults receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP.
While using APRETUDE, HIV-1 testing should be conducted prior to initiating APRETUDE (with or without an oral lead-in with oral cabotegravir) and prior to each injection of APRETUDE. Adolescents may benefit from more frequent visits and counseling to support adherence to the dosing and testing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of APRETUDE in pediatric participants younger than 12 years of age or weighing <35 kg have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is required in elderly individuals. There are limited data available on the use of APRETUDE in individuals aged 65 years and older. In general, caution should be exercised in administration of APRETUDE in elderly individuals, reflecting greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Renal Impairment
Based on studies with oral cabotegravir, no dosage adjustment of APRETUDE is necessary for individuals with mild (creatinine clearance ≥60 to <90 mL/min), moderate (creatinine clearance ≥30 to <60 mL/min) or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≥15 to <30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . In individuals with end-stage renal disease not on dialysis, effects on the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir are unknown. As cabotegravir is >99% protein bound, dialysis is not expected to alter exposures of cabotegravir.
Hepatic Impairment
Based on studies with oral cabotegravir, no dosage adjustment of APRETUDE is necessary for individuals with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B). The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
APRETUDE is contraindicated in individuals:
- with unknown or positive HIV-1 status [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 )] .
- with previous hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
- receiving the following coadministered drugs for which significant decreases in cabotegravir plasma concentrations may occur due to uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A1 enzyme induction, which may result in reduced effectiveness [see Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] :
- Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
- Antimycobacterials: Rifampin, rifapentine
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Comprehensive management to reduce the risk of HIV-1 acquisition. (5.1 )
- Potential risk of developing resistance to APRETUDE if an individual acquires HIV-1 either before or while taking APRETUDE or following discontinuation of APRETUDE. Reassess risk of HIV-1 acquisition and test before each injection to confirm HIV-1 negative status. (5.2 )
- Residual concentrations of cabotegravir may remain in the systemic circulation of individuals up to 12 months or longer. (5.3 )
- Serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with cabotegravir and include Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Discontinue APRETUDE immediately if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions develop. (5.4 )
- Hepatotoxicity has been reported in individuals receiving cabotegravir. Clinical and laboratory monitoring should be considered. Discontinue APRETUDE if hepatotoxicity is suspected. (5.5 )
- Depressive disorders have been reported with APRETUDE. Prompt evaluation is recommended for depressive symptoms. (5.6 )
Comprehensive Management to Reduce the Risk of HIV-1 Infection
Use APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP to reduce the risk of HIV-1 infection as part of a comprehensive prevention strategy including adherence to the administration schedule and safer sex practices, including condoms, to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). APRETUDE is not always effective in preventing HIV-1 acquisition [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . The time from initiation of APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP to maximal protection against HIV-1 infection is unknown.
Risk for HIV-1 acquisition includes behavioral, biological, or epidemiologic factors including, but not limited to, condomless sex, past or current STIs, self-identified HIV risk, having sexual partners of unknown HIV-1 viremic status, or sexual activity in a high prevalence area or network.
Counsel individuals on the use of other prevention measures (e.g., consistent and correct condom use; knowledge of partner(s)’ HIV-1 status, including viral suppression status; regular testing for STIs that can facilitate HIV-1 transmission). Inform individuals about and support their efforts in reducing sexual risk behavior.
Use APRETUDE to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 only in individuals confirmed to be HIV‑1 negative [see Contraindications (4 )] . HIV-1 resistance substitutions may emerge in individuals with undiagnosed HIV‑1 infection who are taking only APRETUDE, because APRETUDE alone does not constitute a complete regimen for HIV-1 treatment [see Microbiology (12.4 )] ; therefore, care should be taken to minimize the risk of initiating or continuing APRETUDE before confirming the individual is HIV-1 negative.
- Prior to initiating APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP, ask seronegative individuals about recent (in past month) potential exposure events (e.g., condomless sex or condom breaking during sex with a partner of unknown HIV-1 status or unknown viremic status, a recent STI), and evaluate for current or recent signs or symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection (e.g., fever, fatigue, myalgia, skin rash).
- If recent (<1 month) exposures to HIV-1 are suspected or clinical symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection are present, use a test approved or cleared by the FDA as an aid in the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection.
When using APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP, HIV-1 testing should be repeated prior to each injection and upon diagnosis of any other STIs [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.5 )] .
- If an HIV-1 test indicates possible HIV-1 infection, or if symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection develop following an exposure event, additional HIV testing to determine HIV status is needed. If an individual has confirmed HIV-1 infection, then the individual must be transitioned to a complete HIV-1 treatment regimen.
Counsel individuals without HIV-1 to strictly adhere to the recommended dosing and testing schedule for APRETUDE in order to reduce the risk of HIV-1 acquisition and the potential development of resistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.5 ), Microbiology (12.4 )] . Some individuals, such as adolescents, may benefit from frequent visits and counseling to support adherence to the dosing and testing schedule [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4 ), Microbiology (12.4 ), Clinical Studies (14 )] .
Potential Risk of Resistance with APRETUDE
There is a potential risk of developing resistance to APRETUDE if an individual acquires HIV-1 either before or while taking APRETUDE or following discontinuation of APRETUDE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.3 )] .
To minimize this risk, it is essential to clinically reassess individuals for risk of HIV-1 acquisition and to test before each injection to confirm HIV-1 negative status. Individuals who are confirmed to have HIV-1 infection must transition to a complete HIV-1 treatment regimen.
Alternative forms of PrEP should be considered following discontinuation of APRETUDE for those individuals at continuing risk of HIV-1 acquisition and initiated within 2 months of the final injection of APRETUDE.
Long-Acting Properties and Potential Associated Risks with APRETUDE
Residual concentrations of cabotegravir may remain in the systemic circulation of individuals for prolonged periods (up to 12 months or longer). It is important to carefully select individuals who agree to the required every-2-month injection dosing schedule because non-adherence to every‑2-monthly injections or missed doses could lead to HIV-1 acquisition and development of resistance.
Healthcare providers should take the prolonged-release characteristics of cabotegravir into consideration when APRETUDE is prescribed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 ), Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.2 ), Overdosage (10 )] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with cabotegravir and include Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] . Administration of cabotegravir oral lead-in dosing was used in clinical studies to help identify participants who may be at risk of a hypersensitivity reaction. Remain vigilant and discontinue APRETUDE if a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ), Contraindications (4 ), Adverse Reactions (6 )] .
Discontinue APRETUDE immediately if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions develop (including, but not limited to, severe rash, or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, mucosal involvement [oral blisters or lesions], conjunctivitis, facial edema, hepatitis, eosinophilia, angioedema, difficulty breathing). Clinical status, including liver transaminases, should be monitored and appropriate therapy initiated. For information regarding the long-acting properties of APRETUDE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity has been reported in a limited number of individuals receiving cabotegravir with or without known pre-existing hepatic disease or identifiable risk factors [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Clinical and laboratory monitoring should be considered and APRETUDE should be discontinued if hepatotoxicity is suspected and individuals managed as clinically indicated. For information regarding the long-acting properties of APRETUDE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Depressive Disorders
Depressive disorders (including depression, depressed mood, major depression, persistent depressive disorder, suicidal ideation, suicide attempt) have been reported with APRETUDE [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . Promptly evaluate individuals with depressive symptoms to assess whether the symptoms are related to APRETUDE and to determine whether the risks of continued therapy outweigh the benefits.
Risk of Reduced Drug Concentration of APRETUDE Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of APRETUDE and other drugs may result in reduced drug concentration of APRETUDE [see Contraindications (4 ), Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3 )] .
See Table 8 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during use of, and after discontinuation of APRETUDE; review concomitant medications during use of APRETUDE [see Drug Interactions (7.3 , 7.4 )] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described below and in other sections of the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials Experience in Adults
The safety assessment of APRETUDE is based on the analysis of data from 2 international, multicenter, double-blind trials, HPTN 083 and HPTN 084 [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
Adverse reactions were reported while on blinded study product following exposure to APRETUDE extended-release injectable suspension and oral cabotegravir tablets as oral lead-in. The median time on blinded study product in HPTN 083 was 65 weeks and 2 days (range: 1 day to 156 weeks and 1 day), with a total exposure on cabotegravir of 3,231 person‑years. The median time on blinded study product in HPTN 084 was 64 weeks and 1 day (range: 1 day to 153 weeks and 1 day), with a total exposure on cabotegravir of 2,009 person‑years.
The most common adverse reactions regardless of severity reported in at least 1% of participants in HPTN 083 or HPTN 084 are presented in Table 4 .
In HPTN 083, 6% of participants in the group receiving APRETUDE intramuscular injection every 2 months and 4% of participants receiving oral TRUVADA [emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)] once daily discontinued due to adverse events (all causality). Non-injection-site–associated adverse events leading to discontinuation and occurring in ≥1% of participants were increased alanine aminotransferase with APRETUDE and TRUVADA.
In HPTN 084, 1% of participants receiving APRETUDE and 1% of participants receiving TRUVADA discontinued due to adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse event (all causality) leading to discontinuation was increased alanine aminotransferase (<1%) with APRETUDE and TRUVADA. The side-by-side tabulation is to simplify presentation; direct comparison across trials should not be made due to differing trials.
| a Adverse reactions defined as “treatment-related” as assessed by the investigator, with exception of injection site reactions, where all injection site reactions were reported regardless of causality. | ||||
| b Participants who received injection: HPTN 083, APRETUDE (n = 2,117) and TRUVADA (n = 2,081); HPTN 084, APRETUDE (n = 1,519) and TRUVADA (n = 1,516). | ||||
| c Pyrexia includes pyrexia, feeling hot, chills, influenza-like illness. | ||||
| d Fatigue includes fatigue, malaise. | ||||
| e Sleep disorders includes insomnia, abnormal dreams. | ||||
| f Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain. | ||||
| g Rash includes rash, erythema, pruritis, macular, papular, maculopapular. | ||||
Adverse Reactions | HPTN 083 | HPTN 084 | ||
APRETUDE Every 2 Months (n = 2,281) | TRUVADA Once Daily (n = 2,285) | APRETUDE Every 2 Months (n = 1,614) | TRUVADA Once Daily (n = 1,610) | |
Injection site reactions b | 82% | 35% | 38% | 11% |
Diarrhea | 4% | 5% | 4% | 4% |
Headache | 4% | 3% | 12% | 13% |
Pyrexia c | 4% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
Fatigue d | 4% | 2% | 3% | 3% |
Sleep disorders e | 3% | 3% | 1% | 1% |
Nausea | 3% | 5% | 4% | 8% |
Dizziness | 2% | 3% | 4% | 6% |
Flatulence | 1% | 1% | <1% | <1% |
Abdominal pain f | 1% | 1% | 2% | 2% |
Vomiting | <1% | 1% | 2% | 5% |
Myalgia | <1% | <1% | 2% | 1% |
Rash g | <1% | <1% | 2% | 1% |
Decreased appetite | <1% | <1% | 2% | 4% |
Somnolence | <1% | <1% | 2% | 2% |
Back pain | <1% | <1% | 1% | <1% |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 0 | <1% | 4% | 4% |
Injection-Associated Adverse Reactions: Local Injection Site Reactions (ISRs) with APRETUDE: The most frequent adverse reactions associated with the intramuscular administration of APRETUDE in HPTN 083 were ISRs. After 20,286 injections, 8,900 ISRs were reported. Of the 2,117 participants who received at least one injection of APRETUDE, 1,740 (82%) participants experienced at least one ISR, of which a total of 3% of participants discontinued APRETUDE because of ISRs. Among the participants who received APRETUDE and experienced at least one ISR, the maximum severity of reactions was mild (Grade 1) in 41% of participants, moderate (Grade 2) in 56% of participants, and severe (Grade 3) in 3% of participants. The median duration of overall ISR events was 4 days. The proportion of participants reporting ISRs at each visit and the severity of the ISRs decreased over time. The most commonly reported ISRs (all causality and grades) in at least 1% of participants who received APRETUDE and experienced at least one ISR from HPTN 083 are presented in Table 5 .
The most frequent adverse reactions associated with the intramuscular administration of APRETUDE in HPTN 084 were ISRs. After 13,068 injections, 1,171 ISRs were reported. Of the 1,519 participants who received at least one injection of APRETUDE, 578 (38%) participants experienced at least one ISR. No participants discontinued APRETUDE because of ISRs. Among the participants who received APRETUDE and experienced at least one ISR, the maximum severity of reactions was mild (Grade 1) in 66% of participants, moderate (Grade 2) in 34% of participants, and severe (Grade 3) in less than 1% of participants. The median duration of overall ISR events was 8 days. The proportion of participants reporting ISRs at each visit and the severity of the ISRs generally decreased over time. The most commonly reported ISRs (all causality and grades) in at least 1% of participants who received APRETUDE and experienced at least one ISR from HPTN 084 are presented in Table 5 .
| a Placebo injectable suspension: intralipid 20% fat emulsion. | ||||
Injection Site Reactions | HPTN 083 | HPTN 084 | ||
APRETUDE (n = 1,740) | TRUVADA a (n = 724) | APRETUDE (n = 578) | TRUVADA a (n = 166) | |
Pain/tenderness | 98% | 95% | 90% | 87% |
Nodules | 15% | 2% | 14% | 2% |
Induration | 15% | <1% | 12% | 2% |
Swelling | 12% | 1% | 18% | 3% |
Bruising | 4% | 4% | 1% | 0 |
Erythema | 4% | 2% | 5% | 2% |
Pruritus | 3% | 3% | 6% | 11% |
Warmth | 3% | 1% | <1% | 0 |
Anesthesia | 1% | 2% | 1% | 2% |
Abscess | <1% | 0 | 2% | 3% |
Discoloration | <1% | 0 | 1% | 0 |
Other Injection-Associated Adverse Reactions: In the HPTN 083 clinical trial, an increased incidence of pyrexia (including pyrexia, feeling hot, chills, influenza-like illness) (4%) was reported by participants receiving APRETUDE compared with participants receiving TRUVADA (<1%). There were no differences reported in the incidence of pyrexia between groups in HPTN 084.
Vasovagal or pre-syncopal reactions considered treatment related were reported in <1% of participants after injection with APRETUDE in HPTN 083. None were reported as treatment related by the investigators in HPTN 084.
Less Common Adverse Reactions: The following select adverse reactions (regardless of severity) occurred in <1% of participants receiving APRETUDE in HPTN 083 or HPTN 084.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatotoxicity.
Investigations: Weight increase (see below).
Psychiatric Disorders: Depression; suicidal ideation, and suicide attempt (these events were observed primarily in participants with a pre‑existing history of depression or other psychiatric illness).
Weight Increase: At the Week 41 and Week 97 timepoints in HPTN 083, participants who received APRETUDE gained a median of 1.2 kg (Interquartile Range [IQR]; -1.0, 3.5; n = 1,623) and 2.1 kg (IQR; -0.9, 5.9; n = 601) in weight from baseline. Those who received TRUVADA gained a median of 0 kg (IQR; -2.1, 2.4; n = 1,611) and 1 kg (IQR; -1.9, 4.0; n = 598) in weight from baseline, respectively.
At the Week 41 and 97 timepoints in HPTN 084, participants who received APRETUDE gained a median of 2 kg (IQR; 0.0, 5.0; n = 1,151) and 4 kg (IQR; 0.0, 8.0; n = 216) in weight from baseline, respectively. Those who received TRUVADA gained a median of 1 kg (IQR; -1.0, 4.0; n = 1,131) and 3 kg (IQR; -1.0, 6.0; n = 218) in weight from baseline, respectively.
Laboratory Abnormalities: Grade 3 or 4 post-baseline maximum toxicity laboratory abnormalities for HPTN 083 or HPTN 084 are summarized in Table 6 .
| ALT = Alanine transaminase, ULN = upper limit of normal, AST = Aspartate aminotransferase. | ||||
Laboratory Parameter | HPTN 083 | HPTN 084 | ||
APRETUDE Every 2 Months (n = 2,281) | TRUVADA Once Daily (n = 2,285) | APRETUDE Every 2 Months (n = 1,614) | TRUVADA Once Daily (n = 1,610) | |
ALT (≥5.0 x ULN) | 2% | 2% | <1% | 1% |
AST (≥5.0 x ULN) | 3% | 3% | <1% | <1% |
Creatine phosphokinase (≥10.0 x ULN) | 15% | 14% | 2% | 2% |
Lipase (≥3.0 x ULN) | 3% | 3% | <1% | <1% |
Creatinine (>1.8 x ULN) or increase to ≥1.5 x baseline) | 3% | 3% | 5% | 4% |
Serum Lipids: Changes from baseline to Month 15 in total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and total cholesterol to HDL ratio in HPTN 083 and HPTN 084 are presented in Table 7 .
| a Nearly 60% of participants with baseline data available had Week 57 data available in both arms of both trials. Within each trial, baseline values were comparable among participants receiving APRETUDE and TRUVADA. | ||||
HPTN 083 | HPTN 084 | |||
APRETUDE | TRUVADA | APRETUDE | TRUVADA | |
Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | +1.0 | -10.0 | +0.2 | -3.9 |
LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | +1.0 | -6.0 | -1.1 | -5.0 |
HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | -0.2 | -3.0 | -0.8 | -2.6 |
Triglycerides (mg/dL) | +2.7 | 0.0 | +3.1 | +0.7 |
Total cholesterol: HDL cholesterol ratio | +0.1 | +0.0 | +0.1 | +0.1 |
Clinical Trials Experience in Adolescents
In adolescents receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP, the safety data were comparable to the safety data reported in adults receiving APRETUDE for HIV-1 PrEP [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4 )].
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of APRETUDE or cabotegravir-containing regimens. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema and urticaria) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Use of Other Antiretroviral Drugs after Discontinuation of APRETUDE
Residual concentrations of cabotegravir may remain in the systemic circulation of individuals for prolonged periods (up to 12 months or longer). These residual concentrations are not expected to affect the exposures of antiretroviral drugs that are initiated after discontinuation of APRETUDE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Drug Interactions (7.4 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect APRETUDE
Cabotegravir is primarily metabolized by UGT1A1 with some contribution from UGT1A9. Drugs that are strong inducers of UGT1A1 or 1A9 are expected to decrease cabotegravir plasma concentrations; therefore, coadministration of APRETUDE with these drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4 )] .
Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Information regarding potential drug interactions with cabotegravir is provided in Table 8 . These recommendations are based on either drug interaction trials following oral administration of cabotegravir or predicted interactions due to the expected magnitude of the interaction [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.7 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Table 8 includes potentially significant interactions but is not all inclusive.
| ↑ = Increase, ↓ = Decrease, ↔ = No change. | ||
Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration | Clinical Comment |
Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine Oxcarbazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin | ↓Cabotegravir | Coadministration is contraindicated with APRETUDE due to potential for significant decreases in plasma concentration of APRETUDE. |
Antimycobacterials: Rifampin Rifapentine | ↓Cabotegravir | |
Antimycobacterial: Rifabutin | ↓Cabotegravir | When rifabutin is started before or concomitantly with the first initiation injection of APRETUDE, the recommended dosing of APRETUDE is one 600-mg (3-mL) injection, followed 2 weeks later by a second 600‑mg (3-mL) initiation injection and monthly thereafter while on rifabutin. When rifabutin is started at the time of the second initiation injection or later, the recommended dosing schedule of APRETUDE is 600‑mg (3 mL) monthly while on rifabutin. After stopping rifabutin, the recommended dosing schedule of APRETUDE is 600-mg (3 mL) every 2 months. |
Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with Cabotegravir
Based on drug interaction study results, the following drugs can be coadministered with cabotegravir (non-antiretrovirals) or given after discontinuation of cabotegravir (antiretrovirals and non-antiretrovirals) without a dose adjustment: etravirine, midazolam, oral contraceptives containing levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol, and rilpivirine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
DESCRIPTION
APRETUDE contains cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension, an HIV INSTI.
The chemical name of cabotegravir is ( 3S,11aR )-N-[(2,4-difluorophenyl)methyl]-6-hydroxy-3-methyl-5,7-dioxo-2,3,5,7,11,11a-hexahydro[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrido[1,2-d]pyrazine-8-carboxamide. The empirical formula is C 19 H 17 F 2 N 3 O 5 and the molecular weight is 405.35 g/mol. It has the following structural formula:
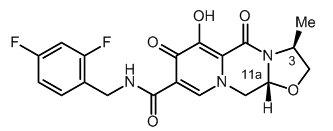
Cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension is a white to light pink free-flowing suspension for intramuscular injection in a sterile single-dose vial. Each vial contains 3 mL of the following: cabotegravir 200 mg/mL and the inactive ingredients mannitol (35 mg/mL), polyethylene glycol (PEG) 3350 (20 mg/mL), polysorbate 20 (20 mg/mL), and Water for Injection.
The vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Cabotegravir is an HIV-1 antiretroviral drug [see Microbiology (12.4 )] in a long-acting formulation.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose of cabotegravir 150 mg orally every 12 hours (10 times the recommended total daily oral lead‑in dosage of APRETUDE), the QT interval is not prolonged to any clinically relevant extent. Administration of 3 doses of cabotegravir 150 mg orally every 12 hours resulted in a geometric mean C max approximately 2.8- and 5.6-fold above the geometric mean steady-state C max associated with the recommended 30-mg dose of oral cabotegravir and the recommended 600-mg dose given every 2 months of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption, Distribution, and Elimination
The pharmacokinetic properties of cabotegravir are provided in Table 9 . The multiple-dose pharmacokinetic parameters are provided in Table 10 . For the pharmacokinetic properties of oral cabotegravir, refer to the full prescribing information for VOCABRIA (cabotegravir).
| CSF = Cerebrospinal fluid. a When taken orally with a high-fat meal versus fasted, the AUC (0-inf) (geometric mean ratio [90% CI] of cabotegravir are 1.14 [1.02, 1.28]). b The clinical relevance of CSF-to-plasma concentration ratios is unknown. Concentrations were measured at steady-state 1 week after intramuscular administration of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspensions given monthly or every 2 months. | |
| c Elimination half-life driven by slow absorption rate from the intramuscular injection site. | |
| d Dosing in mass balance studies: single-dose oral administration of [ 14 C] cabotegravir. | |
Absorption a | |
T max (days), median | 7 |
Distribution | |
% Bound to human plasma proteins | >99.8 |
Blood-to-plasma ratio | 0.52 |
CSF-to-plasma concentration ratio (median [range]) b | 0.003 |
(0.002 to 0.004) | |
Elimination | |
t 1/2 (weeks), mean c | 5.6 to 11.5 |
Metabolism | |
Metabolic pathways | UGT1A1 |
UGT1A9 (minor) | |
Excretion | |
Major route of elimination | Metabolism |
% of dose excreted as total 14 C (unchanged drug) in urine d | 27 (0) |
% of dose excreted as total 14 C (unchanged drug) in feces d | 59 (47) |
| IM = Intramuscular. | ||||
| a Pharmacokinetic parameter values were based on individual post-hoc estimates from cabotegravir population pharmacokinetic models for patients in Phase 3 treatment studies of HIV treatment. | ||||
| b tau is dosing interval: 24 hours for oral administration, 1 month for the initial injection, and 2 months for every 2 months for intramuscular injections of extended-release injectable suspension. | ||||
| c Oral lead-in pharmacokinetic parameter values represent steady state. | ||||
| d Initial injection C max values primarily reflect oral dosing because the initial injection was administered on the same day as the last oral dose; however, AUC (0-tau) and the C tau values reflect the initial injection. When administered without oral lead-in to recipients with HIV-1 (n = 110), the observed cabotegravir geometric mean (5th, 95th percentile) C max (1-week post‑initial injection) was 1.89 mcg/mL (0.438, 5.69) and C tau was 1.43 mcg/mL (0.403, 3.90). | ||||
| e Pharmacokinetic parameter values represent steady state. | ||||
Dosing Phase | Dosage Regimen | Geometric Mean (5 th , 95 th Percentile) a | ||
AUC (0-tau) b (mcg•h/mL) | C max (mcg/mL) | C tau b (mcg/mL) | ||
Oral lead-in c | 30 mg | 145 | 8.0 | 4.6 |
once daily | (93.5, 224) | (5.3, 11.9) | (2.8, 7.5) | |
Initial injection d | 600 mg IM | 1,591 | 8.0 | 1.5 |
initial dose | (714; 3,245) | (5.3, 11.9) | (0.65, 2.9) | |
Every-2-month injection e | 600 mg IM | 3,764 | 4.0 | 1.6 |
every 2 months | (2,431; 5,857) | (2.3, 6.8) | (0.8, 3.0) | |
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir were observed based on age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, or UGT1A1 polymorphisms. There are no data available for the use of cabotegravir in participants with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus co-infection in PrEP studies.
Renal Impairment: With oral cabotegravir, no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir are expected in individuals with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. Cabotegravir has not been studied in participants with end-stage renal disease not on dialysis. As cabotegravir is >99% protein bound, dialysis is not expected to alter exposures of cabotegravir [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 )] .
Hepatic Impairment: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir are expected in mild to moderate (Child-Pugh A or B) hepatic impairment. The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on the pharmacokinetics of cabotegravir has not been studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 )] .
Gender: Population pharmacokinetic analyses revealed no clinically relevant effect of gender on the exposure of cabotegravir. In addition, no clinically relevant differences in plasma cabotegravir concentrations were observed in PrEP studies by gender, including in cisgender men and transgender women (+/- hormone use). Therefore, no dose adjustment is necessary based on gender.
Geriatrics: No dose adjustment is required in elderly individuals. There are limited data available on the use of cabotegravir in individuals aged 65 years and older. In general, caution should be exercised in administration of cabotegravir in elderly individuals, reflecting greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5 )] .
Pediatrics: Population pharmacokinetic analyses revealed no clinically relevant differences in exposure between adolescent participants and adult participants with and without HIV-1 from the cabotegravir development program; therefore, no dosage adjustment is needed for adolescents weighing ≥35 kg (Table 11 ).
| IM = intramuscular. a Pharmacokinetic parameter values were based on individual post-hoc estimates from population pharmacokinetic models in both adolescents with HIV-1 (n = 147) weighing 35.2 to 98.5 kg and adolescents without HIV-1 (n = 62) weighing 39.9 to 167 kg. b tau is dosing interval: 24 hours for oral administration, 1 month for the initial injection, and 2 months for every 2 months for intramuscular injections of extended-release injectable suspension. c Oral lead-in pharmacokinetic parameter values represent steady state. d Initial injection C max values primarily reflect oral dosing because the initial injection was administered on the same day as the last oral dose; however, the AUC (0-tau) and C tau values reflect the initial injection. e Pharmacokinetic parameter values represent steady state. | ||||
Dosing Phase | Dosage Regimen | Geometric Mean (5 th , 95 th Percentile) a | ||
AUC (0-tau) b (mcg•h/mL) | C max (mcg/mL) | C tau b (mcg/mL) | ||
Oral lead-in c | 30 mg | 203 | 10.7 | 6.43 |
once daily | (136, 320) | (7.36, 16.6) | (4.15, 10.5) | |
Initial injection d | 600 mg IM | 2,085 | 10.8 | 1.88 |
initial dose | (1,056; 4,259) | (7.42, 16.6) | (0.801, 3.71) | |
Every-2-month injection e | 600 mg IM | 5,184 | 5.10 | 2.54 |
every 2 months | (3,511; 7,677) | (3.06, 8.24) | (1.25, 4.19) | |
Drug Interaction Studies
Cabotegravir is not a clinically relevant inhibitor of the following enzymes and transporters: cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4; UGT1A1, 1A3, 1A4, 1A6, 1A9, 2B4, 2B7, 2B15, and 2B17; P-glycoprotein (P‑gp); breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP); bile salt export pump (BSEP); organic cation transporter (OCT)1, OCT2; organic anion transporter polypeptide (OATP)1B1, OATP1B3; multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter (MATE) 1, MATE 2-K; and multidrug resistance protein (MRP)2 or MRP4.
In vitro, cabotegravir inhibited renal OAT1 (IC 50 = 0.81 microM) and OAT3 (IC 50 = 0.41 microM). Based on physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling, cabotegravir may increase the AUC of OAT1/3 substrates up to approximately 80%.
In vitro, cabotegravir did not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4.
Simulations using PBPK modeling show that no clinically significant interaction is expected during coadministration of cabotegravir with drugs that inhibit UGT1A1.
In vitro, cabotegravir was not a substrate of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, or OCT1.
Cabotegravir is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP in vitro; however, because of its high permeability, no alteration in cabotegravir absorption is expected with coadministration of P-gp or BCRP inhibitors.
Drug interaction studies were not conducted with injectable cabotegravir. Drug interaction studies with oral cabotegravir are summarized in Tables 12 and 13 .
| n = Maximum number of participants with data, CI = Confidence Interval. | |||||
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of Cabotegravir | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Cabotegravir Pharmacokinetic Parameters with/without Coadministered Drugs No Effect = 1.00 | ||
C max | AUC | C tau or C 24 | |||
Etravirine | 30 mg | 12 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
200 mg twice daily | once daily | (0.99, 1.09) | (0.96, 1.06) | (0.94, 1.06) | |
Rifabutin | 30 mg | 12 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.74 |
300 mg once daily | once daily | (0.76, 0.90) | (0.74, 0.83) | (0.70, 0.78) | |
Rifampin | 30-mg | 15 | 0.94 | 0.41 | 0.50 |
600 mg once daily | single dose | (0.87, 1.02) | (0.36, 0.46) | (0.44, 0.57) | |
Rilpivirine | 30 mg | 11 | 1.05 | 1.12 | 1.14 |
25 mg once daily | once daily | (0.96, 1.15) | (1.05, 1.19) | (1.04, 1.24) | |
| n = Maximum number of participants with data, CI = Confidence Interval; NA = Not available. | |||||
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of Cabotegravir | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered Drug with/without Cabotegravir No Effect = 1.00 | ||
C max | AUC | C tau or C 24 | |||
Ethinyl estradiol | 30 mg | 19 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 1.00 |
0.03 mg once daily | once daily | (0.83, 1.03) | (0.97, 1.08) | (0.92, 1.10) | |
Levonorgestrel | 30 mg | 19 | 1.05 | 1.12 | 1.07 |
0.15 mg once daily | once daily | (0.96, 1.15) | (1.07, 1.18) | (1.01, 1.15) | |
Midazolam | 30 mg | 12 | 1.09 | 1.10 | NA |
3 mg | once daily | (0.94, 1.26) | (0.95, 1.26) | ||
Rilpivirine | 30 mg | 11 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.92 |
25 mg once daily | once daily | (0.85, 1.09) | (0.89, 1.09) | (0.79, 1.07) | |
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Cabotegravir inhibits HIV integrase by binding to the integrase active site and blocking the strand transfer step of retroviral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) integration that is essential for the HIV replication cycle. The mean 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 ) value of cabotegravir in a strand transfer assay using purified recombinant HIV-1 integrase was 3.0 nM.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Cabotegravir exhibited antiviral activity against laboratory strains of HIV-1 (subtype B, n = 4) with mean 50 percent effective concentration (EC 50 ) values of 0.22 to 1.7 nM in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and 293 cells. Cabotegravir demonstrated antiviral activity in PBMCs against a panel of 24 HIV-1 clinical isolates (3 in each of group M subtypes A, B, C, D, E, F, and G and 3 in group O) with a median EC 50 value of 0.19 nM (range: 0.02 to 1.06 nM, n = 24). The median EC 50 value against subtype B clinical isolates was 0.05 nM (range: 0.02 to 0.50 nM, n = 3). Against clinical HIV-2 isolates, the median EC 50 value was 0.12 nM (range: 0.10 to 0.14 nM, n = 3).
In cell culture, cabotegravir was not antagonistic in combination with the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) rilpivirine, or the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) FTC, lamivudine (3TC), or TDF.
Resistance
Cell Culture: Cabotegravir-resistant viruses were selected during passage of HIV-1 strain IIIB in MT-2 cells in the presence of cabotegravir. Amino acid substitutions in integrase that emerged and conferred decreased susceptibility to cabotegravir included Q146L (fold change: 1.3 to 4.6), S153Y (fold change: 2.8 to 8.4), and I162M (fold change: 2.8). The integrase substitution T124A also emerged alone (fold change: 1.1 to 7.4 in cabotegravir susceptibility), in combination with S153Y (fold change: 3.6 to 6.6 in cabotegravir susceptibility) or I162M (2.8-fold change in cabotegravir susceptibility). Cell culture passage of virus harboring integrase substitutions Q148H, Q148K, or Q148R selected for additional substitutions (C56S, V72I, L74M, V75A, T122N, E138K, G140S, G149A, and M154I), with substituted viruses having reduced susceptibility to cabotegravir of 2.0- to 410-fold change. The combinations of E138K+Q148K and V72I+E138K+Q148K conferred the greatest reductions of 53- to 260‑fold change and 410‑fold change, respectively.
Clinical Trials: There were 12 incident infections and 4 prevalent infections among participants in the APRETUDE arm of HPTN 083. Genotypic data were generated for viruses from 13 of these 16 participants (4 participants with prevalent infections and 9 participants with incident infections) and phenotypic data were generated for 3 of these viruses. INSTI resistance-associated substitutions were detected in 5 viruses from participants who achieved target plasma concentrations of cabotegravir (≥0.65 mcg/mL [1.6 μM]) and included R263K (2-fold less susceptible to cabotegravir), E138A+Q148R (6-fold less susceptible to cabotegravir), E138K+Q148K, G140A+Q148R (13-fold less susceptible to cabotegravir), and L74I+E138E/K+G140G/S+Q148R+E157Q.
There were 3 incident infections and 1 prevalent infection among participants in the APRETUDE arm of HPTN 084. All 3 incident infections occurred during periods with cabotegravir exposures below the target concentration. No variants expressing INSTI resistance-associated substitutions were detected.
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance has been observed among INSTIs. Cabotegravir had reduced susceptibility (>5-fold change) to recombinant HIV-1 strain NL432 viruses harboring the following integrase amino acid substitutions: G118R, Q148K, Q148R, T66K+L74M, E92Q+N155H, E138A+Q148R, E138K+Q148K/R, G140C+Q148R, G140S+Q148H/K/R, Y143H+N155H, and Q148R+N155H (range: 5.1- to 81-fold). The substitutions E138K+Q148K and Q148R+N155H conferred the greatest reductions in susceptibility of 81- and 61-fold, respectively.
Virologic failure isolates from cabotegravir plus rilpivirine treatment in FLAIR, ATLAS, and ATLAS-2M exhibited cross-resistance to INSTIs and NNRTIs. All confirmed virologic isolates with genotypic evidence of cabotegravir resistance had cross-resistance to elvitegravir and raltegravir but retained phenotypic susceptibility to dolutegravir and when tested bictegravir.
Viruses harboring E138A+Q148R or G140A+Q148R with reduced susceptibility to cabotegravir were isolated from participants using APRETUDE in HPTN 083. These viruses remained susceptible to bictegravir and dolutegravir but had cross-resistance to elvitegravir and raltegravir.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Two-year carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats were conducted with cabotegravir. In mice, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were observed at cabotegravir exposures (AUC) up to approximately 8 times (males) and 7 times (females) higher than those in humans at the RHD. In rats, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were observed at cabotegravir exposures up to approximately 26 times higher than those in humans at the RHD.
Mutagenesis
Cabotegravir was not genotoxic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay, mouse lymphoma assay, or in the in vivo rodent micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In rats, no effects on fertility were observed at cabotegravir exposures (AUC) >20 times (male) and 28 times (female) the exposure in humans at the RHD.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical Trials in Adults for HIV-1 Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis
The safety and efficacy of APRETUDE to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection were evaluated in 2 randomized, double-blind, controlled, multinational trials, HPTN 083 in men and transgender women without HIV-1 who have sex with men and have evidence of high-risk behavior for HIV-1 infection and HPTN 084 in cisgender women without HIV-1 at risk of acquiring HIV-1.
Participants randomized to receive APRETUDE initiated oral lead-in dosing with 1 oral cabotegravir 30-mg tablet and a placebo daily for up to 5 weeks, followed by APRETUDE 600‑mg (3-mL) intramuscular injection at months 1 and 2 and every 2 months thereafter and a daily placebo tablet. Participants randomized to receive TRUVADA initiated oral TRUVADA (TDF 300 mg/FTC 200 mg) and placebo daily for up to 5 weeks, followed by oral TRUVADA daily and placebo intramuscular injection at months 1 and 2 and every 2 months thereafter.
Trial 201738 (HPTN 083 [NCT02720094])
In HPTN 083, a non-inferiority study, 4,566 cisgender men and transgender women who have sex with men were randomized 1:1 and received either APRETUDE (n = 2,281) or TRUVADA (n = 2,285) as blinded study medication up to Week 153.
At baseline, the median age of participants was 26 years, 12% were transgender women, 72% were non-White, and 67% were younger than 30 years.
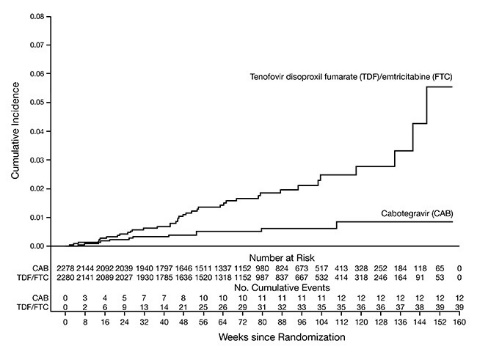
The primary endpoint was the rate of incident HIV-1 infections among participants randomized to daily oral cabotegravir and intramuscular injections of APRETUDE every 2 months compared with daily oral TRUVADA (corrected for early stopping). The primary analysis demonstrated the superiority of APRETUDE compared with TRUVADA with a 66% reduction in the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection, hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.34 (0.18, 0.62); further testing revealed 1 of the infections on APRETUDE to be prevalent then yielding a 69% reduction in the risk of HIV-1 incident infection relative to TRUVADA (Table 14 ).
| a mITT from Supplemental Virology Report. | |||
| b Following the primary analysis, extended retrospective virologic testing was performed to better characterize the timing of HIV-1 infections. As a result, 1 of the 13 HIV-1 incident infections in participants receiving APRETUDE was determined to be a prevalent infection. The original hazard ratio (95% CI) from the primary analysis is 0.34 (0.18, 0.62). | |||
APRETUDE (N = 2,278) | TRUVADA (N = 2,281) | Superiority P Value | |
Person-years | 3,211 | 3,193 | |
HIV-1 infections (incidence rate per 100 person-years) | 12 b (0.37) | 39 (1.22) | |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.31 (0.16, 0.58) | 0.0003 | |
Figure 1. Cumulative Incidence of HIV-1 Infections in HPTN 083
Results from all subgroup analyses were consistent with the overall protective effect. A lower rate of incident HIV‑1 infections was observed for participants randomized to APRETUDE compared with participants randomized to TRUVADA (Table 15 ).
| a mITT from Supplemental Virology Report. b Cisgender men who have sex with men. c Transgender women who have sex with men. | |||||
Subgroup | APRETUDE Incidence per 100 Person-Years | APRETUDE Person-Years | TRUVADA Incidence per 100 Person-Years | TRUVADA Person-Years | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) |
Age | |||||
<30 years | 0.47 | 2,110 | 1.66 | 1,987 | 0.29 |
(0.15, 0.59) | |||||
≥30 years | 0.18 | 1,101 | 0.50 | 1,206 | 0.39 |
(0.08, 1.84) | |||||
Gender | |||||
MSM b | 0.35 | 2,836 | 1.14 | 2,803 | 0.32 |
(0.16, 0.64) | |||||
TGW c | 0.54 | 371 | 1.80 | 389 | 0.34 |
(0.08, 1.56) | |||||
Race (US) | |||||
Black | 0.58 | 691 | 2.28 | 703 | 0.26 |
(0.09, 0.76) | |||||
Non-Black | 0.00 | 836 | 0.50 | 801 | 0.11 |
(0.00, 2.80) | |||||
Region | |||||
US | 0.26 | 1,528 | 1.33 | 1,504 | 0.21 |
(0.07, 0.60) | |||||
Latin America | 0.49 | 1,020 | 1.09 | 1,011 | 0.47 |
(0.17, 1.35) | |||||
Asia | 0.35 | 570 | 1.03 | 581 | 0.39 |
(0.08, 1.82) | |||||
Africa | 1.08 | 93 | 2.07 | 97 | 0.63 |
(0.06, 6.50) | |||||
Trial 201739 (HPTN 084 [NCT03164564])
In HPTN 084, a superiority study, 3,224 cisgender women were randomized 1:1 and received either APRETUDE (n = 1,614) or TRUVADA (n = 1,610) as blinded study medication up to Week 153.
At baseline, the median age of participants was 25 years, >99% were non-White, >99% were cisgender women, and 49% were <25 years of age.
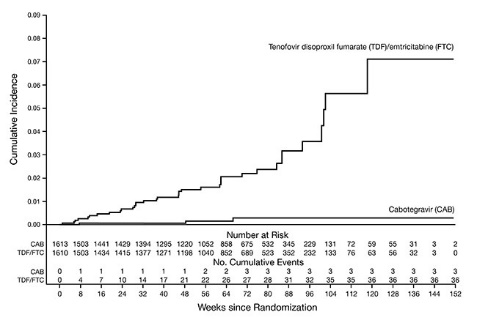
The primary endpoint was the rate of incident HIV-1 infections among participants randomized to oral cabotegravir and injections of APRETUDE compared with oral TRUVADA (corrected for early stopping). The primary analysis demonstrated the superiority of APRETUDE compared with TRUVADA with an 88% reduction in the risk of acquiring incident HIV-1 infection, hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.12 (0.05, 0.31); further testing revealed 1 of the infections on APRETUDE to be prevalent then yielding a 90% reduction in the risk of HIV-1 incident infection relative to TRUVADA (Table 16 ).
| a mITT from Supplemental Virology Report. | |||
| b Following the primary analysis, extended retrospective virologic testing was performed to better characterize the timing of HIV-1 infections. As a result, 1 of the 4 HIV-1 incident infections in participants receiving APRETUDE was determined to be a prevalent infection. The original hazard ratio (95% CI) from the primary analysis is 0.12 (0.05, 0.31). | |||
APRETUDE (N = 1,613) | TRUVADA (N = 1,610) | Superiority P Value | |
Person-years | 1,960 | 1,946 | |
HIV-1 incident infections (incidence rate per 100 person-years) | 3 b (0.15) | 36 (1.85) | |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.27) | <0.0001 | |
Figure 2. Cumulative Incidence of HIV-1 Infections in HPTN 084
Results from pre-planned subgroup analyses were consistent with the overall protective effect. A lower rate of incident HIV-1 infections was observed for participants randomized to APRETUDE compared with participants randomized to TRUVADA (Table 17 ).
| a mITT from Supplemental Virology Report. | |||||
Subgroup | APRETUDE Incidence per 100 Person-Years | APRETUDE Person-Years | TRUVADA Incidence per 100 Person-Years | TRUVADA Person-Years | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) |
Age | |||||
<25 years | 0.23 | 868 | 2.34 | 853 | 0.12 |
(0.03, 0.46) | |||||
≥25 years | 0.09 | 1,093 | 1.46 | 1,093 | 0.09 |
(0.02, 0.49) | |||||
Body Mass Index | |||||
<30 | 0.22 | 1,385 | 1.88 | 1,435 | 0.12 |
(0.04, 0.38) | |||||
≥30 | 0.00 | 575 | 1.76 | 511 | 0.04 |
(0.00, 0.93) | |||||
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
APRETUDE is supplied in a kit containing one 600-mg/3-mL single-dose (200-mg/mL) vial of cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension, 1 syringe, 1 vial adapter, and 1 needle for intramuscular injection (23 gauge, 1½ inch) (NDC 49702-264-23). The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Store APRETUDE at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F) in the original carton until ready to use. Exposure up to 30°C permitted. Do not freeze. Do not mix with any other product or diluent.
If the pack has been stored in the refrigerator, the vial should be brought to room temperature prior to administration (not to exceed 30°C [86°F]).
Once the suspension has been drawn into the syringe, the injection should be administered as soon as possible, but may remain in the syringe for up to 2 hours. The filled syringes should not be placed in the refrigerator. If the medicine remains in the syringe for more than 2 hours, the filled syringe and needle must be discarded [see Dosage and Administration (2.7 )] .
 | |
Overview: A complete dose of APRETUDE requires 1 injection: 600-mg (3 mL) of cabotegravir. APRETUDE is a suspension that does not need further dilution or reconstitution. Carefully follow these instructions when preparing the suspension for injection to avoid leakage. APRETUDE is for gluteal intramuscular use only. Note: The ventrogluteal site is recommended. | |
| |
Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Exposure up to 30°C (86°F) permitted. Do not freeze. | |
Prior to administration: | |
| |
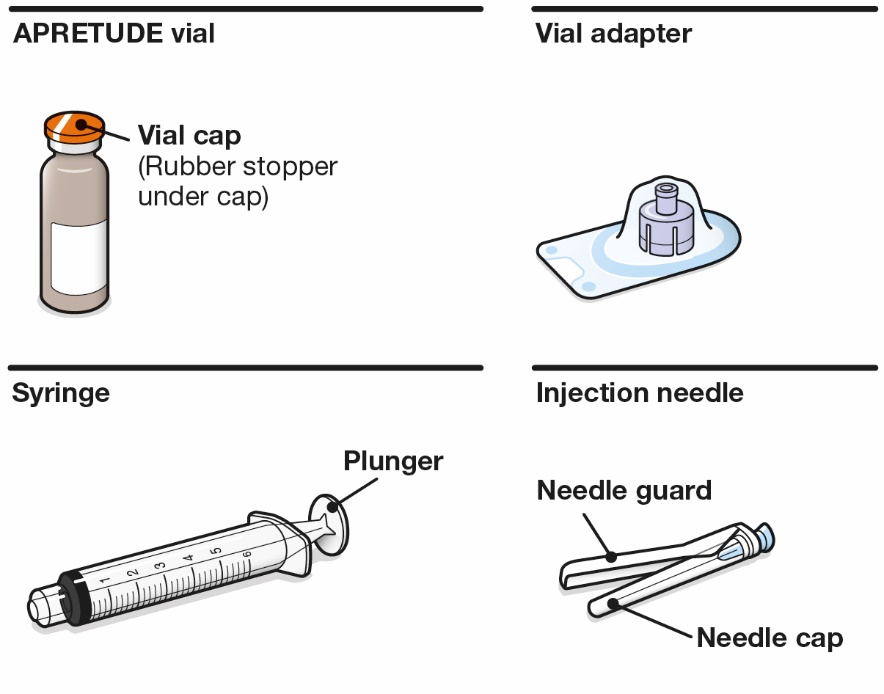 | |
Your pack contains: | |
Consider the individual’s build and use medical judgment to select an appropriate injection needle length. | |
You will also need: | |
| |
Preparation: | |
1. Inspect the vial. | |
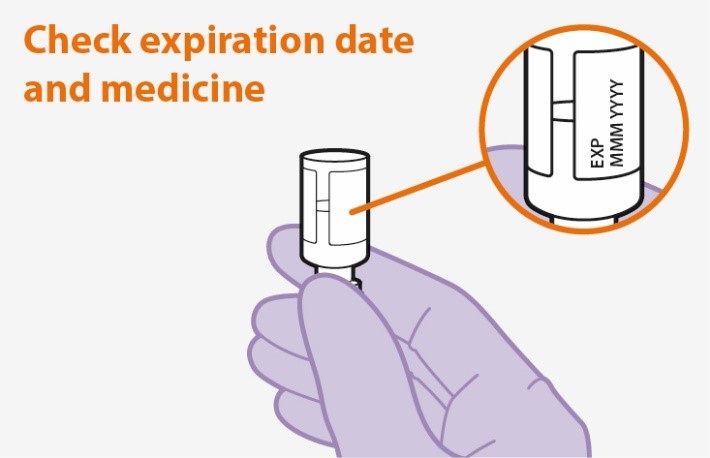 Figure A |
|
2. Shake the vial vigorously. | |
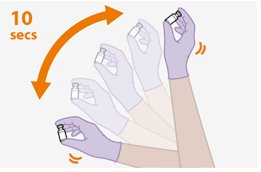 Figure B |
|
3. Inspect suspension. | |
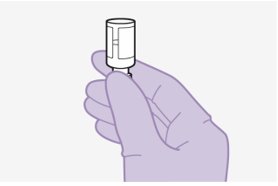 Figure C |
|
4. Remove the vial cap. | |
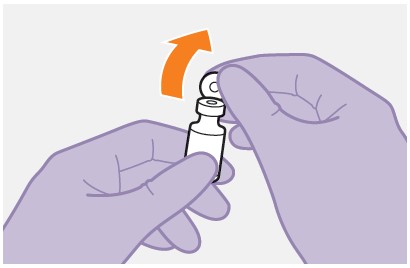 Figure D |
|
5. Peel open the vial adapter. | |
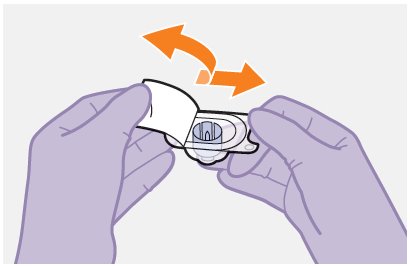 Figure E |
|
6. Place vial on flat surface and attach the vial adapter. | |
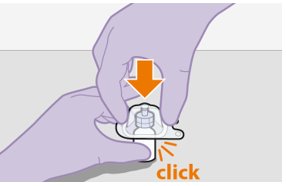 Figure F |
|
7. Lift off the packaging. | |
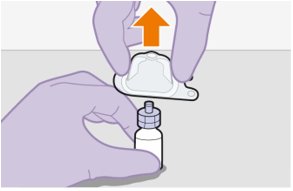 Figure G |
|
8. Prepare the syringe. | |
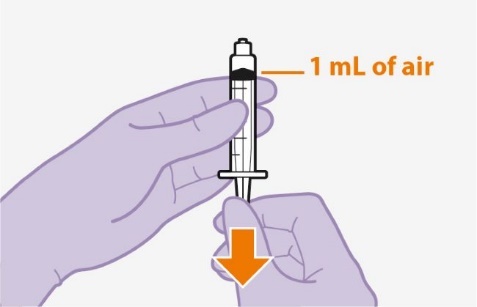 Figure H |
|
9. Attach the syringe. | |
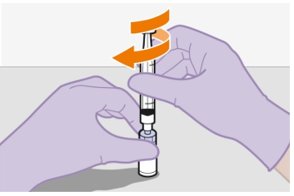 Figure I |
|
10. Press the plunger. | |
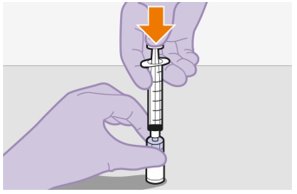 Figure J |
|
11. Slowly draw up the dose. | |
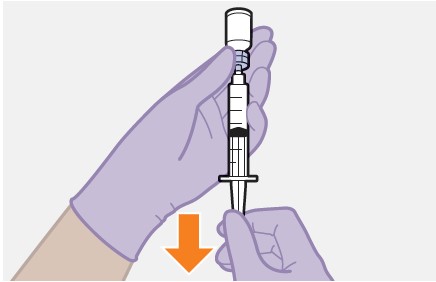 Figure K |
|
12. Unscrew the syringe. | |
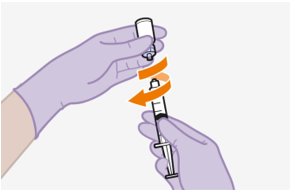 Figure L |
|
13. Attach the needle. | |
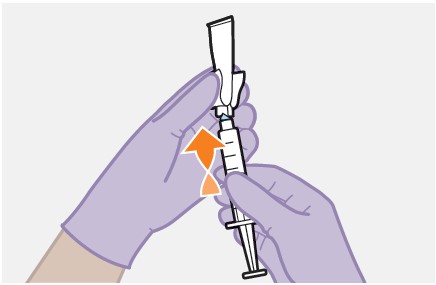 Figure M |
|
Injection: | |
14. Prepare the injection site. | |
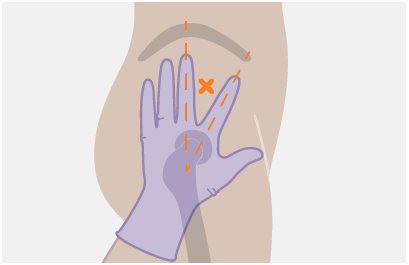 Figure N |
|
15. Remove the cap. | |
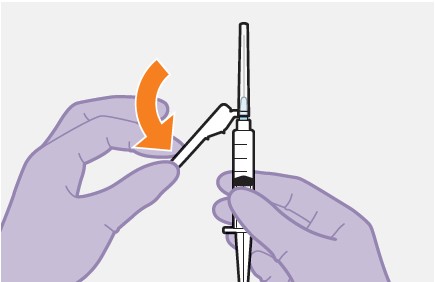 Figure O |
|
16. Remove extra liquid from the syringe. | |
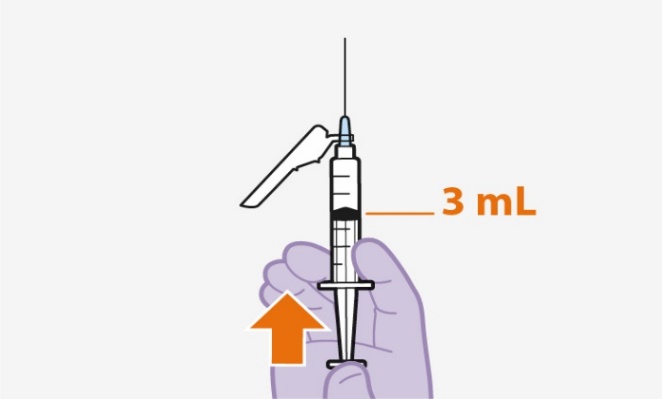 Figure P |
|
17. Stretch the skin. | |
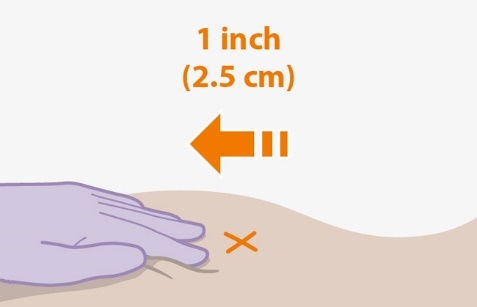 Figure Q |
|
18. Insert the needle. | |
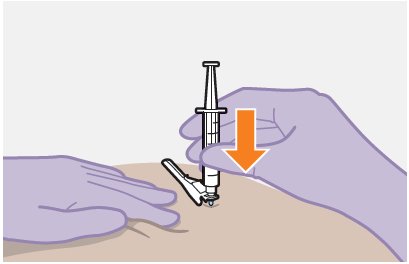 Figure R |
|
19. Inject the dose of medicine. | |
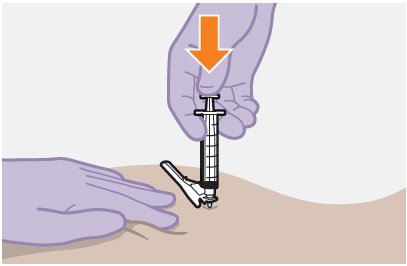 Figure S |
|
20. Assess the injection site. | |
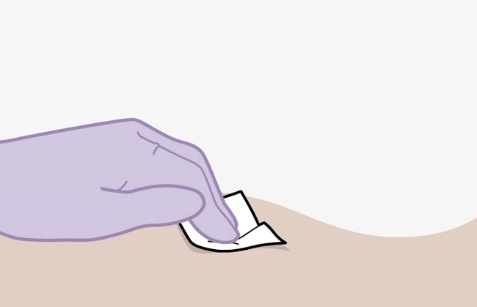 Figure T |
|
21. Make the needle safe. | |
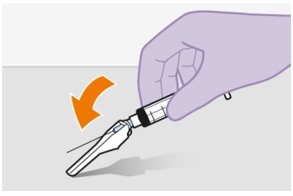 Figure U |
|
 Figure V |
|
After injection: | |
22. Dispose safely. | |
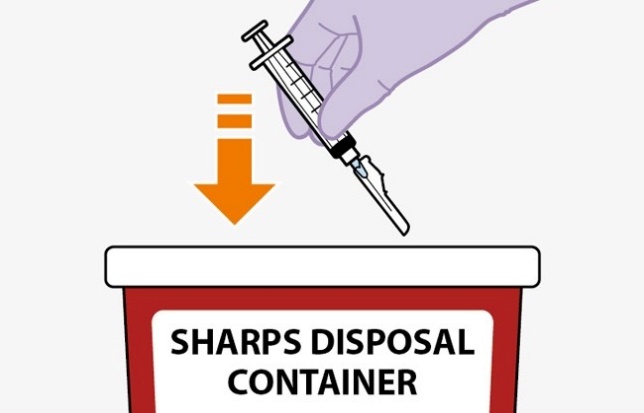 Figure W |
|
Questions and Answers | |
| |
Manufactured for: ViiV Healthcare Durham, NC 27701 | |
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the ViiV Healthcare group of companies. ©2024 ViiV Healthcare group of companies or its licensor. APR:5IFU | |
- This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 9/2024
Mechanism of Action
Cabotegravir is an HIV-1 antiretroviral drug [see Microbiology (12.4 )] in a long-acting formulation.
 Storage information
Storage information