Austedo XR prior authorization resources
Most recent Austedo XR prior authorization forms
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Austedo XR patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosing Information
The dose of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO is determined individually for each patient based on reduction of chorea or tardive dyskinesia and tolerability. Table 1 displays the recommended dosage and important administration instructions of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO when first prescribed to patients who are not being switched from tetrabenazine (a related VMAT2 inhibitor).
Table 1: Recommended Dosage and Important Administration Instructions for AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO
| AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablet | AUSTEDO tablet | |
| Recommended Starting Dosage | 12 mg once daily (12 mg per day) | 6 mg twice daily (12 mg per day) |
| Recommended Dose Titration | The dosage of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO may be increased at weekly intervals in increments of 6 mg per day based on reduction of chorea or tardive dyskinesia, and tolerability, up to a maximum recommended daily dosage of 48 mg [see Clinical Trials (14.1 , 14.2 )] . | |
| Important Administration Instructions |
|
|
| Switching Between AUSTEDO and AUSTEDO XR | When switching between AUSTEDO tablets (twice daily) and AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets (once daily), switch to the same total daily dosage. | |
Switching Patients from Tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
Discontinue tetrabenazine and initiate AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO the following day. The recommended initial dosing regimen of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in patients switching from tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Initial Dosing Regimen when Switching from Tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
| Current tetrabenazine daily dosage | Initial regimen of AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablet | Initial regimen of AUSTEDO tablet |
|---|---|---|
12.5 mg | 6 mg once daily | 6 mg once daily |
25 mg | 12 mg once daily | 6 mg twice daily |
37.5 mg | 18 mg once daily | 9 mg twice daily |
50 mg | 24 mg once daily | 12 mg twice daily |
62.5 mg | 30 mg once daily | 15 mg twice daily |
75 mg | 36 mg once daily | 18 mg twice daily |
87.5 mg | 42 mg once daily | 21 mg twice daily |
100 mg | 48 mg once daily | 24 mg twice daily |
After patients are switched to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, the dose may be adjusted at weekly intervals [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
Dosage Adjustment with Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Dosage Adjustment in Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers
In patients who are poor CYP2D6 metabolizers, the total daily dosage of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should not exceed 36 mg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 )].
Discontinuation and Interruption of Treatment
Treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO can be discontinued without tapering. Following treatment interruption of greater than one week, AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO therapy should be re-titrated when resumed. For treatment interruption of less than one week, treatment can be resumed at the previous maintenance dose without titration.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Austedo XR prescribing information
WARNING: DEPRESSION AND SUICIDALITY IN PATIENTS WITH HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Anyone considering the use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO must balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the risk of depression and suicidality and should be instructed to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician.
Particular caution should be exercised in treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation, which are increased in frequency in Huntington’s disease. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosing Information
The dose of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO is determined individually for each patient based on reduction of chorea or tardive dyskinesia and tolerability. Table 1 displays the recommended dosage and important administration instructions of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO when first prescribed to patients who are not being switched from tetrabenazine (a related VMAT2 inhibitor).
Table 1: Recommended Dosage and Important Administration Instructions for AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO
| AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablet | AUSTEDO tablet | |
| Recommended Starting Dosage | 12 mg once daily (12 mg per day) | 6 mg twice daily (12 mg per day) |
| Recommended Dose Titration | The dosage of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO may be increased at weekly intervals in increments of 6 mg per day based on reduction of chorea or tardive dyskinesia, and tolerability, up to a maximum recommended daily dosage of 48 mg [see Clinical Trials (14.1 , 14.2 )] . | |
| Important Administration Instructions |
|
|
| Switching Between AUSTEDO and AUSTEDO XR | When switching between AUSTEDO tablets (twice daily) and AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets (once daily), switch to the same total daily dosage. | |
Switching Patients from Tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
Discontinue tetrabenazine and initiate AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO the following day. The recommended initial dosing regimen of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in patients switching from tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Initial Dosing Regimen when Switching from Tetrabenazine to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO
| Current tetrabenazine daily dosage | Initial regimen of AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablet | Initial regimen of AUSTEDO tablet |
|---|---|---|
12.5 mg | 6 mg once daily | 6 mg once daily |
25 mg | 12 mg once daily | 6 mg twice daily |
37.5 mg | 18 mg once daily | 9 mg twice daily |
50 mg | 24 mg once daily | 12 mg twice daily |
62.5 mg | 30 mg once daily | 15 mg twice daily |
75 mg | 36 mg once daily | 18 mg twice daily |
87.5 mg | 42 mg once daily | 21 mg twice daily |
100 mg | 48 mg once daily | 24 mg twice daily |
After patients are switched to AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, the dose may be adjusted at weekly intervals [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
Dosage Adjustment with Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Dosage Adjustment in Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers
In patients who are poor CYP2D6 metabolizers, the total daily dosage of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should not exceed 36 mg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 )].
Discontinuation and Interruption of Treatment
Treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO can be discontinued without tapering. Following treatment interruption of greater than one week, AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO therapy should be re-titrated when resumed. For treatment interruption of less than one week, treatment can be resumed at the previous maintenance dose without titration.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are available in the following strengths:
- The 6 mg extended-release tablets are round, grey-coated tablets, with “Q6” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 12 mg extended-release tablets are round, blue-coated tablets, with “Q12” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 18 mg extended-release tablets are round, light grey-coated tablets, with “Q18” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 24 mg extended-release tablets are round, purple-coated tablets, with “Q24” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 30 mg extended-release tablets are round, light orange-coated tablets, with “Q30” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 36 mg extended-release tablets are round, light purple-coated tablets, with “Q36” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 42 mg extended-release tablets are round, orange-coated tablets, with “Q42” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 48 mg extended-release tablets are round, pink-coated tablets, with “Q48” printed in black ink on one side.
AUSTEDO tablets are available in the following strengths:
- The 6 mg tablets are round, purple-coated tablets, with “SD” over “6” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 9 mg tablets are round, blue-coated tablets, with “SD” over “9” printed in black ink on one side.
- The 12 mg tablets are round, beige-coated tablets, with “SD” over “12” printed in black ink on one side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in pregnant women. Administration of deutetrabenazine to rats during organogenesis produced no clear adverse effect on embryofetal development. However, administration of tetrabenazine to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation resulted in an increase in stillbirths and postnatal offspring mortality [see Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of deutetrabenazine (5, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) or tetrabenazine (30 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats during organogenesis had no clear effect on embryofetal development. The highest dose tested was 6 times the maximum recommended human dose of 48 mg/day, on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis.
The effects of deutetrabenazine when administered during organogenesis to rabbits or during pregnancy and lactation to rats have not been assessed.
Tetrabenazine had no effects on embryofetal development when administered to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day. When tetrabenazine was administered to female rats (doses of 5, 15, and 30 mg/kg/day) from the beginning of organogenesis through the lactation period, an increase in stillbirths and offspring postnatal mortality was observed at 15 and 30 mg/kg/day, and delayed pup maturation was observed at all doses.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of deutetrabenazine or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Chorea associated with Huntington’s Disease and Tardive Dyskinesia
The safety and effectiveness of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO have not been established in pediatric patients for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease or for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
Tourette Syndrome
The safety and effectiveness of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO have not been established in pediatric patients for the treatment of Tourette syndrome.
Efficacy was not demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in pediatric patients aged 6 to 16 years with Tourette syndrome. One study evaluated fixed doses of deutetrabenazine over 8 weeks (NCT03571256); the other evaluated flexible doses of deutetrabenazine over 12 weeks (NCT03452943). The studies included a total of 274 pediatric patients who received at least one dose of deutetrabenazine or placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was the change from baseline to end-of-treatment on the Yale Global Tic Severity Scale Total Tic Score (YGTSS-TTS). The estimated treatment effect of deutetrabenazine on the YGTSS-TTS was not statistically significantly different from placebo in either study. The placebo subtracted least squares means difference in YGTSS-TTS from baseline to end-of-treatment was -0.7 (95% CI: -4.1, 2.8) in the flexible dose study and -0.8 (95% CI: -3.9, 2.3) for the primary analysis in the fixed dose study.
The following adverse reactions were reported in frequencies of at least 5% of pediatric patients treated with AUSTEDO and with a greater incidence than in pediatric patients receiving placebo (AUSTEDO vs placebo): headache (includes: migraine, migraine with aura, and headache; 13% vs 9%), somnolence (includes: sedation, hypersomnia, and somnolence; 11% vs 2%), fatigue (8% vs 3%), increased appetite (5% vs <1%), and increased weight (5% vs <1%).
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Deutetrabenazine orally administered to juvenile rats from postnatal days 21 through 70 (at 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg/day) resulted in an increased incidence of tremor, hyperactivity, and adverse increases in motor activity at ≥5 mg/kg/day, and reduced body weight and food consumption at 10 mg/kg/day. There was no reproductive or early embryonic toxicity up to the highest dose. All drug-related findings were reversible after a drug-free period. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) in juvenile rats was 2.5 mg/kg/day. These drug-related findings were similar to those observed in adult rats; however, the juvenile rats were more sensitive.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of hepatic, renal, and cardiac dysfunction, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of deutetrabenazine and its primary metabolites has not been studied; however, in a clinical study conducted with tetrabenazine, a closely related VMAT2 inhibitor, there was a large increase in exposure to tetrabenazine and its active metabolites in patients with hepatic impairment. The clinical significance of this increased exposure has not been assessed, but because of concerns for a greater risk for serious adverse reactions, the use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in patients with hepatic impairment is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Although the pharmacokinetics of deutetrabenazine and its metabolites have not been systematically evaluated in patients who do not express the drug metabolizing enzyme, it is likely that the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ would be increased similarly to taking a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor (approximately 3-fold). In patients who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, the daily dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should not exceed 36 mg [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients:
- With Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
- With hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
- Taking reserpine. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] .
- Taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Drug Interactions (7.3 )] .
- Taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine [see Drug Interactions (7.6 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Patients with Huntington’s disease are at increased risk for depression, and suicidal ideation or behaviors (suicidality). AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk for suicidality in patients with Huntington’s disease.
In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, suicidal ideation was reported by 2% of patients treated with AUSTEDO, compared to no patients on placebo; no suicide attempts and no completed suicides were reported. Depression was reported by 4% of patients treated with AUSTEDO.
When considering the use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, the risk of suicidality should be balanced against the need for treatment of chorea. All patients treated with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should be observed for new or worsening depression or suicidality. If depression or suicidality does not resolve, consider discontinuing treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the risks of depression, worsening depression, and suicidality associated with AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO, and should be instructed to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Patients with Huntington’s disease who express suicidal ideation should be evaluated immediately.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s disease is a progressive disorder characterized by changes in mood, cognition, chorea, rigidity, and functional capacity over time. VMAT2 inhibitors, including AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO, may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity.
Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects, including sedation/somnolence, depression and suicidality, parkinsonism, akathisia, restlessness, and cognitive decline. It may be difficult to distinguish between adverse reactions and progression of the underlying disease; decreasing the dose or stopping the drug may help the clinician to distinguish between the two possibilities. In some patients, the underlying chorea itself may improve over time, decreasing the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO.
QTc Prolongation
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] .
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias. Certain circumstances may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including (1) bradycardia; (2) hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; (3) concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; and (4) presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission. While NMS has not been observed in patients receiving AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, it has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine (a closely related VMAT2 inhibitor). Clinicians should be alerted to the signs and symptoms associated with NMS. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatinine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria, rhabdomyolysis, and acute renal failure. The diagnosis of NMS can be complicated; other serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal disorders can present with similar signs and symptoms. Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever, and primary central nervous system pathology.
The management of NMS should include (1) immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; (2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and (3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for NMS.
Recurrence of NMS has been reported with resumption of drug therapy. If treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is needed after recovery from NMS, patients should be monitored for signs of recurrence.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness in patients with Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia.
In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with Huntington’s disease, akathisia, agitation, or restlessness was reported by 4% of patients treated with AUSTEDO, compared to 2% of patients on placebo; in patients with tardive dyskinesia, 2% of patients treated with AUSTEDO and 1% of patients on placebo experienced these events.
Patients receiving AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should be monitored for signs and symptoms of restlessness and agitation, as these may be indicators of developing akathisia. If a patient develops akathisia during treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors.
Because rigidity can develop as part of the underlying disease process in Huntington’s disease, it may be difficult to distinguish between potential drug-induced parkinsonism and progression of underlying Huntington’s disease. Drug-induced parkinsonism has the potential to cause more functional disability than untreated chorea for some patients with Huntington’s disease.
Postmarketing cases of parkinsonism in patients treated with AUSTEDO for tardive dyskinesia have been reported. Signs and symptoms in reported cases have included bradykinesia, gait disturbances, which led to falls in some cases, and the emergence or worsening of tremor. In most cases, the development of parkinsonism occurred within the first two weeks after starting or increasing the dose of AUSTEDO. In cases in which follow-up clinical information was available, parkinsonism was reported to resolve following discontinuation of AUSTEDO therapy.
If a patient develops parkinsonism during treatment with AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence
Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial examining patients with Huntington’s disease, 11% of AUSTEDO-treated patients reported somnolence compared with 4% of patients on placebo and 9% of AUSTEDO-treated patients reported fatigue compared with 4% of placebo-treated patients.
Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness to maintain the safety of themselves or others, such as operating a motor vehicle or operating hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them.
Hyperprolactinemia
Serum prolactin levels were not evaluated in the AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO development program. Tetrabenazine, a closely related VMAT2 inhibitor, elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. Following administration of 25 mg of tetrabenazine to healthy volunteers, peak plasma prolactin levels increased 4- to 5-fold.
Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin-dependent in vitro , a factor of potential importance if AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is being considered for a patient with previously detected breast cancer. Although amenorrhea, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence can be caused by elevated serum prolactin concentrations, the clinical significance of elevated serum prolactin concentrations for most patients is unknown.
Chronic increase in serum prolactin levels (although not evaluated in the AUSTEDO XR, AUSTEDO, or tetrabenazine development programs) has been associated with low levels of estrogen and increased risk of osteoporosis. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO.
Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues
Since deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues, it could accumulate in these tissues over time. This raises the possibility that AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause toxicity in these tissues after extended use. Neither ophthalmologic nor microscopic examination of the eye has been conducted in the chronic toxicity studies in a pigmented species such as dogs. Ophthalmologic monitoring in humans was inadequate to exclude the possibility of injury occurring after long-term exposure.
The clinical relevance of deutetrabenazine’s binding to melanin-containing tissues is unknown. Although there are no specific recommendations for periodic ophthalmologic monitoring, prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- QTc Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Parkinsonism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Sedation and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
- Hyperprolactinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )]
- Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The studies described below were conducted with AUSTEDO tablets; adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Patients with Huntington’s Disease
Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] was a randomized, 12-week, placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with Huntington’s disease. A total of 45 patients received AUSTEDO, and 45 patients received placebo. Patients ranged in age between 23 and 74 years (mean 54 years); 56% were male, and 92% were Caucasian. The most common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 8% of AUSTEDO-treated patients were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. Adverse reactions occurring in 4% or more of patients treated with AUSTEDO, and with a greater incidence than in patients on placebo, are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in Patients with Huntington's Disease (Study 1) Experienced by at Least 4% of Patients on AUSTEDO and with a Greater Incidence than on Placebo
| Adverse Reaction | AUSTEDO (N = 45) % | Placebo (N = 45) % |
|---|---|---|
Somnolence | 11 | 4 |
Diarrhea | 9 | 0 |
Dry mouth | 9 | 7 |
Fatigue | 9 | 4 |
Urinary tract infection | 7 | 2 |
Insomnia | 7 | 4 |
Anxiety | 4 | 2 |
Constipation | 4 | 2 |
Contusion | 4 | 2 |
One or more adverse reactions resulted in a reduction of the dose of study medication in 7% of patients in Study 1. The most common adverse reaction resulting in dose reduction in patients receiving AUSTEDO was dizziness (4%).
Agitation led to discontinuation in 2% of patients treated with AUSTEDO in Study 1.
Patients with Tardive Dyskinesia
The data described below reflect 410 tardive dyskinesia patients participating in clinical trials. AUSTEDO was studied primarily in two 12-week, placebo-controlled trials (fixed dose, dose escalation) [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] . The population was 18 to 80 years of age, and had tardive dyskinesia and had concurrent diagnoses of mood disorder (33%) or schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder (63%). In these studies, AUSTEDO was administered in doses ranging from 12-48 mg per day. All patients continued on previous stable regimens of antipsychotics; 71% and 14% respective atypical and typical antipsychotic medications at study entry.
The most common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 3% of AUSTEDO-treated patients and greater than placebo were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. The adverse reactions occurring in >2% or more patients treated with AUSTEDO (12-48 mg per day) and greater than in placebo patients in two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia (Study 1 and Study 2) are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions in 2 Placebo-Controlled Tardive Dyskinesia Studies (Study 1 and Study 2) of 12-week Treatment on AUSTEDO Reported in at Least 2% of Patients and Greater than Placebo
Adverse Reaction | AUSTEDO (N=279) (%) | Placebo (N=131) (%) |
Nasopharyngitis | 4 | 2 |
Insomnia | 4 | 1 |
Depression/ Dysthymic disorder | 2 | 1 |
Akathisia/Agitation/Restlessness | 2 | 1 |
One or more adverse reactions resulted in a reduction of the dose of study medication in 4% of AUSTEDO-treated patients and in 2% of placebo-treated patients.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
A reduction in AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose may be necessary when adding a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor in patients maintained on a stable dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO. Concomitant use of strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine, bupropion) has been shown to increase the systemic exposure to the active dihydro-metabolites of deutetrabenazine by approximately 3-fold. The daily dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO should not exceed 36 mg per day in patients taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Reserpine
Reserpine binds irreversibly to VMAT2 and the duration of its effect is several days. Prescribers should wait for chorea or dyskinesia to reemerge before administering AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO to help reduce the risk of overdosage and major depletion of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should not be used concomitantly with reserpine [see Contraindications (4 )] .
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Contraindications (4 )] .
Neuroleptic Drugs
The risk of parkinsonism, NMS, and akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO with dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics.
Alcohol or Other Sedating Drugs
Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )].
Concomitant Tetrabenazine or Valbenazine
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients currently taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine. AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO may be initiated the day following discontinuation of tetrabenazine [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )].
DESCRIPTION
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO tablets are formulated with deutetrabenazine, a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor for oral administration. The molecular weight of deutetrabenazine is 323.46; the pKa is 6.31. Deutetrabenazine is a hexahydro-dimethoxybenzoquinolizine derivative and has the following chemical name: ( RR, SS )-1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 11b-hexahydro-9, 10-di(methoxy-d 3 )-3-(2-methylpropyl)-2H-benzo[a]quinolizin-2-one.
The molecular formula for deutetrabenazine is C 19 H 21 D 6 NO 3 . Deutetrabenazine is a racemic mixture containing the following structures:
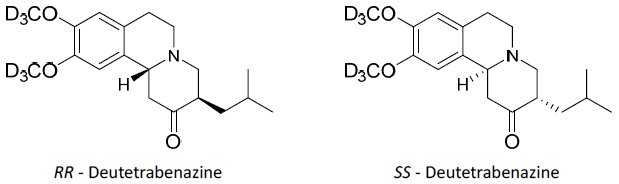
Deutetrabenazine is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol. AUSTEDO XR
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets contain 6 mg, 12 mg, 18 mg, 24 mg, 30 mg, 36 mg, 42 mg, or 48 mg deutetrabenazine, and the following inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, butyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, cellulose acetate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyethylene oxide, polyvinyl alcohol, propylene glycol, shellac, sodium chloride, talc, titanium dioxide, and FD&C red #40 lake. The 6 mg, 12 mg, 18 mg, 30 mg, 36 mg, and 42 mg extended-release tablets also contain FD&C yellow #6 lake. The 6 mg, 12 mg, 24 mg, and 36 mg extended-release tablets also contain FD&C blue #2 lake. The 18 mg extended-release tablets also contain carmine. AUSTEDO XR Delivery System Components and Performance AUSTEDO XR uses osmotic pressure to deliver deutetrabenazine at a controlled rate. The delivery system, which resembles a round tablet in appearance, consists of a bilayer core tablet that contains deutetrabenazine along with other excipients. The biologically inert components of the tablet remain intact during gastrointestinal transit and are eliminated in the stool.
AUSTEDO
AUSTEDO tablets contain 6 mg, 9 mg, or 12 mg deutetrabenazine, and the following inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, butyl alcohol, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, polysorbate 80, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, propylene glycol, shellac, talc, titanium dioxide, and FD&C blue #2 lake. The 6 mg tablets also contain FD&C red #40 lake. The 12 mg tablets also contain FD&C yellow #6 lake.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism by which deutetrabenazine exerts its effects in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and chorea in patients with Huntington’s disease is unknown but is believed to be related to its effect as a reversible depletor of monoamines (such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine) from nerve terminals. The major circulating metabolites (α-dihydrotetrabenazine [HTBZ] and β-HTBZ) of deutetrabenazine, are reversible inhibitors of VMAT2, resulting in decreased uptake of monoamines into synaptic vesicles and depletion of monoamine stores.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the maximum recommended dose, AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO do not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent. An exposure-response analysis on QTc prolongation from a study in extensive or intermediate (EM) and poor CYP2D6 metabolizers (PM) showed that a clinically-relevant effect can be excluded at exposures following single doses of 24 and 48 mg of AUSTEDO.
Melanin Binding
Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues (i.e., eye, skin, fur) in pigmented rats. After a single oral dose of radiolabeled deutetrabenazine, radioactivity was still detected in eye and fur at 35 days following dosing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 )].
Pharmacokinetics
After oral dosing, plasma concentrations of deutetrabenazine are low compared to that of the active deuterated metabolites because of the extensive hepatic metabolism of deutetrabenazine.
AUSTEDO XR
Systemic exposure (i.e., peak plasma concentrations [C max ] and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve [AUC]) for deutetrabenazine and the active, deuterated dihydro metabolites (HTBZ), α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ, increased proportionally to dose following single doses of AUSTEDO XR over the recommended clinical dosage range (6 mg to 48 mg).
AUSTEDO
Systemic exposure (C max and AUC) for the active metabolites increased proportionally to dose following single or multiple doses of deutetrabenazine (6 mg to 24 mg and 7.5 mg twice daily to 22.5 mg twice daily).
Absorption
Following oral administration of deutetrabenazine, the extent of absorption is at least 80%.
AUSTEDO XR
Peak plasma concentrations (C max ) of deutetrabenazine, deuterated α-HTBZ, and β-HTBZ are reached within approximately 3 hours, followed by sustained plateaus for several hours allowing for a 24-hour dosing interval.
AUSTEDO
Peak plasma concentrations (C max ) of deutetrabenazine, deuterated α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are reached within 3 to 4 hours after dosing.
Effect of Food
AUSTEDO XR
The effects of food on the bioavailability of AUSTEDO XR were studied in subjects administered a single dose with and without food. Food had no effect on C max or AUC of deutetrabenazine, α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
AUSTEDO
The effects of food on the bioavailability of AUSTEDO were studied in subjects administered a single dose with and without food. Food had no effect on AUC of α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ, although C max was increased by approximately 50% in the presence of food [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
Distribution
The median volume of distribution (Vc/F) of the α-HTBZ, and the β-HTBZ metabolites of deutetrabenazine are approximately 500 L and 730 L, respectively.
Results of PET-scan studies in humans show that following intravenous injection of 11 C-labeled tetrabenazine or α-HTBZ, radioactivity is rapidly distributed to the brain, with the highest binding in the striatum and lowest binding in the cortex.
The protein binding of deutetrabenazine and deuterated α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ in human plasma at the concentration of 0.1 µM is 82%, 57%, and 49% respectively, with no preferential binding of drug-related total radioactivity to the cellular components of human blood.
Elimination
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are primarily renally eliminated in the form of metabolites.
The half-life of the active deuterated α-HTBZ, β-HTBZ, and total (α+β)-HTBZ metabolites is approximately 12 hours, 7.5 hours, and 9 to 11 hours, respectively.
The clearance values (CL/F) of the α-HTBZ, and β-HTBZ metabolites of AUSTEDO are approximately 65 L/hour and 200 L/hour, respectively, for a 70 kg HD or TD patient with functional CYP2D6 metabolism in the fed state.
The elimination half-life and clearance of AUSTEDO XR are similar to that of AUSTEDO.
Metabolism
In vitro experiments in human liver microsomes demonstrate that deutetrabenazine is extensively biotransformed, mainly by carbonyl reductase, to its major active metabolites, α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ, which are subsequently metabolized primarily by CYP2D6, with minor contributions of CYP1A2 and CYP3A4/5, to form several minor metabolites.
Excretion
In a mass balance study in 6 healthy subjects, 75% to 86% of the deutetrabenazine dose was excreted in the urine, and fecal recovery accounted for 8% to 11% of the dose. Urinary excretion of the α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ metabolites from deutetrabenazine each accounted for less than 10% of the administered dose. Sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of the α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ metabolites of deutetrabenazine, as well as products of oxidative metabolism, accounted for the majority of metabolites in the urine.
Specific Populations
Male and Female Patients
There is no apparent effect of gender on the pharmacokinetics of α-HTBZ and β‑HTBZ of deutetrabenazine.
Patients with Renal Impairment
No clinical studies have been conducted to assess the effect of renal impairment on the PK of deutetrabenazine and its primary metabolites.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of deutetrabenazine and its primary metabolites has not been studied. However, in a clinical study conducted to assess the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tetrabenazine, a closely related VMAT2 inhibitor, the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ was up to 40% greater in patients with hepatic impairment, and the mean tetrabenazine C max in patients with hepatic impairment was up to 190-fold higher than in healthy subjects [see Contraindications (4 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.6 )] .
Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Although the pharmacokinetics of deutetrabenazine and its metabolites have not been systematically evaluated in patients who do not express the drug metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6, it is likely that the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ would be increased similarly to taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (approximately 3-fold) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ), Drug Interactions (7.1 )] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of Other Drugs on AUSTEDO/AUSTEDO XR
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
In vitro studies indicate that the α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ metabolites of deutetrabenazine are substrates for CYP2D6. The effect of CYP2D6 inhibition on the pharmacokinetics of deutetrabenazine and its metabolites was studied in 24 healthy subjects following a single 22.5 mg dose of deutetrabenazine given after 8 days of administration of the strong CYP2D6 inhibitor paroxetine 20 mg daily. In the presence of paroxetine, systemic exposure (AUC inf ) of α-HTBZ was 1.9-fold higher and β-HTBZ was 6.5-fold higher, resulting in approximately 3-fold increase in AUC inf for total (α+β)-HTBZ. Paroxetine decreased the clearance of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ metabolites of AUSTEDO with corresponding increases in mean half-life of approximately 1.5-fold and 2.7-fold, respectively. In the presence of paroxetine, C max of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ were 1.2-fold and 2.2-fold higher, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.1 )].
The effect of moderate or weak CYP2D6 inhibitors such as duloxetine, terbinafine, amiodarone, or sertraline on the exposure of deutetrabenazine and its metabolites has not been evaluated.
Transporters
In vitro studies showed that at clinically relevant concentrations, deutetrabenazine and its active metabolites are not substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and BCRP transporters. Deutetrabenazine and its active metabolites are unlikely substrates of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OCT1.
Effect of AUSTEDO/AUSTEDO XR on Other Drugs
CYP Enzymes
In vitro studies showed that at clinically relevant concentrations, deutetrabenazine, and its active metabolites did not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 enzymes, and did not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4 enzymes.
Transporters
In vitro studies demonstrated that at clinically relevant concentrations, deutetrabenazine and its active metabolites did not inhibit the following transporters: P-gp, BCRP, BSEP, MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, and OCT2.
Minor Metabolites
The deutetrabenazine metabolites, 2-methylpropanoic acid of β-HTBZ (M1) and monohydroxy tetrabenazine (M4), have been evaluated in a panel of in vitro drug-drug interaction studies; the results indicate that M1/M4 are not expected to cause clinically relevant drug interactions.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No carcinogenicity studies were performed with deutetrabenazine.
No increase in tumors was observed in p53 +/– transgenic mice treated orally with tetrabenazine at doses of 0, 5, 15, and 30 mg/kg/day for 26 weeks.
Mutagenesis
Deutetrabenazine and its deuterated α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ metabolites were negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation and chromosome aberration in human peripheral blood lymphocytes) assays in the presence or absence of metabolic activation and in the in vivo micronucleus assay in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
The effects of deutetrabenazine on fertility have not been evaluated. Oral administration of deutetrabenazine (doses of 5, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) to female rats for 3 months resulted in estrous cycle disruption at all doses; the lowest dose tested was similar to the maximum recommended human dose (48 mg/day) on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis.
Oral administration of tetrabenazine (doses of 5, 15, or 30 mg/kg/day) to female rats prior to and throughout mating, and continuing through day 7 of gestation, resulted in disrupted estrous cyclicity at doses greater than 5 mg/kg/day. No effects on mating and fertility indices or sperm parameters (motility, count, density) were observed when males were treated orally with tetrabenazine at doses of 5, 15 or 30 mg/kg/day prior to and throughout mating with untreated females.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The studies described below establishing effectiveness for Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia were conducted with AUSTEDO tablets. The efficacy of AUSTEDO XR is based on a relative bioavailability study comparing AUSTEDO XR tablets administered once daily and AUSTEDO tablets administered twice daily [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Chorea Associated with Huntington’s Disease
The efficacy of AUSTEDO as a treatment for chorea associated with Huntington's disease was established primarily in Study 1, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trial conducted in 90 ambulatory patients with manifest chorea associated with Huntington’s disease. The diagnosis of Huntington’s disease was based on family history, neurological exam, and genetic testing. Treatment duration was 12 weeks, including an 8-week dose titration period and a 4-week maintenance period, followed by a 1-week washout. Patients were not blinded to discontinuation. AUSTEDO was started at 6 mg per day and titrated upward, at weekly intervals, in 6 mg increments until satisfactory treatment of chorea was achieved, intolerable side effects occurred, or until a maximal dose of 48 mg per day was reached. The primary efficacy endpoint was the Total Maximal Chorea Score, an item of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS). On this scale, chorea is rated from 0 to 4 (with 0 representing no chorea) for 7 different parts of the body. The total score ranges from 0 to 28.
Of the 90 patients enrolled, 87 patients completed the study. The mean age was 54 (range 23 to 74). Patients were 56% male and 92% Caucasian. The mean dose after titration was 40 mg per day. Table 5 and Figure 1 summarize the effects of AUSTEDO on chorea based on the Total Maximal Chorea Score. Total Maximal Chorea Scores for patients receiving AUSTEDO improved by approximately 4.4 units from baseline to the maintenance period (average of Week 9 and Week 12), compared to approximately 1.9 units in the placebo group. The treatment effect of -2.5 units was statistically significant (p<0.0001). The Maintenance Endpoint is the mean of the Total Maximal Chorea Scores for the Week 9 and Week 12 visits. At the Week 13 follow-up visit (1 week after discontinuation of the study medication), the Total Maximal Chorea Scores of patients who had received AUSTEDO returned to baseline (Figure 1).
| Motor Endpoint | AUSTEDO N = 45 | Placebo N = 45 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
Change in Total Chorea Score • from Baseline to Maintenance Therapy † | -4.4 | -1.9 | <0.0001 |
• TMC is a subscale of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS) † Primary efficacy endpoint
Figure 1: Total Maximal Chorea Score Over Time in Study 1
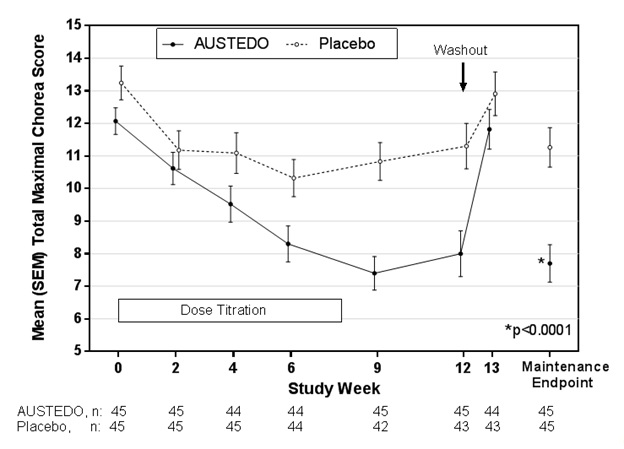
Figure 2: Distribution of the Change in Total Maximal Chorea Scores in Study 1
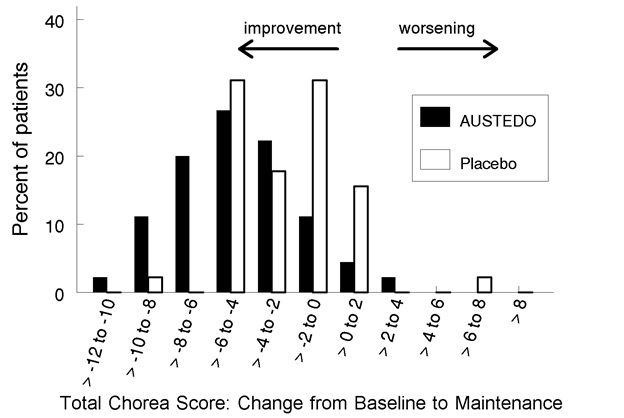
Figure 2 shows the distribution of values for the change in Total Maximal Chorea Score in Study 1. Negative values indicate a reduction in chorea and positive numbers indicate an increase in chorea.
A patient-rated global impression of change assessed how patients rated their overall Huntington’s disease symptoms. Fifty-one percent of patients treated with AUSTEDO rated their symptoms as “Much Improved” or “Very Much Improved” at the end of treatment, compared to 20% of placebo-treated patients.
In a physician-rated clinical global impression of change, physicians rated 42% percent of patients treated with AUSTEDO as “Much Improved” or “Very Much Improved” at the end of treatment compared to 13% of placebo-treated patients.
Tardive Dyskinesia
The efficacy of AUSTEDO in the treatment for tardive dyskinesia was established in two 12‑week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trials conducted in 335 adult ambulatory patients with tardive dyskinesia caused by use of dopamine receptor antagonists. Patients had a history of using a dopamine receptor antagonist (antipsychotics, metoclopramide) for at least 3 months (or 1 month in patients 60 years of age and older). Concurrent diagnoses included schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder (62%) and mood disorder (33%). With respect to concurrent antipsychotic use, 64% of patients were receiving atypical antipsychotics, 12% were receiving typical or combination antipsychotics, and 24% were not receiving antipsychotics.
The Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) was the primary efficacy measure for the assessment of tardive dyskinesia severity. The AIMS is a 12-item scale; items 1 to 7 assess the severity of involuntary movements across body regions and these items were used in this study. Each of the 7 items was scored on a 0 to 4 scale, rated as: 0=not present; 1=minimal, may be extreme normal (abnormal movements occur infrequently and/or are difficult to detect); 2=mild (abnormal movements occur infrequently and are easy to detect); 3=moderate (abnormal movements occur frequently and are easy to detect) or 4 =severe (abnormal movements occur almost continuously and/or of extreme intensity). The AIMS total score (sum of items 1 to 7) could thus range from 0 to 28, with a decrease in score indicating improvement.
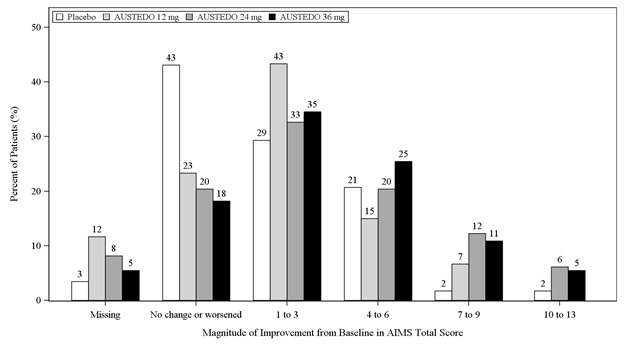
In Study 1, a 12-week, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial, adults with tardive dyskinesia were randomized 1:1:1:1 to 12 mg AUSTEDO, 24 mg AUSTEDO, 36 mg AUSTEDO, or placebo. Treatment duration included a 4-week dose escalation period and an 8-week maintenance period followed by a 1-week washout. The dose of AUSTEDO was started at 12 mg per day and increased at weekly intervals in 6 mg/day increments to a dose target of 12 mg, 24 mg or 36 mg per day. The population (n= 222) was 21 to 81 years old (mean 57 years), 48% male, and 79% Caucasian. In Study 1, the AIMS total score for patients receiving AUSTEDO demonstrated statistically significant improvement, from baseline to Week 12, of 3.3 and 3.2 units for the 36 mg and 24 mg arms, respectively, compared with 1.4 units in placebo (Study 1 in Table 6). The improvements on the AIMS total score over the course of the study are displayed in Figure 3. Data did not suggest substantial differences in efficacy across various demographic groups. The treatment response rate distribution, based on magnitude of AIMS total score from baseline to week 12 is displayed in Figure 4.
The mean changes in the AIMS total score by visit are shown in Figure 3.
In Study 2, a 12-week, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose trial, adults with tardive dyskinesia (n=113) received daily doses of placebo or AUSTEDO, starting at 12 mg per day with increases allowed in 6-mg increments at 1-week intervals until satisfactory control of dyskinesia was achieved, until intolerable side effects occurred, or until a maximal dose of 48 mg per day was reached. Treatment duration included a 6-week dose titration period and a 6-week maintenance period followed by a 1-week washout. The population was 25 to 75 years old (mean 55 years), 48% male, and 70% Caucasian. Patients were titrated to an optimal dose over 6 weeks. The average dose of AUSTEDO after treatment was 38.3 mg per day. There was no evidence suggesting substantial differences in efficacy across various demographic groups. In Study 2, AIMS total score for patients receiving AUSTEDO demonstrated statistically significant improvement by 3.0 units from baseline to endpoint (Week 12), compared with 1.6 units in the placebo group with a treatment effect of -1.4 units. Table 6 summarizes the effects of AUSTEDO on tardive dyskinesia based on the AIMS.
| Study | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: AIMS Total Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Treatment Effect (95% CI) | ||
Study 1 | AUSTEDO 36 mg• (n= 55) | 10.1 (3.21) | -3.3 (0.42) | -1.9 (-3.09, -0.79) |
AUSTEDO 24 mg (n= 49) | 9.4 (2.93) | -3.2 (0.45) | -1.8 (-3.00, -0.63) | |
AUSTEDO 12 mg (n= 60) | 9.6 (2.40) | -2.1 (0.42) | -0.7 (-1.84, 0.42) | |
Placebo (n= 58) | 9.5 (2.71) | -1.4 (0.41) | ||
Study 2 | AUSTEDO (12-48 mg/day)• (n= 56) | 9.7 (4.14) | -3.0 (0.45) | -1.4 (-2.6, -0.2) |
Placebo (n= 57) | 9.6 (3.78) | -1.6 (0.46) | ||
•Dose that was statistically significantly different from placebo after adjusting for multiplicity.
LS Mean = Least-squares mean; SD = Standard deviation; SE = Standard error; CI = 2-sided 95% confidence interval
Figure 3: Least Square Means of Change in AIMS Total Score from Baseline for AUSTEDO Compared to Placebo (Study 1)
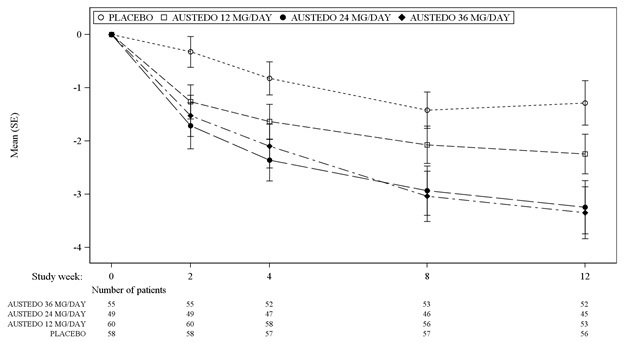
SE = Standard error
Figure 4: Percent of Patients with Specified Magnitude of AIMS Total Score Improvement at the End of Week 12 (Study 1)
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are supplied in the following configurations:
Strength | Description | Package Configuration | NDC Code |
| 6 mg | Round, grey-coated tablets, with “Q6” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-470-56 |
| 12 mg | Round, blue-coated tablets, with “Q12” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-471-56 |
| 18 mg | Round, light grey-coated tablets, with “Q18” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-479-56 |
| 24 mg | Round, purple-coated tablets, with “Q24” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-472-56 |
| 30 mg | Round, light orange-coated tablets, with “Q30” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-473-56 |
| 36 mg | Round, light purple-coated tablets, with “Q36” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-474-56 |
| 42 mg | Round, orange-coated tablets, with “Q42” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-475-56 |
| 48 mg | Round, pink-coated tablets, with “Q48” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 30 count | 68546-476-56 |
AUSTEDO XR Patient Titration Kits are supplied in the following configuration:
| Strength | Description | Package Configuration | NDC Code |
4-Week Patient Titration Kit | |||
12 mg | Round, blue-coated tablets, with “Q12” printed in black ink on one side | Titration Kit / 28 count Each Titration Kit contains 1 child-resistant blister pack, containing one foil card with extended-release tablets in the following configuration: Seven 12 mg tablets taken during Week 1; seven 18 mg tablets taken during Week 2; seven 24 mg tablets taken during Week 3; and seven 30 mg tablets taken during Week 4. | 68546-477-29 |
18 mg | Round, light grey-coated tablets, with “Q18” printed in black ink on one side | ||
| 24 mg | Round, purple-coated tablets, with “Q24” printed in black ink on one side | ||
30 mg | Round, light orange-coated tablets, with “Q30” printed in black ink on one side | ||
AUSTEDO tablets are supplied in the following configurations:
Strength | Description | Package Configuration | NDC Code |
6 mg | Round, purple-coated tablets, with “SD” over “6” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 60 count | 68546-170-60 |
9 mg | Round, blue-coated tablets, with “SD” over “9” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 60 count | 68546-171-60 |
12 mg | Round, beige-coated tablets, with “SD” over “12” printed in black ink on one side | Bottle with child-resistant cap / 60 count | 68546-172-60 |
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] . Protect from light and moisture. Dispense in original containers or in tight containers as defined in USP.
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism by which deutetrabenazine exerts its effects in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and chorea in patients with Huntington’s disease is unknown but is believed to be related to its effect as a reversible depletor of monoamines (such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine) from nerve terminals. The major circulating metabolites (α-dihydrotetrabenazine [HTBZ] and β-HTBZ) of deutetrabenazine, are reversible inhibitors of VMAT2, resulting in decreased uptake of monoamines into synaptic vesicles and depletion of monoamine stores.