Get your patient on Butalbital, Aspirin, And Caffeine - Butalbital, Aspirin, And Caffeine capsule (Butalbital, Aspirin, And Caffeine)
Butalbital, Aspirin, And Caffeine - Butalbital, Aspirin, And Caffeine capsule prescribing information
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One or 2 capsules every 4 hours. Total daily dose should not exceed 6 capsules. Extended and repeated use of this product is not recommended because of the potential for physical dependence.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules is contraindicated under the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity or intolerance to aspirin, caffeine, or butalbital.
- Patients with a hemorrhagic diathesis (e.g., hemophilia, hypoprothrombinemia, von Willebrand’s disease, the thrombocytopenias, thrombasthenia and other ill-defined hereditary platelet dysfunctions, severe vitamin K deficiency and severe liver damage).
- Patients with the syndrome of nasal polyps, angioedema and bronchospastic reactivity to aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in such patients.
- Peptic ulcer or other serious gastrointestinal lesions.
- Patients with porphyria.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent adverse reactions are drowsiness and dizziness. Less frequent adverse reactions are lightheadedness and gastrointestinal disturbances including nausea, vomiting, and flatulence. A single incidence of bone marrow suppression has been reported with the use of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules. Several cases of dermatological reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme have been reported.
Drug Interactions
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
In patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids and chronic use of aspirin, withdrawal of corticosteroids may result in salicylism because corticosteroids enhance renal clearance of salicylates and their withdrawal is followed by return to normal rates of renal clearance.
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules may enhance the effects of:
- Oral anticoagulants, causing bleeding by inhibiting prothrombin formation in the liver and displacing anticoagulants from plasma protein binding sites.
- Oral antidiabetic agents and insulin, causing hypoglycemia by contributing an additive effect, if dosage of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules exceeds maximum recommended daily dosage.
- 6-mercaptopurine and methotrexate, causing bone marrow toxicity and blood dyscrasias by displacing these drugs from secondary binding sites, and, in the case of methotrexate, also reducing its excretion.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, increasing the risk of peptic ulceration and bleeding by contributing additive effects.
- Other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules may diminish the effects of:
Uricosuric agents such as probenecid and sulfinpyrazone, reducing their effectiveness in the treatment of gout. Aspirin competes with these agents for protein binding sites.
DESCRIPTION
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules, USP is supplied in capsule form for oral administration.
Each capsule contains the following active ingredients:
| butalbital, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . | 50 mg |
| aspirin, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | 500 mg |
| caffeine, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . | 40 mg |
Butalbital (5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid) is a short- to intermediate-acting barbiturate. It has the following structural formula:
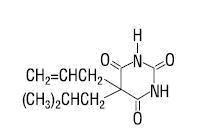
C 11 H 16 N 2 O 3 molecular weight 224.26
Aspirin (benzoic acid, 2-(acetyloxy)-) is an analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory. It has the following structural formula:
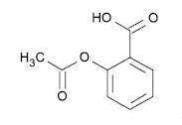
C 9 H 8 O 4 molecular weight 180.16
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is a central nervous system stimulant. It has the following structural formula:
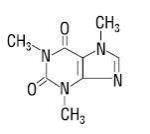
C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 molecular weight 194.19
Inactive Ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, stearic acid, sodium lauryl sulfate, and talc. Gelatin capsules contain FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Green No. 3, FD&C Yellow No. 5, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, titanium dioxide and gelatin. The capsules are printed with edible ink.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacologically, Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules combines the analgesic properties of aspirin with the anxiolytic and muscle relaxant properties of butalbital.
The clinical effectiveness of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules in tension headache has been established in double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-clinic trials. A factorial design study compared Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules with each of its major components. This study demonstrated that each component contributes to the efficacy of Butalbital, Aspirin, Caffeine Capsules in the treatment of the target symptoms of tension headache (headache pain, psychic tension, and muscle contraction in the head, neck, and shoulder region). For each symptom and the symptom complex as a whole, Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules was shown to have significantly superior clinical effects to either component alone.
Pharmacokinetics
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Aspirin
The systemic availability of aspirin after an oral dose is highly dependent on the dosage form, the presence of food, the gastric emptying time, gastric pH, antacids, buffering agents, and particle size. These factors affect not necessarily the extent of absorption of total salicylates but more the stability of aspirin prior to absorption.
During the absorption process and after absorption, aspirin is mainly hydrolyzed to salicylic acid and distributed to all body tissues and fluids, including fetal tissues, breast milk, and the central nervous system (CNS). Highest concentrations are found in plasma, liver, renal cortex, heart, and lung. In plasma, about 50%-80% of the salicylic acid and its metabolites are loosely bound to plasma proteins.
The clearance of total salicylates is subject to saturable kinetics; however, first-order elimination kinetics are still a good approximation for doses up to 650 mg. The plasma half-life for aspirin is about 12 minutes and for salicylic acid and/or total salicylates is about 3 hours.
The elimination of therapeutic doses is through the kidneys either as salicylic acid or other biotransformation products. The renal clearance is greatly augmented by an alkaline urine as is produced by concurrent administration of sodium bicarbonate or potassium citrate.
The biotransformation of aspirin occurs primarily in the hepatocytes. The major metabolites are salicyluric acid (75%), the phenolic and acyl glucuronides of salicylate (15%), and gentisic and gentisuric acid (1%). The bioavailability of the aspirin component of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules is equivalent to that of a solution except for a slower rate of absorption. A peak concentration of 8.8 mcg/mL was obtained at 40 minutes after a 650 mg dose.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Butalbital
Butalbital is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is expected to distribute to most of the tissues in the body. Barbiturates, in general, may appear in breast milk and readily cross the placental barrier. They are bound to plasma and tissue proteins to a varying degree and binding increases directly as a function of lipid solubility.
Elimination of butalbital is primarily via the kidney (59%-88% of the dose) as unchanged drug or metabolites. The plasma half-life is about 35 hours. Urinary excretion products included parent drug (about 3.6% of the dose), 5-isobutyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) barbituric acid (about 24% of the dose), 5-allyl-5(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid (about 4.8% of the dose), products with the barbituric acid ring hydrolyzed with excretion of urea (about 14% of the dose), as well as unidentified materials. Of the material excreted in the urine, 32% was conjugated.
The bioavailability of the butalbital component of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules is equivalent to that of a solution except for a decrease in the rate of absorption. A peak concentration of 2,020 ng/mL is obtained at about 1.5 hours after a 100 mg dose.
The in vitro plasma protein binding of butalbital is 45% over the concentration range of 0.5-20 mcg/mL. This falls within the range of plasma protein binding (20%-45%) reported with other barbiturates such as phenobarbital, pentobarbital, and secobarbital sodium. The plasma-to-blood concentration ratio was almost unity indicating that there is no preferential distribution of butalbital into either plasma or blood cells.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Caffeine
Like most xanthines, caffeine is rapidly absorbed and distributed in all body tissues and fluids, including the CNS, fetal tissues, and breast milk.
Caffeine is cleared rapidly through metabolism and excretion in the urine. The plasma half-life is about 3 hours. Hepatic biotransformation prior to excretion results in about equal amounts of 1-methylxanthine and 1-methyluric acid. Of the 70% of the dose that has been recovered in the urine, only 3% was unchanged drug.
The bioavailability of the caffeine component for Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules is equivalent to that of a solution except for a slightly longer time to peak. A peak concentration of 1,660 ng/mL was obtained in less than an hour for an 80 mg dose.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
HOW SUPPLIED
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Capsules, USP Green cap with a beige body. Each half of capsule is imprinted with a double line encircling the entire circumference.
Bottles of 100 are supplied with child-resistant closures ......... NDC 79739-7192-1
Bottles of 500 are supplied with child-resistant closures ......... NDC 79739-7192-5
Store and Dispense Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight container. Protect from moisture.
Rx only
Manufactured By: LGM Pharma Solutions, LLC Irvine, CA 92614
7192-PD Rev 07/2021