Get your patient on Cablivi (Caplacizumab)
Cablivi prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Cablivi patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- CABLIVI should be administered upon the initiation of plasma exchange therapy. The recommended dose of CABLIVI is as follows: (2.1 )
- First day of treatment: 11 mg bolus intravenous injection at least 15 minutes prior to plasma exchange followed by an 11 mg subcutaneous injection after completion of plasma exchange on day 1.
- Subsequent treatment during daily plasma exchange: 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily following plasma exchange.
- Treatment after the plasma exchange period: 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily for 30 days beyond the last plasma exchange.
- If after initial treatment course, sign(s) of persistent underlying disease such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels remain present, treatment may be extended for a maximum of 28 days.
- Discontinue CABLIVI if the patient experiences more than 2 recurrences of aTTP, while on CABLIVI.
- The first dose should be administered by a healthcare provider as a bolus intravenous injection. Administer subsequent doses subcutaneously in the abdomen. (2.3 )
Recommended Dose and Schedules
CABLIVI should be administered upon initiation of plasma exchange therapy. The recommended dose of CABLIVI is as follows:
- First day of treatment : 11 mg bolus intravenous injection at least 15 minutes prior to plasma exchange followed by an 11 mg subcutaneous injection after completion of plasma exchange on day 1.
- Subsequent days of treatment during daily plasma exchange : 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily following plasma exchange.
- Treatment after plasma exchange period : 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily continuing for 30 days following the last daily plasma exchange. If after initial treatment course, sign(s) of persistent underlying disease such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels remain present, treatment may be extended for a maximum of 28 days.
Discontinue CABLIVI if the patient experiences more than 2 recurrences of aTTP, while on CABLIVI.
Avoid concomitant use of antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Missed Dose
Administer the first dose of CABLIVI intravenously before the initial plasma exchange. If the administration of the first intravenous dose of CABLIVI is missed and plasma exchange is already administered, administer the first CABLIVI dose intravenously and administer the next dose subcutaneously on the following day according to the usual dosing schedule. If a dose of CABLIVI is missed during the plasma exchange period, it should be given as soon as possible. If a dose of CABLIVI is missed after the plasma exchange period, it can be administered within 12 hours of the scheduled time of administration. Beyond 12 hours, the missed dose should be skipped and the next daily dose administered according to the usual dosing schedule.
Discontinuation for Surgery and Other Interventions
Withhold CABLIVI treatment 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures, or other invasive interventions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Reconstitution and Administration Instructions
The first dose of CABLIVI should be administered by a healthcare provider as a bolus intravenous injection. Administer subsequent doses subcutaneously in the abdomen. Avoid injections around the navel. Do not administer consecutive injections in the same abdominal quadrant.
Adult patients may self-inject, or adult caregivers may inject CABLIVI subcutaneously after proper instruction on the preparation and administration of CABLIVI, including aseptic technique [see Instructions for Use ] if a healthcare provider determines that it is appropriate. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, CABLIVI must be administered by a healthcare provider or an adult caregiver.
- If the carton was not stored at room temperature, allow the CABLIVI vial and diluent syringe to reach room temperature [25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F)] by holding them in your hands for 10 seconds. Do not use any other way to warm up the vial and syringe.
- Reconstitute CABLIVI before administration using the provided syringe containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, to yield an 11 mg/mL single-dose solution.
- Using aseptic technique throughout the preparation of the solution, attach the vial adapter to the vial containing CABLIVI.
- Remove the plastic cap from the syringe and attach it to the vial adapter by twisting it clockwise until it cannot twist any further.
- Slowly push the syringe plunger down until the syringe is empty. Do not remove the syringe from the vial adapter.
- Gently swirl the vial until the cake or powder is completely dissolved. Do not shake.
- Visually inspect that the reconstituted solution is clear and colorless.
- Withdraw all of the clear, colorless reconstituted solution from the vial into the syringe. Label the CABLIVI syringe.
- Administer the full amount of reconstituted solution.
- For the initial intravenous injection, if using an intravenous line, the glass syringe should be connected to a standard Luer lock and flushed with either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
- Use the CABLIVI solution immediately. If not, use CABLIVI within 4 hours after reconstitution when stored in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Cablivi prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CABLIVI is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- CABLIVI should be administered upon the initiation of plasma exchange therapy. The recommended dose of CABLIVI is as follows: (2.1 )
- First day of treatment: 11 mg bolus intravenous injection at least 15 minutes prior to plasma exchange followed by an 11 mg subcutaneous injection after completion of plasma exchange on day 1.
- Subsequent treatment during daily plasma exchange: 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily following plasma exchange.
- Treatment after the plasma exchange period: 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily for 30 days beyond the last plasma exchange.
- If after initial treatment course, sign(s) of persistent underlying disease such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels remain present, treatment may be extended for a maximum of 28 days.
- Discontinue CABLIVI if the patient experiences more than 2 recurrences of aTTP, while on CABLIVI.
- The first dose should be administered by a healthcare provider as a bolus intravenous injection. Administer subsequent doses subcutaneously in the abdomen. (2.3 )
Recommended Dose and Schedules
CABLIVI should be administered upon initiation of plasma exchange therapy. The recommended dose of CABLIVI is as follows:
- First day of treatment : 11 mg bolus intravenous injection at least 15 minutes prior to plasma exchange followed by an 11 mg subcutaneous injection after completion of plasma exchange on day 1.
- Subsequent days of treatment during daily plasma exchange : 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily following plasma exchange.
- Treatment after plasma exchange period : 11 mg subcutaneous injection once daily continuing for 30 days following the last daily plasma exchange. If after initial treatment course, sign(s) of persistent underlying disease such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels remain present, treatment may be extended for a maximum of 28 days.
Discontinue CABLIVI if the patient experiences more than 2 recurrences of aTTP, while on CABLIVI.
Avoid concomitant use of antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Missed Dose
Administer the first dose of CABLIVI intravenously before the initial plasma exchange. If the administration of the first intravenous dose of CABLIVI is missed and plasma exchange is already administered, administer the first CABLIVI dose intravenously and administer the next dose subcutaneously on the following day according to the usual dosing schedule. If a dose of CABLIVI is missed during the plasma exchange period, it should be given as soon as possible. If a dose of CABLIVI is missed after the plasma exchange period, it can be administered within 12 hours of the scheduled time of administration. Beyond 12 hours, the missed dose should be skipped and the next daily dose administered according to the usual dosing schedule.
Discontinuation for Surgery and Other Interventions
Withhold CABLIVI treatment 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures, or other invasive interventions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Reconstitution and Administration Instructions
The first dose of CABLIVI should be administered by a healthcare provider as a bolus intravenous injection. Administer subsequent doses subcutaneously in the abdomen. Avoid injections around the navel. Do not administer consecutive injections in the same abdominal quadrant.
Adult patients may self-inject, or adult caregivers may inject CABLIVI subcutaneously after proper instruction on the preparation and administration of CABLIVI, including aseptic technique [see Instructions for Use ] if a healthcare provider determines that it is appropriate. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, CABLIVI must be administered by a healthcare provider or an adult caregiver.
- If the carton was not stored at room temperature, allow the CABLIVI vial and diluent syringe to reach room temperature [25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F)] by holding them in your hands for 10 seconds. Do not use any other way to warm up the vial and syringe.
- Reconstitute CABLIVI before administration using the provided syringe containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, to yield an 11 mg/mL single-dose solution.
- Using aseptic technique throughout the preparation of the solution, attach the vial adapter to the vial containing CABLIVI.
- Remove the plastic cap from the syringe and attach it to the vial adapter by twisting it clockwise until it cannot twist any further.
- Slowly push the syringe plunger down until the syringe is empty. Do not remove the syringe from the vial adapter.
- Gently swirl the vial until the cake or powder is completely dissolved. Do not shake.
- Visually inspect that the reconstituted solution is clear and colorless.
- Withdraw all of the clear, colorless reconstituted solution from the vial into the syringe. Label the CABLIVI syringe.
- Administer the full amount of reconstituted solution.
- For the initial intravenous injection, if using an intravenous line, the glass syringe should be connected to a standard Luer lock and flushed with either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
- Use the CABLIVI solution immediately. If not, use CABLIVI within 4 hours after reconstitution when stored in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 11 mg as a white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. However, there are potential risks of hemorrhage in the mother and fetus associated with use of CABLIVI (see Clinical Considerations ) . In animal reproduction studies, there was no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes with intramuscular administration of caplacizumab-yhdp during organogenesis in guinea pigs at exposures approximately 30 times the AUC in humans at the recommended subcutaneous injection dose of 11 mg (see Data ) .
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background rate of major birth defects and miscarriage in the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background rate of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions
CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Maternal adverse reactions
All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Data
Animal data
Two separate reproduction studies were conducted in pregnant guinea pigs with administration of caplacizumab-yhdp during the organogenesis period.
In an embryo-fetal development study, caplacizumab-yhdp was administered intramuscularly at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day from gestational day (GD) 6 to GD 41 in guinea pigs. No maternal toxicity or adverse developmental outcomes were observed.
In a toxicokinetic study assessing the exposure of caplacizumab-yhdp in the dams and fetuses, caplacizumab-yhdp was administered once daily to female guinea pigs at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (corresponding to a drug exposure of approximately 30 times the AUC in humans at the recommended dose of 11 mg) by intramuscular injection from GD 6 to GD 41 or GD 61. Exposure to caplacizumab-yhdp was observed in the dams and fetuses, with no effects on embryo-fetal development.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of caplacizumab-yhdp in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for CABLIVI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CABLIVI, or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CABLIVI in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy have been established. Use of CABLIVI for this indication is supported by evidence from an observational, retrospective chart review and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation data [see Adverse Reactions (6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of CABLIVI in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of CABLIVI did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Hepatic Impairment
No formal studies with CABLIVI have been conducted in patients with severe acute or chronic hepatic impairment and no data regarding the use of CABLIVI in these populations are available. Due to a potential increased risk of bleeding, use of CABLIVI in patients with severe hepatic impairment requires close monitoring for bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of the excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hemorrhage: Serious and fatal bleeding can occur. Risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies or on concomitant antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt treatment. Withhold CABLIVI 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures, or other invasive interventions. (5.1 )
Hemorrhage
CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
In the postmarketing setting, cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g., hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents, thrombolytic drugs, heparin, or anticoagulants. Interrupt use of CABLIVI if clinically significant bleeding occurs. If needed, von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
TITAN and HERCULES
The safety of CABLIVI was evaluated in two placebo-controlled clinical studies (HERCULES, in which 71 patients received CABLIVI; and TITAN, in which 35 patients received CABLIVI). The data described below and in the Warnings and Precautions reflect exposure to CABLIVI during the blinded periods of both studies, which include 106 patients with aTTP who received at least one dose, age 18 to 79 years, of whom 69% were female and 73% were White. The median treatment duration with CABLIVI was 35 days (range 1–77 days).
The most frequently reported adverse reactions (>15%) were epistaxis, headache and gingival bleeding. Seven patients (7%) in the CABLIVI group experienced an adverse reaction leading to study drug discontinuation. None of the adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were observed in more than 1% of patients.
Among 106 patients treated with CABLIVI during the TITAN and HERCULES studies, serious bleeding adverse reactions reported in ≥2% patients included epistaxis (4%) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (2%).
Adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients treated with CABLIVI and more frequently than in those treated with placebo across the pooled data from the two trials are summarized in Table 1. Urticaria was seen during plasma exchange.
| Adverse Reaction by Body System | CABLIVI (N=106) n (%) | Placebo (N=110) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Gingival bleeding | 17 (16) | 3 (3) |
| Rectal hemorrhage | 4 (4) | 0 (0) |
| Abdominal wall hematoma | 3 (3) | 1 (1) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue | 16 (15) | 10 (9) |
| Pyrexia | 14 (13) | 12 (11) |
| Injection site hemorrhage | 6 (6) | 1 (1) |
| Catheter site hemorrhage | 6 (6) | 5 (5) |
| Injection site pruritus | 3 (3) | 0 (0) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Back pain | 7 (7) | 4 (4) |
| Myalgia | 6 (6) | 2 (2) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 22 (21) | 15 (14) |
| Paresthesia | 13 (12) | 11 (10) |
| Renal and urinary disorders | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 6 (6) | 4 (4) |
| Hematuria | 4 (4) | 3 (3) |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | ||
| Vaginal hemorrhage | 5 (5) | 2 (2) |
| Menorrhagia | 4 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Epistaxis | 31 (29) | 6 (6) |
| Dyspnea | 10 (9) | 5 (5) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Urticaria | 15 (14) | 7 (6) |
Pediatric Patients
The safety of CABLIVI in patients aged ≤18 years with aTTP was evaluated in an observational, retrospective chart review (OBS17325) [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . The most commonly reported events were epistaxis in 4 (13.3%) patients and tachycardia in 4 (13.3%) patients. One serious bleeding adverse reaction (hemorrhage urinary tract) was reported. The adverse reaction profile in pediatric patients 12 years and older with aTTP was consistent with that in adults.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of CABLIVI. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to caplacizumab-yhdp exposure.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
- Injection site reactions including injection site pain, injection site bruising and injection site erythema
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Concomitant use of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents with CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding. Monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use. (7 )
Concomitant Use of Anticoagulants, Thrombolytic Drugs, Heparin or Antiplatelet Agents
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant, thrombolytic drugs, heparin or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DESCRIPTION
Caplacizumab-yhdp is a von Willebrand factor (vWF)-directed antibody fragment that consists of two identical humanized building blocks, linked by a three-alanine linker. Caplacizumab-yhdp is produced in Escherichia coli by recombinant DNA technology and has an approximate molecular weight of 28 kDa.
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) for injection is a sterile, white, preservative-free, lyophilized powder. Each single-dose vial delivers 11 mg caplacizumab-yhdp, anhydrous citric acid (0.18 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.10 mg), sucrose (62 mg), and trisodium citrate dihydrate (4.91 mg). After reconstitution with 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the final concentration is 11 mg/mL, at a pH of approximately 6.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Caplacizumab-yhdp targets the A1-domain of vWF, and inhibits the interaction between vWF and platelets, thereby reducing both vWF-mediated platelet adhesion and platelet consumption.
Pharmacodynamics
Ristocetin cofactor (RICO) activity was used to assess vWF activity. Subcutaneous doses of caplacizumab-yhdp at greater than or equal to the approved recommended dosage to healthy subjects and patients with aTTP decreased RICO activity levels to below 20% approximately 4 hours post-dose. RICO activity returned to baseline values within 7 days of drug discontinuation.
Caplacizumab-yhdp decreased vWF antigen and factor VIII:C levels. These reductions were transient and returned to baseline upon cessation of treatment.
Pharmacokinetics
Caplacizumab-yhdp pharmacokinetics depends on the expression of the target vWF and are not dose proportional. Higher levels of vWF antigen increase the fraction of drug-target complex retained in the circulation. Steady-state was reached following the first administration of CABLIVI in healthy subjects, with minimal accumulation. Following a single subcutaneous dose of 10 mg caplacizumab-yhdp to healthy subjects the mean (CV%) peak concentration (C max ) was 528 (20%) ng/mL and AUC 0–24 was 7951 (16%). Following subcutaneous dosing of 10 mg caplacizumab-yhdp daily for 14 days to healthy subjects, the mean (CV%) C max was 348 (30%) ng/mL and AUC 0–τ was 6808 (26%) hr∙ng/mL.
Absorption
The bioavailability of subcutaneous caplacizumab-yhdp is approximately 90%.
The maximum concentration was observed 6 to 7 hours after subcutaneous dosing of 10 mg caplacizumab-yhdp once daily in healthy subjects.
Distribution
Caplacizumab-yhdp central volume of distribution is 6.33 L in patients with aTTP.
Elimination
The half-life of caplacizumab-yhdp is concentration and target-level dependent.
Metabolism
The available data suggest target-bound caplacizumab-yhdp is metabolized within the liver. Because caplacizumab-yhdp is a monoclonal antibody fragment, it is expected to be catabolized by various proteolytic enzymes.
Excretion
The available nonclinical data suggest unbound caplacizumab-yhdp is cleared renally.
Antidrug Antibodies
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of caplacizumab-yhdp were observed in patients with pre-existing or treatment-emergent anti-drug antibodies.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of caplacizumab-yhdp were observed based on age (18 to 79 years), sex (66% females), race (White [83%] and Black [17%]), blood group (O [41%] and other groups [59%]), or renal impairment (mild [CrCl: 60 to 90 mL/min], moderate [CrCl: 30 to 60 mL/min] or severe [CrCl: 15 to 30 mL/min]). The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of caplacizumab-yhdp is unknown [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Pediatric population
A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) population model was developed using clinical data from adult populations following intravenous and subcutaneous administration of caplacizumab-yhdp. Simulations performed based on this PK/PD model showed that the predicted caplacizumab-yhdp exposure and suppression of von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF:Ag) are similar in pediatric patients ≥12 years of age to those in adults when the adult dose (11 mg/day) is used in children.
Drug Interaction Studies
No dedicated drug-drug interaction studies with caplacizumab-yhdp have been conducted.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of caplacizumab-yhdp.
The prevalence of pre-existing antibodies binding to caplacizumab-yhdp observed during clinical studies and during evaluation of commercially available human samples varied between 4% and 63%. In aTTP patients, pre-existing antibodies can be produced by the patient or can originate from donor plasma during plasma exchange. No clinically apparent impact of these pre-existing antibodies on clinical efficacy or safety was found. Treatment-emergent anti-drug antibodies (TE ADA) against caplacizumab-yhdp were detected in 3% of patients treated with CABLIVI in the HERCULES study. In the HERCULES study, TE ADA were further characterized as having neutralizing potential. There was no clinically apparent impact on clinical efficacy or safety.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been performed to evaluate the potential of caplacizumab-yhdp for carcinogenicity or genotoxicity.
Animal reproduction studies assessing the effects of caplacizumab-yhdp on male and female fertility have not been conducted.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of CABLIVI for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP) in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy was established in a pivotal multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (HERCULES) (NCT02553317).
HERCULES
A total of 145 patients were enrolled in the HERCULES study; the median age was 45 (range: 18 to 79) years, 69% were female, 73% were White. Patients were randomized to either CABLIVI (n=72) or placebo (n=73). Patients in both groups received plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy. Patients were stratified according to the severity of neurological involvement (Glasgow Coma Scale score ≤12 or 13 to 15). Patients with sepsis, infection with E. coli 0157, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation or congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura were not eligible for enrollment.
Patients received a single 11 mg CABLIVI bolus intravenous injection or placebo prior to the first plasma exchange on study, followed by a daily subcutaneous injection of 11 mg CABLIVI or placebo after completion of plasma exchange, for the duration of the daily plasma exchange period and for 30 days thereafter. If after the initial treatment course, sign(s) of persistent underlying disease such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels remained present, treatment was extended for 7-day intervals for a maximum of 28 days.
The median treatment duration with CABLIVI was 35 days.
The clinical trial protocol specified the CABLIVI dose as 10 mg, to be delivered by withdrawing all of the reconstituted solution from the vial and administering the full amount. A dose recovery study showed that the mean dose that can be withdrawn from a vial is 11 mg. Therefore, based on the dose recovery study, the mean dose delivered in the trial was 11 mg.
The efficacy of CABLIVI in patients with aTTP was established based on time to platelet count response (platelet count ≥150,000/µL followed by cessation of daily plasma exchange within 5 days). Time to platelet count response was shorter among patients treated with CABLIVI, compared to placebo.
Figure 1: Platelet Response over Time
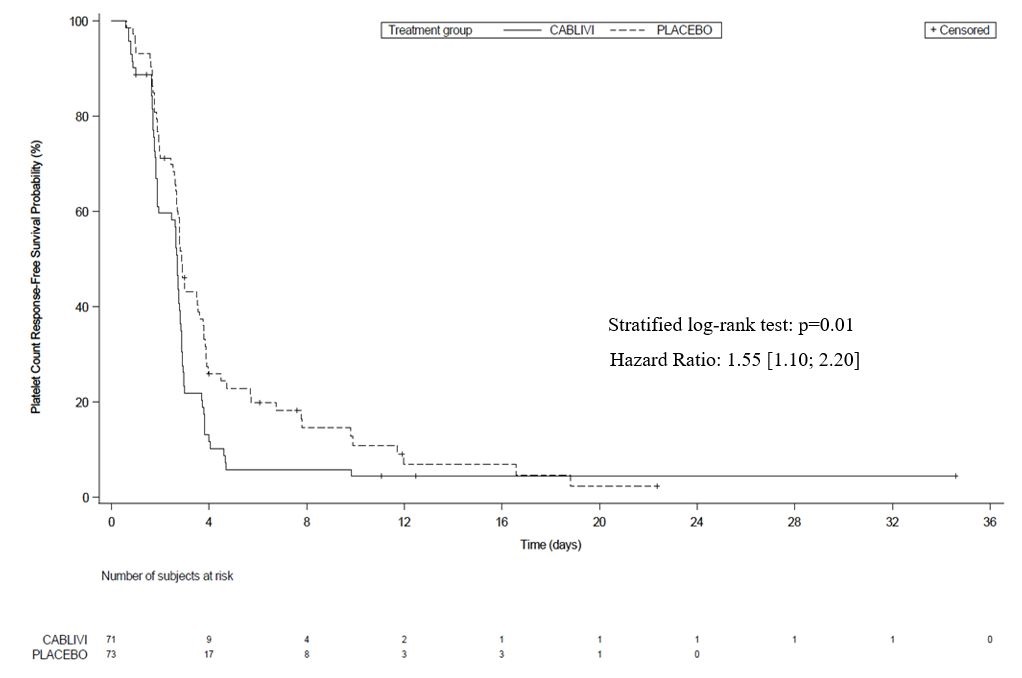
Treatment with CABLIVI resulted in a lower number of patients with TTP-related death, recurrence of TTP, or at least one treatment-emergent major thromboembolic event (a composite endpoint) during the treatment period (see Table 2 ).
| Number of patients with | CABLIVI N=72 | Placebo N=73 |
|---|---|---|
| n (%) Based on 71 patients who received at least one dose of study drug. | n (%) | |
| N = number of patients within the population of interest (by treatment group) n = number of patients with events; TTP = thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; ITT = intent to treat. | ||
| TTP-related death | 0 | 3 (4.1) |
| Recurrence of TTP (exacerbation) Exacerbation defined as thrombocytopenia after initial recovery of platelet count (platelet count ≥150,000/µL with subsequent stop of daily plasma exchange within 5 days) that required reinitiation of daily plasma exchange during the 30-day post daily plasma exchange period. | 3 (4.2) | 28 (38.4) |
| At least one treatment-emergent major thromboembolic event | 6 (8.5) | 6 (8.2) |
| Total p<0.0001 | 9 (12.7) | 36 (49.3) |
The proportion of patients with a recurrence of TTP in the overall study period (the drug treatment period plus the 28-day follow-up period after discontinuation of drug treatment) was lower in the CABLIVI group (9/72 patients [13%]) compared to the placebo group (28/73 patients [38%] (p<0.001). In the 6 patients in the CABLIVI group who experienced a recurrence of TTP during the follow-up period (i.e., a relapse defined as recurrent thrombocytopenia after initial recovery of platelet count (platelet count ≥150,000/µL) that required reinitiation of daily plasma exchange, occurring after the 30-day post daily plasma exchange period), ADAMTS13 activity levels were <10% at the end of the study drug treatment, indicating that the underlying immunological disease was still active at the time CABLIVI was stopped.
Pediatric Patients
The efficacy of CABLIVI in the treatment of pediatric patients with aTTP was evaluated in 30 patients (≤18 years of age) from an observational, retrospective chart review study OBS17325. The median age at CABLIVI initiation was 15 years (range: 2 to 18 years). Twenty-one patients (70%) were older than 12 years of age and 9 patients (30%) were less than or equal to 12 years old at aTTP diagnosis. The median body weight was 72.4 kg (range: 9 to 130 kg) at CABLIVI initiation. The median study duration was 0.31 years. The median duration of CABLIVI treatment was 31 days. Among the 30 patients, 29 received plasma exchange treatment that began after CABLIVI was initiated and among these the median duration of plasma exchange treatment was 6 days. Most of the patients (90%) received CABLIVI adult dose at first initiation.
Major efficacy outcomes included clinical remission, time to platelet count response, refractory disease, and disease recurrence (see Table 3 ).
| Major Efficacy Outcomes | Response n/N N represents the number of patients enrolled who received at least one dose of caplacizumab; n represents the number of patients who had achieved the efficacy outcome. (%) (95% CI) Two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) is based on Wilson score interval. |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation: aTTP=acquired-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; CI=Confidence interval; LDH=lactate dehydrogenase; ULN=upper limit of normal; TPE=therapeutic plasma exchange. | |
| Proportion of patients achieving clinical remission Proportion of patients achieving clinical remission, defined as platelet count remaining ≥150×10 9 /L and a LDH level <1.5× ULN for ≥30 days after cessation of TPE. | 24/30 (80.0%) (62.7%, 90.5%) |
| Time to platelet count response Time to platelet count response, defined as time from caplacizumab initiation to initial platelet count ≥150×10 9 /L with subsequent stop of daily TPE within 5 days. | Median time 5 days |
| Proportion of patients with refractory aTTP Proportion of patients with refractory aTTP, defined as lack of doubling of platelet count after four days of caplacizumab treatment and LDH level >ULN range. | 2/30 (6.7%) (1.9%, 21.3%) |
| Proportion of patients with recurrent disease Proportion of patients with recurrent disease (aTTP exacerbation, defined as recurrence ≤30 days after last TPE, or relapse, defined as recurrence >30 days after last TPE). | Relapse of aTTP: 2/30 (6.7%) (1.9%, 21.3%) Exacerbation: 0/30 (0.0%) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
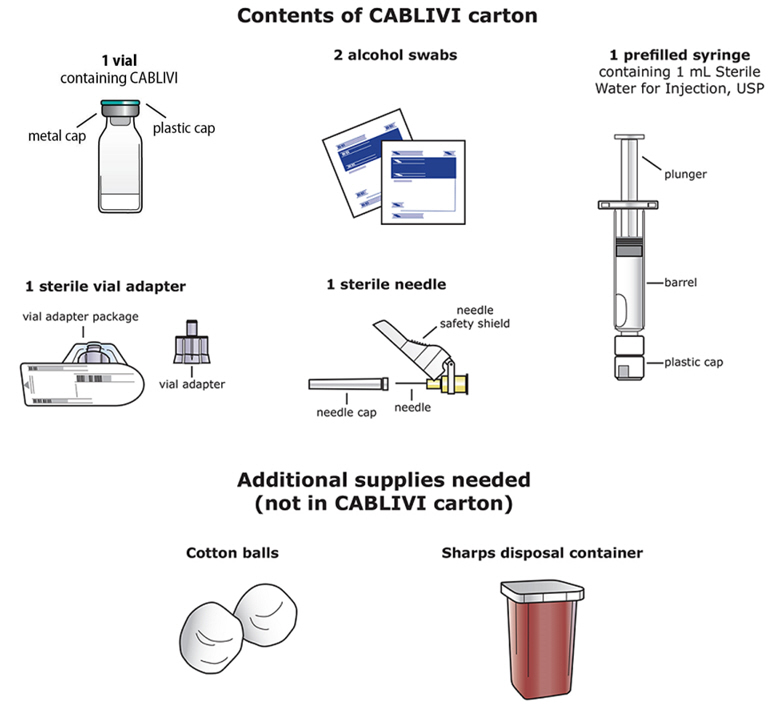
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) for injection is a sterile, white, preservative-free, lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. Each carton (NDC 58468-0225-1) contains:
- one 11 mg CABLIVI single-dose vial (NDC 58468-0227-1)
- one 1 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, prefilled glass syringe (diluent for CABLIVI) (NDC 58468-0229-1)
- one sterile vial adapter
- one sterile hypodermic needle (30 gauge)
- two individually packaged alcohol swabs
Storage
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Unopened vials may be stored in the original carton at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for a single period of up to 2 months. Do not return CABLIVI to the refrigerator after it has been stored at room temperature.
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CABLIVI ® [cab-LIV-ee] (caplacizumab-yhdp) for injection, for subcutaneous use single-dose vial | |
|---|---|
| This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | |
| This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject CABLIVI. Be sure that you read, understand, and follow this Instructions for Use before you inject CABLIVI and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. Your healthcare provider should show you or your caregiver how to prepare and inject CABLIVI properly before your first injection. In children 12 years of age and older, CABLIVI must be given by a healthcare provider or an adult caregiver. Talk to your healthcare provider or call 1-800-745-4447 if you have any questions. | |
Important Information You Need to Know Before Injecting CABLIVI :
| |
Storing CABLIVI
| |
Each CABLIVI carton contains:
| |
 | |
Preparing to inject a dose of CABLIVI :
|  Figure A Figure A |
Step 1: Bring the vial and syringe to room temperature
| 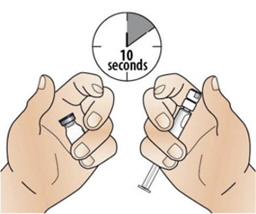 Figure B Figure B |
Step 2: Clean the rubber stopper
| 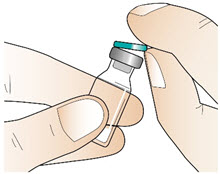 Figure C Figure C |
| 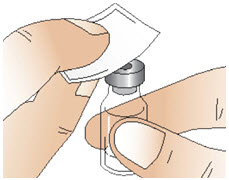 Figure D Figure D |
Step 3: Attach the vial adapter
| 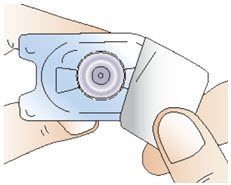 Figure E Figure E |
| 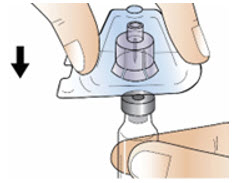 Figure F Figure F |
Step 4: Prepare the syringe
| 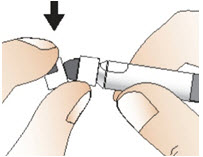 Figure G Figure G |
Step 5: Connect the syringe to adapter and vial
| 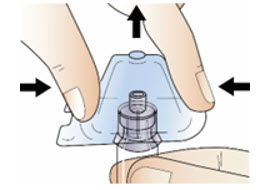 Figure H Figure H |
| 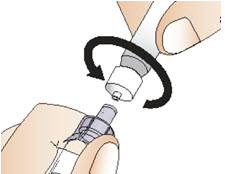 Figure I Figure I |
Step 6: Prepare the solution
| 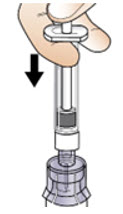 Figure J Figure J |
| 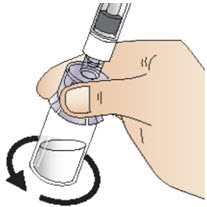 Figure K Figure K |
| 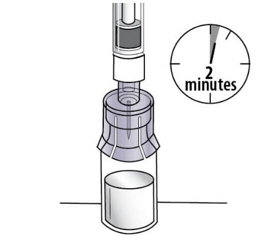 Figure L Figure L |
Step 7: Draw up solution
| 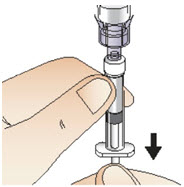 Figure M Figure M |
Step 8: Detach the syringe
| 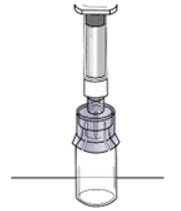 Figure N Figure N |
| 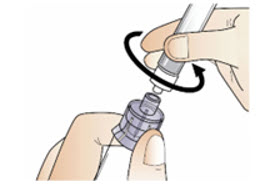 Figure O Figure O |
Step 9: Attach the needle
| 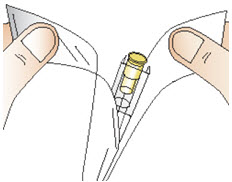 Figure P Figure P |
| 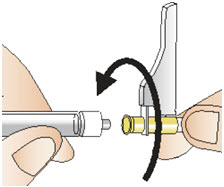 Figure Q Figure Q |
| 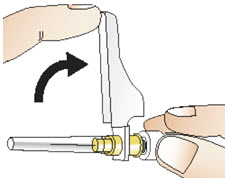 Figure R Figure R |
Step 10: Prepare your injection site
| 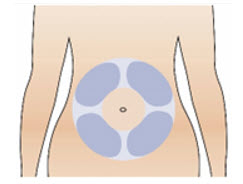 Figure S Figure S |
| 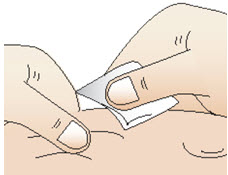 Figure T Figure T |
Step 11: Inject CABLIVI
| 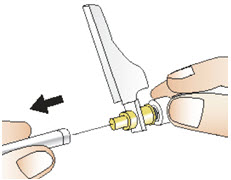 Figure U Figure U |
| 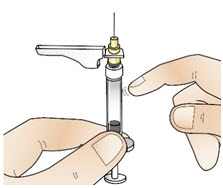 Figure V Figure V |
| 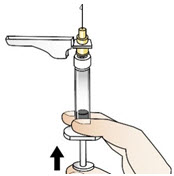 Figure W Figure W |
| 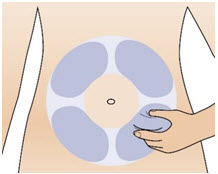 Figure X Figure X |
| 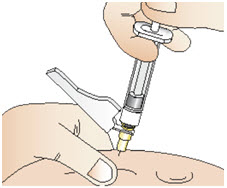 Figure Y Figure Y |
Step 12: After your injection
| 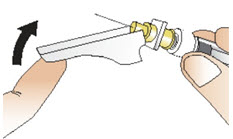 Figure Z Figure Z |
Step 13: Dispose of the used syringe and vial.
| |
Manufactured by: Ablynx N.V. Technologiepark 21 9052 Ghent (Zwijnaarde), Belgium A SANOFI COMPANY U.S. License No. 2085
Distributed by: Genzyme Corporation Cambridge, MA 02141 A SANOFI COMPANY
For more information go to www.CABLIVI.com or call 1-800-745-4447
Revised 12/2025
Mechanism of Action
Caplacizumab-yhdp targets the A1-domain of vWF, and inhibits the interaction between vWF and platelets, thereby reducing both vWF-mediated platelet adhesion and platelet consumption.