Get your patient on Carboprost Tromethamine - Carboprost Tromethamine solution (Carboprost Tromethamine)
Carboprost Tromethamine - Carboprost Tromethamine solution prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carboprost tromethamine injection Sterile Solution is indicated for aborting pregnancy between the 13th and 20th weeks of gestation as calculated from the first day of the last normal menstrual period and in the following conditions related to second trimester abortion:
- Failure of expulsion of the fetus during the course of treatment by another method;
- Premature rupture of membranes in intrauterine methods with loss of drug and insufficient or absent uterine activity;
- Requirement of a repeat intrauterine instillation of drug for expulsion of the fetus;
- Inadvertent or spontaneous rupture of membranes in the presence of a previable fetus and absence of adequate activity for expulsion.
Carboprost tromethamine injection is indicated for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage due to uterine atony which has not responded to conventional methods of management. Prior treatment should include the use of intravenously administered oxytocin, manipulative techniques such as uterine massage and, unless contraindicated, intramuscular ergot preparations. Studies have shown that in such cases, the use of carboprost tromethamine injection has resulted in satisfactory control of hemorrhage, although it is unclear whether or not ongoing or delayed effects of previously administered ecbolic agents have contributed to the outcome. In a high proportion of cases, carboprost tromethamine injection used in this manner has resulted in the cessation of life threatening bleeding and the avoidance of emergency surgical intervention.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Abortion and Indications 1–4
An initial dose of 1 mL of Carboprost tromethamine injection Sterile Solution (containing the equivalent of 250 micrograms of carboprost) is to be administered deep in the muscle with a tuberculin syringe. Subsequent doses of 250 micrograms should be administered at 1½ to 3½ hour intervals depending on uterine response.
An optional test dose of 100 micrograms (0.4 mL) may be administered initially. The dose may be increased to 500 micrograms (2 mL) if uterine contractility is judged to be inadequate after several doses of 250 micrograms (1 mL).
The total dose administered of carboprost tromethamine should not exceed 12 milligrams and continuous administration of the drug for more than two days is not recommended.
For Refractory Postpartum Uterine Bleeding
An initial dose of 250 micrograms of carboprost tromethamine injection Sterile Solution (1 mL of Carboprost tromethamine injection) is to be given deep, intramuscularly. In clinical trials it was found that the majority of successful cases (73%) responded to single injections. In some selected cases, however, multiple dosing at intervals of 15 to 90 minutes was carried out with successful outcome. The need for additional injections and the interval at which these should be given can be determined only by the attending physicians as dictated by the course of clinical events. The total dose of carboprost tromethamine injection, USP should not exceed 2 milligrams (8 doses).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity (including anaphylaxis and angioedema) to Carboprost tromethamine injection Sterile Solution [see ADVERSE REACTIONS, Post-marketing Experience ]
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease
- Patients with active cardiac, pulmonary, renal or hepatic disease
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse effects of Carboprost tromethamine Sterile Solution are generally transient and reversible when therapy ends. The most frequent adverse reactions observed are related to its contractile effect on smooth muscle.
In patients studied, approximately two-thirds experienced vomiting and diarrhea, approximately one-third had nausea, one-eighth had a temperature increase greater than 2°F, and one- fourteenth experienced flushing.
The pretreatment or concurrent administration of antiemetic and antidiarrheal drugs decreases considerably the very high incidence of gastrointestinal effects common with all prostaglandins used for abortion. Their use should be considered an integral part of the management of patients undergoing abortion with carboprost tromethamine injection.
Of those patients experiencing a temperature elevation, approximately one-sixteenth had a clinical diagnosis of endometritis. The remaining temperature elevations returned to normal within several hours after the last injection.
Adverse effects observed during the use of carboprost tromethamine injection for abortion and for hemorrhage, not all of which are clearly drug related, in decreasing order of frequency include:
| Vomiting | Nervousness |
| Diarrhea | Nosebleed |
| Nausea | Sleep disorders |
| Flushing or hot flashes | Dyspnea |
| Chills or shivering | Tightness in chest |
| Coughing | Wheezing |
| Headaches | Posterior cervical |
| Endometritis | perforation |
| Hiccough | Weakness |
| Dysmenorrhea-like | Diaphoresis |
| pain | Dizziness |
| Paresthesia | Blurred vision |
| Backache | Epigastric pain |
| Muscular pain | Excessive thirst |
| Breast tenderness | Twitching eyelids |
| Eye pain | Gagging, retching |
| Drowsiness | Dry throat |
| Dystonia | Sensation of choking |
| Asthma | Thyroid storm |
| Injection site pain | Syncope |
| Tinnitus | Palpitations |
| Vertigo | Rash |
| Vaso-vagal syndrome | Upper respiratory |
| Dryness of mouth | infection |
| Hyperventilation | Leg cramps |
| Respiratory distress | Perforated uterus |
| Hematemesis | Anxiety |
| Taste alterations | Chest pain |
| Urinary tract infection | Retained placental |
| Septic shock | fragment |
| Torticollis | Shortness of breath |
| Lethargy | Fullness of throat |
| Hypertension | Uterine sacculation |
| Tachycardia | Faintness, light- |
| Pulmonary edema | headedness |
| Endometritis from | Uterine rupture |
| IUCD |
The most common complications when Carboprost tromethamine injection was utilized for abortion requiring additional treatment after discharge from the hospital were endometritis, retained placental fragments, and excessive uterine bleeding, occurring in about one in every 50 patients.
Post-marketing experience
Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. Anaphylactic reaction, Anaphylactic shock, Anaphylactoid reaction, Angioedema).
Drug Interactions
Carboprost tromethamine may augment the activity of other oxytocic agents. Concomitant use with other oxytocic agents is not recommended.
DESCRIPTION
Carboprost tromethamine injection, USP Sterile Solution, an oxytocic, contains the tromethamine salt of the (15S)-15 methyl analogue of naturally occurring prostaglandin F2α in a solution suitable for intramuscular injection. Carboprost tromethamine is the established name for the active ingredient in Carboprost tromethamine injection, USP. Four other chemical names are:
- (15S)-15-methyl prostaglandin F2α tromethamine salt
- 7-(3α,5α-dihydroxy-2ß-[(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methyl- trans -1-octenyl]-1α-cyclopentyl]- cis -5-heptenoic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
- (15S)-9α,11α,15-trihydroxy-15-methylprosta- cis -5, trans -13-dienoic acid tromethamine salt
- (15S)-15-methyl PGF2α-THAM
The structural formula is represented below:
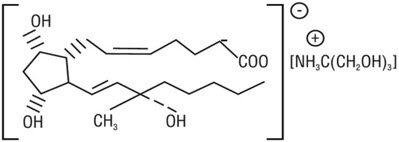
The molecular formula is C 25 H 47 O 8 N. The molecular weight of carboprost tromethamine is 489.64. It is a white to slightly off-white crystalline powder. It generally melts between 95° and 105°C, depending on the rate of heating.
Carboprost tromethamine dissolves readily in water at room temperature at a concentration greater than 75 mg/mL.
Each mL of carboprost tromethamine injection, USP Sterile Solution contains carboprost tromethamine equivalent to 250 mcg of carboprost, 83 mcg tromethamine, 9 mg sodium chloride, and 9.45 mg benzyl alcohol added as preservative. When necessary, pH is adjusted with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid. The solution is sterile.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Carboprost tromethamine administered intramuscularly stimulates in the gravid uterus myometrial contractions similar to labor contractions at the end of a full term pregnancy. Whether or not these contractions result from a direct effect of carboprost on the myometrium has not been determined. Nonetheless, they evacuate the products of conception from the uterus in most cases.
Postpartum, the resultant myometrial contractions provide hemostasis at the site of placentation.
Carboprost tromethamine also stimulates the smooth muscle of the human gastrointestinal tract. This activity may produce the vomiting or diarrhea or both that is common when carboprost tromethamine is used to terminate pregnancy and for use postpartum. In laboratory animals and also in humans carboprost tromethamine can elevate body temperature. With the clinical doses of carboprost tromethamine used for the termination of pregnancy, and for use postpartum, some patients do experience transient temperature increases.
In laboratory animals and in humans large doses of carboprost tromethamine can raise blood pressure, probably by contracting the vascular smooth muscle. With the doses of carboprost tromethamine used for terminating pregnancy, this effect has not been clinically significant. In laboratory animals and also in humans carboprost tromethamine can elevate body temperature. With the clinical doses of carboprost tromethamine used for the termination of pregnancy, some patients do experience temperature increases. In some patients, carboprost tromethamine may cause transient bronchoconstriction.
Drug plasma concentrations were determined by radioimmunoassay in peripheral blood samples collected by different investigators from 10 patients undergoing abortion. The patients had been injected intramuscularly with 250 micrograms of carboprost at two hour intervals. Blood levels of drug peaked at an average of 2060 picograms/mL one-half hour after the first injection then declined to an average concentration of 770 picograms/mL two hours after the first injection just before the second injection. The average plasma concentration one-half hour after the second injection was slightly higher (2663 picograms/mL) than that after the first injection and decreased again to an average of 1047 picograms/mL by two hours after the second injection. Plasma samples were collected from 5 of these 10 patients following additional injections of the prostaglandin. The average peak concentrations of drug were slightly higher following each successive injection of the prostaglandin, but always decreased to levels less than the preceding peak values by two hours after each injection.
Five women who had delivery spontaneously at term were treated immediately postpartum with a single injection of 250 micrograms of carboprost tromethamine. Peripheral blood samples were collected at several times during the four hours following treatment and carboprost tromethamine levels were determined by radioimmunoassay. The highest concentration of carboprost tromethamine was observed at 15 minutes in two patients (3009 and 2916 picograms/mL), at 30 minutes in two patients (3097 and 2792 picograms/mL), and at 60 minutes in one patient (2718 picograms/mL).
HOW SUPPLIED
Carboprost tromethamine injection, USP Sterile Solution is available in the following packages:
1 mL single-dose vial NDC 70594-112-01
10 × 1 mL single-dose vials NDC 70594-112-02
Each mL of carboprost tromethamine injection contains carboprost tromethamine equivalent to 250 mcg of carboprost.
Carboprost tromethamine injection must be refrigerated at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F).
Discard unused portion.