Get your patient on Chlorthalidone - Chlorthalidone tablet (Chlorthalidone)
Chlorthalidone - Chlorthalidone tablet prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Diuretics such as chlorthalidone are indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effect of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
Chlorthalidone is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy.
Chlorthalidone has also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction, such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure.
Usage in Pregnancy
The routine use of diuretics in an otherwise healthy woman is inappropriate and exposes mother and fetus to unnecessary hazard. Diuretics do not prevent development of toxemia of pregnancy, and there is no satisfactory evidence that they are useful in the treatment of developed toxemia. Edema during pregnancy may arise from pathologic causes or from the physiologic and mechanical consequences of pregnancy. Chlorthalidone is indicated in pregnancy when edema is due to pathologic causes, just as it is in the absence of pregnancy (however, see PRECAUTIONS , below). Dependent edema in pregnancy, resulting from restriction of venous return by the expanded uterus, is properly treated through elevation of the lower extremities and use of support hose; use of diuretics to lower intravascular volume in this case is illogical and unnecessary. There is hypervolemia during normal pregnancy that is harmful to neither the fetus nor the mother (in the absence of cardiovascular disease), but that is associated with edema, including generalized edema, in the majority of pregnant women. If this edema produces discomfort, increased recumbency will often provide relief. In rare instances, this edema may cause extreme discomfort that is not relieved by rest. In these cases, a short course of diuretics may provide relief and be appropriate.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Therapy should be initiated with the lowest possible dose. This dose should be titrated according to individual patient response to gain maximal therapeutic benefit while maintaining lowest dosage possible. A single dose given in the morning with food is recommended; divided daily doses are unnecessary.
Hypertension
Initiation
Therapy, in most patients, should be initiated with a single daily dose of 25 mg. If the response is insufficient after a suitable trial, the dosage may be increased to a single daily dose of 50 mg. If additional control is required, the dosage of chlorthalidone may be increased to 100 mg once daily or a second antihypertensive drug (step 2 therapy) may be added. Dosage above 100 mg daily usually does not increase effectiveness. Increases in serum uric acid and decreases in serum potassium are dose-related over the 25 to 100 mg/day range.
Maintenance
Maintenance doses may be lower than initial doses and should be adjusted according to individual patient response. Effectiveness is well sustained during continued use.
Edema
Initiation
Adults, initially 50 to 100 mg daily, or 100 mg on alternate days. Some patients may require 150 to 200 mg at these intervals or up to 200 mg daily. Dosages above this level, however, do not usually produce a greater response.
Maintenance
Maintenance doses may often be lower than initial doses and should be adjusted according to individual patient response. Effectiveness is well sustained during continued use.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Anuria.
Known hypersensitivity to chlorthalidone or other sulfonamide-derived drugs.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been observed, but there is not enough systematic collection of data to support an estimate of their frequency.
Gastrointestinal System Reactions: anorexia, gastric irritation, nausea, vomiting, cramping, diarrhea, constipation, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), pancreatitis.
Central Nervous System Reactions: dizziness, vertigo, paresthesias, headache, xanthopsia.
Hematologic Reactions: leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia.
Dermatologic-Hypersensitivity Reactions: purpura, photosensitivity, rash, urticaria, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis, cutaneous vasculitis), Lyell's syndrome (toxic epidermal necrolysis).
Cardiovascular Reactions: orthostatic hypotension may occur and may be aggravated by alcohol, barbiturates, or narcotics.
Other Adverse Reactions: hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hyperuricemia, muscle spasm, weakness, restlessness, impotence.
Whenever adverse reactions are moderate or severe, chlorthalidone dosage should be reduced or therapy withdrawn.
Drug Interactions
Chlorthalidone may add to or potentiate the action of other antihypertensive drugs. Potentiation occurs with ganglionic peripheral adrenergic blocking drugs.
Medication such as digitalis may also influence serum electrolytes. Warning signs, irrespective of cause, are: dryness of mouth, thirst, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, muscle pains or cramps, muscular fatigue, hypotension, oliguria, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting.
Insulin requirements in diabetic patients may be increased, decreased, or unchanged. Higher dosage of oral hypoglycemic agents may be required. Latent diabetes mellitus may become manifest during chlorthalidone administration.
Chlorthalidone and related drugs may increase the responsiveness to tubocurarine.
Chlorthalidone and related drugs may decrease arterial responsiveness to norepinephrine. This diminution is not sufficient to preclude effectiveness of the pressor agent for therapeutic use.
DESCRIPTION
Chlorthalidone is an oral antihypertensive/diuretic. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double-ring system is incorporated in its structure. It is 2-Chloro-5(1- hydroxy-3-oxo-1-isoindolinyl) benzenesulfonamide with the following structural formula:
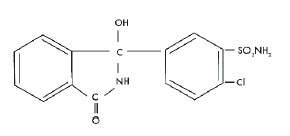
Molecular Formula: C 14 H 11 ClN 2 O 4 S Molecular Weight: 338.76
Chlorthalidone, USP is practically insoluble in water, in ether, and in chloroform; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol.
Chlorthalidone tablets are available containing either 25 mg or 50 mg of chlorthalidone, USP and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, D&C Yellow No. 10, magnesium stearate. The 50 mg Tablets also contain FD&C Blue No. 1.
FDA approved dissolution specification differs from that of the USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Chlorthalidone is an oral diuretic with prolonged action (48-72 hours) and low toxicity. The major portion of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The diuretic effect of the drug occurs in approximately 2.6 hours and continues for up to 72 hours. The mean half-life following a 50 to 200 mg dose is 40 hours. In the first order of absorption, the elimination half-life is 53 hours following a 50 mg dose, and 60 hours following a 100 mg dose. Approximately 75 percent of the drug is bound to plasma proteins, 58 percent of the drug being bound to albumin. This is caused by an increased affinity of the drug to erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase. Nonrenal routes of elimination have yet to be clarified. Data are not available regarding percentage of dose as unchanged drug and metabolites, concentration of the drug in body fluids, degree of uptake by a particular organ or in the fetus, or passage across the blood-brain barrier.
The drug produces copious diuresis with greatly increased excretion of sodium and chloride. At maximal therapeutic dosage, chlorthalidone is approximately equal in its diuretic effect to comparable maximal therapeutic doses of benzothiadiazine diuretics. The site of action appears to be the cortical diluting segment of the ascending limb of Henle's loop of the nephron.
HOW SUPPLIED
Chlorthalidone Tablets, USP are available containing 25 mg or 50 mg of chlorthalidone, USP.
The 25 mg tablets are pale yellow, round, tablet debossed with "TP 25" on one side and plain on other side. They are available as follows:
NDC 51224-018-50 bottles of 100 tablets NDC 51224-018-70 bottles of 1000 tablets
The 50 mg tablets are pale green, round, scored tablet debossed with "TP" in the top of the score and "50" in the bottom of the score and plain on other side. They are available as follows:
NDC 51224-118-50 bottles of 100 tablets NDC 51224-118-70 bottles of 1000 tablets
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP for Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.