Get your patient on Ebglyss (Lebrikizumab-Lbkz)
Patient education
Administration guides
Patient support program
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Financial assistance & copay programs
Specialty pharmacy coordination
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to EBGLYSS treatment, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. (2.1 )
- The recommended dosage of EBGLYSS is 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at Week 0 and Week 2, followed by 250 mg (one injection) every 2 weeks until Week 16 or later, when adequate clinical response is achieved. The maintenance dose is EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks. (2.2 )
- Administer by subcutaneous injection. (2.4 )
Vaccination Prior to Administration of EBGLYSS
Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of EBGLYSS is an initial dose of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at Week 0 and Week 2, followed by 250 mg every two weeks until Week 16 or later, when adequate clinical response is achieved. The maintenance dosage is 250 mg every four weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
Concomitant Topical Therapies
EBGLYSS can be used with or without topical corticosteroids (TCS). Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) may be used, but reserved for sensitive areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Important Administration Instructions
- EBGLYSS is for subcutaneous administration.
- EBGLYSS is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the subcutaneous injection technique of EBGLYSS. Adult patients may self-inject, or caregivers may give EBGLYSS after training in subcutaneous injection technique. For pediatric patients, caregivers may give injections after training in subcutaneous injection technique.
- Sites for injection include the abdomen, thigh, and back of the upper arm. Administration of EBGLYSS in the back of the upper arm may be performed by a caregiver or healthcare provider.
- Alternate the injection site with each injection. Do not inject EBGLYSS within 2 inches (5 cm) of the navel or into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, hard, or in an area of skin that is affected by atopic dermatitis or skin lesions.
- It is not necessary to allow EBGLYSS prefilled pen or EBGLYSS prefilled syringe to warm up to room temperature before use.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. EBGLYSS is a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particles, is discolored or cloudy [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 ), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )] .
- Refer to the Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations [see Instructions for Use] .
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Ebglyss prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EBGLYSS is indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 40 kg with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. EBGLYSS can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to EBGLYSS treatment, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. (2.1 )
- The recommended dosage of EBGLYSS is 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at Week 0 and Week 2, followed by 250 mg (one injection) every 2 weeks until Week 16 or later, when adequate clinical response is achieved. The maintenance dose is EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks. (2.2 )
- Administer by subcutaneous injection. (2.4 )
Vaccination Prior to Administration of EBGLYSS
Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of EBGLYSS is an initial dose of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at Week 0 and Week 2, followed by 250 mg every two weeks until Week 16 or later, when adequate clinical response is achieved. The maintenance dosage is 250 mg every four weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
Concomitant Topical Therapies
EBGLYSS can be used with or without topical corticosteroids (TCS). Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) may be used, but reserved for sensitive areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Important Administration Instructions
- EBGLYSS is for subcutaneous administration.
- EBGLYSS is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the subcutaneous injection technique of EBGLYSS. Adult patients may self-inject, or caregivers may give EBGLYSS after training in subcutaneous injection technique. For pediatric patients, caregivers may give injections after training in subcutaneous injection technique.
- Sites for injection include the abdomen, thigh, and back of the upper arm. Administration of EBGLYSS in the back of the upper arm may be performed by a caregiver or healthcare provider.
- Alternate the injection site with each injection. Do not inject EBGLYSS within 2 inches (5 cm) of the navel or into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, hard, or in an area of skin that is affected by atopic dermatitis or skin lesions.
- It is not necessary to allow EBGLYSS prefilled pen or EBGLYSS prefilled syringe to warm up to room temperature before use.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. EBGLYSS is a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particles, is discolored or cloudy [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 ), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16 )] .
- Refer to the Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations [see Instructions for Use] .
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
EBGLYSS is a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown solution available as follows:
- Injection: 250 mg/2 mL in a single-dose prefilled pen
- Injection: 250 mg/2 mL (125 mg/mL) in a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle shield
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data on lebrikizumab-lbkz use in pregnant women are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Monoclonal antibodies are actively transported across the placenta (see Clinical Considerations) . In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed after subcutaneous administration of lebrikizumab-lbkz to cynomolgus monkeys during organogenesis at doses up to 18 times the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data) .
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Report pregnancies to Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979).
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses and peaks during the third trimester. Therefore, EBGLYSS may be present in infants exposed in utero. The potential clinical impact of EBGLYSS exposure in infants exposed in utero should be considered.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryofetal development study, no malformations or embryofetal toxicity were observed in fetuses from pregnant cynomolgus monkeys administered lebrikizumab-lbkz during organogenesis at doses up to 150 mg/kg initial dose followed by 50 mg/kg per week by subcutaneous injection, which was associated with plasma exposure (C avg,ss ) approximately 18 times the human exposure at the MRHD. Lebrikizumab-lbkz crossed the placenta in monkeys.
In a prenatal and postnatal development study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were administered lebrikizumab-lbkz during organogenesis to parturition at doses up to 150 mg/kg initial dose followed by 50 mg/kg per week by subcutaneous injection, which was associated with plasma exposure (C avg,ss ) approximately 18 times the human exposure at the MRHD. No embryofetal toxicity or malformations, or effects on morphological, functional, or immunological development were observed in the infants from birth through 6 months of age.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of lebrikizumab-lbkz in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Endogenous IgG and monoclonal antibodies are transferred in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed infant to lebrikizumab-lbkz are unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for EBGLYSS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from EBGLYSS or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EBGLYSS have been established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 40 kg with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. A total of 372 pediatric subjects were exposed to EBGLYSS with 270 subjects exposed to EBGLYSS for at least one year. The safety and effectiveness were generally consistent between pediatric and adult subjects [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ), Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
The safety and effectiveness of EBGLYSS have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age and pediatric patients 12 years and older who weigh less than 40 kg.
Geriatric Use
Of the 1348 adult subjects with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis exposed to EBGLYSS, a total of 123 were 65 years or older, and 29 subjects were 75 years or older. Clinical studies of EBGLYSS did not include sufficient numbers of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
EBGLYSS is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity to lebrikizumab-lbkz or any excipients of EBGLYSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema and urticaria, have occurred after administration of EBGLYSS. Discontinue EBGLYSS in the event of a serious hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1 )
- Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to a healthcare provider. (5.2 )
- Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating EBGLYSS. If patients become infected while receiving EBGLYSS and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with EBGLYSS until the infection resolves. (5.3 )
- Vaccinations: Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with EBGLYSS. (5.4 )
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and urticaria, have been reported with use of EBGLYSS. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue EBGLYSS and institute appropriate therapy.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
Conjunctivitis and keratitis adverse reactions have been reported in clinical trials.
Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in atopic dermatitis subjects who received EBGLYSS compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. Most subjects with conjunctivitis or keratitis recovered during the treatment period [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Advise patients to report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections
Patients with known helminth infections were excluded from participation in clinical studies. It is unknown if EBGLYSS will influence the immune response against helminth infections by inhibiting IL-13 signaling.
Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating treatment with EBGLYSS. If patients become infected while receiving EBGLYSS and do not respond to antihelminth treatment, discontinue treatment with EBGLYSS until the infection resolves.
Vaccinations
EBGLYSS may alter a patient’s immunity and increase the risk of infection following administration of live vaccines. Prior to therapy with EBGLYSS, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. Avoid use of live vaccines immediately prior to or during treatment with EBGLYSS. No data are available on the response to live vaccines.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying and controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Atopic Dermatitis
The safety of EBGLYSS was evaluated across 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials in subjects with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis including 3 phase 3 trials (ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, ADhere) and 1 phase 2 dose ranging trial (KGAF). In these 4 trials, mean age was 37 years; 50% of subjects were male; 62% were White, 13% were Black, and 20% were Asian. In terms of co-morbid conditions, in the phase 3 trials, 30% of the subjects had asthma, 50% had allergic rhinitis, 31% had food allergy, and 14% had allergic conjunctivitis at baseline.
A total of 891 subjects were treated with EBGLYSS for at least 1 year in the atopic dermatitis development program.
ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and KGAF compared the safety of EBGLYSS monotherapy to placebo. ADhere compared the safety of EBGLYSS + TCS to placebo + TCS through 16 weeks. All subjects from the phase 3 trials were allowed to enroll in the long-term extension study.
Weeks 0 to 16
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks monotherapy group, or in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks + TCS group, all at a higher rate than placebo during the first 16 weeks of treatment.
a Integrated analysis of ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and the phase 2 dose finding trial (KGAF) | ||||
b Analysis of TCS concomitant therapy trial ADhere | ||||
c EBGLYSS 500 mg at Week 0 and Week 2, followed by 250 mg every two weeks | ||||
d Conjunctivitis cluster includes conjunctivitis, conjunctivitis allergic, and conjunctivitis bacterial | ||||
e Injection Site Reactions cluster includes injection site-related: pain, erythema, reaction, discomfort, dermatitis, pruritus, swelling, and rash | ||||
| Adverse Reactions | EBGLYSS Monotherapy a | EBGLYSS + TCS b | ||
| EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W c N = 638 n (%) | Placebo N = 338 n (%) | EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W c + TCS N = 145 n (%) | Placebo + TCS N = 66 n (%) | |
| Conjunctivitis d | 61 (10) | 10 (3) | 7 (5) | 0 |
| Injection Site Reactions e | 16 (3) | 4 (1) | 4 (3) | 1 (2) |
| Herpes Zoster | 3 (<1) | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 |
In the monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and KGAF) through Week 16, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 2.4% in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks group and 1.8% in the placebo group. In the TCS trial (ADhere) through Week 16, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 2.1% in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks + TCS group and 0% in the placebo + TCS group. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of EBGLYSS compared to the placebo group were conjunctivitis and keratitis (0.6% vs. 0.3%), and injection site reactions (0.2% vs. 0) in the monotherapy trials; and conjunctivitis (0.7% vs. 0), and injection site reactions (0.7% vs. 0) in the TCS trial.
Eosinophilia
Increased post-baseline blood eosinophils were observed at a higher frequency in EBGLYSS-treated subjects compared to placebo. During the first 16 weeks, eosinophilia (>5000 cells/mcL) was observed in 0.4% in the EBGLYSS-treated subjects and 0% in subjects receiving placebo. Blood eosinophil elevations were generally transient and did not result in discontinuation.
Safety Weeks 16 to 52
Among those EBGLYSS-treated subjects who responded at Week 16 and who were re-randomized in the maintenance period of the monotherapy trials ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2, a total of 113 and 118 subjects received EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks, respectively. The safety profile of EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks was generally consistent with EBGLYSS every 2 weeks during Weeks 16 to 52. The safety profile of EBGLYSS during maintenance treatment was generally consistent with the safety profile observed through Week 16.
Specific Adverse Drug Reactions
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. Most cases of conjunctivitis and keratitis were mild or moderate in severity and recovered or resolved without treatment interruption or discontinuation.
During the initial 16-week treatment period of the monotherapy trials, conjunctivitis, including allergic conjunctivitis, was reported by 61 subjects (10%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks group and 10 subjects (3%) in the placebo group. In the TCS concomitant therapy trial, conjunctivitis was reported by 7 subjects (5%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks + TCS group compared to 0% in the placebo + TCS group. During the 16-week placebo-controlled induction period, 68 subjects reported 73 events of conjunctivitis. All events were nonserious and mild or moderate in severity. Conjunctivitis led to treatment discontinuation in 3 subjects. The exposure adjusted incidence rate of conjunctivitis for subjects treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks was 30.6 events per 100 patient years through Week 16 (KGAF, ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, ADhere).
During the maintenance treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2) from 16 to 52 weeks, conjunctivitis, including allergic conjunctivitis, was reported by 2 subjects (1.8%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks group and 12 subjects (10.1%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks group, compared to 5 subjects (8.3%) in the placebo group. During the maintenance treatment period, 14 subjects treated with EBGLYSS reported 18 events of conjunctivitis. All events were mild or moderate in severity. Conjunctivitis led to treatment discontinuation in 2 subjects in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks group. The exposure adjusted incidence rate of conjunctivitis for subjects treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks was 18.3 events per 100 patient years and for those treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks was 20.6 events per 100 patient years through Week 52 (ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, ADhere + the long-term extension study).
During the initial 16-week treatment period of the monotherapy trials, keratitis, including atopic and vernal keratoconjunctivitis, was reported by 4 subjects (0.6%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks group and 1 subject (0.3%) in the placebo group. In the TCS concomitant therapy trial, vernal keratoconjunctivitis was reported by 1 subject (0.7%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks + TCS group, compared to 0% in the placebo + TCS group. All events were nonserious and mild or moderate in severity. Keratitis led to treatment discontinuation in 2 subjects. The exposure adjusted incidence rate of keratitis for subjects treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks was 2.2 events per 100 patient years through Week 16 (KGAF, ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, ADhere).
During the maintenance treatment period of the monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2) from 16 to 52 weeks, atopic keratoconjunctivitis was reported by 1 subject (0.8%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks group, and vernal keratoconjunctivitis was reported by 1 subject (0.9%) in the EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks group, compared to 0% in the placebo group. One (0.9%) event of severe vernal keratoconjunctivitis in an EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks subject led to treatment discontinuation. The exposure adjusted incidence rate of keratitis for subjects treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks was 1.0 event per 100 patient years and for those treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 4 weeks was 0.7 events per 100 patient years through Week 52 (ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, ADhere + the long-term extension study).
Injection Site Reactions
Injection site reactions were reported by 3% of the EBGLYSS group and 1% of the placebo group in the first 16 weeks of the monotherapy trials. Incidence of injection site reactions declined with continued treatment. Most events were mild or moderate and recovered without treatment discontinuation.
DESCRIPTION
Lebrikizumab-lbkz, an interleukin-13 antagonist, is an immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that binds to interleukin (IL)-13 and inhibits IL-13 signaling. Lebrikizumab-lbkz is produced in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells by recombinant DNA technology. Lebrikizumab-lbkz has an approximate molecular weight of 145 kDa.
EBGLYSS (lebrikizumab-lbkz) injection is a sterile, preservative free, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown solution for subcutaneous use. EBGLYSS is available as either a 250 mg/2 mL single-dose prefilled pen or a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle shield. The EBGLYSS prefilled pen and prefilled syringe with needle shield are not made with natural rubber latex.
Each prefilled pen or prefilled syringe delivers 250 mg lebrikizumab-lbkz in 2 mL solution which also contains glacial acetic acid (1.8 mg), histidine (6.2 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.6 mg), sucrose (119.6 mg) and Water for Injection. The pH is 5.4 – 6.0.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Lebrikizumab-lbkz is an IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity and slow off-rate to interleukin (IL)-13 and allows IL-13 to bind to IL-13Rα1 but inhibits human IL-13 signaling through the IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα1 receptor complex. IL-13 is a naturally occurring cytokine that is involved in Type 2 inflammation, which is an important component in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Lebrikizumab-lbkz inhibits IL-13-induced responses including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and IgE. Lebrikizumab-lbkz-bound IL-13 can still bind IL-13Rα2 allowing subsequent internalization and natural clearance of IL-13.
Pharmacodynamics
In clinical studies, lebrikizumab-lbkz reduced the levels of serum periostin, total immunoglobulin E (IgE), CC chemokine ligand (CCL)17 [thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC)], CCL18 [pulmonary and activation-regulated chemokine (PARC)], and CCL13 [monocyte chemotactic protein-4 (MCP-4)]. The clinical relevance of these biomarkers is not completely understood.
Pharmacokinetics
Lebrikizumab-lbkz steady-state exposure following either a subcutaneous dose of 250 mg every 2 weeks or every 4 weeks in patients with atopic dermatitis are presented in Table 2 . Lebrikizumab-lbkz exposure increases dose-proportionally over a subcutaneous dose range of 37.5 to 500 mg. Lebrikizumab-lbkz steady state is achieved at Week 4 following the approved recommended loading doses.
C max = Maximum concentration, C avg = Average concentration, C trough = Trough concentration | |||
a Following approved recommended loading doses | |||
| Lebrikizumab-lbkz Dosage a | C max | C avg | C trough |
| 250 mg every 2 weeks | 108 mcg/mL | 100 mcg/mL | 87 mcg/mL |
| 250 mg every 4 weeks | 63 mcg/mL | 51 mcg/mL | 36 mcg/mL |
Absorption
Following a single subcutaneous 250 mg dose of lebrikizumab-lbkz, peak serum concentrations were achieved approximately 7 to 8 days post dose. The absolute bioavailability for a subcutaneous dose was approximately 86%.
Injection site locations did not influence the absorption of lebrikizumab-lbkz.
Distribution
The lebrikizumab-lbkz steady-state volume of distribution is 5.14 L.
Metabolism/Elimination
Lebrikizumab-lbkz is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG.
The lebrikizumab-lbkz half-life is 24.5 days and clearance is 0.154 L/day. Lebrikizumab-lbkz exhibits linear elimination that is independent of dose.
Specific Populations
Age, Sex, Race
Age, sex, or race did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of lebrikizumab-lbkz.
Weight
Lebrikizumab-lbkz trough concentrations were lower in subjects with higher body weight.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Specific clinical pharmacology studies to evaluate the effects of renal impairment and hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of lebrikizumab-lbkz have not been conducted. Lebrikizumab-lbkz, as a monoclonal antibody, is not expected to undergo significant hepatic or renal elimination. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of lebrikizumab-lbkz were observed in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
The effect of lebrikizumab-lbkz on the PK of co-administered medications has not been studied.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of EBGLYSS or of other drug products.
Antibodies to lebrikizumab-lbkz developed in 4/145 (2.8%) of subjects treated with EBGLYSS 250 mg every 2 weeks followed by 250 mg every four weeks during the 12-month treatment period in EBGLYSS studies. Most of these antibodies were neutralizing and of low titer. Similar results were observed in pediatric subjects who received EBGLYSS up to 12 months. The presence of anti-drug antibodies was not associated with changes to pharmacokinetics, efficacy, or safety of lebrikizumab-lbkz. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown because of the low occurrence of ADA.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of lebrikizumab-lbkz.
No effects on fertility parameters such as reproductive organs, reproductive hormones or menstrual cycle length were observed in sexually mature female cynomolgus monkeys that were administered intravenous doses of lebrikizumab-lbkz up to 25 mg/kg/week for 37 weeks, which was associated with plasma exposure (C avg,ss ) approximately 15 times the human exposure at the MRHD. No effects on reproductive organs or sperm analysis were observed in sexually mature male cynomolgus monkeys that were administered subcutaneous doses of lebrikizumab-lbkz up to 25 mg/kg/week for 13 weeks, which was associated with plasma exposure (C avg,ss ) approximately 11 times the human exposure at the MRHD.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Atopic Dermatitis
Three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2 and ADhere (NCT04146363, NCT04178967, NCT04250337) enrolled a total of 1062 subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis not adequately controlled by topical medication(s) and who were candidates for systemic therapy. A total of 148 subjects (14%) were 12 to <18 years who weighed at least 40 kg and 914 (86%) were adult subjects. Disease severity was defined by an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥3 in the overall assessment of AD lesions on a severity scale of 0 to 4, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 72, and a minimum body surface area involvement of ≥10%.
At baseline, 50% of subjects were male, 63% were White, 11% were Black or African American, and 21% were Asian; 12.8% identified as Hispanic or Latino, 63% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD) and 37% of subjects had a baseline IGA of 4 (severe AD). The baseline mean EASI was 29, and the baseline Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) was 7 on a scale of 0-10. Of all subjects, 99% had received prior treatment for AD.
In all three trials, subjects in the EBGLYSS group received subcutaneous injections of EBGLYSS 500 mg at Week 0 and at Week 2, followed by 250 mg every other week (Q2W) through Week 16.
To evaluate the maintenance and durability of response in the monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2), subjects originally randomized to EBGLYSS who achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1, or at least a 75% reduction in EASI from baseline [EASI-75] at Week 16 and did not require rescue therapy were re-randomized to an additional 36 weeks of either a maintenance dose of EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W (every 2 weeks), EBGLYSS 250 mg Q4W (every 4 weeks), or placebo.
Subjects who did not achieve IGA 0 or 1 or EASI-75 at Week 16 or subjects who required rescue therapy during the first 16 weeks were treated with open-label EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W.
In the concomitant therapy trial (ADhere), subjects received EBGLYSS + TCS or placebo + TCS. Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) were permitted for sensitive areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
All three trials assessed the primary endpoint, the proportion of subjects who achieved an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline at Week 16. Other evaluated outcomes at Week 16 included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 and EASI-90, and improvement in itch severity as defined by a reduction of at least 4 points on an 11-point Pruritus NRS. ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2 also evaluated the maintenance and durability of response through Week 52.
The results of the EBGLYSS monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2) are presented in Table 3 .
a Subjects who received rescue therapy or discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were analyzed as non-responders. Data after treatment discontinuation due to any other reason were considered missing. Any missing data was imputed using MCMC-MI. | ||||||
b Subjects received 500 mg of EBGLYSS at Week 0 and Week 2, and 250 mg Q2W up to Week 16 | ||||||
c Primary endpoint. Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 (“clear” or “almost clear”) and a reduction of ≥2 points on a 0-4 IGA scale | ||||||
| ADvocate 1 | ADvocate 2 | |||||
| EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W b | Placebo | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W b | Placebo | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | |
| Number of subjects | 283 | 141 | -- | 281 | 146 | -- |
| IGA 0 or 1 c | 43% | 13% | 30% (22%, 38%) | 33% | 11% | 22% (14%, 30%) |
| EASI-75 | 59% | 16% | 42% (33%, 51%) | 52% | 18% | 33% (24%, 42%) |
| EASI-90 | 38% | 9% | 29% (21%, 36%) | 31% | 10% | 21% (13%, 28%) |
| Number of subjects with baseline Pruritus NRS score ≥4 | 263 | 130 | -- | 253 | 134 | -- |
| Pruritus NRS ≥4 point improvement | 46% | 13% | 33% (25%, 41%) | 40% | 12% | 28% (20%, 37%) |
The proportion of EBGLYSS-treated subjects who achieved IGA 0 or 1 (with ≥2-point improvement from baseline) by visit in ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2 are presented in Figure 1 .
Figure 1: Proportion of Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis achieving IGA 0 or 1, with a ≥2-point improvement from baseline through Week 16 in ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2

The proportion of EBGLYSS-treated subjects who achieved at least a 4-point improvement from baseline in Pruritus NRS by visit in ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2 are presented in Figure 2 .
Figure 2: Proportion of Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis with ≥4-point improvement in Pruritus NRS through Week 16 in ADvocate 1 or ADvocate 2

Examination of age, sex, and White, Asian, Black or African American race subgroups did not identify differences in response to EBGLYSS among these subgroups. The database was not large enough to adequately assess differences in effects in other races.
The results in the concomitant therapy trial (ADhere) at Week 16, where subjects received EBGLYSS + TCS or placebo + TCS were consistent with the results in the monotherapy trials (ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2).
Maintenance and Durability of Response (Week 16 to Week 52)
EBGLYSS-treated subjects achieving IGA 0 or 1 or EASI-75, and who did not receive rescue therapy at Week 16 were re-randomized to 36 weeks of maintenance treatment with EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W, EBGLYSS 250 mg Q4W, or placebo in ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2. The results are presented in Table 4 .
a Subjects who received systemic rescue therapy, discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were analyzed as non-responders. Data after topical rescue medication or treatment discontinuation due to any other reason were considered missing. Any missing data were imputed using MCMC-MI. | ||||||
b Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 (“clear” or “almost clear”) and a reduction of ≥2 points on a 0-4 IGA scale | ||||||
| ADvocate 1 | ADvocate 2 | |||||
| EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W | EBGLYSS 250 mg Q4W | Placebo | EBGLYSS 250 mg Q2W | EBGLYSS 250 mg Q4W | Placebo | |
| Number of subjects who were IGA of 0 or 1 Responders at Week 16 b | 45 | 45 | 22 | 32 | 32 | 16 |
| IGA of 0 or 1 b at Week 52 | 76% | 74% | 47% | 65% | 81% | 50% |
| Number of subjects who were EASI-75 Responders at Week 16 | 61 | 62 | 30 | 51 | 53 | 27 |
| EASI-75 at Week 52 | 79% | 79% | 61% | 77% | 85% | 72% |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
EBGLYSS (lebrikizumab-lbkz) injection is a sterile, preservative free, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown solution, available in a single-dose prefilled pen or a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle shield. Each prefilled pen and prefilled syringe with needle shield is designed to deliver 250 mg of EBGLYSS in 2 mL.
EBGLYSS is supplied as:
| Pack Size | NDC | |
| Prefilled Pen | ||
| 250 mg/2 mL single-dose | Carton of 1 | 0002-7772-11 |
| Prefilled syringe with needle shield | ||
| 250 mg/2 mL (125 mg/mL) single-dose | Carton of 1 | 0002-7797-11 |
Storage and Handling
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
If necessary, EBGLYSS can be stored at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for up to 7 days in the original carton. Dispose of EBGLYSS that has been left at room temperature for longer than 7 days.
Store in the original carton to protect from light until use.
Do not freeze. Do not use EBGLYSS if it has been frozen.
Do not shake.
Do not microwave, run hot water over it, or leave it in direct sunlight.
Not made with natural rubber latex.
Discard the EBGLYSS single-dose prefilled pen or prefilled syringe with needle shield after use in a puncture-resistant container.
PREFILLED PEN INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE |
| EBGLYSS ™ [EHB-glihs] |
| (lebrikizumab-lbkz) |
| injection, for subcutaneous use |
| Single-Dose Prefilled Pen |
| This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject EBGLYSS. |
| Before you use the EBGLYSS Prefilled Pen (Pen), read and carefully follow all the step-by-step instructions. |
 |
| Important information you need to know before injecting EBGLYSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE |
| Before you use the EBGLYSS Pen, read and carefully follow all the step-by-step instructions. |
| Parts of the EBGLYSS Pen |
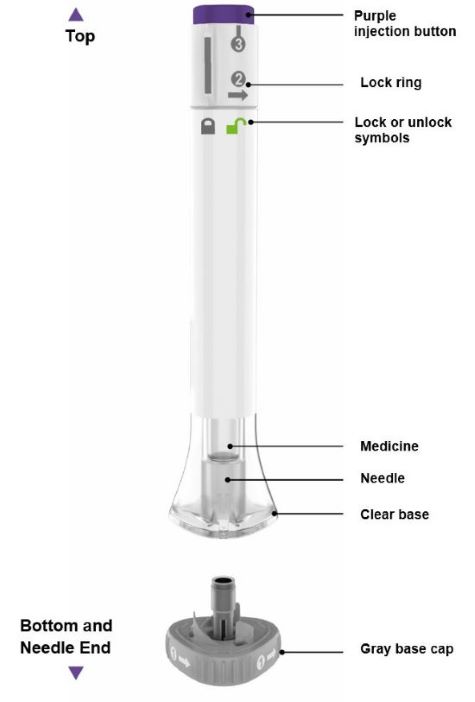 |
| Preparing to inject EBGLYSS | ||
| Gather supplies and EBGLYSS Pen: | ||
|
| |
| Note: You do not need to allow your Pen to warm up to room temperature before use. | ||
| Inspect the Pen and the medicine | ||
| Leave the gray base cap on until you are ready to inject. Make sure you have the right medicine. The medicine inside should be clear. It may be colorless to slightly yellow to slightly brown. | ||
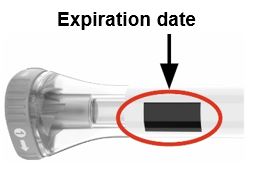 | Do not use the Pen (see Disposing of EBGLYSS ) if the:
| |
| Wash your hands with soap and water | ||
| Choose and clean your injection site | ||
| Your healthcare provider can help you choose the injection site that is best for you. Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe and let dry. | ||
 | You or another person may inject into these areas. |
|
 | Another person should inject into this area. |
|
| Injecting EBGLYSS | ||||||||||
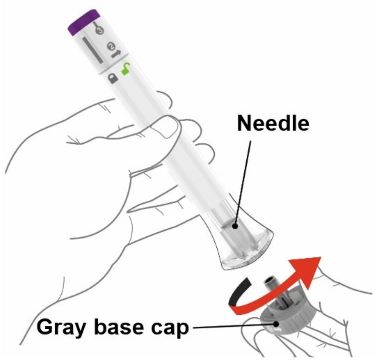
| 1 | Uncap the Pen |  | ||||||||
|  | Make sure the Pen is locked . | ||||||||
| When you are ready to inject, twist off the gray base cap and throw it away in your household trash. Do not put the gray base cap back on; this could damage the needle. Do not touch the needle inside the clear base. | ||||||||||
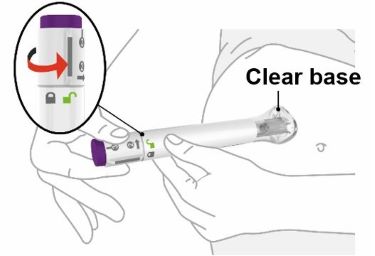
| 2 | Place and unlock | |||||||||
| Place and hold the clear base flat and firmly against the skin. | |||||||||
 | Keep the clear base on the skin, then turn the lock ring to the unlock position. | |||||||||
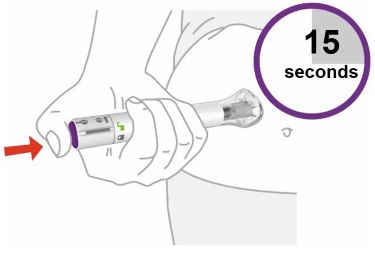
| 3 | Press and hold for 15 seconds | |||||||||
| Press and hold the purple injection button and listen for 2 loud clicks:
| |||||||||
| You will know the injection is complete when the gray plunger is visible. |
| |||||||||
| Disposing of EBGLYSS | ||||||||||
| Dispose of (throw away) the used Pen | ||||||||||
 | Put the used EBGLYSS Pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. | |||||||||
| Do not throw away (dispose of) the EBGLYSS Pen in your household trash. | ||||||||||
| If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is: | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container. | ||||||||||
| Commonly asked questions | ||||||||||
| Q. | What if I see air bubbles in the Pen? | |||||||||
| A. | Air bubbles are normal. They will not harm you or affect your dose. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if my Pen is not at room temperature? | |||||||||
| A. | You do not need to allow your Pen to warm up to room temperature before injecting. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if there is a drop of liquid on the tip of the needle when I remove the gray base cap? | |||||||||
| A. | A drop of liquid on the tip of the needle is normal. This will not harm you or affect your dose. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if I unlock the Pen and press the purple injection button before twisting off the gray base cap? | |||||||||
| A. | Do not remove the gray base cap. Throw away (dispose of) the Pen and use a new one. | |||||||||
| Q. | Do I need to hold the purple injection button down until the injection is complete? | |||||||||
| A. | You do not need to hold the purple injection button down, but it may help you keep the Pen steady and firm against your skin. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if the needle did not retract after my injection? | |||||||||
| A. | Do not touch the needle or replace the gray base cap. Store the Pen in a safe place to avoid an accidental needlestick and contact Lilly at 1-800-Lilly-Rx (1-800-545-5979) for instructions on how to return the Pen. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if there is a drop of liquid or blood on my skin after my injection? | |||||||||
| A. | This is normal. Press a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site. Do not rub the injection site. | |||||||||
| Q. | How can I tell if my injection is complete? | |||||||||
| A. | After you press the purple injection button, you will hear 2 loud clicks. The second loud click tells you that your injection is complete. You will also see the gray plunger at the top of the clear base. The injection may take up to 15 seconds. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if I remove the Prefilled Pen before the second loud click or before the gray plunger stops moving? | |||||||||
| A. | You may not have received your full dose. Do not give another injection. Call your healthcare provider for help. | |||||||||
| Q. | What if I heard more than 2 clicks during my injection, 2 loud clicks and 1 soft one. Did I get my complete injection? | |||||||||
| A. | Some people may hear a soft click right before the second loud click. That is the normal operation of the Prefilled Pen. Do not remove the Prefilled Pen from your skin until you hear the second loud click. | |||||||||
| If you have more questions about how to use the EBGLYSS Prefilled Pen: | ||||||||||
|  | Scan this code to launch www.ebglyss.com | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Storing EBGLYSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Keep your Pen and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
Read the Patient Information insert for EBGLYSS inside this box to learn more about your medicine.
Eli Lilly and Company Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA US License Number 1891
EBGLYSS is a trademark of Eli Lilly and Company. Copyright © 2024, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: MAY 2025 EBG-0003-PEN-IFU-20250521
Mechanism of Action
Lebrikizumab-lbkz is an IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity and slow off-rate to interleukin (IL)-13 and allows IL-13 to bind to IL-13Rα1 but inhibits human IL-13 signaling through the IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα1 receptor complex. IL-13 is a naturally occurring cytokine that is involved in Type 2 inflammation, which is an important component in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Lebrikizumab-lbkz inhibits IL-13-induced responses including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and IgE. Lebrikizumab-lbkz-bound IL-13 can still bind IL-13Rα2 allowing subsequent internalization and natural clearance of IL-13.