Empaveli prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Empaveli patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PNH (2.2 )
Recommended dosage is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly.
C3G or Primary IC-MPGN (2.3 )
- Recommended dosage for adults is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly.
- Recommended dosage for pediatric patients is dependent upon patient weight. See full prescribing information for the recommended dosage in patients with C3G or IC-MPGN. (2.2 )
- EMPAVELI can be administered via a commercially available pump or with EMPAVELI Injector. (2.4 )
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
Recommended Vaccination and Prophylaxis
Vaccinate patients against encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis (serogroups A, C, W, Y and B), according to current ACIP recommendations at least 2 weeks prior to initiation of EMPAVELI therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
If urgent EMPAVELI therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines for Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis , according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible.
Healthcare professionals who prescribe EMPAVELI must enroll in the REMS for EMPAVELI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Recommended Dosage - PNH
The recommended dose of EMPAVELI is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Dosage for patients switching to EMPAVELI from C5 inhibitors
To reduce the risk of hemolysis with abrupt treatment discontinuation:
- For patients switching from eculizumab, initiate EMPAVELI while continuing eculizumab at its current dose. After 4 weeks, discontinue eculizumab before continuing on monotherapy with EMPAVELI.
- For patients switching from ravulizumab, initiate EMPAVELI no more than 4 weeks after the last dose of ravulizumab.
Dose Adjustment
- For lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels greater than 2 × the upper limit of normal (ULN), adjust the dosing regimen to 1,080 mg every three days.
- In the event of a dose increase, monitor LDH twice weekly for at least 4 weeks.
Missed Dose
- Administer EMPAVELI as soon as possible after a missed dose. Resume the regular dosing schedule following administration of the missed dose.
Recommended Dosage - C3G or Primary IC-MPGN
For adults (18 years and older)
The recommended dose of EMPAVELI is 1,080 mg (20 mL) administered subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
For pediatric patients (12 years to less than 18 years of age)
For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer EMPAVELI dose and volume based upon body weight, according to the schedule in Table 1. Administer the recommended dose of EMPAVELI subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
| Patient Body Weight | First dose (infusion volume) | Second dose (infusion volume) | Maintenance dose (infusion volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg or higher | 1,080 mg (20 mL) | 1,080 mg (20 mL) | 1,080 mg twice weekly (20 mL) |
| 35 kg to less than 50 kg | 648 mg (12 mL) | 810 mg (15 mL) | 810 mg twice weekly (15 mL) |
| Less than 35 kg | 540 mg (10 mL) | 540 mg (10 mL) | 648 mg twice weekly (12 mL) |
Missed Dose
Administer EMPAVELI as soon as possible after a missed dose. Resume the regular dosing schedule following administration of the missed dose.
Administration
EMPAVELI is for subcutaneous administration using:
- A commercially available infusion pump with a reservoir of at least 20 mL OR
- EMPAVELI Injector, a single-use, disposable on body injector
EMPAVELI is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Patients may self-administer or caregivers may administer EMPAVELI after proper training by a healthcare professional on how to prepare and administer EMPAVELI.
Follow the steps below and use aseptic technique to prepare and administer EMPAVELI, either by an infusion pump or EMPAVELI Injector:
- Prior to use‚ allow EMPAVELI to reach room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for approximately 30 minutes. Keep the vial in the carton until ready for use to protect from light.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. EMPAVELI is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish solution. Do not use if the liquid looks cloudy, contains particles, or is dark yellow.
- Discard any unused portion of EMPAVELI.
Preparation with Infusion Pump
- Refer to the EMPAVELI Instructions for Use and the infusion pump manufacturer's instructions for full preparation and administration information.
- Use a needleless transfer device (such as a vial adapter) or a transfer needle to fill the syringe.
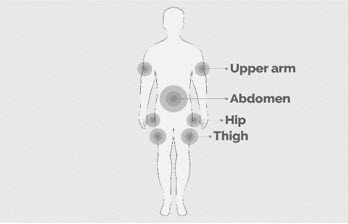
- Rotate infusion sites (i.e., abdomen, thighs, hips, upper arms) from one infusion to the next. Do not infuse where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid infusing into tattoos, scars, or stretch marks.
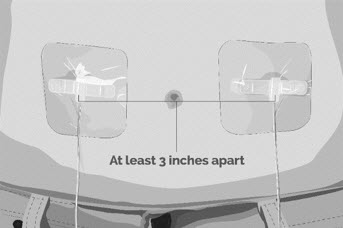
- If multi-infusion sets are needed, ensure the infusion sites are at least 3 inches apart.
- The typical infusion time is approximately 30 minutes (if using two infusion sites) or approximately 60 minutes (if using one infusion site).
Preparation with EMPAVELI Injector
- Refer to the EMPAVELI Injector Instructions for Use, which comes with the device.
- Use a needleless transfer device (such as a vial adapter).
- EMPAVELI Injector is for abdominal subcutaneous use only. Rotate the site of each subcutaneous administration. Do not inject where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into tattoos, scars, or stretch marks.
- Injection time is approximately 30 to 60 minutes.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Empaveli prescribing information
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS CAUSED BY ENCAPSULATED BACTERIA
EMPAVELI, a complement inhibitor, increases the risk of serious infections, especially those caused by encapsulated bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae , Neisseria meningitidis , and Haemophilus influenzae type B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . Life-threatening and fatal infections with encapsulated bacteria have occurred in patients treated with complement inhibitors. These infections may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early.
- Complete or update vaccination for encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI, unless the risks of delaying therapy with EMPAVELI outweigh the risk of developing a serious infection. Comply with the most current Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommendations for vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria in patients receiving a complement inhibitor. See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) for additional guidance on the management of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
- Patients receiving EMPAVELI are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by encapsulated bacteria, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination. Monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infections and evaluate immediately if infection is suspected.
Because of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the EMPAVELI REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EMPAVELI is a complement inhibitor indicated:
- for the treatment of adult patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). (1.1 )
- for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) or primary immune-complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (IC-MPGN), to reduce proteinuria. (1.2 )
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
EMPAVELI ® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
C3 glomerulopathy or primary immune-complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
EMPAVELI ® is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) or primary immune-complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (IC-MPGN), to reduce proteinuria.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PNH (2.2 )
Recommended dosage is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly.
C3G or Primary IC-MPGN (2.3 )
- Recommended dosage for adults is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly.
- Recommended dosage for pediatric patients is dependent upon patient weight. See full prescribing information for the recommended dosage in patients with C3G or IC-MPGN. (2.2 )
- EMPAVELI can be administered via a commercially available pump or with EMPAVELI Injector. (2.4 )
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
Recommended Vaccination and Prophylaxis
Vaccinate patients against encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis (serogroups A, C, W, Y and B), according to current ACIP recommendations at least 2 weeks prior to initiation of EMPAVELI therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
If urgent EMPAVELI therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines for Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis , according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible.
Healthcare professionals who prescribe EMPAVELI must enroll in the REMS for EMPAVELI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Recommended Dosage - PNH
The recommended dose of EMPAVELI is 1,080 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Dosage for patients switching to EMPAVELI from C5 inhibitors
To reduce the risk of hemolysis with abrupt treatment discontinuation:
- For patients switching from eculizumab, initiate EMPAVELI while continuing eculizumab at its current dose. After 4 weeks, discontinue eculizumab before continuing on monotherapy with EMPAVELI.
- For patients switching from ravulizumab, initiate EMPAVELI no more than 4 weeks after the last dose of ravulizumab.
Dose Adjustment
- For lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels greater than 2 × the upper limit of normal (ULN), adjust the dosing regimen to 1,080 mg every three days.
- In the event of a dose increase, monitor LDH twice weekly for at least 4 weeks.
Missed Dose
- Administer EMPAVELI as soon as possible after a missed dose. Resume the regular dosing schedule following administration of the missed dose.
Recommended Dosage - C3G or Primary IC-MPGN
For adults (18 years and older)
The recommended dose of EMPAVELI is 1,080 mg (20 mL) administered subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
For pediatric patients (12 years to less than 18 years of age)
For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer EMPAVELI dose and volume based upon body weight, according to the schedule in Table 1. Administer the recommended dose of EMPAVELI subcutaneously twice weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
| Patient Body Weight | First dose (infusion volume) | Second dose (infusion volume) | Maintenance dose (infusion volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg or higher | 1,080 mg (20 mL) | 1,080 mg (20 mL) | 1,080 mg twice weekly (20 mL) |
| 35 kg to less than 50 kg | 648 mg (12 mL) | 810 mg (15 mL) | 810 mg twice weekly (15 mL) |
| Less than 35 kg | 540 mg (10 mL) | 540 mg (10 mL) | 648 mg twice weekly (12 mL) |
Missed Dose
Administer EMPAVELI as soon as possible after a missed dose. Resume the regular dosing schedule following administration of the missed dose.
Administration
EMPAVELI is for subcutaneous administration using:
- A commercially available infusion pump with a reservoir of at least 20 mL OR
- EMPAVELI Injector, a single-use, disposable on body injector
EMPAVELI is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Patients may self-administer or caregivers may administer EMPAVELI after proper training by a healthcare professional on how to prepare and administer EMPAVELI.
Follow the steps below and use aseptic technique to prepare and administer EMPAVELI, either by an infusion pump or EMPAVELI Injector:
- Prior to use‚ allow EMPAVELI to reach room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for approximately 30 minutes. Keep the vial in the carton until ready for use to protect from light.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. EMPAVELI is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish solution. Do not use if the liquid looks cloudy, contains particles, or is dark yellow.
- Discard any unused portion of EMPAVELI.
Preparation with Infusion Pump
- Refer to the EMPAVELI Instructions for Use and the infusion pump manufacturer's instructions for full preparation and administration information.
- Use a needleless transfer device (such as a vial adapter) or a transfer needle to fill the syringe.
- Rotate infusion sites (i.e., abdomen, thighs, hips, upper arms) from one infusion to the next. Do not infuse where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid infusing into tattoos, scars, or stretch marks.
- If multi-infusion sets are needed, ensure the infusion sites are at least 3 inches apart.
- The typical infusion time is approximately 30 minutes (if using two infusion sites) or approximately 60 minutes (if using one infusion site).
Preparation with EMPAVELI Injector
- Refer to the EMPAVELI Injector Instructions for Use, which comes with the device.
- Use a needleless transfer device (such as a vial adapter).
- EMPAVELI Injector is for abdominal subcutaneous use only. Rotate the site of each subcutaneous administration. Do not inject where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into tattoos, scars, or stretch marks.
- Injection time is approximately 30 to 60 minutes.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 1,080 mg/20 mL (54 mg/mL) clear, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are insufficient data on EMPAVELI use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated PNH in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ) . The use of EMPAVELI may be considered following an assessment of the risks and benefits.
Treatment of pregnant cynomolgus monkeys with pegcetacoplan at a subcutaneous dose of 28 mg/kg/day (2.9 times human exposure based on AUC) from the gestation period through parturition resulted in a statistically significant increase in abortions or stillbirths compared to controls (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or fetal/neonatal risk
PNH in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal outcomes, including worsening cytopenias, thrombotic events, infections, bleeding, miscarriages and increased maternal mortality, and adverse fetal outcomes, including fetal death and premature delivery.
Data
Animal Data
Animal reproduction studies with pegcetacoplan were conducted in cynomolgus monkeys. Pegcetacoplan treatment of pregnant cynomolgus monkeys at a subcutaneous dose of 28 mg/kg/day (2.9 times human exposure based on AUC) from the gestation period through parturition resulted in a statistically significant increase in abortions and stillbirths compared to controls. No increase in abortions or stillbirths occurred at a dose of 7 mg/kg/day (1.3 times human exposure based on AUC). No maternal toxicity or teratogenic effects were observed in offspring delivered at term. No developmental effects were observed in infants up to 6 months postpartum. Systemic exposure to pegcetacoplan of less than 1% of maternal levels was detected in fetuses from monkeys treated with 28 mg/kg/day from the period of organogenesis through the second trimester.
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether pegcetacoplan is secreted in human milk or whether there is potential for absorption and harm to the infant. There are no data on the effects of pegcetacoplan on milk production. Pegcetacoplan is present in milk of lactating monkeys (see Animal Data ) . Since many medicinal products are secreted into human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reaction in a breastfeeding child, breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment and for 40 days after the last dose.
Data
Animal Data
Pegcetacoplan was detectable in milk of lactating monkeys at less than 1% concentration of serum levels but was not detectable in the serum of nursing infants.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
EMPAVELI may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to treatment with EMPAVELI. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with EMPAVELI and for 40 days after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EMPAVELI for the treatment of C3G or primary IC-MPGN have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. Use of EMPAVELI for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well controlled trial that enrolled 55 pediatric patients aged 12 years and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . The safety and effectiveness of EMPAVELI in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with C3G or IC-MPGN have not been established.
Safety and effectiveness of EMPAVELI in pediatric patients with PNH have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of EMPAVELI did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between geriatric and younger patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
EMPAVELI is contraindicated:
- in patients with hypersensitivity to pegcetacoplan or to any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
- for initiation in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae , Neisseria meningitidis , and Haemophilus influenzae type B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria. (5.1 )
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Monitor patients for infusion-related reactions and institute appropriate medical management as needed. (5.3 )
- Interference with Laboratory Tests: Use of silica reagents in coagulation panels may result in artificially prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). (5.5 )
Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria
EMPAVELI, a complement inhibitor, increases a patient's susceptibility to serious, life-threatening, or fatal infections caused by encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae , Neisseria meningitidis (caused by any serogroup, including non-groupable strains), and Haemophilus influenzae type B. Life-threatening and fatal infections with encapsulated bacteria have occurred in both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients treated with complement inhibitors. The initation of EMPAVELI treatment is contraindicated in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Complete or update vaccination against encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to administration of the first dose of EMPAVELI, according to the most current ACIP recommendations for patients receiving a complement inhibitor. Revaccinate patients in accordance with ACIP recommendations considering the duration of therapy with EMPAVELI. Note that, ACIP recommends an administration schedule in patients receiving complement inhibitors that differs from the administration schedule in the vaccine prescribing information. If urgent EMPAVELI therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines against encapsulated bacteria according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible. Various durations and regimens of antibacterial drug prophylaxis have been considered, but the optimal durations and drug regimens for prophylaxis and their efficacy have not been studied in unvaccinated or vaccinated patients receiving complement inhibitors, including EMPAVELI. The benefits and risks of treatment with EMPAVELI, as well as the benefits and risks of antibacterial drug prophylaxis in unvaccinated or vaccinated patients, must be considered against the known risks for serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Vaccination does not eliminate the risk of serious encapsulated bacterial infections, despite development of antibodies following vaccination. Closely monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infection and evaluate patients immediately if an infection is suspected. Inform patients of these signs and symptoms and instruct patients to seek immediate medical care if these signs and symptoms occur. Promptly treat known infections. Serious infection may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early. Consider interruption of EMPAVELI in patients who are undergoing treatment for serious infections.
EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
EMPAVELI REMS
EMPAVELI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called EMPAVELI REMS, because of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Notable requirements of the EMPAVELI REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must enroll in the REMS.
- Prescribers must counsel patients about the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
- Prescribers must provide the patients with the REMS educational materials.
- Prescribers must assess patient vaccination status for encapsulated bacteria and vaccinate if needed according to current ACIP recommendations two weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI.
- Prescribers must provide a prescription for antibacterial drug prophylaxis if treatment must be started urgently, and the patient is not up to date with vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria according to current ACIP recommendations at least two weeks prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI.
- Pharmacies that dispense EMPAVELI must be certified in the EMPAVELI REMS and must verify prescribers are certified.
- Patients must receive counseling from the prescriber about the need to receive vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria per ACIP recommendations, the need to take antibiotics as directed by the prescriber, and the signs and symptoms of serious infections.
- Patients must be instructed to carry the Patient Safety Card with them at all times during and for 2 months following treatment discontinuation with EMPAVELI.
Further information is available at www.empavelirems.com or 1-888-343-7073
Infusion-Related Reactions
Systemic hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., facial swelling, rash, urticaria, pyrexia) have occurred in patients treated with EMPAVELI, which may resolve after treatment with antihistamines. Cases of anaphylaxis leading to treatment discontinuation have been reported. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (including anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue EMPAVELI infusion immediately, institute appropriate treatment, per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms are resolved.
Monitoring PNH Manifestations after Discontinuation of EMPAVELI
After discontinuing treatment with EMPAVELI, closely monitor for signs and symptoms of hemolysis, identified by elevated LDH levels along with sudden decrease in PNH clone size or hemoglobin, or reappearance of symptoms such as fatigue, hemoglobinuria, abdominal pain, dyspnea, major adverse vascular events (including thrombosis), dysphagia, or erectile dysfunction. Monitor any patient who discontinues EMPAVELI for at least 8 weeks to detect hemolysis and other reactions. If hemolysis, including elevated LDH, occurs after discontinuation of EMPAVELI, consider restarting treatment with EMPAVELI.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
There may be interference between silica reagents in coagulation panels and EMPAVELI that results in artificially prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT); therefore, avoid the use of silica reagents in coagulation panels.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Study in Complement-Inhibitor Experienced Adult Patients with PNH (Study APL2-302)
The data described below reflect the exposure in 80 adult patients with PNH who received EMPAVELI (n=41) or eculizumab (n=39) at the recommended dosing regimens for 16 weeks. Serious adverse reactions were reported in 7 (17%) patients with PNH receiving EMPAVELI. The most common serious adverse reaction in patients treated with EMPAVELI was infections (5%). The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) with EMPAVELI were injection-site reactions, infections, diarrhea, abdominal pain, respiratory tract infection, viral infection, and fatigue.
Table 2 describes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI in Study APL2-302.
| Adverse Reaction | EMPAVELI (N=41) n (%) | Eculizumab (N=39) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Injection-site reaction Grouped terms Term includes injection-site erythema, injection-site reaction, injection-site swelling, injection-site induration, injection-site bruising, injection-site pain, injection-site pruritus, vaccination site reaction, administration site swelling, injection-site hemorrhage, injection -site edema, injection-site warmth, administration site pain, application site pain, injection-site mass, injection-site rash, vaccination site pain | 16 (39) | 2 (5) |
| Fatigue | 5 (12) | 9 (23) |
| Chest pain | 3 (7) | 1 (3) |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Infections | 12 (29) | 10 (26) |
| Respiratory tract infection | 6 (15) | 5 (13) |
| Viral Infection | 5 (12) | 3 (8) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 9 (22) | 1 (3) |
| Abdominal pain | 8 (20) | 4 (10) |
| Musculoskeletal disorders | ||
| Back pain | 3 (7) | 4 (10) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 3 (7) | 9 (23) |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Systemic hypertension | 3 (7) | 1 (3) |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in less than 5% of patients include:
- Intestinal ischemia
- Biliary sepsis
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
After the randomized control period, 77 patients continued the study, and all were treated with EMPAVELI monotherapy at the recommended dosing regimen for up to 48 weeks. Serious adverse reactions were reported in 18 patients (23%). Additional adverse reactions reported in >5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI during the open-label part of the study compared to the randomized controlled part in Table 1 were cough (12%), arthralgia (8%), oropharyngeal pain (8%), pyrexia (8%), pain in extremity (7%), thrombocytopenia (7%), abdominal distension (5%), acute kidney injury (5%), anxiety (5%), and myalgia (5%). One patient (1%) died due to COVID-19 infection.
Description of Select Adverse Reactions
Injection-Site Reactions
Injection/infusion-site reactions (e.g., erythema, swelling, induration, pruritus, and pain) have been reported during Study APL2-302. These reactions were mild or moderate in severity.
Diarrhea
Seventeen cases of diarrhea have been reported during the 48 weeks. Fifteen of the cases were mild and two were moderate.
Study in Complement-Inhibitor Naïve Adult Patients with PNH (Study APL2-308)
The data described below reflect the exposure in adult patients with PNH who received EMPAVELI (n=46) or the control arm (supportive care excluding complement inhibitors) (n=18) in Study APL2-308 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . One patient (2%) who received EMPAVELI died due to septic shock. Serious adverse reactions were reported in 6 (13%) patients with PNH receiving EMPAVELI. The most common adverse reaction (≥10%) in patients treated with EMPAVELI were injection site reactions, infections, viral infection, pain in extremity, hypokalemia, arthralgia, dizziness, abdominal pain, rash, and headache.
Table 3 describes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of patients treated with EMPAVELI in Study APL2‑308.
| Adverse Reaction | EMPAVELI (N=46) n (%) | Control Arm Control Arm = supportive care (excluding complement inhibitors) (N=18) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Exposure Adjusted Rate (per 100 pt yrs) | Exposure Adjusted Rate (per 100 pt yrs) | |
| EMPAVELI (N=46) group includes patients who received EMPAVELI at any point during the study, including patients randomized to EMPAVELI (N=35) and patients randomized to the control arm and crossed over to EMPAVELI treatment (N=11). | ||
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Injection-site reaction Grouped terms Term includes injection-site bruising, injection-site hemorrhage, injection-site swelling, application site reaction, infusion-site pruritus, injection-site erythema, injection-site rash, puncture site reaction. | 12 (26) 42 | 0 0 |
| Pyrexia | 4(9) 14 | 0 0 |
| Peripheral edema | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||
| Infections | 9 (20) 32 | 4 (22) 74 |
| Viral infection | 6 (13) 21 | 2 (11) 37 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Pain in extremity | 6 (13) 21 | 0 0 |
| Arthralgia | 5 (11) 18 | 0 0 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Hypokalemia | 6 (13) 21 | 2 (11) 37 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 5 (11) 18 | 0 0 |
| Headache | 5 (11) 18 | 0 0 |
| Somnolence | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 5 (11) 18 | 1 (6) 18 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash | 5(11) 18 | 0 0 |
| Ecchymosis | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Erythema | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | 3 (7) 11 | 1 (6) 18 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough | 4 (9) 14 | 0 0 |
| Epistaxis | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Blood creatinine increased | 3 (7) 11 | 0 0 |
C3 Glomerulopathy or Primary IC-MPGN
Study in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of age and older with C3G or primary IC-MPGN (Study APL2-C3G-310)
The data described below reflects the exposure in adult (n=35) and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older (n=28) with native kidney C3G (n=46), native kidney primary IC-MPGN (n=12), or recurrent C3G following kidney transplant (n=5) who received EMPAVELI at the recommended dosing regimens during the 26-week placebo-controlled period of APL2-C3G-310. Serious adverse reactions due to viral infections resulting in hospitalizations occurred in 2 (3%) patients with C3G or primary IC-MPGN receiving EMPAVELI and 1 (2%) patient on placebo. One patient (2%) on EMPAVELI with native kidney C3G died because of respiratory failure due to COVID-19 pneumonia; there were no deaths in the placebo arm.
Table 4 describes the adverse reactions that were reported in ≥5% of patients (adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older) treated with EMPAVELI and at a greater incidence than placebo in APL2-C3G-310. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were similar to those seen in adults.
The placebo-controlled period of APL2-C3G-310 was followed by a 26-week open-label period. During the open-label period, one patient with native kidney C3G had a serious adverse event of pneumonia secondary to Streptococcus pneumoniae , and one patient with recurrent C3G following kidney transplant developed herpes zoster meningoencephalitis while on concomitant immunosuppression, leading to treatment discontinuation.
| Adverse Reaction | EMPAVELI (N=63) n (%) | Placebo (N=61) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Infusion-site reactions Term includes the following reactions at the infusion site: erythema, pruritus, swelling, bruising, induration, pain, hemorrhage, discomfort, oedema, rash, and hypoaesthesia. | 16 (25) | 14 (23) |
| Pyrexia | 12 (19) | 6 (10) |
| Fatigue | 4 (6) | 1 (2) |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Nasopharyngitis | 11 (18) | 7 (12) |
| Influenza | 7 (11) | 3 (5) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 6 (10) | 4 (7) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough | 6 (10) | 1 (2) |
Study in Adult recurrent C3G or primary IC-MPGN following kidney transplant (Study APL2-C3G-204)
In a study in 13 adults with recurrent C3G or primary IC-MPGN after kidney transplant (NCT#04572854), one patient with primary IC-MPGN experienced a serious adverse event of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia while on EMPAVELI and concurrent immunosuppressive medications.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of EMPAVELI. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to EMPAVELI exposure.
- Anaphylaxis and urticaria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
DESCRIPTION
EMPAVELI contains pegcetacoplan, a complement inhibitor. Pegcetacoplan is a symmetrical molecule comprised of two identical pentadecapeptides covalently bound to the ends of a linear 40-kiloDalton (kDa) PEG molecule. The peptide portions of pegcetacoplan contain 1-methyl-L-tryptophan (Trp(Me)) in position 4 and amino(ethoxyethoxy)acetic acid (AEEA) in position 14.
The molecular weight of pegcetacoplan is approximately 43.5 kDa. The molecular formula is C 1970 H 3848 N 50 O 947 S 4 . The structure of pegcetacoplan is shown below.

EMPAVELI injection is a sterile, clear, colorless to slightly yellowish aqueous solution for subcutaneous use and is supplied in a 20-mL single-dose vial. Each 1 mL of solution contains 54 mg of pegcetacoplan, 41 mg of sorbitol, 0.384 mg of glacial acetic acid, 0.490 mg of sodium acetate trihydrate, and Water for Injection USP. EMPAVELI may also contain sodium hydroxide and/or additional glacial acetic acid for adjustment to a target pH of 5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Pegcetacoplan binds to complement protein C3 and its activation fragment C3b, thereby regulating the cleavage of C3 and the generation of downstream effectors of complement activation.
In PNH, extravascular hemolysis (EVH) is facilitated by C3b opsonization while intravascular hemolysis (IVH) is mediated by the downstream membrane attack complex (MAC). Pegcetacoplan acts proximally in the complement cascade controlling both C3b-mediated EVH and terminal complement-mediated IVH.
In C3G and primary IC-MPGN, complement dysregulation and overactivation causes deposition of C3 fragments in glomeruli, which contributes to the pathogenesis of C3G and is thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of IC-MPGN. Pegcetacoplan binds C3 and its activation fragment C3b, therefore inhibiting C3 activation, decreasing C3 glomerular fragment deposition, and decreasing C5 convertase activity and subsequent assembly of C5b-9.
Pharmacodynamics
In patients with PNH administered multiple doses of pegcetacoplan, the mean C3 concentration increased from 94 mg/dL at baseline to 380 mg/dL at Week 16 and sustained through Week 48 (Study APL2-302). In study APL2-308, the mean C3 concentration increased from 95 mg/dL at baseline to 356 mg/dL at Week 26 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
The percentage of PNH Type II + III RBCs increased from 66.2% at baseline to 93.9% at Week 16 and sustained through Week 48 (Study APL2-302). In Study APL2-308, the mean percentage of PNH Type II + III RBCs increased from 42.4% at baseline to 90% at Week 26.
The mean percentage of PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition decreased from 17.8% at baseline to 0.2% at Week 16 and sustained through Week 48 (Study APL2-302). In Study APL2-308, the mean percentage of PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition decreased from 2.85% at baseline to 0.09% at Week 26.
In patients with C3G or primary IC-MPGN administered pegcetacoplan SC infusion twice weekly, mean (SD) serum C3 levels increased from 62 (48) mg/dL at baseline to 371 (120) mg/dL at Week 26 compared to no change with placebo. Mean (SD) plasma soluble C5b-9 levels decreased from 903 (698) ng/mL at baseline to 290 (249) ng/mL at Week 26 with EMPAVELI compared to no change with placebo. Of patients with evaluable kidney biopsies (n=69), 74% of patients on pegcetacoplan had a decrease in C3 complement staining by at least 2 orders of magnitude from baseline to Week 26 compared to 12% on placebo.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended dose of EMPAVELI, no large mean increases in QTc interval (i.e., greater than 20 msec) were observed.
Pharmacokinetics
In patients with PNH, the serum pegcetacoplan concentrations achieved steady-state approximately 4 to 6 weeks following the first dose. The exposure of pegcetacoplan increased proportionally over a dose range from 45 to 1,440 mg (0.04 to 1.33 times the approved recommended dose). The mean (CV%) trough serum concentration observed at Week 16 was 706 (15.1%) mcg/mL and sustained through Week 48 (Study APL2-302). In Study APL2-308, mean (CV%) trough serum concentration was 744 (25.5%) mcg/mL at Week 26.
In patients with C3G or primary IC-MPGN, serum pegcetacoplan concentrations reached steady state approximately 4 to 8 weeks following twice weekly SC infusion. The mean (CV%) trough serum concentrations ranged between 716 (31%) and 766 (23%) mcg/mL from Week 4 to Week 26.
Absorption
The median T max of pegcetacoplan is between 108 and 144 hours (4.5 to 6 days) after a single dose.
Distribution
The mean (CV%) volume of distribution of pegcetacoplan is approximately 3.98 L (32%) in patients with PNH.
The estimated mean (CV%) volume of distribution of pegcetacoplan is approximately 4.79 L (38%) and 4.58 L (29%) in patients with C3G or primary IC-MPGN, respectively.
Elimination
The estimated mean (CV%) of clearance (CL) is 0.36 L/day (30%) and median effective half-life of elimination (t 1/2 ) is 8.6 days in patients with PNH.
The estimated mean (CV%) of clearance (CL) is 0.32 L/day (54%) and median t 1/2 is 10.2 days in patients with C3G. The estimated mean (CV%) of clearance (CL) is 0.3 L/day (51%) and median t 1/2 is 10.8 days in patients with primary IC-MPGN.
Metabolism
Pegcetacoplan is expected to be metabolized into small peptides and amino acids by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
There were no clinically significant differences on the pharmacokinetics of pegcetacoplan based on age (19 to 81 years old), sex, race (Asian vs. non‑Asian), renal impairment, and hepatic function as evaluated by total bilirubin (0.06‑8.8 mg/dL), albumin (1.8‑5.5 g/dL), aspartate aminotransferase (6‑302 IU/L), or alanine aminotransferase (4‑209 IU/L).
In patients with C3G or primary IC-MPGN, there were no clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of pegcetacoplan based on age (12 to 74 years old), diagnosis (C3G vs primary IC-MPGN), and urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) (133-13300 mg/g).
Immunogenicity
PNH
There is insufficient information to characterize the anti-drug antibody response to EMPAVELI and the effects of anti-drug antibodies on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of pegcetacoplan products in PNH patients.
C3G or primary IC-MPGN
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the study described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies.
During the 26-week placebo-controlled period in Study APL2-C3G-310, 14 of 62 participants (23%) with C3G or primary IC-MPGN randomized to pegcetacoplan developed anti–pegcetacoplan peptide antibodies. Two of 62 participants (3%) developed anti–pegcetacoplan peptide neutralizing antibodies. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-drug antibodies on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of pegcetacoplan over the treatment duration of 26 weeks.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal carcinogenicity studies of pegcetacoplan have not been conducted.
Pegcetacoplan was not mutagenic when tested in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) and was not genotoxic in an in vitro assay in human TK6 cells or in an in vivo micronucleus assay in mice.
Effects of pegcetacoplan on fertility have not been studied in animals. There were no microscopic abnormalities in male or female reproductive organs in toxicity studies in rabbits and monkeys.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In toxicology studies in rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys, epithelial vacuolation and infiltrates of vacuolated macrophages were observed in multiple tissues, including the renal tubules, following daily subcutaneous doses of pegcetacoplan up to 7 times the human dose. These findings are attributable to uptake of the PEG moieties of pegcetacoplan. Renal degeneration was observed microscopically in rabbits at exposures (C max and AUC) less than those for the human dose, and in monkeys at exposures approximately 2.7-fold those for the human dose. The clinical significance of these findings is uncertain.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
The efficacy and safety of EMPAVELI in patients with PNH were assessed in two open-label, randomized-controlled Phase 3 studies: Study APL2-302 (NCT03500549) and Study APL2-308 (NCT04085601). All patients who completed the studies were eligible to enroll in a separate long-term extension study.
In both studies, patients were vaccinated against Streptococcus pneumoniae , Neisseria meningitidis types A, C, W, Y, and B, and Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib), either within 2 years prior to Day 1 or within 2 weeks after starting treatment with EMPAVELI. Patients vaccinated after initiation of treatment with EMPAVELI received prophylactic treatment with appropriate antibiotics until 2 weeks after vaccination. In addition, prophylactic antibiotic therapy was administered at the discretion of the investigator in accordance with local treatment guidelines for patients with PNH receiving treatment with a complement inhibitor.
A dose of 1,080 mg twice weekly was used for patients randomized to the EMPAVELI group of each study. If required, the dose of EMPAVELI could be adjusted to 1,080 mg every 3 days. EMPAVELI was administered as a subcutaneous infusion; the infusion time was approximately 20 to 40 minutes.
Study in Complement-Inhibitor Experienced Adult Patients with PNH (Study APL2-302)
The study enrolled patients with PNH who had been treated with a stable dose of eculizumab for at least the previous 3 months and with Hb levels less than 10.5 g/dL.
Eligible patients entered a 4-week run-in period during which they received EMPAVELI 1,080 mg subcutaneously twice weekly in addition to their current dose of eculizumab. Patients were then randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either 1,080 mg of EMPAVELI twice weekly or their current dose of eculizumab through the duration of the 16-week randomized controlled period (RCP).
Randomization was stratified based on the number of packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusions within the 12 months prior to Day -28 (<4; ≥4) and platelet count at screening (<100,000/mm 3 ; ≥100,000/mm 3 ). Following completion of the RCP, all patients entered a 32-week open-label period (OLP) and received monotherapy with EMPAVELI. Patients initially randomized to eculizumab entered a second 4-week run-in period during which they received EMPAVELI in addition to eculizumab before continuing on to receive EMPAVELI monotherapy. All patients who completed the 48-week period were eligible to enroll in a separate long-term extension study.
A total of 80 patients were randomized to receive treatment, 41 to EMPAVELI and 39 to eculizumab. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally well balanced between treatment groups (see Table 5 ). The median times from PNH diagnosis to Day -28 were 6 and 9.7 years, respectively, for EMPAVELI and eculizumab. The baseline mean total PNH RBC clone sizes (Type III) were 47% for EMPAVELI and 50% for eculizumab. Twenty-nine percent and 23% of patients had a history of major adverse vascular events, and 37% and 26% had a history of thrombosis for patients receiving EMPAVELI or eculizumab, respectively. Within 28 days prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI or eculizumab, respectively, 34% and 31% of patients used anti-thrombotic agents (anti-platelet and/or anticoagulants). During Study APL2-302, 37% and 36% of patients on EMPAVELI and eculizumab, respectively, used antithrombotic agents. A total of 38 patients in the group treated with EMPAVELI and 39 patients in the eculizumab group completed the 16-week RCP and continued into the 32-week OLP. Because of adverse reactions of hemolysis, 3 patients were discontinued from the EMPAVELI group during the RCP. Two out of 41 patients in the EMPAVELI group needed the dose adjustment to 1,080 mg every 3 days.
| Parameter | Statistics | EMPAVELI (N=41) | Eculizumab (N=39) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean (SD) | 50.2 (16.3) | 47.3 (15.8) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | n (%) | 27 (65.9) | 22 (56.4) |
| Race | |||
| Asian | n (%) | 5 (12.2) | 7 (17.9) |
| Black or African American | n (%) | 2 (4.9) | 0 |
| White | n (%) | 24 (58.5) | 25 (64.1) |
| Other | n (%) | 0 | 1 (2.6) |
| Not reported | n (%) | 10 (24.4) | 6 (15.4) |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | n (%) | 2 (4.9) | 1 (2.6) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | n (%) | 29 (70.7) | 32 (82.1) |
| Not reported | n (%) | 10 (24.4) | 6 (15.4) |
| Hemoglobin level (g/dL) | Mean (SD) | 8.7 (1.1) | 8.7 (0.9) |
| Absolute reticulocyte count (10 9 cells/L) | Mean (SD) | 218 (75) | 216 (69.1) |
| LDH level (U/L) | Mean (SD) | 257.5 (97.7) | 308.6 (284.8) |
| Number of transfusions in last 12 months prior to Day -28 | Mean (SD) | 6.1 (7.3) | 6.9 (7.7) |
| <4 | n (%) | 20 (48.8) | 16 (41) |
| ≥4 | n (%) | 21 (51.2) | 23 (59) |
The efficacy of EMPAVELI was based on change from baseline to Week 16 (during RCP) in hemoglobin level. Baseline was defined as the average of measurements recorded prior to taking the first dose of EMPAVELI. Supportive efficacy data included transfusion avoidance, defined as the proportion of patients who did not require a transfusion during the RCP, and change from baseline to Week 16 in absolute reticulocyte count (ARC).
EMPAVELI was superior to eculizumab for the change from baseline in hemoglobin level at Week 16 ( p <0.0001). The adjusted mean change from baseline in hemoglobin level was 2.37 g/dL in the group treated with EMPAVELI versus -1.47 g/dL in the eculizumab group (Figure 1), demonstrating an adjusted mean increase of 3.84 g/dL with EMPAVELI compared to eculizumab at Week 16 (95% CI, 2.33-5.34).
Figure 1: Adjusted Mean (± SE) Change from Baseline to Week 16 in Hemoglobin (g/dL) in Study APL2-302 Treatment effect estimates from a mixed model are shown. The mixed model contained the categorical effects of treatment, visit, treatment by visit interaction, and stratification factors (transfusion history and platelet count at screening), and the continuous covariate of baseline value. |
|
Non-inferiority was demonstrated in the endpoints of transfusion avoidance and change from baseline in ARC at Week 16.
The adjusted means, treatment differences, and confidence intervals (CIs) for additional efficacy results are shown in Table 6.
| EMPAVELI (N=41) | Eculizumab (N=39) | Difference (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transfusion avoidance , n (%) | 35 (85%) | 6 (15%) | 63% Difference in percentages and 95% CI were based on the stratified Miettinen–Nurminen method. (48%, 77%) |
| Change from baseline in ARC (10 9 cells/L), LS LS = Least square mean (SE) SE = Standard error | -136 (6.5) | 28 (11.9) | -164 (-189.9, -137.3) |
Efficacy was generally similar across subgroups based on sex, race, and age.
All 77 patients who completed the RCP entered the 32- week OLP, during which all patients received EMPAVELI, resulting in a total exposure of up to 48 weeks. Between Week 16 and Week 48, 10 patients discontinued the study, all due to adverse reactions, and thirteen patients had a dose adjustment to 1,080 mg every three days. The efficacy results at Week 48 were generally consistent with those at Week 16.
Study in Complement-Inhibitor Naïve Adult Patients with PNH (Study APL2-308)
Study APL2-308 enrolled patients with PNH who had not been treated with any complement inhibitor within 3 months prior to enrollment and with Hb levels less than the lower limit of normal (LLN). Eligible patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive EMPAVELI or supportive care [excluding complement inhibitors (e.g., transfusions, corticosteroids, supplements such as iron, folate, and vitamin B 12 ), hereafter referred to as the control arm] through the duration of the 26-week treatment period. Randomization was stratified based on the number of packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusions within the 12 months prior to Day -28 (<4; ≥4). At any point during the study, a patient assigned to the control arm treatment group who had Hb levels ≥2 g/dL below baseline or presented with a PNH associated thromboembolic event was offered cross-over to EMPAVELI for the remainder of the study.
A total of 53 patients were randomized, 35 to EMPAVELI and 18 to the control arm. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally well balanced between treatment groups (see Table 7 ). The mean times from PNH diagnosis to Day 1 were 5.7 and 5.5 years, respectively, for EMPAVELI and the control arm. The baseline mean total PNH RBC clone sizes (Type III) were 31% for EMPAVELI and 28% for the control arm. In the EMPAVELI group, 2.9% of patients had a history of major adverse vascular events. Two patients (5.7%) in the EMPAVELI group and 3 patients (16.7%) in the control arm group had a history of at least 1 type of thrombosis. Within 28 days prior to the first dose of EMPAVELI or the control arm, respectively, 17.1% and 27.8% of patients used anti-thrombotic agents (anti-platelet and/or anticoagulants). During Study APL2-308, 8.6% and 0% of patients on EMPAVELI and the control arm, respectively, used antithrombotic agents. Eleven of 18 patients randomized to the control transitioned to cross-over therapy with EMPAVELI due to a decreased Hb level ≥2 g/dL below baseline. Three patients treated with EMPAVELI required dose adjustment to 1,080 mg every 3 days. Three patients (5.7%; two patients in the EMPAVELI group and one patient in the control arm group) discontinued the study, none due to an adverse reaction.
| Parameter | Statistics | EMPAVELI (N=35) | Control Arm Control Arm = supportive care (excluding complement inhibitors) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N=18) | |||
| Age (years) | Mean (SD) | 42.2 (12.7) | 49.1 (15.6) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | n (%) | 16 (45.7) | 8 (44.4) |
| Race | |||
| American Indian or Alaska | n (%) | 9 (25.7) | 2 (11.1) |
| Native | |||
| Asian | n (%) | 23 (65.7) | 16 (88.9) |
| Black or African American | n (%) | 2 (5.7) | 0 |
| Other | n (%) | 1 (2.9) | 0 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | n (%) | 12 (34.3) | 2 (11.1) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | n (%) | 23 (65.7) | 16 (88.9) |
| Hemoglobin level (g/dL) | Mean (SD) | 9.4 (1.4) | 8.7 (0.8) |
| Absolute reticulocyte count (10 9 cells/L) | Mean (SD) | 230.2 (81) | 180.3 (109.1) |
| LDH level (U/L) | Mean (SD) | 2151 (909.4) | 1945.9 (1003.7) |
| Number of transfusions in last 12 months prior to Day -28 | Mean (SD) | 3.9 (4.4) | 5.1 (5) |
| <4 | n (%) | 21 (60) | 8 (44.4) |
| ≥4 | n (%) | 14 (40) | 10 (55.6) |
The efficacy of EMPAVELI was based on the percentage of patients achieving hemoglobin stabilization, defined as avoidance of a >1 g/dL decrease in hemoglobin levels from baseline in the absence of transfusion, and the change from baseline in LDH level. Supportive efficacy data included change from baseline in absolute reticulocyte count (ARC), change from baseline in hemoglobin, and transfusion avoidance, defined as the proportion of patients who did not require a transfusion through Week 26. Baseline was defined as the average of measurements recorded prior to taking the first dose of EMPAVELI or prior to randomization to the control arm treatment group.
Efficacy results are shown in Table 8 below.
| EMPAVELI (N=35) | Control Arm Control Arm = supportive care (excluding complement inhibitors) | Difference (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N=18) | p-value | ||
| Data collected after cross-over from the control arm is excluded in analyses. | |||
| Hemoglobin Stabilization Patients who crossed over from the control arm group to the EMPAVELI group, withdrew from the study, or were lost to follow up are considered as failing to achieve the criteria. (n, %) | 30 (85.7%) | 0 (0%) | 73% (57%, 89%) p<0.0001 p-value is obtained by stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test. |
| Change from Baseline in LDH The post baseline missing values (including the values after cross-over from the control arm) are imputed using a multiple imputation method. (LS LS = Least square Mean CFB, SE SE = Standard error ) | -1870 (101) | -400 (313) | -1470 (-2113.4, -827.3) p<0.0001 |
| Change from baseline in ARC (LSMean CFB, SE) | -123 (9.2) | -19 (25.2) | -103 (-158.9, -48.7) p = 0.0002 |
| Change from baseline in Hb (LSMean CFB, SE) | 2.9 (0.38) | 0.3 (0.76) | 2.7 (0.99, 4.35) p = 0.0019 |
| Transfusion Avoidance (n, %) | 32 (91%) | 1 (6%) | 72% (56%, 89%) p<0.0001 |
C3 Glomerulopathy (C3G) or Primary Immune-Complex Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (IC-MPGN)
The efficacy of EMPAVELI in reducing proteinuria in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with native kidney C3G, native kidney IC-MPGN, or recurrent C3G following kidney transplant was demonstrated in Study APL2-C3G-310. Safety and effectiveness of EMPVAELI in patients with recurrent IC-MPGN following kidney transplant have not been established.
APL2-C3G-310 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that included 124 adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older and weighing at least 30 kg with biopsy-proven, native kidney or post-transplant recurrent C3G, or native kidney primary IC-MPGN, eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , proteinuria ≥1 g/day, and urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1 g/g (NTC 05067127). For at least 12 weeks before randomization and throughout the 26-week placebo-controlled period, patients were required to be on stable and optimized doses of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers and/or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Immunosuppressant medication doses (e.g., steroids no higher than 20 mg daily, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus) had to be stable for at least 12 weeks before randomization and throughout the 26-week placebo-controlled period.
Patients were randomized (1:1) to EMPAVELI or placebo, administered twice weekly as a subcutaneous (SC) infusion for 26 weeks. Randomization was stratified by post-transplant recurrence and by kidney biopsy obtained within 28 weeks of screening. Adults and pediatric patients weighing 50 kg or more received EMPAVELI 1,080 mg (20 mL) twice weekly. Pediatric patients weighing 35 kg to less than 50 kg received 648 mg (12 mL) for the first infusion and 810 mg (15 mL) for each infusion thereafter. Pediatric patients weighing 30 kg to less than 35 kg received EMPAVELI 540 mg (10 mL) for the first 2 infusions and 648 mg (12 mL) twice weekly thereafter.
Patients were vaccinated against Streptococcus pneumoniae , Neisseria meningitidis types A, C, W, Y, and B, and Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) at least 14 days prior to randomization, unless documented evidence existed that participants received the recommended vaccinations or were non-responders to vaccination.
At baseline, the mean age was 26 years (range 12 to 74 years); 57% were female, 73% White, 15% Asian, 1% Black or African American, and 11% others. The study population included 55 pediatric patients 12 years to less than 18 years of age; mean age 14.7 years (28 randomized to EMPAVELI and 27 to placebo). Disease type was reasonably balanced between the treatment groups. Overall, 88 patients (71%) had native kidney C3G, 27 patients (22%) had native kidney primary IC-MPGN, and 8 patients (6%) had post-kidney transplant recurrent C3G. At baseline, mean UPCR from triplicate first morning urine (FMU) collections was 3.1 g/g and 2.5 g/g in the pegcetacoplan and placebo groups, respectively; mean eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) was 79 and 87 in the pegcetacoplan and placebo groups, respectively; and mean baseline serum albumin was approximately 3.4 g/dL in both treatment groups.
Approximately 91% of patients were treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB), 72% with immunosuppressants (e.g., mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus), 40% with systemic corticosteroids, and 11% with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Use of each of these medications was balanced between the treatment groups.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the log-transformed ratio of UPCR (sampled from first morning urine collections) at Week 26 compared to baseline. At Week 26, the geometric mean UPCR ratio relative to baseline was 0.33 (95% CI: 0.25, 0.43) and 1.03 (95% CI: 0.91, 1.16) in the EMPAVELI and placebo groups, respectively, resulting in a 68% reduction in UPCR from baseline in the EMPAVELI group compared to placebo (p<0.0001). The treatment effect was consistent across all subgroups including disease type, age, transplant status (C3G), sex, race, baseline disease characteristics (eGFR and UPCR), and immunosuppressant use.
Figure 2 shows the geometric mean UPCR ratio compared to baseline over time.
| Abbreviations: FMU = first-morning spot urine; UPCR = urine protein-to-creatinine ratio. |
| Figure 2: Geometric Mean of UPCR Ratio Compared to Baseline Over 26 Weeks of Treatment - Study APL2-C3G-310 |
 |
During the 26-week placebo-controlled period, 49% of patients in the EMPAVELI group achieved a composite renal endpoint defined as a ≥50% reduction in UPCR and stable eGFR (≤15% reduction from baseline) compared with 3% of patients in the placebo group (odds ratio [95% CI] of 27 [6, 124], p<0.0001). Sixty percent of patients in the EMPAVELI group achieved a 50% or greater reduction in UPCR from baseline to Week 26 compared with 5% in the placebo arm, and 68% of patients in the EMPAVELI group had a stable eGFR (≤15% reduction from baseline to Week 26) compared with 59% in the placebo group. Over the first 6 months of treatment, EMPAVELI reduced the loss of kidney function compared to placebo (Figure 3). The efficacy of EMPAVELI in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older was similar to adults.
| Abbreviations: LS = least square |
| LS Mean (95% CI) of difference between EMPAVELI and placebo at Week 26 is 6.31 (0.50, 12.12) mL/min/1.73m 2 . |
| Figure 3: LS Mean of eGFR Compared to Baseline Over 26 Weeks of Treatment - Study APL2-C3G-310 |
 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
EMPAVELI injection is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish aqueous solution for subcutaneous infusion supplied as 1,080 mg/20 mL (54 mg/mL) solution in 20-mL single-dose vials.
EMPAVELI is available in 20-mL single-dose vials individually packaged in cartons that are supplied in 8-count convenience cartons. NDC 73606-010-01.
Storage and Handling
Store vials of EMPAVELI refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not use beyond the expiration date stamped on the carton.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE EMPAVELI ® (em-puh-vel-ee) (pegcetacoplan) injection, for subcutaneous use infusion pump
Important Information
This Instructions for Use is for the infusion pump only. If using EMPAVELI Injector, follow the Instructions for Use that comes with the EMPAVELI Injector.
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using EMPAVELI with an infusion pump and each time you get a refill as there may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you or your caregiver how to infuse EMPAVELI the right way before you use it for the first time. Ask your healthcare provider about any instructions you do not understand.
How should I store EMPAVELI?
- Store vials of EMPAVELI in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original carton to protect from light.
- Do not use EMPAVELI past the expiration date stamped on the carton.
Keep EMPAVELI and all medicines out of the reach of children.
| Step 1 | Prepare for infusion Before you start:
| |
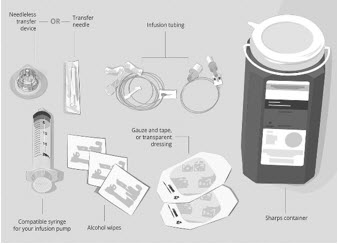
Gather your supplies (See Figure A ):
| Figure A: Supplies
| |
| Clean your work surface well using an alcohol wipe. | ||
| Wash your hands well with soap and water. Dry your hands. | ||
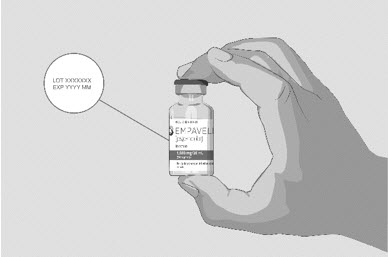
| Step 2 | Check the vial and liquid
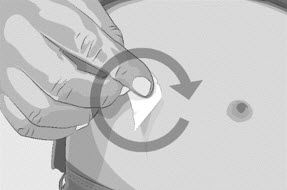
| Figure B
|
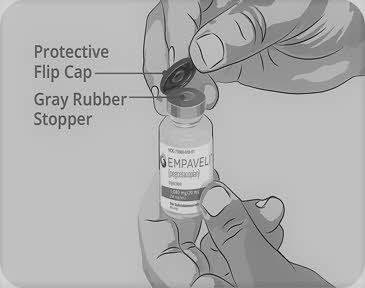
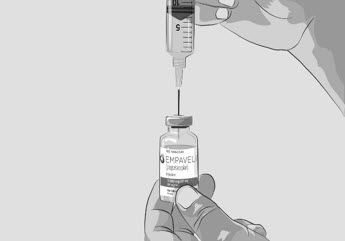
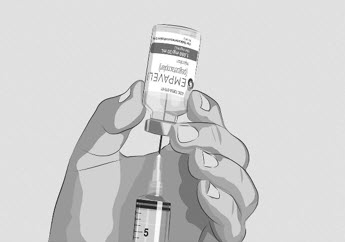
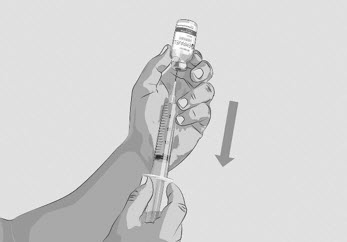
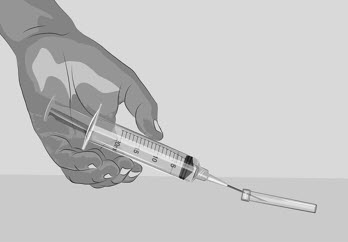
| Step 3 | Prepare and fill syringe
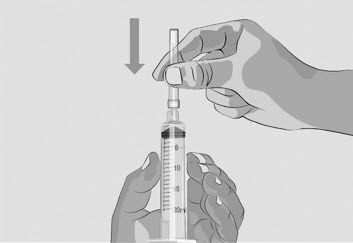
Do not touch the exposed gray rubber stopper after wiping. | Figure C
|
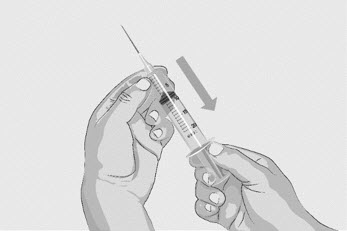
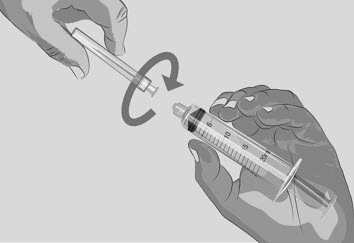
Option 1: If using a needleless transfer device (such as a vial adapter), follow the instructions provided by the device manufacturer. OR Option 2: If transfer is done using a transfer needle and a syringe, follow the instructions below:
| Figure D
| |
| Figure F
| |
| Figure G
| |
| Figure H
| |
| Figure I
| |
| Figure J
| |
| Step 4 | Prepare infusion pump and tubing
| |
| Step 5 | Prepare the infusion site(s)
| Figure K
|
| Figure L
| |
| Figure M
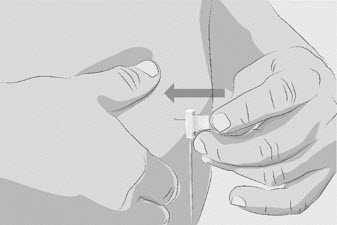
| |
| Step 6 | Insert and secure the infusion needle(s)
| Figure N
|
| Figure O
| |
| Step 7 | Start infusion
| |
| Step 8 | Complete infusion
| |
| Step 9 | Record infusion
| |
| Step 10 | Clean up
| |
| Step 11 | Dispose of (throw away) used needles and syringes and EMPAVELI infusion tubing.
| Figure P
|
Call 1-866-692-7527 to speak with an Apellis representative. Manufactured for: Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 100 Fifth Avenue Waltham, MA 02451 Copyright © 2025 Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. EMPAVELI is a registered trademark of Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised 7/2025
EMP-IFU-28Jul2025-5.0
Mechanism of Action
Pegcetacoplan binds to complement protein C3 and its activation fragment C3b, thereby regulating the cleavage of C3 and the generation of downstream effectors of complement activation.
In PNH, extravascular hemolysis (EVH) is facilitated by C3b opsonization while intravascular hemolysis (IVH) is mediated by the downstream membrane attack complex (MAC). Pegcetacoplan acts proximally in the complement cascade controlling both C3b-mediated EVH and terminal complement-mediated IVH.
In C3G and primary IC-MPGN, complement dysregulation and overactivation causes deposition of C3 fragments in glomeruli, which contributes to the pathogenesis of C3G and is thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of IC-MPGN. Pegcetacoplan binds C3 and its activation fragment C3b, therefore inhibiting C3 activation, decreasing C3 glomerular fragment deposition, and decreasing C5 convertase activity and subsequent assembly of C5b-9.