Evotaz prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Evotaz patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Pretreatment testing: Renal laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. Hepatic testing should be performed in patients with underlying liver disease prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: One tablet once daily, taken orally with food in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg. (2.2)
- Renal impairment: EVOTAZ is not recommended for use in treatment-experienced patients with end-stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis. (2.3 , 8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: EVOTAZ is not recommended in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment. (2.4 , 8.7)
Laboratory Testing Prior to Initiation and During Treatment with EVOTAZ
Renal Testing
Renal laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. Renal laboratory testing should include estimated creatinine clearance, serum creatinine, and urinalysis with microscopic examination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6) ] . Cobicistat decreases estimated creatinine clearance due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine without affecting actual renal glomerular function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
When coadministering EVOTAZ with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF), assess estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein at baseline and routinely monitor during treatment. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also monitor serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Hepatic Testing
Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in patients with underlying liver disease prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
Recommended Dosage
EVOTAZ is a fixed-dose tablet containing 300 mg of atazanavir and 150 mg of cobicistat. The recommended dosage of EVOTAZ is one tablet taken once daily orally with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients with HIV-1:
- Adult patients
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg
Administer EVOTAZ in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Dose separation may be required when taken with H 2 -receptor antagonists or proton-pump inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) ] .
Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended in treatment-experienced patients with HIV-1 who have end-stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
EVOTAZ coadministered with tenofovir DF is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 70 mL/min. Coadministration of EVOTAZ and tenofovir DF in combination with concomitant or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Not Recommended in Patients with Any Degree of Hepatic Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Not Recommended During Pregnancy
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use during pregnancy and should not be initiated in pregnant individuals due to substantially lower exposures of cobicistat and consequently, lower exposures of atazanavir, during the second and third trimesters. An alternative regimen is recommended for individuals who become pregnant during therapy with EVOTAZ [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .

Evotaz prescribing information
Contraindications (4 ) | 05/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EVOTAZ is a two-drug combination of atazanavir, a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease inhibitor, and cobicistat, a CYP3A inhibitor indicated for use in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV‑1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg. (1)
Limitations of Use
Use of EVOTAZ in treatment-experienced patients should be guided by the number of baseline primary protease inhibitor resistance substitutions. (1)
1.1 Indications
EVOTAZ ® is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in the following populations [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.3) ] :
- Adult patients
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg.
1.2 Limitations of Use
Use of EVOTAZ in treatment-experienced patients should be guided by the number of baseline primary protease inhibitor resistance substitutions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Pretreatment testing: Renal laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. Hepatic testing should be performed in patients with underlying liver disease prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: One tablet once daily, taken orally with food in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg. (2.2)
- Renal impairment: EVOTAZ is not recommended for use in treatment-experienced patients with end-stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis. (2.3 , 8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: EVOTAZ is not recommended in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment. (2.4 , 8.7)
Laboratory Testing Prior to Initiation and During Treatment with EVOTAZ
Renal Testing
Renal laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. Renal laboratory testing should include estimated creatinine clearance, serum creatinine, and urinalysis with microscopic examination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6) ] . Cobicistat decreases estimated creatinine clearance due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine without affecting actual renal glomerular function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
When coadministering EVOTAZ with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF), assess estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein at baseline and routinely monitor during treatment. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also monitor serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Hepatic Testing
Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in patients with underlying liver disease prior to initiation of EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
Recommended Dosage
EVOTAZ is a fixed-dose tablet containing 300 mg of atazanavir and 150 mg of cobicistat. The recommended dosage of EVOTAZ is one tablet taken once daily orally with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients with HIV-1:
- Adult patients
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg
Administer EVOTAZ in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Dose separation may be required when taken with H 2 -receptor antagonists or proton-pump inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) ] .
Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended in treatment-experienced patients with HIV-1 who have end-stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
EVOTAZ coadministered with tenofovir DF is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 70 mL/min. Coadministration of EVOTAZ and tenofovir DF in combination with concomitant or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Not Recommended in Patients with Any Degree of Hepatic Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Not Recommended During Pregnancy
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use during pregnancy and should not be initiated in pregnant individuals due to substantially lower exposures of cobicistat and consequently, lower exposures of atazanavir, during the second and third trimesters. An alternative regimen is recommended for individuals who become pregnant during therapy with EVOTAZ [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
EVOTAZ tablets contain 342 mg atazanavir sulfate, equivalent to 300 mg of atazanavir, and 150 mg of cobicistat and are oval, biconvex, pink, film-coated, and debossed with “3641” on one side and plain on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to EVOTAZ during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use during pregnancy and should not be initiated in pregnant individuals [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] ; use of an alternative regimen is recommended for individuals who become pregnant during therapy with EVOTAZ. Pharmacokinetic data from studies conducted in pregnant individuals receiving cobicistat showed substantially lower exposures during the second and third trimesters, and consequently also for the coadministered antiretroviral agent. Consult the full prescribing information for cobicistat for additional information. Pharmacokinetic data from the evaluation of atazanavir and cobicistat in a limited number of pregnant individuals showed a similar trend in lower exposures of the antiretroviral component, atazanavir.
Prospective pregnancy data from the APR are not sufficient to adequately assess the risk of birth defects or miscarriage. Atazanavir use during pregnancy has been evaluated in a limited number of individuals. Available data from the APR show no increase in the risk of overall major birth defects for atazanavir compared with the background rate for major birth defects of 2.7% in a U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) (see Data) . The rate of miscarriage is not reported in the APR. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15−20%.
In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes was observed following oral administration of the components of EVOTAZ (atazanavir or cobicistat) to pregnant rats and rabbits (see Data) . During organogenesis in the rat and rabbit, atazanavir exposures (AUC) were similar to those observed at the human clinical dose (300 mg/day atazanavir boosted with 100 mg/day ritonavir), while exposures were up to 1.4 (rats) and 3.3 (rabbits) times human exposures at the maximal recommended human dose (MRHD) of 150 mg (see Data) .
Clinical Considerations
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use during pregnancy and should not be initiated in pregnant individuals. An alternative regimen is recommended for individuals who become pregnant during therapy with EVOTAZ (see Risk Summary) .
Maternal Adverse Reactions
Atazanavir
Reports of lactic acidosis syndrome, sometimes fatal, and symptomatic hyperlactatemia have occurred in pregnant individuals using atazanavir in combination with nucleoside analogues, which are associated with an increased risk of lactic acidosis syndrome.
Hyperbilirubinemia occurs frequently in patients who take atazanavir, including pregnant individuals. Refer to the atazanavir prescribing information for use of atazanavir in pregnancy.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Atazanavir
Infants exposed to atazanavir in utero may develop severe hyperbilirubinemia during the first few days of life.
Data
Human Data
Atazanavir
The APR has received prospective reports of live births following exposure to atazanavir-containing regimens during pregnancy, including 1361 exposures in the first trimester and 737 exposures in second/third trimester. Birth defects occurred in live births in 30 of 1361 (2.2%, 95% CI: 1.5% to 3.1%) with first trimester exposure to atazanavir-containing regimens and 17 of 737 (2.3%, 95% CI: 1.3% to 3.7%) with second/third trimester exposure to atazanavir-containing regimens. There was no increase in the overall rate of birth defects for atazanavir compared with the background birth defect rate of 2.7% in the U.S. reference population of the MACDP.
Cobicistat
The APR has received prospective reports of live births following exposure to cobicistat-containing regimens during pregnancy, including 347 exposures in the first trimester and 79 exposures in the second/third trimester. Birth defects occurred in 13 of 347 (3.7%, 95% CI: 2.0% to 6.3%) live births with first trimester exposure and 1 of 79 (1.3%, 95% CI: 0.0% to 6.9%) with second/third trimester exposure to cobicistat-containing regimens. Among pregnant individuals in the U.S. reference population, the background rate of birth defects is 2.7%. There was no increase in the overall rate of birth defects for cobicistat compared with the background birth defect rate of 2.7% in the U.S. reference population of the MACDP. Methodological limitations of the APR include the use of MACDP as the external comparator group. Limitations of using an external comparator include differences in methodology and populations, as well as confounding due to the underlying disease.
Animal Data
Atazanavir
Atazanavir was administered orally to pregnant rats (at 0, 200, 600, and 1920 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (at 0, 4, 15, and 60 mg/kg/day) during organogenesis (on gestation Days 6 through 15 and 7 through 19, respectively). No significant toxicological effects were observed in embryo-fetal toxicity studies performed with atazanavir at exposures (AUC) approximately 1.2 times higher (rats) and 0.7 times (rabbits) human exposures at the MRHD. In a rat pre- and postnatal developmental study, atazanavir was administered orally at doses of 0, 50, 220, and 1000 mg/kg/day from gestation Day 6 to postnatal Day 20. At a maternal toxic dose (1000 mg/kg/day), atazanavir caused body weight loss or weight gain suppression in the animal offspring at atazanavir exposures (AUC) of approximately 1.3 times higher than human exposures at the MRHD.
Cobicistat
Cobicistat was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 0, 25, 50, 125 mg/kg/day on gestation Day 6 to 17. Maternal toxicity was noted at 125 mg/kg/day and was associated with increases in post-implantation loss and decreased fetal weights. No malformations were noted at doses up to 125 mg/kg/day. Systemic exposures (AUC) at 50 mg/kg/day in pregnant females were 1.4 times higher than the human exposures at the MRHD. In pregnant rabbits, cobicistat was administered orally at doses of 0, 20, 50, and 100 mg/kg/day during the gestation Days 7 to 20. No maternal or embryo/fetal effects were noted at the highest dose of 100 mg/kg/day. Systemic exposures (AUC) at 100 mg/kg/day were 3.3 times higher than exposures at the MRHD.
In a pre- and postnatal developmental study in rats, cobicistat was administered orally at doses of 0, 10, 30, and 75 mg/kg from gestation Day 6 to postnatal Day 20, 21, or 22. At doses of 75 mg/kg/day of cobicistat, neither maternal nor developmental toxicity was noted. Systemic exposures (AUC) at this dose were 0.9 times lower than exposures at the MRHD.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the effects of EVOTAZ on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Atazanavir has been detected in human milk. No data are available regarding atazanavir effects on milk production. Atazanavir was present in the milk of lactating rats and was associated with neonatal growth retardation that reversed after weaning. Cobicistat is present in rat milk (see Data) . There is no information regarding the presence of cobicistat in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Potential risks of breastfeeding include: (1) HIV-1 transmission (in infants without HIV-1), (2) developing viral resistance (in infants with HIV-1), and (3) adverse reactions in a breastfed infant similar to those seen in adults.
Data
Animal Data
Cobicistat: During the prenatal and postnatal development toxicology study at doses up to 75 mg/kg/day, mean cobicistat milk to plasma ratio of up to 1.9 was measured 2 hours after administration to rats on lactation Day 10.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Atazanavir and cobicistat, components of EVOTAZ, interact with certain oral contraceptives [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.3) ] . Nonhormonal forms of contraceptive should be considered.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EVOTAZ for the treatment of HIV-1 in pediatric participants weighing at least 35 kg was established through a study with components of EVOTAZ. Use of EVOTAZ for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults, and by pharmacokinetic, safety, and virologic data from an open-label trial of components of EVOTAZ (Study GS-US-216-0128) in pediatric participants with HIV-1 aged 12 years and older. The safety in these participants through 48 weeks was similar to that in antiretroviral treatment-naive adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of EVOTAZ in the pediatric population weighing less than 35 kg have not been established. Atazanavir, a component of EVOTAZ, is not recommended for use in pediatric patients below the age of 3 months due to the risk of kernicterus.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with the components of EVOTAZ did not include sufficient numbers of participants aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger participants. In general, appropriate caution should be exercised in the administration and monitoring of EVOTAZ in elderly patients reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use in treatment-experienced patients with HIV-1 who have end-stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
EVOTAZ is not recommended for use in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The concomitant use of EVOTAZ and the following drugs in Table 1, are contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening events or loss of therapeutic effect [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 , 5.9) , Drug Interactions (7) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
EVOTAZ is contraindicated:
- in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, or toxic skin eruptions) to any of the components of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- when coadministered with drugs that strongly induce CYP3A4, which may lead to lower exposure of EVOTAZ resulting in potential loss of efficacy and development of possible resistance (Table 5).
- when coadministered with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A or UGT1A1 for clearance, and for which elevated plasma concentrations of the interacting drugs are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (see Table 5).
For additional information, including clinical comments and potential impact on exposure levels associated with drugs that are contraindicated with EVOTAZ, refer to Table 5 [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ] .
- Coadministration is contraindicated with, but not limited to, the following drugs:
| Drug Class | Drugs within class that are contraindicated with EVOTAZ |
|---|---|
| a Refer to Table 5 for sildenafil when administered for erectile dysfunction [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ]. | |
| b Refer to Table 5 for parenterally administered midazolam [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ]. | |
Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist | alfuzosin |
Antianginal | ranolazine |
Antiarrhythmics | dronedarone |
Anticonvulsants | carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin |
Antigout | colchicine (when used in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment) |
Antimycobacterials | rifampin |
Antineoplastics | apalutamide, encorafenib, irinotecan, ivosidenib |
Antipsychotics | lurasidone, pimozide |
Ergot Derivatives | dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine |
Hepatitis C Direct-Acting Antivirals | elbasvir/grazoprevir; glecaprevir/pibrentasvir |
Herbal Products | St. John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum ) |
Hormonal Contraceptives | drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol |
Lipid-modifying Agents | lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin |
Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor | nevirapine |
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitor | sildenafil a when administered for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension |
Protease Inhibitors | indinavir |
Sedative/hypnotics | triazolam, orally administered midazolam b |
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Cardiac conduction abnormalities: PR interval prolongation may occur in some patients. Consider ECG monitoring in patients with preexisting conduction system disease or when administered with other drugs that may prolong the PR interval. (5.1 , 6 , 7.3 , 12.2 , 17 )
- Severe skin reactions: Discontinue if severe rash develops. (5.2 , 6.1 , 17 )
- Assess creatinine clearance (CLcr) before initiating treatment. Consider alternative medications that do not require dosage adjustments in patients with renal impairment. (5.3 )
- When cobicistat, a component of EVOTAZ, is used in combination with a tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF)-containing regimen, cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome have been reported. (5.4 )
- When used with tenofovir DF, assess urine glucose and urine protein at baseline and monitor CLcr, urine glucose, and urine protein. Monitor serum phosphorus in patients with or at risk for renal impairment. Coadministration with tenofovir DF is not recommended in patients with CLcr below 70 mL/min or in patients also receiving a nephrotoxic agent. (5.4 )
- Chronic kidney disease has been reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients with HIV-1 treated with atazanavir, with or without ritonavir. Consider alternatives in patients at high risk for renal disease or with preexisting renal disease. Monitor renal laboratory tests prior to therapy and during treatment with EVOTAZ. Consider discontinuation of EVOTAZ in patients with progressive renal disease. (5.5 )
- Nephrolithiasis and cholelithiasis have been reported. Consider temporary interruption or discontinuation. (5.6 , 6 )
- Hepatotoxicity: Patients with hepatitis B or C are at risk of increased transaminases or hepatic decompensation. Monitor hepatic laboratory tests prior to therapy and during treatment. (2.5 , 5.7 , 8.7 )
- Antiretrovirals that are not recommended: EVOTAZ is not recommended for use with ritonavir or products containing ritonavir, or in combination with other antiretroviral drugs that require CYP3A inhibition to achieve adequate exposures (e.g., other protease inhibitors and elvitegravir). (5.9 )
- Hyperbilirubinemia: Most patients experience asymptomatic increases in indirect bilirubin, which is reversible upon discontinuation. If a concomitant transaminase increase occurs, evaluate for alternative etiologies. (5.10 , 6 )
- Patients receiving EVOTAZ may develop immune reconstitution syndrome (5.11 ), new onset or exacerbations of diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia (5.12 , 6 ), and redistribution/accumulation of body fat (5.13 ).
- Hemophilia: Spontaneous bleeding may occur and additional factor VIII may be required. (5.14 )
Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities
Atazanavir prolongs the PR interval of the electrocardiogram in some patients. In healthy participants and in participants with HIV-1 treated with atazanavir, abnormalities in atrioventricular (AV) conduction were asymptomatic and generally limited to first-degree AV block. There have been reports of second-degree AV block and other conduction abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Overdosage (10) ] . In clinical trials of atazanavir in participants with HIV-1 that included electrocardiograms, asymptomatic first-degree AV block was observed in 6% of participants treated with atazanavir (n=920) and 5% of participants (n=118) treated with atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir. Because of limited clinical experience in patients with preexisting conduction system disease (e.g., marked first-degree AV block or second- or third-degree AV block), consider ECG monitoring in these patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
Severe Skin Reactions
Cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, and toxic skin eruptions, including drug rash, eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, have been reported in patients receiving atazanavir [see Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . EVOTAZ should be discontinued if severe rash develops.
Mild-to-moderate maculopapular skin eruptions have also been reported in atazanavir clinical trials. These reactions had a median time to onset of 7.3 weeks and median duration of 1.4 week and generally did not result in treatment discontinuation.
Effects on Serum Creatinine
Cobicistat decreases estimated creatinine clearance due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine without affecting actual renal glomerular function. This effect should be considered when interpreting changes in estimated creatinine clearance in patients initiating EVOTAZ, particularly in patients with medical conditions or receiving drugs needing monitoring with estimated creatinine clearance.
Prior to initiating therapy with EVOTAZ, assess estimated creatinine clearance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Dosage recommendations are not available for drugs that require dosage adjustments in cobicistat-treated patients with renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Drug Interactions (7.3) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . Consider alternative medications that do not require dosage adjustments in patients with renal impairment.
Although cobicistat may cause modest increases in serum creatinine and modest declines in estimated creatinine clearance without affecting renal glomerular function, patients who experience a confirmed increase in serum creatinine of greater than 0.4 mg/dL from baseline should be closely monitored for renal safety.
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment When Used with Tenofovir DF
Renal impairment, including cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome, has been reported when cobicistat was used in an antiretroviral regimen that contained tenofovir DF. Therefore, coadministration of EVOTAZ and tenofovir DF is not recommended in patients who have an estimated creatinine clearance below 70 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
• When EVOTAZ is used with tenofovir DF, document urine glucose and urine protein at baseline and perform routine monitoring of estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein during treatment.
• Measure serum phosphorus in patients with or at risk for renal impairment.
• Coadministration of EVOTAZ and tenofovir DF in combination with concomitant or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent is not recommended.
In a clinical trial over 144 weeks (N=692), 10 (2.9%) participants treated with atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and tenofovir DF and 11 (3.2%) participants treated with atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir and tenofovir DF discontinued study drug due to a renal adverse event. Seven of the 10 participants (2.0% overall) in the cobicistat group had laboratory findings consistent with proximal renal tubulopathy leading to study drug discontinuation, compared to 7 of 11 participants (2.0% overall) in the ritonavir group. One participant in the cobicistat group had renal impairment at baseline (e.g., estimated creatinine clearance less than 70 mL/min). The laboratory findings in these 7 participants treated with cobicistat, with evidence of proximal tubulopathy improved but did not completely resolve in all participants upon discontinuation of cobicistat coadministered with atazanavir and tenofovir DF. Renal replacement therapy was not required in any participant.
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease in patients with HIV-1 treated with atazanavir, with or without ritonavir, has been reported during postmarketing surveillance. Reports included biopsy-proven cases of granulomatous interstitial nephritis associated with the deposition of atazanavir drug crystals in the renal parenchyma. Consider alternatives to EVOTAZ in patients at high risk for renal disease or with preexisting renal disease. Renal laboratory testing (including serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, and urinalysis with microscopic examination) should be conducted in all patients prior to initiating therapy with EVOTAZ and continued during treatment with EVOTAZ. Expert consultation is advised for patients who have confirmed renal laboratory abnormalities while taking EVOTAZ. In patients with progressive kidney disease, discontinuation of EVOTAZ may be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.3 ) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Nephrolithiasis and Cholelithiasis
Cases of nephrolithiasis and/or cholelithiasis have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients with HIV-1 receiving atazanavir therapy. Some patients required hospitalization for additional management and some had complications. Because these events were reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made. If signs or symptoms of nephrolithiasis and/or cholelithiasis occur, temporary interruption or discontinuation of therapy may be considered [see Adverse Reactions (6 , 6.1 )] .
Hepatotoxicity
Patients with underlying hepatitis B or C virus or marked elevations in transaminases may be at increased risk for developing further transaminase elevations or hepatic decompensation. In these patients, hepatic laboratory testing should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with EVOTAZ and during treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
Initiation of EVOTAZ, a CYP3A inhibitor, in patients receiving medications metabolized by CYP3A or initiation of medications metabolized by CYP3A in patients already receiving EVOTAZ, may increase plasma concentrations of medications metabolized by CYP3A.
Initiation of medications that inhibit or induce CYP3A may increase or decrease concentrations of EVOTAZ, respectively.
Increased concentrations of EVOTAZ may lead to:
• clinically significant adverse reactions, potentially leading to severe, life threatening, or fatal events from higher exposures of concomitant medications.
• clinically significant adverse reactions from higher exposures of EVOTAZ.
Decreased concentrations of EVOTAZ may lead to:
• loss of therapeutic effect of EVOTAZ and possible development of resistance.
See Table 5 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ] . Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during EVOTAZ therapy; review concomitant medications during EVOTAZ therapy; and monitor for the adverse reactions associated with the concomitant medications [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
When used with concomitant medications, EVOTAZ may result in different drug interactions than those observed or expected with atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir. Complex or unknown mechanisms of drug interactions preclude extrapolation of drug interactions with atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir to certain EVOTAZ interactions [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Antiretrovirals that are Not Recommended
EVOTAZ is not recommended in combination with other antiretroviral drugs that require CYP3A inhibition to achieve adequate exposures (e.g., other HIV protease inhibitors or elvitegravir) because dosing recommendations for such combinations have not been established and coadministration may result in decreased plasma concentrations of the antiretroviral agents, leading to loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance.
EVOTAZ is not recommended in combination with ritonavir or products containing ritonavir due to similar effects of cobicistat and ritonavir on CYP3A.
See Drug Interactions (7) for additional recommendations on use with other antiretroviral agents.
Hyperbilirubinemia
Most patients taking atazanavir experience asymptomatic elevations in indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin related to inhibition of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). This hyperbilirubinemia is reversible upon discontinuation of atazanavir. Hepatic transaminase elevations that occur with hyperbilirubinemia should be evaluated for alternative etiologies. No long-term safety data are available for patients experiencing persistent elevations in total bilirubin greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Alternative antiretroviral therapy to EVOTAZ may be considered if jaundice or scleral icterus associated with bilirubin elevations presents cosmetic concerns for patients [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including atazanavir, a component of EVOTAZ. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium , cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia
New-onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of preexisting diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients with HIV-1 receiving protease inhibitor therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued protease inhibitor therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and a causal relationship between protease inhibitor therapy and these events has not been established.
Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance” have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
Hemophilia
There have been reports of increased bleeding, including spontaneous skin hematomas and hemarthrosis, in patients with hemophilia type A and B treated with protease inhibitors. In some patients, additional factor VIII was given. In more than half of the reported cases, treatment with protease inhibitors was continued or reintroduced. A causal relationship between protease inhibitor therapy and these events has not been established.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- cardiac conduction abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- effects on serum creatinine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- new onset or worsening renal impairment when used with tenofovir DF [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- chronic kidney disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- nephrolithiasis and cholelithiasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- hyperbilirubinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
For additional safety information about atazanavir and cobicistat, consult the full prescribing information for these individual products.
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trial Experience in Adult Participants
The safety of atazanavir and cobicistat coadministered as single agents is based on Week 144 data from a Phase 3 trial, Study GS-US-216-0114, in which 692 antiretroviral treatment-naive participants with HIV-1 received:
- atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF (N=344) or
- atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF (N=348).
The most common adverse reactions (Grades 2-4) and reported in ≥5% of participants in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group were jaundice (6%) and rash (5%).
The proportion of participants who discontinued study treatment due to adverse events regardless of severity, was 11% in both the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir groups. Table 2 lists the frequency of adverse reactions (Grades 2-4) occurring in at least 2% of participants in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group in Study GS-US-216-0114.
| Atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF (n=344) | Atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF (n=348) | |
|---|---|---|
Jaundice | 6% | 3% |
Rash b | 5% | 4% |
Ocular icterus | 4% | 2% |
Nausea | 2% | 2% |
Diarrhea | 2% | 1% |
Headache | 2% | 1% |
a Frequencies of adverse reactions are based on Grades 2-4 adverse events attributed to study drugs. b Rash events include dermatitis allergic, drug hypersensitivity, pruritus generalized, eosinophilic pustular folliculitis, rash, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculopapular, rash morbilliform, rash papular, and urticaria.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Selected adverse reactions of at least moderate severity (≥ Grade 2) occurring in less than 2% of participants receiving atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF are listed below. These events have been included because of investigator’s assessment of potential causal relationship and were considered serious or have been reported in more than one participant treated with atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and reported with greater frequency compared with the atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir group.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: vomiting, upper abdominal pain
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: fatigue
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: rhabdomyolysis
Psychiatric Disorders: depression, abnormal dreams, insomnia
Renal and Urinary Disorders: nephropathy, Fanconi syndrome acquired, nephrolithiasis
Laboratory Abnormalities
The frequency of laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3-4) occurring in at least 2% of participants in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group in Study GS-US-216-0114 is presented in Table 3.
| 144 weeks Atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF | 144 weeks Atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF | |
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter Abnormality | (n=344) | (n=348) |
| a For participants with serum amylase >1.5 × upper limit of normal, lipase test was also performed. The frequency of increased lipase (Grades 3-4) occurring in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group (N=46) and atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir group (N=35) was 7% and 3%, respectively. | ||
Total Bilirubin (>2.5 × ULN) | 73% | 66% |
Creatine Kinase (≥10.0 × ULN) | 8% | 9% |
Urine RBC (Hematuria) (>75 RBC/HPF) | 6% | 3% |
ALT (>5.0 × ULN) | 6% | 3% |
AST (>5.0 × ULN) | 4% | 3% |
GGT (>5.0 × ULN) | 4% | 2% |
Serum Amylase a (>2.0 × ULN) | 4% | 2% |
Urine Glucose (Glycosuria ≥1000 mg/dL) | 3% | 3% |
Neutrophils (<750/mm 3 ) | 3% | 2% |
Serum Glucose (Hyperglycemia) (≥250 mg/dL) | 2% | 2% |
Increase in Serum Creatinine: Cobicistat, a component of EVOTAZ, has been shown to increase serum creatinine and decrease estimated creatinine clearance due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine without affecting actual renal glomerular function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . In Study GS-US-216-0114, increases in serum creatinine and decreases in estimated creatinine clearance occurred early in treatment in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group, after which they stabilized. The mean (± SD) change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) by Cockcroft-Gault method after 144 weeks of treatment was −15.1 ± 16.5 mL/min in the atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat group and −8.0 ± 16.8 mL/min in the atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir group.
Serum Lipids
Changes from baseline in total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides are presented in Table 4. In both groups, mean values for serum lipids remained within the normal range for each laboratory test. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
| Atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF | Atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline mg/dL | Week 144 change from baseline a | Baseline mg/dL | Week 144 change from baseline a | |
| a The change from baseline is the mean of within-participant changes from baseline for participants with both baseline and Week 144 values and excludes participants receiving an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drug. | ||||
Total Cholesterol (fasted) | 163 [N=219] | +11 [N=219] | 165 [N=227] | +13 [N=227] |
HDL-cholesterol (fasted) | 43 [N=218] | +7 [N=218] | 43 [N=228] | +6 [N=228] |
LDL-cholesterol (fasted) | 102 [N=218] | +11 [N=218] | 104 [N=228] | +16 [N=228] |
Triglycerides (fasted) | 130 [N=219] | +14 [N=219] | 131 [N=227] | +14 [N=227] |
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trial Experience in Pediatric Participants
Although no clinical trial with EVOTAZ as the fixed-dose tablet was conducted in a pediatric population, the safety of atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat plus two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors was evaluated in treatment-experienced virologically suppressed participants with HIV-1 between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years (N=14) through Week 48 in an open-label clinical trial (Study GS-US-216-0128) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Results from this study showed that the safety profile of atazanavir and cobicistat coadministered with a background regimen was similar to that in adults.
Postmarketing Experience
See the full prescribing information for atazanavir for postmarketing information on atazanavir.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of EVOTAZ can alter the concentration of other drugs and other drugs may alter the concentration of EVOTAZ, which may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions. The potential drug-drug interactions must be considered prior to and during therapy. (4 , 7 , 12.3)
Potential for EVOTAZ to Affect Other Drugs
Atazanavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A and UGT1A1 and a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8. Cobicistat is an inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP2D6. The transporters that cobicistat inhibits include P-glycoprotein (P-gp), BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3.
Coadministration of EVOTAZ with drugs highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ] . Coadministration of EVOTAZ and drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A, UGT1A1 and/or CYP2D6 or drugs that are substrates of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1 and/or OATP1B3 may result in increased plasma concentrations of the other drug that could increase or prolong its therapeutic effects and adverse reactions which may require dose adjustments and/or additional monitoring as shown in Table 5. Use of EVOTAZ is not recommended when coadministered with drugs highly dependent on CYP2C8 for clearance with narrow therapeutic indices (e.g., paclitaxel, repaglinide) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3; Table 7) ] .
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect EVOTAZ
Atazanavir and cobicistat are CYP3A4 substrates; therefore, drugs that induce CYP3A4 may decrease atazanavir and cobicistat plasma concentrations and reduce the therapeutic effect of EVOTAZ, leading to development of resistance to atazanavir (see Table 5). Cobicistat is also metabolized by CYP2D6 to a minor extent.
Coadministration of EVOTAZ with other drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 may increase the plasma concentrations of cobicistat and atazanavir (see Table 5).
Atazanavir solubility decreases as pH increases. Reduced plasma concentrations of atazanavir are expected if proton-pump inhibitors, antacids, buffered medications, or H 2 -receptor antagonists are administered with EVOTAZ (see Table 5) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Table 5 provides dosing recommendations as a result of drug interactions with the components of EVOTAZ. These recommendations are based either on observed drug interactions in studies of cobicistat, atazanavir, or atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir or predicted drug interactions based on the expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious events or loss of therapeutic effect of EVOTAZ [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.8) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
| Concomitant Drug Class: Specific Drugs | Effect b on Concentration | Clinical Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a For magnitude of interactions see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3; Table 7) . b ↑ = Increase, ↓ = Decrease, ↔ = No change. | |||
HIV Antiretroviral Agents: Nucleoside and Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs and NtRTIs) | |||
didanosine buffered formulations enteric-coated (EC) capsules | ↓ atazanavir ↓ didanosine | It is recommended that EVOTAZ be given with food 2 hours before or 1 hour after didanosine buffered formulations. Simultaneous administration of didanosine EC and atazanavir with food results in a decrease in didanosine exposure. Thus, EVOTAZ and didanosine EC should be administered at different times. | |
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | ↓ atazanavir ↑ tenofovir | Patients receiving EVOTAZ and tenofovir should be monitored for tenofovir-associated adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] . | |
HIV Antiretroviral Agents: Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) | |||
nevirapine | ↓ atazanavir ↑ nevirapine | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with nevirapine is contraindicated due to potential for loss of atazanavir therapeutic effect and development of resistance, and potential for nevirapine-associated adverse reactions [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
efavirenz | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↔ efavirenz | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with efavirenz is not recommended because it may result in a loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to atazanavir. | |
etravirine | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with etravirine is not recommended because it may result in the loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to atazanavir. | |
HIV Antiretroviral Agents: CCR5 Antagonist | |||
maraviroc | ↑ maraviroc | When coadministering maraviroc and EVOTAZ, patients should receive maraviroc 150 mg twice daily. | |
HIV Antiretroviral Agents: Protease Inhibitor | |||
indinavir | Coadministration with indinavir is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ] . Both atazanavir and indinavir are associated with indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia. | ||
ritonavir or products containing ritonavir | ↑ atazanavir | Coadministration of EVOTAZ and ritonavir or ritonavir-containing regimens is not recommended due to similar effects of cobicistat and ritonavir on CYP3A [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] . | |
Hepatitis C Antiviral Agents | |||
sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/ voxilaprevir | ↑ voxilaprevir | Coadministration with EVOTAZ is not recommended. | |
Other Agents | |||
Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin | ↑ alfuzosin | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with alfuzosin is contraindicated due to the potential for increased alfuzosin concentrations, which can result in hypotension [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Antacids and buffered medications (please also see H 2 -receptor antagonists and proton-pump inhibitors below) | ↓ atazanavir | With concomitant use, administer a minimum of 2 hours apart. | |
Antianginal: ranolazine | ↑ ranolazine | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with ranolazine is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Antiarrhythmics: dronedarone | ↑ dronedarone | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with dronedarone is contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
amiodarone, quinidine lidocaine (systemic), disopyramide, flecainide mexiletine, propafenone digoxin | ↑ other antiarrhythmics ↑ digoxin | Clinical monitoring is recommended upon coadministration with antiarrhythmics. When coadministering EVOTAZ with digoxin, titrate the digoxin dose and monitor digoxin concentrations. | |
Antibacterials (macrolide or ketolide antibiotics): clarithromycin erythromycin telithromycin | ↑ atazanavir ↑ cobicistat ↑ clarithromycin ↑ erythromycin ↑ telithromycin | Consider alternative antibiotics. | |
Anticancer Agents: irinotecan | ↑ irinotecan | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with irinotecan is contraindicated due to potential for increased irinotecan toxicity [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
(e.g., dasatinib, nilotinib, vinblastine, vincristine) | ↑ other anticancer agents | A decrease in the dosage or an adjustment of the dosing interval of dasatinib or nilotinib may be necessary upon coadministration with EVOTAZ. Consult the dasatinib and nilotinib full prescribing information for dosing instructions. For vincristine and vinblastine, monitor for hematologic or gastrointestinal side effects. | |
Anticoagulants: Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) apixaban | ↑ apixaban | Due to potentially increased bleeding risk, dosing recommendations for coadministration of apixaban with EVOTAZ depends on the apixaban dose. Refer to apixaban dosing instructions for coadministration with strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitors in apixaban prescribing information. | |
rivaroxaban | ↑ rivaroxaban | Coadministration of EVOTAZ and rivaroxaban is not recommended because it may lead to increased bleeding risk. | |
betrixaban dabigatran etexilate edoxaban | ↑ betrixaban ↑ dabigatran ↑ edoxaban | Due to potentially increased bleeding risk, dosing recommendations for coadministration of betrixaban, dabigatran, or edoxaban with a P-gp inhibitor such as EVOTAZ depends on DOAC indication and renal function. Refer to DOAC dosing instructions for coadministration with P-gp inhibitors in DOAC prescribing information. | |
warfarin | warfarin: effect unknown | Monitor the International Normalized Ratio (INR) when EVOTAZ is coadministered with warfarin. | |
Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin Anticonvulsants with CYP3A induction effects that are NOT contraindicated (e.g., eslicarbazepine, oxcarbazepine) | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance [see Contraindications (4) ] . Consider alternative anticonvulsant or antiretroviral therapy to avoid potential changes in exposures. If coadministration is necessary, monitor for lack or loss of virologic response. | |
Anticonvulsants that are metabolized by CYP3A (e.g., clonazepam) | ↑ clonazepam | Clinical monitoring of anticonvulsants is recommended with EVOTAZ coadministration. | |
Other anticonvulsants (e.g., lamotrigine) | lamotrigine: effects unknown | Monitoring of lamotrigine concentrations is recommended with EVOTAZ coadministration. | |
Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (e.g., paroxetine) | SSRIs: effects unknown | When coadministering with SSRIs, TCAs, or trazodone, careful dose titration of the antidepressant to the desired effect, using the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose, and monitoring for antidepressant response are recommended. | |
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) (e.g., amitriptyline, desipramine, imipramine, nortriptyline) | ↑ TCAs | ||
Other Antidepressants (e.g., trazodone) | ↑ trazodone | ||
Antifungals: ketoconazole, itraconazole | ↑ atazanavir ↑ cobicistat ↑ ketoconazole ↑ itraconazole | Specific dosing recommendations are not available for coadministration of EVOTAZ with either itraconazole or ketoconazole. | |
voriconazole | effects unknown | Coadministration with voriconazole is not recommended unless the benefit/risk assessment justifies the use of voriconazole. | |
Antigout: colchicine | ↑ colchicine | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with colchicine in patients with renal or hepatic impairment is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Contraindications (4) ] . Recommended dosage of colchicine when administered with EVOTAZ: Treatment of gout flares: 0.6 mg (1 tablet) for 1 dose, followed by 0.3 mg (half tablet) 1 hour later. Treatment course should be repeated no earlier than 3 days. Prophylaxis of gout flares: If the original regimen was 0.6 mg twice a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once a day. If the original regimen was 0.6 mg once a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once every other day. Treatment of familial Mediterranean fever (FMF): Maximum daily dose of 0.6 mg (may be given as 0.3 mg twice a day). | |
Antimycobacterials: Rifabutin | atazanavir: effect unknown cobicistat: effect unknown ↑ rifabutin | A rifabutin dose reduction of up to 75% (e.g., 150 mg every other day or 3 times per week) is recommended. Increased monitoring for rifabutin-associated adverse reactions, including neutropenia and uveitis, is warranted. | |
rifampin | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat | Coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Antineoplastics: apalutamide | ↓ atazanavir ↓cobicistat | Coadministration with apalutamide is contraindicated due to the potential for substantial decrease in plasma concentrations of atazanavir and cobicistat, which may result in loss of virologic response of EVOTAZ and possible resistance to atazanavir or to other protease inhibitors. [see Contraindications (4) ] . Mechanism: The mechanism of interaction is CYP3A4 induction by apalutamide. | |
ivosidenib | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↑ ivosidenib | Coadministration with ivosidenib is contraindicated due to the potential for loss of virologic response of EVOTAZ, development of resistance, and risk of serious adverse events such as QT interval prolongation. [see Contraindications (4) ] . Mechanism: The mechanism of interaction is CYP3A4 induction by ivosidenib. | |
encorafenib | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↑ encorafenib | Coadministration with encorafenib is contraindicated due to the potential for loss of virologic response of EVOTAZ, development of resistance, and risk of serious adverse events such as QT interval prolongation. [see Contraindications (4) ] . Mechanism: The mechanism of interaction is CYP3A4 induction by encorafenib. | |
Antiplatelets: ticagrelor | ↑ ticagrelor | Coadministration with ticagrelor is not recommended due to the potential increase of the antiplatelet activity of ticagrelor. | |
clopidogrel | ↓ clopidogrel active metabolite | Coadministration with clopidogrel is not recommended due to the potential reduction of the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel. | |
prasugrel | ↔ prasugrel active metabolite | No dose adjustment is needed when prasugrel is coadministered with atazanavir and/or cobicistat. | |
Antipsychotics: lurasidone | ↑ lurasidone | Coadministration with lurasidone is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
pimozide | ↑ pimozide | Coadministration with pimozide is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
quetiapine | ↑ quetiapine | Initiation of EVOTAZ in patients taking quetiapine: Consider alternative antiretroviral therapy to avoid increases in quetiapine exposures. If coadministration is necessary, reduce the quetiapine dose to 1/6 of the current dose and monitor for quetiapine-associated adverse reactions. Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on adverse reaction monitoring. Initiation of quetiapine in patients taking EVOTAZ: Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for initial dosing and titration of quetiapine. | |
(e.g., perphenazine, risperidone, thioridazine) | ↑ antipsychotic | A decrease in the dose of antipsychotics that are metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2D6 may be needed when coadministered with EVOTAZ. | |
Beta-agonist (inhaled): salmeterol | ↑ salmeterol | Coadministration with salmeterol is not recommended due to an increased risk of cardiovascular adverse reactions associated with salmeterol, including QT prolongation, palpitations, and sinus tachycardia. | |
Beta-Blockers: (e.g., metoprolol, carvedilol, timolol) | ↔ atazanavir ↑ beta-blockers | Clinical monitoring is recommended when beta-blockers that are metabolized by CYP2D6 are coadministered with EVOTAZ. | |
Calcium channel blockers: (e.g., amlodipine, diltiazem, felodipine, nifedipine, and verapamil) | ↑ calcium channel blocker | Clinical monitoring is recommended for coadministration with calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A. ECG monitoring is recommended. | |
Corticosteroids: e.g., betamethasone budesonide ciclesonide dexamethasone fluticasone methylprednisolone mometasone triamcinolone | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↑ corticosteroids | Coadministration with oral dexamethasone or other systemic corticosteroids that induce CYP3A may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to atazanavir. Consider alternative corticosteroids. Coadministration with corticosteroids (all routes of administration) whose exposures are significantly increased by strong CYP3A inhibitors can increase the risk for Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression. Alternative corticosteroids including beclomethasone, prednisone, and prednisolone (whose PK and/or PD are less affected by strong CYP3A inhibitors relative to other studied steroids) should be considered, particularly for long-term use. | |
Kinase inhibitors: fostamatinib | ↑ R406 active metabolite of fostamatinib | Coadministration with fostamatinib may increase the plasma concentration of R406, the active metabolite of fostamatinib. Monitor for toxicities of R406 exposure resulting in dose-related adverse events such as hepatotoxicity and neutropenia. Fostamatinib dose reduction may be required. | |
Endothelin receptor antagonists: bosentan | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↑ bosentan | Initiation of bosentan in patients taking EVOTAZ: For patients who have been receiving EVOTAZ for at least 10 days, start bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based on individual tolerability. Initiation of EVOTAZ in patients taking bosentan: Discontinue bosentan at least 36 hours before starting EVOTAZ. After at least 10 days following initiation of EVOTAZ, resume bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based on individual tolerability. Switching from atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir to EVOTAZ: Maintain bosentan dose. | |
Gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist Receptor (GnRH): elagolix | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat ↑ elagolix | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with elagolix may result in decreased plasma concentrations of atazanavir and/or cobicistat. Concomitant use of elagolix 200 mg twice daily with EVOTAZ for more than 1 month is not recommended due to the potential risk of adverse events such as bone loss and hepatic transaminase elevations. Limit concomitant use of elagolix 150 mg once daily with EVOTAZ to 6 months. In addition, monitor virologic responses due to the potential reduction in atazanavir/cobicistat exposure. | |
Ergot Derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine | ↑ ergot derivatives | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with ergot derivatives is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening events such as acute ergot toxicity, characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Hepatitis C Direct-Acting Antivirals : elbasvir/grazoprevir | ↑ grazoprevir | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with elbasvir/grazoprevir is contraindicated due to increased risk of ALT elevations [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir | ↑ glecaprevir ↑ pibrentasvir | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with glecaprevir/ pibrentasvir is contraindicated due to increased risk of ALT elevations [see Contraindications (4 )] . | |
Herbal Products : St. John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum) | ↓ atazanavir ↓ cobicistat | Coadministration of products containing St. John’s wort and EVOTAZ is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
H 2 ‑Receptor antagonists (H 2 RA ) : (e.g., famotidine) | ↓ atazanavir | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with tenofovir DF and an H 2 RA in treatment-experienced patients is not recommended. Administer EVOTAZ either at the same time or at a minimum of 10 hours after a dose of the H 2 RA. The dose of the H 2 RA should not exceed a dose comparable to famotidine 40 mg twice daily in treatment-naive patients or 20 mg twice daily in treatment-experienced patients. | |
Lipid-modifying agents: Other lipid-modifying agents: lomitapide | ↑ lomitapide | Coadministration with lomitapide is contraindicated due to the potential for risk of markedly increased transaminase levels and hepatoxicity [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors : lovastatin simvastatin | ↑lovastatin ↑simvastatin | Coadministration with lovastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated due to the potential for serious reactions such as myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: atorvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin | ↑ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Coadministration of EVOTAZ with atorvastatin is not recommended. For HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that are not contraindicated with EVOTAZ, start with the lowest recommended dose and titrate while monitoring for safety (e.g., myopathy). Dosage recommendations with rosuvastatin are as follows. Rosuvastatin dose should not exceed 10 mg/day. | |
Hormonal contraceptives: drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol | ↑ drospirenone | Coadministration with drospirenone-containing products is contraindicated due to the potential for drospirenone-associated hyperkalemia [see Contraindications (4) ]. | |
(e.g., progestin/estrogen) | progestin and estrogen: effects unknown | No data are available to make recommendations on the coadministration of EVOTAZ and oral or other hormonal contraceptives. Alternative nonhormonal forms of contraception should be considered. | |
Immunosuppressants: (e.g., cyclosporine, everolimus, sirolimus, tacrolimus) | ↑ immunosuppressants | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for these immunosuppressants when coadministered with EVOTAZ. | |
Narcotic analgesics: For treatment of opioid dependence: buprenorphine, naloxone, methadone | buprenorphine or buprenorphine/naloxone: effects unknown methadone: effects unknown | Initiation of buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone or methadone in patients taking EVOTAZ: Carefully titrate the dose of buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone or methadone to the desired effect; use the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose. Initiation of EVOTAZ in patients taking buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone or methadone: A dose adjustment for buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone or methadone may be needed. Monitor clinical signs and symptoms. | |
fentanyl | ↑ fentanyl | When EVOTAZ is coadministered with fentanyl, careful monitoring of therapeutic and adverse effects of fentanyl (including potentially fatal respiratory depression) is recommended. | |
tramadol | ↑ tramadol | When EVOTAZ is coadministered with tramadol, a decreased dose of tramadol may be needed. | |
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors: avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil | ↑ PDE-5 inhibitors | Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH): Coadministration of EVOTAZ with sildenafil is contraindicated due to the potential for sildenafil-associated adverse events (which include visual disturbances, hypotension, priapism, and syncope) [see Contraindications (4) ] .
| |
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction:
| |||
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPI): (e.g., omeprazole) | ↓ atazanavir | In treatment-naive patients, administer EVOTAZ a minimum of 12 hours after administration of the PPI. The dose of the PPI should not exceed a dose comparable to omeprazole 20 mg daily. In treatment-experienced patients, coadministration of EVOTAZ with PPI is not recommended. | |
Sedatives/Hypnotics: Benzodiazepines midazolam (oral) triazolam | ↑ midazolam ↑ triazolam | Coadministration of triazolam or orally administered midazolam is contraindicated due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening events such as prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression. Triazolam and orally administered midazolam are extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 [see Contraindications (4) ] . | |
Other Benzodiazepines : clorazepate diazepam estazolam flurazepam parenterally administered midazolam | ↑ sedatives/hypnotics | Parenterally administered midazolam: Coadministration should be done in a setting which ensures close clinical monitoring and appropriate medical management in case of respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation. Dosage reduction for midazolam should be considered, especially if more than a single dose of midazolam is administered. | |
Other Sedatives/Hypnotics: buspirone, zolpidem | With other sedatives/hypnotics that are CYP3A metabolized, a dose reduction may be necessary and clinical monitoring is recommended. | ||
Drugs with No Observed or Predicted Interactions with the Components of EVOTAZ
Based on known metabolic profiles, clinically significant drug interactions are not expected between EVOTAZ and acetaminophen, atenolol, dapsone, fluconazole, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, or azithromycin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3; Table 7) ].
DESCRIPTION
EVOTAZ ® is a fixed-dose tablet for oral administration containing the active ingredients atazanavir and cobicistat. Atazanavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor. Cobicistat is a mechanism-based inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes of the CYP3A family. EVOTAZ tablets contain 342 mg of atazanavir sulfate, equivalent to 300 mg of atazanavir, and 150 mg of cobicistat, as well as the following inactive ingredients in the tablet core: croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, and stearic acid. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, red iron oxide, talc, titanium dioxide, triacetin.
Atazanavir: Atazanavir is present as the sulfate salt. The chemical name for atazanavir sulfate is (3 S ,8 S ,9 S ,12 S )-3,12-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-8-hydroxy-4,11-dioxo-9-(phenylmethyl)-6-[[4-(2-pyridinyl)phenyl]methyl]-2,5,6,10,13-pentaazatetradecanedioic acid dimethyl ester, sulfate (1:1). Its molecular formula is C 38 H 52 N 6 O 7 •H 2 SO 4 , which corresponds to a molecular weight of 802.9 (sulfuric acid salt). The free base molecular weight is 704.9. Atazanavir sulfate has the following structural formula:
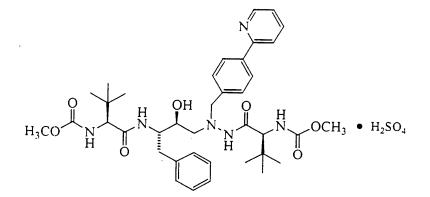
Atazanavir sulfate is a white to pale-yellow crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water (4-5 mg/mL, free base equivalent) with the pH of a saturated solution in water being about 1.9 at 24 ± 3°C.
Cobicistat: The chemical name for cobicistat is 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl [(2 R ,5 R )-5-{[(2 S )-2-[(methyl{[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)amino]-4-(morpholin-4-yl)butanoyl]amino}-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]carbamate. It has a molecular formula of C 40 H 53 N 7 O 5 S 2 and a molecular weight of 776.0. It has the following structural formula:
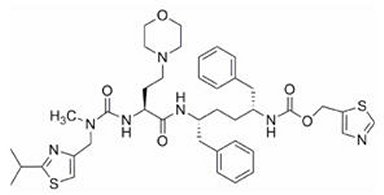
Cobicistat is adsorbed onto silicon dioxide. Cobicistat on silicon dioxide is a white to pale yellow solid with a solubility of 0.1 mg/mL in water at 20°C.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
EVOTAZ is a fixed-dose tablet consisting of the HIV-1 antiretroviral drug, atazanavir and the CYP3A inhibitor, cobicistat [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ] .
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Atazanavir: In a thorough QT/QTc study in 72 healthy participants (Study AI424-076), atazanavir 400 mg and 800 mg (C max was 1.2 times and 2.4 times the C max observed with the recommended dosage of EVOTAZ, respectively) without a CYP3A inhibitor did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent. Asymptomatic prolongation of the PR interval was noted in participants receiving atazanavir. The mean (±SD) maximum change in PR interval from the predose for atazanavir 400 mg (n=65), atazanavir 800 mg (n=66), and placebo (n=67) was 24 (±15) msec, 60 (±25) msec, and 13 (±11) msec, respectively. Steady state atazanavir exposures (C max and AUC tau ) observed in this healthy participant study exceeded those observed in participants treated with atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat. There is limited information on the potential for a pharmacodynamic interaction in humans between atazanavir and other drugs that prolong the PR interval of the electrocardiogram [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
In 1793 participants with HIV-1 receiving antiretroviral regimens, QTc prolongation was comparable in the atazanavir-containing and comparator regimens. No atazanavir-treated healthy participant or participant with HIV-1 in clinical trials had a QTc interval >500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Cobicistat: In a thorough QT/QTc study conducted in 48 healthy participants (Study GS-US-216-0107), cobicistat 250 mg (1.7 times the recommended dosage in EVOTAZ) and 400 mg (2.7 times the recommended dosage in EVOTAZ) did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent. Asymptomatic prolongation of the PR interval was noted in participants receiving cobicistat. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) difference in PR from placebo after baseline correction was 9.5 (12.1) msec for 250 mg and 20.2 (22.8) msec for 400 mg dose of cobicistat .
Effects on Serum Creatinine
The effect of cobicistat on serum creatinine was investigated in Study GS-US-216-0121, conducted in participants with normal renal function (eGFR ≥80 mL/min, N=12) and mild-to-moderate renal impairment (eGFR 50-79 mL/min, N=18). A statistically significant change in estimated glomerular filtration rate, calculated by Cockcroft-Gault method (eGFR CG ) from baseline, was observed after 7 days of treatment with cobicistat 150 mg among participants with normal renal function (−9.9 ± 13.1 mL/min) and mild-to-moderate renal impairment (−11.9 ± 7.0 mL/min). No statistically significant changes in eGFR CG were observed compared to baseline for participants with normal renal function or mild-to-moderate renal impairment 7 days after cobicistat was discontinued. The actual glomerular filtration rate, as determined by the clearance of probe drug iohexol, was not altered from baseline following treatment with cobicistat among participants with normal renal function and mild-to-moderate renal impairment, indicating that cobicistat inhibits tubular secretion of creatinine, reflected as a reduction in eGFR CG , without affecting the actual glomerular filtration rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of the components of EVOTAZ (atazanavir 300 mg and cobicistat 150 mg) were evaluated in healthy adult participants (Study AI424-511). Results are summarized in Table 6.
| Atazanavir | Cobicistat | |
|---|---|---|
| a Following EVOTAZ dosing under fasted conditions. b Values refer to geometric mean ratio (fed / fasted) and (90% confidence interval). c Dosing in mass balance study: cobicistat (single dose administration of [14C] cobicistat after multiple dosing of cobicistat for six days). ND = not determined. | ||
Absorption | ||
T max (h) | 2.0 | 2.0 |
Effect of light meal (relative to fasting) AUC ratio b | 1.28 (1.17,1.40) | 1.24 (1.15,1.34) |
Effect of high fat meal (relative to fasting) AUC ratio b | 0.96 (0.81,1.13) | 1.12 (1.01,1.23) |
Effect of light meal (relative to fasting) C24 ratio b | 1.35 (1.22,1.50) | ND |
Effect of high fat meal (relative to fasting) C24 ratio b | 1.23 (1.02,1.48) | ND |
Distribution | ||
% Bound to human plasma proteins | 86 | ~98 |
Source of protein binding data | In vitro | In vitro |
Blood-to-plasma ratio | ND | 0.5 |
Metabolism | ||
Metabolism | CYP3A (major) Glucuronidation, N-dealkylation, hydrolysis, oxygenation with dehydrogenation (minor) | CYP3A (major) CYP2D6 (minor) |
Elimination | ||
Major route of elimination | Metabolism | Metabolism |
t 1/2 (h) | 7.2 a | 3.5 |
% Of dose excreted in urine | ND | 8.2 c |
% Of dose excreted in feces | ND | 86.2 c |
The pharmacokinetics of atazanavir was evaluated in participants with HIV-1 who received atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with cobicistat 150 mg in combination with emtricitabine/tenofovir DF. The steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat are shown in Table 7 [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
| Parameter | Atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and emtricitabine/tenofovir DF (n=22) |
|---|---|
AUC (µg•h/mL) | 46.13 ± 26.18 |
C max (µg/mL) | 3.91 ± 1.94 |
C tau (µg/mL) | 0.80 ± 0.72 |
Specific Populations
Pediatric
In pediatric participants aged 12 to less than 18 years who received atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with cobicistat 150 mg (N=12), atazanavir exposures (AUC tau , C max , and C tau ) were 20-60% higher than in adults; the increases were not considered clinically significant (Table 8).
| Atazanavir PK Parameter | Geometric Mean (CV%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pediatric participants (N=12) a | Adult participants (N=30) b | |
| CV=Coefficient of Variation a From intensive PK analysis of Study GS-US-216-0128 b From pooled intensive PK analysis of trials with atazanavir + cobicistat. | ||
AUC tau (µg/hr/mL) | 49.48 (49.1) | 39.96 (52.1) |
C max (µg/mL) | 4.32 (49.9) | 3.54 (45.8) |
C tau (µg/mL) | 0.91 (96.4) | 0.58 (84.7) |
Renal Impairment
Atazanavir: In healthy participants, the renal elimination of unchanged atazanavir was approximately 7% of the administered dose. In study AI424-105, atazanavir was studied in adult participants (n=20) with severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, using 24-hour urinary creatinine and serum creatinine levels), including those on hemodialysis, at multiple doses of 400 mg once daily. The mean atazanavir C max was 9% lower, AUC was 19% higher, and C min was 96% higher in participants with severe renal impairment not undergoing hemodialysis (n=10), than in age-, weight-, and gender-matched participants with normal renal function. In a 4-hour dialysis session, 2.1% of the administered dose was removed. When atazanavir was administered either prior to, or following hemodialysis (n=10), the geometric means for C max , AUC, and C min were approximately 25% to 43% lower compared to participants with normal renal function. The mechanism of this decrease is unknown.
Cobicistat: No clinically relevant differences in cobicistat pharmacokinetics were observed between participants with severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, using the Cockcroft-Gault method) and healthy participants in Study GS-US-216-0124 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
EVOTAZ has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Atazanavir: Increased concentrations of atazanavir are expected in those with moderately or severely impaired hepatic function (Study AI424-015).
Cobicistat: No clinically relevant differences in cobicistat pharmacokinetics were observed between participants with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) and healthy participants (Study GS-US-183-0133). The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of cobicistat has not been studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Pregnancy and Postpartum
Pharmacokinetic data from studies conducted in pregnant individuals receiving cobicistat showed substantially lower exposures during the second and third trimesters, and consequently also for the coadministered antiretroviral agent. Consult the full prescribing information for cobicistat for additional information. Pharmacokinetic data from the evaluation of atazanavir and cobicistat in a limited number of pregnant individuals showed a similar trend in lower exposures of the antiretroviral component, atazanavir.
Gender, Age, and Race
Atazanavir: No clinically important differences in atazanavir pharmacokinetics were observed based on age or gender.
Cobicistat: No clinically relevant differences in cobicistat pharmacokinetics were observed based on race or gender.
Assessment of Drug Interactions
Atazanavir has been shown in vivo not to induce its own metabolism, nor to increase the biotransformation of some drugs metabolized by CYP3A. In a multiple-dose study, atazanavir decreased the urinary ratio of endogenous 6β-OH cortisol to cortisol versus baseline, indicating that CYP3A production was not induced.
The effects of cobicistat on the exposure of coadministered drugs are summarized in Table 9.
| Note: The information listed below is not a comprehensive list of all the available drug interaction data for concomitant medications with cobicistat-containing regimens. Please refer to the U.S. prescribing information for antiretroviral medications administered in combination with cobicistat for additional drug interaction information. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Coadministered Drug Dose/Schedule | Cobicistat Dose/Schedule | Ratio (90% Confidence Interval) of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters with/without cobicistat; No effect = 1.00 | |
| C max | AUC | |||
| a All interaction studies conducted in healthy participants. b Studies of cobicistat conducted in the presence of atazanavir 300 mg. | ||||
atorvastatin | 10 mg single dose (n=16) | 150 mg QD (n=16) | 18.85 b (13.53, 26.27) | 9.22 b (7.58, 11.22) |
desipramine | 50 mg single dose (n=8) | 150 mg QD (n=8) | 1.24 (1.08, 1.44) | 1.65 (1.36, 2.02) |
digoxin | 0.5 mg single dose (n=22) | 150 mg QD (n=22) | 1.41 (1.29, 1.55) | 1.08 (1.00, 1.17) |
drospirenone/ ethinyl estradiol | 3 mg drospirenone single dose (n=14) | 150 mg QD (n=14) | 1.12 b (1.05, 1.19) | 2.30 b (2.00, 2.64) |
0.02 ethinyl estradiol single dose (n=14) | 150 mg QD (n=14) | 0.82 b (0.76, 0.89) | 0.78 b (0.73, 0.85) | |
efavirenz | 600 mg single dose (n=17) | 150 mg QD (n=17) | 0.87 (0.80, 0.94) | 0.93 (0.89, 0.97) |
rosuvastatin | 10 mg single dose (n=16) | 150 mg QD (n=16) | 10.58 b (8.72, 12.83) | 3.42 b (2.87, 4.07) |
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
EVOTAZ is a fixed-dose tablet of atazanavir and the CYP3A inhibitor cobicistat. Atazanavir is an azapeptide HIV-1 protease inhibitor that selectively inhibits the virus-specific processing of viral Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins in HIV-1-infected cells, thus preventing formation of mature virions. Cobicistat is a mechanism-based inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A). Inhibition of CYP3A-mediated metabolism by cobicistat increases the systemic exposure of the CYP3A substrate atazanavir.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Atazanavir exhibits anti−HIV-1 activity with a mean 50% effective concentration (EC 50 value) in the absence of human serum of 2 to 5 nM against a variety of laboratory and clinical HIV-1 isolates grown in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, macrophages, CEM-SS cells, and MT‑2 cells. Atazanavir has activity against HIV-1 Group M subtype viruses A, B, C, D, AE, AG, F, G, and J isolates in cell culture. Atazanavir has variable activity against HIV-2 isolates (1.9-32 nM), with EC 50 values above the EC 50 values of failure isolates. Two-drug combination antiviral activity studies with atazanavir showed no antagonism in cell culture with NNRTIs (delavirdine, efavirenz, and nevirapine), protease inhibitors (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir), NRTIs (abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir, zalcitabine, and zidovudine), the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide, and two compounds used in the treatment of viral hepatitis, adefovir and ribavirin, without enhanced cytotoxicity.
Cobicistat does not inhibit recombinant HIV-1 protease in a biochemical assay and has no detectable antiviral activity in cell culture against HIV-1, hepatitis B or C virus. The antiviral activity in cell culture of selected HIV-1 antiretroviral drugs was not antagonized by cobicistat.
Resistance
In Cell Culture: HIV-1 isolates with a decreased susceptibility to atazanavir have been selected in cell culture and obtained from patients treated with atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir. HIV-1 isolates with 93- to 183-fold reduced susceptibility to atazanavir from three different viral strains were selected in cell culture by 5 months. The substitutions in these HIV-1 viruses that contributed to atazanavir resistance include I50L, N88S, I84V, A71V, and M46I. Changes were also observed at the protease cleavage sites following drug selection. Recombinant viruses containing the I50L substitution without other major protease inhibitor substitutions were growth impaired and displayed increased susceptibility in cell culture to other protease inhibitors (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir). The I50L and I50V substitutions yielded selective resistance to atazanavir and amprenavir, respectively, and did not appear to be cross-resistant.
Clinical Studies: Resistance to EVOTAZ is driven by atazanavir as cobicistat lacks antiviral activity. For the complete atazanavir resistance-associated substitutions, refer to the atazanavir full prescribing information.
Clinical Studies of Treatment-Naive Adult Participants Receiving Atazanavir 300 mg Coadministered with Cobicistat 150 mg: In an analysis of adult participants who received atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat through Week 144 (Study GS-US-216-0114), evaluable genotypic data from paired baseline and treatment-failure isolates from participants who had HIV-1 RNA greater than or equal to 400 copies/mL were available for all 21 virologic failures in this group (6%, 21/344). Among the 21 participants, 3 developed the emtricitabine resistance-associated substitution M184V. No participant developed the tenofovir resistance-associated substitution K65R or K70E, or any primary resistance substitution associated with protease inhibitors. In the ritonavir group, evaluable genotypic data were available for all 19 virologic failures (5%, 19/348). Among the 19 participants, 1 developed the emtricitabine resistance-associated substitution M184V with no tenofovir or protease inhibitor resistance-associated substitutions.
Clinical Study of Pediatric Participants Receiving Atazanavir Coadministered with Cobicistat: In an as-treated analysis of pediatric participants between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years who received atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat plus two NRTIs in Study GS-US-216-0128, 3 of 14 participants qualified for resistance analysis through Week 48; 1 had evaluable data and no significant resistance-associated substitutions in protease or reverse transcriptase [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance among protease inhibitors has been observed. Baseline phenotypic and genotypic analyses of clinical isolates from atazanavir clinical trials of protease inhibitor-experienced participants with HIV-1 showed that isolates cross-resistant to multiple protease inhibitors were cross-resistant to atazanavir. Greater than 90% of the isolates with substitutions that included I84V or G48V were resistant to atazanavir. Greater than 60% of isolates containing L90M, G73S/T/C, A71V/T, I54V, M46I/L, or a change at V82 were resistant to atazanavir, and 38% of isolates containing a D30N substitution in addition to other changes were resistant to atazanavir. Isolates resistant to atazanavir were also cross-resistant to other protease inhibitors with >90% of the isolates resistant to indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir, and 80% resistant to amprenavir. In treatment-experienced patients, protease inhibitor-resistant viral isolates that developed the I50L substitution in addition to other protease inhibitor resistance-associated substitution were also cross-resistant to other protease inhibitors.
International AIDS Society (IAS)-defined protease inhibitor resistance substitutions, depending on the number and type, may confer a reduced virologic response to atazanavir. Please refer to the “Baseline Genotype/Phenotype and Virologic Outcome Analyses” section in the atazanavir full prescribing information.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Atazanavir: Long-term carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats were carried out with atazanavir for two years. In the mouse study, drug-related increases in hepatocellular adenomas were found in females at 360 mg/kg/day. The systemic drug exposure (AUC) at the NOAEL in females, (120 mg/kg/day) was 2.8 times and in males (80 mg/kg/day) was 2.9 times higher than those in humans at the clinical dose (300 mg/day atazanavir coadministered with 100 mg/day ritonavir, nonpregnant patients). In the rat study, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were observed at doses up to 1200 mg/kg/day, for which AUCs were 1.1 (males) or 3.9 (females) times those measured in humans at the clinical dose.
Cobicistat: In a long-term carcinogenicity study in mice, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were observed at doses up to 50 and 100 mg/kg/day (males and females, respectively). Cobicistat exposures at these doses were approximately 7 (male) and 16 (females) times, respectively, the human systemic exposure at the therapeutic daily dose. In a long-term carcinogenicity study of cobicistat in rats, an increased incidence of follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in the thyroid gland was observed at doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg/day in males, and at 30 mg/kg/day in females. The follicular cell findings are considered to be rat-specific, secondary to hepatic microsomal enzyme induction and thyroid hormone imbalance, and are not relevant for humans. At the highest doses tested in the rat carcinogenicity study, systemic exposures were approximately 2 times the human systemic exposure at the therapeutic daily dose.
Mutagenesis
Atazanavir: Atazanavir tested positive in an in vitro clastogenicity test using primary human lymphocytes, in the absence and presence of metabolic activation. Atazanavir tested negative in the in vitro Ames reverse-mutation assay, in vivo micronucleus and DNA repair tests in rats, and in vivo DNA damage test in rat duodenum (comet assay).
Cobicistat: Cobicistat was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial test (Ames test), mouse lymphoma or rat micronucleus assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Atazanavir: At the systemic drug exposure levels (AUC) 0.9 (in male rats) or 2.3 (in female rats) times that of the human clinical dose, (300 mg/day atazanavir coadministered with 100 mg/day ritonavir) significant effects on mating, fertility, or early embryonic development were not observed.
Cobicistat: Cobicistat did not affect fertility in male or female rats at daily exposures (AUC) approximately 3-fold higher than human exposures at the recommended 150 mg daily dose. Fertility was normal in the offspring of rats exposed daily from before birth ( in utero ) through sexual maturity at daily exposures (AUC) of approximately similar human exposures at the recommended 150 mg daily dose.
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trial Results in Treatment-Naive Adult Participants with HIV-1 Study GS-US-216-0114
The safety and efficacy of atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial (Study GS-US-216-0114 [NCT01108510]) in treatment-naive participants with HIV-1 infection with baseline estimated creatinine clearance above 70 mL/min (N=692). Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with cobicistat 150 mg once daily or atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with ritonavir 100 mg once daily. All participants received concomitant treatment with 300 mg of tenofovir DF and 200 mg of emtricitabine once a day administered as a single tablet. Randomization was stratified by screening HIV-1 RNA level (≤100,000 copies/mL or >100,000 copies/mL).
The mean age of participants was 37 years (range: 19-70); 83% were male, 60% were White, 18% were Black, and 12% were Asian. The mean baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.8 log 10 copies/mL (range: 3.2-6.4). The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 352 cells/mm 3 (range: 1-1455) and 17% had CD4+ cell counts ≤200 cells/mm 3 . Forty percent (40%) of patients had baseline viral loads >100,000 copies/mL.
Virologic outcomes in Study GS-US-216-0114 through Week 144 are presented in Table 10. In Study GS-US-216-0114, the mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell count at Week 144 was 281 cells/mm 3 in patients receiving atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat and 297 cells/mm 3 in patients receiving atazanavir coadministered with ritonavir.
| Atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with cobicistat 150 mg (once daily) + emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (n=344) | Atazanavir 300 mg coadministered with ritonavir 100 mg + emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (n=348) | |
|---|---|---|
| a Week 144 window is between Day 967 and 1050 (inclusive). b Includes participants who had ≥50 copies/mL in the Week 48 window; participants who discontinued early due to lack or loss of efficacy; participants who discontinued for reasons other than an adverse event, death or lack or loss of efficacy and at the time of discontinuation had a viral value of ≥50 copies/mL. c Includes participants who discontinued due to adverse event or death at any time point from Day 1 through the time window if this resulted in no virologic data on treatment during the specified window. There were no deaths reported in Study GS-US-216-0114. d Includes participants who discontinued for reasons other than an adverse event, death, or lack or loss of efficacy (e.g., withdrew consent, lost to follow-up, etc). | ||
HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL | 72% | 74% |
Treatment Difference | −2.1% (95% CI = −8.7%, 4.5%) | |
HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL b | 8% | 5% |
No Virologic Data at Week 48 Window | 20% | 21% |
Discontinued Study Drug Due to AE or Death c | 11% | 11% |
| 8% | 10% |
| <1% | <1% |
Clinical Trial Results in Virologically Suppressed Pediatric Participants with HIV-1 Infection– Study GS-US-216-0128
Study GS-US-216-0128 (NCT02016924) was a Phase 2/3 multicenter, open-label trial to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat in pediatric participants ages 12 years and older with HIV-1 who were virologically suppressed and had a baseline estimated creatinine clearance ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . Participants were on a stable antiretroviral regimen (for at least 3 months), consisting of atazanavir administered with ritonavir, combined with 2 nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). They were switched from ritonavir to cobicistat 150 mg once daily and continued atazanavir (N=14) and 2 NRTIs.
The mean age of participants was 14 years (range 12–17 years); median weight was 53 kg; 71% were male, 57% were Asian, 29% were White, 14% were Black, and 71% were not Hispanic or Latino. At baseline, 13/14 participants had plasma HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL and 1 participant had plasma HIV‑1 RNA of 50 copies/mL.
In participants who switched to atazanavir coadministered with cobicistat, 93% (13/14) of participants remained suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL), and 1 participant experienced virologic failure at Week 48. From a median baseline CD4+ cell count and CD4+% of 770 cells/mm 3 (range 486 to 1765 cells/mm 3 ) and 33% (range 23% to 45%), respectively, the median change from baseline in CD4+ cell count and CD4+% at Week 48 was ‑60 cells/mm 3 (range ‑500 to 705 cells/mm 3 ) and ‑0.3% (range ‑6% to 8%), respectively.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
EVOTAZ ® tablets, 300 mg atazanavir and 150 mg cobicistat, are oval, biconvex, pink, film-coated, debossed with “3641” on one side and plain on the other side. Each bottle contains 30 tablets (NDC-0003-3641-11), a silica gel desiccant and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
Store EVOTAZ tablets at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed.
Mechanism of Action
EVOTAZ is a fixed-dose tablet consisting of the HIV-1 antiretroviral drug, atazanavir and the CYP3A inhibitor, cobicistat [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ] .