Get your patient on Famotidine - Famotidine powder, For Suspension (Famotidine)
Famotidine - Famotidine powder, For Suspension prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Famotidine for oral suspension is indicated in adults for the treatment of:
- active duodenal ulcer (DU).
- active gastric ulcer (GU).
- symptomatic nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- erosive esophagitis due to GERD, diagnosed by biopsy.
- treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasias).
- reduction of the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Famotidine for oral suspension is indicated in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older for the treatment of:
- peptic ulcer disease.
- GERD with or without esophagitis and ulcerations.
Famotidine for oral suspension is indicated in pediatric patients from birth to less than 1 year of age for the treatment of:
- GERD.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended adult dosage by indication (2.1 ):
Active DU 40 mg once daily; or 20 mg twice daily Active GU 40 mg once daily Symptomatic Nonerosive GERD 20 mg twice daily Erosive Esophagitis due to GERD 20 mg twice daily; or 40 mg twice daily Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions 20 mg every 6 hours; adjust to patient needs; maximum 160 mg every 6 hours Risk Reduction of DU Recurrence 20 mg once daily - Recommended pediatric dosage by indication (2.2 ):
Peptic Ulcer Disease 1 year to less than 17 years Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg once daily; or 0.25 mg/kg twice daily; may increase to 1 mg/kg once daily at bedtime or 0.5 mg/kg twice daily; Maximum of 40 mg per day GERD Birth to less than 3 months Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg once daily; may increase to 1 mg/kg once daily; 3 months to less than 1 year Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg twice daily; may increase to 1 mg/kg twice daily; Maximum of 40 mg per day GERD with or without esophagitis and ulcerations 1 year to less than 17 years 0.5 mg/kg twice daily Maximum of 40 mg twice daily - See full prescribing information for complete dosing information in adults and pediatrics, recommended treatment duration by indication, and dosage adjustment for adult patients with renal impairment. (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3 )
Administration (2.3 ) :
- Take once daily before bedtime or twice daily in the morning and before bedtime with or without food.
Recommended Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage and duration of famotidine for oral suspension, USP in adults with normal renal function is shown in Table 1.
| Indication | Recommended Dosage | Recommended Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Active DU | 40 mg once daily; or 20 mg twice daily Both dosages demonstrated effectiveness in clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14)] . . | Up to 8 weeks In clinical trials, the majority of patients healed within 4 weeks. For patients who do not heal after 4 weeks, consider an additional 2 to 4 weeks of treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . , Longer treatment durations have not been studied in clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2, 14.3)] . |
| Active GU | 40 mg once daily. | Up to 8 weeks |
| Symptomatic nonerosive GERD | 20 mg twice daily. | Up to 6 weeks |
| Erosive esophagitis due to GERD, diagnosed by endoscopy | 20 mg twice daily; or 40 mg twice daily. | Up to 12 weeks |
| Pathological hypersecretory conditions | Starting dosage: 20 mg every 6 hours; adjust dosage to individual patient needs. Maximum dosage 160 mg every 6 hours. | As clinically indicated |
| Reduction of the risk of DU recurrence | 20 mg once daily. | 1 year , or as clinically indicated |
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage and duration of famotidine for oral suspension, USP in pediatric patients with normal renal function is shown in Table 2.
| Indication | Pediatric Age Range | Recommended Dosage After preparation, the concentration of famotidine oral suspension, USP is 8 mg/mL [See Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peptic Ulcer Disease | 1 year to less than 17 years | Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg once daily; or 0.25 mg/kg twice daily. May increase to 1 mg/kg once daily at bedtime or 0.5 mg/kg twice daily. Maximum of 40 mg per day. | 8 weeks Treatment duration based on adult recommendations (see Table 1) . Individualize the dose and duration based upon clinical response and/or pH determinations (gastric or esophageal) and endoscopy. |
| GERD | Birth to less than 3 months | Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg once daily. May increase to 1 mg/kg once daily. | Up to 8 weeks , Use conservative measures (e.g., thickened feedings) concurrently [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] . , After 4 weeks of treatment re-evaluate the patient. Consider an additional 4 weeks of treatment if treatment benefit outweighs potential risks. |
| 3 months to less than 1 year | Starting dosage 0.5 mg/kg twice daily. May increase to 1 mg/kg twice daily. Maximum of 40 mg per day. | ||
| GERD with or without esophagitis and ulcerations | 1 year to less than 17 years | 0.5 mg/kg twice daily Maximum of 40 mg twice daily. | 6 to 12 weeks |
Recommended Dosage in Adults with Renal Impairment
Recommended dosage adjustments for adults with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/min) by indication are shown in Table 3. Use the lowest effective dosage [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
A safe and effective dosage has not been established in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
| Indication | Recommended Maximum Dosages | |
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine clearance 30 to 60 mL/minute | Creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute | |
| Active DU | 20 mg once daily; or 40 mg every other day | 10 mg once daily; or 20 mg every other day |
| Active GU | 20 mg once daily; or 40 mg every other day | 10 mg once daily; or 20 mg every other day |
| Symptomatic nonerosive GERD | 20 mg once daily | 10 mg once daily; or 20 mg every other day |
| Erosive esophagitis due to GERD, diagnosed by endoscopy Dosage adjustments for renal impairment are provided for both dosing regimens (20 mg twice daily and 40 mg twice daily) which showed effectiveness for the treatment of erosive esophagitis in clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] . | 20 mg once daily; or 40 mg every other day The dosage required to treat pathological hypersecretory conditions may exceed the maximum dosage evaluated in patients with impaired renal function. The risk for increased adverse reactions in renally impaired patients treated with famotidine for oral suspension, USP for pathological hypersecretory conditions is unknown. | 10 mg once daily; or 20 mg every other day |
| 40 mg once daily | 20 mg once daily | |
| Pathological hypersecretory conditions | Avoid use | |
| Reduction of the risk of DU recurrence | 10 mg once daily; or 20 mg every other day | 10 mg every other day |
Administration Instructions
Preparation of Constituted Suspension by a Healthcare Provider Prior to Dispensing
- Prior to dispensing, constitute famotidine for oral suspension, USP by slowly adding below volume of purified water to the bottle.
- Shake vigorously for 5 to 10 seconds immediately after adding the water.
- The constituted suspension contains 40 mg of famotidine, USP per 5 mL, and should be a smooth, mobile, white to off-white, and homogeneous suspension.
Bottle Size Volume of Purified Water for Reconstitution 50 mL 46 mL 100 mL 92 mL 150 mL 138 mL
Administration and Storage of Constituted Suspension
- Shake the bottle of constituted famotidine, USP suspension vigorously for 5 to 10 seconds prior to each use.
- Take famotidine for oral suspension, USP once daily before bedtime or twice daily in the morning and before bedtime, as recommended.
- Famotidine for oral suspension, USP may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Famotidine for oral suspension, USP may be given with antacids.
- Store the constituted suspension at 25°C (77°F). Protect from freezing. Discard unused constituted suspension after 30 days.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Famotidine for oral suspension 400 mg, 800 mg and 1,200 mg is a white to off-white powder containing 40 mg of famotidine per 5 mL. When constituted as directed, famotidine for oral suspension is a smooth, mobile, white to off-white, homogeneous suspension with a cherry-banana-mint flavor,
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data with H 2 -receptor antagonists, including famotidine, in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse development effects were observed with oral administration of famotidine at doses up to approximately 243 and 122 times, respectively, the recommended human dose of 80 mg per day for the treatment of erosive esophagitis (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproductive studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at oral doses of up to 2,000 and 500 mg/kg/day, respectively, and in both species at intravenous doses of up to 200 mg/kg/day and have revealed no significant evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to famotidine. While no direct fetotoxic effects have been observed, sporadic abortions occurring only in mothers displaying marked decreased food intake were seen in some rabbits at oral doses of 200 mg/kg/day (about 49 times the recommended human dose of 80 mg per day, based on body surface area) or higher. There are, however, no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are limited data available on the presence of famotidine in human breast milk. There were no effects on the breastfed infant. There are no data on famotidine effects on milk production. Famotidine is present in the milk of lactating rats (see Data ) .
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for famotidine and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from famotidine for oral suspension or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Transient growth depression was observed in young rats suckling from mothers treated with maternotoxic doses of famotidine at least 600 times the usual human dose.
Pediatric Use
Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD With or Without Esophagitis and Ulcerations
Pediatric Patients One Year to Less than 17 Years of Age
The safety and effectiveness of famotidine for oral suspension have been established in pediatric patients 1 year to less than 17 years of age for the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and GERD with or without esophagitis and ulcerations. Use of famotidine in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of famotidine in adults with additional pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data in pediatric patients 1 year to less than 17 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 , 12.3) ] . The safety and effectiveness of famotidine for oral suspension for the treatment of peptic ulcer disease in pediatric patients less than one year of age have not been established.
GERD
Pediatric Patients Less Than One Year of Age
The safety and effectiveness of famotidine for oral suspension have been established in pediatric patients from birth to less than 1 year of age for the treatment of GERD. The use of famotidine this is age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of famotidine in adults and with supportive data in pediatric patients from birth to less than 1 year of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 , 12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.7) ] .
Other Conditions
The safety and effectiveness for the treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions and reduction of risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence have not been established in pediatric patients.
A safe and effective dosage has not been established in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
Geriatric Use
Of the 1,442 famotidine-treated patients in clinical studies, approximately 10% were 65 and older. In these studies, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between elderly and younger patients. In post marketing experience, CNS adverse reactions have been reported in elderly patients with and without renal impairment receiving famotidine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Famotidine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to famotidine for oral suspension may be greater in elderly patients, particularly those with impaired renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
In general, use the lowest effective dose of famotidine for oral suspension for an elderly patient and monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Renal Impairment
CNS adverse reactions and prolonged QT intervals have been reported in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . The clearance of famotidine is reduced in adults with moderate and severe renal impairment compared to adults with normal renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . No dosage adjustment is needed in adults with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 60 mL/minute). Dosage reduction is recommended in adults with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/minute) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . Data are not available to establish a safe and effective dosage in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Famotidine for oral suspension is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) to famotidine or other histamine-2 (H 2 ) receptor antagonists.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Adverse Reactions : Elderly patients and patients with renal impairment at increased risk; reduce the dosage. (2.2 , 5.1 , 8.5 , 8.6 )
- GI Malignancy : Absence of GI symptoms does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy; evaluate prior to initiating therapy. (5.2 )
Central Nervous System Adverse Reactions
Central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions, including confusion, delirium, hallucinations, disorientation, agitation, seizures, and lethargy, have been reported in elderly patients and patients with moderate and severe renal impairment treated with famotidine. Since famotidine blood levels are higher in patients with renal impairment than in patients with normal renal function, dosage adjustments are recommended in patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Concurrent Gastric Malignancy
In adults, symptomatic response to therapy with famotidine for oral suspension does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy. Consider evaluation for gastric malignancy in adult patients who have a suboptimal response or an early symptomatic relapse after completing treatment with famotidine for oral suspension.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions are: headache, dizziness, constipation, and diarrhea. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC at 1-855-899-9180 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of famotidine for oral suspension has been established based on adequate and well-controlled studies of another oral famotidine product [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . The following is a summary of the adverse reactions reported in those studies.
Oral famotidine was studied in 7 U.S. and international placebo- and active-controlled trials in approximately 2,500 patients [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . A total of 1,442 patients were treated with famotidine, including 302 treated with 40 mg twice daily, 456 treated with 20 mg twice daily, 461 treated with 40 mg once daily, and 396 treated with 20 mg once daily. The population was 17 to 91 years old, fairly well distributed between sex and race; however, the predominant race was Caucasian.
The following adverse reactions occurred in greater than or equal to 1% of famotidine-treated patients: headache, dizziness and constipation.
The following other adverse reactions were reported in less than 1% of patients in clinical trials:
Body as a Whole: fever, asthenia, fatigue
Cardiovascular: palpitations
Gastrointestinal: elevated liver enzymes, vomiting, nausea, abdominal discomfort, anorexia, dry mouth
Hematologic: thrombocytopenia
Hypersensitivity: orbital edema, rash, conjunctival injection, bronchospasm
Musculoskeletal: musculoskeletal pain, arthralgia
Nervous System/Psychiatric: seizure, hallucinations, depression, anxiety, decreased libido, insomnia, somnolence
Skin: pruritus, dry skin, flushing
Special Senses: tinnitus, taste disorder
Other: impotence
Pediatric Patients Less Than One Year of Age
In a clinical study in 35 pediatric patients less than 1 year of age with GERD symptoms, two patients discontinued due to adverse reactions. Agitation observed in 5 patients resolved when famotidine was discontinued [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
Post marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of famotidine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: arrhythmia, AV block, prolonged QT interval
Gastrointestinal: cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis
Hematologic: agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, leukopenia
Hypersensitivity: anaphylaxis, angioedema, facial edema, urticaria
Musculoskeletal: rhabdomyolysis, muscle cramps
Nervous System/Psychiatric: confusion, agitation, paresthesia
Respiratory: interstitial pneumonia
Skin: toxic epidermal necrolysis/Stevens-Johnson syndrome
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs Dependent on Gastric pH for Absorption : Systemic exposure of the concomitant drug may be significantly reduced leading to loss of efficacy. See full prescribing information for a list of interacting drugs. (7.1 )
- Tizanidine (CYP1A2) Substrate : Potential for substantial increases in blood concentrations of tizanidine resulting in hypotension, bradycardia or excessive drowsiness; avoid concomitant use, if possible. (7.2 )
Drugs Dependent on Gastric pH for Absorption
Famotidine can reduce the absorption of other drugs, due to its effect on reducing intragastric acidity, leading to loss of efficacy of the concomitant drug.
Concomitant administration of famotidine for oral suspension with dasatinib, delavirdine mesylate, cefditoren, and fosamprenavir is not recommended.
See the prescribing information for other drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption for administration instructions, including atazanavir, erlotinib, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, nilotinib, and rilpivirine.
Tizanidine (CYP1A2 Substrate)
Although not studied clinically, famotidine is considered a weak CYP1A2 inhibitor and may lead to substantial increases in blood concentrations of tizanidine, a CYP1A2 substrate. Avoid concomitant use with famotidine for oral suspension. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor for hypotension, bradycardia or excessive drowsiness. Refer to the full prescribing information for tizanidine.
DESCRIPTION
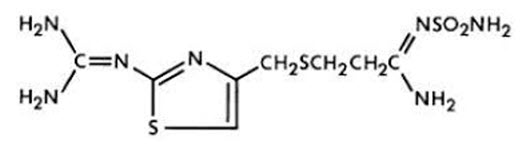
The active ingredient in famotidine for oral suspension, USP is a histamine-2 (H 2 ) receptor antagonist. Famotidine, USP is N' -(aminosulfonyl)-3-[[[2-[(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]propanimidamide. The empirical formula of famotidine, USP is C 8 H 15 N 7 O 2 S 3 and its molecular weight is 337.43. Its structural formula is:
Each 5 mL of famotidine for oral suspension, USP when prepared as directed contains 40 mg of famotidine, USP and the following inactive ingredients: carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, flavors (banana, cherry and peppermint), fumaric acid, microcrystalline cellulose, sucrose, xanthan gum. Added as preservatives are sodium benzoate 0.42%, sodium methyl paraben 0.08%, and sodium propyl paraben 0.02%.
Famotidine, USP is a white to pale yellow-white crystalline compound that is freely soluble in dimethylformamide and in glacial acetic acid, slightly soluble in methanol, very slightly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in ethanol, chloroform, ether and in ethyl acetate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Famotidine is a competitive inhibitor of histamine-2 (H 2 ) receptors. The primary clinically important pharmacologic activity of famotidine is inhibition of gastric secretion. Both the acid concentration and volume of gastric secretion are suppressed by famotidine, while changes in pepsin secretion are proportional to volume output.
Pharmacodynamics
Adults
Famotidine inhibited both basal and nocturnal gastric secretion, as well as secretion stimulated by food and pentagastrin. After oral administration of famotidine, the onset of the antisecretory effect occurred within one hour; the maximum effect was dose-dependent, occurring within one to three hours. Duration of inhibition of secretion by doses of 20 mg and 40 mg was 10 hours to 12 hours.
Single evening oral doses of 20 mg and 40 mg inhibited basal and nocturnal acid secretion in all subjects; mean nocturnal gastric acid secretion was inhibited by 86% and 94%, respectively, for a period of at least 10 hours. The same doses given in the morning suppressed food-stimulated acid secretion in all subjects. The mean suppression was 76% and 84%, respectively, 3 to 5 hours after administration, and 25% and 30%, respectively, 8 to 10 hours after administration. In some subjects who received the 20 mg dose, however, the antisecretory effect was dissipated within 6 hours to 8 hours. There was no cumulative effect with repeated doses. The nocturnal intragastric pH was raised by evening doses of 20 mg and 40 mg of famotidine to mean values of 5.0 and 6.4, respectively. When famotidine was given after breakfast, the basal daytime interdigestive pH at 3 and 8 hours after 20 mg or 40 mg of famotidine was raised to about 5.
Famotidine had little or no effect on fasting or postprandial serum gastrin levels. Gastric emptying and exocrine pancreatic function were not affected by famotidine.
In clinical pharmacology studies, systemic effects of famotidine in the CNS, cardiovascular, respiratory, or endocrine systems were not noted. Also, no anti-androgenic effects were noted. Serum hormone levels, including prolactin, cortisol, thyroxine (T 4 ), and testosterone, were not altered after treatment with famotidine.
Pediatric Patients
Pharmacodynamics of famotidine, assessed by gastric pH, were evaluated in 5 pediatric patients 2 years to 13 years of age using the sigmoid E max model. These data suggest that the relationship between serum concentration of famotidine and gastric acid suppression is similar to that observed in adults (see Table 4 ).
| EC 50 (ng/mL) Using the Sigmoid E max model, serum concentrations of famotidine associated with 50% maximum gastric acid reduction are presented as means ± SD. | |
|---|---|
| Pediatric Patients | 26 ± 13 |
| Adults | |
| Healthy adult subjects | 26.5 ± 10.3 |
| Adult patients with upper GI bleeding | 18.7 ± 10.8 |
In a study examining the effect of famotidine on gastric pH and duration of acid suppression in pediatric patients, four pediatric patients ages 11 to 15 years of age using the oral formulation at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, maintained a gastric pH above 5 for 13.5 ± 1.8 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Famotidine is incompletely absorbed. The bioavailability of oral doses is 40% to 45%. Bioavailability may be slightly increased by food, or slightly decreased by antacids; however, these effects are of no clinical consequence.
Peak famotidine plasma levels occur in 1 to 3 hours. Plasma levels after multiple dosages are similar to those after single doses.
Distribution
Fifteen to 20% of famotidine in plasma is protein bound.
Elimination
Metabolism
Famotidine undergoes minimal first-pass metabolism. Twenty-five to 30% of an oral dose was recovered in the urine as unchanged compound. The only metabolite identified in humans is the S-oxide.
Excretion
Famotidine has an elimination half-life of 2.5 to 3.5 hours. Famotidine is eliminated by renal (65% to 70%) and metabolic (30% to 35%) routes. Renal clearance is 250 to 450 mL/minute, indicating some tubular excretion.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Infants from birth to 12 Months
After a single oral dose administration of 0.5 mg/kg orally in patients from birth to 12 months, the bioavailability is approximately 42%.
The AUC increased 1.4-fold after single oral dose of 1 mg/kg compared to 0.5 mg/kg and 2.7-fold after multiple oral doses of 1 mg/kg compared to 0.5 mg/kg.
Plasma clearance is reduced and elimination half-life is prolonged in pediatric patients from birth to 3 months of age compared to older pediatric patients. Following intravenous administration of 0.5 mg/kg, CL Total was 0.13 ± 0.06 L/hr/kg, 0.21 ± 0.06 L/hr/kg, and 0.49 ± 0.17 L/hr/kg in pediatric patients <1 month of age, <3 months of age, and >3 to 12 months of age, respectively. Elimination half-life was 10.5 hours, 8.1 hours, and 4.5 hours in pediatric patients <1 month of age, <3 months of age, and >3 to 12 months of age, respectively.
Patients 11 Years to 15 Years
The mean bioavailability in 8 pediatric patients was 50% compared to adult values of 42% to 49%.
Pharmacokinetic parameters in pediatrics 11 years to 15 years is compared to infants from birth to 12 months in Table 5.
| Infants from Birth to 12 months (N=5) | Pediatric Patients 11 Years to 15 Years (N=8) | |
|---|---|---|
| AUC 0-∞ (ng∙hr/mL) arithmetic mean ± S.D. | 645 ± 249 | 580 ± 60 |
| C max (ng/mL) | 79.2 | 97.3 |
| T max (hr) median | 2.0 (1/0, 4.1) observed minimum and maximum values | 2.3 (2.1, 2.9) reported minimum and maximum values |
| T 1/2 (hr) | 5.82 | 2.13 |
Patients with Renal Impairment
In adult patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute), the systemic exposure (AUC) of famotidine increased at least 5-fold. In adult patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance between 30 to 60 mL/minute), the AUC of famotidine increased at least 2-fold [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Human Organic Anion Transporter (OAT) 1 and 3: In vitro studies indicate that famotidine is a substrate for OAT1 and OAT3. Following coadministration of probenecid (1,500 mg), an inhibitor of OAT1 and OAT3, with a single oral 20 mg dose of famotidine in 8 healthy subjects, the serum AUC 0-10h of famotidine increased from 424 to 768 ng∙hr/mL and the maximum serum concentration (C max ) increased from 73 to 113 ng/mL. Renal clearance, urinary excretion rate and amount of famotidine excreted unchanged in urine were decreased. The clinical relevance of this interaction is unknown.
Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion Protein 1 (MATE-1): An in vitro study showed that famotidine is an inhibitor of MATE-1. However, no clinically significant interaction with metformin, a substrate for MATE-1, was observed.
CYP1A2: Famotidine is a weak CYP1A2 inhibitor.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenic potential of famotidine was assessed in a 106-week oral carcinogenicity study in rats and a 92-week oral carcinogenicity study in mice. In the 106-week study in rats and the 92-week study in mice at oral doses of up to 2,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 243 and 122 times, respectively, based on body surface area, the recommended human dose of 80 mg per day for the treatment of erosive esophagitis), there was no evidence of carcinogenic potential for famotidine.
Famotidine was negative in the microbial mutagen test (Ames test) using Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli with or without rat liver enzyme activation at concentrations up to 10,000 mcg/plate. In in vivo studies in mice, with a micronucleus test and a chromosomal aberration test, no evidence of a mutagenic effect was observed.
In studies with rats given oral doses of up to 2,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 243 times, based on body surface area, the recommended human dose of 80 mg per day) fertility and reproductive performance were not affected.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and effectiveness of famotidine for oral suspension have been established based on adequate and well-controlled studies of another oral famotidine product . The following is a summary of the efficacy results reported in those studies.
Active Duodenal Ulcer
In a U.S. multicenter, double-blind trial in adult outpatients with endoscopically confirmed duodenal ulcer (DU), orally administered famotidine was compared to placebo. As shown in Table 6, 70% of patients treated with famotidine 40 mg at bedtime were healed by Week 4. Most patients' DU healed within 4 weeks.
Patients not healed by Week 4 were continued in the trial. By Week 8, 83% of patients treated with famotidine had healed DU, compared to 45% of patients treated with placebo. The incidence of DU healing with famotidine was greater than with placebo at each time point based on proportion of endoscopically confirmed healed DUs. Trials have not assessed the safety of famotidine in uncomplicated active DU for periods of more than 8 weeks.
| Famotidine 40 mg at bedtime (N=89) | Famotidine 20 mg twice daily (N=84) | Placebo at bedtime (N=97) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 2 | 32% p<0.001 vs. placebo | 38% | 17% |
| Week 4 | 70% | 67% | 31% |
In this study, time to relief of daytime and nocturnal pain was shorter for patients receiving famotidine than for patients receiving placebo; patients receiving famotidine also took less antacid than patients receiving placebo.
Active Gastric Ulcer
In both a U.S. and an international multicenter, double-blind trials in patients with endoscopically confirmed active gastric ulcer (GU), orally administered famotidine 40 mg at bedtime was compared to placebo. Antacids were permitted during the trials, but consumption was not significantly different between the famotidine and placebo groups.
As shown in Table 7, the incidence of GU healing confirmed by endoscopy (dropouts counted as unhealed) with famotidine was greater than placebo at Weeks 6 and 8 in the U.S. trial, and at Weeks 4, 6 and 8 in the international trial.
In these trials, most famotidine-treated patients healed within 6 weeks. Trials have not assessed the safety of famotidine in uncomplicated active GU for periods of more than 8 weeks.
| U.S. Study (N=149) | International Study (N=294) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Famotidine 40 mg at bedtime (N=74) | Placebo at bedtime (N=75) | Famotidine 40 mg at bedtime (N=149) | Placebo at bedtime (N=145) | |
| Week 4 | 45% | 39% | 47% p≤0.01 vs. placebo | 31% |
| Week 6 | 66% | 44% | 65% | 46% |
| Week 8 | 78% p≤0.05 vs. placebo | 64% | 80% | 54% |
Time to complete relief of daytime and nighttime pain was statistically significantly shorter for patients receiving famotidine than for patients receiving placebo; however, neither trial demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the proportion of patients whose pain was relieved by the end of the trial (Week 8).
Symptomatic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Orally administered famotidine was compared to placebo in a U.S. trial that enrolled patients with symptoms of GERD and without endoscopic evidence of esophageal erosion or ulceration. As shown in Table 8, patients treated with famotidine 20 mg twice daily had greater improvement in symptomatic GERD than patients treated with 40 mg at bedtime or placebo.
| Famotidine 20 mg twice daily (N=154) | Famotidine 40 mg at bedtime (N=149) | Placebo at bedtime (N=73) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 6 | 82% p≤0.01 vs. placebo | 69% | 62% |
Erosive Esophagitis due to GERD
Healing of endoscopically verified erosion and symptomatic improvement were studied in a U.S. and an international double-blind trials. Healing was defined as complete resolution of all erosions visible with endoscopy. The U.S. trial comparing orally administered famotidine 40 mg twice daily to placebo and orally administered famotidine 20 mg twice daily showed a significantly greater percentage of healing of erosive esophagitis for famotidine 40 mg twice daily at Weeks 6 and 12 (Table 9).
| Famotidine 40 mg twice daily (N=127) | Famotidine 20 mg twice daily (N=125) | Placebo twice daily (N=66) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 6 | 48% p≤0.01 vs. placebo , p≤0.01 vs. famotidine 20 mg twice daily | 32% | 18% |
| Week 12 | 69% , p≤0.05 vs. famotidine 20 mg twice daily | 54% | 29% |
As compared to placebo, patients in the U.S. trial who received famotidine had faster relief of daytime and nighttime heartburn, and a greater percentage of famotidine-treated patients experienced complete relief of nighttime heartburn. These differences were statistically significant.
In the international trial, when orally administered famotidine 40 mg twice daily was compared to orally administered ranitidine 150 mg twice daily, a statistically significantly greater percentage of healing of erosive esophagitis was observed with famotidine 40 mg twice daily at Week 12 (Table 10). There was, however, no significant difference in symptom relief among treatment groups.
| Famotidine 40 mg twice daily (N=175) | Famotidine 20 mg twice daily (N=93) | Ranitidine 150 mg twice daily (N=172) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 6 | 48% | 52% | 42% |
| Week 12 | 71% p≤0.05 vs. ranitidine 150 mg twice daily | 68% | 60% |
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions
In trials of patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome with or without multiple endocrine neoplasias, famotidine significantly inhibited gastric acid secretion and controlled associated symptoms. Orally administered famotidine dosages from 20 mg to 160 mg every 6 hours maintained basal acid secretion below 10 mEq/hour; initial dosages were titrated to the individual patient need and subsequent adjustments were necessary with time in some patients.
Risk Reduction of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
Two randomized, double-blind, multicenter trials in patients with endoscopically confirmed healed DUs demonstrated that patients receiving treatment with orally administered famotidine 20 mg at bedtime had lower rates of DU recurrence, as compared with placebo.
- In the U.S. trial, DU recurrence within 12 months was 2.4 times greater in patients treated with placebo than in the patients treated with famotidine. The 89 famotidine-treated patients had a cumulative observed DU recurrence rate of 23%, compared to a 57% in the 89 patients receiving placebo (p<0.01).
- In the international trial, the cumulative observed DU recurrence within 12 months in the 307 famotidine-treated patients was 36%, compared to 76% in the 325 patients who received placebo (p<0.01).
Controlled trials have not extended beyond one year.
GERD in Pediatric Patients Less than 1 Year of Age
In a double-blind, randomized, treatment-withdrawal study, 35 pediatric patients less than 1 year of age who were diagnosed with GERD, primarily by history of vomiting (spitting up) and irritability (fussiness), were treated for up to 4 weeks with famotidine oral suspension 0.5 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg administered once daily for patients less than 3 months of age and administered twice daily for patients 3 months to less than 12 months of age. Caregivers were instructed to provide conservative treatment including thickened feedings. After 4 weeks of treatment, patients were randomly withdrawn from the treatment and followed an additional 4 weeks for vomiting (spitting up), irritability (fussiness) and global assessments of improvement. The study patients ranged in age at entry from 1.3 to 10.5 months (mean 5.6 ± 2.9 months), 57% were female, 91% were white and 6% were black. Most patients (27/35) continued into the treatment-withdrawal phase of the study. Most patients improved during the initial treatment phase of the study. Results of the treatment-withdrawal phase were difficult to interpret because of small numbers of patients.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Famotidine for oral suspension, USP 40 mg/5 mL is supplied as follows:
| NDC | Amount of Famotidine | Quantity when reconstituted | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0832-6045-50 0832-6045-10 0832-6045-15 | 400 mg 800 mg 1,200 mg | 50 mL 100 mL 150 mL | White to off-white powder. When constituted as directed, famotidine suspension is a smooth, mobile, off-white, homogeneous suspension with a cherry-banana-mint flavor. |
Prior to dispensing, constitute famotidine for oral suspension, USP [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Storage
Store famotidine for oral suspension dry powder and constituted suspension at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from freezing. Discard unused constituted suspension after 30 days.
Dispense in a USP tight, light-resistant container.
Mechanism of Action
Famotidine is a competitive inhibitor of histamine-2 (H 2 ) receptors. The primary clinically important pharmacologic activity of famotidine is inhibition of gastric secretion. Both the acid concentration and volume of gastric secretion are suppressed by famotidine, while changes in pepsin secretion are proportional to volume output.