Filspari prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Filspari patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to initiating treatment with FILSPARI, discontinue use of renin- angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors and endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) (2.1 , 4 , 7.1 ).
- Initiate treatment with FILSPARI at 200 mg orally once daily. After 14 days, increase to 400 mg once daily, as tolerated. When resuming FILSPARI after an interruption, consider re-titration (2.4 ).
- Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole with water prior to the morning or evening meal (2.5 ).
2.1 General Considerations
2.2 Monitoring
Initiate treatment with FILSPARI only after measuring aminotransferase levels and total bilirubin. Avoid initiation in patients with elevated aminotransferases greater than 3 times ULN. Continue required monitoring every 3 months during treatment with FILSPARI [see Dosage and Administration (2.6 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
2.3 Pregnancy Testing
2.4 Recommended Dosage
Initiate treatment with FILSPARI at 200 mg orally once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily, as tolerated. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI after an interruption, consider titration of FILSPARI, starting at 200 mg once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] .
2.5 Administration
- Instruct patient to swallow tablets whole with water prior to the morning or evening meal.
- Maintain the same dosing pattern in relationship to meals.
- If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. Do not take double or extra doses.
2.6 Dosage Adjustment for Aminotransferase Elevations
If aminotransferase levels increase, adjust monitoring and treatment plan according to Table 1 .
Do not resume treatment in patients who have experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity or in patients whose hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin have not returned to pretreatment levels.
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; INR = international normalized ratio; ULN = upper limit of normal. | |
ALT/AST levels | Treatment and monitoring recommendations |
Greater than 3 times and less than or equal to 8 times ULN | Confirm elevation with a repeat measure. If confirmed, interrupt treatment, and monitor aminotransferase levels and bilirubin at least weekly, and INR as needed, until the levels return to pretreatment values and the patient is asymptomatic. Do not resume treatment if any of the following occurs without other cause found:
If treatment is resumed, initiate FILSPARI at 200 mg once daily, with reassessment of hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin within 3 days. Close monitoring is required in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.4 )] . |
Greater than 8 times ULN | Stop treatment permanently if no other cause found. |
2.7 Dosage Modification for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with FILSPARI.
If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt treatment with FILSPARI [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Filspari prescribing information
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY and EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program called the FILSPARI REMS. Under the FILSPARI REMS, prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must enroll in the program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 )] .
Hepatotoxicity
Some Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERAs) have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. In clinical studies, elevations in aminotransferases (ALT or AST) of at least 3-times the Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge.
Measure transaminases and bilirubin before initiating treatment and then every 3 months during treatment. Interrupt treatment and closely monitor patients who develop aminotransferase elevations more than 3-times ULN [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.6 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
FILSPARI should generally be avoided in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3-times ULN) at baseline because monitoring for hepatotoxicity may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.6 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
FILSPARI is contraindicated for use during pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm if used by pregnant patients. Therefore, in patients who can become pregnant, exclude pregnancy prior to initiation of FILSPARI. Advise use of effective contraception before the initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for two weeks after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue FILSPARI as soon as possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FILSPARI is indicated to slow kidney function decline in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) who are at risk for disease progression.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Prior to initiating treatment with FILSPARI, discontinue use of renin- angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors and endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) (2.1 , 4 , 7.1 ).
- Initiate treatment with FILSPARI at 200 mg orally once daily. After 14 days, increase to 400 mg once daily, as tolerated. When resuming FILSPARI after an interruption, consider re-titration (2.4 ).
- Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole with water prior to the morning or evening meal (2.5 ).
2.1 General Considerations
2.2 Monitoring
Initiate treatment with FILSPARI only after measuring aminotransferase levels and total bilirubin. Avoid initiation in patients with elevated aminotransferases greater than 3 times ULN. Continue required monitoring every 3 months during treatment with FILSPARI [see Dosage and Administration (2.6 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
2.3 Pregnancy Testing
2.4 Recommended Dosage
Initiate treatment with FILSPARI at 200 mg orally once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily, as tolerated. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI after an interruption, consider titration of FILSPARI, starting at 200 mg once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] .
2.5 Administration
- Instruct patient to swallow tablets whole with water prior to the morning or evening meal.
- Maintain the same dosing pattern in relationship to meals.
- If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. Do not take double or extra doses.
2.6 Dosage Adjustment for Aminotransferase Elevations
If aminotransferase levels increase, adjust monitoring and treatment plan according to Table 1 .
Do not resume treatment in patients who have experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity or in patients whose hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin have not returned to pretreatment levels.
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; INR = international normalized ratio; ULN = upper limit of normal. | |
ALT/AST levels | Treatment and monitoring recommendations |
Greater than 3 times and less than or equal to 8 times ULN | Confirm elevation with a repeat measure. If confirmed, interrupt treatment, and monitor aminotransferase levels and bilirubin at least weekly, and INR as needed, until the levels return to pretreatment values and the patient is asymptomatic. Do not resume treatment if any of the following occurs without other cause found:
If treatment is resumed, initiate FILSPARI at 200 mg once daily, with reassessment of hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin within 3 days. Close monitoring is required in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.4 )] . |
Greater than 8 times ULN | Stop treatment permanently if no other cause found. |
2.7 Dosage Modification for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with FILSPARI.
If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt treatment with FILSPARI [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] .
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FILSPARI is supplied as film-coated, modified oval, white to off-white tablets debossed on one side and plain on the other in the following strengths:
200 mg debossed with “105” 400 mg debossed with “021”
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed (8.2 ).
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on data from animal reproductive toxicity studies, FILSPARI may cause fetal harm, including birth defects and fetal death, when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4 )] . Available data from reports of pregnancy in clinical trials with FILSPARI are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Available data from postmarketing reports and published literature over decades of use with ERA in the same class as FILSPARI have not identified an increased risk of fetal harm; however, these data are limited. Methodological limitations of these postmarketing reports and published literature include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and missing data. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal ERA use. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of sparsentan to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis at 10-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) in mg/day caused teratogenic effects in rats, including craniofacial malformations, skeletal abnormalities, increased embryo-fetal lethality, and reduced fetal weights (see Data) . Advise pregnant patients of the potential risk to the fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies in pregnant rats and rabbits, teratogenicity and/or developmental toxicity were observed, which were attributed to the antagonism of endothelin type A (ET A ) and angiotensin II type 1 (AT 1 ) receptors.
In pregnant rats, oral administration of sparsentan throughout organogenesis at doses of 80, 160, and 240 mg/kg/day resulted in dose-dependent teratogenic effects in the form of craniofacial malformations, skeletal abnormalities, increased embryo-fetal lethality, and reduced fetal weights at all doses tested. The area under the curve (AUC) at the lowest dose tested (80 mg/kg/day) was approximately 10 times the AUC at the MRHD of 400 mg/day. In pregnant rabbits, oral administration of sparsentan throughout organogenesis at doses of 2.5, 10 and 40 mg/kg/day resulted in maternal death and abortions at 10 and 40 mg/kg/day which provided exposures approximately 0.1 times and 0.2 times the AUC at the MRHD, respectively. An increase in a fetal variation (supernumerary cervical ribs) occurred at the high dose of 40 mg/kg/day.
In the pre- and postnatal development study in rats, oral administration of sparsentan during pregnancy and the lactational period at doses of 5, 20, or 80 mg/kg/day resulted in maternal death, body weight loss/reduced body weight gain, and adverse clinical signs at 80 mg/kg/day. An increase in pup deaths occurred at 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the AUC at MRHD) during the neonatal period through weaning, and decreased growth occurred at ≥ 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.6 times the AUC at the MRHD) after weaning. The NOAEL for pre- and postnatal development in rats was 5 mg/kg/day, approximately 0.7 times the AUC at the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of sparsentan in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effect on milk production. Because of the potential for adverse reactions, such as hypotension in breastfed infants, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with FILSPARI.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on data from animal reproductive toxicity studies, FILSPARI may cause fetal harm, including birth defects and fetal death, when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Pregnancy Testing Exclude pregnancy before initiating FILSPARI in females of reproductive potential. The patient should contact their physician immediately for pregnancy testing if onset of menses is delayed or pregnancy is suspected. If the pregnancy test is positive, the physician and patient should discuss the risks to their pregnancy and the fetus.
Contraception Patients who can become pregnant who are using FILSPARI must use an effective method of contraception prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for two weeks after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI to prevent pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of FILSPARI in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in the PROTECT study of FILSPARI, 15 (7.4%) were 65 and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
Elevations in ALT or AST of at least 3-fold ULN have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . While no concurrent elevations in bilirubin greater than 2-times ULN or cases of liver failure were observed in FILSPARI-treated patients in clinical trials, some endothelin receptor antagonists have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. To reduce the risk of potential serious hepatotoxicity, measure serum aminotransferase levels and total bilirubin prior to initiation of treatment and then every 3 months during treatment [See Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Advise patients with symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity (nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, fatigue, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, fever, or itching) to immediately stop treatment with FILSPARI and seek medical attention. If aminotransferase levels are abnormal at any time during treatment, interrupt FILSPARI and monitor as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.6 )] .
Consider re-initiation of FILSPARI only when hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin return to pretreatment values and only in patients who have not experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.6 )] .
Avoid initiation of FILSPARI in patients with elevated aminotransferases (greater than 3-times ULN) because monitoring hepatotoxicity in these patients may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.6 ), and Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
5.2 FILSPARI REMS
For all patients, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the FILSPARI REMS because of the risk of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
Important requirements of the FILSPARI REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the FILSPARI REMS by enrolling and completing training.
- All patients must enroll in the FILSPARI REMS prior to initiating treatment and comply with monitoring requirements [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 , 2.6 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- Pharmacies that dispense FILSPARI must be certified with the FILSPARI REMS and must dispense only to patients who are authorized to receive FILSPARI.
Further information is available at www.filsparirems.com or 1-833-513-1325.
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal reproduction studies, FILSPARI may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated for use during pregnancy. The available human data for endothelin receptor antagonists do not establish the presence or absence of fetal harm related to the use of FILSPARI. Counsel patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment with FILSPARI. Advise patients who can become pregnant to use effective contraception prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for two weeks after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue FILSPARI as soon as possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Contraindications (4 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
5.4 Hypotension
Hypotension has been observed in patients treated with ARBs and endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) and was observed in clinical studies with FILSPARI. In the PROTECT trial, there was a greater incidence of hypotension-associated adverse events, some serious, including dizziness, in patients treated with FILSPARI compared to irbesartan [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
In patients at risk for hypotension, consider eliminating or adjusting other antihypertensive medications and maintaining appropriate volume status.
If hypotension develops, despite elimination or reduction of other antihypertensive medications, consider a dose reduction or dose interruption of FILSPARI. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further dosing of FILSPARI, which can be given once blood pressure has stabilized.
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury
Monitor kidney function periodically. Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system can cause acute kidney injury. Patients whose kidney function may depend in part on the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, severe congestive heart failure, or volume depletion) may be at particular risk of developing acute kidney injury on FILSPARI. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in kidney function while on FILSPARI.
5.6 Hyperkalemia
Monitor serum potassium periodically and treat appropriately. Patients with advanced kidney disease or taking concomitant potassium-increasing drugs (e.g., potassium supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics), or using potassium-containing salt substitutes are at increased risk for developing hyperkalemia. Dosage reduction or discontinuation of FILSPARI may be required [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
5.7 Fluid Retention
Fluid retention may occur with endothelin receptor antagonists and has been observed in clinical studies with FILSPARI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . FILSPARI has not been evaluated in patients with heart failure.
If clinically significant fluid retention develops, evaluate the patient to determine the cause and the potential need to initiate or modify the dose of diuretic treatment then consider modifying the dose of FILSPARI.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinically significant adverse reactions that appear in other sections of the label include:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Acute Kidney Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Fluid Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of FILSPARI was evaluated in PROTECT (NCT03762850 ), a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled clinical study in adults with IgAN.
The data below reflect FILSPARI exposure in 202 patients with a median duration of 110 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions are presented in Table 2 .
| 1 Includes related terms. 2 Elevations in ALT or AST greater than 3-fold ULN. | ||
FILSPARI (N = 202) n (%) | Irbesartan (N = 202) n (%) | |
Hyperkalemia 1 | 34 (17) | 27 (13) |
Hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension) | 33 (16) | 13 (6) |
Peripheral edema 1 | 33 (16) | 29 (14) |
Dizziness 1 | 32 (16) | 14 (7) |
Anemia | 16 (8) | 9 (4) |
Acute kidney injury | 12 (6) | 5 (2) |
Transaminase elevations 2 | 7 (3.5) | 8 (4.0) |
Laboratory Tests
Initiation of FILSPARI may cause an initial small decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that occurs within the first 4 weeks of starting therapy and then stabilizes.
The incidence of a hemoglobin decrease >2 g/dL compared to baseline and below the lower limit of normal was greater for the FILSPARI arm (19%) compared to the irbesartan arm (13%). This decrease is thought to be in part due to hemodilution. There were no treatment discontinuations due to anemia or hemoglobin decrease in the PROTECT study.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use. Increased sparsentan exposure (2.7 , 7.2 , 12.3 ).
- Moderate CYP3A inhibitors: Monitor adverse reactions. Increased sparsentan exposure (7.2 , 12.3 ).
- Strong CYP3A inducers: Avoid concomitant use. Decreased sparsentan exposure (7.3 , 12.3 ).
- Antacids: Avoid use within 2 hours before or after use of sparsentan. May decrease exposure to sparsentan (7.4 , 11 ).
- Acid reducing agents: Avoid concomitant use. May decrease exposure to sparsentan (7.4 ).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including selective cyclooxygenase (COX-2) inhibitors: Monitor for signs of worsening renal function. Increased risk of kidney injury (7.5 ).
- CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 substrates: Monitor for substrate efficacy. Decreased exposure of these substrates (7.6 , 12.3 ).
- Sensitive P-gp and BCRP substrates: Avoid concomitant use. Increased exposure to substrates (7.7 , 12.3 ).
- Agents Increasing Serum Potassium: Increased risk of hyperkalemia, monitor serum potassium frequently (5.6 , 7.8 ).
7.1 Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and ERAs
7.2 Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of FILSPARI with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt treatment with FILSPARI. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI, consider dose titration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 , 2.7 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Monitor blood pressure, serum potassium, edema, and kidney function regularly when used concomitantly with moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 , 5.5 , 5.6 , 5.7 )] . No FILSPARI dose adjustment is needed.
Sparsentan is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases sparsentan C max and AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may increase the risk of FILSPARI adverse reactions.
7.3 Strong CYP3A Inducers
Avoid concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer. Sparsentan is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases sparsentan C max and AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
7.4 Antacids and Acid Reducing Agents
Administer FILSPARI 2 hours before or after administration of antacids. Avoid concomitant use of acid reducing agents (histamine H2 receptor antagonist and PPI proton pump inhibitor) with FILSPARI. Sparsentan exhibits pH-dependent solubility [see Description (11 )] . Antacids or acid reducing agents may decrease sparsentan exposure which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
7.5 Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs), Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors
Monitor for signs of worsening renal function with concomitant use with NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors). In patients with volume depletion (including those on diuretic therapy) or with impaired kidney function, concomitant use of NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors) with drugs that antagonize the angiotensin II receptor may result in deterioration of kidney function, including possible kidney failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )] . These effects are usually reversible.
7.6 CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 Substrates
Monitor for efficacy of the concurrently administered CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 substrates and consider dosage adjustment in accordance with the Prescribing Information. Sparsentan is an inducer of CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19. Sparsentan decreases exposure of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may reduce efficacy related to these substrates.
7.7 P-gp and BCRP Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of sensitive substrates of P-gp and BCRP with FILSPARI. Sparsentan is an inhibitor of P-gp and BCRP. Sparsentan may increase exposure of these transporter substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
7.8 Agents Increasing Serum Potassium
Monitor serum potassium frequently in patients treated with FILSPARI and other agents that increase serum potassium. Concomitant use of FILSPARI with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, potassium-containing salt substitutes, or other drugs that raise serum potassium levels may result in hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )] .
11 DESCRIPTION
FILSPARI (sparsentan) is an endothelin and angiotensin II receptor antagonist. The chemical name of sparsentan is 2-[4-[(2-butyl-4-oxo-1,3-diazaspiro[4.4]non-1-en-3-yl)methyl]-2-(ethoxymethyl)phenyl]-N-(4,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)benzenesulfonamide.
Sparsentan is a white to off-white powder, which is practically insoluble in water. Sparsentan has pH-dependent solubility, with intrinsic solubility of 1.48 and 0.055 mg/mL under pH 1.2 and 6.8, respectively. Sparsentan has a molecular weight of 592.76 g/mol, a molecular formula of C 32 H 40 N 4 O 5 S, and the following structure:
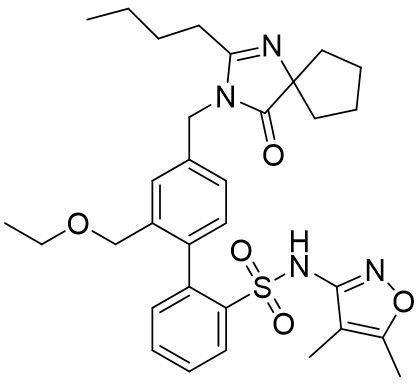
FILSPARI is available as film-coated 200 mg and 400 mg strength immediate release tablets for oral administration.
The inactive ingredients in FILSPARI are colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate. Film-coating is composed of macrogol/polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sparsentan is a single molecule with antagonism of the endothelin type A receptor (ET A R) and the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT 1 R). Sparsentan has high affinity for both the ET A R (Ki= 12.8 nM) and the AT 1 R (Ki=0.36 nM), and greater than 500-fold selectivity for these receptors over the endothelin type B and angiotensin II subtype 2 receptors. Endothelin 1 and angiotensin II are thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of IgAN via the ETAR and AT1R, respectively.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Dose-response information is not available. At the recommended dose regimen, no statistically significant exposure-response (E-R) relationship was identified between sparsentan exposure and the percentage reduction from baseline in UPCR at Week 36 over the observed sparsentan exposure range. No clinically meaningful E-R relationships were observed for hypotension of any grade and peripheral edema worst grade. A statistically significant relationship was observed between sparsentan exposures and the incidence of hyperkalemia of any grade.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a randomized, positive-, and placebo-controlled study in healthy subjects, sparsentan caused QTcF prolongation with maximal mean effect of 8.8 msec (90% CI: 5.9, 11.8) at 800 mg and 8.1 msec (90% CI: 5.2, 11.0) at 1600 mg. The underlying mechanism behind the observed QTc prolongation is unknown but is unlikely to be mediated via direct inhibition of hERG channels. At the recommended dose, no clinically relevant QTc prolongation (i.e., >20 msec) is expected.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of sparsentan are presented as geometric mean (% coefficient of variation) unless otherwise specified. The C max and AUC of sparsentan increase less than proportionally following administration of single doses of 200 mg to 1600 mg. Sparsentan showed time-dependent pharmacokinetics which may be related to the drug inducing its own metabolism over time. Steady-state plasma levels are reached within 7 days with no accumulation of exposure at the approved recommended dosage. Following a single oral dose of 400 mg sparsentan, the mean C max and AUC are 7.0 μg/mL and 83.0 μg×h/mL, respectively. Following daily doses of 400 mg sparsentan, the steady-state mean C max and AUC are 6.5 μg/mL and 63.6 μg×h/mL, respectively.
Absorption
Following a single oral dose of 400 mg sparsentan, the median (minimum to maximum) time to peak plasma concentration is approximately 3 hours (2 to 8 hours).
Effect of Food
Sparsentan AUC and C max increased by 22% and 108%, respectively, following administration of a single oral 800 mg dose with a high fat, high calorie meal (1000 kcal, 50% fat) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] . No clinically significant differences in sparsentan pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of a single 200 mg dose with a high fat, high calorie meal.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution at steady state is 61.4 L at the approved recommended dosage.
Sparsentan is >99% bound to human plasma proteins.
Elimination
The clearance of sparsentan is time-dependent which may be related to the drug inducing its own metabolism over time. The apparent clearance (CL/F) of sparsentan is 3.88 L/h following the initial 400 mg dose then increases to 5.11 L/h at steady state.
The half-life of sparsentan is estimated to be 9.6 hours at steady state.
Metabolism
Cytochrome P450 3A is the major isozyme responsible for the metabolism of sparsentan.
Excretion
After a single dose of radiolabeled sparsentan 400 mg to healthy subjects, approximately 80% of the dose was recovered in feces (9% unchanged) and 2% in urine (negligible amount unchanged). 82% of the dosed radioactivity was recovered within a 10-day collection period.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of sparsentan were observed based on age (18 – 73 years), sex, race, mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), or mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A or B). Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) and eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 have not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Effect of Other Drugs on Sparsentan
Strong CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use with itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased sparsentan C max by 25% and AUC by 174%.
Moderate CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use with cyclosporine (moderate CYP3A inhibitor) increased sparsentan C max by 41% and AUC by 70%.
Strong CYP3A inducers: Coadministration of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease sparsentan C max by 23% and AUC 0-inf by 47% at steady state.
Effect of Sparsentan on Other Drugs
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A4 substrate) or pitavastatin (OATP1B1, OATP1B3, P-gp, and BCRP substrate) were observed when co-administered with sparsentan. In addition, sparsentan had no clinically significant effect on serum creatinine levels (an endogenous biomarker of OAT2, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2K) or on 6β-hydroxycortisol (an endogenous biomarker of OAT3).
CYP2B6 substrates: Concomitant use with sparsentan decreased the exposure of bupropion (CYP2B6 substrate) C max by 32% and AUC by 33%.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Sparsentan is a substrate of CYP3A. Sparsentan is both an inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A and an inducer of CYP2B6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19.
Transporters: Sparsentan is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP but is not a substrate of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3. Sparsentan is an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B3, and OAT3 but does not inhibit MRP, OATP1B1, NTCP, OCT2, OAT1, MATE1, or MATE2K at relevant concentrations.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis : In the two-year rat carcinogenicity study, there was no evidence of increased incidence of neoplasia in male rats orally administered at 15 mg/kg/day (the only dose evaluated) and in female rats orally administered up to 240 mg/kg/day, which provided an exposure approximately 0.7 times and 26 times the AUC at the MRHD, respectively. In the 26-week transgenic mouse study, there was no evidence of increased incidence of neoplasia in male and female mice orally administered sparsentan at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day.
Mutagenesis : There was no evidence of mutagenicity or clastogenicity for sparsentan in in vitro bacteria reverse mutation and chromosomal aberration assays, or in an in vivo rat micronucleus study.
Impairment of fertility : In a fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, oral administration of sparsentan at doses of 20, 80, and 320 mg/kg/day for at least 36 (females) and 49 (males) days did not result in any adverse effects on estrous cycles, mating, fertility, sperm evaluation, or pregnancy incidence at doses up to 320 mg/kg/day, which provided approximately 10 and 14 times the AUC at the MRHD for males and females, respectively. Male reproductive organ toxicity was not evident in chronic toxicity studies with sparsentan at exposures up to 10 times and 1.3 times the AUC at the MRHD in rats and monkeys, respectively.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effect of FILSPARI on proteinuria and kidney function (estimated glomerular filtration rate, eGFR) was assessed in a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, multicenter, global study (PROTECT, NCT03762850 ) in adults with biopsy-proven primary IgAN, eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , and total urine protein ≥1.0 g/day on a stable dose of maximally-tolerated RAS inhibitor treatment. Patients with chronic kidney disease due to another condition in addition to IgAN or those who had been recently treated with systemic immunosuppressants were excluded.
Patients were randomized (1:1) to either FILSPARI (400 mg once daily following 200 mg once daily for 14 days) or irbesartan (300 mg once daily following 150 mg once daily for 14 days). Rescue immunosuppressive treatment could be initiated per investigator discretion during the trial. Concomitant use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, other RAS inhibitors, and aldosterone blockers were prohibited.
The primary efficacy endpoint for the interim analysis was the change from baseline in urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR) at Week 36 based on the first 281 randomized patients who had reached the Week 36 visit. The key secondary efficacy endpoint for the final analysis was the rate of change in eGFR over a 110-week period following initiation of randomized therapy.
The 404 patients who enrolled and received study medication had a mean age of 46 years (range 18 to 76 years); 70% were male, 67% White, 28% Asian, and 1% Black or African American. Approximately 78% had a history of hypertension, 11% had diabetes or impaired fasting glucose, and 56% had hematuria based on urine dipstick. At baseline, the mean eGFR was 57 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , the geometric mean UPCR was 1.2 g/g, and 49 (12%) patients had proteinuria >3.5 g/24 hours.
Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratio (UPCR)
The trial met the prespecified primary endpoint of relative change from baseline in UPCR at Week 36 based on an interim analysis of 281 randomized patients who had reached the Week 36 visit. The interim analysis showed a 45% decrease in UPCR at Week 36 relative to baseline for patients treated with FILSPARI compared to a 15% decrease for patients treated with irbesartan resulting in a 35% reduction in the ratio of mean UPCR (95% CI: 23% to 45% reduction; p<0.0001). In the final analysis of 404 randomized patients, the treatment effects in UPCR observed at Week 36 and Week 110 were consistent with the results obtained at the interim analysis. The mean percent change from baseline over the course of the double-blind period is displayed in Figure 1 .
| Adjusted GMPC of UPCR was based on MMRM stratified by screening eGFR and total urine protein excretion. MMRM analysis includes UPCR data during the double-blind period up to Week 110 regardless of treatment discontinuation or immunosuppressive therapy initiation. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation under assumptions of missing at random and missing not at random depending on the patient’s intercurrent event status. Baseline was defined as the last non-missing observation on or prior to the start of dosing. Counts in axis table represent number of subjects with observed UPCR data by visit and treatment group. BL=baseline; CI=confidence interval; FAS=full analysis set; GMPC=geometric mean percent change; LS=least squares; MMRM=mixed-model repeated measures; N= number of subjects with available data at the time of analysis; UPCR=urine protein/creatinine ratio. |
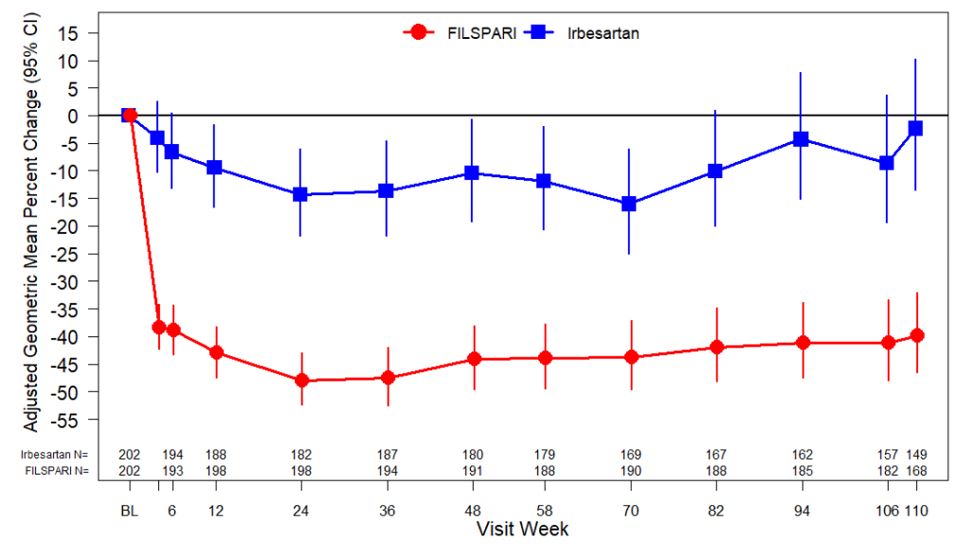 |
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR)
In the final analysis of 404 randomized patients, FILSPARI reduced the rate of decline in kidney function from baseline to Week 110 compared to irbesartan. The mean eGFR slope from baseline to Week 110 was -3.0 mL/min/1.73 m 2 per year for FILSPARI and -4.2 mL/min/1.73 m 2 per year for irbesartan, corresponding to a treatment effect of 1.2 mL/min/1.73 m 2 per year (95 %CI: 0.2 to 2.1; p=0.0168). The mean change from baseline in eGFR during the double-blind period is shown in Figure 2 . The treatment effect on the rate of change in eGFR through Week 110 was generally consistent across key subgroups, including key demographic (such as age, sex, race, ethnicity, and region) and baseline disease (such as baseline BMI and baseline proteinuria) characteristics. The treatment benefit with FILSPARI on the rate of change in eGFR through Week 110 was not evident in patients with an eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; however, there was a small number of patients in this subgroup.
| •eGFR was calculated using the CKD-EPI equation. Baseline was defined as the last non-missing observation on or prior to the start of dosing. The analysis includes eGFR data during the double-blind period up to Week 110 regardless of treatment discontinuation or immunosuppressive therapy initiation. Rescue immunosuppressive treatment for IgAN was initiated in 7 (3%) and 18 (9%) patients in the FILSPARI and irbesartan group respectively. BL=baseline; CI=confidence interval; CKD-EPI=Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; FAS=full analysis set; IgAN=immunoglobulin A nephropathy; LS=least squares; N=number of subjects with available data at the time of analysis. |
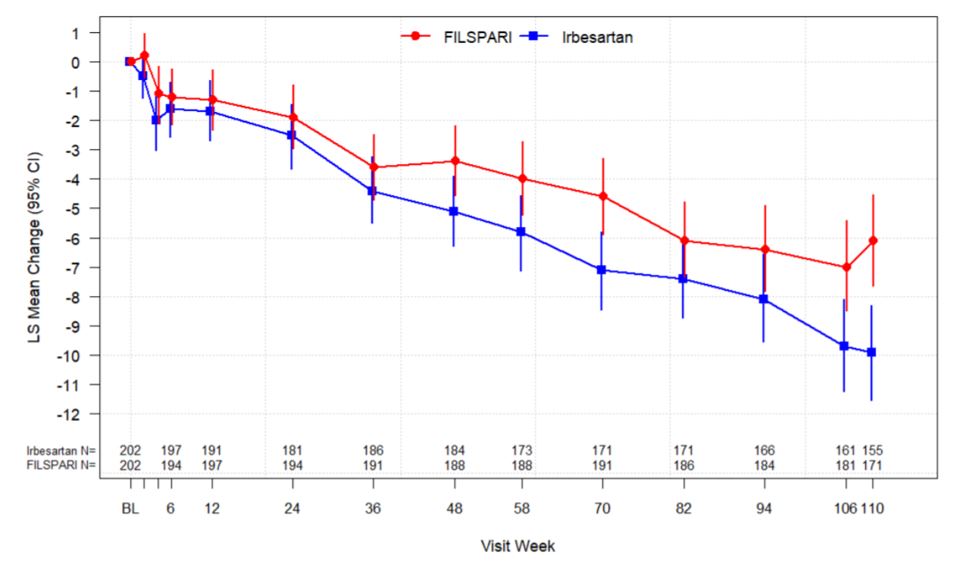 |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FILSPARI is supplied in bottles of 30 film-coated tablets.
- 200 mg tablets are film-coated, modified oval, white to off-white, debossed with “105” on one side and plain on the other side, available in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant caps (NDC 68974-200-30).
- 400 mg tablets are film-coated, modified oval, white to off-white, debossed with “021” on one side and plain on the other side, available in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant caps (NDC 68974-400-30).
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store FILSPARI in its original container.
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sparsentan is a single molecule with antagonism of the endothelin type A receptor (ET A R) and the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT 1 R). Sparsentan has high affinity for both the ET A R (Ki= 12.8 nM) and the AT 1 R (Ki=0.36 nM), and greater than 500-fold selectivity for these receptors over the endothelin type B and angiotensin II subtype 2 receptors. Endothelin 1 and angiotensin II are thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of IgAN via the ETAR and AT1R, respectively.