Get your patient on Fyarro (Sirolimus)
Fyarro prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Fyarro patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dosage of FYARRO is 100 mg/m 2 administered as an IV infusion over 30 minutes on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of FYARRO is 100 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Table 1 lists the recommended dose reductions of FYARRO for adverse reactions.
| Dose Reduction | Dose |
| First Dose Reduction | 75 mg/m 2 (25% reduction from 100 mg/m 2 ) |
| Second Dose Reduction | 56 mg/m 2 (25% reduction from 75 mg/m 2 ) |
| Third Dose Reduction Permanently discontinue FYARRO in patients who are unable to tolerate FYARRO after three dose reductions. | 45 mg/m 2 (20% reduction from 56 mg/m 2 ) |
Table 2 lists the recommended dosage modifications of FYARRO for adverse reactions.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Severity based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03. | Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| Stomatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )] | Grade ≥3 |
|
| Interstitial Lung Disease / Non- Infectious Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
|
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with CYP3A4 and/or P-gp Inhibitors and Inducers
Reduce the dosage of FYARRO to 56 mg/m 2 when used concomitantly with a moderate or weak cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitor. Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are strong CYP3A4 and/or P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors and inducers and with grapefruit and grapefruit juice [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage modification of FYARRO in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment is described in Table 3 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Closely monitor patients with hepatic impairment for increased toxicity. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 )] .
| Hepatic Impairment (based on NCI criteria) | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Mild (total bilirubin ≤ULN, AST >ULN or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5×ULN, any AST) | 75 mg/m 2 |
| Moderate (total bilirubin >1.5 to 3.0×ULN, any AST) | 56 mg/m 2 |
Preparation and Administration
FYARRO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1
FYARRO is supplied as a sterile lyophilized powder for reconstitution before use. READ ENTIRE PREPARATION INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO RECONSTITUTION.
Preparation:
1.000000000000000e+00 Aseptically, reconstitute each vial by injecting 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
2.000000000000000e+00 Slowly inject the 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, over a minimum of 1 minute, using the sterile syringe to direct the solution flow onto the INSIDE WALL OF THE VIAL.
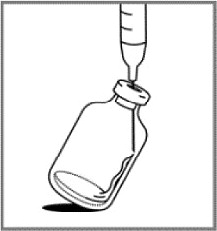
3.000000000000000e+00 DO NOT INJECT the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, directly on to the lyophilized powder, which has a cake-like appearance, as this will result in foaming.
4.000000000000000e+00 Once the injection is complete, allow the vial to sit for a minimum of 5 minutes to ensure proper wetting of the lyophilized powder.
5.000000000000000e+00 Gently swirl and/or invert the vial slowly for at least 2 minutes until complete dissolution of any powder occurs. Avoid shaking the vial to prevent the generation of foam.
6 . If foaming or clumping occurs, let suspension stand for at least 15 minutes until foam subsides. If foaming or clumping is present after one hour, do not use the reconstituted suspension.
Each mL of the reconstituted formulation will contain 5 mg sirolimus.
The reconstituted suspension should be milky and homogenous without visible particulates. If particulates or settling are visible, the vial should be gently inverted again to ensure complete resuspension prior to use. Discard the reconstituted suspension if precipitates are observed. Discard any unused portion.
7.000000000000000e+00 Transfer the volume of FYARRO required for the calculated dose into an empty sterile PVC or polyolefin infusion bag for administration without further dilution.
The use of medical devices containing silicone oil as a lubricant (e.g., syringes and intravenous bags) to reconstitute and administer FYARRO may result in the formation of proteinaceous strands.
Visually inspect reconstituted FYARRO suspension in the infusion bag prior to administration. Discard reconstituted suspension if particulate matter, proteinaceous strands, or discoloration are observed.
Administration:
Administer the reconstituted FYARRO suspension intravenously over 30 minutes.
Stability
Unopened vials of FYARRO are stable until the date indicated on the package when stored between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original package. Neither freezing nor thawing adversely affects the stability of the product.
Stability of Reconstituted Suspension in the Vial
Reconstituted FYARRO in the vial should be used immediately but may be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for a maximum of 6 hours stored in the original carton to protect it from light. Discard any unused portion.
Stability of Reconstituted Suspension in the Infusion Bag
The suspension for infusion when prepared as recommended in an infusion bag should be used immediately but may be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and protected from light for a maximum of 9 hours.
The total maximum combined refrigerated storage time of reconstituted FYARRO in the vial and in the infusion bag is 15 hours. This may be followed by storage in the infusion bag at ambient temperature (approximately 25°C) and lighting conditions for a maximum of 4 hours. Discard any unused portion.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Fyarro prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FYARRO ™ is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dosage of FYARRO is 100 mg/m 2 administered as an IV infusion over 30 minutes on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of FYARRO is 100 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Table 1 lists the recommended dose reductions of FYARRO for adverse reactions.
| Dose Reduction | Dose |
| First Dose Reduction | 75 mg/m 2 (25% reduction from 100 mg/m 2 ) |
| Second Dose Reduction | 56 mg/m 2 (25% reduction from 75 mg/m 2 ) |
| Third Dose Reduction Permanently discontinue FYARRO in patients who are unable to tolerate FYARRO after three dose reductions. | 45 mg/m 2 (20% reduction from 56 mg/m 2 ) |
Table 2 lists the recommended dosage modifications of FYARRO for adverse reactions.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Severity based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03. | Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| Stomatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )] | Grade ≥3 |
|
| Interstitial Lung Disease / Non- Infectious Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade ≥3 |
| |
| Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
|
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with CYP3A4 and/or P-gp Inhibitors and Inducers
Reduce the dosage of FYARRO to 56 mg/m 2 when used concomitantly with a moderate or weak cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitor. Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are strong CYP3A4 and/or P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors and inducers and with grapefruit and grapefruit juice [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage modification of FYARRO in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment is described in Table 3 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Closely monitor patients with hepatic impairment for increased toxicity. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 )] .
| Hepatic Impairment (based on NCI criteria) | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Mild (total bilirubin ≤ULN, AST >ULN or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5×ULN, any AST) | 75 mg/m 2 |
| Moderate (total bilirubin >1.5 to 3.0×ULN, any AST) | 56 mg/m 2 |
Preparation and Administration
FYARRO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1
FYARRO is supplied as a sterile lyophilized powder for reconstitution before use. READ ENTIRE PREPARATION INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO RECONSTITUTION.
Preparation:
1.000000000000000e+00 Aseptically, reconstitute each vial by injecting 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
2.000000000000000e+00 Slowly inject the 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, over a minimum of 1 minute, using the sterile syringe to direct the solution flow onto the INSIDE WALL OF THE VIAL.

3.000000000000000e+00 DO NOT INJECT the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, directly on to the lyophilized powder, which has a cake-like appearance, as this will result in foaming.
4.000000000000000e+00 Once the injection is complete, allow the vial to sit for a minimum of 5 minutes to ensure proper wetting of the lyophilized powder.
5.000000000000000e+00 Gently swirl and/or invert the vial slowly for at least 2 minutes until complete dissolution of any powder occurs. Avoid shaking the vial to prevent the generation of foam.
6 . If foaming or clumping occurs, let suspension stand for at least 15 minutes until foam subsides. If foaming or clumping is present after one hour, do not use the reconstituted suspension.
Each mL of the reconstituted formulation will contain 5 mg sirolimus.
The reconstituted suspension should be milky and homogenous without visible particulates. If particulates or settling are visible, the vial should be gently inverted again to ensure complete resuspension prior to use. Discard the reconstituted suspension if precipitates are observed. Discard any unused portion.
7.000000000000000e+00 Transfer the volume of FYARRO required for the calculated dose into an empty sterile PVC or polyolefin infusion bag for administration without further dilution.
The use of medical devices containing silicone oil as a lubricant (e.g., syringes and intravenous bags) to reconstitute and administer FYARRO may result in the formation of proteinaceous strands.
Visually inspect reconstituted FYARRO suspension in the infusion bag prior to administration. Discard reconstituted suspension if particulate matter, proteinaceous strands, or discoloration are observed.
Administration:
Administer the reconstituted FYARRO suspension intravenously over 30 minutes.
Stability
Unopened vials of FYARRO are stable until the date indicated on the package when stored between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original package. Neither freezing nor thawing adversely affects the stability of the product.
Stability of Reconstituted Suspension in the Vial
Reconstituted FYARRO in the vial should be used immediately but may be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for a maximum of 6 hours stored in the original carton to protect it from light. Discard any unused portion.
Stability of Reconstituted Suspension in the Infusion Bag
The suspension for infusion when prepared as recommended in an infusion bag should be used immediately but may be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and protected from light for a maximum of 9 hours.
The total maximum combined refrigerated storage time of reconstituted FYARRO in the vial and in the infusion bag is 15 hours. This may be followed by storage in the infusion bag at ambient temperature (approximately 25°C) and lighting conditions for a maximum of 4 hours. Discard any unused portion.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injectable suspension: white to yellow, sterile lyophilized powder containing 100 mg of sirolimus formulated as albumin-bound particles in single-dose vial for reconstitution.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Hepatic Impairment : Reduce the dose of FYARRO in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.4 , 8.6 )
- Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential : May impair fertility in females and males. (5.9 , 5.10 , 8.3 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal studies and the mechanism of action, FYARRO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] . Although there are no data on the use of FYARRO in pregnant women, there are limited data on the use of sirolimus during pregnancy. In animal studies, oral sirolimus was embryo/fetotoxic in rats [see Data ] at sub-therapeutic doses. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproductive studies in animals have not been performed with FYARRO. Studies with an oral formulation of sirolimus have shown that it crosses the placenta and is toxic to the conceptus.
In rat embryo-fetal development studies, pregnant rats were administered an oral formulation of sirolimus during the period of organogenesis (Gestational Day 6-15). Sirolimus produced embryo-fetal lethality at 0.5 mg/kg and reduced fetal weight at 1 mg/kg. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for fetal toxicity in rats was 0.1 mg/kg. Maternal toxicity (weight loss) was observed at 2 mg/kg. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 1 mg/kg.
In rabbit embryo-fetal development studies, pregnant rabbits were administered an oral formulation of sirolimus during the period of organogenesis (Gestational Day 6-18). There were no effects on embryo-fetal development at doses up to 0.05 mg/kg; however, at doses of 0.05 mg/kg and above, the ability to sustain a pregnancy was impaired (i.e., embryo-fetal abortion or early resorption). Maternal toxicity (decreased body weight) was observed at 0.05 mg/kg. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 0.025 mg/kg.
In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, pregnant females were dosed with an oral formation of sirolimus during gestation and lactation (Gestational Day 6 through Lactation Day 20). An increased incidence of dead pups occurred at 0.5 mg/kg, resulting in reduced live litter size. At 0.1 mg/kg, there were no adverse effects on offspring. Sirolimus did not cause maternal toxicity or affect developmental parameters in the surviving offspring (e.g., morphological development, motor activity, learning, or fertility assessment) at 0.5 mg/kg, the highest oral dose tested.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of FYARRO in human milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production.
It is not known whether sirolimus is present in human milk. There are no data on its effects on the breastfed infant or milk production. The pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of sirolimus in infants are not known. Sirolimus is present in the milk of lactating rats. There is potential for serious adverse effects from sirolimus in breastfed infants based on mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from FYARRO, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with FYARRO and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
FYARRO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating FYARRO.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FYARRO and for 12 weeks after the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FYARRO and for 12 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Although there are no data on the impact of FYARRO on fertility, based on available clinical findings with oral formulation of sirolimus and findings in animals, male and female fertility may be compromised by the treatment with FYARRO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 ), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] . Ovarian cysts and menstrual disorders (including amenorrhea and menorrhagia) have been reported in females with the use of oral formulation of sirolimus. Azoospermia has been reported in males with the use of oral formulation sirolimus and has been reversible upon discontinuation in most cases.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of FYARRO in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 34 patients treated with FYARRO, 44% were 65 years of age and older, and 6% were 75 years of age and older. Clinical studies of FYARRO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Hepatic Impairment
CONTRAINDICATIONS
FYARRO is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity to sirolimus, other rapamycin derivatives, or albumin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Stomatitis : Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.1 )
- Myelosuppression : Monitor blood counts prior to and during FYARRO treatment as clinically indicated. Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.2 )
- Infections : May result from immunosuppression. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.3 )
- Hypokalemia and hyperglycemia : Monitor serum potassium and glucose prior to starting FYARRO and as clinically indicated. Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.4 , 5.5 )
- ILD/Non-Infectious Pneumonitis : Monitor for new or worsening respiratory symptoms or radiological changes. Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.6 )
- Hemorrhage : Monitor for signs and symptoms. Withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.7 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions : Monitor for hypersensitivity during and following each FYARRO infusion. Monitor for at least 2 hours following completion of the first infusion and as clinically indicated for each subsequent infusion. Reduce the rate, interrupt infusion, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.8 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential hazard to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.9 )
- Male Infertility : Azoospermia or oligospermia may occur. (5.10 )
- Immunizations : Avoid live vaccines (5.11 )
Stomatitis
Stomatitis, including mouth ulcers and oral mucositis, occurred in 79% of patients treated with FYARRO, including 18% Grade 3. Stomatitis was most often first reported within 8 weeks of treatment. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )]
Myelosuppression
FYARRO can cause myelosuppression including anemia, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Anemia occurred in 68% of patients; 6% were Grade 3. Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia occurred in 35% of patients each.
Obtain blood counts at baseline and every 2 months for the first year of treatment and every 3 months thereafter, or more frequently if clinically indicated. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Infections
FYARRO can cause infections. Infections such as urinary tract infections (UTI), upper respiratory tract infections and sinusitis occurred in 59% of patients. Grade 3 infections occurred in 12% of patients, including a single case each of a UTI, pneumonia, skin, and abdominal infections. Monitor patients for infections, including opportunistic infections. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Hypokalemia
FYARRO can cause hypokalemia. Hypokalemia occurred in 44% of patients, including 12% Grade 3 events. Monitor potassium levels prior to starting FYARRO and implement potassium supplementation as medically indicated. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Hyperglycemia
FYARRO can cause hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia occurred in 12% of patients treated with FYARRO, all of which were Grade 3 events. Monitor fasting serum glucose prior to starting FYARRO. During treatment, monitor serum glucose every 3 months in non-diabetic patients, or as clinically indicated. Monitor serum glucose more frequently in diabetic patients. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Interstitial Lung Disease / Non-Infectious Pneumonitis
FYARRO can cause interstitial lung disease (ILD) / non-infectious pneumonitis. ILD / non-infectious pneumonitis occurred in 18% of patients treated with FYARRO, of which all were Grades 1 or 2. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Hemorrhage
FYARRO can cause serious and sometimes fatal hemorrhage. Hemorrhage occurred in 24% of patients treated with FYARRO, including Grade 3 and Grade 5 events in 2.9% of patients each [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue FYARRO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
FYARRO can cause hypersensitivity reactions [see Contraindications (4 )] .
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis and hypersensitivity vasculitis have been observed with administration of the oral formulation of sirolimus.
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been observed with human albumin administration.
Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of infusion reactions during and following each FYARRO infusion in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available. Monitor patients for at least 2 hours after the first infusion and as clinically needed for each subsequent infusion.
Reduce the rate, interrupt infusion, or permanently discontinue FYARRO based on severity and institute appropriate medical management as needed.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on animal studies and the mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] , FYARRO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal studies, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) inhibitors caused embryo-fetal toxicity when administered during the period of organogenesis at maternal exposures that were equal to or less than human exposures at the recommended lowest starting dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to avoid becoming pregnant and to use effective contraception while using FYARRO and for 12 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
Male Infertility
Immunizations and Risks Associated with Live Vaccines
No studies in conjunction with immunization have been conducted with FYARRO. Immunization during FYARRO treatment may be ineffective. Update immunizations according to immunization guidelines prior to initiating FYARRO, if possible. Immunization with live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and avoid close contact with those who have received live vaccines while on FYARRO. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of FYARRO should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines for patients on immunosuppressive therapies.
Risk of Transmission of Infectious Agents with Human Albumin
FYARRO contains human albumin, a derivative of human blood. Human albumin carries only a remote risk of transmission of viral diseases because of effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes. A theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) also is considered extremely remote. No cases of transmission of viral diseases or CJD have ever been associated with albumin.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been associated with FYARRO in clinical trials and are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label [see Warnings and Precautions (5 )] .
Stomatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) / Non-Infectious Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of FYARRO was assessed in a single-arm study (AMPECT). Thirty-four patients received FYARRO 100 mg/m 2 on Days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Among the 34 patients who received FYARRO, 16 (47%) were exposed for 6 months or longer and 7 (21%) were exposed for greater than 1 year.
The median age of patients who received FYARRO was 59.5 years (range 27 to 78 years), 82% were female and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status was 0 (76%) or 1 (24%). Race was 71% White, 9% Black, 9% Asian, 3% Hawaiian/Pacific Islander and 9% Other/Not Reported. Ethnicity was 82% not Hispanic or Latino, 15% Hispanic or Latino, and 3% Not Reported.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14 (41%) patients who received FYARRO. Serious adverse reactions in >5% of patients, including 4 (12%) patients with infection and 2 (6%) patients each with abdominal pain, dehydration, and upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1 (2.9%) patient who received FYARRO and experienced upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Permanent discontinuation of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3 (9%) patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of FYARRO included pneumonitis, anemia, and noninfective cystitis.
Dosage interruptions of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 22 (65%) patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >5% of patients included stomatitis in 6 (18%) patients, pneumonitis in 5 (15%) patients, anemia in 3 (9%) patients, and dehydration, dermatitis acneiform, and thrombocytopenia in 2 (6%) patients each.
Dose reductions of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 12 (35%) patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in >5% of patients included stomatitis and pneumonitis in 3 (9%) patients each.
The most common adverse reactions (≥30%) were stomatitis in 27 (79%) patients, fatigue and rash in 23 (68%) patients each, infection in 20 (59%) patients, nausea and edema in 17 (50%) patients each, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain and decreased weight in 16 (47%) patients each, decreased appetite in 15 (44%) patients, cough in 12 (35%) patients, and vomiting and dysgeusia in 11 (32%) patients each. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥6%) were decreased lymphocytes in 7 (21%) patients, increased glucose and decreased potassium in 4 (12%) patients each, decreased phosphate in 3 (9%) patients, and decreased hemoglobin and increased lipase in 2 (6%) patients each.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions in AMPECT.
| FYARRO (N=34) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 4 No Grade 4 reactions were reported (%) |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Stomatitis Includes stomatitis, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, esophageal ulcer | 79 | 18 |
| Nausea | 50 | 0 |
| Diarrhea Includes diarrhea and enteritis | 47 | 2.9 |
| Vomiting | 32 | 2.9 |
| Abdominal Pain Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and epigastric discomfort | 29 | 6 |
| Constipation | 24 | 2.9 |
| Dry Mouth | 15 | 0 |
| Hemorrhoids | 12 | 0 |
| General disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 68 | 2.9 |
| Edema Includes face edema, generalized edema, edema, edema peripheral, and periorbital edema | 50 | 2.9 |
| Pyrexia | 24 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Includes dermatitis acneiform, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, and skin exfoliation | 68 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 24 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 18 | 0 |
| Dry Skin | 12 | 0 |
| Nail disorder | 12 | 0 |
| Infections | ||
| Infections Includes all reported infections, including but not limited to, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, sinusitis , skin infection, folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngitis streptococcal, pneumonia, vaginal infection | 59 | 12 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | ||
| Decreased appetite | 44 | 0 |
| Dehydration | 15 | 6 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Dysgeusia | 32 | 0 |
| Headache | 29 | 0 |
| Peripheral neuropathy Includes dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy | 15 | 0 |
| Dizziness Includes dizziness, dizziness postural, and vertigo | 12 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Weight decreased | 47 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain Includes arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity | 47 | 2.9 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough Includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome | 35 | 0 |
| Pneumonitis | 18 | 0 |
| Dyspnea Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional | 12 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 29 | 2.9 |
| Hemorrhage Includes epistaxis, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, post procedural hemorrhage, and upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Includes one fatal adverse reaction of upper GI hemorrhage | 24 | 2.9 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 21 | 2.9 |
| Eye disorders | ||
| Vision blurred | 12 | 0 |
| Grading according to NCI CTCAE Version 4.03 | ||
Table 5 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in AMPECT.
| FYARRO The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 33 to 34 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. (N=34) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality Grading according to NCI CTCAE Version 4.03 | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 82 | 21 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 68 | 6 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 41 | 0 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 35 | 0 |
| Decreased platelets | 35 | 0 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased creatinine | 82 | 0 |
| Increased triglycerides | 52 | 0 |
| Increased cholesterol | 48 | 3 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 47 | 2.9 |
| Decreased potassium | 44 | 12 |
| Decreased magnesium | 42 | 0 |
| Decreased albumin | 35 | 2.9 |
| Increased aspartate transaminase (AST) | 32 | 2.9 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 29 | 0 |
| Decreased sodium | 24 | 2.9 |
| Decreased calcium | 15 | 0 |
| Decreased glucose | 15 | 0 |
| Decreased phosphate | 15 | 9 |
| Increased lipase | 12 | 6 |
| Increased glucose | 12 | 12 |
| Increased sodium | 12 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients included enteritis, edema, pancytopenia, acute kidney injury, and acute coronary syndrome.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of Other Drugs on FYARRO
CYP3A4 and/or P-gp Inhibitors or Inducers
CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inhibitors may increase sirolimus concentrations, which may increase the risk of FYARRO adverse reactions. CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inducers may decrease sirolimus concentrations, which may reduce FYARRO effectiveness.
- Strong CYP3A4 and/or P-gp Inhibitors or Inducers: Avoid concomitant use of FYARRO with strong CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
- Grapefruit or Grapefruit Juice: Avoid concomitant use of FYARRO with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
- Moderate or Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Reduce the dosage of FYARRO when used concomitantly with a moderate or weak CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
- Moderate or Weak CYP3A4 Inducers: Use of FYARRO may result in decreased effectiveness.
DESCRIPTION
FYARRO (sirolimus protein-bound particles for injectable suspension) (albumin-bound) is sirolimus formulated as albumin-bound nanoparticles. The active ingredient in FYARRO is sirolimus bound to albumin which exists in the nanoparticles in a non-crystalline, amorphous state.
Sirolimus is a mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) inhibitor. Sirolimus is a macrocyclic lactone produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus . The chemical name of sirolimus is [3S[3R•[S•(1R•,3S•,4S•)),6S•,7E,9S•,10S•,12S•,14R•,15E,17E,19E,21R•,23R•,26S•, 27S•,3 4aR•]]- 9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-Hexadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy 3-[2-(4-hydroxy-3- methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethyl]-10,21-dimethoxy-6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-23,27-epoxy-3H- pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone. Its empirical formula is C 51 H 79 NO 13 , and the molecular weight is 914.2. The structural formula of sirolimus is illustrated as follows:
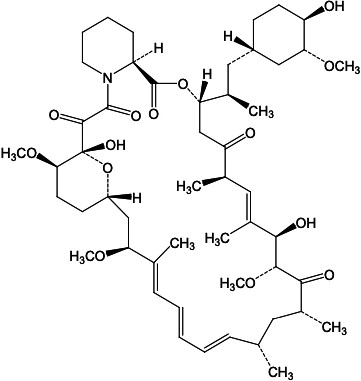
Sirolimus is a white to off-white crystalline powder and is insoluble in water but freely soluble in benzyl alcohol, chloroform, acetone, and acetonitrile.
FYARRO is supplied as a white to yellow, sterile, lyophilized powder for reconstitution with 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP prior to intravenous infusion. Each single-dose vial contains 100 mg of sirolimus (bound to human albumin) and approximately 850 mg of human albumin (containing sodium caprylate and sodium acetyltryptophanate). Each milliliter (mL) of reconstituted suspension contains 5 mg sirolimus formulated as albumin-bound particles.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sirolimus in FYARRO is an inhibitor of mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR, previously known as mammalian target of rapamycin). mTOR, a serine threonine kinase, is downstream of the PI3K/AKT pathway, controls key cellular processes such as cell survival, growth, and proliferation, and is commonly dysregulated in several human cancers. In cells, sirolimus binds to the immunophilin, FK Binding Protein-12 (FKBP-12), to generate an immunosuppressive complex. The sirolimus-FKBP-12 complex binds to and inhibits activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Inhibition of mTOR by sirolimus has been shown to reduce cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and glucose uptake in in vitro and in vivo studies. In a nonclinical study in athymic mice bearing human tumor xenografts, intravenous administration of FYARRO resulted in higher tumor accumulation of sirolimus, inhibition of an mTOR target in the tumor, and tumor growth inhibition compared to administration of an oral formulation of sirolimus at the same weekly total dose.
Pharmacodynamics
Sirolimus exposure-response relationship has not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of FYARRO on the QTc interval has not been adequately characterized.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following administration of FYARRO at the recommended dosage, the estimated mean (%CV) C max and AUC 0-inf of sirolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors were 2590 ng/mL (30% CV) and 22100 ng∙h/mL (50% CV), respectively.
Distribution
The protein binding of sirolimus is >99%, primarily to serum albumin in vitro .
Elimination
The mean elimination half-life of sirolimus is approximately 59 hours (41% CV).
Metabolism
Sirolimus is metabolized by CYP3A4.
Excretion
Following a single radiolabeled sirolimus oral dose to human subjects, 91% and 2% of the radioactivity was recovered in feces and urine, respectively.
Specific Populations
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of sirolimus based on age (18 to 78 years), sex, mild or moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to 89 mL/min). The effect of race, severe renal impairment, and hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sirolimus is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
No studies evaluating the drug interaction potential of FYARRO have been conducted.
Sirolimus is a substrate for both CYP3A4 and P-gp.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity, mutagenesis, or fertility studies were conducted with FYARRO.
Carcinogenicity studies have been conducted in mice and rats with an oral formulation of sirolimus. In an 86-week female mouse study, there was a statistically significant increase in malignant lymphoma at all dose levels compared with controls. In a second mouse study, hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma in males were considered sirolimus-related. In a 104-week rat study, there were no significant findings.
Sirolimus was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, a Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosomal aberration assay, a mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay, or an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
When female rats were treated by gavage with an oral formulation of sirolimus and mated to untreated males, female fertility was decreased at 0.5 mg/kg due to decreased implantation. In addition, reduced ovary and uterus weight were observed. The NOAEL for female rat fertility was 0.1 mg/kg.
When male rats were treated by gavage with an oral formulation of sirolimus and mated to untreated females, male fertility was decreased at 2 mg/kg. Atrophy of testes, epididymides, prostate, seminiferous tubules, and reduced sperm counts were observed. The NOAEL for male rat fertility was 0.5 mg/kg.
Testicular tubular degeneration was also seen in a 4-week intravenous study of sirolimus in monkeys at 0.1 mg/kg.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of FYARRO was assessed in a single-arm study (AMPECT). Thirty-four patients received FYARRO 100 mg/m 2 on Days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Among the 34 patients who received FYARRO, 16 (47%) were exposed for 6 months or longer and 7 (21%) were exposed for greater than 1 year.
The median age of patients who received FYARRO was 59.5 years (range 27 to 78 years), 82% were female and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status was 0 (76%) or 1 (24%). Race was 71% White, 9% Black, 9% Asian, 3% Hawaiian/Pacific Islander and 9% Other/Not Reported. Ethnicity was 82% not Hispanic or Latino, 15% Hispanic or Latino, and 3% Not Reported.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14 (41%) patients who received FYARRO. Serious adverse reactions in >5% of patients, including 4 (12%) patients with infection and 2 (6%) patients each with abdominal pain, dehydration, and upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1 (2.9%) patient who received FYARRO and experienced upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Permanent discontinuation of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3 (9%) patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of FYARRO included pneumonitis, anemia, and noninfective cystitis.
Dosage interruptions of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 22 (65%) patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >5% of patients included stomatitis in 6 (18%) patients, pneumonitis in 5 (15%) patients, anemia in 3 (9%) patients, and dehydration, dermatitis acneiform, and thrombocytopenia in 2 (6%) patients each.
Dose reductions of FYARRO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 12 (35%) patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in >5% of patients included stomatitis and pneumonitis in 3 (9%) patients each.
The most common adverse reactions (≥30%) were stomatitis in 27 (79%) patients, fatigue and rash in 23 (68%) patients each, infection in 20 (59%) patients, nausea and edema in 17 (50%) patients each, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain and decreased weight in 16 (47%) patients each, decreased appetite in 15 (44%) patients, cough in 12 (35%) patients, and vomiting and dysgeusia in 11 (32%) patients each. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥6%) were decreased lymphocytes in 7 (21%) patients, increased glucose and decreased potassium in 4 (12%) patients each, decreased phosphate in 3 (9%) patients, and decreased hemoglobin and increased lipase in 2 (6%) patients each.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions in AMPECT.
| FYARRO (N=34) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 4 No Grade 4 reactions were reported (%) |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Stomatitis Includes stomatitis, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, esophageal ulcer | 79 | 18 |
| Nausea | 50 | 0 |
| Diarrhea Includes diarrhea and enteritis | 47 | 2.9 |
| Vomiting | 32 | 2.9 |
| Abdominal Pain Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and epigastric discomfort | 29 | 6 |
| Constipation | 24 | 2.9 |
| Dry Mouth | 15 | 0 |
| Hemorrhoids | 12 | 0 |
| General disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 68 | 2.9 |
| Edema Includes face edema, generalized edema, edema, edema peripheral, and periorbital edema | 50 | 2.9 |
| Pyrexia | 24 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Includes dermatitis acneiform, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, and skin exfoliation | 68 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 24 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 18 | 0 |
| Dry Skin | 12 | 0 |
| Nail disorder | 12 | 0 |
| Infections | ||
| Infections Includes all reported infections, including but not limited to, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, sinusitis , skin infection, folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngitis streptococcal, pneumonia, vaginal infection | 59 | 12 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | ||
| Decreased appetite | 44 | 0 |
| Dehydration | 15 | 6 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Dysgeusia | 32 | 0 |
| Headache | 29 | 0 |
| Peripheral neuropathy Includes dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy | 15 | 0 |
| Dizziness Includes dizziness, dizziness postural, and vertigo | 12 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Weight decreased | 47 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain Includes arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity | 47 | 2.9 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough Includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome | 35 | 0 |
| Pneumonitis | 18 | 0 |
| Dyspnea Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional | 12 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 29 | 2.9 |
| Hemorrhage Includes epistaxis, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, post procedural hemorrhage, and upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Includes one fatal adverse reaction of upper GI hemorrhage | 24 | 2.9 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 21 | 2.9 |
| Eye disorders | ||
| Vision blurred | 12 | 0 |
| Grading according to NCI CTCAE Version 4.03 | ||
Table 5 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in AMPECT.
| FYARRO The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 33 to 34 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. (N=34) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality Grading according to NCI CTCAE Version 4.03 | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 82 | 21 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 68 | 6 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 41 | 0 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 35 | 0 |
| Decreased platelets | 35 | 0 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased creatinine | 82 | 0 |
| Increased triglycerides | 52 | 0 |
| Increased cholesterol | 48 | 3 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 47 | 2.9 |
| Decreased potassium | 44 | 12 |
| Decreased magnesium | 42 | 0 |
| Decreased albumin | 35 | 2.9 |
| Increased aspartate transaminase (AST) | 32 | 2.9 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 29 | 0 |
| Decreased sodium | 24 | 2.9 |
| Decreased calcium | 15 | 0 |
| Decreased glucose | 15 | 0 |
| Decreased phosphate | 15 | 9 |
| Increased lipase | 12 | 6 |
| Increased glucose | 12 | 12 |
| Increased sodium | 12 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients included enteritis, edema, pancytopenia, acute kidney injury, and acute coronary syndrome.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FYARRO (sirolimus protein-bound particles for injectable suspension) (albumin-bound) is a white to yellow, sterile lyophilized powder supplied as:
NDC 80803-153-50, 100 mg of sirolimus in a single-dose vial. Each carton contains 1 vial.
Store the vials in the original cartons at 2° to 8°C [USP Refrigerated Temperature] (36° to 46°F).
Retain in the original package to protect from light.
FYARRO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1
Mechanism of Action
Sirolimus in FYARRO is an inhibitor of mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR, previously known as mammalian target of rapamycin). mTOR, a serine threonine kinase, is downstream of the PI3K/AKT pathway, controls key cellular processes such as cell survival, growth, and proliferation, and is commonly dysregulated in several human cancers. In cells, sirolimus binds to the immunophilin, FK Binding Protein-12 (FKBP-12), to generate an immunosuppressive complex. The sirolimus-FKBP-12 complex binds to and inhibits activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Inhibition of mTOR by sirolimus has been shown to reduce cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and glucose uptake in in vitro and in vivo studies. In a nonclinical study in athymic mice bearing human tumor xenografts, intravenous administration of FYARRO resulted in higher tumor accumulation of sirolimus, inhibition of an mTOR target in the tumor, and tumor growth inhibition compared to administration of an oral formulation of sirolimus at the same weekly total dose.