Get your patient on Gilotrif (Afatinib)
Gilotrif prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Gilotrif patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patient Selection for Non-Resistant EGFR Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
Select patients for first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC with GILOTRIF based on the presence of non-resistant EGFR mutations in tumor specimens [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of EGFR mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of GILOTRIF is 40 mg orally once daily until disease progression or no longer tolerated by the patient.
Take GILOTRIF at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
Do not take a missed dose within 12 hours of the next dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Withhold GILOTRIF for:
- Grade• 3 or higher adverse reactions
- Diarrhea of Grade 2 persisting for 2 or more consecutive days while taking anti-diarrheal medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Cutaneous reactions of Grade 2 that are prolonged (lasting more than 7 days) or intolerable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
• National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE), v 3.0
Resume treatment when the adverse reaction fully resolves, returns to baseline, or improves to Grade 1. Reinstitute GILOTRIF at a reduced dose, i.e., 10 mg per day less than the dose at which the adverse reaction occurred.
Permanently discontinue GILOTRIF for:
- Life-threatening bullous, blistering, or exfoliating skin lesions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Confirmed interstitial lung disease (ILD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Severe drug-induced hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Persistent ulcerative keratitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]
- Severe or intolerable adverse reaction occurring at a dose of 20 mg per day
Dosage Modification for Pre-Existing Severe Renal Impairment
The recommended dosage of GILOTRIF in patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR•] 15 to 29 mL/min /1.73 m 2 ) is 30 mg orally once daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
• Use the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD] formula to estimate eGFR.
Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
P-glycoprotein Inhibitors
Reduce GILOTRIF daily dose by 10 mg if not tolerated for patients who require therapy with a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor. Resume the previous dose after discontinuation of the P-gp inhibitor as tolerated [see Drug Interactions (7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
P-glycoprotein Inducers
Increase GILOTRIF daily dose by 10 mg as tolerated for patients who require chronic therapy with a P-gp inducer. Resume the previous dose 2 to 3 days after discontinuation of the P-gp inducer [see Drug Interactions (7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Gilotrif prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GILOTRIF is a kinase inhibitor indicated for:
- First-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have non-resistant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test (1.1 ) Limitations of Use : Safety and efficacy of GILOTRIF were not established in patients whose tumors have resistant EGFR mutations (1.1 )
- Treatment of patients with metastatic, squamous NSCLC progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy (1.2 )
EGFR Mutation-Positive, Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
GILOTRIF is indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have non-resistant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Limitations of Use : The safety and efficacy of GILOTRIF have not been established in patients whose tumors have resistant EGFR mutations [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Previously Treated, Metastatic Squamous NSCLC
GILOTRIF is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patient Selection for Non-Resistant EGFR Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
Select patients for first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC with GILOTRIF based on the presence of non-resistant EGFR mutations in tumor specimens [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of EGFR mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of GILOTRIF is 40 mg orally once daily until disease progression or no longer tolerated by the patient.
Take GILOTRIF at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
Do not take a missed dose within 12 hours of the next dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Withhold GILOTRIF for:
- Grade• 3 or higher adverse reactions
- Diarrhea of Grade 2 persisting for 2 or more consecutive days while taking anti-diarrheal medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Cutaneous reactions of Grade 2 that are prolonged (lasting more than 7 days) or intolerable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
• National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE), v 3.0
Resume treatment when the adverse reaction fully resolves, returns to baseline, or improves to Grade 1. Reinstitute GILOTRIF at a reduced dose, i.e., 10 mg per day less than the dose at which the adverse reaction occurred.
Permanently discontinue GILOTRIF for:
- Life-threatening bullous, blistering, or exfoliating skin lesions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Confirmed interstitial lung disease (ILD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Severe drug-induced hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Persistent ulcerative keratitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]
- Severe or intolerable adverse reaction occurring at a dose of 20 mg per day
Dosage Modification for Pre-Existing Severe Renal Impairment
The recommended dosage of GILOTRIF in patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR•] 15 to 29 mL/min /1.73 m 2 ) is 30 mg orally once daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
• Use the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD] formula to estimate eGFR.
Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
P-glycoprotein Inhibitors
Reduce GILOTRIF daily dose by 10 mg if not tolerated for patients who require therapy with a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor. Resume the previous dose after discontinuation of the P-gp inhibitor as tolerated [see Drug Interactions (7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
P-glycoprotein Inducers
Increase GILOTRIF daily dose by 10 mg as tolerated for patients who require chronic therapy with a P-gp inducer. Resume the previous dose 2 to 3 days after discontinuation of the P-gp inducer [see Drug Interactions (7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GILOTRIF is available as:
- 40 mg tablets: light blue, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T40" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side.
- 30 mg tablets: dark blue, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T30" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side.
- 20 mg tablets: white to slightly yellowish, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T20" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation : Advise women not to breastfeed (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] , GILOTRIF can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of GILOTRIF in pregnant women. Administration of afatinib to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at exposures approximately 0.2 times the exposure in humans at the recommended dose of 40 mg daily resulted in embryotoxicity and, in rabbits showing maternal toxicity, increased abortions at late gestational stages (see Data ) . Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus .
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, administration of afatinib to pregnant animals at doses of 5 mg/kg (approximately 0.2 times the exposure by AUC at the recommended human dose of 40 mg daily) or greater during the period of organogenesis caused increased post-implantation loss, and in animals showing maternal toxicity, abortion at late gestational stages. In the same study, at the high dose level of 10 mg/kg (approximately 0.7 times the exposure by AUC at the recommended human dose of 40 mg daily), there were reduced fetal weights, and increases in the incidence of runts, as well as visceral and dermal variations. In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, there were skeletal alterations consisting of incomplete or delayed ossifications and reduced fetal weight at a dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately twice the exposure based on AUC at the recommended human dose of 40 mg daily).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of afatinib in human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Afatinib was present in the milk of lactating rats (see Data ) . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from GILOTRIF, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with GILOTRIF and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
Data
Afatinib was present in the milk of lactating rats at concentrations 80 and 150 times higher than those found in plasma at 1 and 6 hours after administration.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
GILOTRIF can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GILOTRIF and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose of GILOTRIF [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Infertility
Based on results from an animal fertility study, GILOTRIF may reduce fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known if the effects on fertility are reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ].
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of GILOTRIF in pediatric patients have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of afatinib were assessed, but not established, in a single-arm, open-label, multicenter trial [NCT02372006] which included 37 pediatric patients 2 to <17 years of age with recurrent/refractory solid tumors with known ErbB pathway deregulation who received 80% of the adult dose per body surface area. No new safety signals were observed in pediatric patients in this trial. In these 37 patients, the pharmacokinetic parameters were within range of values in adults.
Geriatric Use
LUX-Lung 3 did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
In LUX-Lung 8, 53% of the 398 patients randomized to receive afatinib were 65 years of age or older and 11% were 75 years or older. In an exploratory subgroup analysis of LUX-Lung 8, the hazard ratio for overall survival (OS) in patients less than 65 years old was 0.68 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.85) and in patients 65 years or older was 0.95 (95% CI: 0.76, 1.19). No overall differences in safety were observed between patients 65 years and older and younger patients.
Renal Impairment
Patients with severe renal impairment have a higher exposure to afatinib than patients with normal renal function. Administer GILOTRIF at a starting dose of 30 mg once daily in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to 29 mL/min /1.73 m 2 as determined by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Adjustments to the starting dose of GILOTRIF are not necessary in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 89 mL/min /1.73 m 2 ). GILOTRIF has not been studied in patients with eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or on dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment
GILOTRIF has not been studied in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment. Adjustments to the starting dose of GILOTRIF are not necessary in patients with mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Closely monitor patients with severe hepatic impairment and adjust GILOTRIF dose if not tolerated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Diarrhea : Diarrhea may result in dehydration and renal failure. Withhold GILOTRIF for severe and prolonged diarrhea not responsive to anti-diarrheal agents. (2.3 , 5.1 )
- Bullous and exfoliative skin disorders : Severe bullous, blistering, and exfoliating lesions occurred in 0.2% of patients. Discontinue for life-threatening cutaneous reactions. Withhold GILOTRIF for severe and prolonged cutaneous reactions. (2.3 , 5.2 )
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD) : Occurs in 1.6% of patients. Withhold GILOTRIF for acute onset or worsening of pulmonary symptoms. Discontinue GILOTRIF if ILD is diagnosed. (2.3 , 5.3 )
- Hepatic toxicity : Fatal hepatic impairment occurs in 0.2% of patients. Monitor with periodic liver testing. Withhold or discontinue GILOTRIF for severe or worsening liver tests. (2.3 , 5.4 )
- Gastrointestinal perforation : Occurs in 0.2% of patients. Permanently discontinue GILOTRIF in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation. (2.3 , 5.5 )
- Keratitis : Occurs in 0.7% of patients. Withhold GILOTRIF for keratitis evaluation. Withhold or discontinue GILOTRIF for confirmed ulcerative keratitis. (2.3 , 5.6 )
- Embryo-fetal toxicity : Can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.7 )
Diarrhea
Diarrhea has resulted in dehydration with or without renal impairment across the clinical experience; some cases were fatal. Grade 3-4 diarrhea occurred in 697 (16%) of the 4257 patients who received GILOTRIF across 44 clinical trials. In LUX-Lung 3, diarrhea occurred in 96% of patients treated with GILOTRIF (n=229), of which 15% were Grade 3 in severity and occurred within the first 6 weeks . Renal impairment as a consequence of diarrhea occurred in 6% of patients treated with GILOTRIF, of which 1.3% were Grade 3. In LUX-Lung 8, diarrhea occurred in 75% of patients treated with GILOTRIF (n=392), of which 10% were Grade 3 in severity and 0.8% were Grade 4 in severity . Renal impairment as a consequence of diarrhea occurred in 7% of patients treated with GILOTRIF, of which 2% were Grade 3 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
For patients who develop prolonged Grade 2 diarrhea lasting more than 48 hours or greater than or equal to Grade 3 diarrhea, withhold GILOTRIF until diarrhea resolves to Grade 1 or less and resume GILOTRIF with appropriate dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ]. Provide patients with an anti-diarrheal agent (e.g., loperamide) for self-administration at the onset of diarrhea and instruct patients to continue anti-diarrheal therapy until loose bowel movements cease for 12 hours.
Bullous and Exfoliative Skin Disorders
Grade 3 cutaneous reactions characterized by bullous, blistering, and exfoliating skin lesions, occurred in 0.2% of the 4257 patients who received GILOTRIF across clinical trials . In LUX-Lung 3, the overall incidence of cutaneous reactions consisting of rash, erythema, and acneiform rash was 90%, and the incidence of Grade 3 cutaneous reactions was 16%. In addition, the incidence of Grade 1-3 palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome was 7%. In LUX-Lung 8, the overall incidence of cutaneous reactions consisting of rash, erythema, and acneiform rash was 70%, and the incidence of Grade 3 cutaneous reactions was 7%. In addition, the incidence of Grade 1-3 palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome was 1.5% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Discontinue GILOTRIF in patients who develop life-threatening bullous, blistering, or exfoliating skin lesions . For patients who develop prolonged Grade 2 cutaneous adverse reactions lasting more than 7 days, intolerable Grade 2 cutaneous reactions, or Grade 3 cutaneous reactions, withhold GILOTRIF until the adverse reaction resolves to Grade 1 or less and resume GILOTRIF with appropriate dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Postmarketing cases consistent with toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS) have been reported in patients receiving GILOTRIF. The cases of TEN and SJS bullous skin reactions result from a distinct and separate mechanism of toxicity than the bullous skin lesions secondary to the pharmacologic action of the drug on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Discontinue GILOTRIF if TEN or SJS is suspected [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease or ILD-like adverse reactions (e.g., lung infiltration, pneumonitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or alveolitis allergic) occurred in 1.6% of the 4257 patients who received GILOTRIF across clinical trials; of these, 0.4% were fatal. The incidence of ILD appeared to be higher in Asian patients (2.3%; 38/1657) as compared to Whites (1.0%; 23/2241). In LUX-Lung 3, the incidence of Grade ≥3 ILD was 1.3% and resulted in death in 1% of GILOTRIF-treated patients. In LUX-Lung 8, the incidence of Grade ≥3 ILD was 0.9% and resulted in death in 0.8% of GILOTRIF-treated patients.
Withhold GILOTRIF during evaluation of patients with suspected ILD and discontinue GILOTRIF in patients with confirmed ILD [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Hepatic Toxicity
In 4257 patients who received GILOTRIF across clinical trials, 9.7% had liver test abnormalities, of which 0.2% were fatal. In LUX-Lung 3, liver test abnormalities of any grade occurred in 17.5% of the patients treated with GILOTRIF, of which 3.5% had Grade 3-4 liver test abnormalities. In LUX-Lung 8, liver test abnormalities of any grade occurred in 6% of the patients treated with GILOTRIF, of which 0.2% had Grade 3-4 liver test abnormalities.
Obtain periodic liver testing in patients during treatment with GILOTRIF. Withhold GILOTRIF in patients who develop worsening of liver function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . In patients who develop severe hepatic impairment while taking GILOTRIF, discontinue treatment.
Gastrointestinal Perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation, including fatal cases, has occurred with GILOTRIF. Gastrointestinal perforation has been reported in 0.2% of patients treated with GILOTRIF among 3213 patients across 17 randomized controlled clinical trials. Patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or anti-angiogenic agents, or patients with increasing age or who have an underlying history of gastrointestinal ulceration, underlying diverticular disease or bowel metastases may be at increased risk of perforation.
Permanently discontinue GILOTRIF in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Keratitis
Keratitis, characterized as acute or worsening eye inflammation, lacrimation, light sensitivity, blurred vision, eye pain, and/or red eye occurred in 0.7% of patients treated with GILOTRIF among 4257 patients across clinical trials, of which 0.05% of patients experienced Grade 3 keratitis. Keratitis was reported in 2.2% patients in LUX-Lung 3, with Grade 3 in 0.4%. In LUX-Lung 8, keratitis was reported in 0.3% patients; there were no patients with ≥Grade 3 keratitis.
Withhold GILOTRIF during evaluation of patients with suspected keratitis, and if diagnosis of ulcerative keratitis is confirmed, interrupt or discontinue GILOTRIF [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . If keratitis is diagnosed, the benefits and risks of continuing treatment should be carefully considered. GILOTRIF should be used with caution in patients with a history of keratitis, ulcerative keratitis, or severe dry eye [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Contact lens use is also a risk factor for keratitis and ulceration.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, GILOTRIF can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of afatinib to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at exposures approximately 0.2 times the exposure in humans at the recommended dose of 40 mg daily resulted in embryotoxicity and, in rabbits showing maternal toxicity, increased abortions at late gestational stages. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose of GILOTRIF [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Bullous and Exfoliative Skin Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Interstitial Lung Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Gastrointestinal Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Keratitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the Warnings and Precautions section reflect exposure to GILOTRIF for clinically significant adverse reactions in 4257 patients enrolled in LUX-Lung 3 (n=229) and LUX-Lung 8 (n=392), and 3636 patients with cancer enrolled in 42 studies of GILOTRIF administered alone or in combination with other anti-neoplastic drugs at GILOTRIF doses ranging from 10-70 mg daily or at doses 10-160 mg in other regimens. The mean exposure was 5.5 months. The population included patients with various cancers, the most common of which were NSCLC, breast, colorectal, brain, and head and neck.
The data described below reflect exposure to GILOTRIF as a single agent in LUX-Lung 3, a randomized, active-controlled trial conducted in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, metastatic NSCLC, and in LUX-Lung 8, a randomized, active-controlled trial in patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy.
EGFR Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
The safety of GILOTRIF was evaluated in 229 EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naïve patients with EGFR mutation-positive, metastatic non-squamous NSCLC enrolled in a randomized (2:1), multicenter, open-label trial (LUX-Lung 3). Patients received either GILOTRIF 40 mg daily until documented disease progression or intolerance to the therapy or pemetrexed 500 mg/m² followed after 30 minutes by cisplatin 75 mg/m² every three weeks for a maximum of six treatment courses. The median exposure was 11 months for patients treated with GILOTRIF and 3.4 months for patients treated with pemetrexed/cisplatin.
The overall trial population had a median age of 61 years; 61% of patients in the GILOTRIF arm and 60% of patients in the pemetrexed/cisplatin arm were younger than 65 years. A total of 64% of patients on GILOTRIF and 67% of pemetrexed/cisplatin patients were female. More than two-thirds of patients were from Asia (GILOTRIF 70%; pemetrexed/cisplatin 72%).
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 29% of patients treated with GILOTRIF. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in patients treated with GILOTRIF were diarrhea (6.6%); vomiting (4.8%); and dyspnea, fatigue, and hypokalemia (1.7% each). Fatal adverse reactions in GILOTRIF-treated patients in LUX-Lung 3 included pulmonary toxicity/ILD-like adverse reactions (1.3%), sepsis (0.43%), and pneumonia (0.43%).
Dose reductions due to adverse reactions were required in 57% of GILOTRIF-treated patients. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to dose reduction in the patients treated with GILOTRIF were diarrhea (20%), rash/acne (19%), paronychia (14%), and stomatitis (10%). Discontinuation of therapy in GILOTRIF-treated patients for adverse reactions was 14.0%. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to discontinuation in GILOTRIF-treated patients were diarrhea (1.3%), ILD (0.9%), and paronychia (0.9%).
Clinical trials of GILOTRIF excluded patients with an abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), i.e., below the institutional lower limit of normal. In LUX-Lung 3, all patients were evaluated for LVEF at screening and every 9 weeks thereafter in the GILOTRIF-treated group and as needed in the pemetrexed/cisplatin group. More GILOTRIF-treated patients (2.2%; n=5) experienced ventricular dysfunction (defined as diastolic dysfunction, left ventricular dysfunction, or ventricular dilation; all
Tables 1 and 2 summarize common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in LUX-Lung 3.
| Adverse Reaction | GILOTRIF n=229 | Pemetrexed/Cisplatin n=111 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 † (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 † (%) | |
| •NCI CTCAE v 3.0 | ||||
| † None of the adverse reactions in this table except stomatitis (one patient on GILOTRIF [0.4%]) were Grade 4 in severity. | ||||
| 1 Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mucosal inflammation, mouth ulceration, oral mucosa erosion, mucosal erosion, mucosal ulceration | ||||
| 2 Includes acne, acne pustular, dermatitis, acneiform dermatitis, dermatosis, drug eruption, erythema, exfoliative rash, folliculitis, rash, rash erythematous, rash follicular, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, skin disorder, skin erosion, skin exfoliation, skin fissures, skin lesion, skin reaction, skin toxicity, skin ulcer | ||||
| 3 Includes paronychia, nail infection, nail bed infection | ||||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 96 | 15 | 23 | 2 |
| Stomatitis 1 | 71 | 9 | 15 | 1 |
| Cheilitis | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash/acneiform dermatitis 2 | 90 | 16 | 11 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 21 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 31 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Infections | ||||
| Paronychia 3 | 58 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Cystitis | 13 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Epistaxis | 17 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Rhinorrhea | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight decreased | 17 | 1 | 14 | 1 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Pyrexia | 12 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Eye disorders | ||||
| Conjunctivitis | 11 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions observed in patients treated with GILOTRIF but that occurred at a higher incidence in pemetrexed/cisplatin-treated patients and not listed elsewhere in section 6 include: decreased appetite (29% Grades 1-4, 4% Grade 3), nausea (25% Grades 1-4, 4% Grade 3), and vomiting (23% Grades 1-4, 4% Grade 3).
| Laboratory Abnormality | GILOTRIF n=229 | Pemetrexed/Cisplatin n=111 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
| •NCI CTCAE v 3.0 | ||||
| Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 54 | 2 | 27 | 1 |
| Increased alkaline phosphate | 51 | 3 | 46 | 1 |
| Decreased creatinine clearance | 49 | 2 | 47 | 1 |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | 46 | 3 | 22 | 1 |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 38 | 9 | 32 | 14 |
| Decreased potassium | 30 | 8 | 11 | 3 |
| Increased bilirubin | 16 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
Previously Treated, Metastatic Squamous NSCLC
The safety of GILOTRIF was evaluated in 392 GILOTRIF-treated patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC enrolled in a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial (LUX-Lung 8). Patients were required to have received at least four cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy, ECOG Performance Status (PS) 0 or 1, and normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Patients received GILOTRIF 40 mg once daily (n=392) or erlotinib 150 mg once daily (n=395). Treatment continued until documented disease progression or intolerance to the therapy. The median exposure was 2.1 months for patients treated with GILOTRIF, 15% were exposed for at least 6 months, and 5% were exposed for at least 12 months.
Among the 392 GILOTRIF-treated patients, the median age was 65 years, 53% were 65 years of age or older, 84% were male, 72% were White, 25% were Asian, ECOG PS 0 (32%) or 1 (68%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 44% of patients treated with GILOTRIF. The most frequent serious adverse reactions in patients treated with GILOTRIF were pneumonia (6.6%), diarrhea (4.6%), and dehydration and dyspnea (3.1% each). Fatal adverse reactions in GILOTRIF-treated patients included ILD (0.5%), pneumonia (0.3%), respiratory failure (0.3%), acute renal failure (0.3%), and general physical health deterioration (0.3%).
The most frequent adverse reactions that led to discontinuation in GILOTRIF-treated patients were diarrhea (4.1%) and rash/acne (2.6%).
Dose reductions due to adverse reactions were required in 27% of GILOTRIF-treated patients and discontinuation of GILOTRIF for adverse reactions was required for 20%. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to dose reduction in the patients treated with GILOTRIF were diarrhea (15%), rash/acne (5.9%), and stomatitis (3.1%).
Tables 3 and 4 summarize common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in LUX-Lung 8.
| Adverse Reaction | GILOTRIF n=392 | Erlotinib n=395 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | |
| •NCI CTCAE v 3.0 | ||||
| 1 Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mucosal inflammation, mouth ulceration, oral mucosa erosion, mucosal erosion, mucosal ulceration | ||||
| 2 Includes acne, dermatitis, acneiform dermatitis, eczema, erythema, exfoliative rash, folliculitis, rash, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, skin exfoliation, skin fissures, skin lesion, skin reaction, skin toxicity, skin ulcer | ||||
| 3 Includes paronychia, nail infection, nail bed infection | ||||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 75 | 11 | 41 | 3 |
| Stomatitis 1 | 30 | 4 | 11 | 1 |
| Nausea | 21 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 13 | 1 | 10 | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash/acneiform dermatitis 2 | 70 | 7 | 70 | 11 |
| Pruritus | 10 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 25 | 3 | 26 | 2 |
| Infections | ||||
| Paronychia 3 | 11 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | GILOTRIF n=392 | Erlotinib n=395 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
| •NCI CTCAE v 3.0 | ||||
| Increased alkaline phosphate | 34 | 2 | 31 | 0 |
| Decreased white blood cell count | 12 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Decreased potassium | 11 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
Other clinically important laboratory abnormalities observed in patients treated with GILOTRIF that are not listed in Table 4 are: increased alanine aminotransferase (10% Grade 1-4; 1% Grade 3-4), increased aspartate aminotransferase (7% Grade 1-4; 1% Grade 3-4), and increased bilirubin (3% Grade 1-4; 0 Grade 3-4).
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions reported in patients treated with GILOTRIF in LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 8 include:
Skin and subcutaneous disorders: nail disorders occurred in 9.2% and 2.8% of patients, respectively.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of GILOTRIF. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Pancreatitis
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis/Stevens Johnson syndrome
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibitors : Co-administration of P-gp inhibitors can increase afatinib exposure. Reduce GILOTRIF by 10 mg per day if not tolerated. (2.5 , 7 )
- P-gp Inducers : Co-administration of chronic P-gp inducers orally can decrease afatinib exposure. Increase GILOTRIF by 10 mg per day as tolerated. (2.5 , 7 )
Effect of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibitors and Inducers
Concomitant taking of P-gp inhibitors (including but not limited to ritonavir, cyclosporine A, ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, verapamil, quinidine, tacrolimus, nelfinavir, saquinavir, and amiodarone) with GILOTRIF can increase exposure to afatinib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Reduce GILOTRIF daily dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Concomitant taking of P-gp inducers (including but not limited to rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, and St. John's wort) with GILOTRIF can decrease exposure to afatinib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Increase GILOTRIF daily dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
DESCRIPTION
GILOTRIF tablets contain afatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor which is a 4-anilinoquinazoline. Afatinib is presented as the dimaleate salt, with the chemical name 2-butenamide, N -[4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-[[(3 S )-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]oxy]-6-quinazolinyl]-4-(dimethylamino)-,(2 E )-, (2 Z )-2-butenedioate (1:2). Its structural formula is:
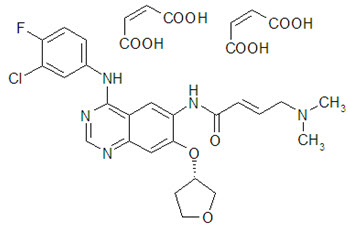
Afatinib dimaleate is a white to brownish yellow powder, water soluble and hygroscopic, with an empirical formula of C 32 H 33 ClFN 5 O 11 , and a molecular weight of 718.1 g/mol.
GILOTRIF tablets for oral administration are available in 40 mg, 30 mg, or 20 mg of afatinib (equivalent to 59.12 mg, 44.34 mg, or 29.56 mg afatinib dimaleate, respectively). The inactive ingredients of GILOTRIF are the following: Tablet Core: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate and Coating: hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide, talc, polysorbate 80, FD&C Blue No. 2 (40 mg and 30 mg tablets only).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Afatinib covalently binds to the kinase domains of EGFR (ErbB1), HER2 (ErbB2), and HER4 (ErbB4) and irreversibly inhibits tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation, resulting in downregulation of ErbB signaling. Certain mutations in EGFR, including non-resistant mutations in its kinase domain, can result in increased autophosphorylation of the receptor, leading to receptor activation, sometimes in the absence of ligand binding, and can support cell proliferation in NSCLC. Non-resistant mutations are defined as those occurring in exons constituting the kinase domain of EGFR that lead to increased receptor activation and where efficacy is predicted by 1) clinically meaningful tumor shrinkage with the recommended dose of afatinib and/or 2) inhibition of cellular proliferation or EGFR tyrosine kinase phosphorylation at concentrations of afatinib sustainable at the recommended dosage according to validated methods. The most commonly found of these mutations are exon 21 L858R substitutions and exon 19 deletions.
Afatinib demonstrated inhibition of autophosphorylation and/or in vitro proliferation of cell lines expressing wild-type EGFR and in those expressing selected EGFR exon 19 deletion mutations, exon 21 L858R mutations, or other less common non-resistant mutations, at afatinib concentrations achieved in patients. In addition, afatinib inhibited in vitro proliferation of cell lines overexpressing HER2.
Treatment with afatinib resulted in inhibition of tumor growth in nude mice implanted with tumors either overexpressing wild type EGFR or HER2 or in an EGFR L858R/T790M double mutant model.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of multiple doses of GILOTRIF (50 mg once daily) on the QTc interval was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm study in patients with relapsed or refractory solid tumors. No large changes in the mean QTc interval (i.e., >20 ms) were detected in the study.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of GILOTRIF tablets, time to peak afatinib plasma concentrations (T max ) is 2 to 5 hours. Maximum concentration (C max ) and area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC 0-INF ) values increased slightly more than dose proportional in the range of 20 to 50 mg. The geometric mean relative bioavailability of 20 mg GILOTRIF tablets was 92% as compared to an oral solution. Steady-state plasma concentrations are achieved within 8 days of repeat dosing of GILOTRIF resulting in an accumulation of 2.8-fold for AUC and 2.1-fold for C max .
Effect of Food
A high-fat meal decreased C max by 50% and AUC 0-INF by 39% relative to the fasted condition [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Distribution
In vitro binding of afatinib to human plasma proteins is approximately 95%.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of afatinib is 37 hours after repeat dosing in cancer patients.
Metabolism
Covalent adducts to proteins are the major circulating metabolites of afatinib and enzymatic metabolism of afatinib is minimal. The metabolites formed by CYP450-dependent reactions were approximately 9% of the total metabolic turnover in sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes. Approximately 2% of the afatinib dose was metabolized by FMO3; the CYP3A4-dependent N-demethylation was not detected.
Excretion
In humans, excretion of afatinib is primarily via the feces (85%) with 4% recovered in the urine following a single oral dose of [ 14 C]-labeled afatinib solution. The parent compound accounted for 88% of the recovered dose.
Specific Populations
Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis, weight, gender, age, and race do not have a clinically important effect on exposure of afatinib.
Patients with Renal Impairment
A pharmacokinetic study was conducted in 14 subjects with normal (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) renal function, 8 subjects with moderate (eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) and 8 subjects with severe (eGFR 15 to 29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) renal impairment. All subjects received a single 40 mg oral dose of GILOTRIF. The geometric mean AUC INF for afatinib was 50% higher in subjects with severe renal impairment and was 22% higher in subjects with moderate renal impairment as compared to subjects with normal renal function. Geometric mean C max was 22% higher in subjects with severe renal impairment and was comparable in subjects with moderate renal impairment to subjects with normal renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] . GILOTRIF has not been studied in patients with eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or on dialysis.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment had no influence on the afatinib exposure following a single dose of GILOTRIF. Subjects with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment have not been studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Drug Interactions Studies
Clincial Studies
Effect of P-gp Inhibitors and Inducers on Afatinib: The effect of ritonavir dosing time relative to a single oral dose of GILOTRIF was evaluated in healthy subjects taking 40 mg of GILOTRIF alone as compared to those after ritonavir (200 mg twice daily for 3 days) co-administration at 6 hours after GILOTRIF administration. The relative bioavailability for AUC 0-INF and C max of afatinib was 119% and 104% when co-administered with ritonavir, and 111% and 105% when ritonavir was administered 6 hours after taking GILOTRIF. In another study, when ritonavir (200 mg twice daily for 3 days) was administered 1 hour before a 20 mg single dose of GILOTRIF, exposure to afatinib increased by 48% for AUC 0-INF and 39% for C max [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Pre-treatment with a potent inducer of P-gp, rifampicin (600 mg once daily for 7 days) decreased the plasma exposure to afatinib by 34% (AUC 0-INF ) and 22% (C max ) [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Afatinib on P-gp: Based on in vitro data, afatinib is an inhibitor of P-gp.
Interaction of Afatinib with BCRP: Based on in vitro data, afatinib is a substrate and an inhibitor of the transporter BCRP.
Effect of Afatinib on CYP450 Enzymes: Afatinib is not an inhibitor or an inducer of CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4) in cultured primary human hepatocytes.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with afatinib.
A marginal response to afatinib was observed in a single tester strain of a bacterial (Ames) mutagenicity assay. No mutagenic or genotoxic potential was identified in an in vitro chromosomal aberration test at non-cytotoxic concentrations as well as in the in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay, the in vivo Comet assay, and an in vivo 4-week oral mutation study in the Muta ™ Mouse.
In a dedicated fertility study, male and female rats received afatinib daily by oral administration at doses of 4, 6, or 8 mg/kg. In males at doses of 6 mg/kg (approximately equal to the exposure by AUC in patients at the recommended human dose of 40 mg daily) or greater, there was an increase in the incidence of low or no sperm count, though overall fertility was not affected; decreases in sperm count were supported by findings of increased apoptosis in the testes and atrophy in the seminal vesicles and the prostate in general toxicology studies. In females at the high dose of 8 mg/kg (approximately 0.63 times the exposure by AUC in patients at the recommended human dose of 40 mg daily), there was a mild decrease in the number of corpora lutea along with a mild increase in post-implantation loss due to early resorptions. In a 4-week general toxicology study, female rats had decreases in ovarian weights at all dose levels; organ weight had not fully recovered by the end of a 2-week recovery period.
CLINICAL STUDIES
EGFR Mutation-Positive, Metastatic NSCLC
The efficacy of GILOTRIF for the first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive, metastatic [Stage IV and Stage IIIb with pleural and/or pericardial effusion as classified by the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC, 6th edition)] NSCLC was established in a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial (LUX-Lung 3 [NCT00949650]). Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive GILOTRIF 40 mg orally once daily (n=230) or intravenous pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) plus cisplatin (75 mg/m 2 ) once every 21 days for up to 6 cycles (n=115). Randomization was stratified according to EGFR mutation category (exon 19 deletion vs exon 21 L858R vs other) and race (Asian vs non-Asian). The major efficacy outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) as assessed by an independent review committee (IRC). Other efficacy outcomes included overall response rate (ORR) and OS. EGFR mutation status was prospectively determined for screening and enrollment of patients by a clinical trial assay (CTA). Tumor samples from 264 patients (178 randomized to GILOTRIF and 86 patients randomized to chemotherapy) were tested retrospectively by the companion diagnostic therascreen ® EGFR RGQ PCR Kit, which is FDA-approved for selection of patients for GILOTRIF treatment.
Among the patients randomized, 65% were female, median age was 61 years, baseline ECOG performance status (PS) was 0 (39%) or 1 (61%), 26% were White and 72% were Asian. The majority of the patients had a tumor sample with an EGFR mutation categorized by the CTA as either exon 19 deletion (49%) or exon 21 L858R substitution (40%), while the remaining 11% had other mutations.
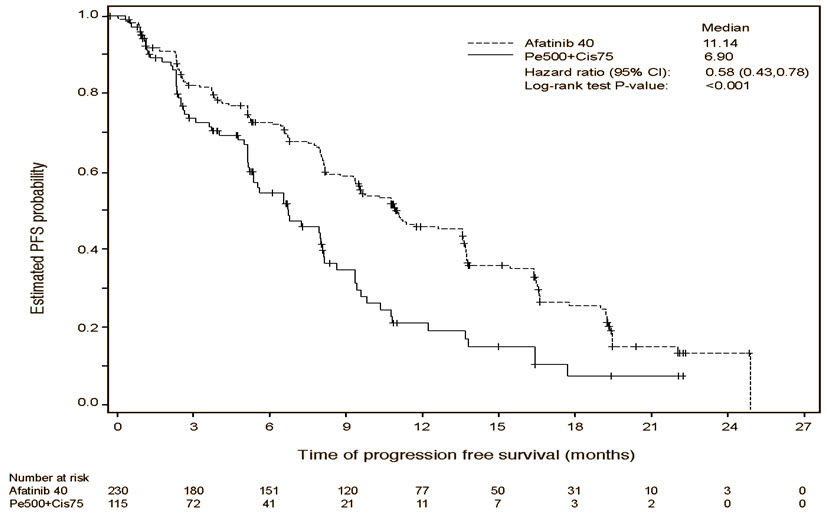
A statistically significant improvement in PFS as determined by the IRC was demonstrated for patients randomized to GILOTRIF compared with those randomized to chemotherapy. See Table 5 and Figure 1 . There was no statistically significant difference for OS between the treatment arms at the final pre-planned analysis.
| GILOTRIF (N=230) | Pemetrexed/Cisplatin (N=115) | |
|---|---|---|
| •Stratified by EGFR mutation status and race. | ||
| HR=hazard ratio; CR=complete response; PR=partial response | ||
| Progression-Free Survival by IRC | ||
| Number of Deaths or Progressions, N (%) | 152 (66.1%) | 69 (60.0%) |
| Median Progression-Free Survival (months) | 11.1 | 6.9 |
| 95% CI | (9.6, 13.6) | (5.4, 8.2) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.58 (0.43, 0.78) | |
| Stratified Log-Rank Test p-value• | <0.001 | |
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of Deaths, N (%) | 140 (60.9%) | 73 (63.5%) |
| Median Overall Survival (months) | 28.2 | 28.2 |
| 95% CI | (24.6, 33.6) | (20.7, 33.2) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.88 (0.66, 1.17) | |
| Stratified Log-Rank Test p-value• | 0.39 | |
| Overall Response Rate (CR + PR) by IRC | ||
| N (%) | 116 (50.4%) | 22 (19.1%) |
| Response Duration | ||
| Median (months) | 12.5 | 6.7 |
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Curve for PFS by Independent Review by Treatment Group in LUX-Lung 3
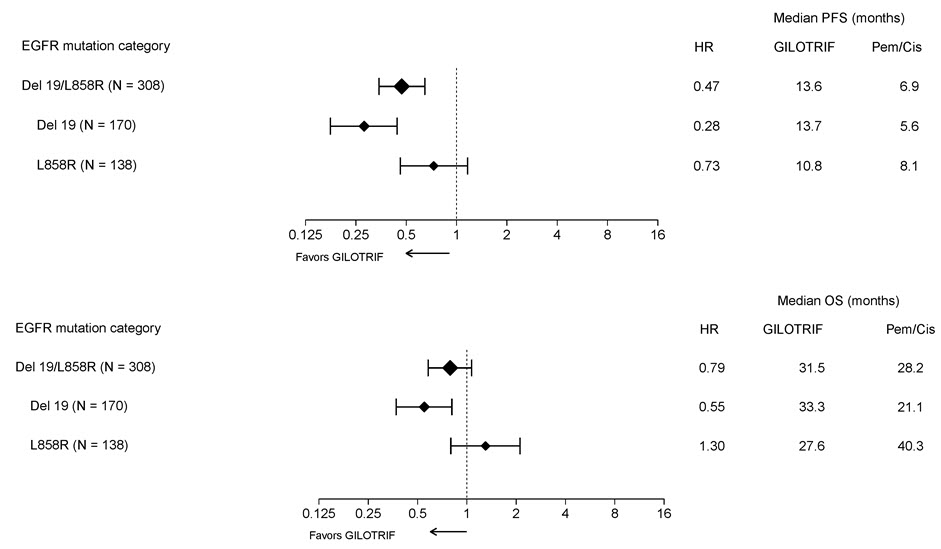
Pre-specified exploratory subgroup analyses were conducted according to the stratification factor of EGFR mutation category. See Figure 2 and text below Figure 2.
Figure 2 Forest Plots of PFS and OS by EGFR Mutation Subgroups in LUX-Lung 3
Overall Response Rate in Other EGFR Mutations
The efficacy of GILOTRIF in patients with NSCLC harboring non-resistant EGFR mutations (S768I, L861Q, and G719X) other than exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R substitutions was evaluated in a pooled analysis of such patients enrolled in one of three clinical trials (LUX-Lung 2 [NCT00525148], LUX-Lung 3 [NCT00949650], and LUX-Lung 6 [NCT01121393]).
- LUX-Lung 2 was a single arm, multicenter study of afatinib 40 or 50 mg orally once daily until disease progression or intolerable side effects. EGFR status was determined by bi-directional Sanger sequencing of tumor tissue.
- LUX-Lung 3 was a randomized, multicenter study comparing treatment with afatinib 40 mg orally once daily to intravenous cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 plus pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 every 21 days for up to 6 cycles. EGFR status was determined by the therascreen ® EGFR RGQ PCR Kit.
- LUX-Lung 6 was a randomized, multicenter study comparing treatment with afatinib 40 mg to intravenous gemcitabine 1000 mg/m 2 on day 1 and day 8 plus cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 on day 1 of a 3-week schedule for up to 6 cycles. EGFR status was determined by the therascreen ® EGFR RGQ PCR Kit.
Among the 75 GILOTRIF-treated patients with uncommon EGFR mutations, 32 patients had a non-resistant EGFR mutation. Among the 32 patients with a confirmed non-resistant EGFR mutation, the median age was 60.5 years (range 32-79), 66% were female, 97% were Asian, 3% were other races, 38% had an ECOG PS of 0, 63% had an ECOG PS 1, 66% were never smokers, 28% were former smokers, and 6% were current smokers. Baseline disease characteristics were 97% Stage IV disease, 3% Stage IIIb disease, and 88% had received no prior systemic therapy for advanced or metastatic disease.
The number of patients, the number of responders, and durations of response in subgroups defined by identified mutation(s) are summarized in Table 6.
| EGFR Mutation | Number of GILOTRIF Treated Patients (N=32) | Number of Confirmed Responses (N=21) | Duration of Response (months) (N=21) |
|---|---|---|---|
| + response ongoing at time of censoring | |||
| S768I | 1 | 1 | 37.3 |
| S768I and G719X | 5 | 4 | 4.1, 13.2, 15.2, 29.5+ |
| S768I and L858R | 2 | 1 | 34.5+ |
| G719X | 8 | 6 | 5.7+, 8.1, 9.6, 23.5+, 25.2, 31.8+ |
| G719X and L861Q | 3 | 2 | 2.8+, 6.8 |
| L861Q | 12 | 7 | 2.8, 4.0, 4.1, 8.3+, 12.9, 15.2, 20.6 |
| L861Q and Del 19 | 1 | 0 | NA |
Previously Treated, Metastatic Squamous NSCLC
The efficacy and safety of GILOTRIF were demonstrated in a randomized, multicenter, open-label, active-controlled study (LUX-Lung 8 [NCT01523587]). Patients were required to have histologically documented, metastatic squamous NSCLC and have experienced disease progression following an adequate course (≥4 cycles) of a platinum-based doublet chemotherapy regimen. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive GILOTRIF 40 mg or erlotinib 150 mg orally once daily until progression. Randomization was stratified by region (Eastern Asia vs other). The major efficacy outcome measure was PFS as assessed by an IRC using RECIST v 1.1. Additional efficacy outcome measures were OS and ORR as assessed by IRC.
Baseline patient demographics of the 795 patients were: median age 64 years (range: 35 to 88); 73% White; 24% Asian; 84% male; 33% ECOG PS 0 and 67% ECOG PS 1; and 95% current or former smokers. With regard to tumor characteristics, 96% had squamous cell histology and 3.5% had mixed cell histology. All patients received platinum-based doublet therapy.
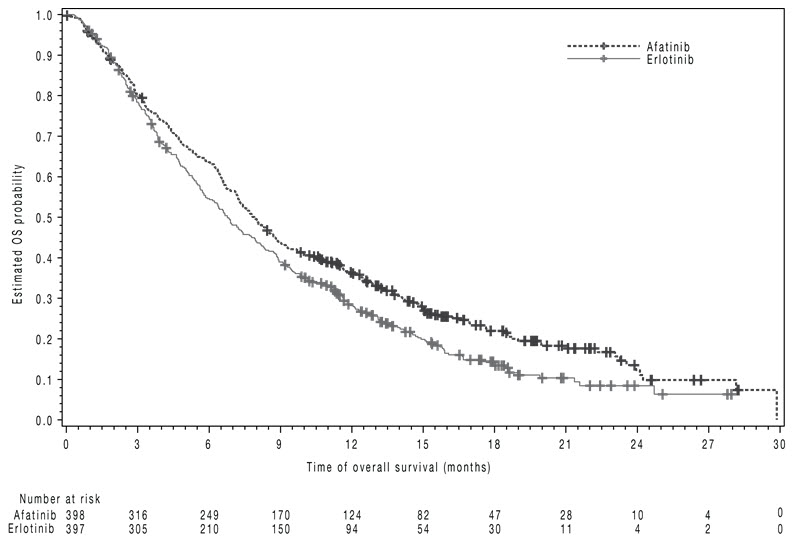
The study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS and OS for patients randomized to GILOTRIF as compared with erlotinib (see Table 7 and Figure 3 ).
| GILOTRIF | Erlotinib | |
|---|---|---|
| •Log-rank test stratified by region. | ||
| HR=hazard ratio | ||
| Overall Survival | ||
| N=398 | N=397 | |
| Number of Deaths, N (%) | 307 (77%) | 325 (82%) |
| Median overall survival (months) | 7.9 | 6.8 |
| 95% CI | (7.2, 8.7) | (5.9, 7.8) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.81 (0.69, 0.95) | |
| p-value• | 0.008 | |
| Progression-Free Survival (PFS) by IRC | ||
| N=335 | N=334 | |
| Number of Events, N (%) | 202 (60%) | 212 (64%) |
| Median PFS (months) | 2.4 | 1.9 |
| 95% CI | (1.9, 2.9) | (1.9, 2.2) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.82 (0.68, 0.998) | |
| p-value• | 0.0427 | |
| Overall Response Rate (ORR) by IRC | ||
| N=335 | N=334 | |
| ORR | 3% | 2% |
| (95% CI) | (1.7, 5.8) | (0.8, 4.3) |
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival in LUX-Lung 8
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
GILOTRIF tablets are available as follows:
| 40 mg: light blue, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T40" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side. | |
| Unit of use bottles of 30 | NDC: 0597-0138-30 |
| 30 mg: dark blue, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T30" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side. | |
| Unit of use bottles of 30 | NDC: 0597-0137-30 |
| 20 mg: white to slightly yellowish, film-coated, round, biconvex, bevel-edged tablets debossed with "T20" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side. | |
| Unit of use bottles of 30 | NDC: 0597-0141-30 |
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense medication in the original container to protect from exposure to high humidity and light.
Mechanism of Action
Afatinib covalently binds to the kinase domains of EGFR (ErbB1), HER2 (ErbB2), and HER4 (ErbB4) and irreversibly inhibits tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation, resulting in downregulation of ErbB signaling. Certain mutations in EGFR, including non-resistant mutations in its kinase domain, can result in increased autophosphorylation of the receptor, leading to receptor activation, sometimes in the absence of ligand binding, and can support cell proliferation in NSCLC. Non-resistant mutations are defined as those occurring in exons constituting the kinase domain of EGFR that lead to increased receptor activation and where efficacy is predicted by 1) clinically meaningful tumor shrinkage with the recommended dose of afatinib and/or 2) inhibition of cellular proliferation or EGFR tyrosine kinase phosphorylation at concentrations of afatinib sustainable at the recommended dosage according to validated methods. The most commonly found of these mutations are exon 21 L858R substitutions and exon 19 deletions.
Afatinib demonstrated inhibition of autophosphorylation and/or in vitro proliferation of cell lines expressing wild-type EGFR and in those expressing selected EGFR exon 19 deletion mutations, exon 21 L858R mutations, or other less common non-resistant mutations, at afatinib concentrations achieved in patients. In addition, afatinib inhibited in vitro proliferation of cell lines overexpressing HER2.
Treatment with afatinib resulted in inhibition of tumor growth in nude mice implanted with tumors either overexpressing wild type EGFR or HER2 or in an EGFR L858R/T790M double mutant model.