Granix prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Granix patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended dose: 5 mcg/kg per day administered as a subcutaneous injection
Administer the first dose no earlier than 24 hours following myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Do not administer within 24 hours prior to chemotherapy (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of GRANIX is 5 mcg/kg per day administered as a subcutaneous injection. Administer the first dose of GRANIX no earlier than 24 hours following myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Do not administer GRANIX within 24 hours prior to chemotherapy.
Daily dosing with GRANIX should continue until the expected neutrophil nadir is passed and the neutrophil count has recovered to the normal range. Monitor complete blood count (CBC) prior to chemotherapy and twice per week until recovery.
General Considerations for Administration
GRANIX may be administered by either a healthcare professional, a patient or caregiver. Before a decision is made to allow GRANIX to be administered by a patient or caregiver, ensure that the patient is an appropriate candidate for self-administration or administration by a caregiver. Proper training on storage, preparation, and administration technique should be provided. If a patient or caregiver is not an appropriate candidate for any reason, then in such patients, GRANIX should be administered by a healthcare professional.
Dispense only the prefilled syringe without a safety needle guard device to patient or caregiver. Instruct patients and caregivers to follow the Instructions for Use provided with the GRANIX prefilled syringe to properly administer an injection after training by a healthcare professional.
Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not administer GRANIX if discoloration or particulates are observed.
The prefilled syringe and vial are for single-dose only. Discard unused portions. GRANIX and all its components are not made with natural rubber latex.
Recommended sites for subcutaneous GRANIX injections include the abdomen (except for the two-inch area around the navel), the front of the middle thighs, the upper outer areas of the buttocks, or the upper back portion of the upper arms. The injection site should be varied daily. GRANIX should not be injected into an area that is tender, red, bruised, or hard, or that has scars or stretch marks.
Important Administration Instructions for Healthcare Professionals
Hold the syringe assembly by the open sides of the device and remove the needle shield.

Expel any extra volume depending on dose needed.

Inject GRANIX subcutaneously as recommended [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Push the plunger as far as it will go to inject all the medication. Injection of the entire prefilled syringe contents is necessary to activate the needle guard.

With the plunger still pressed all the way down, remove the needle from the skin.

Slowly let go of the plunger and allow the empty syringe to move up inside the device until the entire needle is guarded.

Discard the syringe assembly in approved containers.


By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Granix prescribing information
Warnings and Precautions, Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patients with Breast and Lung Cancer (5.8) 11 / 2023
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GRANIX is indicated to reduce the duration of severe neutropenia in adult and pediatric patients 1 month and older with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with a clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended dose: 5 mcg/kg per day administered as a subcutaneous injection
Administer the first dose no earlier than 24 hours following myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Do not administer within 24 hours prior to chemotherapy (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of GRANIX is 5 mcg/kg per day administered as a subcutaneous injection. Administer the first dose of GRANIX no earlier than 24 hours following myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Do not administer GRANIX within 24 hours prior to chemotherapy.
Daily dosing with GRANIX should continue until the expected neutrophil nadir is passed and the neutrophil count has recovered to the normal range. Monitor complete blood count (CBC) prior to chemotherapy and twice per week until recovery.
General Considerations for Administration
GRANIX may be administered by either a healthcare professional, a patient or caregiver. Before a decision is made to allow GRANIX to be administered by a patient or caregiver, ensure that the patient is an appropriate candidate for self-administration or administration by a caregiver. Proper training on storage, preparation, and administration technique should be provided. If a patient or caregiver is not an appropriate candidate for any reason, then in such patients, GRANIX should be administered by a healthcare professional.
Dispense only the prefilled syringe without a safety needle guard device to patient or caregiver. Instruct patients and caregivers to follow the Instructions for Use provided with the GRANIX prefilled syringe to properly administer an injection after training by a healthcare professional.
Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not administer GRANIX if discoloration or particulates are observed.
The prefilled syringe and vial are for single-dose only. Discard unused portions. GRANIX and all its components are not made with natural rubber latex.
Recommended sites for subcutaneous GRANIX injections include the abdomen (except for the two-inch area around the navel), the front of the middle thighs, the upper outer areas of the buttocks, or the upper back portion of the upper arms. The injection site should be varied daily. GRANIX should not be injected into an area that is tender, red, bruised, or hard, or that has scars or stretch marks.
Important Administration Instructions for Healthcare Professionals
Hold the syringe assembly by the open sides of the device and remove the needle shield.

Expel any extra volume depending on dose needed.

Inject GRANIX subcutaneously as recommended [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Push the plunger as far as it will go to inject all the medication. Injection of the entire prefilled syringe contents is necessary to activate the needle guard.

With the plunger still pressed all the way down, remove the needle from the skin.

Slowly let go of the plunger and allow the empty syringe to move up inside the device until the entire needle is guarded.

Discard the syringe assembly in approved containers.

DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GRANIX is a clear, colorless, preservative-free solution available as:
Prefilled Syringe:
Injection: 300 mcg/0.5 mL solution in single-dose prefilled syringe
Injection: 480 mcg/0.8 mL solution in single-dose prefilled syringe
Vial:
Injection: 300 mcg/mL solution in single-dose vial
Injection: 480 mcg/1.6 mL (300 mcg/mL) solution in single-dose vial
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
GRANIX should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited published data on filgrastim product use during pregnancy are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of tbo-filgrastim to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis resulted in increased spontaneous abortion and fetal malformations at systemic exposures 50 to 90 times the human exposure expected at the recommended human dose (see Data) . GRANIX should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryofetal developmental study, pregnant rabbits were administered subcutaneous doses of tbo-filgrastim during the period of organogenesis at 1, 10 and 100 mcg/kg/day. Increased abortions were evident in rabbits treated with tbo-filgrastim at 100 mcg/kg/day. This dose was maternally toxic as demonstrated by reduced body weight. Other embryofetal findings at this dose level consisted of post-implantation loss‚ decrease in mean live litter size and fetal weight, and fetal malformations such as malformed hind limbs and cleft palate. The dose of 100 mcg/kg/day corresponds to a systemic exposure (AUC) of approximately 50 to 90 times the exposures observed in patients treated with the clinical tbo-filgrastim dose of 5 mcg/kg/day.
Lactation
No data are available regarding the presence of tbo-filgrastim in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed child, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Another filgrastim product was detected in human milk for up to 3 days after filgrastim administration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, including splenic rupture, acute respiratory distress syndrome and serious allergic reactions, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with GRANIX and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GRANIX have been established for pediatric patients 1 month to < 17 years old (no data for the age group < 1 month old). Use of GRANIX in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of GRANIX in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)] with additional safety and pharmacokinetics data from a single-arm trial of 50 pediatric patients with solid tumors treated with GRANIX for chemotherapy-induced neutropenia. The 50 pediatric patients had a median age of 9.2 years (range, 1.4 to 15.9 years); 2 were infants (1 month to < 2 years old), 30 were children (2 to < 12 years old), and 18 were adolescents (12 to < 17 years old). The pharmacokinetics and safety profile of GRANIX in the pediatric population were similar to those seen in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Geriatric Use
Among 677 cancer patients enrolled in clinical trials of GRANIX, a total of 111 patients were 65 years of age and older, and 14 patients were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients age 65 and older and younger patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GRANIX is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to filgrastim products or pegfilgrastim products [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Splenic Rupture: Evaluate patients who report left upper abdominal or shoulder pain for an enlarged spleen or splenic rupture (5.1 )
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Monitor for and manage immediately. Discontinue GRANIX if suspected (5.2 )
- Serious Allergic Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: Permanently discontinue GRANIX in patients with serious allergic reactions (5.3 )
- Sickle Cell Disorders: Severe and sometimes fatal crisis can occur. Discontinue GRANIX if suspected (5.4 )
- Glomerulonephritis: Evaluate and consider dose reduction or interruption of GRANIX if causality is likely (5.5 )
- Capillary Leak Syndrome: Monitor if symptoms develop and administer standard symptomatic treatment (5.6 )
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Monitor patients with breast and lung cancer using GRANIX in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML. (5.8 )
Splenic Rupture
Splenic rupture, including fatal cases, can occur following administration of filgrastim products. Evaluate patients who report upper abdominal or shoulder pain for an enlarged spleen or splenic rupture. Discontinue GRANIX if splenic rupture is suspected or confirmed.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can occur in patients receiving filgrastim products. Evaluate patients who develop fever and lung infiltrates or respiratory distress after receiving GRANIX, for ARDS. Discontinue GRANIX in patients with ARDS.
Serious Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients receiving GRANIX. Reactions can occur on initial exposure. The administration of antihistamines‚ steroids‚ bronchodilators‚ and/or epinephrine may reduce the severity of the reactions. Permanently discontinue GRANIX in patients with serious allergic reactions. Do not administer GRANIX to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to filgrastim or pegfilgrastim.
Sickle Cell Disorders
Severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving filgrastim products. Discontinue GRANIX if sickle cell crisis occurs.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis can occur in patients receiving filgrastim products. The diagnoses were based on azotemia, hematuria (microscopic and macroscopic), proteinuria, and renal biopsy. Generally, events of glomerulonephritis resolved after dose reduction or discontinuation of the filgrastim product. If glomerulonephritis is suspected, evaluate for cause. If causality is likely, consider dose reduction or interruption of GRANIX.
Capillary Leak Syndrome
Capillary leak syndrome (CLS) can occur in patients receiving filgrastim products and is characterized by hypotension, hypoalbuminemia, edema and hemoconcentration. Episodes vary in frequency, severity and may be life-threatening if treatment is delayed. Patients who develop symptoms of capillary leak syndrome should be closely monitored and receive standard symptomatic treatment, which may include a need for intensive care.
Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells
The granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G‑CSF) receptor through which GRANIX acts has been found on tumor cell lines. The possibility that GRANIX acts as a growth factor for any tumor type, including myeloid malignancies and myelodysplasia, diseases for which GRANIX is not approved, cannot be excluded.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patients with Breast and Lung Cancer
Patients with Severe Chronic Neutropenia
Confirm the diagnosis of SCN before initiating GRANIX therapy.
MDS and AML have been reported to occur in the natural history of congenital neutropenia without cytokine therapy. Cytogenetic abnormalities, transformation to MDS, and AML have also been observed in patients treated with GRANIX for SCN. Based on available data including a postmarketing surveillance study, the risk of developing MDS and AML appears to be confined to the subset of patients with congenital neutropenia. Abnormal cytogenetics and MDS have been associated with the eventual development of myeloid leukemia. The effect of GRANIX on the development of abnormal cytogenetics and the effect of continued GRANIX administration in patients with abnormal cytogenetics or MDS are unknown. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML in these settings. If a patient with SCN develops abnormal cytogenetics or myelodysplasia‚ the risks and benefits of continuing GRANIX should be carefully considered.
Patients with Breast and Lung Cancer
MDS and AML have been associated with the use of GRANIX in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in patients with breast and lung cancer. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML in these settings.
Leukocytosis
White blood cell counts of 100‚000/mm 3 or greater were observed in approximately 2% of patients receiving filgrastim products at dosages above 5 mcg/kg/day. In patients with cancer receiving GRANIX as an adjunct to myelosuppressive chemotherapy‚ to avoid the potential risks of excessive leukocytosis‚ it is recommended that GRANIX therapy be discontinued if the ANC surpasses 10‚000/mm 3 after the chemotherapy-induced ANC nadir has occurred. Monitor CBCs at least twice weekly during therapy. Dosages of GRANIX that increase the ANC beyond 10‚000/mm 3 may not result in any additional clinical benefit. In patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy‚ discontinuation of filgrastim products therapy usually resulted in a 50% decrease in circulating neutrophils within 1 to 2 days‚ with a return to pretreatment levels in 1 to 7 days.
Simultaneous Use with Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy Not Recommended
The safety and efficacy of filgrastim products, including GRANIX, given simultaneously with cytotoxic chemotherapy have not been established. Because of the potential sensitivity of rapidly dividing myeloid cells to cytotoxic chemotherapy‚ do not use GRANIX in the period 24 hours before through 24 hours after the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
The safety and efficacy of GRANIX have not been evaluated in patients receiving concurrent radiation therapy. Avoid the simultaneous use of GRANIX with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Nuclear Imaging
Increased hematopoietic activity of the bone marrow in response to growth factor therapy has been associated with transient positive bone-imaging changes. Consider this when interpreting bone-imaging results.
Aortitis
Aortitis has been reported in patients receiving another filgrastim product. It may occur as early as the first week after start of therapy. Manifestations may include generalized signs and symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, malaise, back pain, and increased inflammatory markers (e.g., c‑reactive protein and white blood cell count). Consider aortitis in patients who develop these signs and symptoms without known etiology. Discontinue GRANIX if aortitis is suspected.
Alveolar Hemorrhage
Alveolar hemorrhage manifesting as pulmonary infiltrates and hemoptysis requiring hospitalization has been reported in healthy donors undergoing peripheral blood progenitor cell (PBPC) collection treated with another filgrastim product. Hemoptysis resolved with discontinuation of filgrastim. The use of GRANIX for PBPC mobilization in healthy donors is not an approved indication.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following potential serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Splenic Rupture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Serious Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Sickle Cell Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Glomerulonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Capillary Leak Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Leukocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 ) ]
- Simultaneous Use with Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy Not Recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 ) ]
- Aortitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12 ) ]
- Alveolar Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients
GRANIX clinical trials safety data are based upon the results of three randomized clinical trials in patients receiving myeloablative chemotherapy for breast cancer (N=348), lung cancer (N=240) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (N=92). In the breast cancer study, 99% of patients were female, the median age was 50 years, and 86% of patients were Caucasian. In the lung cancer study, 80% of patients were male, the median age was 58 years, and 95% of patients were Caucasian. In the non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma study, 52% of patients were male, the median age was 55 years, and 88% of patients were Caucasian. In all three studies a placebo (Cycle 1 of the breast cancer study only) or a non-U.S.-approved filgrastim product were used as controls. Both GRANIX and the non-U.S.-approved filgrastim product were administered at 5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once daily beginning one day after chemotherapy for at least five days and continued to a maximum of 14 days or until an ANC of ≥10,000 x 10 6 /L after nadir was reached.
Bone pain was the most frequent treatment-emergent adverse reaction that occurred in at least 1% or greater in patients treated with GRANIX at the recommended dose and was numerically two times more frequent than in the placebo group. The overall incidence of bone pain in Cycle 1 of treatment was 3.4% (3.4% GRANIX, 1.4% placebo, 7.5% non-U.S.-approved filgrastim product).
Leukocytosis In clinical studies, leukocytosis (WBC counts > 100,000 x 10 6 /L) was observed in less than 1% patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving GRANIX. No complications attributable to leukocytosis were reported in clinical studies.
Additional Adverse Reactions Other adverse reactions known to occur following administration of filgrastim products include myalgia, headache, vomiting, cutaneous vasculitis and thrombocytopenia.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients GRANIX clinical trials safety data in pediatric patients are based upon the results of one single-arm clinical trial in 50 pediatric patients who received myelosuppressive chemotherapy for treatment of solid tumors without marrow involvement [see Use in Special Populations (8.4 )] . In this study, GRANIX was administered at 5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once daily beginning one day after chemotherapy. The most common (>5%) adverse reactions included thrombocytopenia (34%), pyrexia (8%), pain in extremity (6%), headache (6%) and diarrhea (6%).
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of GRANIX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Sweet’s syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis), asthenia, diarrhea, and fatigue
DESCRIPTION
GRANIX (tbo-filgrastim) is a non-glycosylated recombinant methionyl human granulocyte colony-stimulating growth factor (r-metHuG-CSF) manufactured by recombinant DNA technology using the bacterium strain E coli K802. It has a molecular weight of approximately 18.8 kDa and is composed of 175 amino acids. The endogenous human G-CSF is glycosylated and does not have the additional methionine amino acid residue in its NH 2 terminal end.
The product is a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution containing tbo-filgrastim, glacial acetic acid, sorbitol, polysorbate 80, sodium hydroxide, and Water for Injection. The product is available in single-dose prefilled syringes that contain either 300 mcg or 480 mcg of tbo-filgrastim at a fill volume of 0.5 mL or 0.8 mL, respectively and single-dose vials that contain either 300 mcg or 480 mcg of tbo-filgrastim at a fill volume of 1 mL or 1.6 mL, respectively. See table below for product composition of each presentation.
Product Composition | ||||
300 mcg/0.5 mL Syringe | 480 mcg/0.8 mL Syringe | 300 mcg/1 mL Vial | 480 mcg/1.6 mL Vial | |
| Tbo-filgrastim | 300 mcg | 480 mcg | 300 mcg | 480 mcg |
Glacial Acetic Acid | 0.3 mg | 0.48 mg | 0.6 mg | 0.96 mg |
Polysorbate 80 | 0.0275 mg | 0.044 mg | 0.055 mg | 0.088 mg |
| Sorbitol | 25 mg | 40 mg | 50 mg | 80 mg |
| Sodium Hydroxide | q.s. to pH 4.2 | q.s. to pH 4.2 | q.s. to pH 4.2 | q.s. to pH 4.2 |
| Water for Injection | q.s. to 0.5 mL | q.s. to 0.8 mL | q.s. to 1 mL | q.s. to 1.6 mL |
| q.s. = quantity sufficient to make | ||||
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Tbo-filgrastim is a human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) produced by recombinant DNA technology. Tbo-filgrastim binds to G-CSF receptors and stimulates proliferation of neutrophils. G-CSF is known to stimulate differentiation commitment and some end-cell functional activation, which increases neutrophil counts and activity.
Pharmacodynamics
The time to the maximum ANC level was between 3 to 5 days and returned to baseline by 21 days following completion of chemotherapy. Doubling the tbo-filgrastim subcutaneous dose from 5 mcg/kg to 10 mcg/kg resulted in a 16% to 19% increase in the maximum ANC level and a 33% to 36% increase in the area under the effect curve for ANC.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At an intravenous dose of 5 mcg/kg, tbo-filgrastim did not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
Tbo-filgrastim exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Increasing the dose of subcutaneous GRANIX from 5 to 10 mcg/kg resulted in an approximate 2.5-fold increase in the maximum serum concentration (C max ) and 3.0-fold increase in the area under the curve (AUC). In adult patients enrolled across three studies, subcutaneous GRANIX 5 mcg/kg resulted in median time to maximal serum tbo-filgrastim concentrations (T max ) within 4 to 6 hours. Geometric mean [coefficient of variation (CV%)] serum C max was 20 to 31 ng/mL [24% to 65%] within 4 to 6 hours. Geometric mean serum tbo-filgrastim area under the curve (AUC 0-12h ) ranged from 151 to 227 ng/mL•h [24% to 60%]. No accumulation in serum tbo-filgrastim concentrations was observed after multiple dosing.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of 5 mcg/kg subcutaneous tbo-filgrastim was 33%.
Metabolism/Elimination
Tbo-filgrastim clearance is primarily dependent on G-CSF receptor-mediated clearance which can be saturated by high serum concentrations of tbo-filgrastim and diminished in neutropenia. The median serum elimination half-life of tbo-filgrastim (5 mcg/kg sc) was 3.0 to 3.5 hours.
Specific Populations
No sex-related differences were observed.
Pediatric Patients:
The geometric mean [coefficient of variation (CV%)] of C max was 18 ng/mL (56%) and AUC 0-12h was 130 ng•hr/mL (52%) following subcutaneous administration of GRANIX 5 mcg/kg in 49 pediatric patients (1.4 to 15.9 years) after chemotherapy. No clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetics of GRANIX were observed between infants, children and adolescents.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment:
Mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 60 to 89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) had no effect on tbo-filgrastim pharmacokinetics. The pharmacokinetics in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment has not been studied. The pharmacokinetics in patients with hepatic impairment has not been studied.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of GRANIX or of other filgrastim products.
While available data suggest that 1.4% of patients developed binding antibodies to filgrastim, the nature and specificity of these antibodies has not been adequately studied. Because of the low occurrence of anti- drug antibodies, the effect of these antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and/or effectiveness of GRANIX is unknown.
Cytopenias resulting from an antibody response to exogenous growth factors have been reported on rare occasions in patients treated with other recombinant growth factors.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and genetic toxicology studies have not been conducted with tbo-filgrastim.
A fertility study was not conducted with tbo-filgrastim. Toxicology studies of up to 26 weeks in rats or monkeys did not reveal findings in male or female reproductive organs that would suggest impairment of fertility.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of GRANIX was evaluated in a multinational, multicenter, randomized and controlled Phase 3 study in 348 chemotherapy-naive patients with high-risk stage II, stage III, or stage IV breast cancer receiving doxorubicin (60 mg/m 2 ) and docetaxel (75 mg/m 2 ) comparing GRANIX to placebo and a non-U.S.-approved filgrastim product as controls. The median age of the patients was 50 years (range 25 to 75 years) with 99% female and 86% Caucasian.
GRANIX, placebo, and the non-U.S.-approved filgrastim product were administered at 5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once daily beginning one day after chemotherapy for at least five days and continued to a maximum of 14 days or until an ANC of ≥10,000 x 10 6 /L after nadir was reached.
GRANIX was superior to placebo in duration of severe neutropenia (DSN) with a statistically significant reduction in DSN (1.1 days vs. 3.8 days, p < 0.0001).
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
GRANIX solution for injection is supplied as a single-dose, preservative-free clear solution, in either a vial or, a prefilled syringe made from Type I glass which has a permanently attached stainless steel needle. The active substance is tbo-filgrastim.
Prefilled Syringes (UltraSafe Passive ® Needle Guard)
GRANIX 300 mcg/0.5 mL: Each prefilled syringe contains 300 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 0.5 mL solution with a blue plunger in:
- Pack of 1 with a safety needle guard in blister: NDC 63459-910-11
- Packs of 10 with a safety needle guard in blisters: NDC 63459-910-15
GRANIX 480 mcg/0.8 mL: Each prefilled syringe contains 480 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 0.8 mL solution with a clear plunger in:
- Pack of 1 with a safety needle guard in blister: NDC 63459-912-11
- Packs of 10 with a safety needle guard in blisters: NDC 63459-912-15
Prefilled Syringes
GRANIX 300 mcg/0.5 mL: Each prefilled syringe contains 300 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 0.5 mL solution with a blue plunger in:
- Pack of 1 without a safety needle guard (for patients and caregivers): NDC 63459-910-17
- Packs of 5 without a safety needle guard (for patients and caregivers): NDC 63459-910-36
GRANIX 480 mcg/0.8 mL: Each prefilled syringe contains 480 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 0.8 mL solution with a clear plunger in:
- Pack of 1 without a safety needle guard (for patients and caregivers): NDC 63459-912-17
- Packs of 5 without a safety needle guard (for patients and caregivers): NDC 63459-912-36
Vials
GRANIX 300 mcg/mL: Each vial contains 300 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 1 mL solution.
- Packs of 10 single-dose vials: (NDC 63459-918-59)
GRANIX 480 mcg/1.6 mL (300 mcg/mL): Each vial contains 480 mcg of tbo-filgrastim in 1.6 mL solution.
- Packs of 10 single-dose vials: (NDC 63459-920-59)
GRANIX and all its components are not made with natural rubber latex [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] .
Store GRANIX in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Protect from light. Within its shelf life, the product may be removed from 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) storage for a single period of up to 5 days between 73°F to 81°F (23°C to 27°C). If not used within 5 days, the product may be returned to 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) up to the expiration date. Dispose of syringes if stored at room temperature for more than 5 days.
Avoid shaking. The solution should be visually inspected prior to use. Only clear solutions without particles should be used. Exposure to 23°F to 30°F (-1°C to -5°C) for up to 72 hours and temperatures as low as 5°F to -13°F (-15°C to -25°C) for up to 24 hours do not adversely affect the stability of GRANIX.
Single-dose syringe and single-dose vial – discard unused portion. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
If GRANIX gets on the skin, wash the area with soap and water. If GRANIX gets in the eyes, thoroughly flush the exposed eye/eyes with water.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE - Prefilled Syringe
GRANIX (GRAN-icks) (tbo-filgrastim) for subcutaneous injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe
Important:
Read the Prescribing information and Patient Package insert for important information about GRANIX.
About the GRANIX syringe
Depending on the prescription that your healthcare provider gave you, you will receive a syringe that provides a dose of either 0.1 mL to 0.5 mL or 0.1 mL to 0.8 mL. If you are prescribed a dose over 0.8 mL, two syringes will be required to reach your prescribed dose. Your healthcare provider will determine how many syringes and the correct dose in milliliters (mL) you will need to give based on your body weight. You should continue to give GRANIX daily until your healthcare provider informs you that your white blood cell count has returned to normal.
Make sure you understand the following:
- How to store your syringes.
- How to read the syringe markings.
- How to adjust the amount of GRANIX in the syringe for your prescribed dose.
- How to prepare and give the injection.
Do not shake syringes.
Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
Do not re-use a syringe. The syringe is for single-use only.
Your first dose of GRANIX is given at least 24 hours after you receive your chemotherapy.
Do not inject GRANIX within 24 hours before your next dose of chemotherapy.
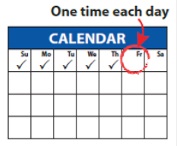
Dosing schedule
Inject your total daily dose 1 time each day as prescribed by your healthcare provider, starting at least 24 hours (1 day) after the end of your chemotherapy cycle.
You should continue to give GRANIX daily until your white blood cell count returns to normal.
How to store your GRANIX syringes
- Store GRANIX in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Store GRANIX in the original carton to protect it from light.
- Do not shake.
- Take GRANIX out of the refrigerator 30 minutes before use and allow it to reach room temperature before preparing an injection.
- GRANIX syringes can be left at room temperature for a single period of up to 5 days, and if not used can be returned to the refrigerator. Throw away (dispose of) any GRANIX syringes that have been left at room temperature for more than 5 days.
- After you inject your dose, throw away (dispose of) any unused GRANIX left in the syringe. Do not save unused GRANIX in the syringe for later use.
Keep GRANIX and all medicines out of the reach of children.
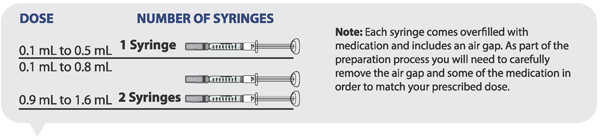
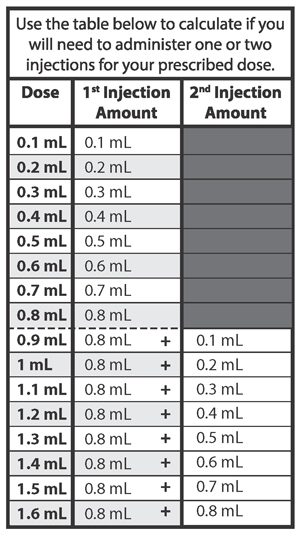
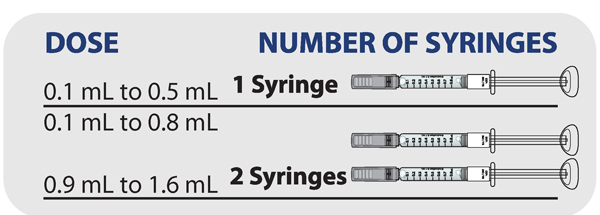
Determining how many syringes you need for your daily dose
- If your prescribed daily dose is 0.5 mL or less, use 1 syringe.
- If your prescribed daily dose is 0.8 mL or less, use 1 syringe.
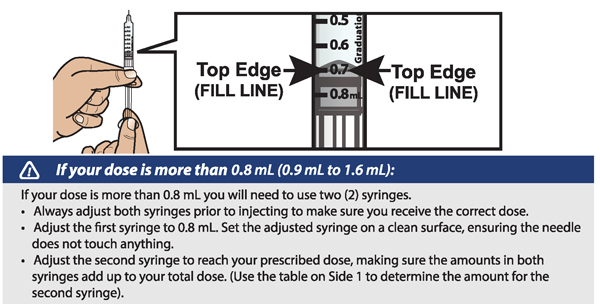
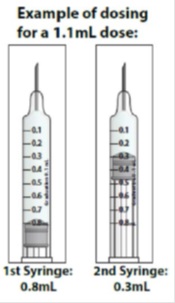
- If your prescribed daily dose is more than 0.8 mL you will need to prepare 2 syringes in order to match your prescribed dose:
- Adjust your first syringe to 0.8 mL.
- Adjust your second syringe to the additional amount required to make up your total prescribed dose.
- Make sure the amounts in both syringes add up to your prescribed dose (See the table to the right to determine how much medicine should be in each syringe).
For example: If your prescribed dose is 1 mL you would prepare 1 syringe with 0.8 mL and a second syringe with 0.2 mL.
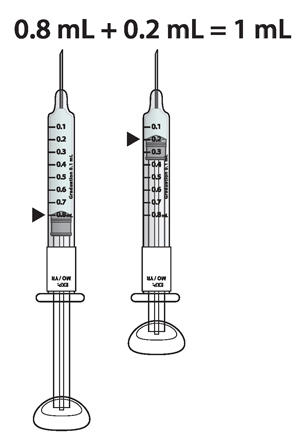
Important : When using 2 syringes always adjust the first syringe to 0.8 mL.
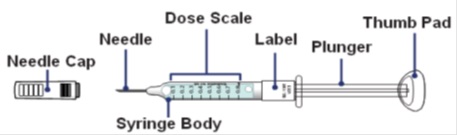
How to read the syringe markings
What the markings on the syringe mean:
The syringe is labeled in 0.1 mL unit increments from 0.1 mL to 0.8 mL. There is a line next to each 0.1 mL unit increment.
To read the dose scale always hold the syringe with the needle-end facing up so that 0.1 mL is at the top and 0.8 mL is at the bottom.
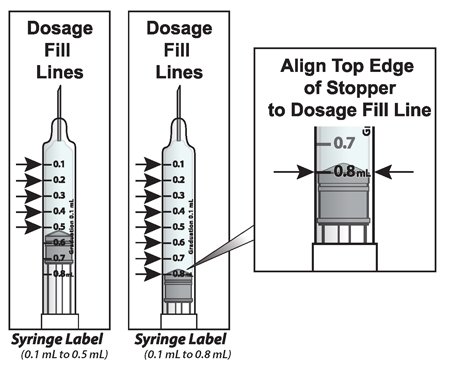
How to adjust the medicine level for your prescribed dose
- When setting your dose, ( See 2C ) you will line up the top edge of the grey rubber stopper with the line on the syringe scale that matches your prescribed dose.
- Note : The top edge of the grey rubber stopper is the edge directly below the dome at the top of the stopper.
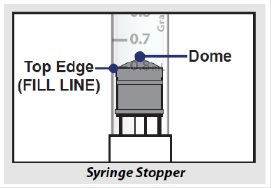
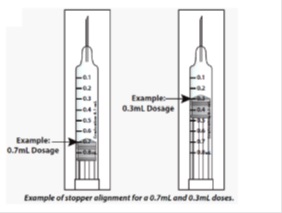
Do not use the top of the cone or the middle or lower edges of the grey stopper to measure your dose.
Injection steps (follow the steps below for each day of dosing)
1. Prepare for injection
1A Each time you inject a dose gather the following supplies:
- GRANIX syringe(s)
- Alcohol swabs
- Paper towel
- Cotton ball or gauze pad
- Adhesive Bandage, if needed
- Sharps disposal container (hard-walled container for discarding syringes)
Note: GRANIX and all of the parts of the prefilled syringe do not contain natural rubber latex.
1B Take the carton with the syringe(s) out of the refrigerator
1C Check the label and the expiration date on the side of the carton

Important: Do not inject if:
- “GRANIX ® (tbo-filgrastim)” is not listed on the carton.
- The expiration date on the syringe label has passed.
1D Remove the syringe(s) from the carton
Open the carton by breaking the tamper proof seal and lifting the lid. Remove the number of syringes required for your daily dose by grasping each at the middle of the syringe body.
After removing your required number of syringes, place the carton back in the refrigerator.
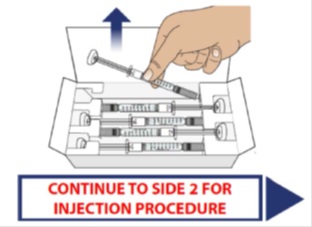
1E Look carefully at the syringe(s) and the medicine
Hold the syringe body and check to make sure it is not damaged.
Inspect the medicine in the syringe. GRANIX should be a clear liquid.
Important: Do not inject if:
- GRANIX ® (tbo-filgrastim) is not listed on the syringe label.
- The medicine is cloudy, discolored, or foamy.
- The medicine contains lumps, flakes, or particles.
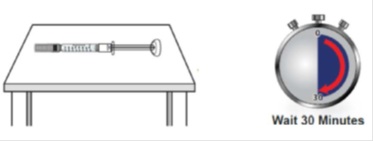
1F Wait 30 minutes for the syringe(s) to warm to room temperature
Wait 30 minutes for GRANIX to naturally warm to room temperature. This will provide a more comfortable injection.
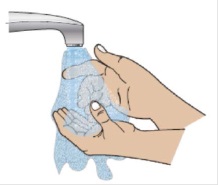
1G Wash your hands
When ready to inject, wash your hands with soap and warm water and dry thoroughly with a clean towel.
1H Choose an injection site
The recommended injection sites are:
If you are self-injecting:
Stomach-area (abdomen): Except for a 2-inch area around the navel (belly button).
Thighs: Top or middle area of thighs.
If a caregiver is injecting GRANIX for you:
Arms: Fleshy areas on upper, back part of the arm.
Upper hip or buttock: Fleshy areas around the back of the upper hips and upper sides of the buttocks.
If 2 injections will be performed, then the second injection should be at least 1 inch away from the first injection.
Choose Injection Site
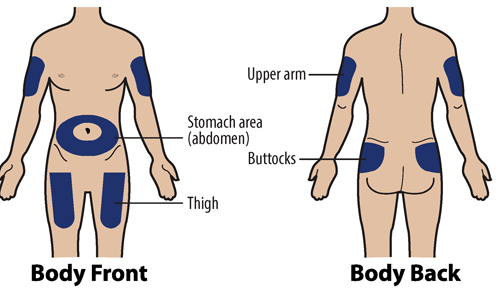
Do not inject into areas that are tender, red, bruised, hard, or have scars or stretch marks.
Important:
- You should select a different injection site each time you give yourself an injection.
- If you want to use the same injection site for a dose requiring 2 injections, make sure the second injection site is at least 1 inch away from the first injection site.
1I Clean the injection site using an alcohol swab
Allow site to dry for 5-10 seconds to avoid stinging.
If giving 2 injections, then the distance between the 2 injection sites should be at least 1 inch apart.
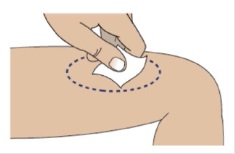
Do not touch or blow on site after cleaning.
2. Adjust medicine level for your prescribed dose
2A Remove the needle cap from the syringe
Place a paper towel on the table.
To remove the needle cap, hold the body of the syringe firmly with 1 hand (with the needle facing away from you).
Pull the needle cap straight off, extending your hand away from the needle.
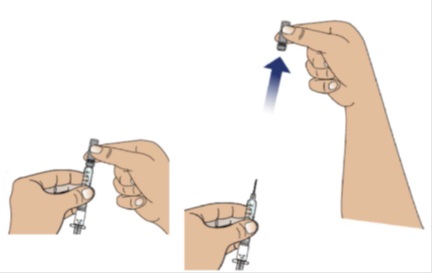
Note: Throw away the needle cap in a sharps disposal container.
Do not recap the needle now or after the injection.
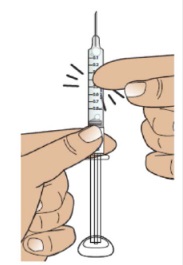
2B Hold the syringe upright and tap
Hold the syringe upright (needle pointing up), as shown.
Gently tap the barrel with your fingers to make sure any air bubbles rise to the top.
2C Slowly and carefully adjust the medicine level
Hold the syringe with the needle pointing up and slightly away from you , as shown. Make sure you can easily see the syringe markings and numbers.
Holding the plunger as shown, very slowly and carefully push the plunger up until the top edge of the grey rubber stopper is even with the line that corresponds to your prescribed dose.
Note:
- If GRANIX gets on your skin, wash your skin with soap and water.
- If GRANIX get in your eyes, flush well with water.
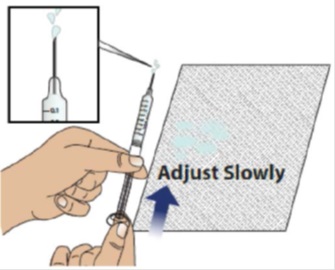
Note: If you accidentally removed too much GRANIX, contact your healthcare provider before giving your injection.
3. INJECT MEDICATION
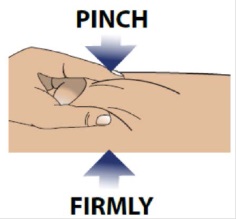
3A Pinch skin
The illustration below is an example only
Use your free hand to firmly pinch the skin you previously cleaned.
3B Insert the needle at a 45 to 90 degree angle
Hold the body of the syringe between your thumb and index finger.
Use a quick motion to fully insert the needle straight into the pinched skin at a 45 to 90 degree angle.
When the needle is inserted, you can release the pinched skin.
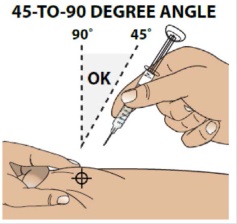
Do not hold or push on the plunger while inserting the needle into the skin.
3C Push the plunger down to inject all of the GRANIX
Use your finger to gently push down on the plunger.
When the plunger head is as far down as it will go, all of the GRANIX has been injected. When done, gently remove the needle from the skin.
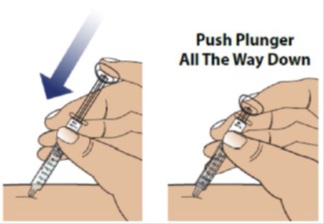
3D Throw away (dispose of) used syringe
Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
3E Treat the injection site if needed and wash your hands
If you see drops of blood at the injection site, you can press a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site for several seconds to stop the bleeding.
Apply bandage, if needed.
When you are finished, wash your hands with soap and warm water and dry thoroughly with a clean towel.
4.000000000000000e+00 Repeat the injection steps with the second syringe (If dose is more than 0.8 mL)
If your dose is more than 0.8 mL:
- Follow instructions 3A through 3E for injecting.
- Choose a different site for your second injection. If you want to use the same part of your body, make sure the second injection site is at least 1 inch away from the first injection site.
If you have any questions or concerns about your dose of GRANIX or how to prepare and give your injections, call your healthcare provider.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by: UAB Teva Baltics Vilnius, Lithuania
U.S. License No. 1803
Distributed by: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. North Wales, PA 19454
Product of Israel
Revised: 11/2023
TBOIFU-004

©2023 Cephalon, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. All rights reserved.
GRANIX is a trademark of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Mechanism of Action
Tbo-filgrastim is a human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) produced by recombinant DNA technology. Tbo-filgrastim binds to G-CSF receptors and stimulates proliferation of neutrophils. G-CSF is known to stimulate differentiation commitment and some end-cell functional activation, which increases neutrophil counts and activity.