Get your patient on Jaypirca (Pirtobrutinib)
Jaypirca patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of JAYPIRCA is 200 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Advise patients of the following:
- Swallow tablets whole with water. Do not cut, crush, or chew tablets.
- Take JAYPIRCA at the same time each day. JAYPIRCA may be taken with or without food.
- If a dose of JAYPIRCA is missed by more than 12 hours, do not make up the dose and take the next dose as scheduled.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dosage modifications of JAYPIRCA for adverse reactions are presented in Table 1 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 , 5.3 , and 5.4 )] .
Dose modification is not recommended for asymptomatic lymphocytosis. Asymptomatic lipase increase may not necessarily warrant dose modification. | ||
a Evaluate the benefit-risk before resuming treatment at the same dose for a Grade 4 non-hematological toxicity. | ||
| Adverse Reaction | Occurrences Requiring Dosage Modification | Modification (Starting Dosage: 200 mg once daily) |
| First occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at original dosage (200 mg once daily) a . |
| Second occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at 100 mg once daily. | |
| Third occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at 50 mg once daily. | |
| Fourth occurrence | Discontinue JAYPIRCA. | |
Dosage Modifications for Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
For patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15-29 mL/min), reduce the JAYPIRCA dose to 100 mg once daily if the current dose is 200 mg once daily otherwise reduce the dose by 50 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg once daily, discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . No dosage adjustment of JAYPIRCA is recommended in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-89 mL/min).
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with JAYPIRCA [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce the JAYPIRCA dose by 50 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg once daily, interrupt JAYPIRCA treatment for the duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 5 half-lives, resume the JAYPIRCA dose that was taken prior to initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor.
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with CYP3A Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers with JAYPIRCA [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . If concomitant use with moderate CYP3A inducers is unavoidable and the current dosage of JAYPIRCA is 200 mg once daily, increase the dose to 300 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg or 100 mg once daily, increase the dose by 50 mg.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jaypirca prescribing information
| Indications and Usage, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (1.2 ) | 12/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JAYPIRCA ® is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) after at least two lines of systemic therapy, including a BTK inhibitor. (1.1 ). This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who have previously been treated with a covalent BTK inhibitor. (1.2 ).
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
JAYPIRCA ® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) after at least two lines of systemic therapy, including a BTK inhibitor.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
JAYPIRCA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who have previously been treated with a covalent BTK inhibitor.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of JAYPIRCA is 200 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Advise patients of the following:
- Swallow tablets whole with water. Do not cut, crush, or chew tablets.
- Take JAYPIRCA at the same time each day. JAYPIRCA may be taken with or without food.
- If a dose of JAYPIRCA is missed by more than 12 hours, do not make up the dose and take the next dose as scheduled.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dosage modifications of JAYPIRCA for adverse reactions are presented in Table 1 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 , 5.3 , and 5.4 )] .
Dose modification is not recommended for asymptomatic lymphocytosis. Asymptomatic lipase increase may not necessarily warrant dose modification. | ||
a Evaluate the benefit-risk before resuming treatment at the same dose for a Grade 4 non-hematological toxicity. | ||
| Adverse Reaction | Occurrences Requiring Dosage Modification | Modification (Starting Dosage: 200 mg once daily) |
| First occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at original dosage (200 mg once daily) a . |
| Second occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at 100 mg once daily. | |
| Third occurrence | Interrupt JAYPIRCA until recovery to Grade 1 or baseline; restart at 50 mg once daily. | |
| Fourth occurrence | Discontinue JAYPIRCA. | |
Dosage Modifications for Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
For patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15-29 mL/min), reduce the JAYPIRCA dose to 100 mg once daily if the current dose is 200 mg once daily otherwise reduce the dose by 50 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg once daily, discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . No dosage adjustment of JAYPIRCA is recommended in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-89 mL/min).
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with JAYPIRCA [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce the JAYPIRCA dose by 50 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg once daily, interrupt JAYPIRCA treatment for the duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 5 half-lives, resume the JAYPIRCA dose that was taken prior to initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor.
Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with CYP3A Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers with JAYPIRCA [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . If concomitant use with moderate CYP3A inducers is unavoidable and the current dosage of JAYPIRCA is 200 mg once daily, increase the dose to 300 mg. If the current dosage is 50 mg or 100 mg once daily, increase the dose by 50 mg.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
Each 50 mg tablet is blue, arc-triangle shaped, film-coated, and debossed with “Lilly 50” on one side and “6902” on the other side.
Each 100 mg tablet is blue, round, film-coated, and debossed with “Lilly 100” on one side and “7026” on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies, JAYPIRCA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on JAYPIRCA use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. In an animal reproduction study, administration of pirtobrutinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis resulted in adverse developmental outcomes, including structural abnormalities, altered fetal growth, and embryo-fetal mortality, at maternal exposures approximately 3-times those in patients at the recommended daily dose of 200 mg (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, pregnant animals were administered oral doses of pirtobrutinib at up to 500 mg/kg twice daily during the period of organogenesis. Doses ≥ 375 mg/kg twice daily caused decreased fetal body weights and increased incidence of malformations and variations in the urinary tract (including absent or abnormal ureters and kidneys), reproductive tract (malpositioned ovaries and misshapen uterus), and bone (misshapen sternebrae). At 500 mg/kg twice daily, total resorption was observed. At 375 mg/kg twice daily in rats, the maternal systemic exposures (AUC) were approximately 3 times the human exposure at 200 mg once daily.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of pirtobrutinib in human milk or the effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with JAYPIRCA and for one week after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on findings from animal studies, JAYPIRCA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating JAYPIRCA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JAYPIRCA and for one week after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of JAYPIRCA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Of the patients with MCL who received the 200 mg dose of JAYPIRCA in BRUIN, 93 (78%) were 65 years of age and older and 39 (33%) were 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Clinical studies of JAYPIRCA did not include sufficient numbers of patients with MCL who were less than 65 years of age to determine whether older patients respond differently from younger adult patients. Of the patients with CLL/SLL who received the 200 mg once daily dose of JAYPIRCA in BRUIN and BRUIN-321, 220 (65%) were 65 years of age and older and 78 (33%) were 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] . No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between younger and older patients.
In the pooled safety population in patients with hematologic malignancies in BRUIN and BRUIN CLL-321, 467 (66%) were 65 years of age and older, while 181 (26%) were 75 years of age and older. Patients aged 65 years and older experienced higher rates of Grade 3 and higher adverse reactions and serious adverse reactions compared to patients who were less than 65 years of age.
Renal Impairment
Severe renal impairment (eGFR15-29 mL/min) increases pirtobrutinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Reduce the JAYPIRCA dosage in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] . No dosage adjustment of JAYPIRCA is recommended in patients with mild (60-89 mL/min) or moderate (30-59 mL/min) renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of JAYPIRCA is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST), moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST), or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any AST) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infections: Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection, evaluate promptly, and treat. (5.1 )
- Hemorrhage: Monitor for bleeding and manage appropriately. (5.2 )
- Cytopenias: Monitor complete blood counts during treatment. (5.3 )
- Cardiac Arrythmias: Monitor for symptoms of arrhythmias and manage appropriately. (5.4 )
- Second Primary Malignancies: Other malignancies have developed, including skin cancers and other carcinomas. Monitor and advise patients to use sun protection. (5.5 )
- Hepatotoxicity, Including Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Monitor hepatic function throughout treatment. (5.6 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.7 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Infections
Fatal and serious infections (including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections) and opportunistic infections have occurred in patients treated with JAYPIRCA. Across clinical trials, Grade 3 or higher infections occurred in 25% of 704 patients, most commonly pneumonia (20%), with fatal infections occurring in 5% of patients. Sepsis occurred in 6% of patients and febrile neutropenia in 3.8%. In patients with CLL/SLL, Grade 3 or higher infections occurred in 32% of patients, with fatal infections occurring in 8%. Opportunistic infections after treatment with JAYPIRCA have included, but are not limited to, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and fungal infection [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Consider prophylaxis, including vaccinations and antimicrobial prophylaxis, in patients who are at increased risk for infections, including opportunistic infections. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection, evaluate promptly, and treat appropriately. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Hemorrhage
Fatal and serious hemorrhage has occurred with JAYPIRCA. Major hemorrhage (defined as Grade 3 or higher bleeding or any central nervous system bleeding) occurred in 2.6% of 704 patients treated with JAYPIRCA, including gastrointestinal hemorrhage; fatal hemorrhage occurred in 0.3% of patients. Bleeding of any grade, excluding bruising and petechiae, occurred in 16% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Major hemorrhage occurred in 0.6% of patients taking JAYPIRCA without antithrombotic agents and 2.0% of patients taking JAYPIRCA with antithrombotic agents. Consider the risks and benefits of antithrombotic agents when co-administered with JAYPIRCA. Monitor patients for signs of bleeding. Based on severity of bleeding, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Consider the benefit-risk of withholding JAYPIRCA for 3 to 7 days pre- and post-surgery depending upon the type of surgery and risk of bleeding.
Cytopenias
JAYPIRCA can cause cytopenias, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia.
Across clinical trials, Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias, including decreased neutrophils (27%), decreased platelets (13%), and decreased hemoglobin (11%) developed in patients treated with JAYPIRCA. Grade 4 decreased neutrophils developed in 15% of patients and Grade 4 decreased platelets developed in 6% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Monitor complete blood counts regularly during treatment. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )].
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, were reported in recipients of JAYPIRCA. Atrial fibrillation or flutter were reported in 3.4% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 atrial fibrillation or flutter reported in 1.6% of 704 patients across clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . Other serious cardiac arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest occurred in 0.4% of patients. Patients with cardiac risk factors, such as hypertension, or previous arrhythmias may be at increased risk.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of arrhythmias (e.g., palpitations, dizziness, syncope, dyspnea) and manage appropriately. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue JAYPIRCA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Second Primary Malignancies
Second primary malignancies, including non-skin carcinomas, developed in 9% of 704 patients treated with JAYPIRCA monotherapy across clinical trials. The most frequent malignancy was non-melanoma skin cancer, reported in 4.4% of 704 patients. Other second primary malignancies included solid tumors (including genitourinary and breast cancers) and melanoma. Advise patients to use sun protection and monitor patients for the development of second primary malignancies.
Hepatotoxicity, Including Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Hepatotoxicity, including severe, life-threatening, and potentially fatal cases of drug-induced liver injury (DILI), has occurred in patients treated with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including JAYPIRCA.
Evaluate bilirubin and transaminases at baseline and throughout treatment with JAYPIRCA. For patients who develop abnormal liver tests after JAYPIRCA, monitor more frequently for liver test abnormalities and clinical signs and symptoms of hepatic toxicity. If DILI is suspected, withhold JAYPIRCA. Upon confirmation of DILI, discontinue JAYPIRCA.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals, JAYPIRCA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of pirtobrutinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused embryo-fetal toxicity including embryo-fetal mortality and malformations at maternal exposures (AUC) approximately 3-times the recommended dose of 200 mg once daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JAYPIRCA and for one week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Second Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Hepatotoxicity, including DILI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in the general patient population.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to JAYPIRCA as a single-agent, administered at 200 mg once daily in 704 patients with hematologic malignancies in the BRUIN and the BRUIN-CLL-321 studies. Among these 704 patients, the median duration of exposure was 12 months; 65% were exposed for at least 6 months and 50% were exposed for at least one year.
In this pooled safety population, the most common (≥ 30%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased neutrophil count (54%), decreased hemoglobin (43%), decreased leukocytes (32%), fatigue (31%), decreased platelets (31%), decreased lymphocyte count (31%), and calcium decreased (30%)
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
BRUIN
The safety of JAYPIRCA was evaluated in the BRUIN trial, an open-label, multicohort, single-arm study in patients with previously treated MCL who received a prior BTK inhibitor [see Clinical Studies (14.1 ) ] . The trial required a platelet count ≥ 50 x 10 9 /L, absolute neutrophil count ≥ 0.75 x 10 9 /L, hepatic transaminases ≤ 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN), and an ECOG performance status of 0 to 2. The trial excluded patients with active central nervous system (CNS) involvement by lymphoma, significant cardiovascular disease, major bleeding or grade ≥ 3 arrhythmia with a prior BTK inhibitor, prolonged QTc interval, or need for a strong CYP3A inhibitor or inducer or strong P-gp inhibitor.
Patients received JAYPIRCA 200 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (n = 128); 36% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 10% were exposed for at least one year. The median number of prior therapies was 3 (range: 1-9). The median age was 71 years (range: 46 to 88 years) and 80% of patients were male. Race was reported for all patients; 78% were White, 14% were Asian, 2.3% were Black, and 2.3% were Hispanic or Latino.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 38% of patients who received JAYPIRCA. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 2% of patients were pneumonia (14%), COVID-19 (4.7%), musculoskeletal pain (3.9%), hemorrhage (2.3%), pleural effusion (2.3%), and sepsis (2.3%). Fatal adverse reactions within 28 days of the last dose of JAYPIRCA occurred in 7% of patients, most commonly due to infections (4.7%) including COVID-19 (3.1% of all patients).
Adverse reactions led to dose reductions in 4.7%, treatment interruption in 32%, and permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in 9%. Adverse reactions that resulted in dosage modification in > 5% of patients included pneumonia and neutropenia. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in > 1% of patients included pneumonia.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 15%), excluding laboratory terms, were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, edema, dyspnea, pneumonia, and bruising.
Table 2 summarizes select adverse reactions in BRUIN.
| JAYPIRCA 200 mg once daily | ||
|---|---|---|
| N = 128 | ||
a Each term listed includes other related terms. | ||
b includes 1 fatality from COVID-19 pneumonia. | ||
c includes 1 fatality from hemorrhage. | ||
| Adverse Reactions a | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) |
| General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 29 | 1.6 |
| Edema | 18 | 0.8 |
| Fever | 13 | - |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain | 27 | 3.9 |
| Arthritis or arthralgia | 12 | 0.8 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 19 | - |
| Constipation | 13 | - |
| Abdominal pain | 11 | 0.8 |
| Nausea | 11 | - |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea | 17 | 2.3 |
| Cough | 14 | - |
| Injury | ||
| Bruising | 16 | - |
| Infections | ||
| Pneumonia | 16 b | 14 |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 10 | 0.8 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Peripheral neuropathy | 14 | 0.8 |
| Dizziness | 10 | - |
| Skin and subcutaneous disorders | ||
| Rash | 14 | - |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hemorrhage | 11 c | 3.1 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% include vision changes, memory changes, headache, urinary tract infection, herpesvirus infection, and tumor lysis syndrome.
Table 3 summarizes laboratory abnormalities in BRUIN.
a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 90 to 127 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory Abnormality | JAYPIRCA a 200 mg once daily | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Hematology | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 42 | 9 |
| Platelet count decreased | 39 | 14 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 36 | 16 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 32 | 15 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Creatinine increased | 30 | 1.6 |
| Calcium decreased | 19 | 1.6 |
| AST increased | 17 | 1.6 |
| Potassium decreased | 13 | 1.6 |
| Sodium decreased | 13 | - |
| Lipase increased | 12 | 4.4 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 11 | - |
| ALT increased | 11 | 1.6 |
| Potassium increased | 11 | 0.8 |
Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in > 5% of patients included neutrophils decreased (10%), platelets decreased (7%), and lymphocytes decreased (6%).
Lymphocytosis : Upon initiation of JAYPIRCA, a temporary increase in lymphocyte counts (defined as absolute lymphocyte count increased ≥ 50% from baseline and a post-baseline value ≥ 5,000/μL) occurred in 34% of MCL patients in BRUIN. The median time to onset of lymphocytosis was 1.1 weeks, with 75% of cases occurring within 2.1 weeks, and the median duration was 11 weeks.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
BRUIN
The safety of JAYPIRCA was evaluated in the BRUIN trial, an open-label, multicohort, single-arm study in 110 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL/SLL, with 98% having received at least two prior lines of systemic therapy including a covalent BTK inhibitor and a BCL-2 inhibitor [see Clinical Studies (14.2 ) ] . The trial required a platelet count ≥ 50 x 10 9 /L, absolute neutrophil count ≥ 0.75 x 10 9 /L, hepatic transaminases ≤ 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN), and an ECOG performance status of 0 to 2. The trial excluded patients with active central nervous system (CNS) involvement by lymphoma, significant cardiovascular disease, major bleeding, uncontrolled or symptomatic arrhythmias, prolonged QTc interval, or need for a strong CYP3A inhibitor or inducer or strong P-gp inhibitor.
Patients received JAYPIRCA 200 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (N = 110); 60% were exposed for at least 1 year and 14% were exposed for at least two years. The median age was 68 years (range: 41 to 88 years) and 67% of patients were male. Race was reported in 110 (100%) patients; of these patients, 89% were White, 4.5% were Black, 1.8% were Asian, and 1.8% were Hispanic or Latino. The median number of prior therapies was 5 (range: 1-11).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 56% of patients who received JAYPIRCA. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients were pneumonia (18%), COVID-19 (9%), sepsis (7%), and febrile neutropenia (7%). Fatal adverse reactions within 28 days of the last dose of JAYPIRCA occurred in 11% of patients, most commonly due to infections (10%), including sepsis (5%) and COVID-19 (2.7%).
Adverse reactions led to dose reductions in 3.6%, treatment interruption in 42%, and permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in 9%. Adverse reactions which resulted in dose reductions of JAYPIRCA in > 1% of patients included neutropenia. Adverse reactions which resulted in treatment interruptions of JAYPIRCA in > 5% of patients included pneumonia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and COVID-19. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in > 1% of patients included second primary malignancy, COVID-19, and sepsis.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%), excluding laboratory terms, were fatigue, bruising, cough, musculoskeletal pain, COVID-19, diarrhea, pneumonia, abdominal pain, dyspnea, hemorrhage, edema, nausea, pyrexia, and headache. Table 4 summarizes select adverse reactions for patients treated on BRUIN.
| JAYPIRCA 200 mg once daily | ||
|---|---|---|
| N = 110 | ||
| Adverse Reactions a | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) |
a Each term listed includes other related terms. | ||
b Includes COVID-19 pneumonia. Includes 1 fatality from COVID-19 and 2 fatalities from COVID-19 pneumonia. | ||
c Includes COVID-19 pneumonia. Includes 2 fatalities from COVID-19 pneumonia and 1 fatality from pneumonia. | ||
d Includes preferred terms hemorrhage, intracranial hemorrhage, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage. | ||
e Includes preferred terms memory impairment, confusional state, encephalopathy, mental status changes. | ||
f Includes preferred terms second primary malignancy and nonmelanoma skin cancers. 1 fatality from metastatic malignant melanoma. | ||
g Includes preferred terms renal failure, chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury. | ||
h Includes preferred terms supraventricular tachycardia, sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation. | ||
| General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 36 | 2.7 |
| Edema | 21 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 20 | 2.7 |
| Injury | ||
| Bruising | 36 | 0 |
| Fall | 14 | 0.9 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough | 33 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 22 | 2.7 |
| Mucositis | 12 | 0.9 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain | 32 | 0.9 |
| Arthritis or arthralgia | 19 | 1.8 |
| Infections | ||
| COVID-19 | 28 b | 7 |
| Pneumonia | 27 c | 16 |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 13 | 2.7 |
| Respiratory tract infection | 11 | 1.8 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 26 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 25 | 2.7 |
| Nausea | 21 | 0 |
| Constipation | 14 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hemorrhage | 22 d | 2.7 |
| Hypertension | 12 | 5 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 20 | 0.9 |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 16 | 3.6 |
| Dizziness | 15 | 0 |
| Neurological changes | 12 e | 2.7 |
| Skin and subcutaneous disorders | ||
| Rash | 19 | 0.9 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 14 | 0 |
| Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified | ||
| Second primary malignancy | 13 f | 2.7 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | ||
| Renal insufficiency | 12 g | 6 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 12 | 0 |
| Cardiac disorders | ||
| Supraventricular tachycardia | 10 h | 5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% include vision changes, lower respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, herpesvirus infection, and tumor lysis syndrome.
Table 5 summarizes laboratory abnormalities in BRUIN.
| Laboratory Abnormality | JAYPIRCA a 200 mg once daily | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 83 to 108 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Hematology | ||
| Neutrophil count decreased | 63 | 45 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 48 | 19 |
| Platelet count decreased | 30 | 15 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 23 | 8 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Calcium decreased | 40 | 2.8 |
| Sodium decreased | 30 | 0 |
| ALT increased | 23 | 2.8 |
| AST increased | 23 | 1.9 |
| Creatinine increased | 23 | 0 |
| Lipase increased | 21 | 7 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 21 | 0 |
Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in > 5% of patients included neutrophils decreased (23%).
••Lymphocytosis : Upon initiation of JAYPIRCA, a temporary increase in lymphocyte counts (defined as absolute lymphocyte count increased ≥ 50% from baseline and a post-baseline value ≥ 5,000/μL) occurred in 64% of CLL/SLL patients in BRUIN. The median time to onset of lymphocytosis was 1.1 weeks, with 75% of cases occurring within 1.1 weeks, and the median duration was 19 weeks.
BRUIN-321
The safety of JAYPIRCA was evaluated in BRUIN CLL-321, a randomized, multicenter, open-label active control trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] . The trial enrolled patients with relapsed or refractory CLL/SLL who were previously treated with a covalent BTK inhibitor. The trial required a platelet count ≥ 50 x 10 9 /L, absolute neutrophil count ≥ 0.75 x 10 9 /L, and an estimated creatinine clearance ≥ 30 mL/min. The trial excluded patients with significant cardiovascular disease including uncontrolled or symptomatic arrhythmias, or major bleeding on a prior covalent BTK inhibitor.
The trial enrolled 238 patients who were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive JAYPIRCA given orally once daily at a dose of 200 mg until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity or investigator's choice of either idelalisib in combination with a rituximab product or bendamustine in combination with a rituximab product [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] . One hundred sixteen patients received JAYPIRCA and 109 patients received investigator's choice of idelalisib and rituximab or bendamustine and rituximab.
The median duration of treatment with JAYPIRCA was 15 months with 78% on treatment for greater than 6 months and 66% for greater than 12 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 47% of patients who received JAYPIRCA. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 3% of patients were pneumonia (21%), COVID-19 (5%), and sepsis (3.4%). Fatal adverse reactions within 30 days of the last dose of JAYPIRCA occurred in 8% of patients, most commonly due to infections (7%), COVID-19 (5%) and pneumonia (3.4%).
Adverse reactions led to permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in 17% of patients, dose reductions in 10%, and treatment interruption in 51%. Adverse reactions which resulted in dose reductions of JAYPIRCA in > 1% of patients included neutropenia. Adverse reactions which resulted in treatment interruptions of JAYPIRCA in > 5% of patients included pneumonia, neutropenia, hemorrhage and COVID-19. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of JAYPIRCA in > 1% of patients included pneumonia, COVID-19, neutropenia, anemia, and cardiac arrythmias.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%), excluding laboratory terms, were pneumonia and upper respiratory tract infections. Table 6 summarizes select adverse reactions for patients treated on BRUIN CLL-321.
a Each term listed includes other related terms. | ||||
b Includes COVID-19 pneumonia. Includes 3 fatalities from COVID-19 pneumonia, 3 fatalities from pneumonia, for JAYPIRCA; includes 3 fatalities from pneumonia for IR and 1 fatality from COVID-19 pneumonia for BR. | ||||
c Includes COVID-19 pneumonia. Includes 3 fatalities from COVID-19 pneumonia and 3 fatalities from COVID-19 for JAYPIRCA and 1 fatality from COVID-19 for IR and 1 fatality from COVID-19 pneumonia for BR. | ||||
| JAYPIRCA | Investigator's Choice | |||
| N = 116 | N = 109 | |||
| Adverse Reactions a | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) |
| Pneumonia | 28 b | 16 | 16 b | 11 |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 21 | 0.9 | 10 | 0 |
| COVID-19 | 17 c | 0.9 | 19 c | 4.6 |
| General Disorders | ||||
| Fatigue | 19 | 2.6 | 26 | 1.8 |
| Edema | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Cough | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0 |
| Fever | 13 | 0.9 | 27 | 0.9 |
| Nausea | 11 | 0.9 | 20 | 0 |
| Headache | 11 | 0.9 | 16 | 0 |
| Hemorrhage | 16 | 2.6 | 7 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain | 19 | 0.9 | 13 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 16 | 0 | 31 | 6 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Disorders | ||||
| Rash | 14 | 2.6 | 20 | 4.6 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% in patients who received JAYPIRCA include vision changes, urinary tract infection, herpes virus infection, and hypertension.
Table 7 summarizes laboratory abnormalities in BRUIN CLL-321.
a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 113 to 114 in the JAYPIRCA arm and from 29 to 31 for bendamustine plus rituximab, and 75 for idelalisib plus rituximab, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one posttreatment value. | ||||
| Laboratory Abnormality | JAYPIRCA a | Investigator's Choice a | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Hematology | ||||
| Neutrophil count decreased | 54 | 26 | 67 | 27 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 45 | 10 | 42 | 8 |
| Platelet count decreased | 37 | 17 | 42 | 9 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| ALT increased | 25 | 1.8 | 46 | 14 |
| Creatinine increased | 25 | 0 | 20 | 1 |
| Calcium decreased | 23 | 0.9 | 31 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 22 | 0.9 | 21 | 1 |
| Bilirubin increased | 21 | 0.9 | 21 | 1 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use. If concomitant use is unavoidable, reduce the JAYPIRCA dose. (2.4 , 7.1 )
- Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use. If concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inducers is unavoidable, increase the JAYPIRCA dose. (2.5 , 7.1 )
- Sensitive CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A, P-gp, or BCRP Substrates: For substrates where minimal concentration changes may increase the risk of adverse reactions, follow recommendations for co-administration with CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A, P-gp, or BCRP inhibitors provided in their approved product labeling. (7.2 )
Effect of Other Drugs on JAYPIRCA
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Pirtobrutinib is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use of JAYPIRCA with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increased pirtobrutinib systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may increase the risk of JAYPIRCA adverse reactions. Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors during treatment with JAYPIRCA. If concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce the JAYPIRCA dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] .
Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of JAYPIRCA with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer decreased pirtobrutinib systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may reduce JAYPIRCA efficacy. Avoid concomitant use of JAYPIRCA with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. If concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inducers is unavoidable, increase the JAYPIRCA dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] .
Effect of JAYPIRCA on Other Drugs
Sensitive CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A, P-gp, or BCRP Substrates
JAYPIRCA is a P-gp inhibitor, a moderate CYP2C8 and BCRP inhibitor, and a weak CYP2C19 and CYP3A inhibitor. Concomitant use of JAYPIRCA with sensitive P-gp, CYP2C8, BCRP, CYP2C19, or CYP3A substrates increased their plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates for drugs which are sensitive to minimal concentration changes. Follow recommendations for sensitive CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A, P-gp, or BCRP substrates provided in their approved product labeling.
DESCRIPTION
Pirtobrutinib is a kinase inhibitor. It is an orally available, small molecule ATP-competitive inhibitor of BTK. The active pharmaceutical ingredient is pirtobrutinib with the molecular formula C 22 H 21 F 4 N 5 O 3 and a molecular weight of 479.44 g/mol. The chemical name for pirtobrutinib is 5-amino-3-{4-[(5-fluoro-2-methoxybenzamido)methyl]phenyl}-1-[(2 S )-1,1,1-trifluoropropan-2-yl]-1 H -pyrazole-4-carboxamide.

Pirtobrutinib is a white to practically white to yellow to brown solid. The aqueous solubility of pirtobrutinib is considered practically insoluble, or insoluble, across the pH 1 to pH 7 range.
Pirtobrutinib tablets are supplied as 50 mg or 100 mg film-coated, debossed tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains inactive ingredients of croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and silicon dioxide. The tablet film coating material contains FD&C Blue #2, hypromellose, titanium dioxide and triacetin.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of action
Pirtobrutinib is a small molecule, noncovalent inhibitor of BTK. BTK is a signaling protein of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. In B-cells, BTK signaling results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Pirtobrutinib binds to wild type BTK and BTK harboring C481 mutations, leading to inhibition of BTK kinase activity. In nonclinical studies, pirtobrutinib inhibited BTK-mediated B-cell CD69 expression and inhibited malignant B-cell proliferation. Pirtobrutinib showed dose-dependent anti-tumor activities in BTK wild type and BTK C481S mutant mouse xenograft models.
Pharmacodynamics
At the recommended dosage of 200 mg once daily, pirtobrutinib trough concentrations exceeded the BTK IC 96 . BTK occupancy is maintained throughout the dosing interval, regardless of the intrinsic rate of BTK turnover.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of a single 900 mg dose of pirtobrutinib (equivalent to approximately 2 times higher than the concentrations achieved at steady state at the recommended dosage of 200 mg once daily) on the QTc interval was evaluated in a placebo-controlled and positive-controlled study in 30 healthy subjects. Pirtobrutinib had no clinically meaningful effect on the change in QTcF interval (i.e., > 10 ms) and there was no relationship between pirtobrutinib exposure and change in QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib were characterized in healthy subjects and in patients with cancer. Pirtobrutinib exposure (AUC) and C max increases proportionally following single oral doses ranging from 300 mg to 800 mg (1.5 to 4 times the approved recommended dosage) and once daily doses ranging from 25 – 300 mg (0.125 to 1.5 times the recommended dosage). Steady state was achieved within 5 days of once daily dosing, and the mean (CV%) accumulation ratio was 1.63 (26.7%) based on AUC after administration of 200 mg dosages.
Following administration of the recommended dosage, the geometric mean (CV%) steady-state AUC and C max of pirtobrutinib were 92705 h•ng/mL (39%) and 6503 ng/mL (25%), respectively. The geometric mean (CV%) AUC 0-24 and C max of pirtobrutinib on Cycle 1 Day 8 were 81800 h•ng/mL (66.6%) and 3670 ng/mL (89.5%), respectively.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of pirtobrutinib after a single oral 200 mg dose is 85.5% (range 75.9% to 90.9%). The median time (range) to reach peak plasma concentration (t max ) is approximately 2 hours (0.833 to 4.15 hours).
Effect of Food
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib were observed following administration of a high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500 to 600 calories from fat) to healthy subjects. A high-fat meal decreased the C max of pirtobrutinib by 23% and delayed tmax by 1 hour. There was no effect on pirtobrutinib AUC.
Distribution
The mean apparent central volume of distribution of pirtobrutinib is 34.2 L. Human protein binding of pirtobrutinib is 96% and is independent of concentration in vitro. Mean blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.79.
Elimination
The effective half-life of pirtobrutinib is approximately 20 hours and the mean (CV%) apparent clearance is 2.05 L/h (35.7 %).
Metabolism
Pirtobrutinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and direct glucuronidation by UGT1A8 and UGT1A9, in vitro.
Excretion
Following a single radiolabeled dose of pirtobrutinib 200 mg to healthy subjects, 37% of the dose was recovered in feces (18% unchanged) and 57% in urine (10% unchanged).
Specific Populations
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib based on age (range 22 – 95 years), sex, race/ethnicity (White 84%, Asian 8%), body weight (range 35.7 – 152 kg), mild (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST), moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST), or severe (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. The effect of other races/ethnicities on the pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib is unknown.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Following a single 200 mg oral dose, the AUC of pirtobrutinib in subjects with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15-29 mL/min) increased by 62% and mean unbound AUC increased by 68% compared to healthy subjects with normal renal function. There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib in subjects with mild (eGFR 60-89 mL/min) or moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-59 mL/min). The effect of renal impairment requiring dialysis on the pharmacokinetics of pirtobrutinib is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Co-administration of a single 200 mg dose of pirtobrutinib with itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased AUC of pirtobrutinib by 49%.
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Verapamil and diltiazem (moderate CYP3A inhibitors) are predicted to increase the AUC of pirtobrutinib by 30% and 20%, respectively.
Strong CYP3A inducers: Coadministration of a single 200 mg dose of pirtobrutinib with rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the AUC of pirtobrutinib by 71%.
Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Efavirenz and bosentan (moderate CYP3A inducers) are predicted to decrease the AUC of pirtobrutinib by 49% and 27%, respectively.
Gastric Reducing Agents: No clinically significant differences in pirtobrutinib pharmacokinetics were observed when co-administered with omeprazole (a proton pump inhibitor).
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors: No clinically significant differences in pirtobrutinib pharmacokinetics were observed when co-administered with itraconazole (P-gp inhibitor).
CYP3A Substrates: Pirtobrutinib increased the AUC and C max of orally administered midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) by 70% and 58%, respectively. Pirtobrutinib did not have a clinically meaningful effect on the exposure of intravenously administered midazolam.
CYP2C8 Substrates: Pirtobrutinib increased the AUC and C max of repaglinide (sensitive CYP2C8 substrate) by 130% and 98%, respectively.
CYP2C19 Substrates: Pirtobrutinib increased the AUC and C max of omeprazole (sensitive CYP2C19 substrate) by 56% and 49%, respectively.
P-gp Substrates: A single 200 mg dose of pirtobrutinib increased the AUC and C max of digoxin (sensitive P-gp substrate) by 17% and 51%, respectively. Multiple doses of pirtobrutinib (200 mg daily) further increased the AUC and C max of digoxin (sensitive P-gp substrate) up to 35% and 55%, respectively.
BCRP Substrates: Multiple doses of pirtobrutinib (200 mg daily) increased the AUC and C max of rosuvastatin (sensitive BCRP substrate) by 140% and 146%, respectively.
CYP1A2 and CYP2C9 Substrates: Pirtobrutinib did not have a clinically meaningful effect on the exposures of caffeine (sensitive CYP1A2 substrate) or S-warfarin (moderate sensitive CYP2C9 substrate).
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: Pirtobrutinib inhibits CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP3A, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6. Pirtobrutinib induces CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP2B6, and CYP2C19.
Transporter Systems: Pirtobrutinib inhibits P-gp and BCRP, but not OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MATE1, or MATE2-K. Pirtobrutinib is not a substrate of the hepatic transporters. Pirtobrutinib is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP, but not OCT1, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or BSEP.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with pirtobrutinib.
Pirtobrutinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay. Pirtobrutinib was aneugenic in in vitro micronucleus assays using human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Pirtobrutinib was not genotoxic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay at doses up to 2000 mg/kg.
Studies to assess the effects of pirtobrutinib on fertility have not been conducted. In repeat-dose toxicity studies of up to 3-months duration conducted with pirtobrutinib in rats and dogs, no effects on male or female reproductive organs were identified.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The efficacy of JAYPIRCA in patients with MCL was evaluated in BRUIN [NCT03740529], an open-label, international, multicohort, single-arm study of JAYPIRCA as monotherapy. Efficacy was based on 120 patients with MCL treated with JAYPIRCA who were previously treated with a BTK inhibitor. JAYPIRCA was given orally at a dose of 200 mg once daily and was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients with active central nervous system lymphoma or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) or CAR-T cell therapy within 60 days were excluded.
The median age was 71 years (range: 46 to 88 years); 79% were male; 78% were White, 14% Asian, 1.7% Black or African American. Seventy-eight percent of patients had the classic/leukemic variant of MCL, 12% had pleomorphic MCL, and 11% had blastoid MCL. The simplified Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (sMIPI) score was low in 15%, intermediate in 59%, and high in 26% of patients. Patients received a median number of 3 prior lines of therapy (range: 1 to 9) with 93% having received 2 or more prior lines. All received 1 or more prior lines of therapy containing a BTK inhibitor; other prior therapies included chemoimmunotherapy in 88%, HSCT in 20%, lenalidomide in 18%, and CAR-T therapy in 9%. The most common prior BTK inhibitors received were ibrutinib (67%), acalabrutinib (30%), and zanubrutinib (8%). Patients may have received more than one prior BTK inhibitor; 83% of patients discontinued the last BTK inhibitor for refractory or progressive disease, 10% discontinued for toxicity, and 5% discontinued for other reasons.
Efficacy was based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), as assessed by an independent review committee (IRC) using 2014 Lugano criteria. Efficacy results are shown in Table 8 . Additionally, the Kaplan-Meier estimate for the DOR rate at 6 months was 65.3% (95% CI: 49.8, 77.1).
CI, confidence interval; CR, complete response; DOR, duration of response; PR, partial response; NE, not estimable. | |
a PET-CT scans were utilized in response assessments (in 41% of patients), with the remainder being assessed by CT scans only. | |
b ORR using CT scan-based assessments in all patients was 48% (95% CI: 38, 57) and CR rate was 13%. | |
c Based on Kaplan-Meier estimation. Estimated median follow-up was 7.3 months. | |
| Outcome | JAYPIRCA 200 mg once daily (N = 120) |
| Overall Response Rate a,b | |
| ORR, n | 60 (50%) |
| (95% CI, %) | 41, 59 |
| CR, n | 15 (13%) |
| PR, n | 45 (38%) |
| Time to Response | |
| Median (range), months | 1.8 (0.8, 4.2) |
| Duration of Response c | |
| Number censored, n | 36 |
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) | 8.3 (5.7, NE) |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
BRUIN
The efficacy of JAYPIRCA in patients with CLL/SLL was evaluated in BRUIN [NCT03740529] an open-label, international, single-arm, multicohort study of JAYPIRCA as monotherapy. Efficacy was based on 108 patients with CLL/SLL treated with JAYPIRCA who were previously treated with at least two prior lines of therapy, including a BTK inhibitor and a BCL-2 inhibitor. JAYPIRCA was given orally at a dose of 200 mg once daily and was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The trial required a platelet count ≥ 50 x 10 9 /L, absolute neutrophil count ≥ 0.75 x 10 9 /L, hepatic transaminases ≤ 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN), and an ECOG performance status of 0 to 2. The trial excluded patients with significant cardiovascular disease, major bleeding, uncontrolled or symptomatic arrhythmias, prolonged QTc interval, or need for a strong CYP3A inhibitor or inducer or strong P-gp inhibitor. Patients with active central nervous system (CNS) involvement by lymphoma or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) within 60 days were excluded.
The median age was 68 years (range: 41 to 88 years); 69% were male; 89% were White, 4.6% Black or African American, 1.9% Asian and 1.9% were Hispanic or Latino. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 or 1 in 91% of patients and 48% of patients had Rai stage III or IV disease. Among those patients with central testing available, 42% (37 of 88 patients) had a C481 BTK mutation, 54% (43 of 79 patients) had 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutation, 93% (77 of 83 patients) had unmutated IGHV, and 22% (16 of 72 patients) had 11q deletion. Patients received a median number of 5 prior lines of therapy (range: 2 to 11). The most common prior BTK inhibitors received were ibrutinib (97%), acalabrutinib (9%), and zanubrutinib (0.9%). Seventy-seven percent of patients discontinued the last BTK inhibitor for refractory or progressive disease, 13% discontinued for toxicity, and 10% discontinued for other reasons.
Efficacy was established based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), as assessed by an independent review committee (IRC) using 2018 iwCLL criteria. Efficacy results are shown in Table 9 -. The median time to response was 3.7 months (range: 1.7, 27.9 months).
CI, confidence interval; PR, partial response. | |
a Based on Kaplan-Meier estimation. Estimated median follow-up was 15.7 months. | |
| Outcome | JAYPIRCA 200 mg once daily (N = 108) |
| Overall Response Rate | |
| ORR, n | 78 (72%) |
| (95% CI, %) | 63, 80 |
| PR, n | 78 (72%) |
| Duration of Response a | |
| Median DOR, months (95% CI) | 12.2 (9.3, 14.7) |
BRUIN-CLL-321
The efficacy of JAYPIRCA in patients with covalent BTK-inhibitor pretreated CLL/SLL was evaluated in a randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (BRUIN-CLL-321, NCT 04666038).
The trial randomized 238 patients who were previously treated for CLL/SLL, including a covalent BTK inhibitor. Patients previously treated with a non-covalent BTK inhibitor were not permitted. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either:
- JAYPIRCA given orally once daily at a dose of 200 mg until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or
- Investigator's choice:
- Idelalisib plus a rituximab product (IR): Idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, in combination with 8 infusions of a rituximab product (375 mg/m 2 intravenously on Day 1 of Cycle 1, followed by 500 mg/m 2 every 2 weeks for 4 doses and then every 4 weeks for 3 doses), with a 28-day cycle length.
- Bendamustine plus a rituximab product (BR): Bendamustine 70 mg/m 2 intravenously (Day 1 and 2 of each 28-day cycle), in combination with a rituximab product (375 mg/m 2 intravenously on Day 1 of Cycle 1, then 500 mg/m 2 on Day 1 of subsequent cycles), for up to 6 cycles.
Crossover to JAYPIRCA monotherapy was permitted for patients in the investigator's choice arm after confirmed disease progression. Of the 119 patients in the investigator's choice arm, 50 crossed over to receive JAYPIRCA therapy.
Randomization was stratified by 17p deletion status and receipt of prior venetoclax treatment. Of the 238 patients randomized, 119 were assigned to JAYPIRCA monotherapy, 82 to IR, and 37 to BR. The median age was 67 years (range: 42 to 90 years); 70% were male; 81% were White, 12% Asian, 2.5% Black or African American, and 4.2% were Hispanic or Latino. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 or 1 in 93% of patients and 46% of patients had Rai stage III or IV disease. Forty four percent had 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutation, 69% had unmutated IGHV, and 41% had complex karyotype. Patients received a median number of 3 prior lines of therapy (range: 1 to 13); 51% had received prior BCL2-inhibitor therapy. The most common prior BTK inhibitors received were ibrutinib (87%), acalabrutinib (16%), and zanubrutinib (7%). Seventy-one percent of patients discontinued the most recent BTK inhibitor for refractory or progressive disease, 17% discontinued for toxicity, and 10% discontinued for other reasons.
The primary efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC) using 2018 iwCLL criteria. The median duration of follow up at the primary analysis was 6.6 months. Efficacy results for the primary analysis are presented in Table 10 and Figure 1 .
CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio. | ||
a Efficacy was assessed using the 2018 International Workshop for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) guidelines | ||
b Based on Kaplan-Meier estimation. | ||
c Based on stratified Cox proportional hazards model. | ||
d 2-sided p-value based on stratified log-rank test | ||
| Parameter a | JAYPIRCA 200 mg once daily (N = 119) | Investigator's Choice of Idelalisib + Rituximab Product or Bendamustine + Rituximab Product (N = 119) |
| Progression-free Survival | ||
| Number of Events, n | 45 (38%) | 50 (42%) |
| Disease Progression | 35 (29%) | 38 (32%) |
| Death | 10 (8%) | 12 (10%) |
| Median PFS (95% CI), months b | 11.2 (9.5, 11.4) | 8.7 (7.2, 10.2) |
| HR (95% CI) c | 0.58 (0.38, 0.89) | |
| P-value d | 0.0105 | |
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Curve of IRC-Assessed PFS in Patients with CLL/SLL Previously Treated with a BTK Inhibitor in BRUIN CLL-321
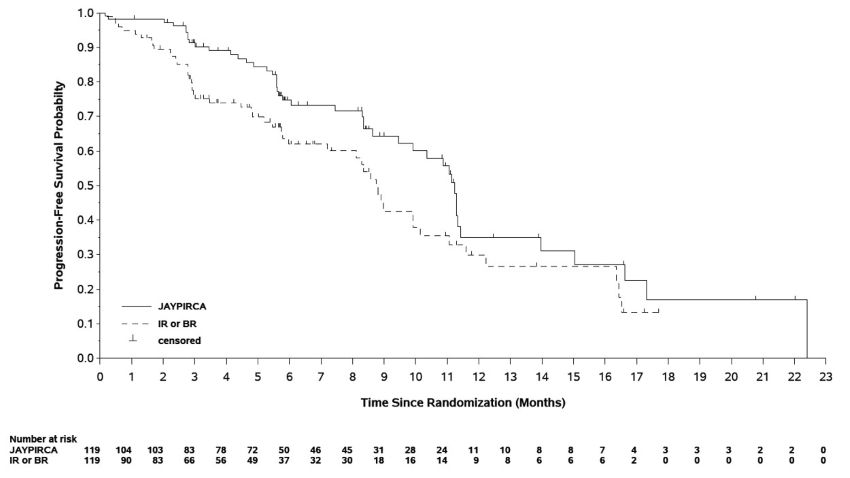
At the primary analysis for PFS the objective response rate (ORR) as assessed by IRC using 2018 iwCLL criteria, was 31.1% (95% CI 23.0, 40.2) in the JAYPIRCA arm and 29.4% (95% CI 21.4, 38.5) in the investigator choice arm.
At an updated analysis with a median follow-up time of 19.8 months, 38 patients (32%) in the JAYPIRCA arm and 32 patients (27%) in the investigator's choice arm died. The unadjusted HR for overall survival (OS) was 1.09 (95% CI: 0.68, 1.75). The ORR was 48.7% (95% CI 39.5, 58.1) in the JAYPIRCA arm and 38.7% (95% CI 29.9, 48.0) in the investigator choice arm.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
JAYPIRCA tablets are supplied as follows:
| Tablet Strength | Description | Package Configuration | NDC Number |
| 50 mg | Blue, film coated, arc-triangle shaped tablets debossed with “Lilly 50” on one side and “6902” on the other side. | Bottle with child-resistant closure. Each bottle contains 30 tablets. | 0002-6902-30 |
| 100 mg | Blue, film coated, round tablets debossed with “Lilly 100” on one side and “7026” on the other side. | Bottle with child-resistant closure. Each bottle contains 60 tablets. | 0002-7026-60 |
Storage and Handling
Store JAYPIRCA tablets at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) ([see USP Controlled Room Temperature]).
Mechanism of action
Pirtobrutinib is a small molecule, noncovalent inhibitor of BTK. BTK is a signaling protein of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. In B-cells, BTK signaling results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Pirtobrutinib binds to wild type BTK and BTK harboring C481 mutations, leading to inhibition of BTK kinase activity. In nonclinical studies, pirtobrutinib inhibited BTK-mediated B-cell CD69 expression and inhibited malignant B-cell proliferation. Pirtobrutinib showed dose-dependent anti-tumor activities in BTK wild type and BTK C481S mutant mouse xenograft models.