Get your patient on Jelmyto (Mitomycin)
Jelmyto prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Jelmyto patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- JELMYTO is for pyelocalyceal use only and not for intravenous use, topical use, or oral administration. (2.1 )
- Administer 1.3 g of sodium bicarbonate orally the evening prior to, the morning of, and 30 minutes prior to instillation procedure (total of 3.9 g). (2.1 )
- The dose of JELMYTO to be instilled is 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or nephrostomy tube, with total instillation volume based on volumetric measurements using pyelography, not to exceed 15 mL (60 mg of mitomycin). (2.2 )
- Instill JELMYTO once weekly for six weeks. For patients with a complete response 3 months after JELMYTO initiation, JELMYTO instillations may be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations. (2.2 )
Important Administration Instructions
See the Instructions for Administration provided separately.
JELMYTO is for pyelocalyceal use only. JELMYTO is not for intravenous use, topical use, or oral administration. Prior to every instillation, instruct the patient to take 1.3 g of sodium bicarbonate orally the evening prior to, the morning of, and 30 minutes prior to the instillation procedure (total of 3.9 g).
General anesthesia, local anesthesia, sedation, prophylactic antibiotics and/or antihistamines may be used at the discretion of the treating urologist. If the patient is to be anesthetized, advise the patient not to take sodium bicarbonate within 30 minutes prior to the treatment.
Consider withholding diuretics one day prior to instillation until 4 hours post-instillation.
When instilling JELMYTO, the entire syringe must be emptied within one minute.
Advise patients that JELMYTO may discolor urine to a violet to blue color following the instillation procedure. Advise patients to avoid contact with urine for at least six hours post-instillation, to void urine sitting on a toilet, and to flush the toilet several times after use.
Recommended Dosage
The dose of JELMYTO to be instilled is 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or a nephrostomy tube, with total instillation volume based on volumetric measurements using pyelography, not to exceed 15 mL (60 mg of mitomycin).
Instill JELMYTO once weekly for six weeks. For patients with a complete response 3 months after JELMYTO initiation, JELMYTO instillations may be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations.
Preparation and Handling
See the Instructions for Pharmacy for preparation provided separately.
JELMYTO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1
JELMYTO must be prepared under chilled conditions. Once reconstituted , the admixture will have a concentration of 4 mg of mitomycin per mL and will appear as a viscous liquid for instillation. Reconstituted JELMYTO has reverse thermal properties with a gelation point of approximately 19°C (66°F). Reconstituted JELMYTO should be instilled as soon as possible after reconstitution. Store reconstituted JELMYTO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 96 hours (4 days). JELMYTO will appear as a semisolid gel when stored under these conditions. Protect reconstituted JELMYTO from light.
JELMYTO must be instilled as a chilled solution using a Uroject12 Lever, a Luer Lock syringe, and a ureteral catheter with molded Luer Lock connector. Once chilled at -3°C to 5°C (27°F to 41°F), JELMYTO will convert to a viscous liquid for instillation and is stable for up to 1 additional hour. Reconstituted JELMYTO must be instilled within 1 hour after it is converted to a viscous liquid.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jelmyto prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JELMYTO ® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with low-grade Upper Tract Urothelial Cancer (LG-UTUC).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- JELMYTO is for pyelocalyceal use only and not for intravenous use, topical use, or oral administration. (2.1 )
- Administer 1.3 g of sodium bicarbonate orally the evening prior to, the morning of, and 30 minutes prior to instillation procedure (total of 3.9 g). (2.1 )
- The dose of JELMYTO to be instilled is 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or nephrostomy tube, with total instillation volume based on volumetric measurements using pyelography, not to exceed 15 mL (60 mg of mitomycin). (2.2 )
- Instill JELMYTO once weekly for six weeks. For patients with a complete response 3 months after JELMYTO initiation, JELMYTO instillations may be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations. (2.2 )
Important Administration Instructions
See the Instructions for Administration provided separately.
JELMYTO is for pyelocalyceal use only. JELMYTO is not for intravenous use, topical use, or oral administration. Prior to every instillation, instruct the patient to take 1.3 g of sodium bicarbonate orally the evening prior to, the morning of, and 30 minutes prior to the instillation procedure (total of 3.9 g).
General anesthesia, local anesthesia, sedation, prophylactic antibiotics and/or antihistamines may be used at the discretion of the treating urologist. If the patient is to be anesthetized, advise the patient not to take sodium bicarbonate within 30 minutes prior to the treatment.
Consider withholding diuretics one day prior to instillation until 4 hours post-instillation.
When instilling JELMYTO, the entire syringe must be emptied within one minute.
Advise patients that JELMYTO may discolor urine to a violet to blue color following the instillation procedure. Advise patients to avoid contact with urine for at least six hours post-instillation, to void urine sitting on a toilet, and to flush the toilet several times after use.
Recommended Dosage
The dose of JELMYTO to be instilled is 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or a nephrostomy tube, with total instillation volume based on volumetric measurements using pyelography, not to exceed 15 mL (60 mg of mitomycin).
Instill JELMYTO once weekly for six weeks. For patients with a complete response 3 months after JELMYTO initiation, JELMYTO instillations may be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations.
Preparation and Handling
See the Instructions for Pharmacy for preparation provided separately.
JELMYTO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1
JELMYTO must be prepared under chilled conditions. Once reconstituted , the admixture will have a concentration of 4 mg of mitomycin per mL and will appear as a viscous liquid for instillation. Reconstituted JELMYTO has reverse thermal properties with a gelation point of approximately 19°C (66°F). Reconstituted JELMYTO should be instilled as soon as possible after reconstitution. Store reconstituted JELMYTO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 96 hours (4 days). JELMYTO will appear as a semisolid gel when stored under these conditions. Protect reconstituted JELMYTO from light.
JELMYTO must be instilled as a chilled solution using a Uroject12 Lever, a Luer Lock syringe, and a ureteral catheter with molded Luer Lock connector. Once chilled at -3°C to 5°C (27°F to 41°F), JELMYTO will convert to a viscous liquid for instillation and is stable for up to 1 additional hour. Reconstituted JELMYTO must be instilled within 1 hour after it is converted to a viscous liquid.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For pyelocalyceal solution: A kit containing the following:
- Two 40 mg (each) single-dose vials of sterile, lyophilized, grey to greyish-purple, cake or powder of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal solution
- One single-dose vial of 20 mL of sterile, clear, colorless gel with or without bubbles at room temperature or clear, colorless liquid at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F), to be used as a vehicle for reconstitution
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, JELMYTO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] . There are no available data on JELMYTO use in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of mitomycin resulted in teratogenicity (see Data ) . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% - 4% and 15% - 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Teratological changes have been noted with mitomycin in animal studies.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of mitomycin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with JELMYTO and for 1 week following the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
JELMYTO can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating JELMYTO.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 6 months following the last dose.
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 3 months following the last dose.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients in the Olympus trial, 75% (53 patients) were 65 years of age and over and 37% (26 patients) were 75 years of age and over. Clinical studies of JELMYTO did not include sufficient numbers of younger patients less than 65 years old to determine whether they respond differently from older patients.
Renal Impairment
No data are available in patients with severe renal impairment. Avoid use of JELMYTO in patients with a Glomerular Filtration Rate of < 30 mL/min.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
JELMYTO is contraindicated in patients with perforation of the bladder or upper urinary tract.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Ureteric Obstruction: Ureteric obstruction may occur. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of ureteric obstruction. Transient or long-term ureteral stents or alternative procedures may be required. Withhold or permanently discontinue JELMYTO based on the severity of the ureteric obstruction. (5.1 )
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia may occur. Monitor blood counts. Withhold or permanently discontinue JELMYTO based on the severity. (5.2 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.3 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Ureteric Obstruction
Ureteric obstruction, including ureteral stenosis and hydronephrosis, occurred in patients receiving JELMYTO.
In the Olympus study, ureteric obstruction was reported in 58% (n=41) of patients receiving JELMYTO, including 17% (n=12) of patients who experienced Grade 3 obstruction. The median time to first onset was 72 days (range: 15-462). Interventions in the 41 patients experiencing ureteric obstruction included ureteral stent placement (88%), balloon dilatation (29%), and nephroureterectomy (4.9%). In the 36 patients who required ureteral stent placement, the median duration of indwelling stents was 52 days (range: 1-292). Ureteric obstruction did not resolve or resolved with sequelae in 44% (n=18) of these patients. Of the 41 patients who experienced ureteric obstruction, 17% (n=7) experienced Grades 1-2 increase in serum creatinine.
In the 42 patients who only received JELMYTO during the treatment phase (no maintenance therapy), ureteric obstruction was reported in 40% (n=17).
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of ureteric obstruction, including flank pain, and fever, and for changes in renal function. Patients who experience obstruction may require transient or long-term ureteral stents or alternative procedures. Withhold or permanently discontinue JELMYTO based on the severity of ureteric obstruction.
Bone Marrow Suppression
The use of JELMYTO can result in bone marrow suppression, particularly thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. In the Olympus study, Grade 3 thrombocytopenia occurred in three patients, Grade 3 anemia in one patient, and Grade 3 neutropenia in one patient. Gross extravasation of JELMYTO via urinary tract perforation or impaired mucosa was not observed in these patients. The following tests should be obtained prior to each treatment: Platelet count, white blood cell count differential and hemoglobin. Withhold JELMYTO for Grade 2 thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Permanently discontinue for Grade 3 or greater thrombocytopenia or neutropenia.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, JELMYTO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of mitomycin resulted in teratogenicity. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 6 months following the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 3 months following the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Ureteric Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Bone Marrow Suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
The safety of JELMYTO was evaluated in Olympus, an open-label, single-arm study in 71 patients with LG-UTUC [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . For the 71 patients treated with JELMYTO during the treatment period, the median number of instillations was 6 (range: 3-6). Following initial treatment, 29 patients were treated with up to 11 doses of maintenance instillations, with a median of 6 instillations (range: 1-11).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients who received JELMYTO. Serious adverse reactions in > 3% of patients included ureteric obstruction (including ureteric stenosis and hydronephrosis), flank pain, and urosepsis. Two deaths occurred due to cerebrovascular accident and failure to thrive.
JELMYTO was permanently discontinued due to an adverse reaction in 17 (24%) patients, including 11 patients who discontinued during the treatment phase and 6 who discontinued during the maintenance phase. Adverse reactions resulting in study drug discontinuation of JELMYTO in > 3% of patients who received JELMYTO included ureteric obstruction.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 37% of patients who received JELMYTO. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in > 3% of patients who received JELMYTO included renal dysfunction, ureteric obstruction, urinary tract infection, and flank pain.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) reported were ureteric obstruction, flank pain, urinary tract infection, hematuria, renal dysfunction, nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, dysuria, and vomiting.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions in Olympus.
| JELMYTO Graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 5.0 (NCI CTCAE v5) (n=71) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) |
| Renal and urinary disorders | ||
| Ureteric Obstruction Includes hydronephrosis, obstructive uropathy, pelvi-ureteric obstruction, ureteric obstruction, ureteric stenosis, and urinary tract obstruction. | 58 | 17 |
| Ureteric stenosis | 44 | 9 |
| Hydronephrosis | 18 | 6 |
| Urinary tract obstruction | 7 | 1.4 |
| Pelvi-ureteric obstruction | 6 | 1.4 |
| Ureteric obstruction | 2.8 | 1.4 |
| Obstructive uropathy | 1.4 | 0 |
| Flank pain Includes flank pain and back pain. | 41 | 2.8 |
| Hematuria Includes hematuria and hemorrhage urinary tract. | 34 | 2.8 |
| Urinary tract infection Includes urinary tract infection, pyelonephritis, and urinary tract infection fungal. | 34 | 4.2 |
| Renal dysfunction Includes renal impairment, acute kidney injury, and renal failure. | 25 | 2.8 |
| Dysuria | 23 | 0 |
| Pollakiuria | 14 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 25 | 1.4 |
| Abdominal pain Includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain lower. | 24 | 1.4 |
| Vomiting | 20 | 4.2 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue Includes asthenia, fatigue, and malaise. | 24 | 1.4 |
| Pyrexia | 13 | 1.4 |
| Chills | 11 | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Anemia | 14 | 1.4 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Includes rash, dermatitis allergic, rash generalized, genital rash, eczema, rash maculo-papular, and skin exfoliation. | 14 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 13 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 10 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 10 | 4.2 |
Selected clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% and ≥ 2% of patients who received JELMYTO in Olympus include urinary tract inflammation, bladder spasm, urosepsis, hypersensitivity, and instillation site pain.
Table 2 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Olympus.
| Laboratory Abnormality Graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 5.0 (NCI CTCAE v5). Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available. | JELMYTO | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 (%) | |
| Hematology | ||
| Anemia | 38 | 0 |
| Lymphopenia | 21 | 2.9 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 21 | 2.8 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) eGFR calculated per MDRD (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) equation | 38 | 11 |
| Creatinine increased | 34 | 0 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 28 | 2.8 |
| Hypocalcemia | 16 | 0 |
| Hyperuricemia | 16 | 16 |
| Hyperkalemia | 13 | 1.4 |
| Hypernatremia | 11 | 0 |
DESCRIPTION
Mitomycin (also known as mitomycin-C) is an alkylating drug isolated from the broth of Streptomyces . Mitomycin is a blue-violet crystalline powder with a molecular formula of C 15 H 18 N 4 O 5 , and a molecular weight of 334.33. Its chemical name is 7-amino-9α-methoxymitosane, and it has the following structural formula:

Mitomycin is heat stable, has a high melting point, and is freely soluble in organic solvents.
JELMYTO is supplied in a kit containing two vials of sterile lyophilized mitomycin for pyelocalyceal solution, 40 mg each, and one vial of 20 mL of sterile hydrogel, to be used as a vehicle for reconstitution.
Mitomycin for pyelocalyceal solution is a sterile, lyophilized, grey to greyish-purple, cake or powder that contains mitomycin 40 mg and mannitol 80 mg in each vial.
Sterile hydrogel is a sterile, clear, colorless gel with or without bubbles at room temperature or clear, colorless liquid at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F), which contains 0.04 g hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 5.67 g poloxamer, 0.21 g polyethylene glycol, and water for injection in each vial.
Once reconstituted, JELMYTO is a clear, purple, viscous liquid at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or semisolid gel at room temperature with a concentration of 4 mg per mL of mitomycin, which may contain a few visible particles and have a pH between 6.0 and 8.0.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Mitomycin inhibits the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The guanine and cytosine content correlates with the degree of mitomycin-induced cross-linking. At high concentrations of the drug, cellular RNA and protein synthesis are also suppressed.
Pharmacodynamics
There is insufficient data to characterize an exposure-response relationship or time course of pharmacodynamic response for mitomycin.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The systemic exposure of mitomycin following instillation of up to 60 mg of mitomycin as JELMYTO into the pyelocalyceal system was evaluated pre-instillation and hourly for up to six hours post-instillation in six patients. The concentrations of mitomycin in plasma were variable and ranged from 2.43 to 12.80 ng/mL over the course of treatment; the mean C max was 6.24 ng/mL, which is estimated to be less than 1% of the expected C max after intravenous administration.
Elimination
Following instillation into the pyelocalyceal system, JELMYTO forms a semisolid gel which dissolves from normal kidney urine flow releasing mitomycin for up to 4 to 6 hours. Mitomycin is eliminated unchanged in the urine. Systemically absorbed mitomycin is rapidly cleared from the serum and approximately 10% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Metabolism
Mitomycin is metabolized primarily in the liver, but metabolism occurs in other tissues as well. It is believed that the rate of clearance is inversely proportional to the maximal serum concentration because of saturation of the degradative pathways.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Adequate long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential from instillation of mitomycin into the pyelocalyceal system have not been conducted. Mitomycin has been found to be carcinogenic in rats and mice. At doses approximating the recommended intravenous clinical dose in humans, mitomycin produced a greater than 100% increase in tumor incidence in male Sprague-Dawley rats, and a greater than 50% increase in tumor incidence in female Swiss mice.
The effect of JELMYTO on fertility is unknown.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of JELMYTO is based on the results of the Olympus study (NCT02793128), an open-label, single-arm, multicenter trial that enrolled 71 patients with treatment-naïve or recurrent non-invasive low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer (LG-UTUC) with at least one measurable papillary tumor 5 to ≤ 15 mm located above the ureteropelvic junction; patients who had larger tumors could have had tumor debulking prior to treatment, in order to meet the criteria. Patients were excluded from the trial for a history of carcinoma in situ (CIS) in the urinary tract, invasive urothelial carcinoma within 5 years, high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma within 2 years; or for BCG treatment within 6 months of JELMYTO treatment. Following biopsy and prior to treatment, patients were required to have at least one remaining visible tumor with a diameter of at least 5 mm.
Patients received JELMYTO 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or nephrostomy tube with total instillation volume based on individualized volumetric measurements using pyelography with the intent to fill the renal pelvis. Patients were treated with 6 instillations once a week. Patients who maintained a complete response (CR) after the initial treatment period were allowed to proceed to the follow-up period. During the initial treatment period, 71 patients were treated with JELMYTO, of whom 41 were subsequently continued in the follow-up period. During the follow-up period, 29 patients received at least one dose of maintenance therapy.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics for the trial population were: median age 71 years (range: 42-87 years); 68% male; 87% White; 90% Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) 0 or 1 and 10% ECOG PS 2. The median number of papillary lesions subsequent to debulking and/or biopsy and prior to treatment was 1 lesion (range: 1, 5), the median diameter of the largest lesion was 8.0 mm (range: 5.0, 15.0), and the median total visible tumor burden was 10.0 mm (range: 5.0, 25.0). Twenty-six (37%) patients underwent tumor debulking during the six weeks preceding enrollment. Of 71 enrolled patients, 48% had tumors located in regions not amenable to endoscopic resection. General anesthesia was used in 37% of patients for at least one instillation during the treatment period and for 83% of patients for at least one instillation during the follow-up period.
The major efficacy outcome measures were CR and durability of CR at 12 months after determination of CR based on ureteroscopic and local pathology assessment. CR was defined as complete absence of tumor lesions in the ipsilateral pyelocalyceal system at 3 months after initiation of JELMYTO by urine cytology and ureteroscopy. Biopsy was performed if warranted. Durability of response in patients with a CR was evaluated at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months following the initial assessment. Assessment of durability of CR subsequent to these evaluations was performed per local standards of care.
Forty-one patients (58%) achieved CR in the study (95% CI: 45%, 69%). Of the 41 patients who achieved CR, 23 (56%) of the patients remained at CR at the 12-month time point for assessment of durability, 8 (20%) experienced recurrence of disease, and 10 (24%) were unable to be evaluated (died, discontinued from the study, or were indeterminate for ongoing response). The median duration of response was not reached (range: 0, 18.8 months and ongoing). One patient, who achieved 6 months of durable CR, was diagnosed with metastatic urothelial carcinoma approximately 4.5 months after the last dose of study medication and died from the disease.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
JELMYTO kit – NDC 72493-103-03
JELMYTO is available in a kit containing the following:
- Two 40 mg (each) single-dose vials of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal solution supplied as a sterile, lyophilized, grey to greyish-purple, cake or powder. (NDC 72493-101-40)
- One 20 mL single-dose vial of sterile hydrogel supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless gel with or without bubbles at room temperature or clear, colorless liquid at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F), to be used as a vehicle for reconstitution. (NDC 72493-102-20)
Storage and Handling
Store the JELMYTO kit at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Avoid excessive heat over 40°C (104°F). Protect from light.
JELMYTO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures . 1
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PHARMACY (IFP) JELMYTO ® (jel-MYE-toe) (mitomycin) for pyelocalyceal solution
Purpose of this Instructions for Pharmacy
This Instructions for Pharmacy contains information on how to prepare JELMYTO using pharmacy supplies and a Chilling Block.
Intended Use of JELMYTO
JELMYTO (mitomycin) for pyelocalyceal solution is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with low-grade Upper Tract Urothelial Cancer (LG-UTUC).
Important Information You Need to Know Before Reconstituting JELMYTO
Once reconstituted with sterile hydrogel, JELMYTO will appear as a semisolid gel. Once chilled, JELMYTO will convert to a viscous liquid.
Reconstituted JELMYTO must be prepared under chilled conditions. A Chilling Block can be used for this purpose. JELMYTO cannot be prepared without the Chilling Block or other means of chilling.
Preparation of JELMYTO must be performed under aseptic conditions.
Storage Conditions and Handling
Instill the JELMYTO solution as soon as possible after reconstitution. Store reconstituted JELMYTO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 96 hours (4 days). Protect from light.
JELMYTO is a cytotoxic anti-cancer drug. Procedures for Proper Handling and Disposal of anti-cancer drugs should be followed.
Supplies Needed:
JELMYTO Kit containing:
|  | |
 |  | |
Pharmacy Supplies (Provided by Your Facility) Do not substitute any of these components .
| 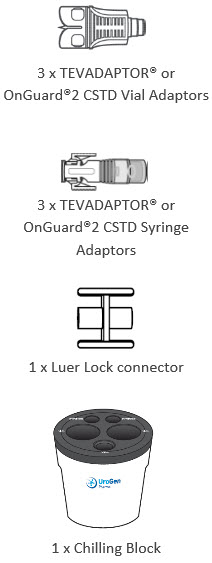 | |
Steps to Prepare JELMYTO Admixture
- A. Freeze Chilling Block The day before preparation, put the Chilling Block in the freezer at -20°C to -12°C (-4°F to 10.4°F) overnight. Note: Please refer to the Chilling Block Instructions for Use for additional information.
- B. Prepare Supplies
- Remove the Chilling Block from the freezer.
- Disinfect the Chilling Block with 70% Isopropyl alcohol or equivalent, as per your pharmacy's policy. Allow it to air dry, and then place it upright inside the hood or isolator.
- Wait 20 minutes before continuing.
- Connect vial adaptors to all three vials.
- Connect a syringe adaptor to one of the 10 mL syringes.
- Connect a syringe adaptor to the 20 mL syringe.
- Place the three vials, the 10 mL syringe, and the 20 mL syringe into the Chilling Block for at least 10 minutes.
- While the vials and syringes are in the Chilling Block, withdraw 2 mL of sterile water into the other 10 mL syringe and set aside for later use.
- C. Create Pre-Wetting Solution (PWS)
- Slowly fill the chilled 20 mL syringe with 14 mL of sterile hydrogel.
- Recap the chilled 20 mL syringe and place it in the Chilling Block.
- Slowly fill the chilled 10 mL syringe with 4 mL of sterile hydrogel.
- Discard the unused portion of sterile hydrogel.
- Replace the needle on 2 mL sterile water syringe with the Luer Lock connector.
- Remove the syringe adaptor from the 4 mL sterile hydrogel syringe.
- Connect the 4 mL sterile hydrogel syringe to the other side of the Luer Lock connector on the 2 mL sterile water syringe.
- Gently mix the sterile water with the sterile hydrogel by pushing the plungers back and forth at least 25 times to create the "pre-wetting solution" (PWS).
- Transfer the 6 mL PWS into one of the syringes.
- Replace the Luer Lock connector on the 6 mL PWS syringe with a new syringe adaptor.
- Place the 6 mL PWS syringe in the Chilling Block.
- D. Mix the Admixture
- Remove both JELMYTO vials from the Chilling Block.
- Gently tap the bottom of each vial on the table to ensure all the mitomycin powder is at the bottom of the vials.
- Remove the chilled 6 mL PWS syringe from the Chilling Block.
- Inject 3 mL of PWS into each JELMYTO vial. Note: To ensure accurate dosing, the contents of each vial must be the same.
- Discard the empty PWS syringe.
- Gently swirl each JELMYTO vial upright at least 15 times, ensuring all powder and admixture is contained at the bottom of the vial. Note: Do not invert or shake the vials.
- Immediately remove the chilled 14 mL sterile hydrogel syringe from the Chilling Block.
- Immediately inject 7 mL of sterile hydrogel into each JELMYTO vial. Note: To ensure accurate dosing, the contents of each vial must be the same.
- Gently swirl each JELMYTO vial upright at least 15 times, ensuring all admixture is contained at the bottom of the vial. Note: Do not invert or shake the vials.
- Recap and place the 20 mL syringe in the Chilling Block.
- Mix the JELMYTO admixture vials:
- Recap and place both JELMYTO vials in the Chilling Block for five minutes .
- Remove both vials and vigorously swirl them upright at least 15 times, ensuring all admixture is contained at the bottom of the vials.
- Place both vials back in the Chilling Block.
- Repeat these steps every five minutes for a total of 30 minutes.
- E. Prepare Admixture Vial
- Remove one JELMYTO vial from the Chilling Block.
- Vigorously swirl the vial upright at least 15 times. Note: Do not invert or shake the vial.
- Using the chilled 20 mL syringe, slowly withdraw 7 mL of admixture from the vial. Note: If you are having difficulty withdrawing the admixture, place the components back in the Chilling Block until the admixture liquifies again.
- Discard the empty JELMYTO vial.
- Remove the remaining JELMYTO vial from the Chilling Block.
- Inject the contents of the 20 mL syringe into that vial. Now all the admixture is contained in one vial.
- Recap the vial adaptor.
- Vigorously swirl the vial upright at least 15 times. Note: Do not invert or shake the vial.
- Your JELMYTO admixture vial is now complete, with a resultant concentration of 4 mg of mitomycin per mL following reconstitution.
- F. Dispense Admixture Vial
- Write the "Discard after" date and time on the supplied admixture label and apply to the prepared JELMYTO admixture vial. You may also substitute your pharmacy's label for dispensing the admixture. Note: The "Discard after" date and time is 96 hours (4 days) from the completion of the preparation at room temperature.
- Place the JELMYTO admixture vial in a light-protective bag.
- Transport to the treatment facility along with the JELMYTO Instructions for Administration.
 Important to Remember
Important to Remember
- All components must be kept cold during the preparation process by placing them in the Chilling Block when they are not in use.
- If you have difficulty pushing the solution or withdrawing the solution at any time, put the components back in the Chilling Block until the product liquifies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
| How do I connect the vial adaptor? Place the vial adaptor over the vial and press down firmly. You will hear a snap which confirms successful attachment. |  |
| How do I connect the syringe adaptor? Screw the Luer Lock end of the syringe adaptor onto the syringe hub until it is finger tight. |  |
| How do I connect the syringe adaptor to the vial adaptor? Place the syringe adaptor over the vial adaptor and align the tabs, then press down firmly. You will hear a snap which confirms successful attachment. |  |
| How do I disconnect the syringe adaptor from the vial adaptor? Pinch the tabs on the syringe adaptor to separate it from the vial adaptor. |  |
| Do I need to put the caps on the syringes and vials before placing them back into the chilling block? YES, the chilling block inserts are not sterile. It is important to maintain aseptic technique. | |
| Do I have to keep the vials upright when mixing? If so, why? YES, the vials should be upright during all mixing to ensure the contents are fully mixed at the bottom of the vial. |  |
| I am having difficulty working with the drug product. It seems to be solidifying. If you are having difficulty pushing the solution or withdrawing the solution, place the components back into the Chilling Block until the product liquifies. | |
This "Instructions for Pharmacy" has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
UroGen Pharma, Inc. Princeton, NJ 08540 www.JELMYTO.com
JELMYTO ® and UroGen ® are registered trademarks of UroGen Pharma, Ltd. TEVADAPTOR ® is a registered trademark of Simplivia Healthcare Ltd. OnGuard ® is a registered trademark of B. Braun Medical Inc.
Copyright© 2022 UroGen Pharma, Inc. All rights reserved.
JEL-IFP-003
IFP-0002025/Ver. 4
Mechanism of Action
Mitomycin inhibits the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The guanine and cytosine content correlates with the degree of mitomycin-induced cross-linking. At high concentrations of the drug, cellular RNA and protein synthesis are also suppressed.