Jevtana prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Jevtana patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dose: JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 administered every three weeks as a one-hour intravenous infusion in combination with oral prednisone 10 mg administered daily throughout JEVTANA treatment. (2.1 )
A dose of 25 mg/m 2 can be used in select patients at the discretion of the treating healthcare provider. (2.1 , 5.1 , 5.2 , 6.1 , 14 )
- JEVTANA requires twodilutions prior to administration. (2.5 )
- Use the entire contentsof the accompanying diluent to achieve a concentration of 10 mg/mL JEVTANA. (2.5 )
- PVC equipment should not be used. (2.5 )
- Premedication Regimen: Administer intravenously 30 minutes before each dose of JEVTANA:
- Antihistamine (dexchlorpheniramine 5 mg or diphenhydramine 25 mg or equivalent antihistamine)
- Corticosteroid (dexamethasone 8 mg or equivalent steroid)
- H 2 antagonist (2.1 )
- Dosage Modifications: See full prescribing information (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
Dosing Information
The recommended dose of JEVTANA is based on calculation of the Body Surface Area (BSA), and is 20 mg/m 2 administered as a one-hour intravenous infusion every three weeks in combination with oral prednisone 10 mg administered daily throughout JEVTANA treatment.
A dose of 25 mg/m 2 can be used in select patients at the discretion of the treating healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Primary prophylaxis with G-CSF is recommended in patients with high-risk clinical features. Consider primary prophylaxis with G-CSF in all patients receiving a dose of 25 mg/m 2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) ] .
Premedicate at least 30 minutes prior to each dose of JEVTANA with the following intravenous medications to reduce the risk and/or severity of hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] :
- antihistamine (dexchlorpheniramine 5 mg, or diphenhydramine 25 mg or equivalent antihistamine),
- corticosteroid (dexamethasone 8 mg or equivalent steroid),
- H 2 antagonist.
Antiemetic prophylaxis is recommended and can be given orally or intravenously as needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
JEVTANA injection single-dose vial requires twodilutions prior to administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Reduce or discontinue JEVTANA dosing for adverse reactions as described in Table 1.
| Toxicity | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|
| Prolonged grade ≥3 neutropenia (greater than 1 week) despite appropriate medication including granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) | Delay treatment until neutrophil count is >1,500 cells/mm 3 , then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. Use G-CSF for secondary prophylaxis. |
| Febrile neutropenia or neutropenic infection | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, and until neutrophil count is >1,500 cells/mm 3 , then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. Use G-CSF for secondary prophylaxis. |
| Grade ≥3 diarrhea or persisting diarrhea despite appropriate medication, fluid and electrolytes replacement | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. |
| Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. |
| Grade ≥3 peripheral neuropathy | Discontinue JEVTANA. |
Patients at a 20 mg/m 2 dose who require dose reduction should decrease dosage of JEVTANA to 15 mg/m 2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Patients at a 25 mg/m 2 dose who require dose reduction should decrease dosage of JEVTANA to 20 mg/m 2 . One additional dose reduction to 15 mg/m 2 may be considered [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Dose Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
- Mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1 to ≤1.5 × Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) or AST >1.5 × ULN): Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 20 mg/m 2 .
- Moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 to ≤3 × ULN and AST = any): Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 15 mg/m 2 based on tolerability data in these patients; however, the efficacy of this dose is unknown.
- Severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN): JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Warning and Precautions (5.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Dose Modifications for Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant drugs that are strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, voriconazole) may increase plasma concentrations of cabazitaxel. Avoid the coadministration of JEVTANA with these drugs. If patients require coadministration of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, consider a 25% JEVTANA dose reduction [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Preparation and Administration
JEVTANA is a hazardous anticancer drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures [see References (15) ] . If JEVTANA first diluted solution, or second (final) dilution for intravenous infusion should come into contact with the skin or mucous, immediately and thoroughly wash with soap and water.
Do not use PVC infusion containers or polyurethane infusions sets for preparation and administration of JEVTANA infusion solution.
JEVTANA should not be mixed with any other drugs.
Preparation
Read this entiresection carefully before mixing and diluting. JEVTANA requires twodilutions prior to administration. Follow the preparation instructions provided below, as improper preparation may lead to overdose [see Overdosage (10) ].
Note: Both the JEVTANA injection and the diluent vials contain an overfill to compensate for liquid loss during preparation. This overfill ensures that after dilution with the entire contentsof the accompanying diluent, there is an initial diluted solution containing 10 mg/mL JEVTANA.
Inspect the JEVTANA injection and supplied diluent vials. The JEVTANA injection is a clear yellow to brownish-yellow viscous solution.
Step 1 – first dilution
Each vial of JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) 60 mg/1.5 mL must first be mixed with the entire contentsof supplied diluent. Once reconstituted, the resultant solution contains 10 mg/mL of JEVTANA.
When transferring the diluent, direct the needle onto the inside wall of JEVTANA vial and inject slowly to limit foaming. Remove the syringe and needle and gently mix the initial diluted solution by repeated inversions for at least 45 seconds to assure full mixing of the drug and diluent. Do not shake.
Let the solution stand for a few minutes to allow any foam to dissipate, and check that the solution is homogeneous and contains no visible particulate matter. It is not required that all foam dissipate prior to continuing the preparation process.
The resulting initial diluted JEVTANA solution (cabazitaxel 10 mg/mL) requires further dilution before administration. The second dilution should be done immediately (within 30 minutes) to obtain the final infusion as detailed in Step 2.
Step 2 – second (final) dilution
Withdraw the recommended dose from the JEVTANA solution containing 10 mg/mL as prepared in Step 1 using a calibrated syringe and further dilute into a sterile 250 mL PVC-free container of either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution for infusion. If a dose greater than 65 mg of JEVTANA is required, use a larger volume of the infusion vehicle so that a concentration of 0.26 mg/mL JEVTANA is not exceeded. The concentration of the JEVTANA final infusion solution should be between 0.10 mg/mL and 0.26 mg/mL.
Remove the syringe and thoroughly mix the final infusion solution by gently inverting the bag or bottle.
As the final infusion solution is supersaturated, it may crystallize over time. Do not use if this occurs and discard.
Fully prepared JEVTANA infusion solution (in either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution) should be used within 8 hours at ambient temperature (including the one-hour infusion), or for a total of 24 hours (including the one-hour infusion) under the refrigerated conditions.
Discard any unused portion.
Administration
Inspect visually for particulate matter, any crystals and discoloration prior to administration. If the JEVTANA first diluted solution or second (final) infusion solution is not clear or appears to have precipitation, it should be discarded.
Use an in-line filter of 0.22 micrometer nominal pore size (also referred to as 0.2 micrometer) during administration.
The final JEVTANA infusion solution should be administered intravenously as a one-hour infusion at room temperature.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jevtana prescribing information
WARNING: NEUTROPENIA AND HYPERSENSITIVITY
WARNING: NEUTROPENIA AND HYPERSENSITIVITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Neutropenic deaths have been reported. Obtain frequent blood counts to monitor for neutropenia. JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with neutrophil counts of ≤1,500 cells/mm 3 . Primary prophylaxis with G-CSF is recommended in patients with high-risk clinical features. Consider primary prophylaxis with G-CSF in all patients receiving a dose of 25 mg/m 2 (4 , 5.1 , 5.2 )
- Severe hypersensitivity can occur and may include generalized rash/erythema, hypotension and bronchospasm. Discontinue JEVTANA immediately if severe reactions occur and administer appropriate therapy. (2.1 , 5.2 )
- Contraindicated if history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to cabazitaxel or to drugs formulated with polysorbate 80. (4 )
Neutropenia : Neutropenic deaths have been reported. Monitor for neutropenia with frequent blood cell counts. JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with neutrophil counts of ≤1,500 cells/mm 3 . Primary prophylaxis with G-CSF is recommended in patients with high-risk clinical features. Consider primary prophylaxis with G-CSF in all patients receiving a dose of 25 mg/m 2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) ] .
Severe hypersensitivity : Severe hypersensitivity reactions can occur and may include generalized rash/erythema, hypotension and bronchospasm. Severe hypersensitivity reactions require immediate discontinuation of the JEVTANA infusion and administration of appropriate therapy. Patients should receive premedication. JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to cabazitaxel or to other drugs formulated with polysorbate 80 [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Contraindications (4) , and Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JEVTANA ® is indicated in combination with prednisone for the treatment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing treatment regimen.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dose: JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 administered every three weeks as a one-hour intravenous infusion in combination with oral prednisone 10 mg administered daily throughout JEVTANA treatment. (2.1 )
A dose of 25 mg/m 2 can be used in select patients at the discretion of the treating healthcare provider. (2.1 , 5.1 , 5.2 , 6.1 , 14 )
- JEVTANA requires twodilutions prior to administration. (2.5 )
- Use the entire contentsof the accompanying diluent to achieve a concentration of 10 mg/mL JEVTANA. (2.5 )
- PVC equipment should not be used. (2.5 )
- Premedication Regimen: Administer intravenously 30 minutes before each dose of JEVTANA:
- Antihistamine (dexchlorpheniramine 5 mg or diphenhydramine 25 mg or equivalent antihistamine)
- Corticosteroid (dexamethasone 8 mg or equivalent steroid)
- H 2 antagonist (2.1 )
- Dosage Modifications: See full prescribing information (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 )
Dosing Information
The recommended dose of JEVTANA is based on calculation of the Body Surface Area (BSA), and is 20 mg/m 2 administered as a one-hour intravenous infusion every three weeks in combination with oral prednisone 10 mg administered daily throughout JEVTANA treatment.
A dose of 25 mg/m 2 can be used in select patients at the discretion of the treating healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Primary prophylaxis with G-CSF is recommended in patients with high-risk clinical features. Consider primary prophylaxis with G-CSF in all patients receiving a dose of 25 mg/m 2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) ] .
Premedicate at least 30 minutes prior to each dose of JEVTANA with the following intravenous medications to reduce the risk and/or severity of hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] :
- antihistamine (dexchlorpheniramine 5 mg, or diphenhydramine 25 mg or equivalent antihistamine),
- corticosteroid (dexamethasone 8 mg or equivalent steroid),
- H 2 antagonist.
Antiemetic prophylaxis is recommended and can be given orally or intravenously as needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
JEVTANA injection single-dose vial requires twodilutions prior to administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Reduce or discontinue JEVTANA dosing for adverse reactions as described in Table 1.
| Toxicity | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|
| Prolonged grade ≥3 neutropenia (greater than 1 week) despite appropriate medication including granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) | Delay treatment until neutrophil count is >1,500 cells/mm 3 , then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. Use G-CSF for secondary prophylaxis. |
| Febrile neutropenia or neutropenic infection | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, and until neutrophil count is >1,500 cells/mm 3 , then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. Use G-CSF for secondary prophylaxis. |
| Grade ≥3 diarrhea or persisting diarrhea despite appropriate medication, fluid and electrolytes replacement | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. |
| Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy | Delay treatment until improvement or resolution, then reduce dosage of JEVTANA by one dose level. |
| Grade ≥3 peripheral neuropathy | Discontinue JEVTANA. |
Patients at a 20 mg/m 2 dose who require dose reduction should decrease dosage of JEVTANA to 15 mg/m 2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Patients at a 25 mg/m 2 dose who require dose reduction should decrease dosage of JEVTANA to 20 mg/m 2 . One additional dose reduction to 15 mg/m 2 may be considered [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Dose Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
- Mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1 to ≤1.5 × Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) or AST >1.5 × ULN): Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 20 mg/m 2 .
- Moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 to ≤3 × ULN and AST = any): Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 15 mg/m 2 based on tolerability data in these patients; however, the efficacy of this dose is unknown.
- Severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN): JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Warning and Precautions (5.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Dose Modifications for Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant drugs that are strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, voriconazole) may increase plasma concentrations of cabazitaxel. Avoid the coadministration of JEVTANA with these drugs. If patients require coadministration of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, consider a 25% JEVTANA dose reduction [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Preparation and Administration
JEVTANA is a hazardous anticancer drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures [see References (15) ] . If JEVTANA first diluted solution, or second (final) dilution for intravenous infusion should come into contact with the skin or mucous, immediately and thoroughly wash with soap and water.
Do not use PVC infusion containers or polyurethane infusions sets for preparation and administration of JEVTANA infusion solution.
JEVTANA should not be mixed with any other drugs.
Preparation
Read this entiresection carefully before mixing and diluting. JEVTANA requires twodilutions prior to administration. Follow the preparation instructions provided below, as improper preparation may lead to overdose [see Overdosage (10) ].
Note: Both the JEVTANA injection and the diluent vials contain an overfill to compensate for liquid loss during preparation. This overfill ensures that after dilution with the entire contentsof the accompanying diluent, there is an initial diluted solution containing 10 mg/mL JEVTANA.
Inspect the JEVTANA injection and supplied diluent vials. The JEVTANA injection is a clear yellow to brownish-yellow viscous solution.
Step 1 – first dilution
Each vial of JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) 60 mg/1.5 mL must first be mixed with the entire contentsof supplied diluent. Once reconstituted, the resultant solution contains 10 mg/mL of JEVTANA.
When transferring the diluent, direct the needle onto the inside wall of JEVTANA vial and inject slowly to limit foaming. Remove the syringe and needle and gently mix the initial diluted solution by repeated inversions for at least 45 seconds to assure full mixing of the drug and diluent. Do not shake.
Let the solution stand for a few minutes to allow any foam to dissipate, and check that the solution is homogeneous and contains no visible particulate matter. It is not required that all foam dissipate prior to continuing the preparation process.
The resulting initial diluted JEVTANA solution (cabazitaxel 10 mg/mL) requires further dilution before administration. The second dilution should be done immediately (within 30 minutes) to obtain the final infusion as detailed in Step 2.
Step 2 – second (final) dilution
Withdraw the recommended dose from the JEVTANA solution containing 10 mg/mL as prepared in Step 1 using a calibrated syringe and further dilute into a sterile 250 mL PVC-free container of either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution for infusion. If a dose greater than 65 mg of JEVTANA is required, use a larger volume of the infusion vehicle so that a concentration of 0.26 mg/mL JEVTANA is not exceeded. The concentration of the JEVTANA final infusion solution should be between 0.10 mg/mL and 0.26 mg/mL.
Remove the syringe and thoroughly mix the final infusion solution by gently inverting the bag or bottle.
As the final infusion solution is supersaturated, it may crystallize over time. Do not use if this occurs and discard.
Fully prepared JEVTANA infusion solution (in either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution) should be used within 8 hours at ambient temperature (including the one-hour infusion), or for a total of 24 hours (including the one-hour infusion) under the refrigerated conditions.
Discard any unused portion.
Administration
Inspect visually for particulate matter, any crystals and discoloration prior to administration. If the JEVTANA first diluted solution or second (final) infusion solution is not clear or appears to have precipitation, it should be discarded.
Use an in-line filter of 0.22 micrometer nominal pore size (also referred to as 0.2 micrometer) during administration.
The final JEVTANA infusion solution should be administered intravenously as a one-hour infusion at room temperature.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) injection is supplied as a kit consisting of the following:
- Cabazitaxel injection: 60 mg/1.5 mL; a clear yellow to brownish-yellow viscous solution
- Diluent: 5.7 mL of 13% (w/w) ethanol in water; a clear colorless solution
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of JEVTANA have not been established in females. There are no human data on the use of JEVTANA in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of cabazitaxel in pregnant rats during organogenesis caused embryonic and fetal death at doses lower than the maximum recommended human dose [see Data ] .
Data
Animal data
In an early embryonic developmental toxicity study in rats, cabazitaxel was administered intravenously for 15 days prior to mating through day 6 of pregnancy, which resulted in an increase in pre-implantation loss at 0.2 mg/kg/day and an increase in early resorptions at ≥0.1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.06 and 0.02 times the C max in patients at the recommended human dose, respectively).
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in rats, cabazitaxel caused maternal and embryo-fetal toxicity consisting of increased postimplantation loss, embryolethality, and fetal deaths when administered intravenously at a dose of 0.16 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.06 times the C max in patients at the recommended human dose). Decreased mean fetal birthweight associated with delays in skeletal ossification was observed at doses ≥0.08 mg/kg. Cabazitaxel crossed the placenta barrier within 24 hours of a single intravenous administration of 0.08 mg/kg to pregnant rats at gestational day 17. A dose of 0.08 mg/kg in rats resulted in a C max approximately 0.02 times that observed in patients at the recommended human dose. Administration of cabazitaxel did not result in fetal abnormalities in rats or rabbits at exposure levels significantly lower than the expected human exposures.
Lactation
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of JEVTANA have not been established in females. There is no information available on the presence of cabazitaxel in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Cabazitaxel or cabazitaxel metabolites are excreted in maternal milk of lactating rats [see Data ] .
Data
Animal data
In a milk excretion study, radioactivity related to cabazitaxel was detected in the stomachs of nursing pups within 2 hours of a single intravenous administration of cabazitaxel to lactating rats at a dose of 0.08 mg/kg (approximately 0.02 times the C max in patients at the recommended human dose). This was detectable 24 hours post dose. Approximately 1.5% of the dose delivered to the mother was calculated to be delivered in the maternal milk.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Males
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose of JEVTANA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Infertility
Males
Based on animal toxicology studies, JEVTANA may impair human fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of JEVTANA in pediatric patients have not been established.
JEVTANA was evaluated in 39 pediatric patients (ages 3 to 18 years) receiving prophylactic G-CSF. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was 30 mg/m 2 intravenously over 1 hour on Day 1 of a 21 day cycle in pediatric patients with solid tumors based on the dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) of febrile neutropenia. No objective responses were observed in 11 patients with refractory high grade glioma (HGG) or diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG). One patient had a partial response among the 9 patients with ependymoma.
Infusion related/hypersensitivity reactions were seen in 10 patients (26%). Three patients experienced serious adverse events of anaphylactic reaction. The incidence of infusion related/hypersensitivity reactions decreased with steroid premedication. The most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events were similar to those reported in adults.
Based on the population pharmacokinetics analysis conducted with data from 31 pediatric patients with cancer (ages 3 to 18 years), the clearances by body surface area were comparable to those in adults.
Geriatric Use
In the TROPIC study, of the 371 patients with prostate cancer treated with JEVTANA every three weeks plus prednisone, 240 patients (64.7%) were 65 years of age and over, while 70 patients (18.9%) were 75 years of age and over. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between patients ≥65 years of age and younger patients. Elderly patients (≥65 years of age) may be more likely to experience certain adverse reactions. The incidence of death due to causes other than disease progression within 30 days of the last cabazitaxel dose were higher in patients who were 65 years of age or greater compared to younger patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . The incidence of grade 3–4 neutropenia and febrile neutropenia were higher in patients who were 65 years of age or greater compared to younger patients. The following grade 1–4 adverse reactions were reported at rates ≥5% higher in patients 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients: fatigue (40% vs 30%), neutropenia (97% vs 89%), asthenia (24% vs 15%), pyrexia (15% vs 8%), dizziness (10% vs 5%), urinary tract infection (10% vs 3%), and dehydration (7% vs 2%), respectively.
In the PROSELICA study, the grade 1–4 adverse reactions reported at rates of at least 5% higher in patients 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients were diarrhea (43% vs 33%), fatigue (30% vs 19%), asthenia (22% vs 13%), constipation (20% vs 13%), clinical neutropenia (13% vs 6%), febrile neutropenia (11% vs 5%), and dyspnea (10% vs 3%).
In the CARD study, the grade 1–4 adverse reactions reported at rates of at least 5% higher in patients 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients were decreased appetite (16% vs 7%), hypertension (5% vs 0), constipation (18% vs 7%), paresthesia (6% vs 0), stomatitis (10% vs 3%), musculoskeletal pain (5% vs 0), fatigue (31% vs 23%), asthenia (30% vs 19%), and edema peripheral (11% vs 0).
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, no significant difference was observed in the pharmacokinetics of cabazitaxel between patients <65 years (n=100) and older (n=70).
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with renal impairment not requiring hemodialysis. Patients presenting with end-stage renal disease (creatinine clearance CL CR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), should be monitored carefully during treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
Cabazitaxel is extensively metabolized in the liver. Patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1 to ≤1.5 × ULN or AST >1.5 × ULN) should have JEVTANA dose of 20 mg/m 2 . Administration of cabazitaxel to patients with mild hepatic impairment should be undertaken with caution and close monitoring of safety [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. The maximum tolerated dose in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 to ≤3.0 × ULN and AST = any) was 15 mg/m 2 , however, the efficacy at this dose level was unknown. JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN) [see Contraindications (4) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with:
- neutrophil counts of ≤1,500/mm 3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to cabazitaxel or to other drugs formulated with polysorbate 80 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Bone marrow suppression (particularly neutropenia) and its clinical consequences (febrile neutropenia, neutropenic infections, and death): Monitor blood counts frequently to determine if dosage modification or initiation of G-CSF is needed. Closely monitor patients with hemoglobin <10 g/dL. (2.2 , 4 , 5.1 )
- Increased toxicities in elderly patients: Patients ≥65 years of age were more likely to experience fatal outcomes and certain adverse reactions, including neutropenia and febrile neutropenia. Monitor closely. (5.2 , 8.5 )
- Hypersensitivity: Severe hypersensitivity reactions can occur. Premedicate with corticosteroids and H 2 antagonists. Discontinue infusion immediately if hypersensitivity is observed and treat as indicated. (4 , 5.3 )
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur. Mortality related to diarrhea has been reported. Rehydrate and treat with antiemetics and antidiarrheals as needed. If experiencing Grade ≥3 diarrhea, dosage should be modified. (2.2 ) Deaths have occurred due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage, perforation and neutropenic enterocolitis. Delay or discontinue JEVTANA and treat as indicated. (5.4 )
- Renal failure, including cases with fatal outcomes, has been reported. Identify cause and manage aggressively. (5.5 )
- Urinary disorders including cystitis: Cystitis, radiation cystitis, and hematuria may occur. Monitor patients who previously received pelvic radiation for signs and symptoms of cystitis. Interrupt or discontinue JEVTANA and provide medical or surgical supportive care, as needed, in patients experiencing severe hemorrhagic cystitis. (5.6 )
- Respiratory disorders: Interstitial pneumonia/pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease and acute respiratory distress syndrome, including fatal outcomes, have been reported. Delay or discontinue JEVTANA and treat as indicated. (5.7 )
- Hepatic impairment: Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 20 mg/m 2 in patients with mild hepatic impairment. Administer JEVTANA at a dose of 15 mg/m 2 in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. (2.3 , 5.8 )
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: JEVTANA can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception. (5.9 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Bone Marrow Suppression
JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with neutrophils ≤1,500/mm 3 [see Contraindications (4) ] . Closely monitor patients with hemoglobin <10 g/dL.
Bone marrow suppression manifested as neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia and/or pancytopenia may occur. Neutropenic deaths have been reported.
TROPIC Trial (JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 )
In the TROPIC trial with G-CSF administered only at the investigator's discretion, 5 patients (1.3%) died from neutropenic infection (sepsis or septic shock); 4 of these patients died in the first 30 days of treatment. One additional patient's death was attributed to neutropenia without a documented infection. Twenty-two (6%) patients discontinued JEVTANA treatment due to neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, infection, or sepsis. Grade 3–4 neutropenia occurred in 82% of patients treated with JEVTANA in the randomized trial [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
PROSELICA Trial (comparison of JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 versus 25 mg/m 2 )
In the PROSELICA trial comparing two doses of JEVTANA, primary prophylaxis with G-CSF was not allowed, but could be administered after development of neutropenia at investigators discretion. Eight patients (1%) on the 20 mg/m 2 arm and 15 patients (3%) on the 25 mg/m 2 arm died from infection; of these, 4 deaths on the 20 mg/m 2 arm and 8 deaths on the 25 mg/m 2 arm occurred within the first 30 days of treatment. Clinically important neutropenia-related events occurred and included febrile neutropenia (2.1% on 20 mg/m 2 arm and 9.2% on 25 mg/m 2 arm), neutropenic infection/sepsis (2.1% on 20 mg/m 2 arm and 6.4% on 25 mg/m 2 arm), and neutropenic deaths (0.3% on 20 mg/m 2 arm and 0.7% on 25 mg/m 2 arm).
Fewer patients receiving JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 were reported to have infectious adverse reactions. Grade 1–4 infections were experienced by 160 patients (28%) on the 20 mg/m 2 arm and 227 patients (38%) on the 25 mg/m 2 arm. Grade 3–4 infections were experienced by 57 patients (10%) on the 20 mg/m 2 arm and 120 patients (20%) on the 25 mg/m 2 arm. Noninferiority for overall survival was demonstrated between these two arms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
CARD Trial (JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 + primary prophylaxis G-CSF)
In the CARD trial where JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 was administered with primary prophylaxis of G-CSF, 1 patient (0.8%) died from sepsis within the first 30 days of treatment. Grade 1–4 neutropenia-related adverse reactions were experienced in 33 patients (26%). Grade 3–4 neutropenias were experienced by 26 patients (21%). Clinically important neutropenia-related events occurred and included febrile neutropenia (3.2%), neutropenic infection/sepsis (0.8%) and neutropenic deaths (0.8%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Based on guidelines for the use of G-CSF and the adverse reactions profile of JEVTANA, primary prophylaxis with G-CSF is recommended in patients with high-risk clinical features (older patients, poor performance status, previous episodes of febrile neutropenia, extensive prior radiation ports, poor nutritional status, or other serious comorbidities) that predispose them to increased complications from prolonged neutropenia. Consider primary prophylaxis with G-CSF in all patients receiving JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 .
Monitoring of complete blood counts is essential on a weekly basis during cycle 1 and before each treatment cycle thereafter so that the dose can be adjusted, if needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Increased Toxicities in Elderly Patients
In a randomized trial (TROPIC), 2% of patients (3/131) <65 years of age and 6% (15/240) ≥65 years of age died of causes other than disease progression within 30 days of the last JEVTANA dose. Patients ≥65 years of age are more likely to experience certain adverse reactions, including neutropenia and febrile neutropenia. The incidence of the following grade 3–4 adverse reactions was higher in patients ≥65 years of age compared to younger patients; neutropenia (87% vs 74%), and febrile neutropenia (8% vs 6%).
In a randomized clinical trial (PROSELICA) comparing two doses of JEVTANA, deaths due to infection within 30 days of starting JEVTANA occurred in 0.7% (4/580) patients on the 20 mg/m 2 arm and 1.3% (8/595) patients on the 25 mg/m 2 arm; all of these patients were >60 years of age.
In PROSELICA, on the 20 mg/m 2 arm, 3% (5/178) of patients <65 years of age and 2% (9/402) ≥65 years of age died of causes other than disease progression within 30 days of the last JEVTANA dose. On the 25 mg/m 2 arm, 2% (3/175) patients <65 years of age and 5% (20/420) ≥65 years of age died of causes other than disease progression within 30 days of the last JEVTANA dose [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
In CARD, a death due to infection within 30 days of starting JEVTANA occurred in 0.8% (1/126) patient who was >75 years of age. There were 2.4% (3/126) of patients who died of causes other than disease progression within 30 days of the last JEVTANA dose; all of these patients were >75 years of age.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions may occur within a few minutes following the initiation of the infusion of JEVTANA, thus facilities and equipment for the treatment of hypotension and bronchospasm should be available. Severe hypersensitivity reactions can occur and may include generalized rash/erythema, hypotension and bronchospasm.
Premedicate all patients prior to the initiation of the infusion of JEVTANA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Observe patients closely for hypersensitivity reactions, especially during the first and second infusions. Severe hypersensitivity reactions require immediate discontinuation of the JEVTANA infusion and appropriate therapy. JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to cabazitaxel or to other drugs formulated with polysorbate 80 [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Nausea, vomiting and severe diarrhea, at times, may occur. Deaths related to diarrhea and electrolyte imbalance occurred in the randomized clinical trials. Intensive measures may be required for severe diarrhea and electrolyte imbalance. Antiemetic prophylaxis is recommended. Treat patients with rehydration, antidiarrheal or antiemetic medications as needed. Treatment delay or dosage reduction may be necessary if patients experience Grade ≥3 diarrhea [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhage and perforation, ileus, enterocolitis, neutropenic enterocolitis, including fatal outcome, have been reported in patients treated with JEVTANA [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . Risk may be increased with neutropenia, age, steroid use, concomitant use of NSAIDs, antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulants, and patients with a prior history of pelvic radiotherapy, adhesions, ulceration and GI bleeding.
Abdominal pain and tenderness, fever, persistent constipation, diarrhea, with or without neutropenia, may be early manifestations of serious gastrointestinal toxicity and should be evaluated and treated promptly. JEVTANA treatment delay or discontinuation may be necessary.
The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions is greater in the patients who have received prior radiation. In PROSELICA, diarrhea was reported in 41% (297/732) of patients who had received prior radiation and in 27% (118/443) of patients without prior radiation. Of the patients who had previously received radiation, more patients on the 25 mg/m 2 arm reported diarrhea, compared to patients on the 20 mg/m 2 arm.
Renal Failure
In the randomized clinical trial (TROPIC), renal failure of any grade occurred in 4% of the patients being treated with JEVTANA, including four cases with fatal outcome. Most cases occurred in association with sepsis, dehydration, or obstructive uropathy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Some deaths due to renal failure did not have a clear etiology. Appropriate measures should be taken to identify causes of renal failure and treat aggressively.
Urinary Disorders Including Cystitis
Cystitis, radiation cystitis, and hematuria, including that requiring hospitalization, has been reported with JEVTANA in patients who previously received pelvic radiation [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . In PROSELICA, cystitis and radiation cystitis were reported in 1.2% and 1.5% of patients who received prior radiation, respectively. Hematuria was reported in 19.4% of patients who received prior radiation and in 14.4% of patients who did not receive prior radiation. Cystitis from radiation recall may occur late in treatment with JEVTANA. Monitor patients who previously received pelvic radiation for signs and symptoms of cystitis while on JEVTANA. Interrupt or discontinue JEVTANA in patients experiencing severe hemorrhagic cystitis. Medical and/or surgical supportive treatment may be required to treat severe hemorrhagic cystitis.
Respiratory Disorders
Interstitial pneumonia/pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease and acute respiratory distress syndrome have been reported and may be associated with fatal outcome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . Patients with underlying lung disease may be at higher risk for these events. Acute respiratory distress syndrome may occur in the setting of infection.
Interrupt JEVTANA if new or worsening pulmonary symptoms develop. Closely monitor, promptly investigate, and appropriately treat patients receiving JEVTANA. Consider discontinuation. The benefit of resuming JEVTANA treatment must be carefully evaluated.
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Cabazitaxel is extensively metabolized in the liver.
JEVTANA is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN) [see Contraindications (4) ] . Dose should be reduced for patients with mild (total bilirubin >1 to ≤1.5 × ULN or AST >1.5 × ULN) and moderate (total bilirubin >1.5 to ≤3.0 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment, based on tolerability data in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] . Administration of JEVTANA to patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment should be undertaken with caution and close monitoring of safety.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, JEVTANA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] . There are no available data in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of cabazitaxel in pregnant rats during organogenesis caused embryonic and fetal death at doses lower than the maximum recommended human dose (approximately 0.06 times the C max in patients at the recommended human dose). Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose of JEVTANA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in another section of the label:
- Bone Marrow Suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Increased Toxicities in Elderly Patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Renal Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Urinary Disorders Including Cystitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Respiratory Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
TROPIC Trial (JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 compared to mitoxantrone)
The safety of JEVTANA in combination with prednisone was evaluated in 371 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated in the randomized TROPIC trial, compared to mitoxantrone plus prednisone.
Deaths due to causes other than disease progression within 30 days of last study drug dose were reported in 18 (5%) JEVTANA-treated patients and 3 (<1%) mitoxantrone-treated patients. The most common fatal adverse reactions in JEVTANA-treated patients were infections (n=5) and renal failure (n=4). The majority (4 of 5 patients) of fatal infection-related adverse reactions occurred after a single dose of JEVTANA. Other fatal adverse reactions in JEVTANA-treated patients included ventricular fibrillation, cerebral hemorrhage, and dyspnea.
The most common (≥10%) grade 1–4 adverse reactions were anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, constipation, asthenia, abdominal pain, hematuria, back pain, anorexia, peripheral neuropathy, pyrexia, dyspnea, dysgeusia, cough, arthralgia, and alopecia.
The most common (≥5%) grade 3–4 adverse reactions in patients who received JEVTANA were neutropenia, leukopenia, anemia, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, and asthenia.
Treatment discontinuations due to adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients who received JEVTANA and 8% of patients who received mitoxantrone. The most common adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation in the JEVTANA group were neutropenia and renal failure. Dose reductions were reported in 12% of JEVTANA-treated patients and 4% of mitoxantrone-treated patients. Dose delays were reported in 28% of JEVTANA-treated patients and 15% of mitoxantrone-treated patients.
| Adverse Reactions | JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 every 3 weeks with prednisone 10 mg daily n=371 | Mitoxantrone 12 mg/m 2 every 3 weeks with prednisone 10 mg daily n=371 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | |
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||
| Anemia Based on laboratory values, JEVTANA: n=369, mitoxantrone: n=370. | 98 | 11 | 82 | 5 |
| Leukopenia | 96 | 69 | 93 | 42 |
| Neutropenia | 94 | 82 | 87 | 58 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 48 | 4 | 43 | 2 |
| Febrile Neutropenia | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 47 | 6 | 11 | <1 |
| Nausea | 34 | 2 | 23 | <1 |
| Vomiting | 22 | 2 | 10 | 0 |
| Constipation | 20 | 1 | 15 | <1 |
| Abdominal Pain Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper, abdominal tenderness, and GI pain. | 17 | 2 | 6 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia Includes gastroesophageal reflux disease and reflux gastritis. | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 37 | 5 | 27 | 3 |
| Asthenia | 20 | 5 | 12 | 2 |
| Pyrexia | 12 | 1 | 6 | <1 |
| Peripheral Edema | 9 | <1 | 9 | <1 |
| Mucosal Inflammation | 6 | <1 | 3 | <1 |
| Pain | 5 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders | ||||
| Hematuria | 17 | 2 | 4 | <1 |
| Dysuria | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Back Pain | 16 | 4 | 12 | 3 |
| Arthralgia | 11 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Muscle Spasms | 7 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Anorexia | 16 | <1 | 11 | <1 |
| Dehydration | 5 | 2 | 3 | <1 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Peripheral Neuropathy Includes peripheral motor neuropathy and peripheral sensory neuropathy. | 13 | <1 | 3 | <1 |
| Dysgeusia | 11 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 8 | 0 | 6 | <1 |
| Headache | 8 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea | 12 | 1 | 4 | <1 |
| Cough | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight Decreased | 9 | 0 | 8 | <1 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Urinary Tract Infection Includes urinary tract infection enterococcal and urinary tract infection fungal. | 8 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||||
| Arrhythmia Includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, atrioventricular block complete, bradycardia, palpitations, supraventricular tachycardia, tachyarrhythmia, and tachycardia. | 5 | 1 | 2 | <1 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hypotension | 5 | <1 | 2 | <1 |
PROSELICA Trial (comparison of two doses of JEVTANA)
In a noninferiority, multicenter, randomized, open-label study (PROSELICA), 1175 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, previously treated with a docetaxel-containing regimen, were treated with either JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 (n=595) or the 20 mg/m 2 (n=580) dose.
Deaths within 30 days of last study drug dose were reported in 22 (3.8%) patients in the 20 mg/m 2 and 32 (5.4%) patients in the 25 mg/m 2 arm. The most common fatal adverse reactions in JEVTANA-treated patients were related to infections, and these occurred more commonly on the 25 mg/m 2 arm (n=15) than on the 20 mg/m 2 arm (n=8). Other fatal adverse reactions in JEVTANA-treated patients included cerebral hemorrhage, respiratory failure, paralytic ileus, diarrhea, acute pulmonary edema, disseminated intravascular coagulation, renal failure, sudden death, cardiac arrest, ischemic stroke, diverticular perforation, and cardiorenal syndrome.
Grade 1–4 adverse reactions occurring ≥5% more commonly in patients on the 25 mg/m 2 versus 20 mg/m 2 arms were leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, febrile neutropenia, decreased appetite, nausea, diarrhea, asthenia, and hematuria.
Grade 3–4 adverse reactions occurring ≥5% more commonly in patients on the 25 mg/m 2 versus 20 mg/m 2 arms were leukopenia, neutropenia, and febrile neutropenia.
Treatment discontinuations due to adverse reactions occurred in 17% of patients in the 20 mg/m 2 group and 20% of patients in the 25 mg/m 2 group. The most common adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were fatigue and hematuria. The patients in the 20 mg/m 2 group received a median of 6 cycles (median duration of 18 weeks), while patients in the 25 mg/m 2 group received a median of 7 cycles (median duration of 21 weeks). In the 25 mg/m 2 group, 128 patients (22%) had a dose reduced from 25 to 20 mg/m 2 , 19 patients (3%) had a dose reduced from 20 to 15 mg/m 2 and 1 patient (0.2%) had a dose reduced from 15 to 12 mg/m 2 . In the 20 mg/m 2 group, 58 patients (10%) had a dose reduced from 20 to 15 mg/m 2 , and 9 patients (2%) had a dose reduced from 15 to 12 mg/m 2 .
| Adverse Reactions | JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 every 3 weeks with prednisone 10 mg daily n=580 | JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 every 3 weeks with prednisone 10 mg daily n=595 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | |
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||
| Anemia Based on laboratory values, JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 : n=577, JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 : n=590. | 99.8 | 10 | 99.7 | 14 |
| Leukopenia | 80 | 29 | 95 | 60 |
| Neutropenia | 67 | 42 | 89 | 73 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 35 | 3 | 43 | 4 |
| Febrile Neutropenia | 2 | 2 | 9 | 9 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 31 | 1 | 40 | 4 |
| Nausea | 25 | 0.7 | 32 | 1 |
| Constipation | 18 | 0.3 | 18 | 0.7 |
| Vomiting | 15 | 1.2 | 18 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain | 6 | 0.5 | 9 | 1 |
| Stomatitis | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0.3 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 25 | 3 | 27 | 4 |
| Asthenia | 15 | 2 | 20 | 2 |
| Edema peripheral | 7 | 0.2 | 9 | 0.2 |
| Pyrexia | 5 | 0.2 | 6 | 0.2 |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||||
| Hematuria | 14 | 2 | 21 | 4 |
| Dysuria | 5 | 0.3 | 4 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 13 | 0.7 | 19 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Back pain | 11 | 0.9 | 14 | 1 |
| Bone pain | 8 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| Arthralgia | 8 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.8 |
| Pain in extremity | 5 | 0.2 | 7 | 0.5 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Dysgeusia | 7 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 7 | 0 | 11 | 0.7 |
| Dizziness | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Headache | 5 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.2 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Urinary tract infection Includes urinary tract infection staphylococcal, urinary tract infection bacterial, urinary tract infection fungal, and urosepsis. | 7 | 2 | 11 | 2 |
| Neutropenic infection Includes neutropenic sepsis. | 3 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea | 5 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.7 |
| Cough | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight decreased | 4 | 0.2 | 7 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 3 | 0 | 6.1 | 0 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||||
| Wrong technique in drug usage process | 0.3 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
CARD Trial (JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 + primary prophylaxis with G-CSF)
The safety of JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 in combination with prednisone/prednisolone and primary prophylaxis G-CSF was evaluated in a randomized, open-label study (CARD) in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who progressed after receiving prior docetaxel-containing regimens and abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide [see Clinical Studies 14.3 ] . This study compared JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 in combination with prednisone/prednisolone and primary prophylaxis with G-CSF to either abiraterone acetate 1000 mg once daily plus prednisone/prednisolone 5 mg twice daily or enzalutamide 160 mg once daily. Among patients receiving JEVTANA, 35% remained on treatment at 6 months and 4.7% remained on treatment at 12 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients receiving JEVTANA. Serious adverse reactions in ≥3% of patients included neutropenia (6%), infections (4.8%), and diarrhea, fatigue, pneumonia, and spinal cord compression (3.2% each). Deaths due to causes other than disease progression were reported in 2.4% of JEVTANA treated patients. Fatal adverse reactions in JEVTANA-treated patients were septic shock, urinary tract infection (UTI), and aspiration (0.8% each).
Treatment discontinuations due to adverse drug reactions occurred in 20% of patients who received JEVTANA and 8% of patients who received abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone or enzalutamide. The adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation in >1% of patients in JEVTANA arm were nervous system disorders, infections/infestations, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Dose interruptions (alone or in combination with dose reduction) due to an adverse reaction occurred in 31% of patients receiving JEVTANA. Dose reductions were reported in 18% of JEVTANA-treated patients. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to dose interruption of JEVTANA were fatigue (7%) and hypersensitivity reaction (3.2%); the most frequent adverse reaction leading to reduction of JEVTANA were neutropenia and peripheral neuropathy (3.9% each).
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions and laboratory hematologic abnormalities in patients in CARD.
The most common (≥10%) adverse reactions were fatigue, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, infections, peripheral neuropathy, hematuria, constipation, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, vomiting, dysgeusia, edema peripheral and lower urinary tract symptoms.
The most common (≥10%) hematologic abnormalities were anemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
| Adverse Reactions | JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 + prednisone/prednisolone + G-CSF | Abiraterone + prednisone/prednisolone or Enzalutamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N=126) | (N=124) | |||
| Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | Grade 1–4 % | Grade 3–4 % | |
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||
| Anemia Based on laboratory values - % calculated using the number of patients with at least one event(n) over the number of patients assessed for each parameter during the on-treatment period. | 99 | 8 | 95 | 4.8 |
| Lymphopenia | 72 | 27 | 55 | 17 |
| Neutropenia | 66 | 45 | 7 | 3.2 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 41 | 3.2 | 16 | 1.6 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue includes asthenia, fatigue, lethargy, malaise. | 53 | 4 | 36 | 2.4 |
| Edema peripheral includes lymphoedema, edema peripheral, peripheral swelling. | 11 | 0.8 | 10 | 1.6 |
| Pyrexia | 6 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Pain | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0.8 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea includes colitis, diarrhea, diarrhea hemorrhagic, gastroenteritis. | 40 | 4.8 | 6 | 0 |
| Nausea | 23 | 0 | 23 | 0.8 |
| Constipation | 15 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper, flank pain, gastrointestinal pain. | 14 | 1.6 | 6 | 0.8 |
| Vomiting | 13 | 0 | 12 | 1.6 |
| Stomatitis | 8 | 0 | 1.6 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 4.8 | 0 | 2.4 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain includes arthralgia, back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, noncardiac chest pain. | 27 | 1.6 | 40 | 6 |
| Pain in extremity | 4.8 | 0 | 11 | 2.4 |
| Bone fracture includes femoral neck fracture, pathological fracture, rib fracture, spinal compression fracture, sternal fracture, thoracic vertebral fracture. | 3.2 | 1.6 | 8 | 2.4 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Infections includes bacteremia, bacteriuria, cellulitis, device related sepsis, Enterobacter sepsis, erysipelas, furuncle, influenza, influenza like illness, localized infection, oral fungal infection, perineal cellulitis, pulmonary sepsis, pyelocaliectasis, pyelonephritis, pyelonephritis acute, respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection viral, sepsis, septic shock, subcutaneous abscess, upper respiratory tract infection, ureteritis, urinary tract infection, urinary tract infection bacterial, urosepsis, viral infection. | 19 | 4 | 14 | 6 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Peripheral neuropathy includes neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, peripheral motor neuropathy, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy. | 18 | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 11 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Polyneuropathy | 6 | 1.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 0.8 | 0 | 4.8 | 0 |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||||
| Hematuria includes hematuria, cystitis hemorrhagic. | 16 | 0.8 | 6 | 1.6 |
| Lower urinary tract symptoms include lower urinary tract symptoms, micturition urgency, nocturia, pollakiuria, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, dysuria. | 10 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| Acute kidney injury includes acute kidney injury, blood creatinine increased, renal failure, renal impairment. | 5 | 2.4 | 10 | 4 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 14 | 0.8 | 15 | 2.4 |
| Hypokalemia | 3.2 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Neoplasms Benign, Malignant and Unspecified (incl cysts and polyps) | ||||
| Cancer pain | 8 | 1.6 | 9 | 2.4 |
| Cardiac disorders includes aortic valve incompetence, aortic valve stenosis, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrioventricular block complete, atrioventricular block second degree, bradycardia, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, cardiac failure, acute coronary syndrome, angina pectoris. | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 3.2 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Pneumonia includes lower respiratory tract infection, lung infection, lung infiltration, pneumonia. | 6 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 0.8 |
| Dyspnea | 6 | 0 | 2.4 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||||
| Fall | 4.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hypertension includes hypertension, hypertensive crisis. | 4 | 2.4 | 8 | 2.4 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight decreased | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 3.2 | 0 | 4.8 | 0 |
Clinically relevant ≥ Grade 3 adverse reactions in <5% of patients who received JEVTANA in combination with prednisone and primary prophylaxis G-CSF: febrile neutropenia (3.2%), pulmonary embolism (1.6%), and neutropenic infection (0.8%).
Hematuria
In study TROPIC, adverse reactions of hematuria, including those requiring medical intervention, were more common in JEVTANA-treated patients. The incidence of grade ≥2 hematuria was 6% in JEVTANA-treated patients and 2% in mitoxantrone-treated patients. Other factors associated with hematuria were well-balanced between arms and do not account for the increased rate of hematuria on the JEVTANA arm.
In study PROSELICA, hematuria of all grades was observed in 18% of patients overall.
In CARD, hematuria of all grades was observed in 16% of patients receiving JEVTANA.
Hepatic Laboratory Abnormalities
The incidences of grade 3–4 increased AST, increased ALT, and increased bilirubin were each ≤1%.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified from clinical trials and/or postmarketing surveillance. Because they are reported from a population of unknown size, precise estimates of frequency cannot be made.
Gastrointestinal: Gastritis, intestinal obstruction.
Respiratory: Interstitial pneumonia/pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Renal and urinary disorders: Radiation recall hemorrhagic cystitis.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Avoid coadministration of JEVTANA with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If patients require coadministration of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, consider a 25% JEVTANA dose reduction. (2.4 , 7.1 , 12.3 )
CYP3A Inhibitors
Cabazitaxel is primarily metabolized through CYP3A [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, voriconazole) may increase plasma concentrations of cabazitaxel. Avoid the coadministration of JEVTANA with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If patients require coadministration of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, consider a 25% JEVTANA dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
DESCRIPTION
JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) injection is an antineoplastic agent belonging to the taxane class that is for intravenous use. It is prepared by semi-synthesis with a precursor extracted from yew needles.
The chemical name of cabazitaxel is (2α,5β,7β,10β,13α)-4-acetoxy-13-({(2R,3S)-3-[(tertbutoxycarbonyl) amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-1-hydroxy-7,10-dimethoxy-9-oxo-5,20-epoxytax-11-en-2-yl benzoate – propan-2-one (1:1).
Cabazitaxel has the following structural formula:
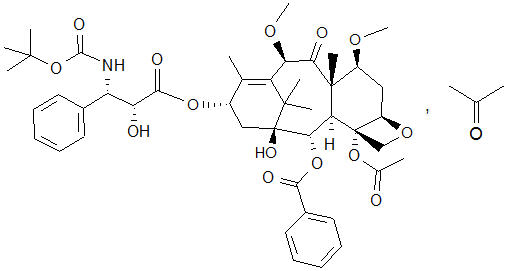
Cabazitaxel is a white to almost-white powder with a molecular formula of C 45 H 57 NO 14 C 3 H 6 O and a molecular weight of 894.01 (for the acetone solvate) / 835.93 (for the solvent free). It is lipophilic, practically insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol.
JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) injection 60 mg/1.5 mL is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, clear yellow to brownish-yellow viscous solution and is available in single-dose vials containing 60 mg cabazitaxel (anhydrous and solvent free) and 1.56 g polysorbate 80 (citric acid monohydrate is used to adjust the pH of the polysorbate 80 between 3.3 to 3.8).
Each mL contains 40 mg cabazitaxel (anhydrous) and 1.04 g polysorbate 80.
DILUENT for JEVTANA is a clear, colorless, sterile, and non-pyrogenic solution containing 13% (w/w) ethanol in water for injection, approximately 5.7 mL.
JEVTANA requires two dilutions prior to intravenous infusion. JEVTANA injection should be diluted only with the supplied DILUENT for JEVTANA, followed by dilution in either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Cabazitaxel is a microtubule inhibitor. Cabazitaxel binds to tubulin and promotes its assembly into microtubules while simultaneously inhibiting disassembly. This leads to the stabilization of microtubules, which results in the inhibition of mitotic and interphase cellular functions.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of cabazitaxel following a single dose of 25 mg/m 2 administered by intravenous infusion on QTc interval was evaluated in 94 patients with solid tumors. No large changes in the mean QT interval (i.e., >20 ms) from baseline based on Fridericia correction method were detected. However, a small increase in the mean QTc interval (i.e., <10 ms) cannot be excluded due to study design limitations.
Pharmacokinetics
A population pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted in 170 patients with solid tumors at doses ranging from 10 to 30 mg/m 2 weekly or every three weeks.
Absorption
Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis, after an intravenous dose of cabazitaxel 25 mg/m 2 every three weeks, the mean C max in patients with metastatic prostate cancer was 226 ng/mL (CV 107%) and was reached at the end of the one-hour infusion (T max ). The mean AUC in patients with metastatic prostate cancer was 991 ng ∙ h/mL (CV 34%).
No major deviation from the dose proportionality was observed from 10 to 30 mg/m 2 in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Distribution
The volume of distribution (V ss ) was 4,864 L (2,643 L/m 2 for a patient with a median BSA of 1.84 m 2 ) at steady state.
In vitro , the binding of cabazitaxel to human serum proteins was 89% to 92% and was not saturable up to 50,000 ng/mL, which covers the maximum concentration observed in clinical trials. Cabazitaxel is mainly bound to human serum albumin (82%) and lipoproteins (88% for HDL, 70% for LDL, and 56% for VLDL). The in vitro blood-to-plasma concentration ratio in human blood ranged from 0.90 to 0.99, indicating that cabazitaxel was equally distributed between blood and plasma.
Metabolism
Cabazitaxel is extensively metabolized in the liver (>95%), mainly by the CYP3A4/5 isoenzyme (80% to 90%), and to a lesser extent by CYP2C8. Cabazitaxel is the main circulating moiety in human plasma. Seven metabolites were detected in plasma (including the 3 active metabolites issued from O-demethylation), with the main one accounting for 5% of cabazitaxel exposure. Around 20 metabolites of cabazitaxel are excreted into human urine and feces.
Elimination
After a one-hour intravenous infusion [ 14 C]-cabazitaxel 25 mg/m 2 , approximately 80% of the administered dose was eliminated within 2 weeks. Cabazitaxel is mainly excreted in the feces as numerous metabolites (76% of the dose); while renal excretion of cabazitaxel and metabolites account for 3.7% of the dose (2.3% as unchanged drug in urine).
Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis, cabazitaxel has a plasma clearance of 48.5 L/h (CV 39%; 26.4 L/h/m 2 for a patient with a median BSA of 1.84 m 2 ) in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Following a one-hour intravenous infusion, plasma concentrations of cabazitaxel can be described by a three-compartment pharmacokinetic model with α-, β-, and γ- half-lives of 4 minutes, 2 hours, and 95 hours, respectively.
Renal Impairment
Cabazitaxel is minimally excreted via the kidney. A population pharmacokinetic analysis carried out in 170 patients including 14 patients with moderate renal impairment (30 mL/min ≤CL CR <50 mL/min) and 59 patients with mild renal impairment (50 mL/min ≤CL CR <80 mL/min) showed that mild to moderate renal impairment did not have meaningful effects on the pharmacokinetics of cabazitaxel. This was confirmed by a dedicated comparative pharmacokinetic study in patients with solid tumors with normal renal function (n=8, CL CR >80 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), or moderate (n=8, 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ≤CL CR <50 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) and severe (n=9, CL CR <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) renal impairment, who received several cycles of cabazitaxel in single IV infusion up to 25 mg/m 2 . Limited pharmacokinetic data were available in patients with end-stage renal disease (n=2, CL CR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ).
Hepatic Impairment
Cabazitaxel is extensively metabolized in the liver.
A dedicated study in 43 cancer patients with hepatic impairment showed no influence of mild (total bilirubin >1 to ≤1.5 × ULN or AST >1.5 × ULN) or moderate (total bilirubin >1.5 to ≤3.0 × ULN) hepatic impairment on cabazitaxel pharmacokinetics. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of cabazitaxel was 20 and 15 mg/m 2 , respectively.
In 3 patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN), a 39% decrease in clearance was observed when compared to patients with mild hepatic impairment (ratio=0.61, 90% CI: 0.36–1.05), indicating some effect of severe hepatic impairment on cabazitaxel pharmacokinetics. The MTD of cabazitaxel in patients with severe hepatic impairment was not established. Based on safety and tolerability data, cabazitaxel dose should be maintained at 20 mg/m 2 in patients with mild hepatic impairment and reduced to 15 mg/m 2 in patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] . Cabazitaxel is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Drug Interactions
A drug interaction study of JEVTANA in 23 patients with advanced cancers has shown that repeated administration of ketoconazole (400 mg orally once daily), a strong CYP3A inhibitor, increased the exposure to cabazitaxel (5 mg/m 2 intravenous) by 25%.
A drug interaction study of JEVTANA in 13 patients with advanced cancers has shown that repeated administration of aprepitant (125 or 80 mg once daily), a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, did not modify the exposure to cabazitaxel (15 mg/m 2 intravenous).
A drug interaction study of JEVTANA in 21 patients with advanced cancers has shown that repeated administration of rifampin (600 mg once daily), a strong CYP3A inducer, decreased the exposure to cabazitaxel (15 mg/m 2 intravenous) by 17%.
A drug interaction study of JEVTANA in 11 patients with advanced cancers has shown that cabazitaxel (25 mg/m 2 administered as a single 1-hour infusion) did not modify the exposure to midazolam, a probe substrate of CYP3A.
Prednisone or prednisolone administered at 10 mg daily did not affect the pharmacokinetics of cabazitaxel.
Based on in vitro studies, the potential for cabazitaxel to inhibit drugs that are substrates of other CYP isoenzymes (1A2, -2B6, -2C9, -2C8, -2C19, -2E1, -2D6, and CYP3A4/5) is low. In addition, cabazitaxel did not induce CYP isozymes (-1A, -2C9 and -3A) in vitro .
In vitro , cabazitaxel did not inhibit the multidrug-resistance protein 1 (MRP1), 2 (MRP2) or organic cation transporter (OCT1). In vitro , cabazitaxel inhibited P-gp, BRCP, and organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP1B1, OATP1B3). However, the in vivo risk of cabazitaxel inhibiting MRPs, OCT1, P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1 or OATP1B3 is low at the dose of 25 mg/m 2 .
In vitro , cabazitaxel is a substrate of P-gp, but not a substrate of MRP1, MRP2, BCRP, OCT1, OATP1B1 or OATP1B3.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of cabazitaxel.
Cabazitaxel was positive for genotoxicity by an aneugenic mechanism in the in vivo micronucleus test, inducing an increase of micronuclei in rats at doses ≥0.5 mg/kg. Cabazitaxel increased numerical aberrations with or without metabolic activation in an in vitro test in human lymphocytes though no induction of structural aberrations was observed. Cabazitaxel did not induce mutations in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test. The positive in vivo genotoxicity findings are consistent with the pharmacological activity of the compound (inhibition of tubulin depolymerization).
In a fertility study performed in female rats at cabazitaxel doses of 0.05, 0.1, or 0.2 mg/kg/day there was no effect of administration of the drug on mating behavior or the ability to become pregnant. In repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats with intravenous cabazitaxel administration once every three weeks for up to 6 months, atrophy of the uterus was observed at the 5 mg/kg dose level (approximately the AUC in patients with cancer at the recommended human dose) along with necrosis of the corpora lutea at doses ≥1 mg/kg (approximately 0.2 times the AUC at the clinically recommended human dose).
In a fertility study in male rats, cabazitaxel did not affect mating performances or fertility at doses of 0.05, 0.1, or 0.2 mg/kg/day. In repeat-dose toxicology studies with intravenous cabazitaxel administration once every three weeks for up to 9 months, degeneration of seminal vesicle and seminiferous tubule atrophy in the testis were observed in rats at a dose of 1 mg/kg (approximately 0.2 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose), and minimal testicular degeneration (minimal epithelial single cell necrosis in epididymis) was observed in dogs treated at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg (approximately 0.1 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose).
CLINICAL STUDIES
TROPIC Trial (JEVTANA + prednisone compared to mitoxantrone)
The efficacy and safety of JEVTANA in combination with prednisone were evaluated in a randomized, open-label, international, multi-center study in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing treatment regimen (TROPIC, NCT00417079).
A total of 755 patients were randomized to receive either JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks for a maximum of 10 cycles with prednisone 10 mg orally daily (n=378), or to receive mitoxantrone 12 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks for 10 cycles with prednisone 10 mg orally daily (n=377) for a maximum of 10 cycles.
This study included patients over 18 years of age with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer either measurable by RECIST criteria or non-measurable disease with rising PSA levels or appearance of new lesions, and ECOG (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group) performance status 0–2. Patients had to have neutrophils >1,500 cells/mm 3 , platelets >100,000 cells/mm 3 , hemoglobin >10 g/dL, creatinine <1.5 × upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin <1 × ULN, AST <1.5 × ULN, and ALT <1.5 × ULN. Patients with a history of congestive heart failure, or myocardial infarction within the last 6 months, or patients with uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and/or hypertension were not included in the study.
Demographics, including age, race, and ECOG performance status (0–2) were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 68 years (range 46–92) and the racial distribution for all groups was 83.9% Caucasian, 6.9% Asian, 5.3% Black, and 4% Others in the JEVTANA group.
Efficacy results for the JEVTANA arm versus the control arm are summarized in Table 5 and Figure 1.
| JEVTANA + Prednisone n=378 | Mitoxantrone + Prednisone n=377 | |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of deaths (%) | 234 (61.9%) | 279 (74.0%) |
| Median survival (month) (95% CI) | 15.1 (14.1–16.3) | 12.7 (11.6–13.7) |
| Hazard Ratio Hazard ratio estimated using Cox model; a hazard ratio of less than 1 favors JEVTANA. (95% CI) | 0.70 (0.59–0.83) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival Curves (TROPIC)
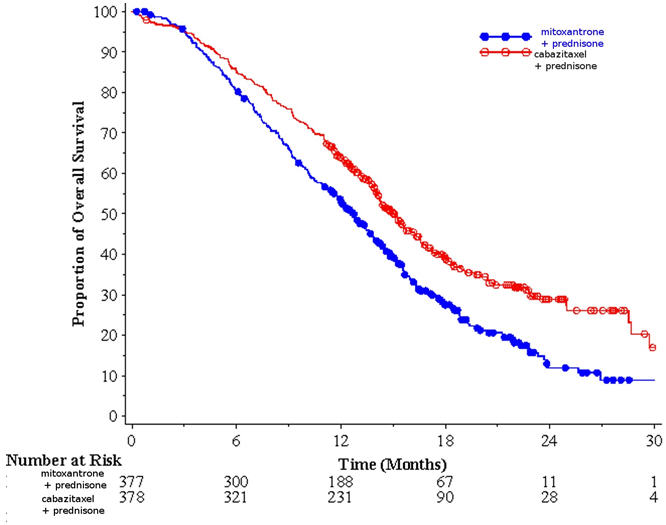
Investigator-assessed tumor response of 14.4% (95% CI: 9.6–19.3) was higher for patients in the JEVTANA arm compared to 4.4% (95% CI: 1.6–7.2) for patients in the mitoxantrone arm, p=0.0005.
PROSELICA Trial (comparison of two doses of JEVTANA)
The efficacy and safety of JEVTANA were evaluated in a noninferiority, multicenter, randomized, open-label study (PROSELICA, NCT01308580). A total of 1200 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, previously treated with a docetaxel-containing regimen were randomized to receive either JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 (n=602) or 20 mg/m 2 (n=598) dose. Overall survival (OS) was the major efficacy outcome.
Demographics, including age, race, and ECOG performance status (0–2) were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 68 years (range 45–89) and the racial distribution for all groups was 87% Caucasian, 6.9% Asian, 2.3% Black, and 3.8% Others in the JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 group. The median age was 69 years (range 45–88) and the racial distribution for all groups was 88.7% Caucasian, 6.6% Asian, 1.8% Black, and 2.8% Others in the JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 group.
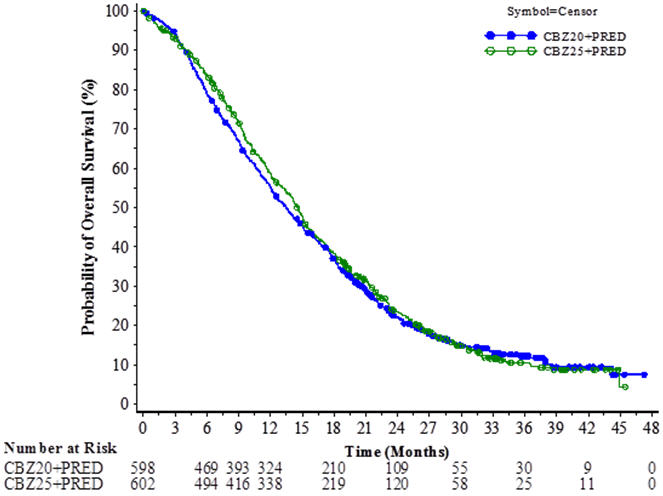
The study demonstrated noninferiority in overall survival (OS) of JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 in comparison with JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 in an intent-to-treat population (see Table 6 and Figure 2 ). Based on the per-protocol population, the estimated median OS was 15.1 months on JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 and 15.9 months on JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 , the observed hazard ratio (HR) of OS was 1.042 (97.78% CI: 0.886, 1.224). Among the subgroup analyses intended for assessing the heterogeneity, no notable difference in OS was observed on the JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 arm compared to the JEVTANA 20 mg/m 2 arm in subgroups based on the stratification factors of ECOG performance status score, measurability of disease, or region.
| CBZ20+PRED n=598 | CBZ25+PRED n=602 | |
|---|---|---|
| CBZ20=Cabazitaxel 20 mg/m 2 , CBZ25=Cabazitaxel 25 mg/m 2 , PRED=Prednisone/Prednisolone. | ||
| CI=confidence interval. | ||
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of deaths, n (%) | 497 (83.1%) | 501 (83.2%) |
| Median survival (95% CI) (months) | 13.4 (12.2 to 14.9) | 14.5 (13.5 to 15.3) |
| Hazard Ratio Hazard ratio is estimated using a Cox Proportional Hazards regression model. A hazard ratio <1 indicates a lower risk of death for Cabazitaxel 20 mg/m 2 with respect to 25 mg/m 2 . (97.78% CI Adjusted for interim OS analyses. The noninferiority margin is 1.214. ) | 1.024 (0.886, 1.184) | |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival Curves (intent-to-treat population) (PROSELICA)
CARD Trial (JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 + prednisone/prednisolone + primary prophylaxis with G-CSF compared to abiraterone acetate + prednisone/prednisolone or enzalutamide)
The efficacy and safety of JEVTANA were evaluated in a multinational, randomized, active-controlled, open-label study (CARD: NCT02485691) in patients with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) previously treated with a docetaxel containing regimen and had progressed within 12 months of initiating either abiraterone or enzalutamide. A total of 255 patients were randomized to receive either JEVTANA 25 mg/m 2 every 3 week plus prednisone/prednisolone 10 mg daily (n=129), abiraterone 1000 mg once daily plus prednisone/prednisolone 5 mg twice daily or enzalutamide 160 mg once daily depending on prior therapy received (n=126). Primary prophylactic G-CSF was administered at each cycle for patients in the JEVTANA arm. This study included patients over 18 years of age with ECOG performance status 0–2. Patients had to have neutrophils >1,500 cells/mm 3 , platelets >100,000 cells/mm 3 , hemoglobin >10 g/dL, creatinine <1.5 × upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin <1 × ULN, AST <1.5 × ULN, and ALT <1.5 × ULN. Patients with a history of congestive heart failure, or myocardial infarction within the last 6 months, or patients with uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and/or hypertension were not included in the study. Randomization was stratified by ECOG performance status (0 or 1 vs 2), time from abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide to disease progression, and receipt of abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide before or after docetaxel containing regimen.
The major efficacy outcome measure was radiographic progression free-survival (rPFS) as defined by Prostate Cancer Working Group-2 (PCWG2) assessed by study investigators. Other efficacy outcome measures included overall survival and objective response rate.
Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced between treatment arms. The overall median age was 70 years (range 45 to 88), 95% of patients had an ECOG PS of 0 to 1 and median Gleason score was 8. A majority of the patients (61%) had their prior treatment with abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide after docetaxel. There were 36% of patients on the cabazitaxel arm with visceral disease (liver 8%, lung 8%, other 20%) and 57% with bone-only disease. Race and ethnicity data were not collected. Approximately 92% of the patients on the cabazitaxel arm received primary prophylaxis with G-CSF therapy during the first 3 cycles and, overall, 90% of the patients on the cabazitaxel arm received primary prophylaxis with G-CSF therapy at each cycle.
Efficacy results from the CARD trial are summarized in Table 7 and Figure 3.
| JEVTANA + prednisone/prednisolone + G-CSF n=129 | Abiraterone + prednisone/prednisolone or Enzalutamide n=126 | |
|---|---|---|
| Radiographic Progression Free Survival (rPFS) | ||
| Number of events (%) Investigator assessed. | 95 (73.6%) | 101 (80.2%) |
| Median rPFS (months) (95% CI) | 8.0 (5.7 to 9.2) | 3.7 (2.8 to 5.1) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.54 (0.40 to 0.73) | |
| p-value Stratified log-rank test, significance threshold = 0.05. | <0.0001 | |
| Overall Survival (OS) Overall survival was statistically significant. | ||
| Median OS [95% CI] (months) | 13.6 [11.5; 17.5] | 11.0 [9.2; 12.9] |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.64 [0.46; 0.89] | |
| p-value | 0.0078 | |
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier of Radiographic PFS (ITT Population)
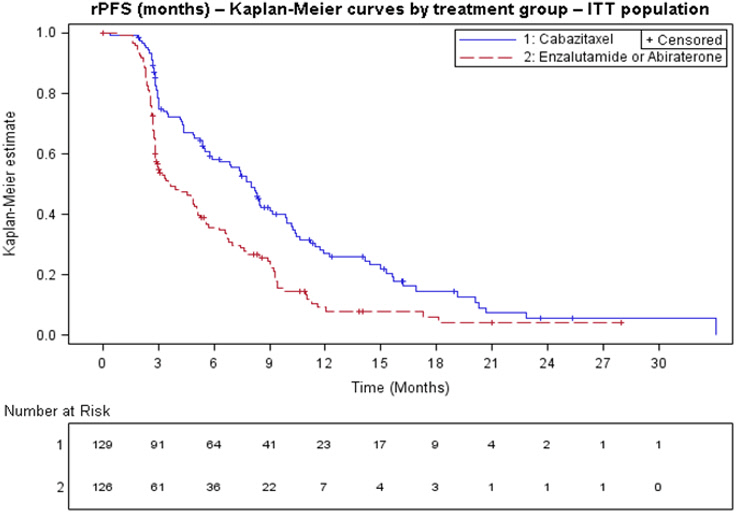
In terms of therapy sequence prior to randomization, rPFS was consistent across the subgroups of patients who received abiraterone acetate/enzalutamide prior to docetaxel (HR=0.61, 95% CI: 0.39, 0.96) and those who received abiraterone acetate/enzalutamide after docetaxel (HR=0.48, 95% CI: 0.32, 0.70).
Objective tumor response rate assessed by study investigators was 36.5% (95% CI: 26.6 to 48.4) for JEVTANA arm versus 11.5% (95% CI: 2.9 to 20.2) for abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone or enzalutamide arm, p=0.004.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
JEVTANA is supplied as a kit, NDC 0024-5824-11, that contains the following:
- One single-dose vial of JEVTANA (cabazitaxel) injection: a clear yellow to brownish-yellow viscous solution of 60 mg/1.5 mL in a clear glass vial with a grey rubber closure, aluminum cap, and light green plastic flip-off cap (JEVTANA vial NDC 0024-5823-15).
- One single-dose vial of Diluent for JEVTANA: a clear colorless solution of 13% (w/w) ethanol in water for injection in a clear glass vial with a grey rubber closure, gold-color aluminum cap, and colorless plastic flip-off cap (diluent vial NDC 0024-5822-01).
Storage
JEVTANA injection and Diluent for JEVTANA:
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C–30°C (59°F–86°F).
Do not refrigerate.
Handling and Disposal
JEVTANA is a hazardous anticancer drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposable procedures [see References (15) ].
Mechanism of Action
Cabazitaxel is a microtubule inhibitor. Cabazitaxel binds to tubulin and promotes its assembly into microtubules while simultaneously inhibiting disassembly. This leads to the stabilization of microtubules, which results in the inhibition of mitotic and interphase cellular functions.