Jublia prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Jublia patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply JUBLIA to affected toenails once daily for 48 weeks, using the integrated flow-through brush applicator. When applying JUBLIA, ensure the toenail, the toenail folds, toenail bed, hyponychium, and the undersurface of the toenail plate, are completely covered.
JUBLIA is for topical use only and not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jublia prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JUBLIA (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% is an azole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail(s) due to Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply JUBLIA to affected toenails once daily for 48 weeks, using the integrated flow-through brush applicator. When applying JUBLIA, ensure the toenail, the toenail folds, toenail bed, hyponychium, and the undersurface of the toenail plate, are completely covered.
JUBLIA is for topical use only and not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
JUBLIA (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% contains 100 mg of efinaconazole in each gram of clear, colorless to pale yellow solution.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available human data for the use of JUBLIA during pregnancy to inform any drug associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies, efinaconazole did not cause malformations or any harm to the fetus when administered to pregnant rabbits and rats during the period of organogenesis at subcutaneous doses up to 112 and 154 times, respectively, the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) based on Area Under the Curve (AUC) comparisons. Embryolethality was observed only in rats in the presence of maternal toxicity at systemic exposures 559 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons. Subcutaneous efinaconazole administration to pregnant rats from the beginning of organogenesis through the end of lactation did not cause embryofetal toxicity or developmental effects at systemic exposures 17 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons (see Data) .
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2 to 4%, and of miscarriage is 15 to 20%, of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Subcutaneous doses of 2, 10 and 50 mg/kg/day efinaconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-16) to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (increased embryofetal deaths, decreased number of live fetuses, and placental effects) was noted at 50 mg/kg/day (559 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 10 mg/kg/day (112 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No malformations were observed at 50 mg/kg/day (559 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Subcutaneous doses of 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg/day efinaconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-19) to pregnant female rabbits. In the presence of maternal toxicity, there was no embryofetal toxicity or malformations at 10 mg/kg/day (154 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 1, 5 and 25 mg/kg/day efinaconazole were administered from the beginning of organogenesis (gestation day 6) through the end of lactation (lactation day 20). In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (increased prenatal pup mortality, reduced live litter sizes and increased postnatal pup mortality) was noted at 25 mg/kg/day. No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 5 mg/kg/day (17 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons). No effects on postnatal development were noted at 25 mg/kg/day (89 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether efinaconazole is excreted in human milk. After repeated subcutaneous administration, efinaconazole was detected in milk of nursing rats. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when JUBLIA is administered to nursing women.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered, along with the mother’s clinical need for JUBLIA, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from JUBLIA.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of JUBLIA were established in patients 6 years and older. Use of JUBLIA in these age groups is supported by evidence from well-controlled trials in adults with additional data from an open-label safety study in 60 pediatric subjects ages 6 to 17 (including a pharmacokinetic study in 17 subjects 12 years to less than 17 years old) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Safety and effectiveness of JUBLIA in pediatric subjects under 6 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in clinical trials of JUBLIA, 11.3% were 65 and over, while none were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety and effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and the younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence >1%) were ingrown toenails, application site dermatitis, application site vesicles, and application site pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bausch Health US, LLC at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two clinical trials, 1227 subjects were treated with JUBLIA, 1161 for at least 24 weeks and 780 for 48 weeks. Adverse reactions reported within 48 weeks of treatment and in at least 1% of subjects treated with JUBLIA and those reported in subjects treated with the vehicle are presented in Table 1 .
Adverse Event, n (%) | JUBLIA (N=1,227) | Vehicle (N=413) |
Ingrown toenail | 28 (2.3%) | 3 (0.7%) |
Application site dermatitis | 27 (2.2%) | 1 (0.2%) |
Application site vesicles | 20 (1.6%) | 0 (0.0%) |
Application site pain | 13 (1.1%) | 1 (0.2%) |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of JUBLIA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Application site erythema and exfoliation
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Onychomadesis, Nail discoloration
DRUG INTERACTIONS
In vitro studies have shown that JUBLIA, at therapeutic concentrations, neither inhibits nor induces cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes.
DESCRIPTION
JUBLIA (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution for topical use. Each gram of JUBLIA contains 100 mg of efinaconazole. Efinaconazole is an azole antifungal with a chemical name of ((2R,3R)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylenepiperidin-1-yl)-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) butan-2-ol). The structural formula for efinaconazole is represented below:

JUBLIA contains the following inactive ingredients: alcohol, anhydrous citric acid, butylated hydroxytoluene, C12-15 alkyl lactate, cyclomethicone, diisopropyl adipate, disodium edetate, and purified water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
JUBLIA topical solution is an azole antifungal [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ].
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of JUBLIA is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Systemic absorption of efinaconazole in 18 adult subjects with severe onychomycosis was determined after application of JUBLIA once daily for 28 days to patients’ 10 toenails and 0.5 cm adjacent skin. The concentration of efinaconazole in plasma was determined at multiple time points over the course of 24-hour periods on days 1, 14, and 28. Efinaconazole mean ± SD plasma C max on Day 28 was 0.67 ± 0.37 ng/mL and the mean ± SD AUC was 12.15 ± 6.91 ng•h/mL. The plasma concentration versus time profile at steady state was generally flat over a 24-hour dosing interval. In a separate study of healthy volunteers, the plasma half-life of efinaconazole following daily applications when applied to all 10 toenails for 7 days was 29.9 hours.
Specific Populations
Pediatric patients
PK of efinaconazole was assessed in 17 pediatric subjects 12 to <17 years of age with moderate to severe onychomycosis following application of JUBLIA once daily to all 10 toenails for 28 days.
The plasma concentrations of efinaconazole in pediatric subjects were relatively flat over a 24-hour dosing interval. The mean ± SD plasma C max and AUC 0-24 for efinaconazole on Day 28 were 0.55±0.38 ng/mL and 11.4±7.68 h•ng/mL, respectively.
Drug Interactions
JUBLIA is considered a non-inhibitor of the CYP450 enzyme family. In in vitro studies using human liver microsomes, efinaconazole did not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2PE1 and CYP3A4 enzyme activities at expected clinical systemic concentrations. In vitro studies in human primary hepatocytes showed that efinaconazole did not induce CYP1A2 or CYP3A4 activities.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Efinaconazole is an azole antifungal. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14α-demethylase involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a constituent of fungal cell membranes.
Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
Efinaconazole has been shown to be active against isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections. Efinaconazole exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.06 mcg/mL or less against most (≥90%) isolates of the following microorganisms:
Trichophyton rubrum
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Mechanism of Resistance
Efinaconazole drug resistance development was studied in vitro against T. mentagrophytes, T. rubrum and C. albicans . Serial passage of fungal cultures in the presence of sub-growth inhibitory concentrations of efinaconazole increased the MIC by up to 4-fold. The clinical significance of these in vitro results is unknown.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in mice was conducted with daily topical administration of 3%, 10% and 30% efinaconazole solution. Severe irritation was noted at the treatment site in all dose groups, which was attributed to the vehicle and confounded the interpretation of skin effects by efinaconazole. The high dose group was terminated at Week 34 due to severe skin reactions. No drug-related neoplasms were noted at doses up to 10% efinaconazole solution (248 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Efinaconazole revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay and Chinese hamster lung cell chromosome aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse peripheral reticulocyte micronucleus assay).
No effects on fertility were observed in male and female rats that were administered subcutaneous doses up to 25 mg/kg/day efinaconazole (279 times the MRHD based on AUC comparisons) prior to and during early pregnancy. Efinaconazole delayed the estrous cycle in females at 25 mg/kg/day but not at 5 mg/kg/day (56 times MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of once daily use of JUBLIA for the treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail were assessed in two 52-week prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trials in subjects 18 years and older (18 to 70 years of age) with 20% to 50% clinical involvement of the target toenail, without dermatophytomas or lunula (matrix) involvement. The trials compared 48 weeks of treatment with JUBLIA to the vehicle solution. The Complete Cure rate was assessed at Week 52 (4 weeks after completion of therapy). Complete cure was defined as 0% involvement of the target toenail (no clinical evidence of onychomycosis of the target toenail) in addition to Mycologic Cure, defined as both negative fungal culture and negative KOH. Table 2 lists the efficacy results for trials 1 and 2.
- Table 2: Efficacy Endpoints
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JUBLIA | Vehicle | JUBLIA | Vehicle | |
| (N=656) | (N=214) | (N=580) | (N=201) | |
| a Complete cure defined as 0% clinical involvement of the target toenail plus negative KOH and negative culture. | ||||
| b Complete or almost complete cure defined as ≤5% affected target toenail area involved and negative KOH and culture. | ||||
| c Mycologic cure defined as negative KOH and negative culture. | ||||
Complete Cure a | 117 17.8% | 7 3.3% | 88 15.2% | 11 5.5% |
Complete or Almost Complete Cure b | 173 26.4% | 15 7.0% | 136 23.4% | 15 7.5% |
Mycologic Cure c | 362 55.2% | 36 16.8% | 310 53.4% | 34 16.9% |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
JUBLIA (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution supplied in a white plastic bottle with an integrated flow-through brush applicator as follows:
- 4 mL (NDC 0187-5400-04)
- 8 mL (NDC 0187-5400-08)
Storage and Handling Conditions:
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Solution is flammable; keep away from heat or flame.
- Protect from freezing.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Keep bottle tightly closed.
- Store in upright position.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
JUBLIA ® (joo-blee-uh)
(efinaconazole)
topical solution, 10%
Important information: JUBLIA is for use on toenails and surrounding skin only. Do not use JUBLIA in your mouth, eyes or vagina. |
Read this Instructions for Use that comes with JUBLIA before you start using it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
How to apply JUBLIA:
Your toenails should be clean and dry before you apply JUBLIA. Wait at least 10 minutes after showering, bathing, or washing before applying JUBLIA. | |
Step 1: Remove the cap from the JUBLIA bottle. | 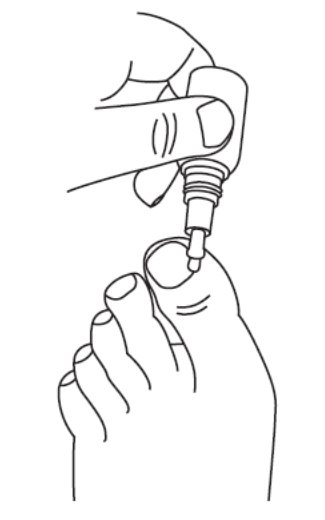 |
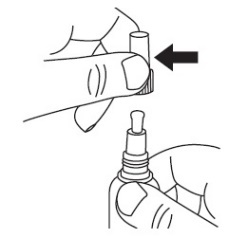
Step 2: Prepare JUBLIA for application.
|  |
|  |
| 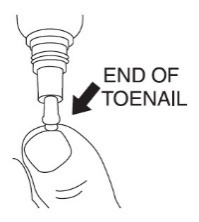 |
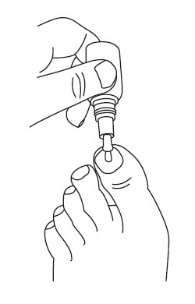
Step 5: After applying JUBLIA, the entire toenail and surrounding skin should be covered with the solution. Let the treated area dry completely before covering it with bedding, socks, or other clothing. | |
Step 6: Replace the cap tightly on the bottle. | |
| |
How should I store JUBLIA?
Keep JUBLIA and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
Distributed by: Bausch Health US, LLC, Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA Manufactured by: Bausch Health Companies Inc., Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, Canada Patented. See https://patents.ortho-dermatologics.com for US patent information. JUBLIA is a registered trademark of Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates. © 2025 Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates | |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 07/2025 9462906
Mechanism of Action
JUBLIA topical solution is an azole antifungal [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ].