Juxtapid prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Juxtapid patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Before treatment, measure ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin; obtain a negative pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential; and initiate a low-fat diet supplying <20% of energy from fat (2.1 ).
- Initiate treatment at 5 mg once daily. Titrate dose based on acceptable safety/tolerability: increase to 10 mg daily after at least 2 weeks; and then, at a minimum of 4-week intervals, to 20 mg, 40 mg, and up to the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg daily (2.1 ).
- Due to reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins/fatty acids: Take daily vitamin E, linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplements (2.1 , 5.4 ).
- Take once daily, whole, with water and without food, at least 2 hours after evening meal (2.2 ).
- Patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis or with baseline mild hepatic impairment should not exceed 40 mg daily (2.5 , 2.6 ).
Initiation and Maintenance of Therapy
Before beginning treatment with JUXTAPID:
- Measure transaminases (ALT, AST), alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] ;
- Obtain a negative pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with JUXTAPID [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] ;
- Initiate a low-fat diet supplying <20% of energy from fat [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
The recommended starting dosage of JUXTAPID is 5 mg once daily, and the dose should be escalated gradually based on acceptable safety and tolerability. Transaminases should be measured prior to any increase in dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . The maintenance dosage of JUXTAPID should be individualized, taking into account patient characteristics such as goal of therapy and response to treatment, to a maximum of 60 mg daily as described in Table 1. Modify dosing for patients taking concomitant weak CYP3A4 inhibitors and for those with renal impairment or baseline hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , (2.5) , and (2.6) ] . Monitor transaminases during treatment with JUXTAPID as described in Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and reduce or withhold dosing for patients who develop transaminase values ≥3× the upper limit of normal (ULN) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
| DOSAGE | DURATION OF ADMINISTRATION BEFORE CONSIDERING INCREASE TO NEXT DOSAGE |
|---|---|
| 5 mg daily | At least 2 weeks |
| 10 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 20 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 40 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 60 mg daily | Maximum recommended dosage |
To reduce the risk of developing a fat-soluble nutrient deficiency due to JUXTAPID's mechanism of action in the small intestine, patients treated with JUXTAPID should take daily supplements that contain 400 international units vitamin E and at least 200 mg linoleic acid, 210 mg alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), 110 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and 80 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
Administration
JUXTAPID should be taken once daily with a glass of water, without food, at least 2 hours after the evening meal because administration with food may increase the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]. Patients should swallow JUXTAPID capsules whole. Capsules should not be opened, crushed, dissolved, or chewed.
Dosing with Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
JUXTAPID is contraindicated with concomitant use of moderate and strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
The recommended maximum dosage of JUXTAPID is 30 mg daily with concomitant use of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as alprazolam, amiodarone, amlodipine, atorvastatin, bicalutamide, cilostazol, cimetidine, cyclosporine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, ginkgo, goldenseal, isoniazid, lapatinib, nilotinib, pazopanib, ranitidine, ranolazine, ticagrelor, zileuton). However, the recommended maximum dosage of JUXTAPID is 40 mg daily with concomitant use of oral contraceptives.
When initiating a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor in a patient already taking JUXTAPID 10 mg daily or more, decrease the dose of JUXTAPID by half; patients taking JUXTAPID 5 mg daily may continue with the same dosage. Careful titration of JUXTAPID may then be considered according to LDL-C response and safety/tolerability to a maximum recommended dosage of 30 mg daily except when coadministered with oral contraceptives, in which case the maximum recommended lomitapide dosage is 40 mg daily [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Dose Modification Based on Elevated Transaminases
Table 2 summarizes recommendations for dose adjustment and monitoring for patients who develop elevated transaminases during therapy with JUXTAPID [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| ALT OR AST | TREATMENT AND MONITORING RECOMMENDATIONS Recommendations based on an ULN of approximately 30-40 international units/L. |
|---|---|
| ≥3× and <5× ULN |
|
| ≥5× ULN |
|
If transaminase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of liver injury (such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, lethargy, flu-like symptoms), increases in bilirubin ≥2× ULN, or active liver disease, discontinue treatment with JUXTAPID and investigate to identify the probable cause [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Dosing in Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients with end-stage renal disease receiving dialysis should not exceed 40 mg daily. There are no data available to guide dosing in other patients with renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
Dosing in Patients with Baseline Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) should not exceed 40 mg daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Juxtapid prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY
JUXTAPID can cause elevations in transaminases. In the JUXTAPID clinical trial, 10 (34%) of the 29 patients treated with JUXTAPID had at least one elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ≥3× upper limit of normal (ULN). There were no concomitant clinically meaningful elevations of total bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR), or alkaline phosphatase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
JUXTAPID also increases hepatic fat, with or without concomitant increases in transaminases. The median absolute increase in hepatic fat was 6% after both 26 and 78 weeks of treatment, from 1% at baseline, measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Hepatic steatosis associated with JUXTAPID treatment may be a risk factor for progressive liver disease, including steatohepatitis and cirrhosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Measure ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin before initiating treatment and then ALT and AST regularly as recommended. During treatment, adjust the dose of JUXTAPID if the ALT or AST are ≥3× ULN. Discontinue JUXTAPID for clinically significant liver toxicity [ see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, JUXTAPID is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the JUXTAPID REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]. Prescribe JUXTAPID only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with HoFH. The safety and effectiveness of JUXTAPID have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH [see Indications and Usage (1) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
JUXTAPID is indicated as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH).
Limitations of Use
- The safety and effectiveness of JUXTAPID have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH, including those with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH).
- The effect of JUXTAPID on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Before treatment, measure ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin; obtain a negative pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential; and initiate a low-fat diet supplying <20% of energy from fat (2.1 ).
- Initiate treatment at 5 mg once daily. Titrate dose based on acceptable safety/tolerability: increase to 10 mg daily after at least 2 weeks; and then, at a minimum of 4-week intervals, to 20 mg, 40 mg, and up to the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg daily (2.1 ).
- Due to reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins/fatty acids: Take daily vitamin E, linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplements (2.1 , 5.4 ).
- Take once daily, whole, with water and without food, at least 2 hours after evening meal (2.2 ).
- Patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis or with baseline mild hepatic impairment should not exceed 40 mg daily (2.5 , 2.6 ).
Initiation and Maintenance of Therapy
Before beginning treatment with JUXTAPID:
- Measure transaminases (ALT, AST), alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] ;
- Obtain a negative pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with JUXTAPID [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] ;
- Initiate a low-fat diet supplying <20% of energy from fat [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
The recommended starting dosage of JUXTAPID is 5 mg once daily, and the dose should be escalated gradually based on acceptable safety and tolerability. Transaminases should be measured prior to any increase in dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . The maintenance dosage of JUXTAPID should be individualized, taking into account patient characteristics such as goal of therapy and response to treatment, to a maximum of 60 mg daily as described in Table 1. Modify dosing for patients taking concomitant weak CYP3A4 inhibitors and for those with renal impairment or baseline hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , (2.5) , and (2.6) ] . Monitor transaminases during treatment with JUXTAPID as described in Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and reduce or withhold dosing for patients who develop transaminase values ≥3× the upper limit of normal (ULN) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
| DOSAGE | DURATION OF ADMINISTRATION BEFORE CONSIDERING INCREASE TO NEXT DOSAGE |
|---|---|
| 5 mg daily | At least 2 weeks |
| 10 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 20 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 40 mg daily | At least 4 weeks |
| 60 mg daily | Maximum recommended dosage |
To reduce the risk of developing a fat-soluble nutrient deficiency due to JUXTAPID's mechanism of action in the small intestine, patients treated with JUXTAPID should take daily supplements that contain 400 international units vitamin E and at least 200 mg linoleic acid, 210 mg alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), 110 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and 80 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
Administration
JUXTAPID should be taken once daily with a glass of water, without food, at least 2 hours after the evening meal because administration with food may increase the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]. Patients should swallow JUXTAPID capsules whole. Capsules should not be opened, crushed, dissolved, or chewed.
Dosing with Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
JUXTAPID is contraindicated with concomitant use of moderate and strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
The recommended maximum dosage of JUXTAPID is 30 mg daily with concomitant use of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as alprazolam, amiodarone, amlodipine, atorvastatin, bicalutamide, cilostazol, cimetidine, cyclosporine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, ginkgo, goldenseal, isoniazid, lapatinib, nilotinib, pazopanib, ranitidine, ranolazine, ticagrelor, zileuton). However, the recommended maximum dosage of JUXTAPID is 40 mg daily with concomitant use of oral contraceptives.
When initiating a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor in a patient already taking JUXTAPID 10 mg daily or more, decrease the dose of JUXTAPID by half; patients taking JUXTAPID 5 mg daily may continue with the same dosage. Careful titration of JUXTAPID may then be considered according to LDL-C response and safety/tolerability to a maximum recommended dosage of 30 mg daily except when coadministered with oral contraceptives, in which case the maximum recommended lomitapide dosage is 40 mg daily [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Dose Modification Based on Elevated Transaminases
Table 2 summarizes recommendations for dose adjustment and monitoring for patients who develop elevated transaminases during therapy with JUXTAPID [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| ALT OR AST | TREATMENT AND MONITORING RECOMMENDATIONS Recommendations based on an ULN of approximately 30-40 international units/L. |
|---|---|
| ≥3× and <5× ULN |
|
| ≥5× ULN |
|
If transaminase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of liver injury (such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, lethargy, flu-like symptoms), increases in bilirubin ≥2× ULN, or active liver disease, discontinue treatment with JUXTAPID and investigate to identify the probable cause [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Dosing in Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients with end-stage renal disease receiving dialysis should not exceed 40 mg daily. There are no data available to guide dosing in other patients with renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
Dosing in Patients with Baseline Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) should not exceed 40 mg daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
5 mg: Orange/orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "5 mg"
10 mg: Orange/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "10 mg"
20 mg: White/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "20 mg"
30 mg: Orange/yellow hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "30 mg"
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to JUXTAPID during pregnancy. For additional information visit www.JUXTAPID.com or call the Global Lomitapide Pregnancy Exposure Registry (PER) at 1-877-902-4099. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to call the PER at 1-877-902-4099 to enroll patients who become pregnant during JUXTAPID treatment.
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies, JUXTAPID use is contraindicated in pregnancy since it may cause fetal harm [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]. Available human data are insufficient to draw conclusions about any drug-associated risks for major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. However, in animal reproduction studies, lomitapide was teratogenic in rats at clinically relevant exposures and in ferrets at exposures estimated to be less than human therapeutic exposure at 60 mg when administered during organogenesis, based on AUC comparisons. Embryo-fetal lethality was observed in rabbits at 6-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 60 mg based on body surface area. If pregnancy is detected, discontinue JUXTAPID.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Oral gavage doses of 0.04, 0.4, or 4 mg/kg/day lomitapide given to pregnant rats from gestation day 6 through organogenesis were associated with fetal malformations at ≥2-times human exposure at the MRHD (60 mg) based on plasma AUC comparisons. Fetal malformations included umbilical hernia, gastroschisis, imperforate anus, alterations in heart shape and size, limb malrotations, skeletal malformations of the tail, and delayed ossification of cranial, vertebral and pelvic bones.
Oral gavage doses of 1.6, 4, 10, or 25 mg/kg/day lomitapide given to pregnant ferrets from gestation day 12 through organogenesis were associated with both maternal toxicity and fetal malformations at exposures that ranged from less than the human exposure at the MRHD to 5-times the human exposure at the MRHD. Fetal malformations included umbilical hernia, medially rotated or short limbs, absent or fused digits on paws, cleft palate, open eye lids, low-set ears, and kinked tail.
Oral gavage doses of 0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg/day lomitapide given to pregnant rabbits from gestation day 6 through organogenesis were not associated with adverse effects at systemic exposures up to 3-times the MRHD of 60 mg based on body surface area comparison. Treatment at doses of ≥20 mg/kg/day, ≥6-times the MRHD, resulted in embryo-fetal lethality.
Pregnant female rats given oral gavage doses of 0.1, 0.3, or 1 mg/kg/day lomitapide from gestation day 7 through termination of nursing on lactation day 20 were associated with malformations at systemic exposures equivalent to human exposure at the MRHD of 60 mg based on AUC. Increased pup mortality occurred at 4-times the MRHD.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of lomitapide in human or animal milk, effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including hepatotoxicity, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with JUXTAPID.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Females of reproductive potential should have a negative pregnancy test before starting JUXTAPID.
Contraception
Based on animal studies, JUXTAPID may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JUXTAPID and for two weeks after the final dose .
The use of JUXTAPID may result in reduced efficacy of oral contraceptives if vomiting or diarrhea occurs. Advise patients using oral contraceptives and who experience vomiting or diarrhea to use an effective alternative contraceptive method until 7 days after resolution of symptoms [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ].
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of JUXTAPID did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dosing for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Renal Impairment
Patients with end-stage renal disease receiving dialysis should not exceed 40 mg daily since lomitapide exposure in these patients increased approximately 50% compared with healthy volunteers. Effects of mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, including those with end-stage renal disease not yet receiving dialysis, on lomitapide exposure have not been studied. However, it is possible that patients with renal impairment who are not yet receiving dialysis may experience increases in lomitapide exposure exceeding 50% [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) should not exceed 40 mg daily since the lomitapide exposure in these patients increased approximately 50% compared with healthy volunteers. JUXTAPID is contraindicated in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) or severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment since the lomitapide exposure in patients with moderate hepatic impairment increased 164% compared with healthy volunteers [see Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
JUXTAPID is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
- Concomitant administration of JUXTAPID with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, as this can increase JUXTAPID exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , Drug Interactions (7.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
- Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (based on Child-Pugh category B or C) and patients with active liver disease, including unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. Discontinue JUXTAPID if pregnancy detected (5.3 , 8.1 , 8.3 ).
- Gastrointestinal adverse reactions occur in 93% of patients and could affect absorption of concomitant oral medications (5.5 ).
Risk of Hepatotoxicity
JUXTAPID can cause elevations in transaminases and hepatic steatosis, as described below [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . To what extent JUXTAPID-associated hepatic steatosis promotes the elevations in transaminases is unknown. Although cases of hepatic dysfunction (elevated transaminases with increase in bilirubin or INR) or hepatic failure have not been reported, there is concern that JUXTAPID could induce steatohepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis over several years. The clinical studies supporting the safety and efficacy of JUXTAPID in HoFH would have been unlikely to detect this adverse outcome given their size and duration [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Elevation of Transaminases
Elevations in transaminases (alanine aminotransferase [ALT] and/or aspartate aminotransferase [AST]) are associated with JUXTAPID. In the clinical trial, 10 (34%) of the 29 patients with HoFH had at least one elevation in ALT or AST ≥3× ULN, and 4 (14%) of the patients had at least one elevation in ALT or AST ≥5× ULN. There were no concomitant or subsequent clinically meaningful elevations in bilirubin, INR, or alkaline phosphatase [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
During the 78-week HoFH clinical trial, no patients discontinued prematurely because of elevated transaminases. Among the 19 patients who subsequently enrolled in the HoFH extension study, one discontinued because of increased transaminases that persisted despite several dose reductions, and one temporarily discontinued because of markedly elevated transaminases (ALT 24× ULN, AST 13× ULN) that had several possible causes, including a drug-drug interaction between JUXTAPID and the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor clarithromycin [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Monitoring of Transaminases
Before initiating JUXTAPID and during treatment, monitor transaminases as recommended in Table 3.
| TIME | RECOMMENDATIONS |
|---|---|
| Before initiating treatment |
|
| During the first year |
|
| After the first year |
|
| At any time during treatment |
|
Hepatic Steatosis
JUXTAPID increases hepatic fat, with or without concomitant increases in transaminases. Hepatic steatosis is a risk factor for progressive liver disease, including steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. The long-term consequences of hepatic steatosis associated with JUXTAPID treatment are unknown. During the HoFH clinical trial, the median absolute increase in hepatic fat was 6% after both 26 weeks and 78 weeks of treatment, from 1% at baseline, measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. Clinical data suggest that hepatic fat accumulation is reversible after stopping treatment with JUXTAPID, but whether histological sequelae remain is unknown, especially after long-term use; protocol liver biopsies were not performed in the HoFH clinical trial.
Alcohol may increase levels of hepatic fat and induce or exacerbate liver injury. It is recommended that patients taking JUXTAPID should not consume more than one alcoholic drink per day.
Caution should be exercised when JUXTAPID is used with other medications known to have potential for hepatotoxicity, such as isotretinoin, amiodarone, acetaminophen (>4 g/day for ≥3 days/week), methotrexate, tetracyclines, and tamoxifen. The effect of concomitant administration of JUXTAPID with other hepatotoxic medications is unknown. More frequent monitoring of liver-related tests may be warranted.
JUXTAPID has not been studied concomitantly with other LDL-lowering agents that can also increase hepatic fat. Therefore, the combined use of such agents is not recommended.
JUXTAPID REMS Program
Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity associated with JUXTAPID therapy, JUXTAPID is available through a restricted program under the REMS. Under the JUXTAPID REMS, only certified healthcare providers and pharmacies may prescribe and distribute JUXTAPID. Further information is available at www.JUXTAPIDREMSProgram.com or by telephone at 1-85-JUXTAPID (1-855-898-2743).
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies, JUXTAPID use is contraindicated in pregnancy since it may cause fetal harm [see Contraindications (4) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ]. In animal reproduction studies in rats and ferrets, embryonic death and fetal malformations were observed at clinically relevant exposures. Females of reproductive potential should have a negative pregnancy test before starting JUXTAPID. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy with JUXTAPID and for two weeks after the final dose. If pregnancy is detected, discontinue JUXTAPID.
Reduced Absorption of Fat-Soluble Vitamins and Serum Fatty Acids
Given its mechanism of action in the small intestine, JUXTAPID may reduce the absorption of fat-soluble nutrients. In the HoFH clinical trial, patients were provided daily dietary supplements of vitamin E, linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). In this trial, the median levels of serum vitamin E, ALA, linoleic acid, EPA, DHA, and arachidonic acid decreased from baseline to Week 26 but remained above the lower limit of the reference range. Adverse clinical consequences of these reductions were not observed with JUXTAPID treatment of up to 78 weeks. Patients treated with JUXTAPID should take daily supplements that contain 400 international units vitamin E and at least 200 mg linoleic acid, 210 mg ALA, 110 mg EPA, and 80 mg DHA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Patients with chronic bowel or pancreatic diseases that predispose to malabsorption may be at increased risk for deficiencies in these nutrients with use of JUXTAPID.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported by 27 (93%) of 29 patients in the HoFH clinical trial. Diarrhea occurred in 79% of patients, nausea in 65%, dyspepsia in 38%, and vomiting in 34%. Other reactions reported by at least 20% of patients include abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, constipation, and flatulence [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Gastrointestinal adverse reactions of severe intensity were reported by 6 (21%) of 29 patients in the HoFH clinical trial, with the most common being diarrhea (4 patients, 14%); vomiting (3 patients, 10%); and abdominal pain, distension, and/or discomfort (2 patients, 7%). Gastrointestinal reactions contributed to the reasons for early discontinuation from the trial for 4 (14%) patients.
There have been postmarketing reports of severe diarrhea with the use of JUXTAPID, including patients being hospitalized because of diarrhea-related complications such as volume depletion. Monitor patients who are more susceptible to complications from diarrhea, such as older patients and patients taking drugs that can lead to volume depletion or hypotension. Instruct patients to stop JUXTAPID and contact their healthcare provider if severe diarrhea occurs or if they experience symptoms of volume depletion such as lightheadedness, decreased urine output, or tiredness. In such cases, consider reducing the dose or suspending use of JUXTAPID.
Absorption of concomitant oral medications may be affected in patients who develop diarrhea or vomiting.
To reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse events, patients should adhere to a low-fat diet supplying <20% of energy from fat and the dosage of JUXTAPID should be increased gradually [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and (2.2) ] .
Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 Inhibitors
CYP3A4 inhibitors increase the exposure of lomitapide, with strong inhibitors increasing exposure approximately 27-fold. Concomitant use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with JUXTAPID is contraindicated [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ]. In the JUXTAPID clinical trials, one patient with HoFH developed markedly elevated transaminases (ALT 24× ULN, AST 13× ULN) within days of initiating the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor clarithromycin. If treatment with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, JUXTAPID should be stopped during the course of treatment.
Grapefruit juice must be omitted from the diet while being treated with JUXTAPID.
Weak CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase the exposure of lomitapide approximately 2-fold; therefore, when JUXTAPID is administered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors, the dose of JUXTAPID should be decreased by half. Careful titration may then be considered based on LDL-C response and safety/tolerability to a maximum recommended dosage of 30 mg daily except when coadministered with oral contraceptives, in which case the maximum recommended lomitapide dosage is 40 mg daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7.2) ].
Risk of Myopathy with Concomitant Use of Simvastatin or Lovastatin
The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, with simvastatin and lovastatin monotherapy is dose related. Lomitapide approximately doubles the exposure to simvastatin; therefore, it is recommended to reduce the dose of simvastatin by 50% when initiating JUXTAPID [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . While taking JUXTAPID, limit simvastatin dosage to 20 mg daily (or 40 mg daily for patients who have previously tolerated simvastatin 80 mg daily for at least one year without evidence of muscle toxicity). Refer to the simvastatin prescribing information for additional dosing recommendations.
Interaction between lovastatin and lomitapide has not been studied. However, the metabolizing enzymes and transporters responsible for the disposition of lovastatin and simvastatin are similar, suggesting that JUXTAPID may increase the exposure of lovastatin; therefore, reducing the dose of lovastatin should be considered when initiating JUXTAPID.
Risk of Supratherapeutic or Subtherapeutic Anticoagulation with Warfarin
JUXTAPID increases the plasma concentrations of warfarin. Increases in the dose of JUXTAPID may lead to supratherapeutic anticoagulation, and decreases in the dose of JUXTAPID may lead to subtherapeutic anticoagulation. Difficulty controlling INR contributed to early discontinuation from the HoFH clinical trial for one of five patients taking concomitant warfarin. Patients taking warfarin should undergo regular monitoring of the INR, especially after any changes in JUXTAPID dosage. The dose of warfarin should be adjusted as clinically indicated [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ] .
Risk of Malabsorption with Rare Hereditary Disorders of Galactose Intolerance
Patients with rare, hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption should avoid JUXTAPID as this may result in diarrhea and malabsorption.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions have been observed and are discussed in detail in other sections of the label:
- Risk of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and serum fatty acids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
One single-arm, open-label, 78-week trial has been conducted in 29 patients with HoFH, 23 of whom completed at least one year of treatment. The initial dosage of JUXTAPID was 5 mg daily, with titration up to 60 mg daily during an 18-week period based on safety and tolerability. In this trial, the mean age was 30.7 years (range, 18 to 55 years), 16 (55%) patients were men, 25 (86%) patients were Caucasian, 2 (7%) were Asian, 1 (3%) was African American, and 1 (3%) was multi-racial [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Five (17%) of the 29 patients with HoFH that participated in the clinical trial discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction. The adverse reactions that contributed to treatment discontinuations included diarrhea (2 patients; 7%) and abdominal pain, nausea, gastroenteritis, weight loss, headache, and difficulty controlling INR on warfarin (1 patient each; 3%).
The most common adverse reactions were gastrointestinal, reported by 27 (93%) of 29 patients. Adverse reactions reported by ≥8 (28%) patients in the HoFH clinical trial included diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain. Other common adverse reactions, reported by 5 to 7 (17-24%) patients, included weight loss, abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, constipation, flatulence, increased ALT, chest pain, influenza, nasopharyngitis, and fatigue.
The adverse reactions reported in at least 10% of patients during the HoFH clinical trial are presented in Table 4.
| ADVERSE REACTION | N (%) |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |
| Diarrhea | 23 (79) |
| Nausea | 19 (65) |
| Dyspepsia | 11 (38) |
| Vomiting | 10 (34) |
| Abdominal pain | 10 (34) |
| Abdominal discomfort | 6 (21) |
| Abdominal distension | 6 (21) |
| Constipation | 6 (21) |
| Flatulence | 6 (21) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 3 (10) |
| Defecation urgency | 3 (10) |
| Rectal tenesmus | 3 (10) |
| Infections | |
| Influenza | 6 (21) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 5 (17) |
| Gastroenteritis | 4 (14) |
| Investigations | |
| Decreased weight | 7 (24) |
| Increased ALT | 5 (17) |
| General Disorders | |
| Chest pain | 7 (24) |
| Fatigue | 5 (17) |
| Fever | 3 (10) |
| Musculoskeletal Disorders | |
| Back pain | 4 (14) |
| Nervous System Disorders | |
| Headache | 3 (10) |
| Dizziness | 3 (10) |
| Respiratory Disorders | |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 4 (14) |
| Nasal congestion | 3 (10) |
| Cardiac Disorders | |
| Angina pectoris | 3 (10) |
| Palpitations | 3 (10) |
Adverse reactions of severe intensity were reported by 8 (28%) of 29 patients, with the most common being diarrhea (4 patients, 14%), vomiting (3 patients, 10%), increased ALT or hepatotoxicity (3 patients, 10%), and abdominal pain, distension, and/or discomfort (2 patients, 7%).
Transaminase Elevations
During the HoFH clinical trial, 10 (34%) of 29 patients had at least one elevation in ALT and/or AST ≥3× ULN (see Table 5 ). No clinically meaningful elevations in total bilirubin or alkaline phosphatase were observed. Transaminases typically fell within one to four weeks of reducing the dose or withholding JUXTAPID.
| N (%) | |
|---|---|
| Upper limits of normal (ULN) ranged from 33-41 international units/L for ALT and 36-43 international units/L for AST. | |
| Total Patients | 29 |
| Maximum ALT | |
| ≥3 to <5 × ULN | 6 (21%) |
| ≥5 to <10 × ULN | 3 (10%) |
| ≥10 to <20 × ULN | 1 (3%) |
| ≥20 × ULN | 0 |
| Maximum AST | |
| ≥3 to <5 × ULN | 5 (17%) |
| ≥5 to <10 × ULN | 1 (3%) |
| ≥10 to <20 × ULN | 0 |
| ≥20 × ULN | 0 |
Among the 19 patients who enrolled in an extension study following the HoFH clinical trial, one discontinued because of increased transaminases that persisted despite several dose reductions, and one temporarily discontinued because of markedly elevated transaminases (ALT 24× ULN, AST 13× ULN) that had several possible causes, including a drug-drug interaction between JUXTAPID and the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor clarithromycin [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Hepatic Steatosis
Hepatic fat was prospectively measured using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in all eligible patients during the HoFH clinical trial. After 26 weeks, the median absolute increase in hepatic fat from baseline was 6%, and the mean absolute increase was 8% (range, 0% to 30%). After 78 weeks, the median absolute increase in hepatic fat from baseline was 6%, and the mean absolute increase was 7% (range, 0% to 18%). Among the 23 patients with evaluable data, on at least one occasion during the trial, 18 (78%) exhibited an increase in hepatic fat >5% and 3 (13%) exhibited an increase >20%. Data from individuals who had repeat measurements after stopping JUXTAPID show that hepatic fat accumulation is reversible, but whether histological sequelae remain is unknown.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of JUXTAPID. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to JUXTAPID exposure.
Musculoskeletal disorders: Myalgia
Skin reactions: Alopecia
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A4 inhibitors increase exposure to lomitapide. Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors are contraindicated with JUXTAPID. Patients must avoid grapefruit juice (4 , 5.6 , 7.1 ).
- When administered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors, the dose of JUXTAPID should be decreased by half. The dosage of JUXTAPID may then be up-titrated to a maximum recommended dosage of 30 mg daily (2.3 , 5.6 , 7.2 ).
- Warfarin: Lomitapide increases plasma concentrations of warfarin. Monitor international normalized ratio (INR) regularly, especially with JUXTAPID dose adjustment (5.8 , 7.3 ).
- Simvastatin and lovastatin exposure increase with JUXTAPID. Limit dose when co-administered with JUXTAPID due to myopathy risk (5.7 , 7.4 ).
- P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Substrates: Consider dose reduction of P-gp substrate because of possible increased absorption with JUXTAPID (7.5 ).
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: Separate JUXTAPID dosing by at least 4 hours (7.6 ).
Moderate and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
A strong CYP3A4 inhibitor has been shown to increase lomitapide exposure approximately 27-fold [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as boceprevir, clarithromycin, conivaptan, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, lopinavir/ritonavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, posaconazole, ritonavir, saquinavir, telaprevir, telithromycin, tipranavir/ritonavir, voriconazole) with lomitapide is contraindicated. Concomitant use of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as amprenavir, aprepitant, atazanavir, ciprofloxacin, crizotinib, darunavir/ritonavir, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, fosamprenavir, imatinib, verapamil) has not been studied, but concomitant use with lomitapide is contraindicated since lomitapide exposure will likely increase significantly in the presence of these inhibitors.
Patients must avoid grapefruit juice while taking JUXTAPID [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as alprazolam, amiodarone, amlodipine, atorvastatin, bicalutamide, cilostazol, cimetidine, cyclosporine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, ginkgo, goldenseal, isoniazid, lapatinib, nilotinib, pazopanib, ranitidine, ranolazine, ticagrelor, zileuton) can increase lomitapide exposure approximately 2-fold [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . When administered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors, the dose of JUXTAPID should be decreased by half. Careful titration of JUXTAPID may then be considered based on LDL-C response and safety/tolerability to a maximum recommended dosage of 30 mg daily except when coadministered with oral contraceptives, in which case the maximum recommended lomitapide dosage is 40 mg daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Warfarin
Lomitapide increases plasma concentrations of both R(+)-warfarin and S(-)-warfarin by approximately 30% and increased the INR 22%. Patients taking warfarin should undergo regular monitoring of INR, particularly after any changes in lomitapide dosage. The dose of warfarin should be adjusted as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
Simvastatin and Lovastatin
The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, with simvastatin and lovastatin monotherapy is dose related. Lomitapide approximately doubles the exposure of simvastatin; therefore, the recommended dose of simvastatin should be reduced by 50% when initiating JUXTAPID [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . While taking JUXTAPID, limit simvastatin dosage to 20 mg daily (or 40 mg daily for patients who have previously tolerated simvastatin 80 mg daily for at least one year without evidence of muscle toxicity). Refer to the simvastatin prescribing information for simvastatin dosing recommendations.
Interaction between lovastatin and lomitapide has not been studied. However, the metabolizing enzymes and transporters responsible for the disposition of lovastatin and simvastatin are similar, suggesting that JUXTAPID may increase the exposure of lovastatin; therefore, reducing the dose of lovastatin should be considered when initiating JUXTAPID.
P-glycoprotein Substrates
Lomitapide is an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Coadministration of lomitapide with P-gp substrates (such as aliskiren, ambrisentan, colchicine, dabigatran etexilate, digoxin, everolimus, fexofenadine, imatinib, lapatinib, maraviroc, nilotinib, posaconazole, ranolazine, saxagliptin, sirolimus, sitagliptin, talinolol, tolvaptan, topotecan) may increase the absorption of P-gp substrates. Dose reduction of the P-gp substrate should be considered when used concomitantly with lomitapide.
Bile Acid Sequestrants
JUXTAPID has not been tested for interaction with bile acid sequestrants. Administration of JUXTAPID and bile acid sequestrants should be separated by at least 4 hours since bile acid sequestrants can interfere with the absorption of oral medications.
DESCRIPTION
JUXTAPID capsules contain lomitapide mesylate, a synthetic lipid-lowering agent for oral administration.
The chemical name of lomitapide mesylate is N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9-[4-[4-[[[4'-(trifluoromethyl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-piperidinyl]butyl]-9 H -fluorene-9-carboxamide, methanesulfonate salt. Its structural formula is:
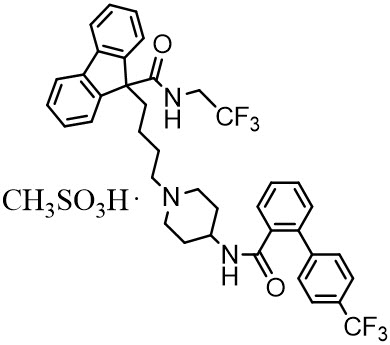
The empirical formula for lomitapide mesylate is C 39 H 37 F 6 N 3 O 2 ∙ CH 4 O 3 S and its molecular weight is 789.8.
Lomitapide mesylate is a white to off-white powder that is slightly soluble in aqueous solutions of pH 2 to 5. Lomitapide mesylate is freely soluble in acetone, ethanol, and methanol; soluble in 2-butanol, methylene chloride, and acetonitrile; sparingly soluble in 1-octanol and 2-propanol; slightly soluble in ethyl acetate; and insoluble in heptane.
Each JUXTAPID capsule contains lomitapide mesylate equivalent to 5, 10, 20, or 30 mg lomitapide free base and the following inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. The capsule shells of all strengths contain gelatin and titanium dioxide; the 5 mg, 10 mg and 30 mg capsules also contain red iron oxide; and the 30 mg capsules also contain yellow iron oxide. The imprinting ink contains shellac, black iron oxide, and propylene glycol.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
JUXTAPID directly binds and inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), which resides in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby preventing the assembly of apo B-containing lipoproteins in enterocytes and hepatocytes. This inhibits the synthesis of chylomicrons and VLDL. The inhibition of the synthesis of VLDL leads to reduced levels of plasma LDL-C.
Pharmacodynamics
Effects on QT Interval
At a concentration 23 times the C max of the maximum recommended dose, lomitapide does not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Upon oral administration of a single 60-mg dose of JUXTAPID, the lomitapide t max is around 6 hours in healthy volunteers. The absolute bioavailability of lomitapide is approximately 7%. Lomitapide pharmacokinetics is approximately dose-proportional for oral single doses from 10-100 mg.
Distribution
The mean lomitapide volume of distribution at steady state is 985-1292 liters. Lomitapide is 99.8% plasma-protein bound.
Metabolism
Lomitapide is metabolized extensively by the liver. The metabolic pathways include oxidation, oxidative N-dealkylation, glucuronide conjugation, and piperidine ring opening. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 metabolizes lomitapide to its major metabolites, M1 and M3, as detected in plasma. The oxidative N-dealkylation pathway breaks the lomitapide molecule into M1 and M3. M1 is the moiety that retains the piperidine ring, whereas M3 retains the rest of the lomitapide molecule in vitro . CYPs 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, and 2C19 may metabolize lomitapide to a small extent to M1. M1 and M3 do not inhibit activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in vitro .
Excretion
In a mass-balance study, a mean of 59.5% and 33.4% of the dose was excreted in the urine and feces, respectively. In another mass-balance study, a mean of 52.9% and 35.1% of the dose was excreted in the urine and feces, respectively. Lomitapide was not detectable in urine samples. M1 is the major urinary metabolite. Lomitapide is the major component in the feces. The mean lomitapide terminal half-life is 39.7 hours.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
A single-dose, open-label study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of 60 mg lomitapide in healthy volunteers with normal hepatic function compared with patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) and moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, lomitapide AUC and C max were 164% and 361% higher, respectively, compared with healthy volunteers. In patients with mild hepatic impairment, lomitapide AUC and C max were 47% and 4% higher, respectively, compared with healthy volunteers. Lomitapide has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10-15) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Renal Impairment
A single-dose, open-label study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of 60 mg lomitapide in patients with end-stage renal disease receiving hemodialysis compared with healthy volunteers with normal renal function. Healthy volunteers had estimated creatinine clearance >80 mL/min by the Cockcroft-Gault equation. Compared with healthy volunteers, lomitapide AUC 0-inf and C max were 40% and 50% higher, respectively, in patients with end-stage renal disease receiving hemodialysis. Effects of mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment as well as end-stage renal disease not yet on dialysis on lomitapide exposure have not been studied [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Drug Interactions
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , (5.7) , (5.8) , and Drug Interactions (7) ].
In vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Lomitapide does not induce CYPs 1A2, 3A4, or 2B6. Lomitapide inhibits CYP3A4. Lomitapide does not inhibit CYPs 1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 2E1. M1 and M3 do not induce CYPs 1A2, 3A4, or 2B6. M1 and M3 do not inhibit CYPs 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, or 3A4. Lomitapide is not a P-gp substrate. Lomitapide inhibits P-gp but does not inhibit breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP).
Effects of other Drugs on Lomitapide
Table 6 summarizes the effect of coadministered drugs on lomitapide AUC and C max .
| COADMINISTERED DRUG | DOSING OF COADMINISTERED DRUG | DOSING OF LOMITAPIDE | RATIO OF LOMITAPIDE EXPOSURE WITH/WITHOUT COADMINISTERED DRUG NO EFFECT = 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | C max | |||
| BID = twice daily; QD = once daily | ||||
| ↑ = increase | ||||
| Contraindicated with lomitapide [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] | ||||
| Ketoconazole | 200 mg BID for 9 days | 60 mg single dose | ↑ 27 | ↑ 15 |
| Adjustment necessary when coadministered with lomitapide [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] | ||||
| AUC | C max | |||
| Atorvastatin | 80 mg QD | 20 mg single dose | ↑2 | ↑2.1 |
| Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) / norgestimate | 0.035 mg EE/ 0.25 mg norgestimate QD | 20 mg single dose | ↑1.3 | ↑1.4 |
Effect of Lomitapide on other Drugs
Table 7 summarizes the effects of lomitapide on the AUC and C max of coadministered drugs.
| COADMINISTERED DRUG | DOSING OF COADMINISTERED DRUG | DOSING OF LOMITAPIDE | CHANGE OF COADMINISTERED DRUG EXPOSURE WITH / WITHOUT LOMITAPIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | C max | ||||
| QD = once daily; INR = international normalized ratio; ↑ = increase; ↓ = decrease | |||||
| Dosage adjustment necessary when coadministered with lomitapide | |||||
| Simvastatin Limit simvastatin dosage to 20 mg daily (or 40 mg daily for patients who have previously tolerated simvastatin 80 mg daily for at least one year without evidence of muscle toxicity). Refer to the simvastatin prescribing information for additional dosing recommendations. | 40 mg single dose | 60 mg QD × 7 days | Simvastatin | ↑ 99% | ↑ 102% |
| Simvastatin acid | ↑ 71% | ↑ 57% | |||
| 20 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Simvastatin | ↑ 62% | ↑65% | |
| Simvastatin acid | ↑ 39% | ↑ 35% | |||
| Warfarin Patients taking warfarin should undergo regular monitoring of the INR, especially after any changes in lomitapide dosage. | 10 mg single dose | 60 mg QD × 12 days | R(+) warfarin | ↑ 28% | ↑ 14% |
| S(-) warfarin | ↑ 30% | ↑ 15% | |||
| INR | ↑ 7% | ↑ 22% | |||
| No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
| Atorvastatin | 20 mg single dose | 60 mg QD × 7 days | Atorvastatin acid | ↑ 52% | ↑63% |
| 20 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Atorvastatin acid | ↑ 11% | ↑19% | |
| Rosuvastatin | 20 mg single dose | 60 mg QD × 7 days | Rosuvastatin | ↑ 32% | ↑ 4% |
| 20 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Rosuvastatin | ↑ 2% | ↑ 6% | |
| Fenofibrate, micronized | 145 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Fenofibric acid | ↓ 10% | ↓29% |
| Ezetimibe | 10 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Total ezetimibe | ↑ 6% | ↑ 3% |
| Extended release niacin | 1000 mg single dose | 10 mg QD × 7 days | Nicotinic acid | ↑ 10% | ↑ 11% |
| Nicotinuric acid | ↓ 21% | ↓ 15% | |||
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg QD × 28 days | 50 mg QD × 8 days | Ethinyl estradiol | ↓ 8% | ↓ 8% |
| Norgestimate | 0.25 mg QD × 28 days | 50 mg QD × 8 days | 17-Deacetyl norgestimate | ↑ 6% | ↑ 2% |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year dietary carcinogenicity study in mice, lomitapide was administered at doses of 0.3, 1.5, 7.5, 15, or 45 mg/kg/day. There were statistically significant increases in the incidences of liver adenomas and carcinomas in males at doses ≥1.5 mg/kg/day (≥2-times the MRHD at 60 mg based on AUC) and in females at ≥7.5 mg/kg/day (≥10-times the human exposure at 60 mg based on AUC). Incidences of small intestinal carcinomas in males and combined adenomas and carcinomas in females were significantly increased at doses ≥15 mg/kg/day (≥23-times the human exposure at 60 mg based on AUC).
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats, lomitapide was administered by oral gavage for up to 99 weeks at doses of 0.25, 1.7, or 7.5 mg/kg/day in males and 0.03, 0.35, or 2.0 mg/kg/day in females. While the design of the study was suboptimal, there were no statistically significant drug-related increases in tumor incidences at exposures up to 6-times (males) and 8-times (females) higher than human exposure at the MRHD based on AUC.
Lomitapide did not exhibit genotoxic potential in a battery of studies, including the in vitro Bacterial Reverse Mutation (Ames) assay, an in vitro cytogenetics assay using primary human lymphocytes, and an oral micronucleus study in rats.
Lomitapide had no effect on fertility in rats at doses up to 5 mg/kg/day at systemic exposures estimated to be 4-times (females) and 5-times (males) higher than in humans at 60 mg based on AUC.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and effectiveness of JUXTAPID as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, were evaluated in a multinational, single-arm, open-label, 78-week trial involving 29 adults with HoFH. A diagnosis of HoFH was defined by the presence of at least one of the following clinical criteria: (1) documented functional mutation(s) in both LDL receptor alleles or alleles known to affect LDL receptor functionality, or (2) skin fibroblast LDL receptor activity <20% normal, or (3) untreated TC >500 mg/dL and TG <300 mg/dL and both parents with documented untreated TC >250 mg/dL.
Among the 29 patients enrolled, the mean age was 30.7 years (range, 18 to 55 years), 16 (55%) were men, and the majority (86%) were Caucasian. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.8 kg/m 2 , with four patients meeting BMI criteria for obesity; one patient had type 2 diabetes. Concomitant lipid-lowering treatments at baseline included one or more of the following: statins (93%), ezetimibe (76%), nicotinic acid (10%), bile acid sequestrant (3%), and fibrate (3%); 18 (62%) were receiving apheresis.
After a six-week run-in period to stabilize lipid-lowering treatments, including the establishment of an LDL apheresis schedule if applicable, JUXTAPID was initiated at 5 mg daily and titrated to daily doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, and 60 mg at weeks 2, 6, 10, and 14, respectively, based on tolerability and acceptable levels of transaminases. Patients were instructed to maintain a low-fat diet (<20% calories from fat) and to take dietary supplements that provided approximately 400 international units vitamin E, 210 mg alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), 200 mg linoleic acid, 110 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and 80 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) per day. After efficacy was assessed at Week 26, patients remained on JUXTAPID for an additional 52 weeks to assess long-term safety. During this safety phase, the dose of JUXTAPID was not increased above each patient's maximum tolerated dose established during the efficacy phase, but changes to concomitant lipid-lowering treatments were allowed.
Twenty-three (79%) patients completed the efficacy endpoint at Week 26, all of whom went on to complete 78 weeks of treatment. Adverse events contributed to premature discontinuation for five patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The maximum tolerated doses during the efficacy period were 5 mg (10%), 10 mg (7%), 20 mg (21%), 40 mg (24%), and 60 mg (34%).
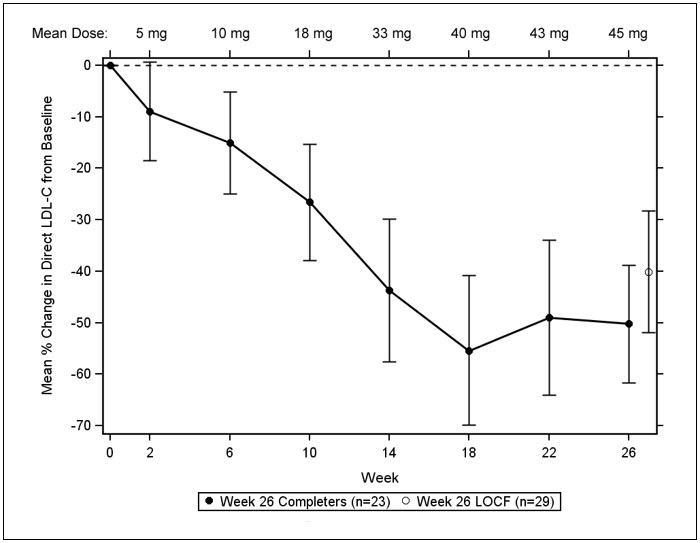
The primary efficacy endpoint was percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 26. At Week 26, the mean and median percent changes in LDL-C from baseline were -40% (paired t-test p<0.001) and -50%, respectively, based on the intent-to-treat population with last observation carried forward (LOCF) for patients who discontinued prematurely. The mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline through Week 26 is shown in Figure 1 for the 23 patients who completed the efficacy period.
| Figure 1: Mean Percent Change in LDL-C from Baseline (Week 26 Completers) |
|---|
| Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals of the mean. |
 |
Changes in lipids and lipoproteins through the efficacy endpoint at Week 26 are presented in Table 8.
| PARAMETER | BASELINE | WEEK 26/LOCF (N=29) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean % Change | |
| LDL-C, direct (mg/dL) | 336 (114) | 190 (104) | -40 Statistically significant compared with baseline based on the pre-specified gatekeeping method for controlling Type I error among the primary and key secondary endpoints. |
| TC (mg/dL) | 430 (135) | 258 (118) | -36 |
| apo B (mg/dL) | 259 (80) | 148 (74) | -39 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 386 (132) | 217 (113) | -40 |
| VLDL-C (mg/dL) | 21 (10) | 13 (9) | -29 |
| TG (mg/dL) Median values with interquartile range and median % change presented for TG. | 92 [72, 128] | 57 [36, 78] | -45 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 44 (11) | 41 (13) | -7 |
After Week 26, during the safety phase of the study, adjustments to concomitant lipid-lowering treatments were allowed. For the study population overall, average reductions in LDL-C, TC, apo B, and non-HDL-C were sustained during chronic therapy.
HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
5 mg capsules:
Orange/orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "5 mg"
| Bottles of 28 | NDC 76431-105-01 |
10 mg capsules:
Orange/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "10 mg"
| Bottles of 28 | NDC 76431-110-01 |
20 mg capsules:
White/white hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "20 mg"
| Bottles of 28 | NDC 76431-120-01 |
30 mg capsules:
Orange/yellow hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "A733" and "30 mg"
| Bottles of 28 | NDC 76431-130-01 |
Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (between 59°F and 86°F). Brief exposure to temperatures up to 40°C (104°F) may be tolerated provided the mean kinetic temperature does not exceed 25°C (77°F); however, such exposure should be minimized. Keep container tightly closed and protect from moisture.
Mechanism of Action
JUXTAPID directly binds and inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), which resides in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby preventing the assembly of apo B-containing lipoproteins in enterocytes and hepatocytes. This inhibits the synthesis of chylomicrons and VLDL. The inhibition of the synthesis of VLDL leads to reduced levels of plasma LDL-C.