Get your patient on Kuvan (Sapropterin Dihydrochloride)
Kuvan patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommendations Prior to KUVAN Treatment
Treatment with KUVAN should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of PKU.
All patients with PKU who are being treated with KUVAN should also be treated with a Phe-restricted diet, including dietary protein and Phe restriction.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dosage of KUVAN is:
Pediatric Patients 1 month to 6 years : 10 mg/kg (actual body weight) administered orally once daily.
Patients 7 years and older : 10 to 20 mg/kg (actual body weight) administered orally once daily.
Administer KUVAN with a meal, preferably at the same time each day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
A missed dose should be administered as soon as possible, but two doses should not be administered on the same day.
Evaluation Period
Existing dietary protein and Phe intake should not be modified during the evaluation period.
If a 10 mg/kg per day starting dose is used, then response to therapy is determined by change in blood Phe following treatment with KUVAN at 10 mg/kg per day for a period of up to 1 month. Blood Phe levels should be checked after 1 week of KUVAN treatment and periodically for up to a month. If blood Phe does not decrease from baseline at 10 mg/kg per day, the dose may be increased to 20 mg/kg per day. Patients whose blood Phe does not decrease after 1 month of treatment at 20 mg/kg per day do not show a biochemical response and treatment with KUVAN should be discontinued in these patients.
If a 20 mg/kg per day starting dose is used, then response to therapy is determined by change in blood Phe following treatment with KUVAN at 20 mg/kg per day for a period of 1 month. Blood Phe levels should be checked after 1 week of KUVAN treatment and periodically during the first month. Treatment should be discontinued in patients who do not show a biochemical response (blood Phe does not decrease) after 1 month of treatment at 20 mg/kg per day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Dosage Adjustment
Once responsiveness to KUVAN has been established, the dosage may be adjusted within the range of 5 to 20 mg/kg per day according to biochemical response to therapy (blood Phe). Periodic blood Phe monitoring is recommended to assess blood Phe control, especially in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Preparation and Administration Instructions
KUVAN Tablets
- KUVAN tablets may be swallowed either as whole tablets or dissolved in 120 to 240 mL of water or apple juice and taken orally within 15 minutes of dissolution.
- It may take a few minutes for the tablets to dissolve.
- To make the tablets dissolve faster, tablets may be stirred or crushed.
- The tablets may not dissolve completely. Patients may see small pieces floating on top of the water or apple juice. This is normal and safe for patients to swallow.
- If after drinking the medicine, patients still see pieces of the tablet in the container, more water or apple juice can be added to make sure all of the medicine is consumed.
- KUVAN tablets may also be crushed and then mixed in a small amount of soft foods such as apple sauce or pudding.
KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution
Patients weighing greater than 10 kg
- KUVAN powder for oral solution should be dissolved in 120 to 240 mL of water or apple juice and taken orally within 30 minutes of dissolution.
- KUVAN powder for oral solution may also be stirred in a small amount of soft food such as apple sauce or pudding.
- Empty the contents of the packet(s) in water, apple juice, or a small amount of soft foods and mix thoroughly. The powder should dissolve completely.
Patients weighing 10 kg or less (use 100 mg packets)
- For infants weighing 10 kg or less, KUVAN powder for oral solution can be dissolved in as little as 5 mL of water or apple juice and a portion of this solution corresponding to a 10 mg/kg dose may be administered orally via an oral dosing syringe.
- Table 1 provides dosing information for infants at the recommended starting dose of 10 mg/kg per day.
- Refer to Table 2 for dosing information at 20 mg/kg per day if dosage adjustment is needed.
Table 1: 10 mg/kg per day Dosing Table for Infants Weighing 10 kg or Less
Patient Weight (kg) | Starting Dose: 10 mg/kg per day• | |||
Dose (mg) | KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution 100 mg Packets Dissolved † | Dilution Volume | Administered Dose volume (mL) § | |
1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 |
2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | 2 |
3 | 30 | 1 | 10 | 3 |
4 | 40 | 1 | 10 | 4 |
5 | 50 | 1 | 10 | 5 |
6 | 60 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
7 | 70 | 1 | 5 | 3.5 |
8 | 80 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
9 | 90 | 1 | 5 | 4.5 |
10 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
•Starting dose for infants is 10 mg/kg per day. Dosing information for 20 mg/kg per day is provided in Table 2.
† Powder for oral solution provided in single use packets containing 100 mg KUVAN per packet.
‡ Volume of water or apple juice to dissolve KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution.
§ Discard remainder of mixture after volume to be administered is drawn.
Table 2: 20 mg/kg per day Dosing Table for Infants Weighing 10 kg or Less
Patient Weight (kg) | 20 mg/kg per day | |||
Dose (mg) | KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution 100 mg Packets • Dissolved | Dilution Volume | Administered (mL) § | |
1 | 20 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
2 | 40 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
3 | 60 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
4 | 80 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
5 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
6 | 120 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
7 | 140 | 2 | 5 | 3.5 |
8 | 160 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
9 | 180 | 2 | 5 | 4.5 |
10 | 200 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
• Powder for oral solution provided in single use packets containing 100 mg KUVAN per packet.
† Volume of water or apple juice to dissolve KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution.
§ Discard remainder of mixture after volume to be administered is drawn.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Kuvan prescribing information
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KUVAN ® is indicated to reduce blood phenylalanine (Phe) levels in adult and pediatric patients one month of age and older with hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) due to tetrahydrobiopterin- (BH4-) responsive Phenylketonuria (PKU). KUVAN is to be used in conjunction with a Phe-restricted diet.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommendations Prior to KUVAN Treatment
Treatment with KUVAN should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of PKU.
All patients with PKU who are being treated with KUVAN should also be treated with a Phe-restricted diet, including dietary protein and Phe restriction.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dosage of KUVAN is:
Pediatric Patients 1 month to 6 years : 10 mg/kg (actual body weight) administered orally once daily.
Patients 7 years and older : 10 to 20 mg/kg (actual body weight) administered orally once daily.
Administer KUVAN with a meal, preferably at the same time each day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
A missed dose should be administered as soon as possible, but two doses should not be administered on the same day.
Evaluation Period
Existing dietary protein and Phe intake should not be modified during the evaluation period.
If a 10 mg/kg per day starting dose is used, then response to therapy is determined by change in blood Phe following treatment with KUVAN at 10 mg/kg per day for a period of up to 1 month. Blood Phe levels should be checked after 1 week of KUVAN treatment and periodically for up to a month. If blood Phe does not decrease from baseline at 10 mg/kg per day, the dose may be increased to 20 mg/kg per day. Patients whose blood Phe does not decrease after 1 month of treatment at 20 mg/kg per day do not show a biochemical response and treatment with KUVAN should be discontinued in these patients.
If a 20 mg/kg per day starting dose is used, then response to therapy is determined by change in blood Phe following treatment with KUVAN at 20 mg/kg per day for a period of 1 month. Blood Phe levels should be checked after 1 week of KUVAN treatment and periodically during the first month. Treatment should be discontinued in patients who do not show a biochemical response (blood Phe does not decrease) after 1 month of treatment at 20 mg/kg per day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Dosage Adjustment
Once responsiveness to KUVAN has been established, the dosage may be adjusted within the range of 5 to 20 mg/kg per day according to biochemical response to therapy (blood Phe). Periodic blood Phe monitoring is recommended to assess blood Phe control, especially in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
Preparation and Administration Instructions
KUVAN Tablets
- KUVAN tablets may be swallowed either as whole tablets or dissolved in 120 to 240 mL of water or apple juice and taken orally within 15 minutes of dissolution.
- It may take a few minutes for the tablets to dissolve.
- To make the tablets dissolve faster, tablets may be stirred or crushed.
- The tablets may not dissolve completely. Patients may see small pieces floating on top of the water or apple juice. This is normal and safe for patients to swallow.
- If after drinking the medicine, patients still see pieces of the tablet in the container, more water or apple juice can be added to make sure all of the medicine is consumed.
- KUVAN tablets may also be crushed and then mixed in a small amount of soft foods such as apple sauce or pudding.
KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution
Patients weighing greater than 10 kg
- KUVAN powder for oral solution should be dissolved in 120 to 240 mL of water or apple juice and taken orally within 30 minutes of dissolution.
- KUVAN powder for oral solution may also be stirred in a small amount of soft food such as apple sauce or pudding.
- Empty the contents of the packet(s) in water, apple juice, or a small amount of soft foods and mix thoroughly. The powder should dissolve completely.
Patients weighing 10 kg or less (use 100 mg packets)
- For infants weighing 10 kg or less, KUVAN powder for oral solution can be dissolved in as little as 5 mL of water or apple juice and a portion of this solution corresponding to a 10 mg/kg dose may be administered orally via an oral dosing syringe.
- Table 1 provides dosing information for infants at the recommended starting dose of 10 mg/kg per day.
- Refer to Table 2 for dosing information at 20 mg/kg per day if dosage adjustment is needed.
Table 1: 10 mg/kg per day Dosing Table for Infants Weighing 10 kg or Less
Patient Weight (kg) | Starting Dose: 10 mg/kg per day• | |||
Dose (mg) | KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution 100 mg Packets Dissolved † | Dilution Volume (mL) ‡ | Administered Dose volume (mL) § | |
1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 |
2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | 2 |
3 | 30 | 1 | 10 | 3 |
4 | 40 | 1 | 10 | 4 |
5 | 50 | 1 | 10 | 5 |
6 | 60 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
7 | 70 | 1 | 5 | 3.5 |
8 | 80 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
9 | 90 | 1 | 5 | 4.5 |
10 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
•Starting dose for infants is 10 mg/kg per day. Dosing information for 20 mg/kg per day is provided in Table 2.
† Powder for oral solution provided in single use packets containing 100 mg KUVAN per packet.
‡ Volume of water or apple juice to dissolve KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution.
§ Discard remainder of mixture after volume to be administered is drawn.
Table 2: 20 mg/kg per day Dosing Table for Infants Weighing 10 kg or Less
Patient Weight (kg) | 20 mg/kg per day | |||
Dose (mg) | KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution 100 mg Packets • Dissolved | Dilution Volume (mL) † | Administered Dose volume (mL) § | |
1 | 20 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
2 | 40 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
3 | 60 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
4 | 80 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
5 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
6 | 120 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
7 | 140 | 2 | 5 | 3.5 |
8 | 160 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
9 | 180 | 2 | 5 | 4.5 |
10 | 200 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
• Powder for oral solution provided in single use packets containing 100 mg KUVAN per packet.
† Volume of water or apple juice to dissolve KUVAN Powder for Oral Solution.
§ Discard remainder of mixture after volume to be administered is drawn.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
KUVAN tablets are for oral use. Each tablet contains 100 mg of sapropterin dihydrochloride. Tablets are round, off-white to light yellow, mottled, and debossed with “177”.
KUVAN powder for oral solution is available as a unit dose packet containing 100 mg of sapropterin dihydrochloride and as a unit dose packet containing 500 mg of sapropterin dihydrochloride. The powder is off-white to yellow in color.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from pregnancy safety studies, pharmacovigilance, and published case reports with KUVAN use during pregnancy have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data) . Uncontrolled blood phenylalanine concentrations before and during pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and fetal adverse effects (see Clinical Considerations ) .
An embryo-fetal development study with sapropterin dihydrochloride in rats using oral doses up to 3 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) given during the period of organogenesis showed no effects. In a rabbit study using oral administration of sapropterin dihydrochloride during the period of organogenesis, a rare defect, holoprosencephaly, was noted at 10 times the MRHD.
All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defects, pregnancy loss, or other adverse pregnancy outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in pregnant women with PKU who maintain blood phenylalanine concentrations greater than 600 micromol/L during pregnancy is greater than the corresponding background risk for pregnant women without PKU.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo‑Fetal Risk
Uncontrolled blood phenylalanine concentrations before and during pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and fetal adverse effects. To reduce the risk of hyperphenylalaninemia-induced fetal adverse effects, blood phenylalanine concentrations should be maintained between 120 and 360 micromol/L during pregnancy and during the 3 months before conception [see Dosage and Administration 2.2) ] .
Data
Human Data
Uncontrolled Maternal PKU
Available data from the Maternal Phenylketonuria Collaborative Study on 468 pregnancies and 331 live births in PKU‑affected women demonstrated that uncontrolled Phe levels above 600 micromol/L are associated with a very high incidence of neurological, cardiac, facial dysmorphism, and growth anomalies. Control of blood phenylalanine during pregnancy is essential to reduce the incidence of Phe-induced teratogenic effects.
Pregnancy Registry Data
Available data from pregnancy sub-registries within the Phenylketonuria Developmental Outcomes and Safety (PKUDOS) Registry and the KUVAN Adult Maternal Pediatric European Registry (KAMPER) have identified 72 live births (79 pregnancies) in women with PKU exposed to sapropterin during pregnancy. Three birth defects were reported, including one case each of microcephaly, cleft palate, and tongue tie. The two major birth defects (microcephaly and cleft palate) were associated with Phe levels greater than 360 micromol/L during pregnancy.
Animal Data
No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in a reproduction study in rats using oral doses of up to 400 mg/kg per day sapropterin dihydrochloride (about 3 times the MRHD of 20 mg/kg per day, based on body surface area) administered during the period of organogenesis. However, in a rabbit reproduction study, oral administration of a maximum dose of 600 mg/kg per day (about 10 times the MRHD, based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis was associated with a non-statistically significant increase in the incidence of holoprosencephaly in two high dose-treated litters (4 fetuses), compared to one control-treated litter (1 fetus).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are insufficient data to assess the presence of sapropterin in human milk and no data on the effects on milk production. In postmarketing pregnancy registries, 13 infants were exposed to KUVAN through breastfeeding. No lactation-related safety concerns were reported in infants of mothers nursing during maternal treatment with KUVAN. There are no data on the effects on milk production. Sapropterin is present in the milk of lactating rats following intravenous administration, but not following oral administration.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for KUVAN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from KUVAN or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pediatric patients with PKU, ages 1 month to 16 years, have been treated with KUVAN in clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14 )].
The efficacy and safety of KUVAN have not been established in neonates. The safety of KUVAN has been established in children younger than 4 years in trials of 6 months duration and in children 4 years and older in trials of up to 3 years in length [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
In children aged 1 month and older, the efficacy of KUVAN has been demonstrated in trials of 6 weeks or less in duration [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
In a multicenter, open-label, single arm study, 57 patients aged 1 month to 6 years who were defined as KUVAN responders after 4 weeks of KUVAN treatment and Phe dietary restriction were treated for 6 months with KUVAN at 20 mg/kg per day. The effectiveness of KUVAN alone on reduction of blood Phe levels beyond 4 weeks could not be determined due to concurrent changes in dietary Phe intake during the study. Mean (±SD) blood Phe values over time for patients aged 1 month to <2 years and 2 to <7 years are shown in Figure 1.
| Figure 1: Mean Blood Phe Level Over Time by Age (years) (N=57) |
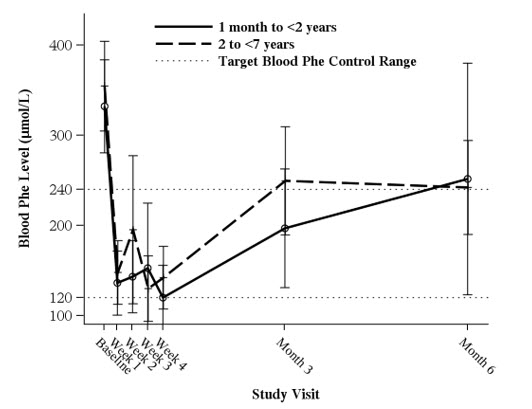 |
| • Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval. |
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of KUVAN in patients with PKU did not include patients aged 65 years and older. It is not known whether these patients respond differently than younger patients.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
KUVAN is not recommended in patients with a history of anaphylaxis to KUVAN. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and rash, have occurred [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] . Signs of anaphylaxis include wheezing, dyspnea, coughing, hypotension, flushing, nausea, and rash. Discontinue treatment with KUVAN in patients who experience anaphylaxis and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Continue dietary protein and Phe restriction in patients who experience anaphylaxis.
Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Inflammation
Gastrointestinal (GI) adverse reactions suggestive of upper GI mucosal inflammation have been reported with KUVAN. Serious adverse reactions included esophagitis and gastritis [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] . If left untreated, these could lead to severe sequelae including esophageal stricture, esophageal ulcer, gastric ulcer, and bleeding and such complications have been reported in patients receiving KUVAN. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of upper GI mucosal inflammation.
Hypophenylalaninemia
In clinical trials of KUVAN, some PKU patients experienced hypophenylalaninemia (low blood Phe) during treatment with KUVAN. In a clinical study of pediatric patients younger than 7 years old treated with KUVAN 20 mg/kg per day, the incidence of hypophenylalaninemia was higher than in clinical trials of older patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Monitoring Blood Phe Levels During Treatment
Prolonged elevations of blood Phe levels in patients with PKU can result in severe neurologic damage, including severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, microcephaly, delayed speech, seizures, and behavioral abnormalities. Conversely, prolonged levels of blood Phe that are too low have been associated with catabolism and endogenous protein breakdown, which has been associated with adverse developmental outcomes. Active management of dietary Phe intake while taking KUVAN is required to ensure adequate Phe control and nutritional balance. Monitor blood Phe levels during treatment to ensure adequate blood Phe level control. Frequent blood monitoring is recommended in the pediatric population [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Lack of Biochemical Response to KUVAN
Some patients with PKU do not show biochemical response (reduction in blood Phe) with treatment with KUVAN. In two clinical trials at a KUVAN dose of 20 mg/kg per day, 56% to 75% of pediatric PKU patients showed a biochemical response to KUVAN, and in one clinical trial at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day, 20% of adult and pediatric PKU patients showed a biochemical response to KUVAN [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
Biochemical response to KUVAN treatment cannot generally be pre-determined by laboratory testing (e.g., molecular testing), and should be determined through a therapeutic trial (evaluation) of KUVAN response [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Interaction with Levodopa
In a 10-year post-marketing safety surveillance program for a non-PKU indication using another sapropterin product, 3 patients with underlying neurological disorders experienced seizures, exacerbation of seizures, over-stimulation, and irritability during co-administration of levodopa and sapropterin. Monitor patients who are receiving levodopa for changes in neurological status during treatment with KUVAN [see Drug Interactions (7 )] .
Hyperactivity
In the KUVAN postmarketing safety surveillance program, 2 patients with PKU experienced hyperactivity when treated with KUVAN [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] . Monitor patients for hyperactivity.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
PKU Clinical Studies
The safety of KUVAN was evaluated in 7 clinical studies in patients with PKU (aged 1 month to 50 years) [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
In Studies 1-4 (controlled and uncontrolled studies), 579 patients with PKU aged 4 to 49 years received KUVAN in doses ranging from 5 to 20 mg/kg per day for lengths of treatment ranging from 1 to 164 weeks. The patient population was evenly distributed in gender, and approximately 95% of patients were Caucasian. The most common adverse reactions (≥4% of patients) were headache, rhinorrhea, pharyngolaryngeal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, cough, and nasal congestion.
The data described in Table 3 reflect exposure of 74 patients with PKU to KUVAN at doses of 10 to 20 mg/kg per day for 6 to 10 weeks in two double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (Studies 2 and 4).
Table 3 enumerates adverse reactions occurring in at least 4% of patients treated with KUVAN in the double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials described above.
Table 3: Summary of Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥4% of Patients in Placebo-Controlled Clinical Studies with KUVAN
MedDRA Preferred Term | Treatment | |
KUVAN (N=74) | Placebo (N=59) | |
No. Patients (%) | No. Patients (%) | |
Headache | 11 (15) | 8 (14) |
Rhinorrhea | 8 (11) | 0 |
Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 7 (10) | 1 (2) |
Diarrhea | 6 (8) | 3 (5) |
Vomiting | 6 (8) | 4 (7) |
Cough | 5 (7) | 3 (5) |
Nasal congestion | 3 (4) | 0 |
In open-label, uncontrolled clinical trials (Studies 1 and 3) all patients received KUVAN in doses of 5 to 20 mg/kg per day, and adverse reactions were similar in type and frequency to those reported in the double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
In Study 5, 65 pediatric patients with PKU aged 1 month to 6 years received KUVAN 20 mg/kg per day for 6 months. Adverse reactions in these patients were similar in frequency and type as those seen in other KUVAN clinical trials except for an increased incidence of low Phe levels. Twenty-five percent (16 out of 65) of patients developed Phe levels below normal for age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Use In Specific Populations (8.4 ), and Clinical Studies (14 )] .
In Study 6, a long term, open-label, extension study of 111 patients aged 4 to 50 years, receiving KUVAN in doses ranging from 5 to 20 mg/kg per day, adverse reactions were similar in type and frequency to those reported in the previous clinical studies. Fifty-five patients received KUVAN both as dissolved and intact tablets. There were no notable differences in the incidence or severity of adverse reactions between the two methods of administration. The mean (± SD) exposure to sapropterin for the entire study population was 659 ± 221 days (maximum 953 days).
In Study 7, 27 pediatric patients with PKU aged 0 to 4 years received KUVAN 10 mg/kg per day or 20 mg/kg per day. Adverse reactions were similar in type and frequency to those observed in other clinical trials, with the addition of rhinitis, which was reported in 2 subjects (7.4%).
Safety Experience from Clinical Studies for Non-PKU Indications
Approximately 800 healthy subjects and patients with disorders other than PKU, some of whom had underlying neurologic disorders or cardiovascular disease, have been administered a different formulation of the same active ingredient (sapropterin) in approximately 19 controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials. In these clinical trials, subjects were administered sapropterin at doses ranging from 1 to 100 mg/kg per day for lengths of exposure from 1 day to 2 years. Serious and severe adverse reactions (regardless of causality) during sapropterin administration were seizures, exacerbation of seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] , dizziness, gastrointestinal bleeding, post-procedural bleeding, headache, irritability, myocardial infarction, overstimulation, and respiratory failure. Common adverse reactions were headache, peripheral edema, arthralgia, polyuria, agitation, dizziness, nausea, pharyngitis, abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, and upper respiratory tract infection.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of KUVAN. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and rash: Most hypersensitivity reactions occurred within several days of initiating treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Gastrointestinal reactions: esophagitis, gastritis, oropharyngeal pain, pharyngitis, esophageal pain, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Hyperactivity: Two cases have been reported. In one case, the patient received an accidental overdosage of KUVAN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 ), Overdosage (10 )] .
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 4 includes drugs with clinically important drug interactions when administered with sapropterin dihydrochloride and instructions for preventing or managing them.
Table 4: Clinically Relevant Drug Interactions
| Levodopa | |
| Clinical Impact | Sapropterin dihydrochloride may increase the availability of tyrosine, a precursor of levodopa. Neurologic events were reported postmarketing in patients receiving sapropterin and levodopa concomitantly for a non-PKU indication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )] . |
| Intervention | Monitor patients for a change in neurologic status. |
| Inhibitors of Folate Synthesis (e.g., methotrexate, valproic acid, phenobarbital, trimethoprim) | |
| Clinical Impact | In vitro and in vivo nonclinical data suggest that drugs that inhibit folate synthesis may decrease the bioavailability of endogenous BH4 by inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved in the recycling (regeneration) of BH4. This reduction in net BH4 levels may increase Phe levels. |
| Intervention | Consider monitoring blood Phe levels more frequently during concomitant administration. An increased dosage of KUVAN may be necessary to achieve a biochemical response. |
| Drugs Affecting Nitric Oxide‑Mediated Vasorelaxation (e.g., PDE-5 inhibitors such as sildenafil, vardenafil, or tadalafil) | |
| Clinical Impact | Both sapropterin dihydrochloride and PDE-5 inhibitors may induce vasorelaxation. A reduction in blood pressure could occur; however, the combined use of these medications has not been evaluated in humans. |
| Intervention | Monitor blood pressure. |
11 DESCRIPTION
KUVAN (sapropterin dihydrochloride) is an orally administered Phenylalanine Hydroxylase activator (or PAH activator). Sapropterin dihydrochloride, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in KUVAN, is a synthetic preparation of the dihydrochloride salt of naturally occurring tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). Sapropterin dihydrochloride is an off-white to light yellow crystals or crystalline powder.
The chemical name of sapropterin dihydrochloride is (6R)-2-amino-6-[(1R,2S)-1,2-dihydroxypropyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4(1H)-pteridinone dihydrochloride and the molecular formula is C 9 H 15 N 5 O 3 ·2HCl with a molecular weight of 314.17.
Sapropterin dihydrochloride has the following structural formula:
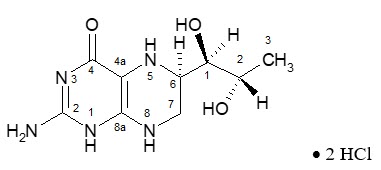
KUVAN is supplied as tablets and powder for oral solution containing 100 mg of sapropterin dihydrochloride (equivalent to 76.8 mg of sapropterin base). KUVAN is also supplied as powder for oral solution containing 500 mg of sapropterin dihydrochloride (equivalent to 384 mg of sapropterin base).
Tablets are round, off-white to light yellow, mottled, and debossed with “177”. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: ascorbic acid (USP), crospovidone (NF), dibasic calcium phosphate (USP), D-mannitol (USP), riboflavin (USP), and sodium stearyl fumarate (NF).
KUVAN powder for oral solution is off-white to yellow in color. Each unit dose packet contains the following inactive ingredients: ascorbic acid (USP), D-mannitol (USP), potassium citrate (USP), and sucralose (NF).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
KUVAN is a synthetic form of BH4, the cofactor for the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). PAH hydroxylates Phe through an oxidative reaction to form tyrosine. In patients with PKU, PAH activity is absent or deficient. Treatment with BH4 can activate residual PAH enzyme activity, improve the normal oxidative metabolism of Phe, and decrease Phe levels in some patients.
Pharmacodynamics
In PKU patients who are responsive to BH4 treatment, blood Phe levels decrease within 24 hours after a single administration of sapropterin dihydrochloride, although maximal effect on Phe level may take up to a month, depending on the patient. A single daily dose of KUVAN is adequate to maintain stable blood Phe levels over a 24-hour period. Twelve patients with blood Phe levels ranging from 516 to 986 μmol/L (mean 747 ± 153 μmol/L) were assessed with 24‑hour blood Phe level monitoring following a daily morning dose of 10 mg/kg per day. The blood Phe level remained stable during a 24‑hour observation period. No substantial increases in blood Phe levels were observed following food intake throughout the 24-hour period.
KUVAN dose-response relationship was studied in an open-label, forced titration study at doses of 5 mg/kg per day, then 20 mg/kg per day, and then 10 mg/kg per day (Study 3) [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Individual blood Phe levels were highly variable among patients. The mean blood Phe level observed at the end of each 2-week dosing period decreased as the dose of sapropterin dihydrochloride increased, demonstrating an inverse relationship between the dose of sapropterin dihydrochloride and mean blood Phe levels.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
A thorough QTc study was performed in 56 healthy adults. This randomized, placebo and active controlled crossover study was conducted to determine if a single supra-therapeutic (100 mg/kg) dose of KUVAN or a single therapeutic dose (20 mg/kg) of KUVAN had an effect on cardiac repolarization. In this study, KUVAN was administered after dissolving tablets in water under fed condition. This study demonstrated a dose-dependent shortening of the QT interval. The maximum placebo-subtracted mean change from baseline of the QTc interval was -3.69 and -8.32 ms (lower bound of 90% CI: -5.3 and -10.6 ms) at 20 and 100 mg/kg, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics
Studies in healthy subjects have shown comparable absorption of sapropterin when tablets are dissolved in water or orange juice and taken under fasted conditions. Administration of dissolved tablets after a high-fat/high-calorie meal resulted in mean increases in C max of 84% and AUC of 87% (dissolved in water). However, there was extensive variability in individual subject values for C max and AUC across the different modes of administration and meal conditions. In the clinical trials of KUVAN, drug was administered in the morning as a dissolved tablet without regard to meals. The mean elimination half-life in PKU patients was approximately 6.7 hours (range 3.9 to 17 hours), comparable with values seen in healthy subjects (range 3.0 to 5.3 hours).
A study in healthy adults with 10 mg/kg of KUVAN demonstrated that the absorption via intact tablet administration was 40% greater than via dissolved tablet administration under fasted conditions based on AUC 0-t . The administration of intact tablets under fed conditions resulted in an approximately 43% increase in the extent of absorption compared to fasted conditions based on AUC 0-t [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of sapropterin including patients from 1 month to 49 years of age showed that body weight is the only covariate substantially affecting clearance or distribution volume (see Table 5). Pharmacokinetics in patients >49 years of age have not been studied.
Table 5: Apparent Plasma Clearance by Age
Parameter | 0 to <1 yr • (N=10) | 1 to <6 yr • (N=57) | 6 to <12 yr † (N=23) | 12 to <18 yr † (N=24) | ≥18 yr † (N=42) |
CL/F (L/hr/kg) Mean ± SD (Median) | 81.5 ± 92.4 (53.6) | 50.7 ± 20.1 (48.4) | 51.7 ± 21.9 (47.4) | 39.2 ± 9.3 (38.3) | 37.9 ± 20.2 (31.8) |
• Evaluated at 20 mg/kg per day dose.
† Evaluated at 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg per day doses.
Metabolism
Sapropterin is a synthetic form of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and is expected to be metabolized and recycled by the same endogenous enzymes. In vivo endogenous BH4 is converted to quinoid dihydrobiopterin and is metabolized to dihydrobiopterin and biopterin. The enzymes dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteridine reductase are responsible for the metabolism and recycling of BH4.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
In healthy subjects, administration of a single dose of KUVAN at the maximum therapeutic dose of 20 mg/kg had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of digoxin (P-gp substrate) administered concomitantly.
In Vitro Studies Where Drug Interaction Potential Was Not Further Evaluated Clinically
The potential for sapropterin to induce or inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes was evaluated in in vitro studies which showed sapropterin did not inhibit CYP 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4/5, nor induce CYP 1A2, 2B6, or 3A4/5.
In vitro sapropterin did not inhibit OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K transporters. The potential for sapropterin to inhibit OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 has not been adequately studied. In vitro, sapropterin inhibits breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) but the potential for a clinically significant increase in systemic exposure of BCRP substrates by KUVAN appears to be low.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 2-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in F-344 rats, and a 78-week carcinogenicity study was conducted in CD-1 mice. In the 104-week oral carcinogenicity study in rats, sapropterin dihydrochloride doses of 25, 80, and 250 mg/kg per day (0.2, 0.7, and 2 times the maximum recommended human dose of 20 mg/kg per day, respectively, based on body surface area) were used. In the 78-week oral carcinogenicity study in mice, sapropterin dihydrochloride doses of 25, 80, and 250 mg/kg per day (0.1, 0.3, and 2 times the recommended human dose, respectively, based on body surface area) were used. In the 2‑year rat carcinogenicity study, there was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of benign adrenal pheochromocytoma in male rats treated with the 250 mg/kg per day (about 2 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on body surface area) dose, as compared to vehicle treated rats. The mouse carcinogenicity study showed no evidence of a carcinogenic effect, but the study was not ideal due to its duration of 78 instead of 104 weeks.
Sapropterin dihydrochloride was genotoxic in the in vitro Ames test at concentrations of 625 µg (TA98) and 5000 µg (TA100) per plate, without metabolic activation. However, no genotoxicity was observed in the in vitro Ames test with metabolic activation. Sapropterin dihydrochloride was genotoxic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells at concentrations of 0.25 and 0.5 mM. Sapropterin dihydrochloride was not mutagenic in the in vivo micronucleus assay in mice at doses up to 2000 mg/kg per day (about 8 times the maximum recommended human dose of 20 mg/kg per day, based on body surface area). Sapropterin dihydrochloride, at oral doses up to 400 mg/kg per day (about 3 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on body surface area) was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive function of male and female rats.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of KUVAN was evaluated in five clinical studies in patients with PKU.
Study 1 was a multicenter, open-label, uncontrolled clinical trial of 489 patients with PKU, ages 8 to 48 years (mean 22 years), who had baseline blood Phe levels ≥ 450 μmol/L and who were not on Phe-restricted diets. All patients received treatment with KUVAN 10 mg/kg per day for 8 days. For the purposes of this study, response to KUVAN treatment was defined as a ≥ 30% decrease in blood Phe from baseline. At Day 8, 96 patients (20%) were identified as responders.
Study 2 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 88 patients with PKU who responded to KUVAN in Study 1. After a washout period from Study 1, patients were randomized equally to either KUVAN 10 mg/kg per day (N=41) or placebo (N=47) for 6 weeks. Efficacy was assessed by the mean change in blood Phe level from baseline to Week 6 in the KUVAN-treated group as compared to the mean change in the placebo group.
The results showed that at baseline, the mean (±SD) blood Phe level was 843 (±300) μmol/L in the KUVAN-treated group and 888 (±323) μmol/L in the placebo group. At Week 6, the KUVAN treated group had a mean (±SD) blood Phe level of 607 (±377) μmol/L, and the placebo group had a mean blood Phe level of 891 (±348) μmol/L. At Week 6, the KUVAN- and placebo treated groups had mean changes in blood Phe level of –239 and 6 μmol/L, respectively (mean percent changes of –29% (±32) and 3% (±33), respectively). The difference between the groups was statistically significant (p < 0.001) (Table 6).
Table 6: Blood Phe Results in Study 2
Sapropterin (N=41) | Placebo (N=47) | |
Baseline Blood Phe Level • (μ mol/L) | ||
Mean (±SD) | 843 (±300) | 888 (±323) |
Percentiles (25 th , 75 th ) | 620, 990 | 618, 1141 |
Week 6 Blood Phe Level (μ mol/L) | ||
Mean (±SD) | 607 (±377) | 891 (±348) |
Percentiles (25 th , 75 th ) | 307, 812 | 619, 1143 |
Mean Change in Blood Phe From Baseline to Week 6 (μ mol/L) | ||
Adjusted Mean (±SE)† | -239 (±38) | 6 (±36) |
Percentiles (25 th , 75 th ) | -397, -92 | -96, 93 |
Mean Percent Change in Blood Phe From Baseline to Week 6 | ||
Mean (±SD) | - 29 (±32) | 3 (±33) |
Percentiles (25 th , 75 th ) | -61, -11 | -13, 12 |
• The mean baseline levels shown in this table represent the mean of 3 pretreatment levels (Wk -2, Wk -1, and Wk 0). Treatment with KUVAN or placebo started at Wk 0.
† p-value < 0.001, adjusted mean and standard error from an ANCOVA model with change in blood Phe level from baseline to Week 6 as the response variable, and both treatment group and baseline blood Phe level as covariates.
Change in blood Phe was noted in the KUVAN-treated group at Week 1 and was sustained through Week 6 (Figure 2).
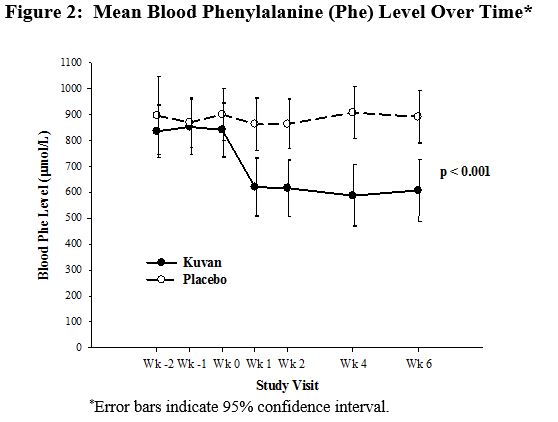
Study 3 was a multicenter, open-label, extension study in which 80 patients who responded to KUVAN treatment in Study 1 and completed Study 2 underwent 6 weeks of forced dose-titration with 3 different doses of KUVAN. Treatments consisted of 3 consecutive 2-week courses of KUVAN at doses of 5, then 20, and then 10 mg/kg per day. Blood Phe level was monitored after 2 weeks of treatment at each dose level. At baseline, mean (±SD) blood Phe was 844 (±398) μmol/L. At the end of treatment with 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg per day, mean (±SD) blood Phe levels were 744 (±384) μmol/L, 640 (±382) μmol/L, and 581 (±399) μmol/L, respectively (Table 7).
Table 7: Blood Phe Results From Forced Dose-Titration in Study 3
KUVAN Dose Level (mg/kg per day) | No. of Patients | Mean (± SD) Blood Phe Level (μ mol/L) | Mean Changes (± SD) in Blood Phe Level From Week 0 (μ mol/L) |
Baseline (No Treatment) | 80 | 844 (±398) | |
5 | 80 | 744 (±384) | ‑100 (±295) |
10 | 80 | 640 (±382) | ‑204 (±303) |
20 | 80 | 581 (±399) | -263 (±318) |
Study 4 was a multicenter study of 90 pediatric patients with PKU, ages 4 to 12 years, who were on Phe‑restricted diets and who had blood Phe levels ≤480 μmol/L at screening. All patients were treated with open-label KUVAN 20 mg/kg per day for 8 days. Response to KUVAN was defined as a ≥30% decrease in blood Phe from baseline at Day 8. At Day 8, 50 patients (56%) had a ≥30% decrease in blood Phe.
Study 5 was an open label, single arm, multicenter trial in 93 pediatric patients with PKU, aged 1 month to 6 years, who had Phe levels greater than or equal to 360 μmol/L at screening. All patients were treated with KUVAN at 20 mg/kg per day and maintained on a Phe-restricted diet. At Week 4, 57 patients (61%) were identified as responders (defined as ≥ 30% decreased in blood Phe from baseline) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) Figure 1 ] .
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
KUVAN Tablets
100 mg sapropterin dihydrochloride, are round, off-white to light yellow, mottled, and debossed with “177”. The tablets are supplied as follows:
NDC 68135-300-02 Bottle of 120 tablets
KUVAN for Oral Solution
Supplied as an off-white to yellow powder supplied in unit dose packets as follows:
100 mg sapropterin dihydrochloride per packet:
NDC 68135-301-22 Carton of 30 unit dose packets
NDC 68135-301-11 Single unit dose packet
500 mg sapropterin dihydrochloride per packet:
NDC 68135-482-11 Carton of 30 unit dose packets
NDC 68135-482-10 Single unit dose packet
Storage
Store KUVAN tablets at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions allowed between 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from moisture.
Store KUVAN for oral solution at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions allowed between 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Kuvan (COO-van)
(sapropterin dihydrochloride)
tablets
Kuvan (COO-van)
(sapropterin dihydrochloride)
powder for oral solution
Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking Kuvan and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your treatment. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about the right dose of Kuvan to take or how to mix it.
Important information:
- Kuvan comes as a tablet or in a packet containing powder.
- Take Kuvan exactly as your doctor tells you. Your doctor should tell you how much Kuvan to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may change your dose of Kuvan depending on how you respond to treatment, or based on your baby’s weight.
- If your baby weighs 22 pounds or less, follow the section called “ Instructions for giving Kuvan powder for oral solution (Kuvan 100 mg packets) to babies who weigh 22 pounds or less ”.
- Take Kuvan 1 time each day with a meal. It is best to take Kuvan at the same time each day.
Instructions for taking Kuvan tablets:
Kuvan tablets can be swallowed whole or dissolved in water or apple juice. You may also crush the tablets and mix in a small amount of soft food, such as apple sauce or pudding.
To dissolve Kuvan tablets:
- Mix Kuvan tablets in 4 ounces to 8 ounces (½ cup to 1 cup) of water or apple juice. It may take a few minutes for the tablets to dissolve. To make the tablets dissolve faster, you can stir or crush them.
- The tablets may not dissolve completely. You may see small pieces floating on top of the water or apple juice. This is normal and safe for you to swallow.
- Drink within 15 minutes.
- After drinking your medicine, if you still see small pieces of the tablet, add more water or apple juice and drink to make sure that you take all of your medicine.
Instructions for taking Kuvan powder for oral solution:
For babies who weigh 22 pounds or less, see the section below called “ Instructions for giving Kuvan powder for oral solution (Kuvan 100 mg packets) to babies who weigh 22 pounds or less.”
Kuvan powder for oral solution should be dissolved in water or apple juice. The powder for oral solution may also be mixed in a small amount of soft foods, such as apple sauce or pudding.
To dissolve Kuvan powder for oral solution:
Be sure that you know what dose of Kuvan your doctor has prescribed and whether you should use Kuvan 100 mg packets, Kuvan 500 mg packets, or both types of packets to prepare your dose.
Open the packet(s) of Kuvan powder for oral solution by folding and tearing, or cutting at the dotted line in the upper right corner of the packet. Open the packet(s) only when you are ready to use them.
Empty the contents of the packet(s) into 4 ounces to 8 ounces (1/2 cup to 1 cup) of water or apple juice.
- Drink within 30 minutes.
Instructions for giving Kuvan powder for oral solution (Kuvan 100 mg packets) to babies who weigh 22 pounds or less:
- The dose of Kuvan is based on body weight. This will change as your baby grows. Your doctor will tell you:
- the number of Kuvan 100 mg packets needed for one dose
- the amount of water or apple juice needed to mix one dose of Kuvan
- the amount of the mixture (powder and water or apple juice) you will need to give your baby his or her prescribed dose of medicine.
- Give your baby the prescribed amount of mixture (powder and water or apple juice) within 30 minutes after mixing. If you are not able to give your baby’s dose within 30 minutes after mixing, pour the unused medicine into the trash. You will need to mix a new dose.
Supplies needed to mix and give your baby’s dose of Kuvan powder for oral solution:
- the number of Kuvan 100 mg packets needed for one dose
- a small cup of water or apple juice
- one 30 mL medicine cup for mixing
- small spoon or clean utensil for mixing
- 10 mL oral dosing syringe
- scissors (optional)
Ask your pharmacist for a 30 mL medicine cup for mixing and an oral dosing syringe if you do not have these supplies.
| Step 1: | Find a clean, flat work surface. | |
| Step 2: | Place a small cup of water or apple juice, the oral dosing syringe, and an empty medicine cup on your clean, flat work surface (see Figure A). | 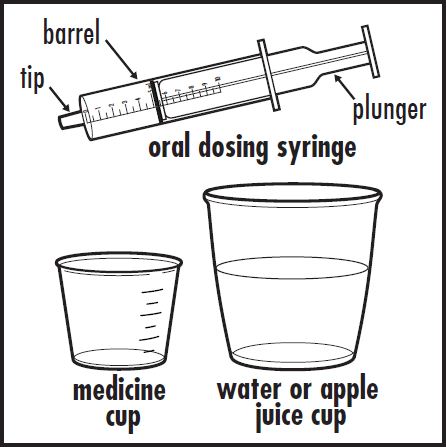 |
| Step 3: | Pour 5 mL or 10 mL of water or apple juice from the small cup into the medicine cup, as instructed by your doctor. Check to make sure that the amount of liquid lines up with the amount that your doctor tells you (see Figure B). | 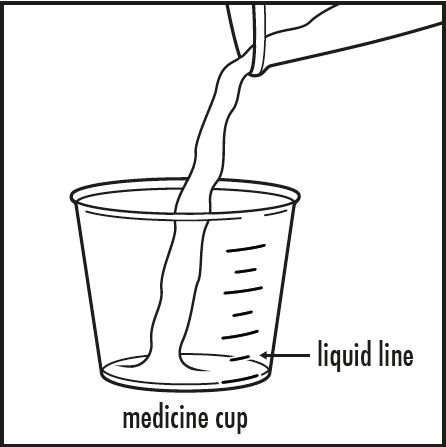 |
| Step 4: | Check the label on the Kuvan packet(s). If the packet is marked Kuvan 100 mg, empty the entire contents of the Kuvan packet into the medicine cup (see Figure C). | 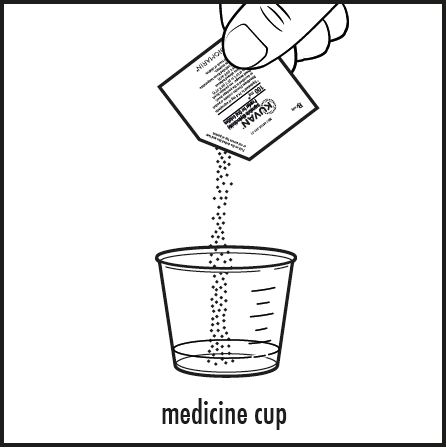 |
| Step 5: | Stir the mixture with the small spoon or other clean utensil until all of the powder completely dissolves (see Figure D). | 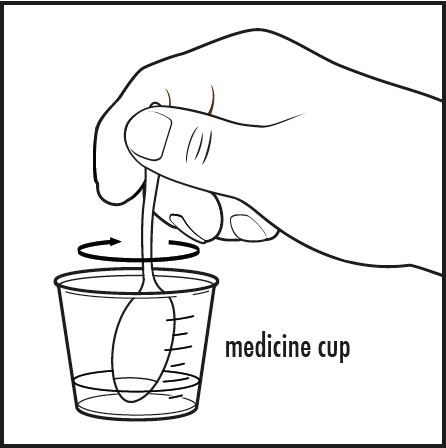 |
| Step 6: | To give a dose of Kuvan to your baby: Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the liquid inside the medicine cup. Pull back on the plunger and draw up the amount of the mixture prescribed by your doctor (see Figure E). | 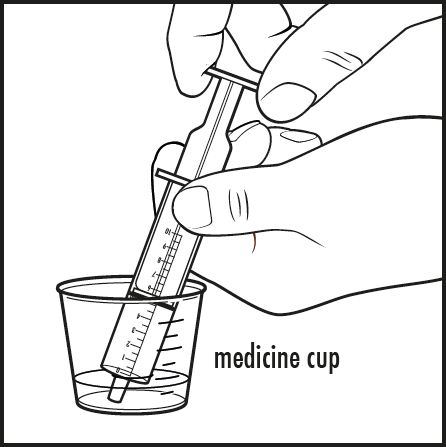 |
| Step 7: | Take the oral dosing syringe out of the medicine cup. Carefully turn the oral dosing syringe so that the tip is pointing up. Check to make sure that the amount of medicine in the oral dosing syringe lines up with the amount of mixture prescribed by your doctor (see Figure F). | 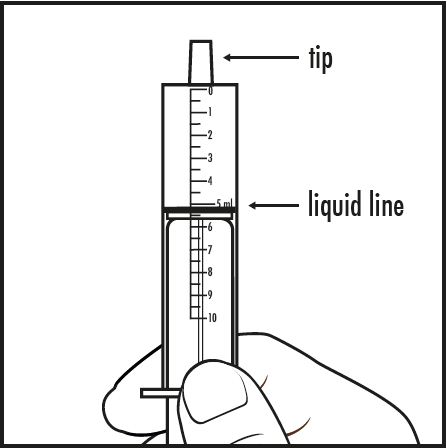 |
| Step 8: | Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into your baby’s mouth. Point the tip of the oral dosing syringe toward either cheek (see Figure G). Push on the plunger slowly, a small amount at a time, until all of the mixture in the oral dosing syringe is given. | 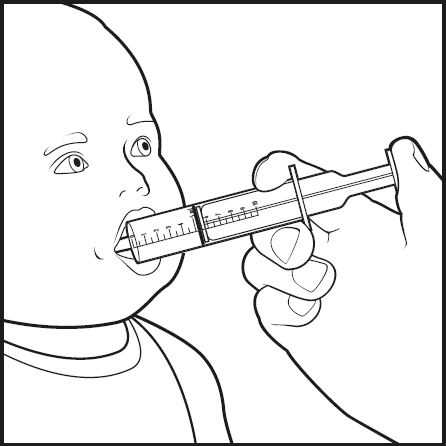 |
| Step 9: | Throw away any remaining mixture. Remove the plunger from the barrel of the oral dosing syringe. Wash the oral dosing syringe and medicine cup with warm water and air dry. When the oral dosing syringe is dry, put the plunger back into the barrel. Store the oral dosing syringe and medicine cup for the next use. |
How should I store Kuvan?
- Store Kuvan at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Kuvan tablets in the original bottle with the cap closed tightly.
- Protect from moisture.
Keep Kuvan and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
Novato, CA 94949
Revised: 07/2015
© BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. All rights reserved.
Kuvan is a registered trademark of BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
v2/2015
Mechanism of Action
KUVAN is a synthetic form of BH4, the cofactor for the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). PAH hydroxylates Phe through an oxidative reaction to form tyrosine. In patients with PKU, PAH activity is absent or deficient. Treatment with BH4 can activate residual PAH enzyme activity, improve the normal oxidative metabolism of Phe, and decrease Phe levels in some patients.