Get your patient on Lampit (Nifurtimox)
Lampit prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- LAMPIT tablets must be taken with food (2.1 )
Dosage of LAMPIT in Pediatric Patients (birth a to less than 18 years of age) (2.2) | |
Body Weight Group | Total Daily Dose of nifurtimox (mg/kg) |
41 kg or greater | 8 to 10 |
Less than 41 kg | 10 to 20 |
a Term newborn with body weight greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
- Administer LAMPIT tablets orally, three times daily with food for 60 days. (2.2 )
- Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with LAMPIT (2.3 , 8.3 ) .
- See Full Prescribing Information for additional important administration instructions. (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.4, 2.5 )
Important Administration Instructions
- LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets are for oral use and must be taken with food.
- LAMPIT tablets are dosed by body weight of the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
- LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets are functionally scored tablets which can be split into one-half (15 mg and 60 mg respectively) at the scored lines by hand. Do not break LAMPIT tablets mechanically with a tablet splitting device [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ) and Instructions for Use] .
- LAMPIT 30 mg and 120 mg tablets can be made into a slurry as an alternative method of administration for patients who cannot swallow the tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] .
- Discontinue consumption of alcohol during treatment with LAMPIT [see Contraindications (4 ) and Drug Interactions (7 )] .
- Complete the full course of treatment to prevent recurrence of the infection.
- If a dose is missed, take the missed dose as soon as possible together with food. However, if it is within 3 hours of the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and continue treatment as prescribed. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
- Administer LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets orally three times a day with food.
- Total daily recommended dosages of LAMPIT are based on the body weight of the patient (see Table 1 ).
- Adjust LAMPIT dosage accordingly if body weight decreases during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )].
- The recommended duration of treatment with LAMPIT is 60 days.
Table 1: Total Daily Recommended Dosages of LAMPIT Based on Body Weight
Age | Body weight group | Total daily dose of nifurtimox (mg/kg) |
Birth a to less than 18 years | 41 kg or greater | 8 to 10 |
Less than 41 kg | 10 to 20 |
a Term newborn with body weight of greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
Table 2: Individual Dosages Based on Body Weight in Pediatric Patients (Birth a to Less than 18 years of age)
Body weight (kg) | Dose (mg) | Number of LAMPIT 30 mg tablets per dose | Number of LAMPIT |
2.5 kg to 4.5 kg | 15 mg | ½ tablet | |
4.6 kg to less than 9 kg | 30 mg | 1 tablet | |
9 kg to less than 13 kg | 45 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
13 kg to less than 18 kg | 60 mg | 2 tablets | ½ tablet |
18 kg to less than 22 kg | 75 mg | 2 ½ tablets | |
22 kg to less than 27 kg | 90 mg | 3 tablets | |
27 kg to less than 35 kg | 120 mg | 4 tablets | 1 tablet |
35 kg to less than 41 kg | 180 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
41 kg to less than 51 kg | 120 mg | 1 tablet | |
51 kg to less than 71 kg | 180 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
71 kg to less than 91 kg | 240 mg | 2 tablets | |
91 kg or greater | 300 mg | 2 ½ tablets |
a Term newborn with body weight of greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
Pregnancy Testing Prior to Initiating LAMPIT
Instructions for Splitting LAMPIT Tablets
Do not break LAMPIT tablets mechanically with a tablet splitting device. A functional score line is used to divide the tablet by hand as follows:
- To split LAMPIT tablet, place the tablet on a flat surface with the score line facing up.
- With the tablet resting on the flat surface, apply enough downward pressure with the index finger centered on the top of the tablet to break it along the score line.
Preparation of a Slurry of LAMPIT as an Alternate Method of Administration
For patients who are unable to swallow whole or half tablets, LAMPIT tablet can be dispersed in water and administered as outlined below.
- Place approximately 2.5 mL of water into a spoon.
- Place the prescribed dose into the water.
- Allow the tablet(s) to disintegrate (typically less than 30 seconds).
- A slurry (liquid suspension) is formed.
- Take the slurry immediately with food.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Lampit prescribing information
Warnings and Precautions, Embryo-Fetal Toxicity (5.2 ) 2/2023
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LAMPIT is indicated in pediatric patients (birth to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 2.5 kg) for the treatment of Chagas disease (American Trypanosomiasis) caused by Trypanosoma cruzi [see Clinical Studies (14 )].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- LAMPIT tablets must be taken with food (2.1 )
Dosage of LAMPIT in Pediatric Patients (birth a to less than 18 years of age) (2.2) | |
Body Weight Group | Total Daily Dose of nifurtimox (mg/kg) |
41 kg or greater | 8 to 10 |
Less than 41 kg | 10 to 20 |
a Term newborn with body weight greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
- Administer LAMPIT tablets orally, three times daily with food for 60 days. (2.2 )
- Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with LAMPIT (2.3 , 8.3 ) .
- See Full Prescribing Information for additional important administration instructions. (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.4, 2.5 )
Important Administration Instructions
- LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets are for oral use and must be taken with food.
- LAMPIT tablets are dosed by body weight of the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
- LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets are functionally scored tablets which can be split into one-half (15 mg and 60 mg respectively) at the scored lines by hand. Do not break LAMPIT tablets mechanically with a tablet splitting device [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 ) and Instructions for Use] .
- LAMPIT 30 mg and 120 mg tablets can be made into a slurry as an alternative method of administration for patients who cannot swallow the tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )] .
- Discontinue consumption of alcohol during treatment with LAMPIT [see Contraindications (4 ) and Drug Interactions (7 )] .
- Complete the full course of treatment to prevent recurrence of the infection.
- If a dose is missed, take the missed dose as soon as possible together with food. However, if it is within 3 hours of the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and continue treatment as prescribed. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
- Administer LAMPIT (30 mg and 120 mg) tablets orally three times a day with food.
- Total daily recommended dosages of LAMPIT are based on the body weight of the patient (see Table 1 ).
- Adjust LAMPIT dosage accordingly if body weight decreases during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )].
- The recommended duration of treatment with LAMPIT is 60 days.
Table 1: Total Daily Recommended Dosages of LAMPIT Based on Body Weight
Age | Body weight group | Total daily dose of nifurtimox (mg/kg) |
Birth a to less than 18 years | 41 kg or greater | 8 to 10 |
Less than 41 kg | 10 to 20 |
a Term newborn with body weight of greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
Table 2: Individual Dosages Based on Body Weight in Pediatric Patients (Birth a to Less than 18 years of age)
Body weight (kg) | Dose (mg) | Number of LAMPIT 30 mg tablets per dose (3 x Daily) | Number of LAMPIT 120 mg tablets per dose (3 x Daily) |
2.5 kg to 4.5 kg | 15 mg | ½ tablet | |
4.6 kg to less than 9 kg | 30 mg | 1 tablet | |
9 kg to less than 13 kg | 45 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
13 kg to less than 18 kg | 60 mg | 2 tablets | ½ tablet |
18 kg to less than 22 kg | 75 mg | 2 ½ tablets | |
22 kg to less than 27 kg | 90 mg | 3 tablets | |
27 kg to less than 35 kg | 120 mg | 4 tablets | 1 tablet |
35 kg to less than 41 kg | 180 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
41 kg to less than 51 kg | 120 mg | 1 tablet | |
51 kg to less than 71 kg | 180 mg | 1 ½ tablets | |
71 kg to less than 91 kg | 240 mg | 2 tablets | |
91 kg or greater | 300 mg | 2 ½ tablets |
a Term newborn with body weight of greater than or equal to 2.5 kg
Pregnancy Testing Prior to Initiating LAMPIT
Instructions for Splitting LAMPIT Tablets
Do not break LAMPIT tablets mechanically with a tablet splitting device. A functional score line is used to divide the tablet by hand as follows:
- To split LAMPIT tablet, place the tablet on a flat surface with the score line facing up.
- With the tablet resting on the flat surface, apply enough downward pressure with the index finger centered on the top of the tablet to break it along the score line.
Preparation of a Slurry of LAMPIT as an Alternate Method of Administration
For patients who are unable to swallow whole or half tablets, LAMPIT tablet can be dispersed in water and administered as outlined below.
- Place approximately 2.5 mL of water into a spoon.
- Place the prescribed dose into the water.
- Allow the tablet(s) to disintegrate (typically less than 30 seconds).
- A slurry (liquid suspension) is formed.
- Take the slurry immediately with food.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
LAMPIT tablets are available as 30 mg and 120 mg tablets.
- 30 mg, yellow, round, biconvex tablets, functionally scored on one side for the division of the tablet into equal doses and marked with ‘30’ on the other side.
- 120 mg, yellow, round, biconvex tablets, functionally scored on one side for the division of the tablet into equal doses and marked with ‘120’ on the other side
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Patients with Renal and or Hepatic Impairment: Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision. (8.6 , 8.000000000000000e+00 7)
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal studies, LAMPIT may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Published postmarketing reports on nifurtimox use during pregnancy are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of birth defects and miscarriage. There are risks to the fetus associated with Chagas disease ( see Clinical Considerations).
Nifurtimox administered orally to pregnant rats, and rabbits during organogenesis was associated with reduced maternal body weights in rats, and abortions, reduced maternal weight gain, and reduced numbers of live fetuses in rabbits when nifurtimox was administered orally during organogenesis at doses approximately equal to the MRHD in rats and 2-times the MRHD in rabbits. An increased incidence of a fetal skeletal malformation (fusion of caudal vertebral bodies) occurred in rabbits at nifurtimox doses approximately 0.2 times the MRHD. In a pre-postnatal study, maternal body weights and fetal body weights of first-generation offspring were reduced at doses approximately equal to or 0.5 times the MRHD, respectively, and several male offspring in the nifurtimox treatment groups exhibited slightly small testes at doses ≥0.2 times the MRHD ( see Data) . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
There is a pregnancy safety study for LAMPIT. If LAMPIT is administered during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving LAMPIT or within six months following the last dose of LAMPIT, healthcare providers should report LAMPIT exposure by calling 1-888-842-2937.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data from case-control and observational studies on chronic Chagas disease during pregnancy are inconsistent in their findings. Some studies showed an increased risk of pregnancy loss, prematurity and neonatal mortality in pregnant women who have chronic Chagas disease while other studies did not demonstrate these findings. Chronic Chagas disease is usually not immediately life-threatening. Since pregnancy findings are inconsistent, treatment of chronic Chagas disease during pregnancy is not recommended due to risk of embryo-fetal toxicity from LAMPIT.
Acute symptomatic Chagas disease is rare in pregnant women; however, symptoms may be serious or life-threatening. If a pregnant woman presents with acute symptomatic Chagas disease, the risks versus benefits of treatment with LAMPIT to the mother and the fetus should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal toxicity study in pregnant rats, 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day nifurtimox were administered orally during the period of organogenesis (GD 6 to GD 17). Maternal body weights, body weight gain, and food consumption were reduced in the 60 mg/kg/day dose group. Treatment with nifurtimox did not produce fetal toxicity and no nifurtimox-related fetal malformations were observed. No maternal toxicity was observed at 30 mg/kg/day nifurtimox (approximately 0.5 times the MRHD based on body surface area comparison) and no adverse fetal effects were observed at 60 mg/kg/day nifurtimox (approximately equivalent to the MRHD based on body surface area comparison).
In pregnant rabbits orally administered 5, 15, and 60 mg/kg/day nifurtimox during the period of organogenesis (GD 6 to GD 20), the high dose was associated with maternal toxicity including reduced body weights and food consumption, and abortions in 8/20 high-dose dams. The mean number of live fetuses/litter and the percent of live fetuses per total implantations per group were significantly lower in the mid- and high-dose groups compared to the control group. Nifurtimox administration was associated with increased fetal and litter incidences of a skeletal malformation (fusion of caudal vertebral bodies) in fetuses in the low-dose group receiving 5 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 0.2-times the MRHD based on body surface area comparison). No maternal toxicity was observed at 15 mg/kg/day which is approximately equivalent to 0.5 times the MRHD based on body surface area comparison.
In a pre-postnatal study, pregnant female rats were orally administered 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day nifurtimox during organogenesis and lactation [GD 6 to lactation day (LD) 21]. Maternal findings included reduced maternal body weights in high-dose dams during gestation and to a lesser degree during lactation. In first-generation offspring, body weights were significantly reduced in males and females in the high-dose group during the lactation and post-lactation periods. Physical development, neurological function, and reproduction of first-generation offspring were not substantially changed in the nifurtimox treatment groups, but 5–20% of male offspring in all the nifurtimox treatment groups exhibited slightly small testes. No adverse maternal effects or fetal effects on first-generation female offspring occurred at 30 mg/kg/day, and no adverse fetal effects on the development of male offspring occurred at 15 mg/kg/day (respectively approximately 0.5- and 0.2-times the MRHD based on body surface area comparison).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Published literature demonstrates that nifurtimox is present in human breast milk with an estimated infant daily dose of less than 15% of the recommended daily dose for pediatric patients with Chagas disease. There were no reports of adverse effects on the small number of infants who were breastfed by mothers taking nifurtimox. There is no information on the effects of nifurtimox on milk production. Monitor infants exposed to LAMPIT through breast milk for vomiting, rash, decreased appetite, pyrexia and irritability.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LAMPIT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from LAMPIT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with LAMPIT.
Contraception
Females
LAMPIT may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LAMPIT and for 6 months after the final dose.
Males
Due to the potential for genotoxicity, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment and for 3 months after the final dose of LAMPIT [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Infertility
Males
Based on findings in rodents, LAMPIT may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential. These effects on fertility were not reversible in 75% of the animals at 11 weeks after dosing [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LAMPIT have been established for the treatment of Chagas disease (American Trypanosomiasis) caused by Trypanosoma cruzi in pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years of age weighing at least 2.5 kg. The efficacy of LAMPIT was demonstrated in pediatric patients 0 to 4 years of age in Trial 1 based on seroconversion to negative on lysate ELISA, recombinant ELISA and IHA at 4 years post-treatment compared to untreated patients. The efficacy of LAMPIT in pediatric patients 5 to <18 years of age was extrapolated from efficacy established in the younger pediatric population. Supportive evidence of efficacy was provided by seroconversion to negative on the F29 ELISA [see Clinical Studies (14 )].
The safety and effectiveness of LAMPIT has not been established in pediatric patients weighing less than 2.5 kg.
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of nifurtimox is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Published literature suggests that blood concentrations of nifurtimox were increased in patients with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis [see, Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )]. Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision.
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of nifurtimox is unknown [Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Potential for Genotoxicity and Carcinogenicity. (5.1 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. Advise males to use condoms with female partners of reproductive potential. (2.3 , 5.2 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
- Worsening Neurological and Psychiatric Conditions: Patients with a history of brain injury, seizures, psychiatric disease, serious behavioral alterations may experience worsening of their conditions when receiving LAMPIT. Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision in these patients or if neurological disturbances or psychiatric drug reactions occur. (5.3 )
- Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions including hypotension, angioedema, dyspnea, pruritus, rash or other severe skin reactions have been reported with the use of nifurtimox, discontinuation of treatment is recommended. (5.4 )
- Decreased Appetite and Weight Loss: Check body weight every 14 days as dosage may need to be adjusted. (5.5 )
- Porphyria: Treatment with nitrofuran derivatives, such as LAMPIT, may precipitate acute attacks of porphyria. Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision in patients with porphyria. (5.6 )
Potential for Genotoxicity and Carcinogenicity
Genotoxicity
Genotoxicity of LAMPIT has been demonstrated in humans, in vitro in several bacterial species and mammalian cell systems, and in vivo in rodents [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] .
A study evaluating the cytogenetic effect of nifurtimox in pediatric patients ranging from 7 months to 14 years of age with Chagas disease demonstrated a 13-fold increase in chromosomal aberrations.
Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenicity has been observed in mice and rats treated chronically with nitrofuran agents which are structurally similar to nifurtimox. Similar data have not been reported for LAMPIT [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] . It is not known whether LAMPIT is associated with carcinogenicity in humans.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies, LAMPIT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, nifurtimox administered orally to pregnant rats, and rabbits during organogenesis was associated with reduced maternal body weights in rats, and abortions, fetal death, and smaller litter sizes in rabbits at doses approximately equivalent to and 2-times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg/kg/day. Fetal malformations were observed in pregnant rabbits administered nifurtimox doses less than the MRHD [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )].
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with LAMPIT [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LAMPIT and for 6 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of LAMPIT [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Worsening of Neurological and Psychiatric Conditions
Patients with a history of brain injury, seizures, psychiatric disease, or serious behavioral alterations may experience worsening of their conditions when receiving LAMPIT. Administer LAMPIT under close medical supervision in these patients and in patients who develop neurological disturbances or psychiatric drug reactions.
Hypersensitivity
Cases of hypersensitivity have been reported in patients receiving therapy with nifurtimox. The hypersensitivity could be a reaction induced by nifurtimox or an immune response triggered by Chagas disease during treatment. Hypersensitivity reactions could be accompanied by hypotension, angioedema (including laryngeal or facial edema), dyspnea, pruritus, rash or other severe skin reactions. At the first sign of serious hypersensitivity, discontinue treatment with LAMPIT [see Contraindications (4 )].
Decreased Appetite and Weight Loss
Decreased appetite and weight loss were reported in patients treated with LAMPIT in the clinical trials. During treatment with LAMPIT, patients can lose their appetite or experience nausea/vomiting which can result in weight loss. Check body weight every 14 days, as the dosage may have to be adjusted [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )].
Porphyria
Treatment with nitrofuran derivatives, such as LAMPIT, may precipitate acute attacks of porphyria. Administer LAMPIT tablets under close medical supervision in patients with porphyria.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or otherwise important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Potential for Genotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Mutagenicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Worsening of Neurological and Psychiatric Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Decreased Appetite and Weight Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Porphyria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described below reflect exposure to LAMPIT in one prospective, randomized, double-blind trial (Trial 1). 330 pediatric patients with serologic evidence of T. cruzi infection and without Chagas disease-related cardiac or gastrointestinal symptoms were randomly assigned in a 2:1 fashion to a 60-day (n=219) or a 30-day (n=111) LAMPIT treatment regimen and were followed up for one year after end of treatment. LAMPIT was administered three times a day with food using a body weight-based dosing. The median treatment duration was 61 days for subjects in the 60-day regimen. The majority (86.7%) of the study population was ≥2 to <18 years of age at randomization.
Discontinuation of LAMPIT due to adverse reactions occurred in 14 of 330 (4.2%) patients overall, 12 of 219 (5.5%) patients in the 60-day arm, and 2 of 111 (1.8%) patients in the 30-day arm. Adverse reactions were reported for 213 of 330 (64.5%) patients. The proportion of patients with adverse reactions was higher in the 60-day regimen (67.1%) compared with the 30-day regimen (59.5%). Most patients with adverse reactions had mild (76.5%) or moderate (22.0%) reactions.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions in patients treated with LAMPIT for 60 days were vomiting (14.6%), abdominal pain (13.2%), headache (12.8%), decreased appetite (10.5%), nausea (8.2%), pyrexia (7.3%), rash (5.5%).
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of LAMPIT-treated patients are shown in Table 3 .
Table 3 Adverse Reactions Reported in (≥1%) Pediatric Patients with Chagas Disease in Trial 1 Treated with LAMPIT for 60 days
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reactions | Incidence |
|---|---|---|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Anemia Eosinophilia | 2.7% 2.3% |
Gastrointestinal disorders | Vomiting Abdominal pain a Nausea Diarrhea | 14.6% 13.2% 8.2% 4.6% |
General disorders and administration site conditions | Pyrexia | 7.3% |
Investigations | Weight decreased | 2.7% |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Decreased appetite | 10.5% |
Nervous system disorders | Headache Dizziness | 12.8% 2.7% |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Rash b Urticaria | 5.5% 2.3% |
a Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper
b Rash includes rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash morbilliform, and rash papular.
Other adverse reactions occurring in 0.1% to less than 1% of patients treated with LAMPIT for 60 days included asthenia, vertigo, arthralgia, myalgia, paresthesia, tremor, irritability, anxiety, pruritus, fatigue, somnolence, seizure, syncope, neutropenia, leukopenia.
Postmarketing Experience
The following safety data were derived during postmarketing surveillance of nifurtimox from outside the United States, including literature data for all age groups (pediatric and adult populations). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Table 4: Postmarketing Adverse Reactions Reported in Pediatric and Adult Populations Treated with Nifurtimox
System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction |
Immune system disorders | Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis |
Ear and labyrinth disorders | Vertigo |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Angioedema Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) |
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders | Muscle weakness |
Nervous system disorders | Amnesia Polyneuropathy |
Psychiatric disorders | Apathy Agitation Psychotic behavior Sleep disorder |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Thrombocytopenia |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Concomitant use of LAMPIT with alcohol may increase the incidence and severity of undesirable effects similar to other nitrofurans and nitroheterocyclic compounds. LAMPIT is contraindicated in patients who consume alcohol during treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) Contraindications (4 )].
DESCRIPTION
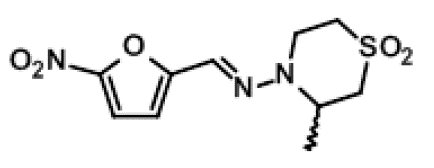
LAMPIT contains nifurtimox, an antiprotozoal. The chemical name is (E)-N-(3-Methyl-1,1-dioxidothiomorpholin-4-yl)-1-(5-nitro-2-furyl)methanimine.
The molecular weight is 287.29 and the molecular formula is C 10 H 13 N 3 O 5 S. The structural formula is:
LAMPIT (nifurtimox) tablets are yellow round, biconvex tablets, each containing 30 mg or 120 mg of nifurtimox, intended for oral use. The 30 mg tablets are functionally scored on one side and marked with ‘30’ on the other side. The 120 mg tablets are functionally scored on one side and marked with ‘120’ on the other side.
The inactive ingredients of the tablets are as follows: calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, magnesium stearate, maize starch, silica colloidal anhydrous and sodium lauryl sulfate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Nifurtimox is an antiprotozoal drug [see Microbiology (12.4 )] .
Pharmacodynamics
Nifurtimox exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamics response are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended dose, nifurtimox treatment does not result in large mean increases (>20 ms) in the QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The mean (%CV) nifurtimox AUC estimates ranged between 1676-2670 µg∙h/L (19–32%) and C max estimates ranged between 425-568 µg/L (26–50%) following administration of single dose 120 mg nifurtimox with food in adult Chagas patients. No clinically significant differences in nifurtimox AUC or C max at the 120 mg dose were observed when using two tablet strengths (30 and 120 mg) or administered as whole or dissolved tablets under fed conditions. The median time to reach maximum concentration (T max ) of nifurtimox under fed conditions was 4 hours (range: 2 to 8 hours).
Effect of Food
Following administration of a single oral dose of 120 mg LAMPIT in adult Chagas patients, nifurtimox C max increased 68%, AUC increased 71%, and T max increased by 1 hour with a high-fat meal (800–1000 calorie, approximately 60% fat) compared to fasted conditions.
Distribution
Nifurtimox passes the blood brain barrier as well as the placental barrier. The plasma proteins binding of nifurtimox is 42%.
Elimination
The mean (%CV) estimates for elimination half-life of nifurtimox ranged between 2.4–3.6 hours (12–37%).
Metabolism
Metabolism of nifurtimox is primarily mediated via nitroreductases. Exploratory investigations identified two major pharmacologically inactive metabolites (M-4, M-6) and several other minor metabolites in pooled human plasma. M-4 is a rearranged cysteine conjugate of nifurtimox with a half-life of approximately 28 hours, and M-6 is postulated to be formed by hydrolytic cleavage of the hydrazone moiety with a half-life of approximately 10 hours.
Excretion
Following administration of nifurtimox under fed and fasted conditions, approximately 44% and 27% of the dose was recovered in urine mainly as metabolites, respectively. Biliary and fecal elimination of nifurtimox and its metabolites has not been evaluated.
Specific Populations
The effect of renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of nifurtimox is unknown. Blood concentrations of nifurtimox increased in patients with ESRD.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
No clinical studies evaluating the drug interaction potential of nifurtimox have been conducted.
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 Enzymes (CYPs): Nifurtimox is not a substrate of CYPs. Nifurtimox and its metabolites (M-4 or M-6) are not inhibitors or inducers of CYPs.
Transporter Systems: Nifurtimox is not a substrate or inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP), and is not an inhibitor of organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATPs), multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) proteins (MATE1/MATE2-K), organic anion transporter 1/3 (OAT1/OAT3), or organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2). Major metabolites (M-4 or M-6) of nifurtimox are not inhibitors of P-gp, BCRP, OATPs, MATE1, MATE2K, OAT1, OAT3, or OCT2 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of nifurtimox is not fully understood. Studies suggest that nifurtimox is metabolized/activated, by Type I (oxygen insensitive) and Type II (oxygen sensitive) nitoreductases (NTR) leading to production of toxic intermediate metabolites and/or reactive oxygen species that induce DNA damage and cell death of both intracellular and extracellular forms of T. cruzi .
Antimicrobial Activity
Nifurtimox is active against all three stages, trypomastigotes, amastigotes, and epimastigotes, of T. cruzi. However, the sensitivity of T. cruzi strains to nifurtimox, from different geographic regions, may vary.
Resistance
In vitro studies suggest the potential for development of resistance in T. cruzi against nifurtimox.
The mechanism of resistance to nifurtimox appears to be multifactorial. Trypanosomal nitroreductase is defined as a key resistance determinate. Either loss of gene copy, mutation of gene or down-regulation of gene expression are sufficient to cause decreased susceptibility of T. cruzi against nitroheterocyclic drugs like nifurtimox. In addition, other mechanisms of resistance like lower drug influx or higher drug efflux are described. However, the clinical relevance of these findings is not known.
Cross-resistance
Nonclinical studies suggest cross-resistance between nifurtimox and benznidazole. This appears to be due to down regulation of Type I NTR localized in the mitochondria.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Adequate long-term carcinogenicity studies for nifurtimox have not been performed. Nitrofurans, which have similar chemical structures to nifurtimox have been reported to be carcinogenic in mice and rats.
Genetic Toxicity
The genotoxicity of nifurtimox has been demonstrated in vitro in several bacterial species and mammalian cell systems and in vivo in mammals.
Nifurtimox was mutagenic in strains of S. typhimurium (TA 98, 100, and 1537) in an Ames assay.
Nifurtimox was genotoxic in human lymphocytes in an in vitro micronucleus assay.
In vivo, nifurtimox was shown to be positive for genotoxicity in a mouse micronucleus assay, a mouse sister-chromatid exchange assay, and a human chromosome aberration assay. However, in a sister-chromatid exchange study in humans, oral doses of nifurtimox did not cause a significant increase in the frequency of sister-chromatid exchange in blood lymphocytes.
Impairment of Fertility
In a study examining the effects of nifurtimox on testicular morphology, male mice fed 0.08% or 0.16% nifurtimox in animal feed for 14 weeks experienced dose-dependent testicular toxicity including complete inhibition of spermatogenesis with the highest dose, evidence of arrested mitosis, signs of pyknosis, and no mature sperm. However, interstitial cells were unchanged, and fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrates were not observed. Nine weeks after the end of nifurtimox exposure, all testicular effects were almost entirely reversed.
In a male and female fertility study in rats, nifurtimox was administered in dietary feed at doses of 150 ppm (equivalent to 7–15 mg/kg), 300 ppm (equivalent to 15–30 mg/kg/day), and 600 ppm (equivalent to 30–60 mg/kg/day) for 10 weeks before mating. Male fertility was completely inhibited in rats administered 30–60 mg/kg/day nifurtimox, but female fertility was not affected for the same dosing regimen. In a recovery study, 11 weeks after the end of dosing, fertility was still inhibited in 75% of male rats administered nifurtimox for 32 weeks indicating a lack of complete reversibility. The nifurtimox dose in male rats that was not associated with inhibition of fertility was considered to be ≤30 mg/kg/day which is approximately equivalent to 0.5 times the MRHD for fertile males based on body surface area comparison.
Clinical Studies
No clinical studies evaluating the drug interaction potential of nifurtimox have been conducted.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
LAMPIT tablets are supplied as follows:
- 30 mg, yellow, round, biconvex tablets, functionally scored on one side and marked with ‘30’ on the other side.
- 120 mg, yellow, round, biconvex tablets, functionally scored on one side and marked with ‘120’ on the other side.
LAMPIT tablets 30 mg are supplied as bottles of 100 tablets with child-resistant closures (NDC 50419-750-01).
LAMPIT tablets 120 mg are supplied as bottles of 100 tablets with child-resistant closures (NDC 50419-751-01).
Storage and Handling
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store LAMPIT tablets in the original bottle with child-resistant closures and do not remove the desiccant.
Keep bottle with child-resistant closures tightly closed and protect from moisture.
Instructions for Use
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE LAMPIT (LAM-pit) (nifurtimox) tablets, for oral use | ||
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to split LAMPIT tablets and how to prepare a tablet and water mixture (called a slurry) if whole tablets or half tablets cannot be swallowed. Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking LAMPIT and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. | ||
 LAMPIT 30 mg tablets | 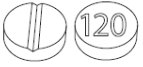 LAMPIT 120 mg tablets | |
Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking LAMPIT | ||
| ||
How to Take LAMPIT | ||
| ||
How to Split LAMPIT Tablets by Hand | ||
Step 1: To split the tablet, place the tablet on a flat surface with the scored line facing up ( See Figure A ). |  Figure A | |
Step 2: With the tablet still on the flat surface, apply enough pressure down on the center of the tablet with your index finger to split it in half along the scored line ( See Figure B ). | 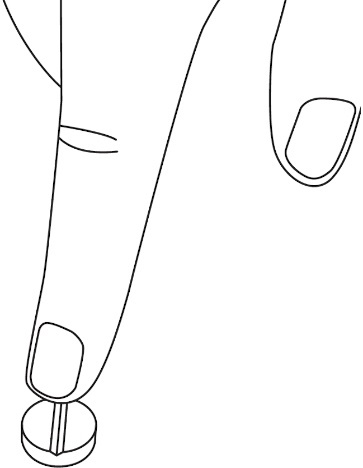 | |
Figure B | ||
Step 3: LAMPIT tablets can be split in half along the scored line ( See Figure C ). | 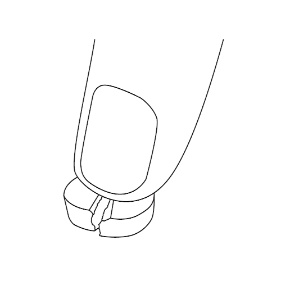 Figure C | |
Step 4: Only use a tablet that has been broken at the scored line ( See Figure D ). | 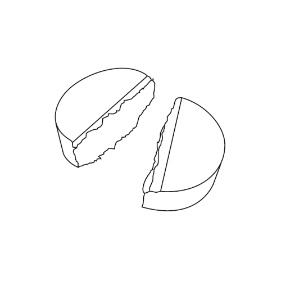 Figure D | |
Do not split LAMPIT tablets in any other way. | ||
Preparing a Tablet and Water Mixture (Slurry) | ||
For people who are not able to swallow whole tablets or half tablets, LAMPIT can be mixed in water. | ||
Step 1: Place approximately one-half teaspoonful (2.5 ml) of water into a spoon (See Figure E ). | 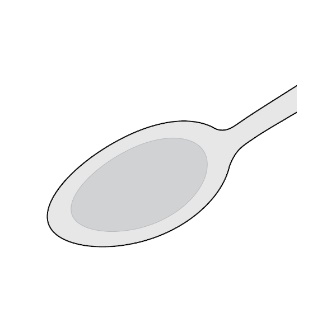 Figure E | |
Step 2: Place the prescribed dose into the water (See Figure F ). | 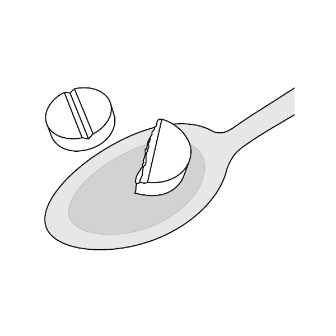 Figure F | |
Step 3: Allow the tablet to dissolve in the water. This should take less than 30 seconds (See Figure G ). |
| |
Figure G | ||
Step 4: A tablet and water mixture (slurry) will form (See Figure H ). |  Figure H | |
Give the tablet and water mixture (slurry) right away with food. Do not mix more than the prescribed dose. | ||
Storing LAMPIT | ||
Keep LAMPIT and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Manufactured for: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ 07981 USA © 2020 Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. For more information, call Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at Bayer at 1-888-842-2937 or go to www.LAMPIT.com Issued: 8/2020 | ||
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Mechanism of Action
Nifurtimox is an antiprotozoal drug [see Microbiology (12.4 )] .