Leqembi prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Leqembi patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Confirm the presence of amyloid beta pathology prior to initiating treatment. (2.1 )
- Obtain a recent baseline brain MRI prior to initiating treatment. (2.4 , 5.1 )
- Obtain an MRI within approximately one week prior to the 3 rd , 5 th , 7 th , and 14 th infusions. If radiographically observed ARIA occurs, treatment recommendations are based on type, severity, and presence of symptoms. (2.4 , 5.1 )
- Recommended starting dosage: 10 mg/kg once every 2 weeks administered after dilution as an intravenous infusion over approximately one hour. (2.2 )
- After 18 months, continue treatment once every 2 weeks or transition to an intravenous or subcutaneous maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
- Recommended maintenance dosage:
- Intravenous infusion: 10 mg/kg once every 4 weeks (2.2 , 2.5 )
- Subcutaneous injection: 360 mg administered once a week using the LEQEMBI IQLIK autoinjector (2.2 , 2.6 ).
- Intravenous infusion: 10 mg/kg once every 4 weeks (2.2 , 2.5 )
- See Full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions. (2.5 , 2.6 )
2.1 Patient Selection
Confirm the presence of amyloid beta pathology prior to initiating treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Initiate LEQEMBI as an intravenous infusion using the starting dosage (see Table 1). After 18 months, the starting dosage may be continued or a transition to maintenance dosage regimen may be considered, which can be administered by either intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection (see Table 1). If transitioning from starting dosage to a maintenance dosage regimen, administer the first maintenance dose two weeks after the last starting dose.
| Route of Administration | Dose | Frequency | Infusion Rate (if Intravenous) |
| Starting Dosage | |||
| Intravenous Only (LEQEMBI) | 10 mg/kg | Once every 2 weeks | Over approximately one hour |
| Maintenance Dosage | |||
| Intravenous (LEQEMBI) | 10 mg/kg | Once every 4 weeks | Over approximately one hour |
| Subcutaneous (LEQEMBI IQLIK) | 360 mg | Once every week | ------------------------ |
For intravenous infusion, use LEQEMBI vials. LEQEMBI vials must be diluted before administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )].
For subcutaneous administration, use LEQEMBI IQLIK [see Dosage and Administration (2.6 )].
2.3 Switching Between Maintenance Dosage Regimens
During maintenance dosage regimen, patients may switch the route of administration (intravenous LEQEMBI or subcutaneous LEQEMBI IQLIK). This transition should be initiated at 1 week following the last maintenance dose of either the intravenous or subcutaneous dosing regimen. Thereafter, follow the dosing schedule for the newly assigned maintenance dosage regimen.
2.4 Monitoring and Dosing Interruption for Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
LEQEMBI can cause amyloid related imaging abnormalities -edema (ARIA-E) and -hemosiderin deposition (ARIA-H) [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Monitoring for ARIA
Obtain a recent baseline brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) prior to initiating treatment with LEQEMBI. Obtain an MRI prior to the 3 rd , 5 th , 7 th , and 14 th infusions. In general, the MRI should be performed within approximately one week before the scheduled infusion of LEQEMBI and reviewed prior to proceeding with the infusion. If a patient experiences symptoms suggestive of ARIA, clinical evaluation should be performed, including an MRI if indicated.
Recommendations for Dosing Interruptions in Patients with ARIA
ARIA-E
The recommendations for dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-E are provided in Table 2.
| Clinical Symptom Severity 1 | ARIA-E Severity on MRI 2 | ||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
| Asymptomatic | May continue dosing | Suspend dosing 3 | Suspend dosing 3 |
| Mild | May continue dosing based on clinical judgment | Suspend dosing 3 | |
| Moderate or Severe | Suspend dosing 3 | ||
| 1 Clinical Symptom Severity Categories: Mild: discomfort noticed, but no disruption of normal daily activity. Moderate: discomfort sufficient to reduce or affect normal daily activity. Severe: incapacitating, with inability to work or to perform normal daily activity. 2 See Table 4 for MRI radiographic severity [Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . 3 Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic resolution and symptoms, if present, resolve; consider a follow-up MRI to assess for resolution 2 to 4 months after initial identification. Resumption of dosing should be guided by clinical judgment. | |||
ARIA-H
The recommendations for dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-H are provided in Table 3.
| Clinical Symptom Severity | ARIA-H Severity on MRI 1 | |||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| Asymptomatic | May continue dosing | Suspend dosing 2 | Suspend dosing 3 | |
| Symptomatic | Suspend dosing 2 | Suspend dosing 2 | ||
| 1 | See Table 4 for MRI radiographic severity [Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . | |||
| 2 | Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve; resumption of dosing should be guided by clinical judgment; consider a follow-up MRI to assess for stabilization 2 to 4 months after initial identification. | |||
| 3 | Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve; use clinical judgment in considering whether to continue treatment or permanently discontinue LEQEMBI. | |||
In patients who develop intracerebral hemorrhage greater than 1 cm in diameter during treatment with LEQEMBI, suspend dosing until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve. Use clinical judgment in considering whether to continue treatment after radiographic stabilization and resolution of symptoms or permanently discontinue LEQEMBI.
2.5 Preparation and Administration of LEQEMBI for Intravenous Infusion
Dilution
- Prior to intravenous administration, LEQEMBI must be diluted in 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Use aseptic technique when preparing the LEQEMBI diluted solution for intravenous infusion.
- Calculate the dose (mg), the total volume (mL) of LEQEMBI solution required, and the number of vials needed based on the patient’s actual body weight and the recommended dose of 10 mg/kg. Each vial contains a LEQEMBI concentration of 100 mg/mL.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Check that the LEQEMBI solution is clear to opalescent and colorless to pale yellow. Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or other foreign particles are present.
- Remove the flip-off cap from the vial. Insert the sterile syringe needle into the vial through the center of the rubber stopper.
- Withdraw the required volume of LEQEMBI from the vial(s) and add to an infusion bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Each vial is for one-time use only. Discard any unused portion.
- Gently invert the infusion bag containing the LEQEMBI diluted solution to mix completely. Do not shake.
- After dilution, immediate use is recommended [see Description (11 )] . If not administered immediately, store LEQEMBI refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 4 hours, or at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for up to 4 hours. Do not freeze.
Administration
• Visually inspect the LEQEMBI diluted solution for particles or discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if it is discolored, opaque, or foreign particles are seen.
• Prior to infusion, allow the LEQEMBI diluted solution to warm to room temperature.
• Infuse the entire volume of the LEQEMBI diluted solution intravenously over approximately one hour through an intravenous line containing a terminal low-protein binding 0.2 micron in-line filter. Flush infusion line to ensure all LEQEMBI is administered.
• Monitor for any signs or symptoms of an infusion-related reaction during the infusion and consider longer periods of observation if clinically indicated. The infusion rate may be reduced, or the infusion may be discontinued, and appropriate therapy administered as clinically indicated. Consider pre-medication at subsequent dosing with antihistamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or corticosteroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
2.6 Preparation and Administration of LEQEMBI IQLIK for Subcutaneous Injection
Instruct patients and/or caregivers on the proper subcutaneous administration of LEQEMBI IQLIK. Direct patients and/or caregivers to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use for additional details on administration [see Instructions for Use ]. Periodically reassess the ability of the patient or caregiver to safely and adequately administer LEQEMBI IQLIK.
• Before injection, remove LEQEMBI IQLIK from the refrigerator and leave at room temperature for 20 minutes. Do not use an external heat source to heat LEQEMBI IQLIK because heat may damage the product.
• Do not shake LEQEMBI IQLIK.
• Visually inspect LEQEMBI IQLIK for particles or discoloration prior to administration. The solution should be a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution, and free of visible particles. Do not use LEQEMBI IQLIK if it is cloudy or there are visible particles.
• Do not use LEQEMBI IQLIK if it looks damaged or has been dropped.
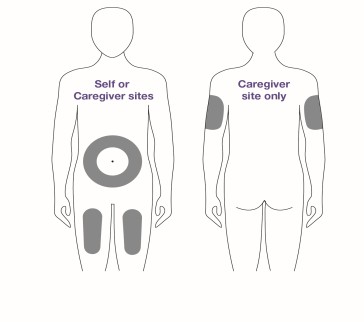
• Sites for injection include the abdomen, upper thigh, and back of the upper arm.
• Do not inject into moles, scars, bruises, tattoos or into areas where the skin is red, hard, tender or injured.
• Monitor for signs or symptoms of an injection reaction.
2.7 Missed Dose
Intravenous Infusion
If a starting dosage or maintenance dosage infusion is missed, administer the next dose as soon as possible.
Subcutaneous Injection
If a scheduled dose of the subcutaneous maintenance dosing regimen is missed, administer LEQEMBI IQLIK as soon as possible up to 6 days after the missed dose and administer the next dose on the regularly scheduled day. Thereafter, resume the original dosing schedule.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Leqembi prescribing information
WARNING: AMYLOID RELATED IMAGING ABNORMALITIES
Monoclonal antibodies directed against aggregated forms of beta amyloid, including LEQEMBI, can cause amyloid related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), characterized as ARIA with edema (ARIA-E) and ARIA with hemosiderin deposition (ARIA-H). Incidence and timing of ARIA vary among treatments. ARIA usually occurs early in treatment and is usually asymptomatic, although serious and life-threatening events can occur. ARIA can be fatal. Serious intracerebral hemorrhage s > 1 cm, some of which have been fatal, have been observed in patients treated with this class of medications. Because ARIA-E can cause focal neurologic deficits that can mimic an ischemic stroke, treating clinicians should consider whether such symptoms could be due to ARIA-E before giving thrombolytic therapy to a patient being treated with LEQEMBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )].
ApoE ε4 Homozygotes
Patients who are apolipoprotein E ε4 (ApoE ε4) homozygotes (approximately 15% of Alzheimer’s disease patients) treated with this class of medications, including LEQEMBI, have a higher incidence of ARIA, including symptomatic, serious, and severe radiographic ARIA, compared to heterozygotes and noncarriers. Testing for ApoE ε4 status should be performed prior to initiation of treatment to inform the risk of developing ARIA. Prior to testing, prescribers should discuss with patients the risk of ARIA across genotypes and the implications of genetic testing results. Prescribers should inform patients that if genotype testing is not performed they can still be treated with LEQEMBI; however, it cannot be determined if they are ApoE ε4 homozygotes and at higher risk for ARIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
Consider the benefit of LEQEMBI for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and potential risk of serious adverse events associated with ARIA when deciding to initiate treatment with LEQEMBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) and Clinical Studies (14 )].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LEQEMBI is indicated for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment with LEQEMBI should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was initiated in clinical trials.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Confirm the presence of amyloid beta pathology prior to initiating treatment. (2.1 )
- Obtain a recent baseline brain MRI prior to initiating treatment. (2.4 , 5.1 )
- Obtain an MRI within approximately one week prior to the 3 rd , 5 th , 7 th , and 14 th infusions. If radiographically observed ARIA occurs, treatment recommendations are based on type, severity, and presence of symptoms. (2.4 , 5.1 )
- Recommended starting dosage: 10 mg/kg once every 2 weeks administered after dilution as an intravenous infusion over approximately one hour. (2.2 )
- After 18 months, continue treatment once every 2 weeks or transition to an intravenous or subcutaneous maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
- Recommended maintenance dosage:
- See Full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions. (2.5 , 2.6 )
2.1 Patient Selection
Confirm the presence of amyloid beta pathology prior to initiating treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Initiate LEQEMBI as an intravenous infusion using the starting dosage (see Table 1). After 18 months, the starting dosage may be continued or a transition to maintenance dosage regimen may be considered, which can be administered by either intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection (see Table 1). If transitioning from starting dosage to a maintenance dosage regimen, administer the first maintenance dose two weeks after the last starting dose.
| Route of Administration | Dose | Frequency | Infusion Rate (if Intravenous) |
| Starting Dosage | |||
| Intravenous Only (LEQEMBI) | 10 mg/kg | Once every 2 weeks | Over approximately one hour |
| Maintenance Dosage | |||
| Intravenous (LEQEMBI) | 10 mg/kg | Once every 4 weeks | Over approximately one hour |
| Subcutaneous (LEQEMBI IQLIK) | 360 mg | Once every week | ------------------------ |
For intravenous infusion, use LEQEMBI vials. LEQEMBI vials must be diluted before administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5 )].
For subcutaneous administration, use LEQEMBI IQLIK [see Dosage and Administration (2.6 )].
2.3 Switching Between Maintenance Dosage Regimens
During maintenance dosage regimen, patients may switch the route of administration (intravenous LEQEMBI or subcutaneous LEQEMBI IQLIK). This transition should be initiated at 1 week following the last maintenance dose of either the intravenous or subcutaneous dosing regimen. Thereafter, follow the dosing schedule for the newly assigned maintenance dosage regimen.
2.4 Monitoring and Dosing Interruption for Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
LEQEMBI can cause amyloid related imaging abnormalities -edema (ARIA-E) and -hemosiderin deposition (ARIA-H) [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Monitoring for ARIA
Obtain a recent baseline brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) prior to initiating treatment with LEQEMBI. Obtain an MRI prior to the 3 rd , 5 th , 7 th , and 14 th infusions. In general, the MRI should be performed within approximately one week before the scheduled infusion of LEQEMBI and reviewed prior to proceeding with the infusion. If a patient experiences symptoms suggestive of ARIA, clinical evaluation should be performed, including an MRI if indicated.
Recommendations for Dosing Interruptions in Patients with ARIA
ARIA-E
The recommendations for dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-E are provided in Table 2.
| Clinical Symptom Severity 1 | ARIA-E Severity on MRI 2 | ||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
| Asymptomatic | May continue dosing | Suspend dosing 3 | Suspend dosing 3 |
| Mild | May continue dosing based on clinical judgment | Suspend dosing 3 | |
| Moderate or Severe | Suspend dosing 3 | ||
| 1 Clinical Symptom Severity Categories: Mild: discomfort noticed, but no disruption of normal daily activity. Moderate: discomfort sufficient to reduce or affect normal daily activity. Severe: incapacitating, with inability to work or to perform normal daily activity. 2 See Table 4 for MRI radiographic severity [Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . 3 Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic resolution and symptoms, if present, resolve; consider a follow-up MRI to assess for resolution 2 to 4 months after initial identification. Resumption of dosing should be guided by clinical judgment. | |||
ARIA-H
The recommendations for dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-H are provided in Table 3.
| Clinical Symptom Severity | ARIA-H Severity on MRI 1 | |||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| Asymptomatic | May continue dosing | Suspend dosing 2 | Suspend dosing 3 | |
| Symptomatic | Suspend dosing 2 | Suspend dosing 2 | ||
| 1 | See Table 4 for MRI radiographic severity [Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . | |||
| 2 | Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve; resumption of dosing should be guided by clinical judgment; consider a follow-up MRI to assess for stabilization 2 to 4 months after initial identification. | |||
| 3 | Suspend until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve; use clinical judgment in considering whether to continue treatment or permanently discontinue LEQEMBI. | |||
In patients who develop intracerebral hemorrhage greater than 1 cm in diameter during treatment with LEQEMBI, suspend dosing until MRI demonstrates radiographic stabilization and symptoms, if present, resolve. Use clinical judgment in considering whether to continue treatment after radiographic stabilization and resolution of symptoms or permanently discontinue LEQEMBI.
2.5 Preparation and Administration of LEQEMBI for Intravenous Infusion
Dilution
- Prior to intravenous administration, LEQEMBI must be diluted in 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Use aseptic technique when preparing the LEQEMBI diluted solution for intravenous infusion.
- Calculate the dose (mg), the total volume (mL) of LEQEMBI solution required, and the number of vials needed based on the patient’s actual body weight and the recommended dose of 10 mg/kg. Each vial contains a LEQEMBI concentration of 100 mg/mL.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Check that the LEQEMBI solution is clear to opalescent and colorless to pale yellow. Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or other foreign particles are present.
- Remove the flip-off cap from the vial. Insert the sterile syringe needle into the vial through the center of the rubber stopper.
- Withdraw the required volume of LEQEMBI from the vial(s) and add to an infusion bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Each vial is for one-time use only. Discard any unused portion.
- Gently invert the infusion bag containing the LEQEMBI diluted solution to mix completely. Do not shake.
- After dilution, immediate use is recommended [see Description (11 )] . If not administered immediately, store LEQEMBI refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 4 hours, or at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for up to 4 hours. Do not freeze.
Administration
• Visually inspect the LEQEMBI diluted solution for particles or discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if it is discolored, opaque, or foreign particles are seen.
• Prior to infusion, allow the LEQEMBI diluted solution to warm to room temperature.
• Infuse the entire volume of the LEQEMBI diluted solution intravenously over approximately one hour through an intravenous line containing a terminal low-protein binding 0.2 micron in-line filter. Flush infusion line to ensure all LEQEMBI is administered.
• Monitor for any signs or symptoms of an infusion-related reaction during the infusion and consider longer periods of observation if clinically indicated. The infusion rate may be reduced, or the infusion may be discontinued, and appropriate therapy administered as clinically indicated. Consider pre-medication at subsequent dosing with antihistamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or corticosteroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
2.6 Preparation and Administration of LEQEMBI IQLIK for Subcutaneous Injection
Instruct patients and/or caregivers on the proper subcutaneous administration of LEQEMBI IQLIK. Direct patients and/or caregivers to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use for additional details on administration [see Instructions for Use ]. Periodically reassess the ability of the patient or caregiver to safely and adequately administer LEQEMBI IQLIK.
• Before injection, remove LEQEMBI IQLIK from the refrigerator and leave at room temperature for 20 minutes. Do not use an external heat source to heat LEQEMBI IQLIK because heat may damage the product.
• Do not shake LEQEMBI IQLIK.
• Visually inspect LEQEMBI IQLIK for particles or discoloration prior to administration. The solution should be a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution, and free of visible particles. Do not use LEQEMBI IQLIK if it is cloudy or there are visible particles.
• Do not use LEQEMBI IQLIK if it looks damaged or has been dropped.
• Sites for injection include the abdomen, upper thigh, and back of the upper arm.
• Do not inject into moles, scars, bruises, tattoos or into areas where the skin is red, hard, tender or injured.
• Monitor for signs or symptoms of an injection reaction.
2.7 Missed Dose
Intravenous Infusion
If a starting dosage or maintenance dosage infusion is missed, administer the next dose as soon as possible.
Subcutaneous Injection
If a scheduled dose of the subcutaneous maintenance dosing regimen is missed, administer LEQEMBI IQLIK as soon as possible up to 6 days after the missed dose and administer the next dose on the regularly scheduled day. Thereafter, resume the original dosing schedule.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Lecanemab-irmb is a clear to opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution, available as:
Intravenous Infusion
- Injection: 500 mg/5 mL (100 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
- Injection: 200 mg/2 mL (100 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
Subcutaneous Injection
- Injection: 360 mg/1.8 mL (200 mg/mL) in a single-dose prefilled autoinjector
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on LEQEMBI use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. No animal studies have been conducted to assess the potential reproductive or developmental toxicity of LEQEMBI.
In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of lecanemab-irmb in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Published data from other monoclonal antibodies generally indicate low passage of monoclonal antibodies into human milk and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed infant. The effects of this limited exposure are unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LEQEMBI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from LEQEMBI or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of LEQEMBI in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In Studies 1 and 2, the age of patients exposed to LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks (n=1059) ranged from 50 to 90 years, with a mean age of 72 years; 81% were 65 years and older, and 39% were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of LEQEMBI have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
LEQEMBI is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to lecanemab-irmb or to any of the excipients of LEQEMBI or LEQEMBI IQLIK. Reactions have included angioedema and anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities (ARIA): Enhanced clinical vigilance for ARIA is recommended during the first 14 weeks of treatment with LEQEMBI. Risk of ARIA, including symptomatic ARIA, was increased in apolipoprotein E ε4 homozygotes compared to heterozygotes and noncarriers. The risk of ARIA-E and ARIA-H is increased in patients with pretreatment microhemorrhages and/or superficial siderosis. If a patient experiences symptoms suggestive of ARIA, clinical evaluation should be performed, including MRI scanning if indicated. (2.4 , 5.1 )
- Infusion-Related Reactions: The infusion rate may be reduced, or the infusion may be discontinued, and appropriate therapy administered as clinically indicated. Consider pre-medication at subsequent dosing with antihistamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or corticosteroids. (5.3 )
5.1 Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
Monoclonal antibodies directed against aggregated forms of beta amyloid, including LEQEMBI, can cause amyloid related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), characterized as ARIA with edema (ARIA-E), which can be observed on MRI as brain edema or sulcal effusions, and ARIA with hemosiderin deposition (ARIA-H), which includes microhemorrhage and superficial siderosis. ARIA can occur spontaneously in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, particularly in patients with MRI findings suggestive of cerebral amyloid angiopathy, such as pretreatment microhemorrhage or superficial siderosis. ARIA-H associated with monoclonal antibodies directed against aggregated forms of beta amyloid generally occurs in association with an occurrence of ARIA-E. ARIA-H of any cause and ARIA-E can occur together.
ARIA usually occurs early in treatment and is usually asymptomatic, although serious and life-threatening events, including seizure and status epilepticus, can occur. ARIA can be fatal. When present, reported symptoms associated with ARIA may include headache, confusion, visual changes, dizziness, nausea, and gait difficulty. Focal neurologic deficits may also occur. Symptoms associated with ARIA usually resolve over time. In addition to ARIA, intracerebral hemorrhages greater than 1 cm in diameter have occurred in patients treated with LEQEMBI.
Consider the benefit of LEQEMBI for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and potential risk of serious adverse events associated with ARIA when deciding to initiate treatment with LEQEMBI.
Incidence of ARIA
Symptomatic ARIA occurred in 3% (29/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI in Study 2 [see Clinical Studies (14 )]. Serious symptoms associated with ARIA were reported in 0.7% (6/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI. Clinical symptoms associated with ARIA resolved in 79% (23/29) of patients during the period of observation. Similar findings were observed in Study 1.
Including asymptomatic radiographic events, ARIA was observed in 21% (191/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 9% (84/897) of patients on placebo in Study 2.
In Study 2, ARIA-E was observed in 13% (113/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 2% (15/897) of patients on placebo. ARIA-H was observed in 17% (152/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 9% (80/897) of patients on placebo. There was no increase in isolated ARIA-H (i.e., ARIA-H in patients who did not also experience ARIA-E) for LEQEMBI compared to placebo.
Incidence of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage greater than 1 cm in diameter was reported in 0.7% (6/898) of patients in Study 2 after treatment with LEQEMBI, compared to 0.1% (1/897) on placebo. Fatal events of intracerebral hemorrhage in patients taking LEQEMBI have been observed.
Risk Factors for ARIA and Intracerebral Hemorrhage
ApoE ε4 Carrier Status
The risk of ARIA, including symptomatic and serious ARIA, is increased in apolipoprotein E ε4 (ApoE ε4) homozygotes.
Approximately 15% of Alzheimer’s disease patients are ApoE ε4 homozygotes. In Study 2, 16% (141/898) of patients in the LEQEMBI arm were ApoE ε4 homozygotes, 53% (479/898) were heterozygotes, and 31% (278/898) were noncarriers. The incidence of ARIA was higher in ApoE ε4 homozygotes (45% on LEQEMBI vs. 22% on placebo) than in heterozygotes (19% on LEQEMBI vs 9% on placebo) and noncarriers (13% on LEQEMBI vs 4% on placebo). Among patients treated with LEQEMBI, symptomatic ARIA-E occurred in 9% of ApoE ε4 homozygotes compared to 2% of heterozygotes and 1% noncarriers. Serious events of ARIA occurred in 3% of ApoE ε4 homozygotes, and approximately 1% of heterozygotes and noncarriers. The recommendations on management of ARIA do not differ between ApoE ε4 carriers and noncarriers [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )]. Testing for ApoE ε4 status should be performed prior to initiation of treatment to inform the risk of developing ARIA. Prior to testing, prescribers should discuss with patients the risk of ARIA across genotypes and the implications of genetic testing results. Prescribers should inform patients that if genotype testing is not performed they can still be treated with LEQEMBI; however, it cannot be determined if they are ApoE ε4 homozygotes and at higher risk for ARIA.
Radiographic Findings of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy (CAA)
Neuroimaging findings that may indicate CAA include evidence of prior intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral microhemorrhage, and cortical superficial siderosis. CAA has an increased risk for intracerebral hemorrhage. The presence of an ApoE ε4 allele is also associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
The baseline presence of at least 2 microhemorrhages or the presence of at least 1 area of superficial siderosis on MRI, which may be suggestive of CAA, have been identified as risk factors for ARIA. Patients were excluded from enrollment in Study 2 for the presence of more than 4 microhemorrhages and additional findings suggestive of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (prior cerebral hemorrhage greater than 1 cm in greatest diameter, superficial siderosis, vasogenic edema) or other lesions (aneurysm, vascular malformation) that could potentially increase the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Concomitant Antithrombotic or Thrombolytic Medication
In Study 2, baseline use of antithrombotic medication (aspirin, other antiplatelets, or anticoagulants) was allowed if the patient was on a stable dose. The majority of exposures to antithrombotic medications were to aspirin. Antithrombotic medications did not increase the risk of ARIA with LEQEMBI. The incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage was 0.9% (3/328 patients) in patients taking LEQEMBI with a concomitant antithrombotic medication at the time of the event, compared to 0.6% (3/545 patients) in those who did not receive an antithrombotic. Patients taking LEQEMBI with an anticoagulant alone or combined with an antiplatelet medication or aspirin had an incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage of 2.5% (2/79 patients), compared to none in patients who received placebo.
Fatal cerebral hemorrhage has occurred in a patient taking an anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody in the setting of focal neurologic symptoms of ARIA and the use of a thrombolytic agent.
Additional caution should be exercised when considering the administration of antithrombotics or a thrombolytic agent (e.g., tissue plasminogen activator) to a patient already being treated with LEQEMBI. Because ARIA-E can cause focal neurologic deficits that can mimic an ischemic stroke, treating clinicians should consider whether such symptoms could be due to ARIA-E before giving thrombolytic therapy in a patient being treated with LEQEMBI.
Caution should be exercised when considering the use of LEQEMBI in patients with factors that indicate an increased risk for intracerebral hemorrhage and in particular for patients who need to be on anticoagulant therapy, or patients with findings on MRI that are suggestive of cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Radiographic Severity
The radiographic severity of ARIA associated with LEQEMBI was classified by the criteria shown in Table 4.
| ARIA Type | Radiographic Severity | ||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
| ARIA-E | FLAIR hyperintensity confined to sulcus and/or cortex/subcortex white matter in one location <5 cm | FLAIR hyperintensity 5 to 10 cm in single greatest dimension, or more than 1 site of involvement, each measuring <10 cm | FLAIR hyperintensity >10 cm with associated gyral swelling and sulcal effacement. One or more separate/ independent sites of involvement may be noted. |
| ARIA-H microhemorrhage | ≤ 4 new incident microhemorrhages | 5 to 9 new incident microhemorrhages | 10 or more new incident microhemorrhages |
| ARIA-H superficial siderosis | 1 focal area of superficial siderosis | 2 focal areas of superficial siderosis | > 2 areas of superficial siderosis |
In Study 2, the majority of ARIA-E radiographic events occurred early in treatment (within the first 7 doses), although ARIA can occur at any time and patients can have more than 1 episode. The maximum radiographic severity of ARIA-E in patients treated with LEQEMBI was mild in 4% (37/898) of patients, moderate in 7% (66/898) of patients, and severe in 1% (9/898) of patients. Resolution on MRI occurred in 52% of ARIA-E patients by 12 weeks, 81% by 17 weeks, and 100% overall after detection. The maximum radiographic severity of ARIA-H microhemorrhage in patients treated with LEQEMBI was mild in 9% (79/898), moderate in 2% (19/898), and severe in 3% (28/898) of patients; superficial siderosis was mild in 4% (38/898), moderate in 1% (8/898), and severe in 0.4% (4/898). Among patients treated with LEQEMBI, the rate of severe radiographic ARIA-E was highest in ApoE ε4 homozygotes 5% (7/141), compared to heterozygotes 0.4% (2/479) or noncarriers 0% (0/278). Among patients treated with LEQEMBI, the rate of severe radiographic ARIA-H was highest in ApoE ε4 homozygotes 13.5% (19/141), compared to heterozygotes 2.1% (10/479) or noncarriers 1.1% (3/278).
Monitoring and Dose Management Guidelines
Recommendations for dosing in patients with ARIA-E depend on clinical symptoms and radiographic severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )]. Recommendations for dosing in patients with ARIA-H depend on the type of ARIA-H and radiographic severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . Use clinical judgment in considering whether to continue dosing in patients with recurrent ARIA-E.
Baseline brain MRI and periodic monitoring with MRI are recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . Enhanced clinical vigilance for ARIA is recommended during the first 14 weeks of treatment with LEQEMBI. If a patient experiences symptoms suggestive of ARIA, clinical evaluation should be performed, including MRI if indicated. If ARIA is observed on MRI, careful clinical evaluation should be performed prior to continuing treatment.
There is no experience in patients who continued dosing through symptomatic ARIA-E, or through asymptomatic but radiographically severe ARIA-E. There is limited experience in patients who continued dosing through asymptomatic but radiographically mild to moderate ARIA-E. There are limited data in dosing patients who experienced recurrent ARIA-E. While experience is limited in these situations, dose management guidelines are provided [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )].
Providers should encourage patients to participate in real world data collection (e.g., registries) to help further the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease and the impact of Alzheimer’s disease treatments. Providers and patients can contact Eisai at 888-274-2378 for a list of currently enrolling programs.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, bronchospasm, and anaphylaxis, have occurred in patients who were treated with LEQEMBI. If LEQEMBI is being administered intravenously, promptly discontinue the infusion upon the first observation of any signs or symptoms consistent with a hypersensitivity reaction, and initiate appropriate therapy. LEQEMBI is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity to lecanemab-irmb or to any of the excipients of LEQEMBI or LEQEMBI IQLIK.
5.3 Infusion-Related Reactions
In Study 2, infusion-related reactions were observed in 26% (237/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 7% (66/897) of patients on placebo; and the majority (75%, 178/237) occurred with the first infusion. Infusion-related reactions were mostly mild (69%) or moderate (28%) in severity. Infusion-related reactions resulted in discontinuations in 1% (12/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI. Symptoms of infusion-related reactions include fever and flu-like symptoms (chills, generalized aches, feeling shaky, and joint pain), nausea, vomiting, hypotension, hypertension, and oxygen desaturation.
After the first infusion in Study 1, 38% of patients treated with LEQEMBI had transient decreased lymphocyte counts to less than 0.9 x10 9 /L, compared to 2% in patients on placebo, and 22% of patients treated with LEQEMBI had transient increased neutrophil counts to greater than 7.9 x10 9 /L, compared to 1% of patients on placebo. Lymphocyte and neutrophil counts were not obtained after the first infusion in Study 2.
Infusion-related reactions can occur during the infusion or after completion of the infusion. In the event of an infusion-related reaction during the infusion, the infusion rate may be reduced, or the infusion may be discontinued, and appropriate therapy initiated as clinically indicated. Consider prophylactic treatment with antihistamines, acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or corticosteroids prior to future infusions.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials with Intravenous Administration
The safety of LEQEMBI has been evaluated in 2090 patients who received at least one dose of LEQEMBI by intravenous infusion. In Studies 1 and 2 in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, 1059 patients received LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks by intravenous infusion [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . Of these 1059 patients, 50% were female, 79% were White, 15% were Asian, 12% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, and 2% were Black. The mean age at study entry was 72 years (range from 50 to 90 years).
In the combined double-blind, placebo-controlled period and long-term extension period of Studies 1 and 2, 1604 patients received LEQEMBI for at least 6 months, 1261 patients for at least 12 months, and 965 patients for 18 months.
In the double-blind, placebo-controlled period in Study 1, patients stopped study treatment because of an adverse reaction in 15% of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 6% patients on placebo; in Study 2, patients stopped study treatment because of an adverse reaction in 7% of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 3% patients on placebo. In Study 1, the most common adverse reaction leading to discontinuation of LEQEMBI was infusion-related reactions that led to discontinuation in 2% (4/161) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 1% (2/245) of patients on placebo. In Study 2, the most common adverse reaction leading to discontinuation of LEQEMBI was ARIA-H microhemorrhages that led to discontinuation in 2% (15/898) of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to <1% (1/897) of patients on placebo.
Table 5 shows adverse reactions that were reported in at least 5% of patients treated with LEQEMBI and at least 2% more frequently than in patients on placebo in Study 1.
| Adverse Reaction | LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks N= 161 % | Placebo N= 245 % |
| Infusion-related reactions | 20 | 3 |
| Headache | 14 | 10 |
| ARIA-E | 10 | 1 |
| Cough | 9 | 5 |
| Diarrhea | 8 | 5 |
Table 6 shows adverse reactions that were reported in at least 5% of patients treated with LEQEMBI and at least 2% more frequently than in patients on placebo in Study 2.
| Adverse Reaction | LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks N= 898 % | Placebo N= 897 % |
| Infusion-related reactions | 26 | 7 |
| ARIA-H | 14 | 8 |
| ARIA-E | 13 | 2 |
| Headache | 11 | 8 |
| Superficial siderosis of central nervous system | 6 | 3 |
| Rash 1 | 6 | 4 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 6 | 4 |
| 1 Rash includes acne, erythema, infusion site rash, injection site rash, rash, rash erythematous, rash pruritic, skin reactions, and urticaria. | ||
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Atrial fibrillation occurred in 3% of patients treated with LEQEMBI, compared to 2% in patients on placebo. In Study 1, lymphopenia or decreased lymphocyte count was reported in 4% of patients treated with LEQEMBI after the first dose, compared to less than 1% of patients on placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]; lymphocytes were not measured after the first dose in Study 2.
Clinical Trials with Subcutaneous Administration
The safety of LEQEMBI IQLIK for maintenance treatment was evaluated in an open-label study, which included 49 patients who received LEQEMBI IQLIK 360 mg by subcutaneous administration once every week. The overall safety profile in these patients was similar to what was observed in patients who received LEQEMBI by intravenous infusion in Study 1 and Study 2. Patients who received LEQEMBI IQLIK experienced localized and systemic injection-related reactions. Localized injection-related reactions included erythema, induration, swelling, heat, pain, pruritis, rash, ecchymosis, and hematoma. Systemic injection-related reactions were observed less frequently, with symptoms of headache, fever, and fatigue. Injection-related reactions in patients receiving LEQEMBI IQLIK were mild or moderate in severity.
11 DESCRIPTION
Lecanemab-irmb is a recombinant humanized immunoglobulin gamma 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody directed against aggregated soluble and insoluble forms of amyloid beta, and is expressed in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Lecanemab-irmb has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa.
LEQEMBI Injection for Intravenous Use
LEQEMBI (lecanemab-irmb) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution for intravenous infusion after dilution. LEQEMBI is supplied in single-dose vials available in concentrations of 500 mg/5 mL (100 mg/mL) or 200 mg/2 mL (100 mg/mL).
Each mL of solution contains 100 mg of lecanemab-irmb and arginine hydrochloride (42.13 mg), histidine (0.18 mg), histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (4.99 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.50 mg), and Water for Injection at an approximate pH of 5.0.
LEQEMBI IQLIK Injection for Subcutaneous Use
LEQEMBI IQLIK (lecanemab-irmb) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution for subcutaneous use. LEQEMBI IQLIK is supplied in a single-dose prefilled autoinjector available in the concentration of 360 mg/1.8 mL with a 29-gauge fixed ½-inch needle. Each LEQEMBI IQLIK autoinjector contains 360 mg/1.8 mL lecanemab-irmb formulated in: arginine hydrochloride (75.83 mg), histidine (0.25 mg), histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (9.09 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.90 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lecanemab-irmb is a humanized immunoglobulin gamma 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody directed against aggregated soluble and insoluble forms of amyloid beta. The accumulation of amyloid beta plaques in the brain is a defining pathophysiological feature of Alzheimer’s disease. LEQEMBI reduces amyloid beta plaques, as evaluated in Study 1 and Study 2 [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Effect of LEQEMBI on Amyloid Beta Pathology
The effect of LEQEMBI on amyloid beta plaque levels in the brain was evaluated using Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging. The PET signal was quantified using both the standard uptake value ratio (SUVR) and Centiloid scale to estimate levels of amyloid beta plaque in composites of brain areas expected to be widely affected by Alzheimer’s disease pathology (frontal, parietal, lateral temporal, sensorimotor, and anterior and posterior cingulate cortices), compared to a brain region expected to be spared of such pathology (cerebellum).
LEQEMBI reduced amyloid beta plaque in a dose- and time-dependent manner in the dose-ranging study (Study 1) and in a time-dependent manner in single-dosing regimen study (Study 2) compared to placebo [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
In Study 1, treatment with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks reduced amyloid beta plaque levels in the brain, producing reductions in PET SUVR compared to placebo at both Weeks 53 and 79 ( P <0.0001). The magnitude of the reduction was time- and dose-dependent.
During an off-treatment period in Study 1 (range from 9 to 59 months; mean of 24 months), SUVR and Centiloid values began to increase with a mean rate of increase of 2.6 Centiloids/year, however, treatment difference relative to placebo at the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled period in Study 1 was maintained.
In Study 2, treatment with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks reduced amyloid beta plaque levels in the brain, producing reductions compared to placebo starting at Week 13 and continuing through Week 79 ( P <0.0001). After Week 79 of treatment with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks, 67% of patients had amyloid levels less than 30 Centiloids as measured by PET. Reduction of amyloid to levels less than 30 Centiloids was inversely related to amyloid PET levels at baseline. The percentage of patients achieving amyloid levels less than 30 Centiloids after continuous treatment with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks is predicted to increase over time. It is predicted that, after Week 79 of treatment with LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, transitioning to a dosing regimen of either LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every 4 weeks or a LEQEMBI IQLIK subcutaneous injection of 360 mg once a week will also continue the reduction in amyloid beta plaque levels. Based on exposure-response modeling, the intravenous (10 mg/kg every 4 weeks) and subcutaneous (360 mg once weekly) maintenance dosing regimens of lecanemab-irmb are predicted to have similar reduction of amyloid beta plaque levels.
An increase in plasma Aβ42/40 ratio (Table 6) and CSF Aβ[1-42] was observed with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks dosing compared to placebo. Exposure-response modeling predicts that, after Week 79 of treatment with LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, transitioning to a dosing regimen of either LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every 4 weeks or a LEQEMBI IQLIK subcutaneous injection of 360 mg once a week will maintain increases in the plasma Aβ42/40 ratio.
Effect of LEQEMBI on Tau Pathophysiology
A reduction in plasma p-tau181 (Table7), CSF p-tau181, and CSF t-tau was observed with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks compared to placebo. Exposure-response modeling predicts that, after Week 79 of treatment with LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every two weeks, transitioning to a dosing regimen of LEQEMBI intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg every 4 weeks or a LEQEMBI IQLIK subcutaneous injection of 360 mg once a week will maintain the reduction in plasma p-tau181.
| Biomarker Endpoints | Study 1 | Study 2 | ||
| LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks | Placebo | LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks | Placebo | |
| Plasma Aβ42/40 2 | N=43 | N=88 | N=797 | N=805 |
| Mean baseline | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at Month 18 3 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Difference from placebo | 0.01 ( P =0.0036) 1 | 0.01 ( P <0.0001) 1 | ||
| Plasma p-tau181 (pg/mL) 2 | N=84 | N=179 | N=746 | N=752 |
| Mean baseline | 4.65 | 4.44 | 3.70 | 3.74 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at Month 18 3 | -1.11 | 0.08 | -0.58 | 0.20 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.20 ( P <0.0001) 1 | -0.78 ( P <0.0001) 1 | ||
| N is the number of patients with baseline value. 1 P values were not statistically controlled for multiple comparisons. 2 Results should be interpreted with caution due to uncertainties in bioanalysis. 3 Month 18 represents Week 79 in Study 1 and Week 77 in Study 2. | ||||
A substudy was conducted in Study 2 to evaluate the effect of LEQEMBI on neurofibrillary tangles composed of tau protein using PET imaging ( 18 F-MK6240 tracer). The PET signal was quantified using the SUVR method to estimate brain levels of tau in brain regions expected to be affected by Alzheimer’s disease pathology (whole cortical gray matter, meta-temporal, frontal, cingulate, parietal, occipital, medial temporal, and temporal) in the study population, compared to a brain region expected to be spared of such pathology (cerebellum). The adjusted mean change from baseline in tau PET SUVR, relative to placebo, was in favor of LEQEMBI in the medial temporal ( P <0.01), meta temporal ( P <0.05), and temporal ( P <0.05) regions. No statistically significant differences were observed for the whole cortical gray matter, frontal, cingulate, parietal, or occipital regions.
Exposure-Response Relationships
Model-based exposure-response analyses demonstrated that higher exposures to lecanemab-irmb were associated with greater reduction in clinical decline on Clinical Dementia Rating scale Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB) and Alzheimer Disease Assessment Scale – Cognitive Subscale 14 (ADAS-Cog14). In addition, higher exposures to lecanemab-irmb were associated with greater reduction in amyloid beta plaque. An association between reduction in amyloid beta plaque and clinical decline on CDR-SB and ADAS-Cog14 was also observed.
Higher exposures to lecanemab-irmb were also associated with greater increase in plasma Aβ42/40 ratio and greater reduction in plasma p-tau181.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Steady-state concentrations of lecanemab-irmb were reached after 6 weeks of 10 mg/kg administered every 2 weeks and systemic accumulation was 1.4-fold. The peak concentration (C max ) and area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC) of lecanemab-irmb increased dose proportionally in the dose range of 0.3 to 15 mg/kg following single dose.
The estimated mean steady-state concentrations of lecanemab-irmb following 10 mg/kg biweekly intravenous infusion, 10 mg/kg monthly intravenous infusion and 360 mg weekly subcutaneous administration by autoinjector are provided in Table 8. Using population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation, the intravenous (10 mg/kg once every 4 weeks) and subcutaneous (360 mg once weekly) maintenance dosing regimens of lecanemab-irmb were predicted to have similar pharmacokinetic exposure.
| C av g ,ss (mcg/mL) Mean (CV%) | |
| Intravenous infusion 10 mg/kg every two weeks | 156 (37.7) |
| Intravenous infusion 10 mg/kg every four weeks | 78.1 (37.7) |
| Subcutaneous injection 360 mg weekly | 83.1 (58.8) |
| •Based on simulations in 1000 virtual patients | |
Absorption
The bioavailability of lecanemab-irmb following subcutaneous administration of 360 mg by autoinjector relative to a 10 mg/kg intravenous infusion in patients was approximately 53% and was not affected by the injection site (abdomen, upper thigh, or back of the upper arm).
Distribution
The mean value (95% CI) for central volume of distribution at steady state is 3.24 (3.18-3.30) L.
Elimination
Lecanemab-irmb is degraded by proteolytic enzymes in the same manner as endogenous IgGs. The clearance of lecanemab-irmb (95% CI) is 0.370 (0.353-0.384) L/day. The terminal half-life is 5 to 7 days.
Specific Populations
Sex, body weight, and albumin were found to impact exposure to lecanemab-irmb. However, none of these covariates were found to be clinically significant.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
No clinical studies were conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of lecanemab-irmb in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Lecanemab-irmb is degraded by proteolytic enzymes and is not expected to undergo renal elimination or metabolism by hepatic enzymes.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADA in the studies described below with the incidence of ADA in other studies, including those of lecanemab-irmb or of other lecanemab products.
Intravenous Infusion
During the 18-month treatment period in Study 2, 3.4% (30/883) of patients treated with LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks developed treatment-emergent anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies, and 1.9% (17/885) developed neutralizing antibodies. Among LEQEMBI-treated patients who developed anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies, mean trough concentrations of lecanemab-irmb were lower at various time points compared to patients who had not developed anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies. Although there was no clear clinically meaningful impact of ADA (including neutralizing antibodies) on the pharmacodynamics, safety, or efficacy in any patient receiving LEQEMBI over the treatment duration of 18 months, given the low incidence of ADA, the available data are too limited to conclusively assess the impact of ADAs on the safety and efficacy of LEQEMBI.
Subcutaneous Injection
After 18 months of intravenous LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg once every 2 weeks, patients who received 360 mg subcutaneous LEQEMBI IQLIK once weekly in the open-label portion of Study 2 were assessed for immunogenicity using a different assay that was drug-tolerant for anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies and neutralizing antibodies. The anti-lecanemab-irmb antibody incidence was 2.0% (1/49) following a median treatment duration of 83 days with 360 mg subcutaneous LEQEMBI IQLIK. Neutralizing anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies were not detected in this patient. Because of the limited data regarding anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies, there is insufficient information to characterize the effects of anti-lecanemab-irmb antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of subcutaneous LEQEMBI IQLIK.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Genotoxicity studies have not been conducted.
Impairment of Fertility
No studies in animals have been conducted to assess the effects of lecanemab-irmb on male or female fertility. No adverse effects on male or female reproductive organs were observed in a 39-week intravenous toxicity study in monkeys administered lecanemab-irmb weekly at doses up to 100 mg/kg. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma exposures (C ave ) approximately 27 times that in humans at the recommended human dose (10 mg/kg every two weeks).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of LEQEMBI was evaluated in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, randomized studies (Study 1, NCT01767311; Study 2 NCT03887455) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (patients with confirmed presence of amyloid pathology and mild cognitive impairment [64% of patients in Study 1; 62% of patients in Study 2] or mild dementia stage of disease [36% of patients in Study 1; 38% of patients in Study 2], consistent with Stage 3 and Stage 4 Alzheimer’s disease). In both studies, patients were enrolled with a Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) global score of 0.5 or 1.0 and a Memory Box score of 0.5 or greater. All patients had a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of ≥22 and ≤30, and had objective impairment in episodic memory as indicated by at least 1 standard deviation below age-adjusted mean in the Wechsler-Memory Scale-IV Logical Memory II (subscale) (WMS-IV LMII). Patients were enrolled with or without concomitant approved therapies (cholinesterase inhibitors and the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist memantine) for Alzheimer’s disease. The dosage of 10 mg/kg administered once every 2 weeks by intravenous infusion was assessed in the 18-month placebo-controlled portions of Study 1 and Study 2 and continued in the optional long-term extension in each study. Transitioning to intravenous 10 mg/kg once every 4 weeks or subcutaneous 360 mg every week after 18 months of dosing is supported by pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling using observed data [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )] ; however, there are limited data to assess the long-term clinical benefit of transitioning to the dosing regimen of intravenous 10 mg/kg once every 4 weeks or subcutaneous 360 mg every week [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Study 1
In Study 1, 856 patients were randomized to receive one of 5 doses (161 of which were randomized to the recommended dosing regimen of 10 mg/kg every two weeks) of intravenous infusion of LEQEMBI or placebo (n=247). Of the total number of patients randomized, 71.4% were ApoE ε4 carriers and 28.6% were ApoE ε4 non-carriers. During the study, the protocol was amended to no longer randomize ApoE ε4 carriers to the 10 mg/kg every two weeks dose arm. ApoE ε4 carriers who had been receiving LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks for 6 months or less were discontinued from study drug. As a result, in the LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg every two weeks arm, 30.3% of patients were ApoE ε4 carriers and 69.7% were ApoE ε4 non-carriers. At baseline, the mean age of randomized patients was 71 years, with a range of 50 to 90 years. Fifty percent of patients were male and 90% were White.
In Study 1, a subgroup of 315 patients were enrolled in the amyloid PET substudy; of these, 277 were evaluated at Week 79. Results from the amyloid beta PET substudy are described in Figure 1 and Table 9. Plasma biomarkers are described in Table 7.
Figure 1 : Reduction in Brain Amyloid Beta Plaque (Adjusted Mean Change from Baseline in Amyloid Beta PET Composite, SUVR and Centiloids) in Study 1

| Biomarker Endpoints | LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks | Placebo |
| Amyloid Beta PET Composite SUVR | N=44 | N=98 |
| Mean baseline | 1.373 | 1.402 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at Week 79 Difference from placebo | -0.306 -0.310 ( P <0.001) 1 | 0.004 |
| Amyloid Beta PET Centiloid | N=44 | N=98 |
| Mean baseline | 78.0 | 84.8 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at Week 79 Difference from placebo | -72.5 -73.5 ( P <0.001) 1 | 1.0 |
| N is the number of patients with baseline value. 1 P values were not statistically controlled for multiple comparisons. | ||
The primary endpoint was change from baseline on a weighted composite score consisting of selected items from the Clinical Dementia Rating scale Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB), MMSE, and Alzheimer Disease Assessment Scale – Cognitive Subscale 14 (ADAS-Cog14) at Week 53. LEQEMBI had a 64% likelihood of 25% or greater slowing of progression on the primary endpoint relative to placebo at Week 53, which did not meet the prespecified success criterion of 80%.
Key secondary efficacy endpoints included the change from baseline in amyloid PET SUVR composite at Week 79 and change from baseline in the CDR-SB and ADAS-Cog14 at Week 79. Results for clinical assessments showed less change from baseline in CDR-SB and ADAS-Cog14 scores at Week 79 in the LEQEMBI group than in patients on placebo (CDR-SB: -0.40 [26%], 90% CI [-0.82, 0.03]; ADAS-Cog14: -2.31 [47%], 90% CI [-3.91, -0.72]).
After the 79-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period of Study 1, patients could enroll in an open-label extension period for up to 260 weeks, which was initiated after a gap period (range 9 to 59 months; mean 24 months) off treatment.
Study 2
In Study 2, 1795 patients were enrolled and randomized 1:1 to receive intravenous infusion of LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg or placebo once every 2 weeks. Of the total number of patients randomized, 69% were ApoE ε4 carriers and 31% were ApoE ε4 non-carriers. Overall median age of patients was 72 years, with a range of 50 to 90 years. Fifty-two percent were women, and 1381 (77%) were White, 303 (17%) were Asian, and 47 (3%) were Black.
The randomization was stratified according to clinical subgroup (mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of the disease); the presence or absence of concomitant approved therapies for Alzheimer’s disease at baseline (cholinesterase inhibitors and the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist memantine); ApoE ε4 carrier status; and geographical region.
The primary efficacy outcome was change from baseline at 18 months in the CDR-SB. Key secondary endpoints included change from baseline at 18 months for the following measures: amyloid Positron Emission Tomography (PET) using Centiloids, ADAS-Cog14, and Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment (ADCS MCI-ADL).
LEQEMBI treatment met the primary endpoint and reduced clinical decline on the global cognitive and functional scale, CDR-SB, compared to placebo at 18 months (-0.45 [-27%], P <0.0001).
Statistically significant differences ( P <0.01) between treatment groups were also seen in the results for ADAS-Cog14 and ADCS MCI-ADL at 18 months, as presented in Table 10.
Both ApoE ε4 carriers and ApoE ε4 noncarriers showed statistically significant treatment differences for the primary endpoint and all secondary endpoints. In an exploratory subgroup analysis of ApoE ε4 homozygotes, which represented 15% of the trial population, a treatment effect was not observed with LEQEMBI treatment on the primary endpoint, CDR-SB, compared to placebo, although treatment effects that favored LEQEMBI were observed for the secondary clinical endpoints, ADAS-Cog14 and ADCS MCI-ADL. Treatment effects on disease-relevant biomarkers (amyloid beta PET, plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, plasma p-tau 181) also favored LEQEMBI in the ApoE ε4 homozygous subgroup.
Starting at six months, across all time points, LEQEMBI treatment showed statistically significant changes in the primary and all key secondary endpoints from baseline compared to placebo; see Figure 2.
| Clinical Endpoints | LEQEMBI 10 mg/kg Every Two Weeks | Placebo |
| CDR-SB | N=859 | N=875 |
| Mean baseline | 3.17 | 3.22 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at 18 months (%) Difference from placebo | 1.21 -0.45 (-27%) ( P <0.0001) | 1.66 |
| ADAS-Cog14 | N=854 | N=872 |
| Mean baseline | 24.45 | 24.37 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at 18 months (%) Difference from placebo | 4.14 -1.44 (-26%) ( P =0.0007) | 5.58 |
| ADCS MCI-ADL | N=783 | N=796 |
| Mean baseline | 41.2 | 40.9 |
| Adjusted mean change from baseline at 18 months Difference from placebo | -3.5 (-37%) 2.0 ( P <0.0001) | -5.5 |
Figure 2 : Adjusted Mean Change from Baseline in CDR-SB in Study 2

16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
LEQEMBI single-dose vials and LEQEMBI IQLIK single-dose prefilled autoinjectors contain lecanemab-irmb as a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, and colorless to pale yellow solution, available as described below.
Intravenous Infusion
Each LEQEMBI glass vial is closed with a stopper and flip cap and is available as follows:
| Strength | Pack Size | NDC |
| Injection: 500 mg/5 mL (100 mg/mL) | Carton of 1 single-dose vial | 62856-215-01 |
| Injection: 200 mg/2 mL (100 mg/mL) | Carton of 1 single-dose vial | 62856-212-01 |
Subcutaneous Injection
Each LEQEMBI IQLIK prefilled autoinjector consists of a 2.25 mL glass syringe with a fixed 29-gauge ½-inch needle with needle guard and is available as follows:
| Strength | Pack Size | NDC |
| Injection: 360 mg/1.8 mL (200 mg/mL) | Carton of 1 single-dose prefilled autoinjector | 62856-220-01 |
LEQEMBI IQLIK is not made with natural rubber latex.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Intravenous Infusion
Unopened Vial
- Store LEQEMBI vials in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- Store in the original carton to protect from light.
- Do not freeze or shake.
Diluted Solution
For storage of the diluted infusion solution, see Dosage and Administration (2.5 ) .
Subcutaneous Injection
- Store LEQEMBI IQLIK autoinjectors in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- Store in original carton to protect from light.
- Do not freeze.
- If needed, the autoinjector can be stored at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) in the original carton for up to 14 days. Once the autoinjector has been stored at room temperature, do not return it to the refrigerator.
- Discard the autoinjector if these conditions are exceeded.
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE LEQEMBI ® IQLIK™ (le-KEM-bee) (lecanemab-irmb) 360 mg/1.8 mL injection, for subcutaneous use single-dose prefilled autoinjector |
| This Instructions for Use contains information on how to prepare and use LEQEMBI IQLIK. |
| Before each use of LEQEMBI IQLIK Read this Instructions for Use before you start using LEQEMBI IQLIK and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you or a caregiver how to use LEQEMBI IQLIK the right way before you use it for the first time. If you have any questions about how to use the autoinjector, contact your healthcare provider. |
Important information
|
Storing LEQEMBI IQLIK
|
The LEQEMBI IQLIK autoinjector 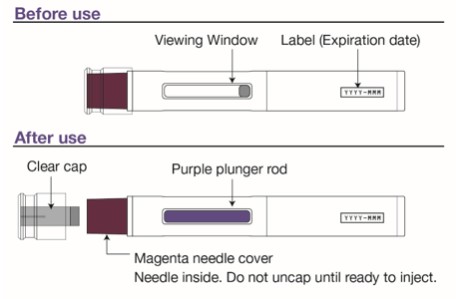 |
Gather Supplies  |
| Preparing to Inject LEQEMBI IQLIK |
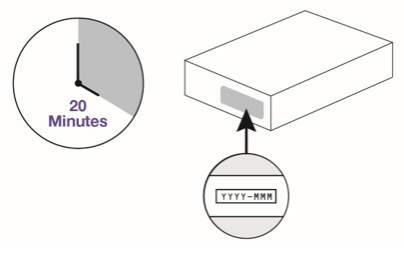
Step 1 Remove carton from the refrigerator and wait 20 minutes for the autoinjector to reach room temperature. Do not try to speed up the warming process in any way because the product may be damaged. Check the carton.
 |
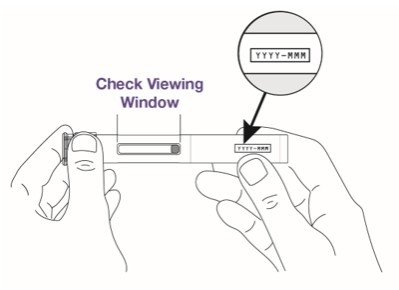
Step 2 Check the autoinjector.
 |
Step 3 Wash your hands with soap and water or use hand sanitizer.  |
Step 4 You can inject into the front of your thighs or stomach area (abdomen). If a caregiver gives you the injection, they may also do it in the back of your upper arm.
 |
| Injecting LEQEMBI IQLIK |
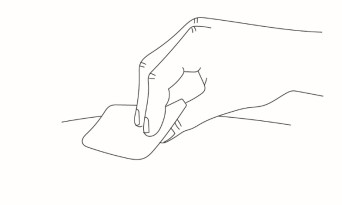
Step 5 Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe and allow the skin to air dry.
 |
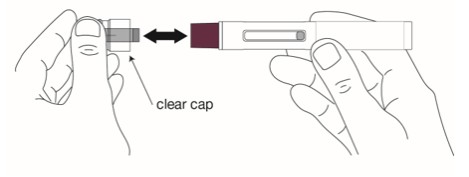
Step 6 Remove the clear cap when you are ready to inject. Hold the autoinjector with 1 hand and firmly pull the clear cap straight off with your other hand.
 |
Step 7 Throw away (dispose of) the cap in the household trash or sharps disposal container. 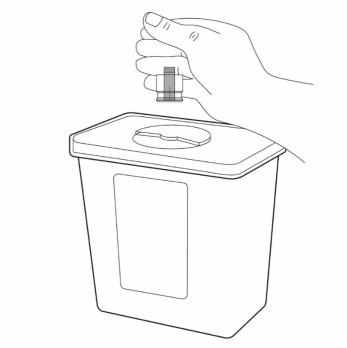 |
Step 8 Place the magenta needle cover at a 90-degree angle flat against the skin. Make sure you can see the viewing window.
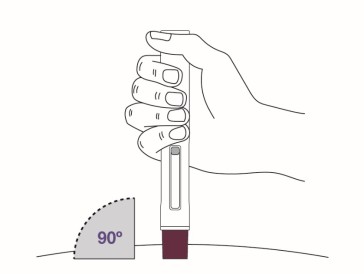 |
Step 9 Push the autoinjector firmly against the skin to start the injection. The injection will start automatically.
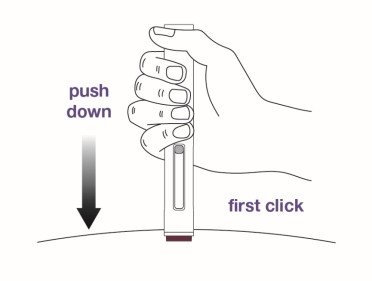 |
Step 10 Continue holding the autoinjector down against the skin for about 10 seconds . You will hear a second click. The purple plunger rod will fill the viewing window. Your injection is complete, but continue holding the autoinjector. 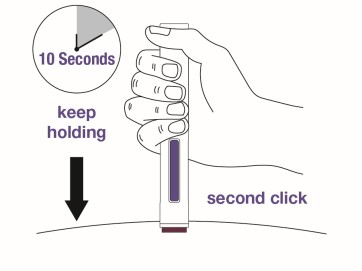 |
Step 11 Keep holding the autoinjector in place for at least 5 more seconds after the injection is complete. 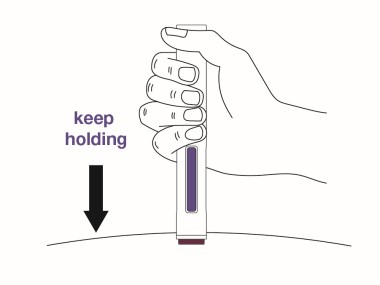 |
Step 12 Remove the autoinjector by pulling it straight up from the injection site.
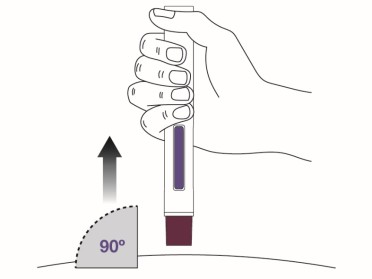 |
Step 13 You may notice a small drop of blood at the injection site. This is normal. Press a cotton ball or gauze on the area.
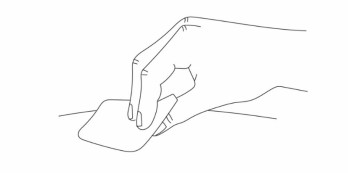 |
Step 14 Throw away (dispose of) the autoinjector in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. 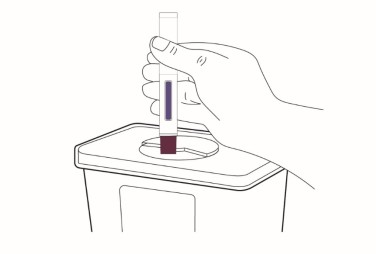 |
Disposing of LEQEMBI IQLIK Do not throw away (dispose of) the autoinjector in the household trash. If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
|
| Manufactured by. Eisai Inc. Nutley, NJ 07110 U.S. License No. 1862 LEQEMBI ® is a registered trademark of Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. LEQEMBI IQLIK™ is a trademark of Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. © 2025 Eisai Inc. and Biogen For more information, go to www.LEQEMBI.com or call 1-888-274-2378. This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved:8/2025 |
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lecanemab-irmb is a humanized immunoglobulin gamma 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody directed against aggregated soluble and insoluble forms of amyloid beta. The accumulation of amyloid beta plaques in the brain is a defining pathophysiological feature of Alzheimer’s disease. LEQEMBI reduces amyloid beta plaques, as evaluated in Study 1 and Study 2 [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .