Leucovorin Calcium
Leucovorin Calcium Prescribing Information
Leucovorin calcium rescue is indicated after high dose methotrexate therapy in osteosarcoma. Leucovorin calcium is also indicated to diminish the toxicity and counteract the effects of impaired methotrexate elimination and of inadvertent overdosages of folic acid antagonists.
Leucovorin calcium is indicated in the treatment of megaloblastic anemias due to folic acid deficiency when oral therapy is not feasible.
Leucovorin is also indicated for use in combination with 5-fluorouracil to prolong survival in the palliative treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Leucovorin should not be mixed in the same infusion as 5-fluorouracil because a precipitate may form.
- Leucovorin is administered at 200 mg/m
2by slow intravenous injection over a minimum of 3 minutes, followed by 5-fluorouracil at 370 mg/m
2by intravenous injection. - Leucovorin is administered at 20 mg/m
2by intravenous injection followed by 5-fluorouracil at 425 mg/m
2by intravenous injection.
5-Fluorouracil and leucovorin should be administered separately to avoid the formation of a precipitate.
Treatment is repeated daily for five days. This five-day treatment course may be repeated at 4 week (28-day) intervals, for 2 courses and then repeated at 4 to 5 week (28 to 35 day) intervals provided that the patient has completely recovered from the toxic effects of the prior treatment course.
In subsequent treatment course, the dosage of 5-fluorouracil should be adjusted based on patient tolerance of the prior treatment course. The daily dosage of 5-fluorouracil should be reduced by 20% for patients who experienced moderate hematologic or gastrointestinal toxicity in the prior treatment course, and by 30% for patients who experienced severe toxicity (see
Parenteral administration is preferable to oral dosing if there is a possibility that the patient may vomit and not absorb the leucovorin. Leucovorin has no effect on non-hematologic toxicities of methotrexate such as the nephrotoxicity resulting from drug and/or metabolite precipitation in the kidney.
Patients being treated with the leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination should have a CBC with differential and platelets prior to each treatment. During the first two courses a CBC with differential and platelets has to be repeated weekly and thereafter once each cycle at the time of anticipated WBC nadir. Electrolytes and liver function tests should be performed prior to each treatment for the first three cycles then prior to every other cycle. Dosage modifications of fluorouracil should be instituted as follows, based on the most severe toxicities:
Diarrhea and/or Stomatitis | WBC/mm3 Nadir | Platelets/mm3 Nadir | 5-FU Dose |
Moderate Severe | 1,000 - 1,900 <1,000 | 25-75,000 <25,000 | decrease 20% decrease 30% |
If no toxicity occurs, the 5-fluorouracil dose may increase 10%. Treatment should be deferred until WBCs are 4,000/mm3and platelets 130,000/mm3. If blood counts do not reach these levels within two weeks, treatment should be discontinued. Patients should be followed up with physical examination prior to each treatment course and appropriate radiological examination as needed. Treatment should be discontinued when there is clear evidence of tumor progression.
Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible pediatric patients.
Preliminary animal and human studies have shown that small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter the CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and, in humans, remain 1 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than the usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration. However, high doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil (see
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when leucovorin is administered to a nursing mother.
See
Clinical studies of leucovorin calcium did not show differences in safety or effectiveness between subjects over 65 and younger subjects. Other clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older patients cannot be ruled out. This drug is known to be excreted by the kidney and the risk of toxic reactions to the drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elder patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Patients being treated with the leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination should have a CBC with differential and platelets prior to each treatment. During the first two courses a CBC with differential and platelets has to be repeated weekly and thereafter once each cycle at the time of anticipated WBC nadir. Electrolytes and liver function tests should be performed prior to each treatment for the first three cycles then prior to every other cycle. Dosage modifications of fluorouracil should be instituted as follows, based on the most severe toxicities:
Diarrhea and/or Stomatitis | WBC/mm3 Nadir | Platelets/mm3 Nadir | 5-FU Dose |
Moderate Severe | 1,000 - 1,900 <1,000 | 25-75,000 <25,000 | decrease 20% decrease 30% |
If no toxicity occurs, the 5-fluorouracil dose may increase 10%. Treatment should be deferred until WBCs are 4,000/mm3and platelets 130,000/mm3. If blood counts do not reach these levels within two weeks, treatment should be discontinued. Patients should be followed up with physical examination prior to each treatment course and appropriate radiological examination as needed. Treatment should be discontinued when there is clear evidence of tumor progression.
2administered by intravenous infusion over 4 hours (see methotrexate package insert for full prescribing information).
Leucovorin rescue at a dose of 15 mg (approximately 10 mg/m
2) every 6 hours for 10 doses starts 24 hours after the beginning of the methotrexate infusion. In the presence of gastrointestinal toxicity, nausea or vomiting, leucovorin should be administered parenterally. Do not administer leucovorin intrathecally.
Serum creatinine and methotrexate levels should be determined at least once daily. Leucovorin administration, hydration, and urinary alkalization (pH of 7.0 or greater) should be continued until the methotrexate level is below 5 x 10
-8M (0.05 micromolar). The leucovorin dose should be adjusted or leucovorin rescue extended based on the following guidelines:
DO NOT ADMINISTER LEUCOVORIN INTRATHECALLY
Clinical Situation | Laboratory Findings | Leucovorin Dosage and Duration |
Normal Methotrexate Elimination | Serum methotrexate level approximately 10 micromolar at 24 hours after administration, 1 micromolar at 48 hours, and less than 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours. | 15 mg PO, IM, or IV q 6 hours for 60 hours (10 doses starting at 24 hours after start of methotrexate infusion). |
Delayed Late Methotrexate Elimination | Serum methotrexate level remaining above 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours, and more than 0.05 micromolar at 96 hours after administration. | Continue 15 mg PO, IM, or IV q 6 hours, until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. |
Delayed Early Methotrexate Elimination and/or Evidence of Acute Renal Injury | Serum methotrexate level of 50 micromolar or more at 24 hours, or 5 micromolar or more at 48 hours after administration, OR; a 100% or greater increase in serum creatinine level at 24 hours after methotrexate administration (e.g., an increase from 0.5 mg/dL to a level of 1 mg/dL or more). | 150 mg IV q 3 hours, until methotrexate level is less than 1 micromolar; then 15 mg IV q 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. |
Patients who experience delayed early methotrexate elimination are likely to develop reversible renal failure. In addition to appropriate leucovorin therapy, these patients require continuing hydration and urinary alkalization, and close monitoring of fluid and electrolyte status, until the serum methotrexate level has fallen to below 0.05 micromolar and the renal failure has resolved.
Some patients will have abnormalities in methotrexate elimination or renal function following methotrexate administration, which are significant but less severe than abnormalities described in the table above. These abnormalities may or may not be associated with significant clinical toxicity. If significant clinical toxicity is observed, leucovorin rescue should be extended for an additional 24 hours (total of 14 doses over 84 hours) in subsequent courses of therapy. The possibility that the patient is taking other medications which interact with methotrexate (e.g., medications which may interfere with methotrexate elimination or binding to serum albumin) should always be reconsidered when laboratory abnormalities or clinical toxicities are observed.
In the treatment of accidental overdosages of folic acid antagonists, intravenous leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting toxicity decreases. In the treatment of accidental overdosages of intrathecally administered folic acid antagonists, do not administer leucovorin intrathecally. LEUCOVORIN MAY BE HARMFUL OR FATAL IF GIVEN INTRATHECALLY.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Because of the benzyl alcohol contained in certain diluents used for reconstituting Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when doses greater than 10 mg/m2are administered, Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP should be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and used immediately (see
Because of the calcium content of the leucovorin solution, no more than 160 mg of leucovorin should be injected intravenously per minute (16 mL of a 10 mg/mL, or 8 mL of a 20 mg/mL solution per minute).
Leucovorin enhances the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. When these drugs are administered concurrently in the palliative therapy of advanced colorectal cancer, the dosage of 5-fluorouracil must be lower than usually administered. Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with 5-fluorouracil alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe and of prolonged duration in patients treated with the combination.
In the first Mayo/NCCTG controlled trial, toxicity, primarily gastrointestinal, resulted in 7% of patients requiring hospitalization when treated with 5-fluorouracil alone or 5-fluorouracil in combination with 200 mg/m2of leucovorin and 20% when treated with 5-fluorouracil in combination with 20 mg/m2of leucovorin. In the second Mayo/NCCTG trial, hospitalizations related to treatment toxicity also appeared to occur more often in patients treated with the low dose leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination than in patients treated with the high dose combination — 11% versus 3%. Therapy with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil must not be initiated or continued in patients who have symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity of any severity, until those symptoms have completely resolved. Patients with diarrhea must be monitored with particular care until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur. In an additional study utilizing higher weekly doses of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin, elderly and/or debilitated patients were found to be at greater risk for severe gastrointestinal toxicity.
Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving leucovorin, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine administration, and most commonly in those with CNS metastases or other predisposing factors, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study.
2should be administered IV, IM, or PO every 6 hours until the serum methotrexate level is less than 10
-8M. In the presence of gastrointestinal toxicity, nausea, or vomiting, leucovorin should be administered parenterally. Do not administer leucovorin intrathecally.
Serum creatinine and methotrexate levels should be determined at 24 hour intervals. If the 24 hour serum creatinine has increased 50% over baseline or if the 24 hour methotrexate level is greater than 5 x 10
-6M or the 48 hour level is greater than 9 x 10
-7M, the dose of leucovorin should be increased to 100 mg/m
2IV every 3 hours until the methotrexate level is less than 10
-8M.
Hydration (3 L/d) and urinary alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate solution should be employed concomitantly. The bicarbonate dose should be adjusted to maintain the urine pH at 7.0 or greater.
Each 50, 100 and 200 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP when reconstituted with 5, 10 and 20 mL, respectively, of sterile diluent yields a leucovorin concentration of 10 mg per mL. Each 350 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP when reconstituted with 17.5 mL of sterile diluent yields a leucovorin concentration of 20 mg per mL. Each 500 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP when reconstituted with 50 mL of sterile diluent yields a leucovorin concentration of 10 mg per mL. Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP contains no preservative. Reconstitute the lyophilized vial products with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP (benzyl alcohol preserved), or Sterile Water for Injection, USP. When reconstituted with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, the resulting solution must be used within 7 days and discard any unused portion. If the product is reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, use immediately and discard any unused portion.
Because of the benzyl alcohol contained in Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, when doses greater than 10 mg/m
2are administered, Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP should be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and used immediately. (See
In the treatment of accidental overdosages of folic acid antagonists, intravenous leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting toxicity decreases. In the treatment of accidental overdosages of intrathecally administered folic acid antagonists, do not administer leucovorin intrathecally. LEUCOVORIN MAY BE HARMFUL OR FATAL IF GIVEN INTRATHECALLY.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Because of the benzyl alcohol contained in certain diluents used for reconstituting Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when doses greater than 10 mg/m2are administered, Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP should be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and used immediately (see
Because of the calcium content of the leucovorin solution, no more than 160 mg of leucovorin should be injected intravenously per minute (16 mL of a 10 mg/mL, or 8 mL of a 20 mg/mL solution per minute).
Leucovorin enhances the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. When these drugs are administered concurrently in the palliative therapy of advanced colorectal cancer, the dosage of 5-fluorouracil must be lower than usually administered. Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with 5-fluorouracil alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe and of prolonged duration in patients treated with the combination.
In the first Mayo/NCCTG controlled trial, toxicity, primarily gastrointestinal, resulted in 7% of patients requiring hospitalization when treated with 5-fluorouracil alone or 5-fluorouracil in combination with 200 mg/m2of leucovorin and 20% when treated with 5-fluorouracil in combination with 20 mg/m2of leucovorin. In the second Mayo/NCCTG trial, hospitalizations related to treatment toxicity also appeared to occur more often in patients treated with the low dose leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination than in patients treated with the high dose combination — 11% versus 3%. Therapy with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil must not be initiated or continued in patients who have symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity of any severity, until those symptoms have completely resolved. Patients with diarrhea must be monitored with particular care until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur. In an additional study utilizing higher weekly doses of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin, elderly and/or debilitated patients were found to be at greater risk for severe gastrointestinal toxicity.
Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving leucovorin, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine administration, and most commonly in those with CNS metastases or other predisposing factors, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study.
Parenteral products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Leucovorin should not be mixed in the same infusion as 5-fluorouracil, since this may lead to the formation of a precipitate.
Leucovorin is improper therapy for pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias secondary to the lack of vitamin B
12. A hematologic remission may occur while neurologic manifestations continue to progress.
Allergic sensitization, including anaphylactoid reactions and urticaria, has been reported following the administration of both oral and parenteral leucovorin. No other adverse reactions have been attributed to the use of leucovorin
The following table summarizes significant adverse events occurring in 316 patients treated with the leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combinations compared against 70 patients treated with 5-fluorouracil alone for advanced colorectal carcinoma. These data are taken from the Mayo/NCCTG large multicenter prospective trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of the combination regimen.
PERCENTAGE OF PATIENTS TREATED WITH LEUCOVORIN/FLUOROURACIL FOR ADVANCED COLORECTAL CARCINOMA REPORTING ADVERSE EXPERIENCES OR HOSPITALIZED FOR TOXICITY
(High LV) /5-FU (N=155) | (Low LV) /5-FU (N=161) | 5-FU Alone (N=70) | ||||
Any % | Grade 3+ (%) | Any % | Grade 3+ (%) | Any % | Grade 3+ (%) | |
Leukopenia | 69 | 14 | 83 | 23 | 93 | 48 |
Thrombocytopenia | 8 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 18 | 3 |
Infection | 8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 2 |
Nausea | 74 | 10 | 80 | 9 | 60 | 6 |
Vomiting | 46 | 8 | 44 | 9 | 40 | 7 |
Diarrhea | 66 | 18 | 67 | 14 | 43 | 11 |
Stomatitis | 75 | 27 | 84 | 29 | 59 | 16 |
Constipation | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | - |
Lethargy/Malaise/Fatigue | 13 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 6 | 3 |
Alopecia | 42 | 5 | 43 | 6 | 37 | 7 |
Dermatitis | 21 | 2 | 25 | 1 | 13 | - |
Anorexia | 14 | 1 | 22 | 4 | 14 | - |
Hospitalization for Toxicity | 5% | 15% | 7% | |||
High LV = Leucovorin 200 mg/m
2, Low LV = Leucovorin 20 mg/m
2
Any = percentage of patients reporting toxicity of any severity
Grade 3+ = percentage of patients reporting toxicity of Grade 3 or higher
Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible pediatric patients.
Preliminary animal and human studies have shown that small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter the CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and, in humans, remain 1 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than the usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration. However, high doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil (see
In the treatment of accidental overdosages of folic acid antagonists, intravenous leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting toxicity decreases. In the treatment of accidental overdosages of intrathecally administered folic acid antagonists, do not administer leucovorin intrathecally. LEUCOVORIN MAY BE HARMFUL OR FATAL IF GIVEN INTRATHECALLY.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Because of the benzyl alcohol contained in certain diluents used for reconstituting Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when doses greater than 10 mg/m2are administered, Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP should be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and used immediately (see
Because of the calcium content of the leucovorin solution, no more than 160 mg of leucovorin should be injected intravenously per minute (16 mL of a 10 mg/mL, or 8 mL of a 20 mg/mL solution per minute).
Leucovorin enhances the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. When these drugs are administered concurrently in the palliative therapy of advanced colorectal cancer, the dosage of 5-fluorouracil must be lower than usually administered. Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with 5-fluorouracil alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe and of prolonged duration in patients treated with the combination.
In the first Mayo/NCCTG controlled trial, toxicity, primarily gastrointestinal, resulted in 7% of patients requiring hospitalization when treated with 5-fluorouracil alone or 5-fluorouracil in combination with 200 mg/m2of leucovorin and 20% when treated with 5-fluorouracil in combination with 20 mg/m2of leucovorin. In the second Mayo/NCCTG trial, hospitalizations related to treatment toxicity also appeared to occur more often in patients treated with the low dose leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination than in patients treated with the high dose combination — 11% versus 3%. Therapy with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil must not be initiated or continued in patients who have symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity of any severity, until those symptoms have completely resolved. Patients with diarrhea must be monitored with particular care until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur. In an additional study utilizing higher weekly doses of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin, elderly and/or debilitated patients were found to be at greater risk for severe gastrointestinal toxicity.
Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving leucovorin, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine administration, and most commonly in those with CNS metastases or other predisposing factors, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study.
Leucovorin is one of several active, chemically reduced derivatives of folic acid. It is useful as an antidote to drugs which act as folic acid antagonists.
Also known as folinic acid, Citrovorum factor, or 5-formyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolic acid, this compound has the chemical designation of Calcium
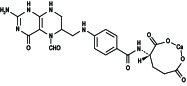
C
20H
21CaN
7O
7M.W.=511.5
Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP is a sterile product indicated for intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) administration and is supplied in 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 350 mg, and 500 mg vials.
Each 50 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when reconstituted with 5 mL of sterile diluent, contains leucovorin (as the calcium salt) 10 mg/mL.
Each 100 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when reconstituted with 10 mL of sterile diluent, contains leucovorin (as the calcium salt) 10 mg/mL.
Each 200 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when reconstituted with 20 mL of sterile diluent, contains leucovorin (as the calcium salt) 10 mg/mL.
Each 350 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when reconstituted with 17.5 mL of sterile diluent, contains leucovorin (as the calcium salt) 20 mg/mL.
Each 500 mg vial of Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when reconstituted with 50 mL of sterile diluent, contains leucovorin (as the calcium salt) 10 mg/mL.
In each dosage form, one milligram of leucovorin calcium contains 0.002 mmol of leucovorin and 0.002 mmol of calcium.
These lyophilized products contain no preservative. The inactive ingredient is Sodium Chloride, USP, added to adjust tonicity. The inactive ingredient is sodium chloride 40 mg/vial for the 50 mg vial, 80 mg/vial for the 100 mg vial, 80 mg/vial for the 200 mg vial, 140 mg/vial for the 350 mg vial, and 450 mg/vial for the 500 mg vial. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid are used to adjust the pH to approximately 8.1 during manufacture. Reconstitute with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, which contains benzyl alcohol (see
In the treatment of accidental overdosages of folic acid antagonists, intravenous leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting toxicity decreases. In the treatment of accidental overdosages of intrathecally administered folic acid antagonists, do not administer leucovorin intrathecally. LEUCOVORIN MAY BE HARMFUL OR FATAL IF GIVEN INTRATHECALLY.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Because of the benzyl alcohol contained in certain diluents used for reconstituting Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP, when doses greater than 10 mg/m2are administered, Leucovorin Calcium for Injection, USP should be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and used immediately (see
Because of the calcium content of the leucovorin solution, no more than 160 mg of leucovorin should be injected intravenously per minute (16 mL of a 10 mg/mL, or 8 mL of a 20 mg/mL solution per minute).
Leucovorin enhances the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. When these drugs are administered concurrently in the palliative therapy of advanced colorectal cancer, the dosage of 5-fluorouracil must be lower than usually administered. Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with 5-fluorouracil alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe and of prolonged duration in patients treated with the combination.
In the first Mayo/NCCTG controlled trial, toxicity, primarily gastrointestinal, resulted in 7% of patients requiring hospitalization when treated with 5-fluorouracil alone or 5-fluorouracil in combination with 200 mg/m2of leucovorin and 20% when treated with 5-fluorouracil in combination with 20 mg/m2of leucovorin. In the second Mayo/NCCTG trial, hospitalizations related to treatment toxicity also appeared to occur more often in patients treated with the low dose leucovorin/5-fluorouracil combination than in patients treated with the high dose combination — 11% versus 3%. Therapy with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil must not be initiated or continued in patients who have symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity of any severity, until those symptoms have completely resolved. Patients with diarrhea must be monitored with particular care until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur. In an additional study utilizing higher weekly doses of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin, elderly and/or debilitated patients were found to be at greater risk for severe gastrointestinal toxicity.
Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving leucovorin, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine administration, and most commonly in those with CNS metastases or other predisposing factors, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study.