Libtayo prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Administration guides
Patient education materials
Treatment initiation and patient onboarding
Patient support program
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Reimbursement information
Financial assistance & copay programs
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer LIBTAYO as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes after dilution. (2.2 )
- Metastatic and locally advanced CSCC and BCC: 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. (2.2 )
- Adjuvant treatment of CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation:
- 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks of total therapy, or
- 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks of total therapy. (2.2 )
- NSCLC: 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.2 )
Patient Selection for NSCLC
Select patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC for treatment with LIBTAYO as a single agent based on PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of PD-L1 expression is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of LIBTAYO are presented in Table 1.
Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with LIBTAYO for recommended dosing information, as appropriate.
| Indication | Recommended dosage of LIBTAYO as an intravenous infusion | Duration of Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Adults with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. |
| Adjuvant treatment of adult patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation | 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks, followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks Or 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks. |
| Adults with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (laBCC) or metastatic BCC (mBCC) | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. |
| Adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Single-agent or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for LIBTAYO is recommended. In general, withhold LIBTAYO for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue LIBTAYO for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for LIBTAYO for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 4.0 | Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| ALT=alanine aminotransferase, AST=aspartate aminotransferase, ULN=upper limit of normal, SJS=Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, TEN=toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS=Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms | ||
| Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
| Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to less than 10 mg per day (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Colitis | Grade 2 or 3 | Withhold |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times the ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times the ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times the ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Endocrinopathies | Grade 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
| Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold |
| Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
| Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
| Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
| Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
| Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Other Adverse Reactions | ||
| Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
- Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. LIBTAYO is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored or contains extraneous particulate matter other than trace amounts of translucent to white particles.
Preparation
- Do not shake the vial(s).
- Withdraw the required volume from the vial(s) of LIBTAYO and transfer into an intravenous (IV) bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 1 mg/mL to 20 mg/mL.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard any unused portion left in the vial(s).
Storage of Diluted Solution
- Store at
- room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for no more than 8 hours from the time of preparation to the end of the infusion or
- under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 10 days from the time of preparation to the end of infusion.
- Allow the diluted solution to come to room temperature prior to administration.
- Do not freeze.
Administration
- Administer by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes through an intravenous line containing a sterile, in-line or add-on 0.2-micron to 5-micron filter.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Libtayo prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LIBTAYO is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody indicated:
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC)
- for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) who are not candidates for curative surgery or curative radiation. (1.1 )
- for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation. (1.1 , 14.1 )
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic BCC (laBCC or mBCC) who have been previously treated with a hedgehog pathway inhibitor or for whom a hedgehog pathway inhibitor is not appropriate. (1.2 )
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- in combination with platinum‐based chemotherapy for the first‐line treatment of adult patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with no EGFR, ALK or ROS1 aberrations and is:
- locally advanced where patients are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation or
- metastatic. (1.3 )
- as single agent for the first-line treatment of adult patients with NSCLC whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression [Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) ≥50%] as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR, ALK or ROS1 aberrations, and is:
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
LIBTAYO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) who are not candidates for curative surgery or curative radiation.
LIBTAYO is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] after surgery and radiation .
Basal Cell Carcinoma
LIBTAYO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (laBCC or mBCC) who have been previously treated with a hedgehog pathway inhibitor or for whom a hedgehog pathway inhibitor is not appropriate.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
LIBTAYO in combination with platinum‐based chemotherapy is indicated for the first‐line treatment of adult patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with no EGFR, ALK or ROS1 aberrations and is:
- locally advanced where patients are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation or
- metastatic.
LIBTAYO as a single agent is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with NSCLC whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression [Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) ≥50%] as determined by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] , with no EGFR, ALK or ROS1 aberrations, and is:
- locally advanced where patients are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation or
- metastatic.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer LIBTAYO as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes after dilution. (2.2 )
- Metastatic and locally advanced CSCC and BCC: 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. (2.2 )
- Adjuvant treatment of CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation:
- 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks of total therapy, or
- 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks of total therapy. (2.2 )
- NSCLC: 350 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.2 )
Patient Selection for NSCLC
Select patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC for treatment with LIBTAYO as a single agent based on PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of PD-L1 expression is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of LIBTAYO are presented in Table 1.
Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with LIBTAYO for recommended dosing information, as appropriate.
| Indication | Recommended dosage of LIBTAYO as an intravenous infusion | Duration of Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Adults with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. |
| Adjuvant treatment of adult patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation | 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks, followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks Or 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks. |
| Adults with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (laBCC) or metastatic BCC (mBCC) | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 24 months. |
| Adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Single-agent or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy | 350 mg every 3 weeks | Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for LIBTAYO is recommended. In general, withhold LIBTAYO for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue LIBTAYO for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for LIBTAYO for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 4.0 | Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| ALT=alanine aminotransferase, AST=aspartate aminotransferase, ULN=upper limit of normal, SJS=Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, TEN=toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS=Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms | ||
| Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
| Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to less than 10 mg per day (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Colitis | Grade 2 or 3 | Withhold |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times the ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times the ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times the ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Endocrinopathies | Grade 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
| Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold |
| Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
| Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
| Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
| Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
| Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Other Adverse Reactions | ||
| Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
- Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. LIBTAYO is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored or contains extraneous particulate matter other than trace amounts of translucent to white particles.
Preparation
- Do not shake the vial(s).
- Withdraw the required volume from the vial(s) of LIBTAYO and transfer into an intravenous (IV) bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 1 mg/mL to 20 mg/mL.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard any unused portion left in the vial(s).
Storage of Diluted Solution
- Store at
- room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for no more than 8 hours from the time of preparation to the end of the infusion or
- under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 10 days from the time of preparation to the end of infusion.
- Allow the diluted solution to come to room temperature prior to administration.
- Do not freeze.
Administration
- Administer by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes through an intravenous line containing a sterile, in-line or add-on 0.2-micron to 5-micron filter.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 350 mg/7 mL (50 mg/mL), clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action, LIBTAYO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] . There are no available data on the use of LIBTAYO in pregnant women. Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-mediated rejection of the developing fetus resulting in fetal death (see Data ) . Human IgG4 immunoglobulins (IgG4) are known to cross the placenta; therefore, LIBTAYO has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with LIBTAYO to evaluate its effect on reproduction and fetal development. A central function of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is to preserve pregnancy by maintaining maternal immune tolerance to the fetus. In murine models of pregnancy, blockade of PD-L1 signaling has been shown to disrupt tolerance to the fetus and to result in an increase in fetal loss; therefore, potential risks of administering LIBTAYO during pregnancy include increased rates of abortion or stillbirth. As reported in the literature, there were no malformations related to the blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling in the offspring of these animals; however, immune-mediated disorders occurred in PD-1 and PD-L1 knockout mice. Based on its mechanism of action, fetal exposure to cemiplimab-rwlc may increase the risk of developing immune-mediated disorders or altering the normal immune response.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of cemiplimab-rwlc in human milk, or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for at least 4 months after the last dose of LIBTAYO.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating LIBTAYO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Contraception
LIBTAYO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LIBTAYO and for at least 4 months after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LIBTAYO have not been established in pediatric patients.
The safety and efficacy of LIBTAYO as a single agent (Part 1, N=25) or in combination with radiation therapy (Part 2, N=22) were evaluated but not established in a two-part, open-label, multi-center trial (Study 1690, NCT03690869) in pediatric patients (birth to < 17 years) with relapsed or refractory solid tumors (Part 1) or relapsed or refractory CNS tumors (Parts 1 and 2) or newly diagnosed CNS tumors (Part 2). No new safety signals were observed in these pediatric patients.
Cemiplimab exposure in 46 pediatric patients aged 1 to < 17 years was within the range of values previously observed in adults given a similar dose based on body weight.
Geriatric Use
LIBTAYO as a Single Agent
Of the 1281 patients with advanced cancers who received LIBTAYO as a single agent in clinical studies, 26% were 65 years up to 75 years and 22% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Of the 358 patients with mCSCC or laCSCC who received LIBTAYO as a single agent in Study 1540, 30% were 65 years up to 75 years and 48% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Of the 205 adult patients with CSCC at high-risk of recurrence who received LIBTAYO as a single agent in the C-POST study, 39% were 65 years up to 75 years and 35% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Of the 138 patients with BCC who received LIBTAYO as a single agent in Study 1620, 27% were 65 years up to 75 years, and 31% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
LIBTAYO in Combination with Platinum-based Chemotherapy
Of the 312 patients with NSCLC who received LIBTAYO in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in Study 16113, 35% were 65 years up to 75 years and 6% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions (5.1 )
- Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, including the following: immune-mediated pneumonitis, immune-mediated colitis, immune-mediated hepatitis, immune-mediated endocrinopathies, immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions, immune-mediated nephritis and renal dysfunction, and solid organ transplant rejection.
- Monitor for early identification and management. Evaluate liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function at baseline and periodically during treatment.
- Withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO based on the severity of reaction. (2.3 )
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Interrupt, slow the rate of infusion, or permanently discontinue based on severity of reaction. (2.3 , 5.2 )
- Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT): Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic HSCT before or after being treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. (5.3 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.4 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
LIBTAYO is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed under Warnings and Precautions may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated reactions.
The incidence and severity of immune-mediated adverse reactions were similar when LIBTAYO was administered as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune-mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. While immune-mediated adverse reactions usually manifest during treatment with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies, immune-mediated adverse reactions can also manifest after discontinuation of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Immune-mediated adverse reactions affecting more than one body system can occur simultaneously.
Early identification and management of immune‐mediated adverse reactions are essential to ensure safe use of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Monitor closely for symptoms and signs that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function at baseline and periodically during treatment. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate appropriate workup to exclude alternative etiologies, including infection. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate.
Withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . In general, if LIBTAYO requires interruption or discontinuation, administer systemic corticosteroid therapy (1 to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reactions are not controlled with corticosteroids.
Toxicity management guidelines for adverse reactions that do not necessarily require systemic steroids (e.g., endocrinopathies and dermatologic reactions) are discussed below.
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated pneumonitis. The definition of immune-mediated pneumonitis included the required use of systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants and the absence of a clear alternate etiology. In patients treated with other PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies the incidence of pneumonitis is higher in patients who have received prior thoracic radiation.
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 2.6% (33/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 4 (0.3%), Grade 3 (0.6%), and Grade 2 (1.6%) adverse reactions. Pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 1.3% of patients and withholding of LIBTAYO in 1.4% of the patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in all patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 61% of the 33 patients. Of the 18 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for pneumonitis, 10 reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these, 4/10 (40%) had recurrence of pneumonitis.
Immune-Mediated Colitis
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated colitis. The definition of immune-mediated colitis included the required use of systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants and the absence of a clear alternate etiology. The primary component of the immune-mediated colitis was diarrhea. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation has been reported in patients with corticosteroid-refractory immune-mediated colitis treated with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. In cases of corticosteroid refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup to exclude alternative etiologies.
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 2% (25/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (0.8%) and Grade 2 (0.9%) adverse reactions. Colitis led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 0.4% of patients and withholding of LIBTAYO in 1.2% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in all patients with colitis. Colitis resolved in 56% of the 25 patients. Of the 16 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for colitis, 6 reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these, 4/6 (67%) had recurrence of colitis.
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated hepatitis. The definition of immune-mediated hepatitis included the required use of systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants and the absence of a clear alternate etiology.
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 2.4% (31/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including fatal (< 0.1%), Grade 4 (0.3%), Grade 3 (1.6%), and Grade 2 (0.2%) adverse reactions. Hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 1.4% of patients and withholding of LIBTAYO in 0.7% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in all patients with hepatitis. Thirteen percent (13%) of these patients (4/31) required additional immunosuppression with mycophenolate. Hepatitis resolved in 39% of the 31 patients. Of the 9 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for hepatitis, 5 patients reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these, 1/5 (20%) had recurrence of hepatitis.
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
LIBTAYO can cause primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency. For Grade 2 or higher adrenal insufficiency, initiate symptomatic treatment, including hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 0.5% (6/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (0.5%) adverse reactions. Adrenal insufficiency led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 1 (< 0.1%) patient. LIBTAYO was withheld in 1 (< 0.1%) patient due to adrenal insufficiency and not reinitiated. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 83% (5/6) patients with adrenal insufficiency; of these, the majority remained on systemic corticosteroids. Adrenal insufficiency resolved in 17% of the 6 patients.
Hypophysitis
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated hypophysitis. Hypophysitis can present with acute symptoms associated with mass effect such as headache, photophobia, or visual field defects. Hypophysitis can cause hypopituitarism. Initiate hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Hypophysitis occurred in 0.5% (7/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (0.2%) and Grade 2 (0.3%) adverse reactions. Hypophysitis led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 1 (< 0.1%) patient and withholding of LIBTAYO in 2 (0.2%) patients. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 86% (6/7) patients with hypophysitis. Hypophysitis resolved in 14% of the 7 patients. Of the 2 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for hypophysitis, none of the patients reinitiated.
Thyroid Disorders
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated thyroid disorders. Thyroiditis can present with or without endocrinopathy. Hypothyroidism can follow hyperthyroidism. Initiate hormone replacement or medical management as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis occurred in 0.6% (8/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 2 (0.3%) adverse reactions. No patient discontinued LIBTAYO due to thyroiditis. Thyroiditis led to withholding of LIBTAYO in 1 (< 0.1%) patient. Systemic corticosteroids were not required in any patient with thyroiditis. Thyroiditis resolved in 13% of the 8 patients.
Blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased and blood thyroid stimulating hormone decreased have also been reported.
Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism occurred in 3% (39/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (< 0.1%) and Grade 2 (0.9%) adverse reactions. No patient discontinued treatment due to hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism led to withholding of LIBTAYO in 7 (0.5%) patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 8% (3/39) of patients with hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism resolved in 56% of the 39 patients. Of the 7 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for hyperthyroidism, 2 patients reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these, none had recurrence of hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism occurred in 7% (87/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (< 0.1%) and Grade 2 (6%) adverse reactions . Hypothyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 3 (0.2%) patients. Hypothyroidism led to withholding of LIBTAYO in 9 (0.7%) patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 1.1% (1/87) of patients. Hypothyroidism resolved in 6% of the 87 patients. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism required long-term thyroid hormone replacement.
Of the 9 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for hypothyroidism, 1 reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement and did not have recurrence of hypothyroidism.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, which can present with diabetic ketoacidosis
Monitor patients for hyperglycemia or other signs and symptoms of diabetes. Initiate treatment with insulin as clinically indicated. Withhold LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Type 1 diabetes mellitus occurred in < 0.1% (1/1281) of patients (Grade 4). No patient discontinued treatment due to type 1 diabetes mellitus. Type 1 diabetes mellitus led to withholding of LIBTAYO in 0.1% of patients, treatment was reinitiated after symptom improvement. Patient received long-term insulin therapy.
Immune-Mediated Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated nephritis. The definition of immune-mediated nephritis included the required use of systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants and the absence of a clear alternate etiology.
Immune-mediated nephritis occurred in 0.7% (9/1281) patients receiving LIBTAYO, including fatal (< 0.1%), Grade 3 (< 0.1%) and Grade 2 (0.5%) adverse reactions. Nephritis led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 0.2% of patients and withholding of LIBTAYO in 0.4% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in all patients with nephritis. Nephritis resolved in 78% of the 9 patients. Of the 5 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for nephritis, 4 reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these, 1/4 (25%) had recurrence of nephritis.
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
LIBTAYO can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis. The definition of immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reaction included the required use of systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants and the absence of a clear alternate etiology. Exfoliative dermatitis, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and DRESS (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms), has occurred with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate non-exfoliative rashes. Withhold or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions occurred in 1.9% (24/1281) of patients receiving LIBTAYO, including Grade 3 (0.9%) and Grade 2 (0.8%) adverse reactions. Dermatologic adverse reactions led to permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in 0.2% of patients and withholding of LIBTAYO in 1.3% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in all patients with immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions. Immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions resolved in 71% of the 24 patients. Of the 17 patients in whom LIBTAYO was withheld for dermatologic adverse reaction, 13 reinitiated LIBTAYO after symptom improvement; of these 5/13 (38%) had recurrence of the dermatologic adverse reaction.
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant immune-mediated adverse reactions occurred at an incidence of <1% in 1281 patients who received LIBTAYO or were reported with the use of other PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies . Severe or fatal cases have been reported for some of these adverse reactions.
Cardiac/Vascular: Myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis
Nervous System: Meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis and demyelination, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis (including exacerbation), Guillain-Barre syndrome, nerve paresis, autoimmune neuropathy
Ocular: Uveitis, iritis, and other ocular inflammatory toxicities. Some cases can be associated with retinal detachment. Various grades of visual impairment to include blindness can occur. If uveitis occurs in combination with other immune-mediated adverse reactions, consider a Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada like syndrome, as this may require treatment with systemic steroids to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis to include increases in serum amylase and lipase levels, gastritis, duodenitis, stomatitis
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: Myositis/polymyositis/dermatomyositis, rhabdomyolysis and associated sequelae including renal failure, arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica
Endocrine: Hypoparathyroidism
Other (Hematologic/Immune): Hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi lymphadenitis), sarcoidosis, immune thrombocytopenia, solid organ transplant rejection, other transplant (including corneal graft) rejection
Infusion-Related Reactions
Severe or life-threatening infusion-related reactions occurred in 0.2% of patients receiving LIBTAYO as a single agent. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions. Common symptoms of infusion-related reaction include nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion or permanently discontinue LIBTAYO based on severity of reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Complications of Allogeneic HSCT
Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) before or after being treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. Transplant-related complications include hyperacute graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD), acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) after reduced intensity conditioning, and steroid-requiring febrile syndrome (without an identified infectious cause). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and allogeneic HSCT.
Follow patients closely for evidence of transplant-related complications and intervene promptly. Consider the benefit versus risks of treatment with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody prior to or after an allogeneic HSCT.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, LIBTAYO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-mediated rejection of the developing fetus resulting in fetal death. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LIBTAYO and for at least 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling.
- Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in Warnings and Precautions reflect exposure to LIBTAYO as a single agent in 1281 patients with advanced cancers in three open-label, single-arm, multicohort studies, and two open-label randomized multi-center studies. These studies included 384 patients with advanced CSCC (Studies 1540 and 1423), 138 patients with advanced BCC (Study 1620), 355 patients with NSCLC (Study 1624), and 404 patients with other advanced solid tumors. LIBTAYO was administered intravenously at doses of 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (n=235), 350 mg every 3 weeks (n=1014), or other doses (n=32). Among the 1281 patients, 53% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 26% were exposed for one year or longer. In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions (≥15%) were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, diarrhea, and anemia. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (≥2%) were lymphopenia, anemia, hyponatremia, hypophosphatemia, increased aspartate aminotransferase, hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, and increased alanine aminotransferase.
The data below also reflect exposure to LIBTAYO as a single agent (either 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks for 36 weeks or 350 mg every 3 weeks for 48 weeks) in the adjuvant setting in 205 patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence after treatment with surgery and radiation (C-POST study), and LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in 312 patients with NSCLC enrolled in a randomized, active controlled trial (Study 16113).
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC)
Study 1540
The safety of LIBTAYO was evaluated in 358 patients with advanced CSCC (metastatic or locally advanced disease) in Study 1540 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Of these 358 patients, 213 had mCSCC (nodal or distant) and 145 had laCSCC. Patients received LIBTAYO 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (n=137) or 350 mg every 3 weeks (n=221) as an intravenous infusion until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or completion of planned treatment. The median duration of exposure was 40 weeks (1 week to 109 weeks).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 41% of patients. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of patients were pneumonia (3.6%), skin infection (3.6%), and pneumonitis (2.8%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5% of patients who received LIBTAYO, including deaths due to infections (2.2%).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 12% of patients. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation in at least 2 patients were pneumonitis, rash, confusional state, general physical health deterioration, hemorrhage, liver function test abnormalities, and musculoskeletal pain.
Dosage interruptions of LIBTAYO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 36% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥2% of patients included diarrhea, infusion-related reaction, upper respiratory tract infection, liver function test abnormalities, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonitis, and rash.
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, rash, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, pruritus, and nausea. The most common Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (≥2%) were hypertension, skin infection, pneumonia, anemia, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, and pneumonitis. The most common (≥4%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline were lymphopenia, hyponatremia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients and Table 4 summarizes Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline in ≥1% of patients receiving LIBTAYO.
| Adverse Reactions | LIBTAYO N = 358 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | |
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) v.4.03 | ||
| General and Administration Site | ||
| Fatigue Fatigue is a composite term that includes fatigue and asthenia | 38 | 2.2 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||
| Rash Rash is a composite term that includes rash, rash maculo-papular, dermatitis, erythema, eczema, dermatitis bullous, rash erythematous, dermatitis acneiform, psoriasis, dermatitis contact, blister, pemphigoid, rash papular, hand dermatitis, skin exfoliation, autoimmune dermatitis, rash pruritic, rash macular, rash pustular, urticaria, dermatitis atopic, drug eruption, eczema asteatotic, skin reaction, dermatitis psoriasiform, eczema nummular, exfoliative rash, and immune-mediated dermatitis | 34 | 1.7 |
| Pruritus Pruritus is a composite term that includes pruritus and pruritus allergic | 22 | 0.3 |
| Actinic keratosis | 10 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain Musculoskeletal pain is a composite term that includes arthralgia, back pain, myalgia, polyarthritis, pain in extremity, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, bone pain, immune-mediated arthritis, and spinal pain | 33 | 2.5 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Diarrhea Diarrhea is a composite term that includes diarrhea, colitis, and autoimmune colitis | 26 | 1.1 |
| Nausea | 21 | 0 |
| Constipation | 13 | 0.3 |
| Vomiting Vomiting is a composite term that includes hematemesis and vomiting | 11 | 0.6 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infection Upper respiratory tract infection is a composite term that includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, influenza-like illness, rhinitis, influenza, viral upper respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection, influenza A virus test positive, and pharyngitis | 14 | 1.1 |
| Skin infection Skin infection is a composite term that includes skin infection, cellulitis, fungal skin infection, and staphylococcal skin infection | 11 | 4.5 |
| Respiratory | ||
| Cough Cough is a composite term that includes cough, productive cough, and upper airway cough syndrome | 12 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||
| Decreased appetite | 11 | 0.6 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache Headache is a composite term that includes headache, sinus headache, and migraine | 10 | 0 |
| Dizziness Dizziness is a composite term that includes dizziness, vertigo, vertigo positional, and dizziness postural | 10 | 0.3 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | Grade 3-4 (%) Percentages are based on the number of patients with at least 1 post-baseline value available for that parameter |
|---|---|
| Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 4.03 | |
| Hematology | |
| Lymphopenia | 7.0 |
| Anemia | 4.1 |
| Electrolytes | |
| Hyponatremia | 4.9 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 4.1 |
| Hypercalcemia | 2.0 |
| Hypokalemia | 1.5 |
| Coagulation | |
| Increased INR | 2.9 |
| Chemistry | |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 1.5 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 1.2 |
Study 1423
In 26 patients with advanced CSCC treated with LIBTAYO in Study 1423 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] , safety data were consistent with those described above from Study 1540.
Adjuvant treatment of CSCC at high risk of recurrence
C-POST study
The safety of LIBTAYO was evaluated in patients with CSCC at high-risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation in the C-POST study [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
Patients were assigned to receive:
- LIBTAYO 350 mg (n=140) or placebo (n=140) intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 weeks, followed by 700 mg LIBTAYO or placebo intravenously every 6 weeks for an additional 36 weeks, or
- LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks (n=65) or placebo (n=64) for up to 48 weeks.
Treatment continued until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks.
The median duration of exposure was 48 weeks (range: 3 weeks to 52 weeks) in LIBTAYO-treated patients.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients who received LIBTAYO. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in ≥1% of patients in the LIBTAYO arm were pneumonia (1.5%), rash (1.5%), diarrhea (1.5%), adrenal insufficiency (1%), and arrhythmia (1%).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 10% of patients who received LIBTAYO. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation in ≥1% of patients were alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, and adrenal insufficiency.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 22% of patients who received LIBTAYO. Adverse reactions leading to interruptions in ≥1% of patients included COVID-19, diarrhea, alanine aminotransferase increased, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection, aspartate aminotransferase increased, edema, dyspnea, pneumonitis, pneumonia, and rash.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients and Table 6 summarizes Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline in ≥1% of patients receiving LIBTAYO.
| Adverse reactions Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 5. | LIBTAYO N=205 | Placebo N=204 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash Includes multiple related terms | 37 | 2 | 21 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 16 | 0.5 | 12 | 0 |
| Endocrine disorders | ||||
| Hypothyroidism | 12 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | LIBTAYO | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 3-4 (%) The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 201 to 203 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 5 | ||
| Hematology | ||
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 6 | 3 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 3.9 | 0 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 3 | 0.5 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 1.5 | 0 |
| Albumin decreased | 1 | 0 |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Calcium decreased | 1 | 1 |
| Potassium decreased | 1 | 0.5 |
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
The safety of LIBTAYO was evaluated in 138 patients with advanced BCC (mBCC N=54, laBCC N=84) in an open-label, single-arm trial (Study 1620) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Patients received LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion for up to 93 weeks or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median duration of exposure was 45 weeks (range: 2.1 weeks to 98 weeks).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in > 1.5% were diarrhea (3.6%), urinary tract infection (3.6%), pneumonia (2.9%), and hemorrhage (2.2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.3% of patients who received LIBTAYO, including acute kidney injury (0.7%) and cachexia worsening due to colitis (0.7%).
Permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 14% of patients. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of LIBTAYO in at least 2 patients were diarrhea, acute kidney injury, general physical health deterioration, and hepatitis.
Dosage interruptions of LIBTAYO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 40% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruptions in > 2% of patients included diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, acute kidney injury, fatigue, fall, headache, infusion-related reaction, hemorrhage, pneumonitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and urinary tract infection.
The most common adverse reactions reported in at least 15% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, rash, upper respiratory tract infection, pruritus, hemorrhage, and hypertension.
The most common Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were hypertension, diarrhea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, visual impairment, and weight decreased. The most common (> 2%) laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline to Grade 3 or 4 were lymphopenia and hyponatremia.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients and Table 8 summarizes Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline in ≥1% of patients receiving LIBTAYO.
| Adverse Reactions | LIBTAYO N = 138 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | |
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) v.4.03 | ||
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue Fatigue is a composite term that includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise | 50 | 4.3 |
| Edema Edema is a composite term that includes peripheral edema, peripheral swelling, and face swelling | 10 | 0.7 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain Musculoskeletal pain is a composite term that includes arthralgia, back pain, pain in extremity, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, musculoskeletal discomfort, and spinal pain | 36 | 2.9 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea Diarrhea is a composite term that includes diarrhea, colitis, autoimmune colitis, and enterocolitis | 33 | 4.3 |
| Nausea | 13 | 0.7 |
| Abdominal pain Abdominal pain is a composite term that includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, and gastrointestinal pain | 12 | 1.4 |
| Constipation | 12 | 0.7 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Rash is a composite term that includes rash maculo-papular, eczema, rash, dermatitis, erythema, dermatitis acneiform, rash pruritic, rash pustular, dermatitis bullous, dyshidrotic eczema, pemphigoid, rash erythematous, urticaria, nodular rash, and skin exfoliation | 30 | 0.7 |
| Pruritus | 19 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infection Upper respiratory tract infection is a composite term that includes upper respiratory tract infection, influenza-like illness, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, viral rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, respiratory tract infection, influenza, viral upper respiratory tract infection, and influenza A virus test positive | 22 | 0 |
| Urinary tract infection Urinary tract infection is a composite term that includes urinary tract infection, cystitis, and urosepsis | 13 | 2.2 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hemorrhage Hemorrhage is a composite term that includes tumor hemorrhage, hematuria, epistaxis, eye hemorrhage, hemoptysis, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhagic diathesis, postmenopausal hemorrhage, rectal hemorrhage, skin hemorrhage, skin neoplasm bleeding, ulcer hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, wound hemorrhage, and subcutaneous hematoma | 18 | 0.7 |
| Hypertension Hypertension is a composite term that includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, and hypertensive crisis | 17 | 9 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 14 | 1.4 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Anemia | 14 | 0.7 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea Dyspnea is a composite term that includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional | 14 | 0 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | ||
| Acute kidney injury Acute kidney injury is a composite term that includes blood creatinine increased, acute kidney injury, renal failure, renal impairment, glomerular filtration rate decreased, and nephropathy toxic | 14 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 13 | 1.4 |
| Dizziness Dizziness is a composite term that includes dizziness and vertigo | 12 | 0 |
| Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy is a composite term that includes paresthesia, dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, peripheral motor neuropathy, burning sensation, neuralgia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy | 11 | 0 |
| Endocrine disorders | ||
| Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is a composite term that includes hypothyroidism, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased, and immune-mediated hypothyroidism | 12 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Liver function test abnormalities Liver function test abnormalities is a composite term that includes alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, bilirubin conjugated increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood bilirubin increased, and gamma-glutamyl transferase increased | 10 | 1.4 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | Grade 3-4 (%) Percentages are based on the number of patients with at least 1 post-baseline value available for that parameter |
|---|---|
| Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 4.03 | |
| Hematology | |
| Lymphopenia | 2.9 |
| Electrolytes | |
| Hyponatremia | 2.9 |
| Hypokalemia | 1.5 |
| Coagulation | |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged | 1.9 |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
First-line treatment of NSCLC with LIBTAYO in Combination with Platinum-based Chemotherapy
The safety of LIBTAYO in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy was evaluated in 465 patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC in Study 16113 [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ]. Patients received LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks plus platinum-based chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles (n=312), or placebo every 3 weeks plus platinum-based chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles (n=153).
Among patients who received LIBTAYO, 70% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 35% were exposed for greater than one year. The safety population characteristics were: median age of 63 years (25 to 82 years), 41% of patients 65 or older, 86% male, 86% White, 14% Asian, 86% had metastatic disease and 14% had locally advanced disease and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status (PS) of 0 (16%) and 1 (83%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients. The most frequent serious adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of patients were pneumonia, anemia, and neutropenia. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients who received LIBTAYO in combination with chemotherapy, including death not otherwise specified (2.9%), sudden death (1.0%), acute hepatitis (0.3%), acute respiratory distress syndrome (0.3%), mesenteric artery thrombosis (0.3%), pneumonia (0.3%), pneumonitis (0.3%), and pulmonary hemorrhage (0.3%). LIBTAYO was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 5% of patients. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation in at least 2 patients were increased alanine aminotransferase and anemia.
Dosage interruptions of LIBTAYO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 33% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruptions in at least 2% of patients were anemia, pneumonia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, COVID-19 infection, and pyrexia.
The most common (≥15%) adverse reactions were alopecia, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, and decreased appetite. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (≥2%) were anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, leukopenia, hyponatremia, thrombocytopenia, hyperglycemia, hypophosphatemia, increased alanine aminotransferase, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, hypokalemia, and increased creatinine.
Table 9 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients and Table 10 summarizes Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving LIBTAYO and chemotherapy.
| Adverse Reactions | LIBTAYO and Chemotherapy (N=312) | Placebo and Chemotherapy (N=153) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 or 4 % | |
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) v. 4.03 | ||||
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 37 | 0 | 43 | 0 |
| Rash Rash is a composite term that includes rash, rash maculo-papular, dermatitis, psoriasis, rash papular, urticaria, dermatitis allergic, erythema, lichen planus, rash macular, rash pruritic, skin reaction, skin toxicity, skin exfoliation, and dermatitis acneiform | 13 | 1.3 | 6 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain Musculoskeletal pain is a composite term that includes arthralgia, back pain, pain in extremity, non-cardiac chest pain, myalgia, bone pain, musculoskeletal pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, arthritis, and spinal pain | 30 | 1.6 | 36 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 25 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Constipation | 14 | 0.3 | 11 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 11 | 1.3 | 7 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue Fatigue is a composite term that includes asthenia, fatigue, and malaise | 23 | 3.8 | 18 | 2 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy is a composite term that includes peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, polyneuropathy, hypoesthesia, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, neuralgia, polyneuropathy in malignant disease, and toxic neuropathy | 23 | 0 | 19 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 17 | 1 | 12 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight decreased | 11 | 1.3 | 8 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea Dyspnea is a composite term that includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional | 13 | 2.2 | 7 | 0.7 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 11 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | LIBTAYO and Chemotherapy | Placebo and Chemotherapy |
|---|---|---|
| Grades 3 or 4 (%) The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 134 to 299 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 4.03 | ||
| Chemistry | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 4 | 1.5 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 3 | 2.1 |
| Increased creatinine | 2 | 1.4 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 1 | 0 |
| Hematology | ||
| Anemia | 10 | 7 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 10 | 8 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 7 | 8 |
| White blood cell decreased | 6 | 4.1 |
| Platelet count decreased | 4.7 | 0.7 |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Hyponatremia | 6 | 4.1 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 3.4 | 7 |
| Hypocalcemia | 3 | 2.1 |
| Hyperkalemia | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| Hypermagnesemia | 2.4 | 2.8 |
| Hypokalemia | 2.3 | 1.4 |
| Hypercalcemia | 1.7 | 0.7 |
| Hypernatremia | 1 | 0 |
First-line treatment of NSCLC with LIBTAYO as a single agent
The safety of LIBTAYO was evaluated in 355 patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC in Study 1624 [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ]. Patients received LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks (n=355) or investigator's choice of chemotherapy (n=342), consisting of paclitaxel plus cisplatin or carboplatin; gemcitabine plus cisplatin or carboplatin; or pemetrexed plus cisplatin or carboplatin followed by optional pemetrexed maintenance. The median duration of exposure was 27.3 weeks (9 days to 115 weeks) in the LIBTAYO group and 17.7 weeks (18 days to 86.7 weeks) in the chemotherapy group. In the LIBTAYO group, 54% of patients were exposed to LIBTAYO for ≥6 months and 22% were exposed for ≥12 months.
The safety population characteristics were: median age of 63 years (31 to 79 years), 44% of patients 65 or older, 88% male, 86%White, 82% had metastatic disease and 18% had locally advanced disease, and ECOG performance score (PS) of 0 (27%) and 1 (73%).
LIBTAYO was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 6% of patients; adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation in at least 2 patients were pneumonitis, pneumonia, ischemic stroke, and increased aspartate aminotransferase. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 28% of patients. The most frequent serious adverse reactions in at least 2% of patients were pneumonia and pneumonitis.
Table 11 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients and Table 12 summarizes Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving LIBTAYO.
| Adverse Reactions | LIBTAYO N=355 | Chemotherapy N=342 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | |
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) v.4.03 | ||||
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain Musculoskeletal pain is a composite term that includes back pain, arthralgia, pain in extremity, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, bone pain, myalgia, neck pain, spinal pain, and musculoskeletal stiffness | 26 | 0.6 | 27 | 1.5 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash Rash is a composite term that includes rash, dermatitis, urticaria, rash maculo-papular, erythema, rash erythematous, rash pruritic, psoriasis, autoimmune dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis bullous, drug eruption, dyshidrotic eczema, lichen planus, and skin reaction | 15 | 1.4 | 6 | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Anemia | 15 | 3.4 | 50 | 16 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue Fatigue is a composite term that includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise | 14 | 1.1 | 26 | 2 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 12 | 0.6 | 18 | 0.3 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Pneumonia Pneumonia is a composite term that includes atypical pneumonia, embolic pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, lung abscess, paracancerous pneumonia, pneumonia, pneumonia bacterial, and pneumonia klebsiella | 11 | 5 | 12 | 5 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough Cough is a composite term that includes cough and productive cough | 11 | 0 | 8 | 0.3 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | LIBTAYO N=355 | Chemotherapy N=342 |
|---|---|---|
| Grades 3-4 Percentages are based on the number of patients with at least 1 post-baseline value available for that parameter % | ||
| Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE v. 4.03 | ||
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 3.9 | 1.2 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 2.7 | 0.3 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 2.4 | 0.3 |
| Increased blood bilirubin | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 1.8 | 1.3 |
| Increased creatinine | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| Hematology | ||
| Lymphopenia | 7 | 9 |
| Anemia | 2.7 | 16 |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Hyponatremia | 6 | 7 |
| Hyperkalemia | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| Hypocalcemia | 3.9 | 3.4 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 2.4 | 4.1 |
| Hypermagnesemia | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| Hypokalemia | 1.5 | 2.2 |
| Hypercalcemia | 1.2 | 2.2 |
DESCRIPTION
Cemiplimab-rwlc is a human programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody. Cemiplimab-rwlc is a recombinant human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1 and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2. Cemiplimab-rwlc is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell suspension culture. Cemiplimab-rwlc has an approximate molecular weight of 146 kDa.
LIBTAYO (cemiplimab-rwlc) injection for intravenous use is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution with a pH of 6. The solution may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles.
Each vial contains 350 mg of cemiplimab-rwlc. Each mL contains cemiplimab-rwlc 50 mg, L-histidine (0.74 mg), L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (1.1 mg), sucrose (50 mg), L-proline (15 mg), polysorbate 80 (2 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Binding of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors and signaling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors.
Cemiplimab-rwlc is a recombinant human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1 and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.
Pharmacodynamics
Cemiplimab exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are not fully characterized.
Pharmacokinetics
Cemiplimab-rwlc pharmacokinetics were observed at steady state in patients with various solid tumors and are presented as mean (% coefficient of variation) unless otherwise specified. The pharmacokinetics of cemiplimab-rwlc increase in a dose proportional manner over the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg (0.2 to 2 times the highest recommended approved dose; assuming a 70 kg patient) administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
At a dosing regimen of 350 mg every 3 weeks, cemiplimab-rwlc minimum concentration is 59 mg/L (47%) and maximum concentration is 171 mg/L (27%). Steady-state is reached in about 4 months.
At a dosing regimen of 350 mg every 3 weeks for 12 weeks followed by 700 mg every 6 weeks, cemiplimab-rwlc minimum concentration after 30 weeks is 50 mg/L (32%).
Distribution
The volume of distribution of cemiplimab-rwlc is 5.9 L (29%).
Elimination
Cemiplimab-rwlc clearance after the first dose is 0.25 L/day (41%) and decreases over time by 11%, resulting in a steady-state clearance of 0.22 L/day (44%). The elimination half-life is 22 days (42%).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of cemiplimab-rwlc were observed based on age (27 to 96 years), race [White (N=932), Asian (N=47), Black (N=21)], sex, body weight (31 to 172 kg), cancer type, albumin level (20 to 93 g/L), renal function (creatinine clearance determined by Cockcroft-Gault) and hepatic function (total bilirubin ≥1 to 3× ULN). The effect of severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin 3× ULN) on the pharmacokinetics of cemiplimab-rwlc is unknown.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of cemiplimab-rwlc or of other cemiplimab products.
During a treatment period ranging from 8 to 19 months in 5 clinical studies, 2% (22/1029) of LIBTAYO-treated patients developed anti-cemiplimab-rwlc antibodies.
There was no clinically significant effect of anti-cemiplimab-rwlc antibodies on PK of cemiplimab-rwlc. Because of the low occurrence of anti-drug antibodies, the effect of these antibodies on the pharmacodynamics, safety, and/or effectiveness of cemiplimab products is unknown.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been performed to assess the potential of cemiplimab-rwlc for carcinogenicity or genotoxicity.
In a 3-month repeat-dose toxicology study in sexually mature cynomolgus monkeys, there were no cemiplimab-rwlc-related effects on fertility parameters (menstrual cycle, semen analysis, or testicular measurements) or in male or female reproductive organs at doses up to the highest dose tested, 50 mg/kg/week (approximately 5.5 to 25.5 times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 350 mg once every 3 weeks).
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In animal models, inhibition of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling increased the severity of some infections and enhanced inflammatory responses. M. tuberculosis –infected PD-1 knockout mice exhibit markedly decreased survival compared with wild-type controls, which correlated with increased bacterial proliferation and inflammatory responses in these animals. PD-L1 and PD-1 knockout mice and mice receiving PD-L1 blocking antibody have also shown decreased survival following infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC)
Advanced CSCC
The efficacy of LIBTAYO in patients with metastatic (nodal or distant) cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) who were not candidates for curative surgery or curative radiation was evaluated in two open-label, multi-center, non-randomized, multicohort studies: Study 1423 (NCT02383212) and Study 1540 (NCT02760498). Both studies excluded patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy with immunosuppressant agents within 5 years; history of solid organ transplant; prior treatment with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies or other immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy; infection with HIV, hepatitis B or hepatitis C; or ECOG PS ≥2.
Patients received LIBTAYO 3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks for up to 48 weeks in Study 1423 or up to 96 weeks (Groups 1 and 2), or 350 mg every 3 weeks for up to 54 weeks (Group 3) in Study 1540. Treatment continued until progression of disease, unacceptable toxicity, or completion of planned treatment. Tumor response assessments were performed every 8 or 9 weeks. The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed objective response rate (ORR), defined as complete response (CR) plus partial response (PR) as assessed by independent central review (ICR), and ICR-assessed duration of response (DOR). For patients with mCSCC without externally visible target lesions, ORR was determined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST 1.1). For patients with externally visible target lesions (laCSCC and mCSCC), ORR was determined by a composite endpoint that integrated ICR assessments of radiologic data (RECIST 1.1) and digital medical photography (WHO criteria).
Study 1540
In the efficacy analysis of 193 patients with advanced CSCC enrolled in Study 1540 who received LIBTAYO at either 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 350 mg every three weeks, 115 had mCSCC and 78 had laCSCC. The median age was 72 years (38 to 96 years); 83% were male; 97% were White, 2% were Asian, 1% were Black or African American, and 1% were race unknown; 45% had ECOG PS 0 and 55% had ECOG PS 1; 34% received at least one prior anti-cancer systemic therapy; 81% received prior cancer-related surgery; and 68% received prior radiotherapy. Among patients with mCSCC, 77% had distant metastases and 23% had only nodal metastases.
For the responding patients presented in Table 13 below, the median time to response was 2.1 months (range: 1.7 to 22.8 months).
Efficacy results based on the final analysis of Study 1540 are presented in Table 13.
| Efficacy Endpoints Median duration of follow up: mCSCC 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks: 18.5 months; laCSCC 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks: 15.5 months; mCSCC 350 mg every 3 weeks: 17.3 months; combined CSCC: 15.7 months | Metastatic CSCC LIBTAYO 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (Group 1) | Locally Advanced CSCC LIBTAYO 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (Group 2) | Metastatic CSCC LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks (Group 3) | Combined CSCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 59 | N = 78 | N = 56 | N = 193 | |
| CI: confidence interval; NR: not reached | ||||
| Confirmed Objective Response Rate (ORR) (%) | ||||
| ORR (95% CI) | 51 (37, 64) | 45 (34, 57) | 46 (33, 60) | 47 (40, 54) |
| Complete response rate Only includes patients with complete healing of prior cutaneous involvement; laCSCC patients in Study 1540 required biopsy to confirm CR | 20 | 13 | 20 | 17 |
| Partial response rate | 31 | 32 | 27 | 30 |
| Duration of Response (DOR) | ||||
| Number of Responders | N = 30 | N = 35 | N = 26 | N = 91 |
| Median DOR in months Based on Kaplan-Meier estimate (Range) | NR (2.8 – 38.9) | 42 (1.9 – 54.6) | 41 (4.2 – 46.3) | 41 (1.9 – 54.6) |
| Patients with observed DOR ≥6 months, n (%) The numerator includes the number of patients whose observed DOR reached at least the specified times of 6 or 12 months. Patients who did not have the opportunity to reach the specified timepoint were included in the denominator only | 28 (93%) | 31 (89%) | 25 (96%) | 84 (92%) |
| Patients with observed DOR ≥12 months, n (%) | 23 (77%) | 24 (69%) | 23 (88%) | 70 (77%) |
Study 1423
Among 26 CSCC patients in Study 1423, 16 had mCSCC and 10 had laCSCC. The median age was 73 years (52 to 88 years); 81% of patients were male; 92% of patients were White; the ECOG PS was 0 (38%) and 1 (62%); 58% of patients had received at least 1 prior anti-cancer systemic therapy; 92% of patients had received prior cancer-related surgery and 81% had received prior radiotherapy. One patient in the mCSCC group was dosed at 1 mg/kg. The rest received 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks.
With a median duration of follow-up of 13.3 months, the confirmed ORR was 50% (95% CI: 30, 70); all responses were PRs. The median time to response was 1.9 months (range: 1.7 to 7.3 months) and 85% of responders had a DOR ≥6 months.
Adjuvant treatment of CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation.
The efficacy of LIBTAYO was evaluated in the C-POST study (NCT03969004), a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial in 415 patients with CSCC at high risk of recurrence after surgery and radiation. Patients were required to complete adjuvant radiation therapy within 2 to 10 weeks of randomization. High risk of recurrence was defined as at least one of the following features:
- Nodal Features:
- Extracapsular extension (ECE) with ≥1 node ≥20 mm, or
- ≥3 involved lymph nodes regardless of ECE
- Non-Nodal Features:
- In-transit metastases (skin or subcutaneous metastases > 2 cm from the primary lesion but not beyond the regional nodal basin),
- Invasion of the skeleton or base of the skull (T4 Lesion),
- Perineural Invasion, or
- Locally recurrent tumor with ≥1 additional adverse feature listed below:
- Multiple ipsilateral nodes
- ≥T3 (≥4 cm diameter or bone erosion or invasion >6 mm)
- Poorly differentiated histology and recurrent lesion ≥20 mm diameter
The study excluded patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy with immunosuppressant agents within 5 years; history of solid organ transplant; prior allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation; uncontrolled HIV, hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection, or ECOG PS ≥2.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive LIBTAYO (N=209) or placebo (n=206). In the LIBTAYO arm, 171 patients received 350 mg LIBTAYO intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 weeks, followed by 700 mg LIBTAYO intravenously every 6 weeks for an additional 36 weeks, and 38 patients received 350 mg LIBTAYO intravenously every 3 weeks for up to 48 weeks. Treatment continued until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 48 weeks.
The major efficacy outcome measure was disease-free survival (DFS) defined as time from randomization to the first documented disease recurrence by investigator assessment or death due to any cause. Overall survival was an additional outcome measure.
The median age was 71 years (range: 33 to 95); 84% were male; 91% were White, 3.1% were Asian, 5.4% were unknown or not reported, 0.5% were other; 9.4% were Hispanic or Latino, 83.4% were not Hispanic or Latino, 7% were unknown or not reported; 64% had ECOG PS of 0 and 36% had ECOG PS of 1. The location of tumor was head and neck (HN) in 83% of patients and non-HN in 17% of patients. The high-risk of recurrence feature was nodal in 58% of patients and non-nodal in 42% of patients.
A statistically significant improvement in DFS was demonstrated in patients randomized to LIBTAYO compared with placebo. Improvement in DFS was similar in both dosage regimens. Efficacy results in C-POST study are summarized in Table 14 and Figure 1.
| Efficacy Endpoints | LIBTAYO | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| N = 209 | N = 206 | |
| CI: confidence interval; NE: not evaluable; NR: not reached | ||
| Disease-Free Survival (DFS) | ||
| Number of events, n (%) | 24 (12%) | 65 (32%) |
Disease recurrences, n (%)
| 18 (9%) 10 (4.8%) 8 (3.8%) | 61 (30%) 26 (13%) 35 (17%) |
| Deaths, n (%) | 6 (2.9%) | 4 (1.9%) |
| Median (95% CI) in months Based on Kaplan-Meier method | NR (NE, NE) | 49.4 (48.5, NE) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Based on stratified proportional hazards model | 0.32 (0.20, 0.51) | |
| p-value Based on a two-sided stratified log-rank test | <0.0001 | |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve of DFS in the C-POST study
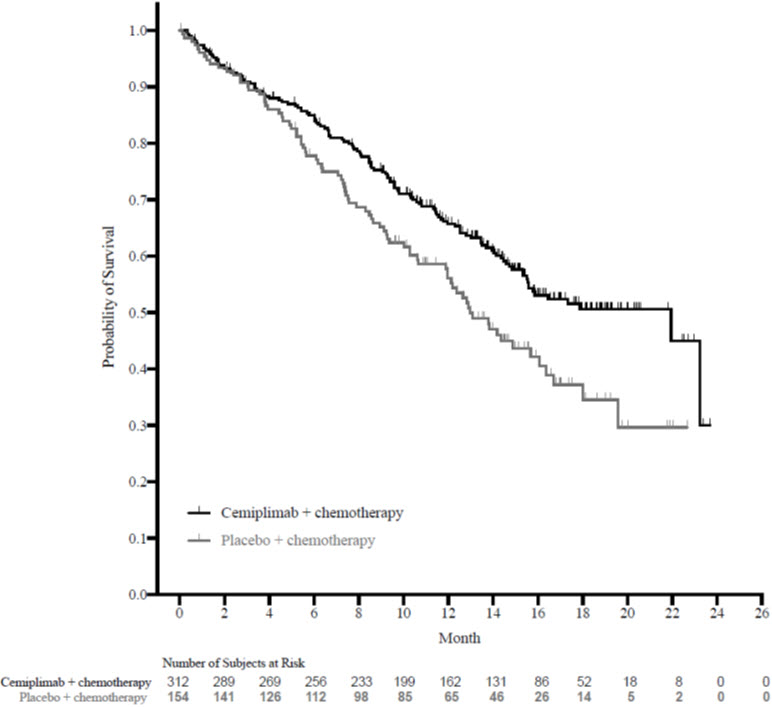
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
The efficacy of LIBTAYO in 138 patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) [unresectable locally advanced (laBCC) or metastatic (nodal or distant) (mBCC)] who had progressed on hedgehog pathway inhibitor (HHI) therapy, had not had an objective response after 9 months on HHI therapy, or were intolerant of prior HHI therapy was evaluated in Study 1620 (NCT03132636), an open-label, multi-center, non-randomized study. The study excluded patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy with immunosuppressant agents within 5 years; history of solid organ transplant; prior treatment with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy or other immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy; infection with HIV, hepatitis B or hepatitis C; or ECOG performance score (PS) ≥2.
Patients received LIBTAYO 350 mg every 3 weeks for up to 93 weeks until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or completion of planned treatment. Tumor assessments were performed every 9 weeks for the first 45 weeks of treatment and every 12 weeks thereafter. The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) as assessed by independent central review (ICR). For patients with mBCC without externally visible target lesions, ORR was determined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST 1.1). For patients with externally visible target lesions (laBCC and mBCC), ORR was determined by a composite endpoint that integrated ICR assessments of radiologic data (RECIST 1.1) and digital medical photography (WHO criteria).
A total of 138 patients with advanced BCC were included in the efficacy analysis of Study 1620. Of these, 39% had mBCC and 61% had laBCC. In patients with laBCC, the median age was 70 years (42 to 89 years); 67% were male; 68% were White and 32% were race not reported/unknown; 61% had ECOG PS 0 and 39% had ECOG PS 1; 83% had received at least 1 prior cancer-related surgery; and 50% had received prior radiotherapy. In patients with mBCC, the median age was 63.5 years (38 to 90 years); 70% were male; 87% were White and 13% were race not reported/unknown; 67% had ECOG PS 0 and 33% had ECOG PS 1; 85% had received at least 1 prior cancer-related surgery; and 59% had received prior radiotherapy. Among patients with mBCC, 35% had distant metastases only, 9% had nodal disease only, and 54% had both distant and nodal disease.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 15. For the responding patients, the median time to response was 3.1 months (range 2 to 10.5 months) for the mBCC group and 4.3 months (range 2.1 to 21.4 months) for the laBCC group.
| Efficacy Endpoints Median duration of follow up: mBCC 8.4 months; laBCC 15.9 months | Metastatic BCC | Locally Advanced BCC |
|---|---|---|
| N = 54 | N = 84 | |
| CI: confidence interval; NR: not reached; +: denotes ongoing at last assessment | ||
| Confirmed Objective Response Rate (ORR) (%) | ||
| ORR (95% CI) | 22 (12, 36) | 32 (22, 43) |
| Complete response rate | 1.9 | 7 |
| Partial response rate | 20 | 25 |
| Duration of Response | ||
| Number of Responders | N = 12 | N = 27 |
| Median DOR in months Based on Kaplan-Meier estimate (Range) | 16.7 (9.0 – 25.8+) | NR (2.1 – 36.8+) |
| Patients with observed DOR ≥6 months, n (%) | 12 (100%) | 23 (85%) |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
First-line treatment of NSCLC with LIBTAYO in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy
The efficacy of LIBTAYO in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy was evaluated in Study 16113 (NCT03409614), a randomized, multi-center, double-blind, active-controlled trial in 466 patients with locally advanced NSCLC who were not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation or with metastatic NSCLC who had not previously received systemic treatment for metastatic NSCLC. Patients were eligible regardless of tumor PD-L1 expression status.
Patients with EGFR, ALK or ROS1 genomic tumor aberrations; a medical condition that required systemic immunosuppression; or ongoing or recent autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy were ineligible. Patients with a history of brain metastases were eligible if they had been adequately treated and had neurologically returned to baseline for at least 2 weeks prior to randomization.
Randomization was stratified by histology (non-squamous vs squamous) and PD-L1 expression (<1% versus 1% to 49% versus ≥50%) according to the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) assay. Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either:
- LIBTAYO 350 mg intravenously (IV) every 3 weeks for 108 weeks plus platinum-based chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles, or
- placebo IV every 3 weeks for 108 weeks plus platinum-based chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles.
Platinum-based chemotherapy in either arm consisted of carboplatin AUC of 5 or 6 and paclitaxel 200 mg/m 2 ; cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 and paclitaxel 200 mg/m 2 ; carboplatin AUC of 5 or 6 and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 ; or cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 . Maintenance pemetrexed was mandatory for patients with non-squamous NSCLC who received a pemetrexed-containing chemotherapy regimen in the first 4 treatment cycles.
Study treatment continued until RECIST 1.1-defined progressive disease, unacceptable toxicity, or 108 weeks. Assessment of tumor status was performed every 9 weeks during year 1 and every 12 weeks after year 1. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS). Additional efficacy outcome measures were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall response rate (ORR) as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR).
The study population characteristics were: median age of 63 years (range: 25 to 84), 40% age 65 or older; 84% male; 87% White, 13% Asian. Fifteen percent had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status (PS) 0 and 84% had ECOG PS 1; 85% had metastatic disease and 15% had stage IIIB or IIIC disease and were not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation per investigator assessment; 57% had non-squamous and 43% had squamous histology; and 7% had history of treated brain metastases at baseline.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS for patients randomized to LIBTAYO in combination with chemotherapy compared with placebo in combination with chemotherapy.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 16 and Figure 2.
| Endpoints | LIBTAYO and Chemotherapy N=312 | Placebo and Chemotherapy N=154 |
|---|---|---|
| BICR: blinded independent central review; CI: confidence interval; NE: not evaluable; +: ongoing response | ||
| Overall Survival | ||
| Deaths, n (%) | 132 (42) | 82 (53) |
| Median in months (95% CI) Based on Kaplan-Meier method | 21.9 (15.5, NE) | 13.0 (11.9, 16.1) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Based on stratified proportional hazards model | 0.71 (0.53, 0.93) | |
| p-value Based on a two-sided p-value | 0.0140 | |
| Progression-free Survival per BICR | ||
| Events, n (%) | 204 (65) | 122 (79) |
| Median in months (95% CI) | 8.2 (6.4, 9.3) | 5.0 (4.3, 6.2) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.56 (0.44, 0.70) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Overall Response Rate per BICR (%) | ||
| ORR (95% CI) Clopper-Pearson exact confidence interval | 43 (38, 49) | 23 (16, 30) |
| Complete response (CR) rate | 2.6 | 0 |
| Partial response (PR) rate | 41 | 23 |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Duration of Response per BICR | ||
| Median in months(range) | 15.6 (1.7, 18.7+) | 7.3 (1.8, 18.8+) |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Curve for OS from Study 16113
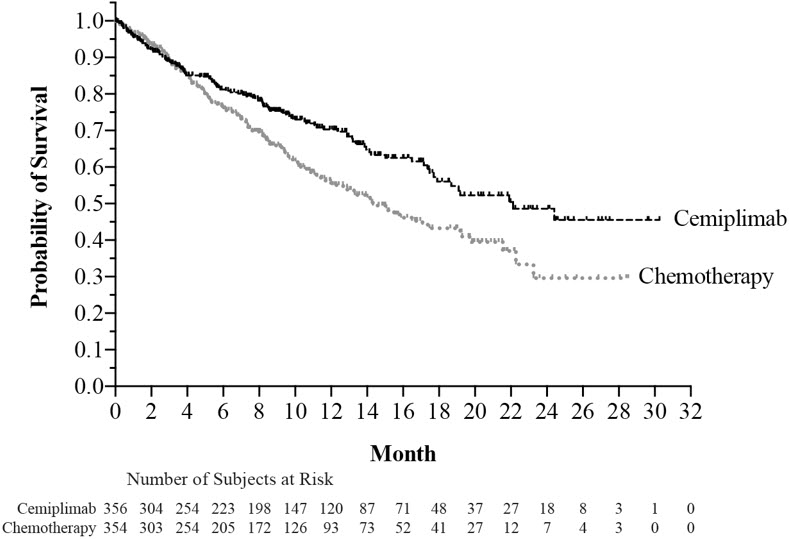
First-line treatment of NSCLC with LIBTAYO as a single agent
The efficacy of LIBTAYO was evaluated in Study 1624 (NCT03088540), a randomized, multi-center, open-label, active-controlled trial in 710 patients with locally advanced NSCLC who were not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation, or with metastatic NSCLC.
Only patients whose tumors had high PD-L1 expression [Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) ≥50%] as determined by an immunohistochemistry assay using the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx kit and who had not received prior systemic treatment for metastatic NSCLC were eligible.
Patients with EGFR, ALK or ROS1 genomic tumor aberrations; a medical condition that required systemic immunosuppression; autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy within 2 years of treatment; or who had never smoked were ineligible. Patients with a history of brain metastases were eligible if they had been adequately treated and had neurologically returned to baseline for at least 2 weeks prior to randomization.
Randomization was stratified by histology (non-squamous vs squamous) and geographic region (Europe vs Asia vs Rest of world). Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive LIBTAYO 350 mg intravenously (IV) every 3 weeks for up to 108 weeks or a platinum-doublet chemotherapy regimen for 4 to 6 cycles followed by optional pemetrexed maintenance for patients with non-squamous histology who received a pemetrexed containing regimen.
Treatment with LIBTAYO continued until RECIST 1.1-defined progressive disease, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 108 weeks. Patients who experienced IRC-assessed RECIST 1.1-defined progressive disease on LIBTAYO therapy were permitted to continue treatment with LIBTAYO (up to an additional 108 weeks) with the addition of 4 cycles of histology-specific chemotherapy until further progression was observed. Of the 203 patients randomized to receive chemotherapy who had IRC-assessed RECIST 1.1- defined disease progression, 150 (74%) patients crossed over to treatment with LIBTAYO. Assessment of tumor status was performed every 9 weeks. The major efficacy outcome measures were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). An additional efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR).
The study population characteristics were: median age of 63 years (range: 31 to 84), 45% age 65 or older; 85% male; 86% White, 11% Asian, and 0.6% Black. Nine percent were Hispanic or Latino. Twenty-seven percent had ECOG PS 0 and 73% had ECOG PS 1; 84% had metastatic disease and 16% had stage IIIB or IIIC disease and were not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation per investigator assessment; 56% had non-squamous and 44% had squamous histology; and 12% had history of treated brain metastases at baseline.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS and PFS for patients randomized to LIBTAYO as compared with chemotherapy.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 17 and Figure 3.
| Endpoints | LIBTAYO N=356 | Chemotherapy N=354 |
|---|---|---|
| BICR: blinded independent central review; CI: confidence interval; NE: not evaluable; +: ongoing response | ||
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of deaths (%) | 108 (30) | 141 (40) |
| Median in months (95% CI) Based on Kaplan-Meier method | 22.1 (17.7, NE) | 14.3 (11.7, 19.2) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Based on stratified proportional hazards model | 0.68 (0.53, 0.87) | |
| p-value | 0.0022 | |
| Progression-free Survival per BICR | ||
| Number of events (%) | 201 (57) | 262 (74) |
| Median in months (95% CI) | 6.2 (4.5, 8.3) | 5.6 (4.5, 6.1) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.59 (0.49, 0.72) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Overall Response Rate per BICR (%) Clopper-Pearson exact confidence interval | ||
| ORR (95% CI) | 37 (32, 42) | 21 (17, 25) |
| Complete response (CR) rate | 3 | 1 |
| Partial response (PR) rate | 33 | 20 |
| Duration of Response per BICR | ||
| Median in months (range) | 21.0 (1.9+, 23.3+) | 6.0 (1.3+, 16.5+) |
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curve for OS from Study 1624
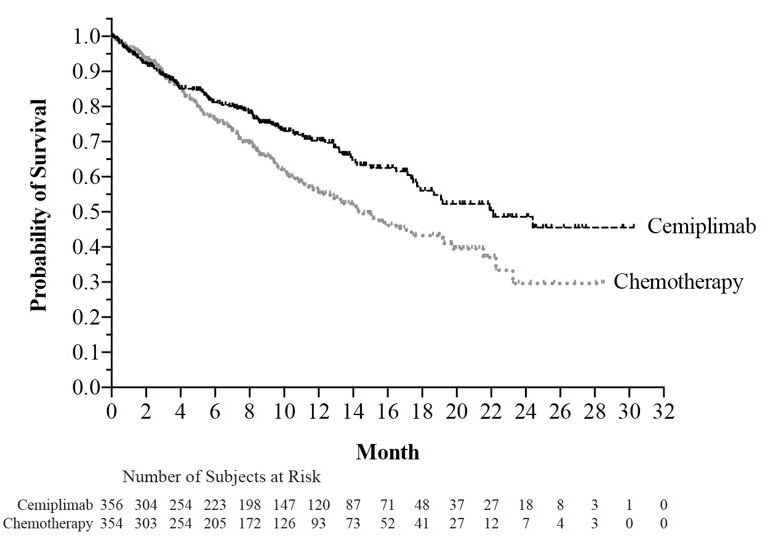
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LIBTAYO (cemiplimab-rwlc) injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles. It is supplied in a carton containing 1 single-dose vial of:
- 350 mg/7 mL (50 mg/mL) (NDC 61755-008-01)
Store in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton. Protect from light.
Do not freeze or shake.
Mechanism of Action
Binding of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors and signaling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors.
Cemiplimab-rwlc is a recombinant human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1 and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.