Litfulo prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Litfulo patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Evaluations and Immunizations Prior to Treatment Initiation
Perform the following evaluations prior to LITFULO initiation:
- Tuberculosis (TB) infection evaluation: LITFULO initiation is not recommended in patients with active TB. For patients with latent TB or those with a negative latent TB test who are at high risk for TB, start preventive therapy for latent TB prior to initiation of LITFULO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines: LITFULO initiation is not recommended in patients with hepatitis B or hepatitis C [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Treatment with LITFULO should not be initiated in patients with an absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) <500/mm 3 or a platelet count <100,000/mm 3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
- Update immunizations according to current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of LITFULO is 50 mg orally once daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Swallow capsules whole. Do not crush, split, or chew LITFULO capsules.
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible unless it is less than 8 hours before the next dose, in which case, skip the missed dose. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
LITFULO is not recommended in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Treatment Interruption or Discontinuation
If treatment interruption is indicated, a temporary treatment interruption for less than 6 weeks is not expected to result in significant loss of regrown scalp hair.
Hematologic Abnormalities
Recommendations for LITFULO treatment interruption or discontinuation for hematologic abnormalities are summarized in Table 1.
| Laboratory Measure | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| ALC = absolute lymphocyte count. | |
Platelet Count | Treatment should be discontinued if platelet count is <50,000/mm 3 |
Lymphocytes | Treatment should be interrupted if ALC is <500/mm 3 and may be restarted once ALC return above this value. |
ALC and platelet counts are recommended before treatment initiation and at 4 weeks after treatment initiation, and thereafter according to routine patient management [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .

Litfulo prescribing information
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS, MORTALITY, MALIGNANCY, MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS (MACE), and THROMBOSIS
- Increased risk of serious bacterial, fungal, viral and opportunistic infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB). Interrupt treatment if serious infection occurs until the infection is controlled. LITFULO should not be given to patients with active tuberculosis. Test for latent TB before and during therapy; treat latent TB prior to use. Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even patients with initial negative, latent TB test. (5.1 )
- Higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death with another Janus kinase inhibitor (JAK) vs. TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. LITFULO is not approved for use in RA patients. (5.2 )
- Malignancies have occurred in patients treated with LITFULO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . Higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancers with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. (5.3 )
- Higher rate of MACE (defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke) with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. (5.4 )
- Thrombosis has occurred in patients treated with LITFULO. Increased incidence of pulmonary embolism, venous and arterial thrombosis with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers. (5.5 )
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LITFULO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of severe alopecia areata in adults and adolescents 12 years and older.
Limitations of Use : Not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, cyclosporine or other potent immunosuppressants.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Evaluations and Immunizations Prior to Treatment Initiation
Perform the following evaluations prior to LITFULO initiation:
- Tuberculosis (TB) infection evaluation: LITFULO initiation is not recommended in patients with active TB. For patients with latent TB or those with a negative latent TB test who are at high risk for TB, start preventive therapy for latent TB prior to initiation of LITFULO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines: LITFULO initiation is not recommended in patients with hepatitis B or hepatitis C [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Treatment with LITFULO should not be initiated in patients with an absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) <500/mm 3 or a platelet count <100,000/mm 3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
- Update immunizations according to current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of LITFULO is 50 mg orally once daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Swallow capsules whole. Do not crush, split, or chew LITFULO capsules.
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible unless it is less than 8 hours before the next dose, in which case, skip the missed dose. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
LITFULO is not recommended in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Treatment Interruption or Discontinuation
If treatment interruption is indicated, a temporary treatment interruption for less than 6 weeks is not expected to result in significant loss of regrown scalp hair.
Hematologic Abnormalities
Recommendations for LITFULO treatment interruption or discontinuation for hematologic abnormalities are summarized in Table 1.
| Laboratory Measure | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| ALC = absolute lymphocyte count. | |
Platelet Count | Treatment should be discontinued if platelet count is <50,000/mm 3 |
Lymphocytes | Treatment should be interrupted if ALC is <500/mm 3 and may be restarted once ALC return above this value. |
ALC and platelet counts are recommended before treatment initiation and at 4 weeks after treatment initiation, and thereafter according to routine patient management [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 50 mg of ritlecitinib, size 3, opaque capsules with yellow body and blue cap. The body is printed with “RCB 50” and the cap is printed with “Pfizer” in black.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
If a patient becomes pregnant while receiving LITFULO, healthcare providers should report LITFULO exposure by calling 1-877-390-2940.
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials with LITFULO use in pregnant women are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of ritlecitinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis caused fetotoxicity and fetal malformations at exposures 49 and 55 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on area under the curve (AUC) comparison, respectively (see Animal Data ) .
The background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. All pregnancies carry some risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risks in the U.S. general population of major birth defects and miscarriages are 2-4% and 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats, oral administration of ritlecitinib from gestation days 6 to 17 decreased fetal body weights and caused fetal skeletal malformations (malformed vertebrae and ribs) and variations (delayed ossification) at doses ≥175 mg/kg/day (49 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Maternal toxicity (lower body weights) was noted at 325 mg/kg/day (102 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). There was no developmental toxicity at 75 mg/kg/day (16 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits, oral administration of ritlecitinib from gestation days 7 to 19 decreased mean fetal body weights and increased visceral malformations (malpositioned kidneys), skeletal malformations (supernumerary sternebrae, absent thoracic arch, and/or fused thoracic centra), and skeletal variations (delayed ossification) at 75 mg/kg/day (55 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). There was no developmental toxicity at doses up to 25 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, oral administration of ritlecitinib from gestation day 6 through lactation day 20 had no effects on pre- and postnatal development at doses up to 75 mg/kg/day (14 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). At 175 mg/kg/day (41 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison), ritlecitinib caused adverse lower postnatal survival and lower offspring body weights, which correlated with delayed sexual maturation in both sexes. Bred females in the F 1 generation also exhibited lower mean numbers of corpora lutea at 175 mg/kg/day.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of ritlecitinib in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Ritlecitinib is present in the milk of lactating rats (see Data ) . When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that it will be present in human milk. Because of the serious adverse effects in adults, including risks of serious infection and malignancy, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with LITFULO and for approximately 14 hours after the last dose (approximately 6 elimination half-lives).
Data
After a single oral 30 mg/kg dose of ritlecitinib to lactating rats, ritlecitinib concentrations in milk over time were higher than those in plasma. The mean milk to plasma AUC ratio was 2.2.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LITFULO for the treatment of alopecia areata have been established in pediatric patients ages 12 years and older. A total of 181 pediatric patients ages 12 to <18 years were enrolled in alopecia areata clinical trials, with 105 pediatric patients ages 12 to <18 years with alopecia areata randomized in a pivotal, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Trial AA-I). Efficacy was consistent between the pediatric patients and adults [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . The adverse reaction profile in the pediatric patients was similar to adults.
The safety and efficacy of LITFULO have not been established in pediatric patients under 12 years of age.
Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is required for patients ≥65 years of age.
A total of 28 patients enrolled in alopecia areata trials were 65 years of age and older, and none were 75 years of age and older. Clinical trials of LITFULO did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
As there is a higher incidence of infections in the elderly population in general, caution should be used when treating the elderly.
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment.
LITFULO is not recommended in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LITFULO is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to ritlecitinib or any of its excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: Discontinue LITFULO if a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs. (5.6 )
- Laboratory Abnormalities: Perform ALC and platelet counts prior to LITFULO initiation. Treatment interruption or discontinuation are recommended based on ALC and platelet count abnormalities. (5.7 )
- Vaccinations: Avoid use of live vaccines during or shortly prior to LITFULO treatment. (5.8 )
Serious Infections
Serious infections have been reported in patients receiving LITFULO. The most frequent serious infections have been appendicitis, COVID-19 infection (including pneumonia), and sepsis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Among opportunistic infections, multi-dermatomal herpes zoster was reported with LITFULO.
Avoid use of LITFULO in patients with an active, serious infection. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating LITFULO in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection
- who have been exposed to TB
- with a history of serious infection or an opportunistic infection
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic TB or mycoses, or
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with LITFULO. Interrupt LITFULO if a patient develops a serious or opportunistic infection. A patient who develops a new infection during treatment with LITFULO should undergo prompt and complete diagnostic testing appropriate for an immunocompromised patient, appropriate antimicrobial therapy should be initiated, and the patient should be closely monitored. LITFULO may be resumed once the infection is controlled.
Tuberculosis
Screen patients for tuberculosis (TB) before starting therapy. LITFULO should not be given to patients with active TB. Anti-TB therapy should be started prior to initiating therapy with LITFULO in patients with a new diagnosis of latent TB or previously untreated latent TB. In patients with a negative latent TB test, consider anti-TB therapy before initiating treatment with LITFULO in those at high risk and consider screening patients at high risk for TB during treatment with LITFULO.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation, including cases of herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster), was reported in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . If a patient develops herpes zoster, consider interrupting treatment until the episode resolves.
Screening for viral hepatitis should be performed in accordance with clinical guidelines before starting therapy with LITFULO. Patients with evidence of HIV infection or hepatitis B or C infection were excluded from clinical trials.
Mortality
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study of another JAK inhibitor in RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, a higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, was observed in patients treated with the JAK inhibitor compared with TNF blockers. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with LITFULO.
Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Malignancies, including non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), were observed in clinical trials of LITFULO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study of another JAK inhibitor in RA patients, a higher rate of malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) was observed in patients treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. A higher rate of lymphomas was observed in patients treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. A higher rate of lung cancers was observed in current or past smokers treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. In this study, current or past smokers had an additional increased risk of overall malignancies.
The risks and benefits of ritlecitinib treatment should be considered prior to initiating or continuing therapy in patients with a known malignancy other than a successfully treated NMSC or cervical cancer.
Periodic skin examination is recommended for patients who are at increased risk for skin cancer.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE)
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study of another JAK inhibitor in RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and non-fatal stroke was observed with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with LITFULO, particularly in patients who are current or past smokers and patients with other cardiovascular risk factors. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur. Discontinue LITFULO in patients that have experienced a myocardial infarction or stroke.
Thromboembolic Events
An event of pulmonary embolism (PE) was reported in a patient receiving LITFULO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . In a ritlecitinib higher dosing group, 1 patient reported an event of retinal artery occlusion.
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study of another JAK inhibitor in RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, higher rates of overall thrombosis, DVT, and PE were observed compared to those treated with TNF blockers.
Avoid LITFULO in patients who may be at increased risk of thrombosis. If symptoms of thrombosis or embolism occur, patients should interrupt LITFULO and be evaluated promptly and treated appropriately.
Hypersensitivity
Serious reactions including anaphylactic reactions, urticaria and rash have been observed in patients receiving LITFULO in clinical trials. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue LITFULO and institute appropriate therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Laboratory Abnormalities
Treatment with LITFULO was associated with decreases in lymphocytes and platelets [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Prior to LITFULO initiation, perform ALC and platelet counts [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . After initiating treatment with LITFULO, treatment interruption or discontinuation are recommended based on ALC and platelet count abnormalities [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Liver Enzyme Elevations – Treatment with LITFULO was associated with increased incidence of liver enzyme elevation compared to placebo. Increases of ALT ≥5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) and increases of AST ≥5 times the ULN were observed in patients in LITFULO clinical trials. Evaluate at baseline and thereafter according to routine patient management. Prompt investigation of the cause of liver enzyme elevation is recommended to identify potential cases of drug-induced liver injury. If increases in ALT or AST are observed and drug-induced liver injury is suspected, interrupt LITFULO until this diagnosis is excluded.
Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) Elevations – Treatment with LITFULO was associated with increased incidence of CPK elevation compared to placebo.
Vaccinations
No data are available on the response to vaccination in patients receiving LITFULO. Use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided during or shortly prior to initiating treatment. Prior to initiating LITFULO, it is recommended that patients be brought up to date with all immunizations, including prophylactic herpes zoster vaccinations, in agreement with current immunization guidelines.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Laboratory Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of LITFULO was evaluated in three randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials and one long-term trial in subjects with alopecia areata, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, who were 12 years of age and older. A total of 1628 subjects were treated with LITFULO representing 2085 subject-years of exposure. There were 1011 subjects with at least 1 year of exposure to LITFULO. In the placebo-controlled period of clinical trials in alopecia areata, a total of 668 subjects were exposed to LITFULO with 130 receiving 50 mg once daily for up to 24 weeks. The median age of subjects was 33 years, 105 (11.9%) subjects were 12 to <18 years old and 22 (2.5%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. The majority of subjects were White (70.7%) and female (63.6%).
Adverse reactions occurring at ≥1% in the treated groups and at a higher rate than placebo are presented in Table 2. A total of 2 (1.5%) subjects treated with LITFULO 50 mg were discontinued from the trials due to adverse reactions.
| LITFULO 50 mg N=130 n (%) | Placebo N=213 n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
Headache Headache includes headache and migraine. | 14 (10.8) | 18 (8.5) |
Diarrhea Diarrhea includes diarrhea and frequent bowel movements. | 13 (10.0) | 8 (3.8) |
Acne Acne includes acne and acne pustular. | 8 (6.2) | 10 (4.7) |
Rash Rash includes rash and dermatitis allergic. | 7 (5.4) | 2 (0.9) |
Urticaria | 6 (4.6) | 3 (1.4) |
Folliculitis | 4 (3.1) | 4 (1.9) |
Pyrexia | 4 (3.1) | 0 |
Dermatitis atopic | 3 (2.3) | 1 (0.5) |
Dizziness | 3 (2.3) | 3 (1.4) |
Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 2 (1.5) | 0 |
Herpes zoster | 2 (1.5) | 0 |
Red blood cell count decreased | 2 (1.5) | 0 |
Stomatitis | 2 (1.5) | 0 |
Specific Adverse Reactions
Exposure adjusted incidence rates were adjusted by clinical trial size for all adverse reactions reported in this section.
Overall Infections
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, overall infections were reported in 66 subjects (80.35 per 100 subject-years) treated with placebo and 43 subjects (74.53 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, overall infections were reported in 645 subjects (50.71 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher.
Serious Infections
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, 3 subjects reported serious infections across all ritlecitinib doses studied. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, serious infections were reported in 12 subjects (0.66 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher. The most common serious infections were related to appendicitis, COVID-19 infection (including pneumonia), and sepsis.
Herpes Zoster
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, herpes zoster was reported in 4 subjects across all ritlecitinib doses studied and 0 subjects treated with placebo. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, herpes zoster was reported in 21 subjects (1.17 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher. Opportunistic infections of multi-dermatomal herpes zoster were reported in 1 subject (0.50 per 100 subject-years) treated with the ritlecitinib higher dose in the placebo-controlled trials and 2 subjects (0.1 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher in all clinical trials.
Malignancy
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, 1 malignancy (breast cancer) was reported in 1 subject (1.33 per 100 subject-years) treated with ritlecitinib higher dose and no malignancy was reported in subjects treated with placebo. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, malignancies excluding NMSC were reported in 7 subjects (0.37 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher.
Thromboembolic Events
Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, pulmonary embolism (PE) was reported in 1 subject (0.06 per 100 subject-years) treated with LITFULO. There was 1 report of retinal artery occlusion and 1 report of acute myocardial infarction.
Urticaria
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, urticaria was reported in 28 subjects treated in all ritlecitinib doses studied and 3 subjects treated with placebo. The rate of urticaria was 8.23 per 100 subject-years in subjects treated with ritlecitinib 50 mg and 4.03 per 100 subject-years in subjects treated with placebo. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, urticaria was reported in 76 subjects treated with LITFULO 50 mg or higher. Among all subjects treated with ritlecitinib 50 mg or higher in the integrated safety analysis, the rate of urticaria was 4.10 per 100 subject-years. The median time to onset of an initial event was 8 weeks; median duration of urticaria was 7 days. Most of the cases were mild to moderate in severity.
Decreased Lymphocyte Counts
Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial confirmed ALC <500/mm 3 occurred in 1 subject (<0.1%) treated with LITFULO 50 mg. Age appeared to be a risk factor for lower ALC in subjects ≥65 years of age.
Decreased Platelet Count
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, treatment with LITFULO was associated with a decrease in platelet count. Maximum effects on platelets were observed within 4 weeks, after which platelet count remained stable at a lower level with continued therapy. Across clinical trials, including the long-term trial, 1 subject (<0.1%) had a confirmed platelet count <100,000/mm 3 . No subject had a confirmed platelet count <75,000/mm 3 .
Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) Elevations
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, events of blood CPK increased were reported in 2 (1.5%) subjects treated with LITFULO 50 mg and 0 subjects treated with placebo.
Liver Enzyme Elevations
In the placebo-controlled trials, for up to 24 weeks, events of increases in liver enzymes ≥3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were observed in subjects treated with LITFULO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of LITFULO on Other Drugs
Table 3 includes clinically significant drug interactions affecting other drugs.
CYP3A Substrates Where Small Concentration Changes May Lead to Serious Adverse Reactions | |
Clinical Impact | Ritlecitinib is a CYP3A inhibitor. Concomitant use of ritlecitinib increases AUC and C max of CYP3A substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these substrates. |
Intervention | Consider additional monitoring and dosage adjustment in accordance with approved product labeling of CYP3A substrates where small concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions when used with LITFULO. |
CYP1A2 Substrates Where Small Concentration Changes May Lead to Serious Adverse Reactions | |
Clinical Impact | Ritlecitinib is a CYP1A2 inhibitor. Concomitant use of ritlecitinib increases AUC and C max of CYP1A2 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these substrates. |
Intervention | Consider additional monitoring and dosage adjustment in accordance with the approved product labeling of CYP1A2 substrates where small concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions when used concomitantly with LITFULO. |
Effects of Other Drugs on LITFULO
Table 4 includes clinically significant drug interactions affecting LITFULO.
CYP3A Inducers | |
Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducer (e.g., rifampin) may decrease AUC and C max of ritlecitinib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may result in loss of or reduced clinical response. |
Intervention | Coadministration with strong inducers of CYP3A is not recommended. |
DESCRIPTION
LITFULO (ritlecitinib) capsules are formulated with ritlecitinib tosylate, a kinase inhibitor.
Ritlecitinib tosylate is a white to off white to pale pink solid which is freely soluble in water. The chemical name is 1-{(2S,5R)-2-Methyl-5-[(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino]piperidin-1-yl}prop-2-en-1-one 4 methylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid.
The molecular formula for ritlecitinib tosylate is C 22 H 27 N 5 O 4 S. The molecular weight is 457.55 g/mol and its structural formula is:
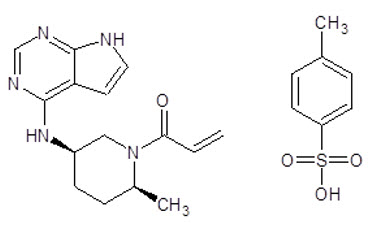
LITFULO is supplied for oral administration as a 50 mg immediate-release capsule. Each capsule contains 50 mg ritlecitinib (equivalent to 80.13 mg ritlecitinib tosylate) and the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone, glyceryl dibehenate, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, and hypromellose (HPMC) capsule shells. The yellow/blue, opaque capsule shells contain Brilliant blue FCF – FD&C Blue, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
LITFULO is a kinase inhibitor.
Ritlecitinib irreversibly inhibits Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family by blocking the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding site. In cellular settings, ritlecitinib inhibits cytokine induced STAT phosphorylation mediated by JAK3-dependent receptors. Additionally, ritlecitinib inhibits signaling of immune receptors dependent on TEC kinase family members. The relevance of inhibition of specific JAK or TEC family enzymes to therapeutic effectiveness is not currently known.
Pharmacodynamics
Lymphocyte Subsets
A dose-dependent early decrease in absolute lymphocyte levels, T lymphocytes (CD3) and T lymphocyte subsets (CD4 and CD8) was associated with LITFULO treatment in patients with alopecia areata. In addition, there was a dose-dependent early decrease in NK cells (CD16/56) which remained stable at the lower level up to Week 48. For the 50 mg QD dose, there was an initial decrease in median lymphocyte levels which remained consistent up to Week 48. There was no change observed in B lymphocytes (CD19) in any treatment group.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At 12 times the mean maximum exposure of the 50 mg once daily dose in patients with alopecia areata, there was no clinically relevant effect on the QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
Ritlecitinib AUC 0-tau and C max increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner up to 200 mg. Steady state was reached approximately by Day 4.
Absorption
The ritlecitinib absolute oral bioavailability is approximately 64%. Ritlecitinib peak plasma concentrations were reached within 1 hour following an oral dose.
Effect of Food
Food does not have a clinically significant impact on the systemic exposures of ritlecitinib. The coadministration of a 100 mg ritlecitinib capsule with a high-fat meal reduced the ritlecitinib C max by ~32% and AUC inf was increased by 11%. In clinical trials, ritlecitinib was administered without regard to meals [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Distribution
Approximately 14% of circulating ritlecitinib is bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
The ritlecitinib mean terminal half-life ranges from 1.3 to 2.3 hours.
Metabolism
The metabolism of ritlecitinib is mediated by multiple pathways with no single route contributing to more than 25% of the total metabolism. These pathways include:
- Glutathione S-transferase (GST): cytosolic GST A1/3, M1/3/5, P1, S1, T2, Z1 and microsomal GST 1/2/3
- CYP enzymes (CYP3A, CYP2C8, CYP1A2, and CYP2C9)
Excretion
Approximately 66% of radiolabeled ritlecitinib dose is excreted in the urine and 20% in the feces. Approximately 4% of the ritlecitinib dose is excreted unchanged drug in urine.
Specific Populations
No clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetics of ritlecitinib were observed based on age (12-73 years), body weight, gender, GST genotype, and race.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The AUC 24 observed in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min) was 55.2% higher compared with the AUC 24 in matched participants with normal renal functions. These differences are not considered clinically significant. Ritlecitinib has not been studied in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min) or moderate (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min) renal impairment, as a clinically relevant increase in ritlecitinib exposure is not expected in these patients. The eGFR and classification of renal function status of patients was done using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula. Ritlecitinib has not been studied in patients with ESRD or in renal transplant recipients.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment had an 18.5% increase in ritlecitinib AUC 24 compared to patients with normal hepatic function. Ritlecitinib has not been studied in patients with mild (Child Pugh A) hepatic impairment, as a clinically relevant increase in ritlecitinib exposure is not expected in these patients.
Ritlecitinib has not been studied in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment and is not recommended for use in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use In Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of other drugs on ritlecitinib
The effect of coadministered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of ritlecitinib is presented in Table 5.
Coadministered Drugs | Regimen of Coadministered Drug | Dose of Ritlecitinib | Ratio Ratios for C max and AUC inf compare coadministration of ritlecitinib with the drug versus administration of ritlecitinib alone. (90% Confidence Interval) | |
C max | AUC inf | |||
Strong CYP3A inhibitor: Itraconazole Drug interaction with CYP3A inhibitor is not clinically significant. | 200 mg once daily × 5 days | 30 mg | 1.03 (0.83, 1.27) | 1.15 (1.05, 1.27) |
Strong CYP enzyme inducer: Rifampin | 600 mg once daily × 8 days | 50 mg | 0.75 (0.63, 0.89) | 0.56 (0.52, 0.60) |
Effect of ritlecitinib on other drugs
The effect of ritlecitinib on the pharmacokinetics of coadministered drugs is presented in Table 6.
Coadministered Drugs | Dose Regimen of Ritlecitinib | Ratio Ratios for C max and AUC inf compare coadministration of the drug with ritlecitinib versus administration of the drug alone. (90% Confidence Interval) | |
C max | AUC inf | ||
Oral contraceptive: Ethinyl estradiol (EE) and levonorgestrel (LN) Drug interactions with ritlecitinib for oral contraceptives, CYP2B6 substrates, CYP2C substrates, and substrates of OATP1B1, BCRP, OAT3, and OCT1 transporters are not clinically significant. | 50 mg once daily × 11 days | EE: 0.92 (0.84, 1.01) LN: 0.80 (0.73, 0.88) | EE: 0.98 (0.91, 1.06) LN AUC last of levonorgestrel was reported in lieu of AUC inf because the terminal phase of levonorgestrel was not well characterized. : 0.88 (0.83, 0.93) |
Sensitive CYP3A substrate: Midazolam [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] | 200 mg once daily × 11 days Ritlecitinib dosage 4 times the approved recommended dosage. | 1.81 (1.48, 2.21) | 2.69 (2.16, 3.36) |
Sensitive CYP1A2 substrate: Caffeine [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] | 200 mg once daily × 9 days | 1.10 (1.04, 1.16) | 2.65 (2.34, 3.00) |
Sensitive CYP2B6 substrate: Efavirenz | 200 mg once daily × 11 days | 0.88 (0.77, 1.01) | 1.00 AUC 0-72 of efavirenz was reported (0.95, 1.04) |
Sensitive CYP2C substrate: Tolbutamide | 200 mg once daily × 10 days | 1.03 (0.97, 1.10) | 0.99 (0.92, 1.07) |
Sensitive OATP1B1, BCRP and OAT3 substrate: Rosuvastatin | 200 mg once daily × 10 days | 0.73 (0.63, 0.83) | 0.87 (0.75, 1.01) |
Sensitive OCT1 substrate: Sumatriptan | 400 mg single dose coadministration Ritlecitinib dosage 8 times the approved recommended dosage. | 0.87 (0.73, 1.03) | 1.30 (1.17, 1.44) |
400 mg single dose 8 hours prior to Sumatriptan | 1.50 (1.26, 1.78) | 1.50 (1.35, 1.66) | |
In Vitro Studies
CYP Related Pathways: Ritlecitinib is not an inhibitor of CYP2D6.
Other Metabolic Pathways: Ritlecitinib is not an inhibitor of uridine 5’ diphospho glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) (UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7), GSTs or sulfotransferases (SULTs).
Transporter Systems: Ritlecitinib is not an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or bile salt export pump (BSEP).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year rat carcinogenicity study, ritlecitinib increased the incidence of combined benign and malignant thymomas in female rats, and thyroid follicular adenomas and combined follicular adenomas and carcinomas in male rats at 100 mg/kg/day (29 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No ritlecitinib-related tumors were noted at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (6.3 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No ritlecitinib-related tumors were noted in a 6-month Tg.rasH2 mouse carcinogenicity study at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day.
Ritlecitinib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames assay). Ritlecitinib was positive in an in vitro micronucleus assay in TK6 cells. However, mechanistic studies determined that ritlecitinib is aneugenic and does not present a clinically relevant genotoxic concern. Additionally, in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay, ritlecitinib was not aneugenic or clastogenic at doses up to 400 mg/kg/day.
Ritlecitinib had no effects on female rat fertility at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (55 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Effects on male rat fertility were noted (higher preimplantation loss resulting in lower number of implantation sites and corresponding lower litter size in naïve females mated with ritlecitinib-dosed males) at 200 mg/kg/day (55 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No effects on male fertility were noted at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (14 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No effects on spermatogenesis (sperm counts, production rate, motility, or morphology) were noted at any dose.
Animal Toxicology and Pharmacology
In two 9-month oral repeat dose toxicity studies in dogs, dose-related reversible axonal dystrophy was noted in the brainstem, spinal cord, sciatic nerve, nerve branches of the vagus nerve, and myenteric/submucosal plexuses of the GI tract at doses ≥20 mg/kg/day (14 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). At 40 mg/kg/day (33 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison), ritlecitinib-related axonal dystrophy caused adverse reversible hearing loss and waveform deficits in brainstem auditory evoked potential (BAEP) testing. BAEP deficits were first noted during Month 7 of dosing and persisted through the end of dosing. No auditory threshold deficits were noted at 6 months after the end of dosing. No BAEP deficits were noted at doses ≤20 mg/kg/day. Additional mechanistic studies provided preliminary evidence that ritlecitinib-related hearing loss was not directly caused by JAK3 or TEC family kinase inhibition, but did not identify the underlying mechanism of axonal dystrophy in dogs.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of LITFULO were evaluated in one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Trial AA-I) in subjects 12 years of age and older with alopecia areata with ≥50% scalp hair loss, including alopecia totalis (AT) and alopecia universalis (AU).
Trial AA-I evaluated a total of 718 subjects who were randomized to one of the following treatment regimens for 48 weeks: 1) 200 mg once daily for 4 weeks followed by 50 mg once daily for 44 weeks; 2) 200 mg once daily for 4 weeks followed by 30 mg once daily for 44 weeks; 3) 50 mg once daily for 48 weeks; 4) 30 mg once daily for 48 weeks; 5) 10 mg once daily for 48 weeks; 6) placebo for 24 weeks followed by 200 mg once daily for 4 weeks and 50 mg once daily for 20 weeks; or 7) placebo for 24 weeks followed by 50 mg once daily for 24 weeks.
The recommended dose of LITFULO is 50 mg once daily and the results for this dose are discussed below.
Across all treatment groups 62% of subjects were female, 68% were White, 26% were Asian, and 4% were Black or African American. The majority of subjects (85%) were adults (≥18 years of age) with a mean age of 33.7 years. A total of 105 (15%) subjects 12 to <18 years of age and 20 (3%) subjects 65 years of age and older were enrolled. The mean baseline Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score ranged from 88.3 to 93.0 across treatment groups; among subjects without AT/AU at baseline, the mean SALT score ranged from 78.3 to 87.0. The majority of subjects had abnormal eyebrows (83%) and eyelashes (75%) at baseline across treatment groups. The median duration since alopecia areata diagnosis was 6.9 years and the median duration of the current alopecia areata episode was 2.5 years. Randomization was stratified by AT/AU status with 46% of subjects classified as AT/AU based upon a baseline SALT score of 100.
Clinical Response
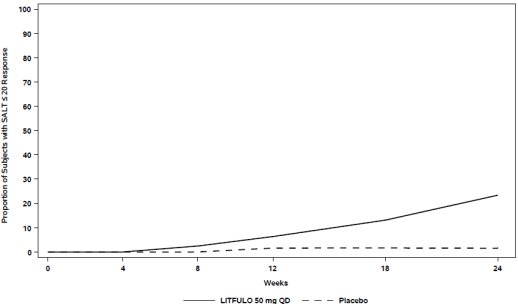
Assessment of scalp hair loss was based on the SALT score. At Week 24, a greater proportion of subjects had a SALT ≤20 response (20% or less of scalp hair loss) and SALT ≤10 response (10% or less of scalp hair loss) with LITFULO compared to placebo (Table 7). The percentage of subjects achieving SALT ≤20 response by visit is shown in Figure 1.
| LITFULO 50 mg QD (N=130) % Responders | Placebo (N=131) % Responders | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; N = total number of subjects; QD = once daily; SALT = Severity of Alopecia Tool. | |||
SALT ≤20 response SALT ≤20 responders were subjects with scalp hair loss of ≤20%. SALT scores range from 0 to 100 with 0 = no scalp hair loss and 100 = total scalp hair loss. | 23.0 | 1.6 | 21.4 (13.4, 29.5) |
SALT ≤10 response SALT ≤10 responders were subjects with scalp hair loss of ≤10%. | 13.4 | 1.5 | 11.9 (5.4, 18.3) |
Figure 1. SALT ≤20 Response through Week 24
| Abbreviations: QD = once daily; SALT = Severity of Alopecia Tool. |
 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LITFULO capsules are packaged in child-resistant, white, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles with polypropylene (PP) cap with a foil heat induction seal liner. The bottles contain 1g of desiccant in a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) canister. Do not eat the desiccant.
Dosage Form | Strength | Description | Bottle Size (number of capsules) | NDC Number |
Capsules | 50 mg of ritlecitinib | Size 3, opaque capsules with yellow body and blue cap. The body is printed with “RCB 50” and the cap is printed with “Pfizer” in black. | 28 count bottle | 0069-0334-28 |
Store LITFULO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep in original package.
Mechanism of Action
LITFULO is a kinase inhibitor.
Ritlecitinib irreversibly inhibits Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family by blocking the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding site. In cellular settings, ritlecitinib inhibits cytokine induced STAT phosphorylation mediated by JAK3-dependent receptors. Additionally, ritlecitinib inhibits signaling of immune receptors dependent on TEC kinase family members. The relevance of inhibition of specific JAK or TEC family enzymes to therapeutic effectiveness is not currently known.