Get your patient on Lyrica (Pregabalin)
Lyrica prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Lyrica patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For adult indications, begin dosing at 150 mg/day. For partial-onset seizure dosing in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older, refer to section 2.4. (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 2.6 )
- Dosing recommendations:
| INDICATION | Dosing Regimen | Maximum Dose |
|---|---|---|
DPN Pain (2.2 ) | 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week |
PHN (2.3 ) | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. |
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric and Adult Patients Weighing 30 kg or More (2.4 ) | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. |
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients Weighing Less than 30 kg (2.4 ) | 1 month to less than 4 years: | 14 mg/kg/day. |
Fibromyalgia (2.5 ) | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. |
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury (2.6 ) | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. |
- Dose should be adjusted in adult patients with reduced renal function. (2.7 )
Important Administration Instructions
LYRICA is given orally with or without food.
When discontinuing LYRICA, taper gradually over a minimum of 1 week [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
Because LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose in adult patients with reduced renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ].
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Adults
The maximum recommended dose of LYRICA is 100 mg three times a day (300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Although LYRICA was also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional significant benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 300 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Postherpetic Neuralgia in Adults
The recommended dose of LYRICA is 75 to 150 mg two times a day, or 50 to 100 mg three times a day (150 to 300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day, or 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief following 2 to 4 weeks of treatment with 300 mg/day, and who are able to tolerate LYRICA, may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day, or 200 mg three times a day (600 mg/day). In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions and the higher rate of treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions, reserve dosing above 300 mg/day for those patients who have on-going pain and are tolerating 300 mg daily [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 1 Month of Age and Older
The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly.
| Age and Body Weight | Recommended Initial Dosage | Recommended Maximum Dosage | Frequency of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
Adults (17 years and older) | 150 mg/day | 600 mg/day | 2 or 3 divided doses |
Pediatric patients weighing 30 kg or more | 2.5 mg/kg/day | 10 mg/kg/day | 2 or 3 divided doses |
Pediatric patients weighing less than 30 kg | 3.5 mg/kg/day | 14 mg/kg/day | 1 month to less than 4 years of age: |
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of LYRICA have been shown to be dose-related.
The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of LYRICA has not been formally studied.
The efficacy of adjunctive LYRICA in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of LYRICA with gabapentin cannot be offered.
Management of Fibromyalgia in Adults
The recommended dose of LYRICA for fibromyalgia is 300 to 450 mg/day. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient benefit with 300 mg/day may be further increased to 225 mg two times a day (450 mg/day). Although LYRICA was also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 450 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury in Adults
The recommended dose range of LYRICA for the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury is 150 to 600 mg/day. The recommended starting dose is 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment with 150 mg two times a day and who tolerate LYRICA may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] .
Dosing for Adult Patients with Renal Impairment
In view of dose-dependent adverse reactions and since LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose in adult patients with reduced renal function. The use of LYRICA in pediatric patients with compromised renal function has not been studied.
Base the dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment on creatinine clearance (CLcr), as indicated in Table 2. To use this dosing table, an estimate of the patient's CLcr in mL/min is needed. CLcr in mL/min may be estimated from serum creatinine (mg/dL) determination using the Cockcroft and Gault equation:
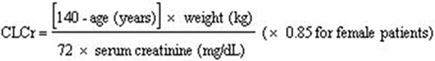
Next, refer to the Dosage and Administration section to determine the recommended total daily dose based on indication, for a patient with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min). Then refer to Table 2 to determine the corresponding renal adjusted dose.
(For example: A patient initiating LYRICA therapy for postherpetic neuralgia with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min), receives a total daily dose of 150 mg/day pregabalin. Therefore, a renal impaired patient with a CLcr of 50 mL/min would receive a total daily dose of 75 mg/day pregabalin administered in two or three divided doses.)
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, adjust the pregabalin daily dose based on renal function. In addition to the daily dose adjustment, administer a supplemental dose immediately following every 4-hour hemodialysis treatment (see Table 2 ).
| Creatinine Clearance (CLcr) (mL/min) | Total Pregabalin Daily Dose (mg/day) Total daily dose (mg/day) should be divided as indicated by dose regimen to provide mg/dose. | Dose Regimen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TID= Three divided doses; BID = Two divided doses; QD = Single daily dose. | |||||
Greater than or equal to 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | BID or TID |
30–60 | 75 | 150 | 225 | 300 | BID or TID |
15–30 | 25–50 | 75 | 100–150 | 150 | QD or BID |
Less than 15 | 25 | 25–50 | 50–75 | 75 | QD |
Supplementary dosage following hemodialysis (mg) Supplementary dose is a single additional dose. | |||||
Patients on the 25 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 25 mg or 50 mg | |||||
Patients on the 25–50 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 50 mg or 75 mg | |||||
Patients on the 50–75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 75 mg or 100 mg | |||||
Patients on the 75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 100 mg or 150 mg | |||||

Lyrica prescribing information
Warnings and Precautions, Respiratory Depression (5.4 ) | 4/2020 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LYRICA is indicated for:
- Management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Management of postherpetic neuralgia
- Adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 1 month of age and older
- Management of fibromyalgia
- Management of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For adult indications, begin dosing at 150 mg/day. For partial-onset seizure dosing in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older, refer to section 2.4. (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 2.6 )
- Dosing recommendations:
| INDICATION | Dosing Regimen | Maximum Dose |
|---|---|---|
DPN Pain (2.2 ) | 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week |
PHN (2.3 ) | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. |
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric and Adult Patients Weighing 30 kg or More (2.4 ) | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. |
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients Weighing Less than 30 kg (2.4 ) | 1 month to less than 4 years: 3 divided doses per day 4 years and older: 2 or 3 divided doses per day | 14 mg/kg/day. |
Fibromyalgia (2.5 ) | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 450 mg/day. |
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury (2.6 ) | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. |
- Dose should be adjusted in adult patients with reduced renal function. (2.7 )
Important Administration Instructions
LYRICA is given orally with or without food.
When discontinuing LYRICA, taper gradually over a minimum of 1 week [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
Because LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose in adult patients with reduced renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ].
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Adults
The maximum recommended dose of LYRICA is 100 mg three times a day (300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Although LYRICA was also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional significant benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 300 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Postherpetic Neuralgia in Adults
The recommended dose of LYRICA is 75 to 150 mg two times a day, or 50 to 100 mg three times a day (150 to 300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day, or 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief following 2 to 4 weeks of treatment with 300 mg/day, and who are able to tolerate LYRICA, may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day, or 200 mg three times a day (600 mg/day). In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions and the higher rate of treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions, reserve dosing above 300 mg/day for those patients who have on-going pain and are tolerating 300 mg daily [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 1 Month of Age and Older
The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly.
| Age and Body Weight | Recommended Initial Dosage | Recommended Maximum Dosage | Frequency of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
Adults (17 years and older) | 150 mg/day | 600 mg/day | 2 or 3 divided doses |
Pediatric patients weighing 30 kg or more | 2.5 mg/kg/day | 10 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 600 mg/day) | 2 or 3 divided doses |
Pediatric patients weighing less than 30 kg | 3.5 mg/kg/day | 14 mg/kg/day | 1 month to less than 4 years of age: 3 divided doses 4 years of age and older: 2 or 3 divided doses |
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of LYRICA have been shown to be dose-related.
The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of LYRICA has not been formally studied.
The efficacy of adjunctive LYRICA in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of LYRICA with gabapentin cannot be offered.
Management of Fibromyalgia in Adults
The recommended dose of LYRICA for fibromyalgia is 300 to 450 mg/day. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient benefit with 300 mg/day may be further increased to 225 mg two times a day (450 mg/day). Although LYRICA was also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 450 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury in Adults
The recommended dose range of LYRICA for the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury is 150 to 600 mg/day. The recommended starting dose is 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment with 150 mg two times a day and who tolerate LYRICA may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] .
Dosing for Adult Patients with Renal Impairment
In view of dose-dependent adverse reactions and since LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose in adult patients with reduced renal function. The use of LYRICA in pediatric patients with compromised renal function has not been studied.
Base the dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment on creatinine clearance (CLcr), as indicated in Table 2. To use this dosing table, an estimate of the patient's CLcr in mL/min is needed. CLcr in mL/min may be estimated from serum creatinine (mg/dL) determination using the Cockcroft and Gault equation:
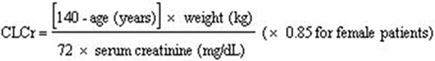
Next, refer to the Dosage and Administration section to determine the recommended total daily dose based on indication, for a patient with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min). Then refer to Table 2 to determine the corresponding renal adjusted dose.
(For example: A patient initiating LYRICA therapy for postherpetic neuralgia with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min), receives a total daily dose of 150 mg/day pregabalin. Therefore, a renal impaired patient with a CLcr of 50 mL/min would receive a total daily dose of 75 mg/day pregabalin administered in two or three divided doses.)
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, adjust the pregabalin daily dose based on renal function. In addition to the daily dose adjustment, administer a supplemental dose immediately following every 4-hour hemodialysis treatment (see Table 2 ).
| Creatinine Clearance (CLcr) (mL/min) | Total Pregabalin Daily Dose (mg/day) Total daily dose (mg/day) should be divided as indicated by dose regimen to provide mg/dose. | Dose Regimen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TID= Three divided doses; BID = Two divided doses; QD = Single daily dose. | |||||
Greater than or equal to 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | BID or TID |
30–60 | 75 | 150 | 225 | 300 | BID or TID |
15–30 | 25–50 | 75 | 100–150 | 150 | QD or BID |
Less than 15 | 25 | 25–50 | 50–75 | 75 | QD |
Supplementary dosage following hemodialysis (mg) Supplementary dose is a single additional dose. | |||||
Patients on the 25 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 25 mg or 50 mg | |||||
Patients on the 25–50 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 50 mg or 75 mg | |||||
Patients on the 50–75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 75 mg or 100 mg | |||||
Patients on the 75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 100 mg or 150 mg | |||||
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, and 300 mg
Oral Solution: 20 mg/mL
[see Description (11) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16) ]
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to LYRICA during pregnancy. To provide information regarding the effects of in utero exposure to LYRICA, physicians are advised to recommend that pregnant patients taking LYRICA enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. This can be done by calling the toll free number 1-888-233-2334, and must be done by patients themselves. Information on the registry can also be found at the website http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/ .
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with LYRICA in pregnant women.
However, in animal reproduction studies, increased incidences of fetal structural abnormalities and other manifestations of developmental toxicity, including skeletal malformations, retarded ossification, and decreased fetal body weight were observed in the offspring of rats and rabbits given pregabalin orally during organogenesis, at doses that produced plasma pregabalin exposures (AUC) greater than or equal to 16 times human exposure at the maximum recommended dose (MRD) of 600 mg/day [see Data ] . In an animal development study, lethality, growth retardation, and nervous and reproductive system functional impairment were observed in the offspring of rats given pregabalin during gestation and lactation. The no-effect dose for developmental toxicity was approximately twice the human exposure at MRD. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2–4% and of miscarriage is 15–20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Data
Animal Data
When pregnant rats were given pregabalin (500, 1250, or 2500 mg/kg) orally throughout the period of organogenesis, incidences of specific skull alterations attributed to abnormally advanced ossification (premature fusion of the jugal and nasal sutures) were increased at greater than or equal to 1250 mg/kg, and incidences of skeletal variations and retarded ossification were increased at all doses. Fetal body weights were decreased at the highest dose. The low dose in this study was associated with a plasma exposure (AUC) approximately 17 times human exposure at the MRD of 600 mg/day. A no-effect dose for rat embryo-fetal developmental toxicity was not established.
When pregnant rabbits were given LYRICA (250, 500, or 1250 mg/kg) orally throughout the period of organogenesis, decreased fetal body weight and increased incidences of skeletal malformations, visceral variations, and retarded ossification were observed at the highest dose. The no-effect dose for developmental toxicity in rabbits (500 mg/kg) was associated with a plasma exposure approximately 16 times human exposure at the MRD.
In a study in which female rats were dosed with LYRICA (50, 100, 250, 1250, or 2500 mg/kg) throughout gestation and lactation, offspring growth was reduced at greater than or equal to 100 mg/kg and offspring survival was decreased at greater than or equal to 250 mg/kg. The effect on offspring survival was pronounced at doses greater than or equal to 1250 mg/kg, with 100% mortality in high-dose litters. When offspring were tested as adults, neurobehavioral abnormalities (decreased auditory startle responding) were observed at greater than or equal to 250 mg/kg and reproductive impairment (decreased fertility and litter size) was seen at 1250 mg/kg. The no-effect dose for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity in rats (50 mg/kg) produced a plasma exposure approximately 2 times human exposure at the MRD.
In the prenatal-postnatal study in rats, pregabalin prolonged gestation and induced dystocia at exposures greater than or equal to 50 times the mean human exposure (AUC (0–24) of 123 µg∙hr/mL) at the MRD.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Small amounts of pregabalin have been detected in the milk of lactating women. A pharmacokinetic study in lactating women detected pregabalin in breast milk at average steady state concentrations approximately 76% of those in maternal plasma. The estimated average daily infant dose of pregabalin from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day) was 0.31 mg/kg/day, which on a mg/kg basis would be approximately 7% of the maternal dose [see Data ] . The study did not evaluate the effects of LYRICA on milk production or the effects of LYRICA on the breastfed infant.
Based on animal studies, there is a potential risk of tumorigenicity with pregabalin exposure via breast milk to the breastfed infant [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] . Available clinical study data in patients greater than 12 years of age do not provide a clear conclusion about the potential risk of tumorigenicity with pregabalin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] . Because of the potential risk of tumorigenicity, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with LYRICA.
Data
A pharmacokinetic study in ten lactating women, who were at least 12 weeks postpartum, evaluated the concentrations of pregabalin in plasma and breast milk. LYRICA 150 mg oral capsule was given every 12 hours (300 mg daily dose) for a total of four doses. Pregabalin was detected in breast milk at average steady-state concentrations approximately 76% of those in maternal plasma. The estimated average daily infant dose of pregabalin from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day) was 0.31 mg/kg/day, which on a mg/kg basis would be approximately 7% of the maternal dose. The study did not evaluate the effects of LYRICA on milk production. Infants did not receive breast milk obtained during the dosing period, therefore, the effects of LYRICA on the breast fed infant were not evaluated.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Male
Effects on Spermatogenesis
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled non-inferiority study to assess the effect of pregabalin on sperm characteristics, healthy male subjects received pregabalin at a daily dose up to 600 mg (n=111) or placebo (n=109) for 13 weeks (one complete sperm cycle) followed by a 13-week washout period (off-drug). A total of 65 subjects in the pregabalin group (59%) and 62 subjects in the placebo group (57%) were included in the per protocol (PP) population. These subjects took study drug for at least 8 weeks, had appropriate timing of semen collections and did not have any significant protocol violations. Among these subjects, approximately 9% of the pregabalin group (6/65) vs. 3% in the placebo group (2/62) had greater than or equal to 50% reduction in mean sperm concentrations from baseline at Week 26 (the primary endpoint). The difference between pregabalin and placebo was within the pre-specified non-inferiority margin of 20%. There were no adverse effects of pregabalin on sperm morphology, sperm motility, serum FSH or serum testosterone levels as compared to placebo. In subjects in the PP population with greater than or equal to 50% reduction in sperm concentration from baseline, sperm concentrations were no longer reduced by greater than or equal to 50% in any affected subject after an additional 3 months off-drug. In one subject, however, subsequent semen analyses demonstrated reductions from baseline of greater than or equal to 50% at 9 and 12 months off-drug. The clinical relevance of these data is unknown.
In the animal fertility study with pregabalin in male rats, adverse reproductive and developmental effects were observed [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ].
Pediatric Use
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy, Postherpetic Neuralgia, and Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Fibromyalgia
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
A 15-week, placebo-controlled trial was conducted with 107 pediatric patients with fibromyalgia, ages 12 through 17 years, at LYRICA total daily doses of 75–450 mg per day. The primary efficacy endpoint of change from baseline to Week 15 in mean pain intensity (derived from an 11-point numeric rating scale) showed numerically greater improvement for the pregabalin-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients, but did not reach statistical significance. The most frequently observed adverse reactions in the clinical trial included dizziness, nausea, headache, weight increased, and fatigue. The overall safety profile in adolescents was similar to that observed in adults with fibromyalgia.
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 1 month have not been established.
4 to Less Than 17 Years of Age with Partial-Onset Seizures
The safety and effectiveness of LYRICA as adjunctive treatment for partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients 4 to less than 17 years of age have been established in a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (n=295) [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . Patients treated with LYRICA 10 mg/kg/day had, on average, a 21.0% greater reduction in partial-onset seizures than patients treated with placebo (p=0.0185). Patients treated with LYRICA 2.5 mg/kg/day had, on average, a 10.5% greater reduction in partial-onset seizures than patients treated with placebo, but the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.2577).
Responder rates (50% or greater reduction in partial-onset seizure frequency) were a key secondary efficacy parameter and showed numerical improvement with LYRICA compared with placebo: the responder rates were 40.6%, 29.1%, and 22.6%, for LYRICA 10 mg/kg/day, LYRICA 2.5 mg/kg/day, and placebo, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) with LYRICA in this study were somnolence, weight increased, and increased appetite [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
The use of LYRICA 2.5 mg/kg/day in pediatric patients is further supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with partial-onset seizures and pharmacokinetic data from adult and pediatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
1 Month to Less than 4 Years of Age with Partial-Onset Seizures
The safety and effectiveness of LYRICA as adjunctive treatment for partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients 1 month to less than 4 years of age have been established in a 14-day double-blind, placebo-controlled study (N=175) [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . The youngest subject evaluated was 3 months of age; use in patients 1 month to less than 3 months of age is supported by additional pharmacokinetic analyses. Patients treated with LYRICA 14 mg/kg/day had, on average, 43.9% greater reduction in partial-onset seizures than patients treated with placebo (p=0.0223). In addition, pediatric patients treated with LYRICA 14 mg/kg/day showed numerical improvement in responder rates (≥50% reduction in partial-onset seizure frequency) compared with placebo (53.6% versus 41.5%). Patients treated with LYRICA 7 mg/kg/day did not show improvement relative to placebo for either endpoint.
The most common dose-related adverse reactions (≥5%) with LYRICA in this study were somnolence, pneumonia, and viral infection [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Juvenile Animal Data
In studies in which pregabalin (50 to 500 mg/kg) was orally administered to young rats from early in the postnatal period (Postnatal Day 7) through sexual maturity, neurobehavioral abnormalities (deficits in learning and memory, altered locomotor activity, decreased auditory startle responding and habituation) and reproductive impairment (delayed sexual maturation and decreased fertility in males and females) were observed at doses greater than or equal to 50 mg/kg. The neurobehavioral changes of acoustic startle persisted at greater than or equal to 250 mg/kg and locomotor activity and water maze performance at greater than or equal to 500 mg/kg in animals tested after cessation of dosing and, thus, were considered to represent long-term effects. The low effect dose for developmental neurotoxicity and reproductive impairment in juvenile rats (50 mg/kg) was associated with a plasma pregabalin exposure (AUC) approximately equal to human exposure at the maximum recommended dose of 600 mg/day. A no-effect dose was not established.
Geriatric Use
In controlled clinical studies of LYRICA in neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, 246 patients were 65 to 74 years of age, and 73 patients were 75 years of age or older.
In controlled clinical studies of LYRICA in neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia, 282 patients were 65 to 74 years of age, and 379 patients were 75 years of age or older.
In controlled clinical studies of LYRICA in epilepsy, there were only 10 patients 65 to 74 years of age, and 2 patients who were 75 years of age or older.
No overall differences in safety and efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patients.
In controlled clinical studies of LYRICA in fibromyalgia, 106 patients were 65 years of age or older. Although the adverse reaction profile was similar between the two age groups, the following neurological adverse reactions were more frequent in patients 65 years of age or older: dizziness, vision blurred, balance disorder, tremor, confusional state, coordination abnormal, and lethargy.
LYRICA is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to LYRICA may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose for elderly patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Renal Impairment
LYRICA is eliminated primarily by renal excretion and dose adjustment is recommended for adult patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. The use of LYRICA in pediatric patients with compromised renal function has not been studied.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LYRICA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to pregabalin or any of its components. Angioedema and hypersensitivity reactions have occurred in patients receiving pregabalin therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Angioedema (e.g., swelling of the throat, head and neck) can occur, and may be associated with life-threatening respiratory compromise requiring emergency treatment. Discontinue LYRICA immediately in these cases. (5.1 )
- Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., hives, dyspnea, and wheezing) can occur. Discontinue LYRICA immediately in these patients. (5.2 )
- Antiepileptic drugs, including LYRICA, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior. (5.3 )
- Respiratory depression: May occur with LYRICA, when used with concomitant CNS depressants or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment. Monitor patients and adjust dosage as appropriate. (5.4 )
- LYRICA may cause dizziness and somnolence and impair patients' ability to drive or operate machinery. (5.5 )
- Increased seizure frequency or other adverse reactions may occur if LYRICA is rapidly discontinued. Withdraw LYRICA gradually over a minimum of 1 week. (5.6 )
- LYRICA may cause peripheral edema. Exercise caution when co-administering LYRICA and thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agents. (5.7 )
Angioedema
There have been postmarketing reports of angioedema in patients during initial and chronic treatment with LYRICA. Specific symptoms included swelling of the face, mouth (tongue, lips, and gums), and neck (throat and larynx). There were reports of life-threatening angioedema with respiratory compromise requiring emergency treatment. Discontinue LYRICA immediately in patients with these symptoms.
Exercise caution when prescribing LYRICA to patients who have had a previous episode of angioedema. In addition, patients who are taking other drugs associated with angioedema (e.g., angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors [ACE-inhibitors]) may be at increased risk of developing angioedema.
Hypersensitivity
There have been postmarketing reports of hypersensitivity in patients shortly after initiation of treatment with LYRICA. Adverse reactions included skin redness, blisters, hives, rash, dyspnea, and wheezing. Discontinue LYRICA immediately in patients with these symptoms.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including LYRICA, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Monitor patients treated with any AED for any indication for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5–100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 3 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
| Indication | Placebo Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients | Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients | Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients | Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Epilepsy | 1.0 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
Psychiatric | 5.7 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
Other | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
Total | 2.4 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing LYRICA or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Respiratory Depression
There is evidence from case reports, human studies, and animal studies associating LYRICA with serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression when co-administered with central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including opioids, or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment. When the decision is made to co-prescribe LYRICA with another CNS depressant, particularly an opioid, or to prescribe LYRICA to patients with underlying respiratory impairment, monitor patients for symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation, and consider initiating LYRICA at a low dose. The management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and reduction or withdrawal of CNS depressants (including LYRICA).
There is more limited evidence from case reports, animal studies, and human studies associating LYRICA with serious respiratory depression, without co-administered CNS depressants or without underlying respiratory impairment.
Dizziness and Somnolence
LYRICA may cause dizziness and somnolence. Inform patients that LYRICA-related dizziness and somnolence may impair their ability to perform tasks such as driving or operating machinery [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ].
In the LYRICA controlled trials in adult patients, dizziness was experienced by 30% of LYRICA-treated patients compared to 8% of placebo-treated patients; somnolence was experienced by 23% of LYRICA-treated patients compared to 8% of placebo-treated patients. Dizziness and somnolence generally began shortly after the initiation of LYRICA therapy and occurred more frequently at higher doses. Dizziness and somnolence were the adverse reactions most frequently leading to withdrawal (4% each) from controlled studies. In LYRICA-treated patients reporting these adverse reactions in short-term, controlled studies, dizziness persisted until the last dose in 30% and somnolence persisted until the last dose in 42% of patients [see Drug Interactions (7) ].
In the LYRICA controlled trials in pediatric patients 4 to less than 17 years of age and 1 month to less than 4 years of age for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, somnolence was reported in 21% and 15% of LYRICA-treated patients compared to 14% and 9% of placebo-treated patients, respectively, and occurred more frequently at higher doses. For patients 1 month to less than 4 years of age, somnolence includes related terms lethargy, sluggishness, and hypersomnia.
Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Abrupt or Rapid Discontinuation
As with all antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), withdraw LYRICA gradually to minimize the potential of increased seizure frequency in patients with seizure disorders.
Following abrupt or rapid discontinuation of LYRICA, some patients reported symptoms including insomnia, nausea, headache, anxiety, hyperhidrosis, and diarrhea.
If LYRICA is discontinued, taper the drug gradually over a minimum of 1 week rather than discontinue the drug abruptly.
Peripheral Edema
LYRICA treatment may cause peripheral edema. In short-term trials of patients without clinically significant heart or peripheral vascular disease, there was no apparent association between peripheral edema and cardiovascular complications such as hypertension or congestive heart failure. Peripheral edema was not associated with laboratory changes suggestive of deterioration in renal or hepatic function.
In controlled clinical trials in adult patients, the incidence of peripheral edema was 6% in the LYRICA group compared with 2% in the placebo group. In controlled clinical trials, 0.5% of LYRICA patients and 0.2% placebo patients withdrew due to peripheral edema.
Higher frequencies of weight gain and peripheral edema were observed in patients taking both LYRICA and a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent compared to patients taking either drug alone. The majority of patients using thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agents in the overall safety database were participants in studies of pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. In this population, peripheral edema was reported in 3% (2/60) of patients who were using thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agents only, 8% (69/859) of patients who were treated with LYRICA only, and 19% (23/120) of patients who were on both LYRICA and thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agents. Similarly, weight gain was reported in 0% (0/60) of patients on thiazolidinediones only; 4% (35/859) of patients on LYRICA only; and 7.5% (9/120) of patients on both drugs.
As the thiazolidinedione class of antidiabetic drugs can cause weight gain and/or fluid retention, possibly exacerbating or leading to heart failure, exercise caution when co-administering LYRICA and these agents.
Because there are limited data on congestive heart failure patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV cardiac status, exercise caution when using LYRICA in these patients.
Weight Gain
LYRICA treatment may cause weight gain. In LYRICA controlled clinical trials in adult patients of up to 14 weeks, a gain of 7% or more over baseline weight was observed in 9% of LYRICA-treated patients and 2% of placebo-treated patients. Few patients treated with LYRICA (0.3%) withdrew from controlled trials due to weight gain. LYRICA associated weight gain was related to dose and duration of exposure, but did not appear to be associated with baseline BMI, gender, or age. Weight gain was not limited to patients with edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
Although weight gain was not associated with clinically important changes in blood pressure in short-term controlled studies, the long-term cardiovascular effects of LYRICA-associated weight gain are unknown.
Among diabetic patients, LYRICA-treated patients gained an average of 1.6 kg (range: -16 to 16 kg), compared to an average 0.3 kg (range: -10 to 9 kg) weight gain in placebo patients. In a cohort of 333 diabetic patients who received LYRICA for at least 2 years, the average weight gain was 5.2 kg.
While the effects of LYRICA-associated weight gain on glycemic control have not been systematically assessed, in controlled and longer-term open label clinical trials with diabetic patients, LYRICA treatment did not appear to be associated with loss of glycemic control (as measured by HbA 1C ).
Tumorigenic Potential
In standard preclinical in vivo lifetime carcinogenicity studies of LYRICA, an unexpectedly high incidence of hemangiosarcoma was identified in two different strains of mice [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] . The clinical significance of this finding is unknown. Clinical experience during LYRICA's premarketing development provides no direct means to assess its potential for inducing tumors in humans.
In clinical studies across various patient populations, comprising 6396 patient-years of exposure in patients greater than 12 years of age, new or worsening-preexisting tumors were reported in 57 patients. Without knowledge of the background incidence and recurrence in similar populations not treated with LYRICA, it is impossible to know whether the incidence seen in these cohorts is or is not affected by treatment.
Ophthalmological Effects
In controlled studies in adult patients, a higher proportion of patients treated with LYRICA reported blurred vision (7%) than did patients treated with placebo (2%), which resolved in a majority of cases with continued dosing. Less than 1% of patients discontinued LYRICA treatment due to vision-related events (primarily blurred vision).
Prospectively planned ophthalmologic testing, including visual acuity testing, formal visual field testing and dilated funduscopic examination, was performed in over 3600 patients. In these patients, visual acuity was reduced in 7% of patients treated with LYRICA, and 5% of placebo-treated patients. Visual field changes were detected in 13% of LYRICA-treated, and 12% of placebo-treated patients. Funduscopic changes were observed in 2% of LYRICA-treated and 2% of placebo-treated patients.
Although the clinical significance of the ophthalmologic findings is unknown, inform patients to notify their physician if changes in vision occur. If visual disturbance persists, consider further assessment. Consider more frequent assessment for patients who are already routinely monitored for ocular conditions [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
Creatine Kinase Elevations
LYRICA treatment was associated with creatine kinase elevations. Mean changes in creatine kinase from baseline to the maximum value were 60 U/L for LYRICA-treated patients and 28 U/L for the placebo patients. In all controlled trials in adult patients across multiple patient populations, 1.5% of patients on LYRICA and 0.7% of placebo patients had a value of creatine kinase at least three times the upper limit of normal. Three LYRICA-treated subjects had events reported as rhabdomyolysis in premarketing clinical trials. The relationship between these myopathy events and LYRICA is not completely understood because the cases had documented factors that may have caused or contributed to these events. Instruct patients to promptly report unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly if these muscle symptoms are accompanied by malaise or fever. Discontinue treatment with LYRICA if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected or if markedly elevated creatine kinase levels occur.
Decreased Platelet Count
LYRICA treatment was associated with a decrease in platelet count. LYRICA-treated subjects experienced a mean maximal decrease in platelet count of 20 × 10 3 /µL, compared to 11 × 10 3 /µL in placebo patients. In the overall database of controlled trials in adult patients, 2% of placebo patients and 3% of LYRICA patients experienced a potentially clinically significant decrease in platelets, defined as 20% below baseline value and less than 150 × 10 3 /µL. A single LYRICA-treated subject developed severe thrombocytopenia with a platelet count less than 20 × 10 3 / µL. In randomized controlled trials, LYRICA was not associated with an increase in bleeding-related adverse reactions.
PR Interval Prolongation
LYRICA treatment was associated with PR interval prolongation. In analyses of clinical trial ECG data in adult patients, the mean PR interval increase was 3–6 msec at LYRICA doses greater than or equal to 300 mg/day. This mean change difference was not associated with an increased risk of PR increase greater than or equal to 25% from baseline, an increased percentage of subjects with on-treatment PR greater than 200 msec, or an increased risk of adverse reactions of second or third degree AV block.
Subgroup analyses did not identify an increased risk of PR prolongation in patients with baseline PR prolongation or in patients taking other PR prolonging medications. However, these analyses cannot be considered definitive because of the limited number of patients in these categories.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Dizziness and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Abrupt or Rapid Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Peripheral Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Weight Gain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Tumorigenic Potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Ophthalmological Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Creatine Kinase Elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Decreased Platelet Count [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
- PR Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In all controlled and uncontrolled trials across various patient populations during the premarketing development of LYRICA, more than 10,000 patients have received LYRICA. Approximately 5000 patients were treated for 6 months or more, over 3100 patients were treated for 1 year or longer, and over 1400 patients were treated for at least 2 years.
Adverse Reactions Most Commonly Leading to Discontinuation in All Premarketing Controlled Clinical Studies
In premarketing controlled trials of all adult populations combined, 14% of patients treated with LYRICA and 7% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LYRICA treatment group, the adverse reactions most frequently leading to discontinuation were dizziness (4%) and somnolence (4%). In the placebo group, 1% of patients withdrew due to dizziness and less than 1% withdrew due to somnolence. Other adverse reactions that led to discontinuation from controlled trials more frequently in the LYRICA group compared to the placebo group were ataxia, confusion, asthenia, thinking abnormal, blurred vision, incoordination, and peripheral edema (1% each).
Most Common Adverse Reactions in All Controlled Clinical Studies in Adults
In premarketing controlled trials of all adult patient populations combined (including DPN, PHN, and adult patients with partial-onset seizures), dizziness, somnolence, dry mouth, edema, blurred vision, weight gain, and "thinking abnormal" (primarily difficulty with concentration/attention) were more commonly reported by subjects treated with LYRICA than by subjects treated with placebo (greater than or equal to 5% and twice the rate of that seen in placebo).
Controlled Studies with Neuropathic Pain Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In clinical trials in adults with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, 9% of patients treated with LYRICA and 4% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LYRICA treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were dizziness (3%) and somnolence (2%). In comparison, less than 1% of placebo patients withdrew due to dizziness and somnolence. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring with greater frequency in the LYRICA group than in the placebo group, were asthenia, confusion, and peripheral edema. Each of these events led to withdrawal in approximately 1% of patients.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 4 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in greater than or equal to 1% of patients with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy in the combined LYRICA group for which the incidence was greater in this combined LYRICA group than in the placebo group. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate".
| Body system Preferred term | 75 mg/day [N=77] % | 150 mg/day [N=212] % | 300 mg/day [N=321] % | 600 mg/day [N=369] % | All PGB PGB: pregabalin [N=979] % | Placebo [N=459] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Body as a whole | ||||||
Asthenia | 4 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
Accidental injury | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
Back pain | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Chest pain | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Face edema | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Digestive system | ||||||
Dry mouth | 3 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 1 |
Constipation | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Flatulence | 3 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Metabolic and nutritional disorders | ||||||
Peripheral edema | 4 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 9 | 2 |
Weight gain | 0 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 0 |
Edema | 0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Hypoglycemia | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Nervous system | ||||||
Dizziness | 8 | 9 | 23 | 29 | 21 | 5 |
Somnolence | 4 | 6 | 13 | 16 | 12 | 3 |
Neuropathy | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
Ataxia | 6 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
Vertigo | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
Confusion | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Euphoria | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Incoordination | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Thinking abnormal Thinking abnormal primarily consists of events related to difficulty with concentration/attention but also includes events related to cognition and language problems and slowed thinking. | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
Tremor | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Abnormal gait | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Amnesia | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Nervousness | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Respiratory system | ||||||
Dyspnea | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Special senses | ||||||
Blurry vision Investigator term; summary level term is amblyopia | 3 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Abnormal vision | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Controlled Studies in Postherpetic Neuralgia
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In clinical trials in adults with postherpetic neuralgia, 14% of patients treated with LYRICA and 7% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LYRICA treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were dizziness (4%) and somnolence (3%). In comparison, less than 1% of placebo patients withdrew due to dizziness and somnolence. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring in greater frequency in the LYRICA group than in the placebo group, were confusion (2%), as well as peripheral edema, asthenia, ataxia, and abnormal gait (1% each).
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 5 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in greater than or equal to 1% of patients with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia in the combined LYRICA group for which the incidence was greater in this combined LYRICA group than in the placebo group. In addition, an event is included, even if the incidence in the all LYRICA group is not greater than in the placebo group, if the incidence of the event in the 600 mg/day group is more than twice that in the placebo group. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate". Overall, 12.4% of all pregabalin-treated patients and 9.0% of all placebo-treated patients had at least one severe event while 8% of pregabalin-treated patients and 4.3% of placebo-treated patients had at least one severe treatment-related adverse event.
| Body system Preferred term | 75 mg/d [N=84] % | 150 mg/d [N=302] % | 300 mg/d [N=312] % | 600 mg/d [N=154] % | All PGB PGB: pregabalin [N=852] % | Placebo [N=398] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Body as a whole | ||||||
Infection | 14 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 4 |
Headache | 5 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 5 |
Pain | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
Accidental injury | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
Flu syndrome | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Face edema | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Digestive system | ||||||
Dry mouth | 7 | 7 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 3 |
Constipation | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
Flatulence | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Vomiting | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Metabolic and nutritional disorders | ||||||
Peripheral edema | 0 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 12 | 4 |
Weight gain | 1 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 0 |
Edema | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 |
Musculoskeletal system | ||||||
Myasthenia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Nervous system | ||||||
Dizziness | 11 | 18 | 31 | 37 | 26 | 9 |
Somnolence | 8 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 16 | 5 |
Ataxia | 1 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 1 |
Abnormal gait | 0 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 1 |
Confusion | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 0 |
Thinking abnormal Thinking abnormal primarily consists of events related to difficulty with concentration/attention but also includes events related to cognition and language problems and slowed thinking. | 0 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 2 |
Incoordination | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
Amnesia | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
Speech disorder | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Respiratory system | ||||||
Bronchitis | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
Special senses | ||||||
Blurry vision Investigator term; summary level term is amblyopia | 1 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 3 |
Diplopia | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
Abnormal vision | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
Eye Disorder | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Urogenital System | ||||||
Urinary Incontinence | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Controlled Studies of Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Adult Patients
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
Approximately 15% of patients receiving LYRICA and 6% of patients receiving placebo in trials of adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LYRICA treatment group, the adverse reactions most frequently leading to discontinuation were dizziness (6%), ataxia (4%), and somnolence (3%). In comparison, less than 1% of patients in the placebo group withdrew due to each of these events. Other adverse reactions that led to discontinuation of at least 1% of patients in the LYRICA group and at least twice as frequently compared to the placebo group were asthenia, diplopia, blurred vision, thinking abnormal, nausea, tremor, vertigo, headache, and confusion (which each led to withdrawal in 2% or less of patients).
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 6 lists all dose-related adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of all LYRICA-treated patients. Dose-relatedness was defined as the incidence of the adverse event in the 600 mg/day group was at least 2% greater than the rate in both the placebo and 150 mg/day groups. In these studies, 758 patients received LYRICA and 294 patients received placebo for up to 12 weeks. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate".
| Body System Preferred Term | 150 mg/d [N=185] % | 300 mg/d [N=90] % | 600 mg/d [N=395] % | All PGB PGB: pregabalin [N=670] Excludes patients who received the 50 mg dose in Study E1. % | Placebo [N=294] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Body as a Whole | |||||
Accidental Injury | 7 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
Pain | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
Digestive System | |||||
Increased Appetite | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
Dry Mouth | 1 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 1 |
Constipation | 1 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | |||||
Weight Gain | 5 | 7 | 16 | 12 | 1 |
Peripheral Edema | 3 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 2 |
Nervous System | |||||
Dizziness | 18 | 31 | 38 | 32 | 11 |
Somnolence | 11 | 18 | 28 | 22 | 11 |
Ataxia | 6 | 10 | 20 | 15 | 4 |
Tremor | 3 | 7 | 11 | 8 | 4 |
Thinking Abnormal Thinking abnormal primarily consists of events related to difficulty with concentration/attention but also includes events related to cognition and language problems and slowed thinking. | 4 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 2 |
Amnesia | 3 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 2 |
Speech Disorder | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 1 |
Incoordination | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 1 |
Abnormal Gait | 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 0 |
Twitching | 0 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
Confusion | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
Myoclonus | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
Special Senses | |||||
Blurred Vision Investigator term; summary level term is amblyopia. | 5 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 4 |
Diplopia | 5 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 4 |
Abnormal Vision | 3 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
Controlled Study of Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 4 to Less Than 17 Years of Age
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
Approximately 2.5% of patients receiving LYRICA and no patients receiving placebo in trials of adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LYRICA treatment group, the adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were somnolence (3 patients), worsening of epilepsy (1 patient), and hallucination (1 patient).
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 7 lists all dose-related adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of all LYRICA-treated patients. Dose-relatedness was defined as an incidence of the adverse event in the 10 mg/kg/day group that was at least 2% greater than the rate in both the placebo and 2.5 mg/kg/day groups. In this study, 201 patients received LYRICA and 94 patients received placebo for up to 12 weeks. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in the clinical study had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate".
| Body System Preferred Term | 2.5 mg/kg/day 2.5 mg/kg/day: Maximum dose 150 mg/day. Includes patients less than 30 kg for whom dose was adjusted to 3.5 mg/kg/day. [N=104] % | 10 mg/kg/day 10 mg/kg/day: Maximum dose 600 mg/day. Includes patients less than 30 kg for whom dose was adjusted to 14 mg/kg/day. [N=97] % | All PGB [N=201] % | Placebo [N=94] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: N=number of patients; PGB = pregabalin. | ||||
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
Salivary hypersecretion | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
Investigations | ||||
Weight increased | 4 | 13 | 8 | 4 |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
Increased appetite | 7 | 10 | 8 | 4 |
Nervous system disorders | ||||
Somnolence | 17 | 26 | 21 | 14 |
Controlled Study of Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 1 Month to Less Than 4 Years of Age
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 8 lists all dose-related adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of all LYRICA-treated patients. Dose-relatedness was defined as an incidence of the adverse event in the 14 mg/kg/day group that was at least 2% greater than the rate in both the placebo and 7 mg/kg/day groups. In this study, 105 patients received LYRICA and 70 patients received placebo for up to 14 days.
| Body System Preferred Term | 7 mg/kg/day [N=71] % | 14 mg/kg/day [N=34] % | All PGB [N=105] % | Placebo [N=70] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: N=number of patients; PGB=pregabalin. | ||||
Nervous system disorders | ||||
Somnolence includes related terms including lethargy, sluggishness, and hypersomnia. | 13 | 21 | 15 | 9 |
Infections and infestations | ||||
Pneumonia | 1 | 9 | 4 | 0 |
Viral infection | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
Controlled Studies with Fibromyalgia
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In clinical trials of patients with fibromyalgia, 19% of patients treated with pregabalin (150–600 mg/day) and 10% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the pregabalin treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were dizziness (6%) and somnolence (3%). In comparison, less than 1% of placebo-treated patients withdrew due to dizziness and somnolence. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring with greater frequency in the pregabalin treatment group than in the placebo treatment group, were fatigue, headache, balance disorder, and weight increased. Each of these adverse reactions led to withdrawal in approximately 1% of patients.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 9 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of patients with fibromyalgia in the 'all pregabalin' treatment group for which the incidence was greater than in the placebo treatment group. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies experienced adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate".
| System Organ Class Preferred term | 150 mg/d [N=132] % | 300 mg/d [N=502] % | 450 mg/d [N=505] % | 600 mg/d [N=378] % | All PGB PGB: pregabalin [N=1517] % | Placebo [N=505] % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders | ||||||
Vertigo | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
Eye Disorders | ||||||
Vision blurred | 8 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 8 | 1 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||||
Dry mouth | 7 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 2 |
Constipation | 4 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 2 |
Vomiting | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
Flatulence | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Abdominal distension | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions | ||||||
Fatigue | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 4 |
Edema peripheral | 5 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 2 |
Chest pain | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Feeling abnormal | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Edema | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Feeling drunk | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||||
Sinusitis | 4 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
Investigations | ||||||
Weight increased | 8 | 10 | 10 | 14 | 11 | 2 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||||
Increased appetite | 4 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 1 |
Fluid retention | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||||
Arthralgia | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Muscle spasms | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
Back pain | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||||
Dizziness | 23 | 31 | 43 | 45 | 38 | 9 |
Somnolence | 13 | 18 | 22 | 22 | 20 | 4 |
Headache | 11 | 12 | 14 | 10 | 12 | 12 |
Disturbance in attention | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
Balance disorder | 2 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 0 |
Memory impairment | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
Coordination abnormal | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Hypoesthesia | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Lethargy | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Tremor | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Psychiatric Disorders | ||||||
Euphoric Mood | 2 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 1 |
Confusional state | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
Anxiety | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Disorientation | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
Depression | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||||
Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
Controlled Studies in Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In clinical trials of adults with neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury, 13% of patients treated with pregabalin and 10% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the pregabalin treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were somnolence (3%) and edema (2%). In comparison, none of the placebo-treated patients withdrew due to somnolence and edema. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring with greater frequency in the pregabalin treatment group than in the placebo treatment group, were fatigue and balance disorder. Each of these adverse reactions led to withdrawal in less than 2% of patients.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 10 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of patients for which the incidence was greater than in the placebo treatment group with neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury in the controlled trials. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies experienced adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate".
| System Organ Class Preferred term | PGB PGB: Pregabalin (N=182) | Placebo (N=174) |
|---|---|---|
| % | % | |
Ear and labyrinth disorders | ||
Vertigo | 2.7 | 1.1 |
Eye disorders | ||
Vision blurred | 6.6 | 1.1 |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
Dry mouth | 11.0 | 2.9 |
Constipation | 8.2 | 5.7 |
Nausea | 4.9 | 4.0 |
Vomiting | 2.7 | 1.1 |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
Fatigue | 11.0 | 4.0 |
Edema peripheral | 10.4 | 5.2 |
Edema | 8.2 | 1.1 |
Pain | 3.3 | 1.1 |
Infections and infestations | ||
Nasopharyngitis | 8.2 | 4.6 |
Investigations | ||
Weight increased | 3.3 | 1.1 |
Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 2.7 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
Muscular weakness | 4.9 | 1.7 |
Pain in extremity | 3.3 | 2.3 |
Neck pain | 2.7 | 1.1 |
Back pain | 2.2 | 1.7 |
Joint swelling | 2.2 | 0 |
Nervous system disorders | ||
Somnolence | 35.7 | 11.5 |
Dizziness | 20.9 | 6.9 |
Disturbance in attention | 3.8 | 0 |
Memory impairment | 3.3 | 1.1 |
Paresthesia | 2.2 | 0.6 |
Psychiatric disorders | ||
Insomnia | 3.8 | 2.9 |
Euphoric mood | 2.2 | 0.6 |
Renal and urinary disorders | ||
Urinary incontinence | 2.7 | 1.1 |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
Decubitus ulcer | 2.7 | 1.1 |
Vascular disorders | ||
Hypertension | 2.2 | 1.1 |
Hypotension | 2.2 | 0 |
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Clinical Studies of LYRICA
Following is a list of treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported by patients treated with LYRICA during all clinical trials. The listing does not include those events already listed in the previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, those events for which a drug cause was remote, those events which were so general as to be uninformative, and those events reported only once which did not have a substantial probability of being acutely life-threatening.
Events are categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients; rare reactions are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients. Events of major clinical importance are described in the Warnings and Precautions section (5).
Body as a Whole – Frequent: Abdominal pain, Allergic reaction, Fever, Infrequent: Abscess, Cellulitis, Chills, Malaise, Neck rigidity, Overdose, Pelvic pain, Photosensitivity reaction, Rare: Anaphylactoid reaction, Ascites, Granuloma, Hangover effect, Intentional Injury, Retroperitoneal Fibrosis, Shock
Cardiovascular System – Infrequent: Deep thrombophlebitis, Heart failure, Hypotension, Postural hypotension, Retinal vascular disorder, Syncope; Rare: ST Depressed, Ventricular Fibrillation
Digestive System – Frequent: Gastroenteritis, Increased appetite; Infrequent: Cholecystitis, Cholelithiasis, Colitis, Dysphagia, Esophagitis, Gastritis, Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, Melena, Mouth ulceration, Pancreatitis, Rectal hemorrhage, Tongue edema; Rare: Aphthous stomatitis, Esophageal Ulcer, Periodontal abscess
Hemic and Lymphatic System – Frequent: Ecchymosis; Infrequent: Anemia, Eosinophilia, Hypochromic anemia, Leukocytosis, Leukopenia, Lymphadenopathy, Thrombocytopenia; Rare: Myelofibrosis, Polycythemia, Prothrombin decreased, Purpura, Thrombocythemia, Alanine aminotransferase increased, Aspartate aminotransferase increased
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders – Rare: Glucose Tolerance Decreased, Urate Crystalluria
Musculoskeletal System – Frequent: Arthralgia, Leg cramps, Myalgia, Myasthenia; Infrequent: Arthrosis; Rare: Chondrodystrophy, Generalized Spasm
Nervous System – Frequent: Anxiety, Depersonalization, Hypertonia, Hypoesthesia, Libido decreased, Nystagmus, Paresthesia, Sedation, Stupor, Twitching; Infrequent: Abnormal dreams, Agitation, Apathy, Aphasia, Circumoral paresthesia, Dysarthria, Hallucinations, Hostility, Hyperalgesia, Hyperesthesia, Hyperkinesia, Hypokinesia, Hypotonia, Libido increased, Myoclonus, Neuralgia; Rare: Addiction, Cerebellar syndrome, Cogwheel rigidity, Coma, Delirium, Delusions, Dysautonomia, Dyskinesia, Dystonia, Encephalopathy, Extrapyramidal syndrome, Guillain-Barré syndrome, Hypalgesia, Intracranial hypertension, Manic reaction, Paranoid reaction, Peripheral neuritis, Personality disorder, Psychotic depression, Schizophrenic reaction, Sleep disorder, Torticollis, Trismus
Respiratory System – Rare: Apnea, Atelectasis, Bronchiolitis, Hiccup, Laryngismus, Lung edema, Lung fibrosis, Yawn
Skin and Appendages – Frequent: Pruritus, Infrequent: Alopecia, Dry skin, Eczema, Hirsutism, Skin ulcer, Urticaria, Vesiculobullous rash; Rare: Angioedema, Exfoliative dermatitis, Lichenoid dermatitis, Melanosis, Nail Disorder, Petechial rash, Purpuric rash, Pustular rash, Skin atrophy, Skin necrosis, Skin nodule, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Subcutaneous nodule
Special senses – Frequent: Conjunctivitis, Diplopia, Otitis media, Tinnitus; Infrequent: Abnormality of accommodation, Blepharitis, Dry eyes, Eye hemorrhage, Hyperacusis, Photophobia, Retinal edema, Taste loss, Taste perversion; Rare: Anisocoria, Blindness, Corneal ulcer, Exophthalmos, Extraocular palsy, Iritis, Keratitis, Keratoconjunctivitis, Miosis, Mydriasis, Night blindness, Ophthalmoplegia, Optic atrophy, Papilledema, Parosmia, Ptosis, Uveitis
Urogenital System – Frequent: Anorgasmia, Impotence, Urinary frequency, Urinary incontinence; Infrequent: Abnormal ejaculation, Albuminuria, Amenorrhea, Dysmenorrhea, Dysuria, Hematuria, Kidney calculus, Leukorrhea, Menorrhagia, Metrorrhagia, Nephritis, Oliguria, Urinary retention, Urine abnormality; Rare: Acute kidney failure, Balanitis, Bladder Neoplasm, Cervicitis, Dyspareunia, Epididymitis, Female lactation, Glomerulitis, Ovarian disorder, Pyelonephritis
Comparison of Gender and Race
The overall adverse event profile of pregabalin was similar between women and men. There are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse experience reports by race.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of LYRICA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Nervous System Disorders – Headache
Gastrointestinal Disorders – Nausea, Diarrhea
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders – Gynecomastia, Breast Enlargement
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders – Bullous pemphigoid
There are postmarketing reports of life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression in patients taking LYRICA with opioids or other CNS depressants, or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment.
In addition, there are postmarketing reports of events related to reduced lower gastrointestinal tract function (e.g., intestinal obstruction, paralytic ileus, constipation) when LYRICA was co-administered with medications that have the potential to produce constipation, such as opioid analgesics.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Since LYRICA is predominantly excreted unchanged in the urine, undergoes negligible metabolism in humans (less than 2% of a dose recovered in urine as metabolites), and does not bind to plasma proteins, its pharmacokinetics are unlikely to be affected by other agents through metabolic interactions or protein binding displacement. In vitro and in vivo studies showed that LYRICA is unlikely to be involved in significant pharmacokinetic drug interactions. Specifically, there are no pharmacokinetic interactions between pregabalin and the following antiepileptic drugs: carbamazepine, valproic acid, lamotrigine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, and topiramate. Important pharmacokinetic interactions would also not be expected to occur between LYRICA and commonly used antiepileptic drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12) ] .
Pharmacodynamics
Multiple oral doses of LYRICA were co-administered with oxycodone, lorazepam, or ethanol. Although no pharmacokinetic interactions were seen, additive effects on cognitive and gross motor functioning were seen when LYRICA was co-administered with these drugs. No clinically important effects on respiration were seen.
DESCRIPTION
Pregabalin is described chemically as ( S )-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. The molecular formula is C 8 H 17 NO 2 and the molecular weight is 159.23. The chemical structure of pregabalin is:
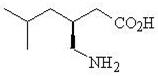
Pregabalin is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with a pK a1 of 4.2 and a pK a2 of 10.6. It is freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic aqueous solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is – 1.35.
LYRICA (pregabalin) Capsules are administered orally and are supplied as imprinted hard-shell capsules containing 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 225, and 300 mg of pregabalin, along with lactose monohydrate, cornstarch, and talc as inactive ingredients. The capsule shells contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. In addition, the orange capsule shells contain red iron oxide and the white capsule shells contain sodium lauryl sulfate and colloidal silicon dioxide. Colloidal silicon dioxide is a manufacturing aid that may or may not be present in the capsule shells. The imprinting ink contains shellac, black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and potassium hydroxide.
LYRICA (pregabalin) oral solution, 20 mg/mL, is administered orally and is supplied as a clear, colorless solution contained in a 16 fluid ounce white HDPE bottle with a polyethylene-lined closure. The oral solution contains 20 mg/mL of pregabalin, along with methylparaben, propylparaben, monobasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, sucralose, artificial strawberry #11545 and purified water as inactive ingredients.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
LYRICA (pregabalin) binds with high affinity to the alpha 2 -delta site (an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels) in central nervous system tissues. Although the mechanism of action of pregabalin has not been fully elucidated, results with genetically modified mice and with compounds structurally related to pregabalin (such as gabapentin) suggest that binding to the alpha 2 -delta subunit may be involved in pregabalin's anti-nociceptive and antiseizure effects in animals. In animal models of nerve damage, pregabalin has been shown to reduce calcium-dependent release of pro-nociceptive neurotransmitters in the spinal cord, possibly by disrupting alpha 2 -delta containing-calcium channel trafficking and/or reducing calcium currents. Evidence from other animal models of nerve damage and persistent pain suggest the anti-nociceptive activities of pregabalin may also be mediated through interactions with descending noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways originating from the brainstem that modulate pain transmission in the spinal cord.
While pregabalin is a structural derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind directly to GABA A , GABA B , or benzodiazepine receptors, does not augment GABA A responses in cultured neurons, does not alter rat brain GABA concentration or have acute effects on GABA uptake or degradation. However, in cultured neurons prolonged application of pregabalin increases the density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport. Pregabalin does not block sodium channels, is not active at opiate receptors, and does not alter cyclooxygenase enzyme activity. It is inactive at serotonin and dopamine receptors and does not inhibit dopamine, serotonin, or noradrenaline reuptake.
Pharmacokinetics
Pregabalin is well absorbed after oral administration, is eliminated largely by renal excretion, and has an elimination half-life of about 6 hours.
Absorption and Distribution
Following oral administration of LYRICA capsules under fasting conditions, peak plasma concentrations occur within 1.5 hours. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is greater than or equal to 90% and is independent of dose. Following single- (25 to 300 mg) and multiple-dose (75 to 900 mg/day) administration, maximum plasma concentrations (C max ) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) values increase linearly. Following repeated administration, steady state is achieved within 24 to 48 hours. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics can be predicted from single-dose data.
The rate of pregabalin absorption is decreased when given with food, resulting in a decrease in C max of approximately 25% to 30% and an increase in T max to approximately 3 hours. However, administration of pregabalin with food has no clinically relevant effect on the total absorption of pregabalin. Therefore, pregabalin can be taken with or without food.
Pregabalin does not bind to plasma proteins. The apparent volume of distribution of pregabalin following oral administration is approximately 0.5 L/kg. Pregabalin is a substrate for system L transporter which is responsible for the transport of large amino acids across the blood brain barrier. Although there are no data in humans, pregabalin has been shown to cross the blood brain barrier in mice, rats, and monkeys. In addition, pregabalin has been shown to cross the placenta in rats and is present in the milk of lactating rats.
Metabolism and Elimination
Pregabalin undergoes negligible metabolism in humans. Following a dose of radiolabeled pregabalin, approximately 90% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine as unchanged pregabalin. The N-methylated derivative of pregabalin, the major metabolite of pregabalin found in urine, accounted for 0.9% of the dose. In preclinical studies, pregabalin (S-enantiomer) did not undergo racemization to the R-enantiomer in mice, rats, rabbits, or monkeys.
Pregabalin is eliminated from the systemic circulation primarily by renal excretion as unchanged drug with a mean elimination half-life of 6.3 hours in subjects with normal renal function. Mean renal clearance was estimated to be 67.0 to 80.9 mL/min in young healthy subjects. Because pregabalin is not bound to plasma proteins this clearance rate indicates that renal tubular reabsorption is involved. Pregabalin elimination is nearly proportional to creatinine clearance (CLcr) [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Pharmacokinetics in Specific Populations
Race
In population pharmacokinetic analyses of the clinical studies in various populations, the pharmacokinetics of LYRICA were not significantly affected by race (Caucasians, Blacks, and Hispanics).
Gender
Population pharmacokinetic analyses of the clinical studies showed that the relationship between daily dose and LYRICA drug exposure is similar between genders.
Renal Impairment and Hemodialysis
Pregabalin clearance is nearly proportional to creatinine clearance (CLcr). Dosage reduction in patients with renal dysfunction is necessary. Pregabalin is effectively removed from plasma by hemodialysis. Following a 4-hour hemodialysis treatment, plasma pregabalin concentrations are reduced by approximately 50%. For patients on hemodialysis, dosing must be modified [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Elderly
Pregabalin oral clearance tended to decrease with increasing age. This decrease in pregabalin oral clearance is consistent with age-related decreases in CLcr. Reduction of pregabalin dose may be required in patients who have age-related compromised renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Pediatric Pharmacokinetics
Pediatric Patients (3 months to less than 17 years of age)
Pregabalin pharmacokinetics were evaluated in 358 pediatric patients 3 months to less than 17 years of age with partial-onset seizures at dose levels of 2.5, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day after single and multiple oral administration of pregabalin. Following oral administration, pregabalin reaches peak plasma concentration at 0.5 hours to 2 hours in the fasted state. Both apparent clearance (CL/F) and apparent volume of distribution increase as body weight increases. A weight-based dosing regimen is necessary to achieve pregabalin exposures in pediatric patients 1 month to less than 17 years of age similar to those observed in adults treated for partial-onset seizures at effective doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ]. The mean t ½ is 3 to 4 hours in pediatric subjects up to 6 years of age, and 4 to 6 hours in those 7 years of age and older. Pregabalin CL/F is nearly proportional to CLcr (mL/min). The relationship is similar in pediatric and adult subjects. When normalized per body weight, CL/F (mL/min/kg) in pediatric subjects weighing less than 30 kg is approximately 40% higher in comparison to subjects weighing greater than or equal to 30 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies
Pregabalin, at concentrations that were, in general, 10-times those attained in clinical trials, does not inhibit human CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 enzyme systems. In vitro drug interaction studies demonstrate that pregabalin does not induce CYP1A2 or CYP3A4 activity. Therefore, an increase in the metabolism of coadministered CYP1A2 substrates (e.g. theophylline, caffeine) or CYP 3A4 substrates (e.g., midazolam, testosterone) is not anticipated.
In Vivo Studies
The drug interaction studies described in this section were conducted in healthy adults, and across various patient populations.
Gabapentin
The pharmacokinetic interactions of pregabalin and gabapentin were investigated in 12 healthy subjects following concomitant single-dose administration of 100-mg pregabalin and 300-mg gabapentin and in 18 healthy subjects following concomitant multiple-dose administration of 200-mg pregabalin every 8 hours and 400-mg gabapentin every 8 hours. Gabapentin pharmacokinetics following single- and multiple-dose administration were unaltered by pregabalin coadministration. The extent of pregabalin absorption was unaffected by gabapentin coadministration, although there was a small reduction in rate of absorption.
Oral Contraceptive
Pregabalin coadministration (200 mg three times a day) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol (1 mg/35 µg, respectively) in healthy subjects.
Lorazepam
Multiple-dose administration of pregabalin (300 mg twice a day) in healthy subjects had no effect on the rate and extent of lorazepam single-dose pharmacokinetics and single-dose administration of lorazepam (1 mg) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of pregabalin.
Oxycodone
Multiple-dose administration of pregabalin (300 mg twice a day) in healthy subjects had no effect on the rate and extent of oxycodone single-dose pharmacokinetics. Single-dose administration of oxycodone (10 mg) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of pregabalin.
Ethanol
Multiple-dose administration of pregabalin (300 mg twice a day) in healthy subjects had no effect on the rate and extent of ethanol single-dose pharmacokinetics and single-dose administration of ethanol (0.7 g/kg) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of pregabalin.
Phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, and lamotrigine
Steady-state trough plasma concentrations of phenytoin, carbamazepine and carbamazepine 10,11 epoxide, valproic acid, and lamotrigine were not affected by concomitant pregabalin (200 mg three times a day) administration.
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients treated with pregabalin and various concomitant medications suggest the following:
| Therapeutic class | Specific concomitant drug studied |
|---|---|
Concomitant drug has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of pregabalin | |
Hypoglycemics | Glyburide, insulin, metformin |
Diuretics | Furosemide |
Antiepileptic Drugs | Tiagabine |
Concomitant drug has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of pregabalin and pregabalin has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of concomitant drug | |
Antiepileptic Drugs | Carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, topiramate, valproic acid |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
A dose-dependent increase in the incidence of malignant vascular tumors (hemangiosarcomas) was observed in two strains of mice (B6C3F1 and CD-1) given pregabalin (200, 1000, or 5000 mg/kg) in the diet for two years. Plasma pregabalin exposure (AUC) in mice receiving the lowest dose that increased hemangiosarcomas was approximately equal to the human exposure at the maximum recommended dose (MRD) of 600 mg/day. A no-effect dose for induction of hemangiosarcomas in mice was not established. No evidence of carcinogenicity was seen in two studies in Wistar rats following dietary administration of pregabalin for two years at doses (50, 150, or 450 mg/kg in males and 100, 300, or 900 mg/kg in females) that were associated with plasma exposures in males and females up to approximately 14 and 24 times, respectively, human exposure at the MRD.
Mutagenesis
Pregabalin was not mutagenic in bacteria or in mammalian cells in vitro , was not clastogenic in mammalian systems in vitro and in vivo , and did not induce unscheduled DNA synthesis in mouse or rat hepatocytes.
Impairment of Fertility
In fertility studies in which male rats were orally administered pregabalin (50 to 2500 mg/kg) prior to and during mating with untreated females, a number of adverse reproductive and developmental effects were observed. These included decreased sperm counts and sperm motility, increased sperm abnormalities, reduced fertility, increased preimplantation embryo loss, decreased litter size, decreased fetal body weights, and an increased incidence of fetal abnormalities. Effects on sperm and fertility parameters were reversible in studies of this duration (3–4 months). The no-effect dose for male reproductive toxicity in these studies (100 mg/kg) was associated with a plasma pregabalin exposure (AUC) approximately 3 times human exposure at the maximum recommended dose (MRD) of 600 mg/day.
In addition, adverse reactions on reproductive organ (testes, epididymides) histopathology were observed in male rats exposed to pregabalin (500 to 1250 mg/kg) in general toxicology studies of four weeks or greater duration. The no-effect dose for male reproductive organ histopathology in rats (250 mg/kg) was associated with a plasma exposure approximately 8 times human exposure at the MRD.
In a fertility study in which female rats were given pregabalin (500, 1250, or 2500 mg/kg) orally prior to and during mating and early gestation, disrupted estrous cyclicity and an increased number of days to mating were seen at all doses, and embryolethality occurred at the highest dose. The low dose in this study produced a plasma exposure approximately 9 times that in humans receiving the MRD. A no-effect dose for female reproductive toxicity in rats was not established.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Dermatopathy
Skin lesions ranging from erythema to necrosis were seen in repeated-dose toxicology studies in both rats and monkeys. The etiology of these skin lesions is unknown. At the maximum recommended human dose (MRD) of 600 mg/day, there is a 2-fold safety margin for the dermatological lesions. The more severe dermatopathies involving necrosis were associated with pregabalin exposures (as expressed by plasma AUCs) of approximately 3 to 8 times those achieved in humans given the MRD. No increase in incidence of skin lesions was observed in clinical studies.
Ocular Lesions
Ocular lesions (characterized by retinal atrophy [including loss of photoreceptor cells] and/or corneal inflammation/mineralization) were observed in two lifetime carcinogenicity studies in Wistar rats. These findings were observed at plasma pregabalin exposures (AUC) greater than or equal to 2 times those achieved in humans given the maximum recommended dose of 600 mg/day. A no-effect dose for ocular lesions was not established. Similar lesions were not observed in lifetime carcinogenicity studies in two strains of mice or in monkeys treated for 1 year.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
The efficacy of the maximum recommended dose of LYRICA for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy was established in three double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies with three times a day dosing, two of which studied the maximum recommended dose. Patients were enrolled with either Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus and a diagnosis of painful distal symmetrical sensorimotor polyneuropathy for 1 to 5 years. A total of 89% of patients completed Studies DPN 1 and DPN 2. The patients had a minimum mean baseline pain score of greater than or equal to 4 on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). The baseline mean pain scores across the two studies ranged from 6.1 to 6.7. Patients were permitted up to 4 grams of acetaminophen per day as needed for pain, in addition to pregabalin. Patients recorded their pain daily in a diary.
Study DPN 1: This 5-week study compared LYRICA 25, 100, or 200 mg three times a day with placebo. Treatment with LYRICA 100 and 200 mg three times a day statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. There was no evidence of a greater effect on pain scores of the 200 mg three times a day dose than the 100 mg three times a day dose, but there was evidence of dose dependent adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . For a range of levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 1 shows the fraction of patients achieving that level of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 1: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity – Study DPN 1
Study DPN 2: This 8-week study compared LYRICA 100 mg three times a day with placebo. Treatment with LYRICA 100 mg three times a day statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. For various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 2 shows the fraction of patients achieving that level of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 2: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity– Study DPN 2
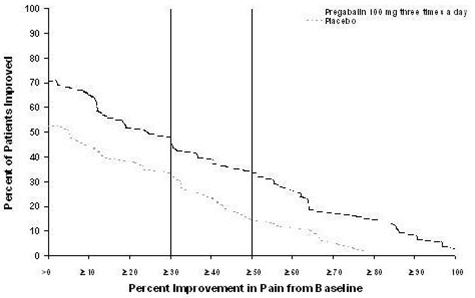
Postherpetic Neuralgia
The efficacy of LYRICA for the management of postherpetic neuralgia was established in three double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies. These studies enrolled patients with neuralgia persisting for at least 3 months following healing of herpes zoster rash and a minimum baseline score of greater than or equal to 4 on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). Seventy-three percent of patients completed the studies. The baseline mean pain scores across the 3 studies ranged from 6 to 7. Patients were permitted up to 4 grams of acetaminophen per day as needed for pain, in addition to pregabalin. Patients recorded their pain daily in a diary.
Study PHN 1: This 13-week study compared LYRICA 75, 150, and 300 mg twice daily with placebo. Patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) between 30 to 60 mL/min were randomized to 75 mg, 150 mg, or placebo twice daily. Patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min were randomized to 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg or placebo twice daily. In patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min treatment with all doses of LYRICA statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. Despite differences in dosing based on renal function, patients with creatinine clearance between 30 to 60 mL/min tolerated LYRICA less well than patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min as evidenced by higher rates of discontinuation due to adverse reactions. For various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 3 shows the fraction of patients achieving that level of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 3: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity– Study PHN 1
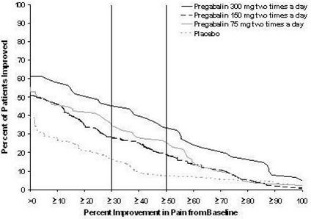
Study PHN 2: This 8-week study compared LYRICA 100 or 200 mg three times a day with placebo, with doses assigned based on creatinine clearance. Patients with creatinine clearance between 30 to 60 mL/min were treated with 100 mg three times a day, and patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min were treated with 200 mg three times daily. Treatment with LYRICA statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. For various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 4 shows the fraction of patients achieving those levels of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 4: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity – Study PHN 2
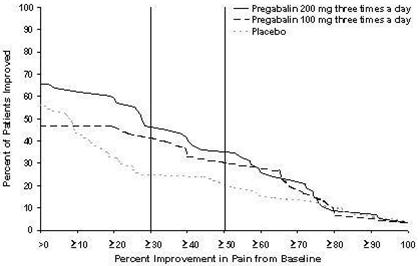
Study PHN 3: This 8-week study compared LYRICA 50 or 100 mg three times a day with placebo with doses assigned regardless of creatinine clearance. Treatment with LYRICA 50 and 100 mg three times a day statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. Patients with creatinine clearance between 30 to 60 mL/min tolerated LYRICA less well than patients with creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min as evidenced by markedly higher rates of discontinuation due to adverse reactions. For various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 5 shows the fraction of patients achieving that level of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 5: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity– Study PHN 3
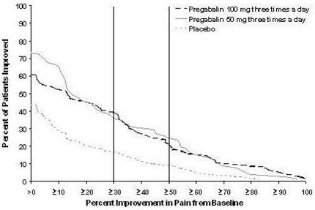
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 1 Month of Age and Older
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Adult Patients
The efficacy of LYRICA as adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in adult patients was established in three 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies. Patients were enrolled who had partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization and were not adequately controlled with 1 to 3 concomitant antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Patients taking gabapentin were required to discontinue gabapentin treatment 1 week prior to entering baseline. During an 8-week baseline period, patients had to experience at least 6 partial-onset seizures with no seizure-free period exceeding 4 weeks. The mean duration of epilepsy was 25 years in these 3 studies and the mean and median baseline seizure frequencies were 22.5 and 10 seizures per month, respectively. Approximately half of the patients were taking 2 concurrent AEDs at baseline. Among the LYRICA-treated patients, 80% completed the double-blind phase of the studies.
Table 11 shows median baseline seizure rates and median percent reduction in seizure frequency by dose.
| Daily Dose of Pregabalin | Dosing Regimen | N | Baseline Seizure Frequency/mo | Median % Change from Baseline | p-value, vs. placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Study E1 | |||||
Placebo | BID | 100 | 9.5 | 0 | |
50 mg/day | BID | 88 | 10.3 | -9 | 0.4230 |
150 mg/day | BID | 86 | 8.8 | -35 | 0.0001 |
300 mg/day | BID | 90 | 9.8 | -37 | 0.0001 |
600 mg/day | BID | 89 | 9.0 | -51 | 0.0001 |
Study E2 | |||||
Placebo | TID | 96 | 9.3 | 1 | |
150 mg/day | TID | 99 | 11.5 | -17 | 0.0007 |
600 mg/day | TID | 92 | 12.3 | -43 | 0.0001 |
Study E3 | |||||
Placebo | BID/TID | 98 | 11 | -1 | |
600 mg/day | BID | 103 | 9.5 | -36 | 0.0001 |
600 mg/day | TID | 111 | 10 | -48 | 0.0001 |
In the first study (E1), there was evidence of a dose-response relationship for total daily doses of LYRICA between 150 and 600 mg/day; a dose of 50 mg/day was not effective. In the first study (E1), each daily dose was divided into two equal doses (twice a day dosing). In the second study (E2), each daily dose was divided into three equal doses (three times a day dosing). In the third study (E3), the same total daily dose was divided into two equal doses for one group (twice a day dosing) and three equal doses for another group (three times a day dosing). While the three times a day dosing group in Study E3 performed numerically better than the twice a day dosing group, this difference was small and not statistically significant.
A secondary outcome measure included the responder rate (proportion of patients with greater than or equal to 50% reduction from baseline in partial seizure frequency). The following figure displays responder rate by dose for two of the studies.
Figure 6: Responder Rate by Adjunctive Epilepsy Study
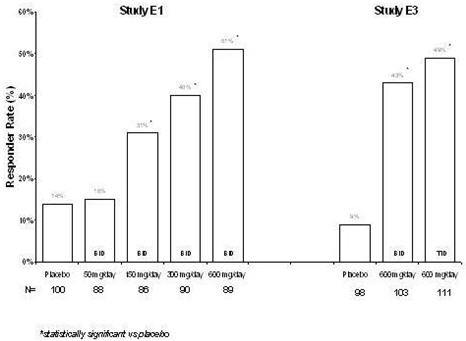
Figure 7: Seizure Reduction by Dose (All Partial-Onset Seizures) for Studies E1, E2, and E3
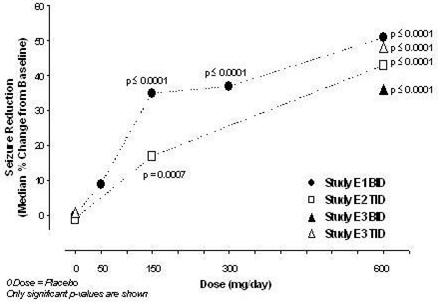
Subset evaluations of the antiseizure efficacy of LYRICA showed no clinically important differences as a function of age, gender, or race.
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients 4 to Less Than 17 Years of Age
The efficacy of LYRICA as adjunctive therapy in partial-onset seizures was established in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in pediatric patients 4 years to less than 17 years of age with partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization. During an 8-week baseline period, patients had to experience at least 6 partial-onset seizures with no seizure-free period exceeding 4 weeks. The mean duration of epilepsy was 6 years and the mean and median baseline seizure frequencies were 57 and 18 seizures per month, respectively. Approximately 74% of the patients were taking 2 to 3 concurrent AEDs at baseline. Among the LYRICA-treated patients, 87% completed the double-blind phase of the study.
In this study, LYRICA 2.5 mg/kg/day (maximum 150 mg/day) and 10 mg/kg/day (maximum 600 mg/day) were compared to placebo. Administration of each daily dose was divided into two equal doses (twice a day dosing). Because of higher weight-normalized clearance in patients with body weight less than 30 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , the LYRICA dose was increased by 40% to 3.5 mg/kg/day for patients weighing less than 30 kg randomized to the 2.5 mg/kg/day group or to 14 mg/kg/day for patients randomized to the 10 mg/kg/day group.
Table 12 shows median baseline seizure rates, median percent change from baseline in seizure rates, and percent difference relative to placebo (derived from the primary analysis model) by dose.
| Daily Dose of LYRICA | N | Median Baseline Seizure Frequency/28 days | Median % Change from Baseline | % Difference Relative to Placebo | p-value, versus placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: BID=twice daily; N=number. | |||||
Placebo | 93 | 16.5 | -16.9 | Not applicable | |
2.5 mg/kg/day (BID) 2.5 mg/kg/day: Maximum dose 150 mg/day. Includes patients less than 30 kg for whom dose was adjusted to 3.5 mg/kg/day. | 104 | 23.8 | -27.3 | -10.5 | 0.2577 |
10 mg/kg/day (BID) 10 mg/kg/day: Maximum dose 600 mg/day. Includes patients less than 30 kg for whom dose was adjusted to 14 mg/kg/day. | 97 | 17.5 | -37.1 | -21.0 | 0.0185 |
There was evidence of a dose-response relationship for total daily doses of LYRICA between 2.5 mg/kg/day and 10 mg/kg/day. A significant improvement in seizure rate was observed for LYRICA 10 mg/kg/day group compared with placebo. While the 2.5 mg/kg/day group performed numerically better than placebo, this difference was not statistically significant.
A key secondary efficacy measure, the responder rate (proportion of patients with greater than or equal to 50% reduction from baseline in partial seizure frequency) showed improvements for LYRICA groups compared with placebo. The following figure displays responder rate by dose:
Figure 8: Responder Rate (Greater than or Equal to 50% Reduction)
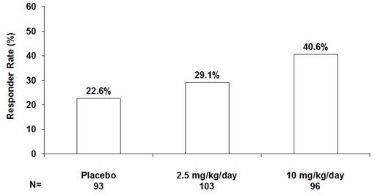
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients 1 Month to Less Than 4 Years of Age
The efficacy of LYRICA as adjunctive therapy in partial-onset seizures was established in a 14-day, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in children 1 month to less than 4 years of age with partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization. The youngest patient evaluated was 3 months of age. During a 48- to 72-hour baseline video electroencephalogram (EEG), patients had to experience at least 2 partial-onset seizures. The mean duration of epilepsy at baseline was 1.6 years and the mean and median baseline seizure frequencies were 12.2 and 4.4 seizures per day, respectively. Approximately 33%, 50%, and 17% of patients were taking 1, 2, or 3 concurrent AEDs at baseline, respectively. Among the LYRICA-treated patients, 97% completed the double-blind phase of the study.
In this study, LYRICA 7 mg/kg/day and 14 mg/kg/day were compared to placebo. Administration of each daily dose was divided into three equal doses (three times a day dosing). The primary endpoint was the 24-hour partial-onset seizure rate based on the comparison of the baseline video EEG to a repeat 48–72 hour video EEG performed at the end of 14 days of double-blind treatment.
Table 13 shows median baseline seizure rates, median percent change from baseline in seizure rates, and percent difference relative to placebo (derived from the primary analysis model) by dose.
| Daily Dose of LYRICA | N | Median Baseline Seizure Frequency/24 hours | Median % Change from Baseline | % Difference Relative to Placebo | p-value, versus placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: N=number of patients | |||||
Placebo | 53 | 2.9 | 22.2 | Not applicable | |
7 mg/kg/day | 59 | 4.7 | 16.8 | 15.1 | 0.4606 |
14 mg/kg/day | 28 | 5.4 | 70.0 | -43.9 | 0.0223 |
A significant improvement in partial-onset seizure rate was observed for LYRICA 14 mg/kg/day group compared with placebo. Patients treated with LYRICA 7 mg/kg/day did not show improvement relative to placebo.
Responder rates (≥50% or greater reduction in partial-onset seizure frequency) were a secondary efficacy parameter; patients treated with LYRICA 14 mg/kg/day showed numerical improvement compared with placebo, while patients treated with LYRICA 7 mg/kg/day did not show improvement relative to placebo: the responder rates were 53.6%, 30.5%, and 41.5% for LYRICA 14 mg/kg/day, LYRICA 7 mg/kg/day, and placebo, respectively.
Management of Fibromyalgia
The efficacy of LYRICA for management of fibromyalgia was established in one 14-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study (F1) and one six-month, randomized withdrawal study (F2). Studies F1 and F2 enrolled patients with a diagnosis of fibromyalgia using the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria (history of widespread pain for 3 months, and pain present at 11 or more of the 18 specific tender point sites). The studies showed a reduction in pain by visual analog scale. In addition, improvement was demonstrated based on a patient global assessment (PGIC), and on the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ).
Study F1 : This 14-week study compared LYRICA total daily doses of 300 mg, 450 mg and 600 mg with placebo. Patients were enrolled with a minimum mean baseline pain score of greater than or equal to 4 on an 11-point numeric pain rating scale and a score of greater than or equal to 40 mm on the 100 mm pain visual analog scale (VAS). The baseline mean pain score in this trial was 6.7. Responders to placebo in an initial one-week run-in phase were not randomized into subsequent phases of the study. A total of 64% of patients randomized to LYRICA completed the study. There was no evidence of a greater effect on pain scores of the 600 mg daily dose than the 450 mg daily dose, but there was evidence of dose-dependent adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study. The results are summarized in Figure 9 and Table 14.
For various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 9 shows the fraction of patients achieving that level of improvement. The figure is cumulative. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as Week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 9: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity – Fibromyalgia Study F1
| Patient Global Impression of Change | ||
|---|---|---|
| Treatment Group (mg/day) | % Any Improvement | 95% CI |
| PGB = Pregabalin | ||
Placebo | 47.6 | (40.0,55.2) |
PGB 300 | 68.1 | (60.9, 75.3) |
PGB 450 | 77.8 | (71.5, 84.0) |
PGB 600 | 66.1 | (59.1, 73.1) |
Study F2 : This randomized withdrawal study compared LYRICA with placebo. Patients were titrated during a 6-week open-label dose optimization phase to a total daily dose of 300 mg, 450 mg, or 600 mg. Patients were considered to be responders if they had both: 1) at least a 50% reduction in pain (VAS) and, 2) rated their overall improvement on the PGIC as "much improved" or "very much improved." Those who responded to treatment were then randomized in the double-blind treatment phase to either the dose achieved in the open-label phase or to placebo. Patients were treated for up to 6 months following randomization. Efficacy was assessed by time to loss of therapeutic response, defined as 1) less than 30% reduction in pain (VAS) from open-label baseline during two consecutive visits of the double-blind phase, or 2) worsening of FM symptoms necessitating an alternative treatment. Fifty-four percent of patients were able to titrate to an effective and tolerable dose of LYRICA during the 6-week open-label phase. Of the patients entering the randomized treatment phase assigned to remain on LYRICA, 38% of patients completed 26 weeks of treatment versus 19% of placebo-treated patients.
When considering return of pain or withdrawal due to adverse events as loss of response (LTR), treatment with LYRICA resulted in a longer time to loss of therapeutic response than treatment with placebo. Fifty-three percent of the pregabalin-treated subjects compared to 33% of placebo patients remained on study drug and maintained a therapeutic response to Week 26 of the study. Treatment with LYRICA also resulted in a longer time to loss of response based on the FIQ Time to worsening of the FIQ was defined as the time to a 1-point increase from double-blind baseline in each of the subscales, and a 5-point increase from double-blind baseline evaluation for the FIQ total score. , and longer time to loss of overall assessment of patient status, as measured by the PGIC Time to PGIC lack of improvement was defined as time to PGIC assessments indicating less improvement than "much improvement." .
Figure 10: Time to Loss of Therapeutic Response, Fibromyalgia Study F2 (Kaplan-Meier Analysis)
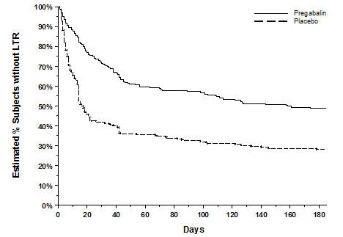
Management of Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury
The efficacy of LYRICA for the management of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury was established in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies. Patients were enrolled with neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury that persisted continuously for at least three months or with relapses and remissions for at least six months. A total of 63% of patients completed study 1 and 84% completed study 2. The patients had a minimum mean baseline pain score of greater than or equal to 4 on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). The baseline mean pain scores across the two studies ranged from 6.5 to 6.7.
Patients were allowed to take opioids, non-opioid analgesics, antiepileptic drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressant drugs if the dose was stable for 30 days prior to screening. Patients were allowed to take acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during the studies.
Study SCI 1 : This 12-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, flexible dose (150–600 mg/day) study compared pregabalin with placebo. The 12-week study consisted of a 3-week dose adjustment phase and a 9-week dose maintenance phase. Treatment with LYRICA 150–600 mg/day statistically significantly improved the endpoint weekly mean pain score, and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 30% and 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. The fraction of patients achieving various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to Week 12 is presented in Figure 11. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 11 : Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity – Study SCI 1
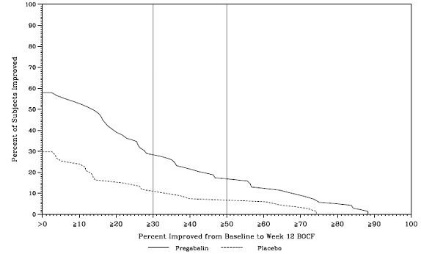
Study SCI 2 : This 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter, flexible dose (150–600 mg/day, in increments of 150 mg) study compared the efficacy, safety and tolerability of pregabalin with placebo. The 16-week study consisted of a 4-week dose adjustment phase and a 12-week dose maintenance phase. Treatment with LYRICA statistically significantly improved the endpoint weekly mean pain score, and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 30% and 50% reduction in pain score from baseline. The fraction of patients achieving various levels of improvement in pain intensity from baseline to Week 16 is presented in Figure 12. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as week 1, which persisted throughout the study.
Figure 12 : Patients Achieving Various Levels of Improvement in Pain Intensity – Study SCI 2
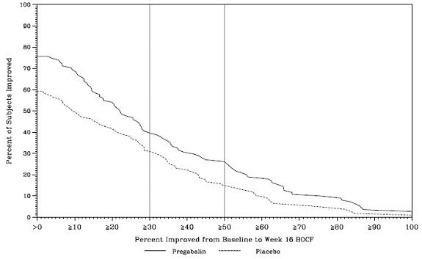
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
25 mg capsules:
White, hard-gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 25" on the body; available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1012-68 |
50 mg capsules:
White, hard-gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 50" and an ink band on the body, available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1013-68 |
Unit-Dose Blister Packages of 100: | NDC 0071-1013-41 |
75 mg capsules:
White/orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 75" on the body; available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1014-68 |
Unit-Dose Blister Packages of 100: | NDC 0071-1014-41 |
100 mg capsules:
Orange, hard-gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 100" on the body, available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1015-68 |
Unit-Dose Blister Packages of 100: | NDC 0071-1015-41 |
150 mg capsules:
White hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 150" on the body, available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1016-68 |
Unit-Dose Blister Packages of 100: | NDC 0071-1016-41 |
200 mg capsules:
Light orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 200" on the body, available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1017-68 |
225 mg capsules:
White/light orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 225" on the body; available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1019-68 |
300 mg capsules:
White/orange hard gelatin capsule printed with black ink "Pfizer" on the cap, "PGN 300" on the body, available in:
Bottles of 90: | NDC 0071-1018-68 |
20 mg/mL oral solution:
16 fluid ounce white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a polyethylene-lined closure:
16 fluid ounce bottle | NDC 0071-1020-01 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) (see USP Controlled Room Temperature).
Mechanism of Action
LYRICA (pregabalin) binds with high affinity to the alpha 2 -delta site (an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels) in central nervous system tissues. Although the mechanism of action of pregabalin has not been fully elucidated, results with genetically modified mice and with compounds structurally related to pregabalin (such as gabapentin) suggest that binding to the alpha 2 -delta subunit may be involved in pregabalin's anti-nociceptive and antiseizure effects in animals. In animal models of nerve damage, pregabalin has been shown to reduce calcium-dependent release of pro-nociceptive neurotransmitters in the spinal cord, possibly by disrupting alpha 2 -delta containing-calcium channel trafficking and/or reducing calcium currents. Evidence from other animal models of nerve damage and persistent pain suggest the anti-nociceptive activities of pregabalin may also be mediated through interactions with descending noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways originating from the brainstem that modulate pain transmission in the spinal cord.
While pregabalin is a structural derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind directly to GABA A , GABA B , or benzodiazepine receptors, does not augment GABA A responses in cultured neurons, does not alter rat brain GABA concentration or have acute effects on GABA uptake or degradation. However, in cultured neurons prolonged application of pregabalin increases the density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport. Pregabalin does not block sodium channels, is not active at opiate receptors, and does not alter cyclooxygenase enzyme activity. It is inactive at serotonin and dopamine receptors and does not inhibit dopamine, serotonin, or noradrenaline reuptake.