Methohexital Sodium - Methohexital Sodium injection prescribing information
Methohexital Sodium for Injection can be used in adults as follows:
- For intravenousinduction of anesthesia prior to the use of other general anesthetic agents.
- For intravenousinduction of anesthesia and as an adjunct to subpotent inhalational anesthetic agents (such as nitrous oxide in oxygen) for short surgical procedures; Methohexital Sodium for Injection may be given by infusion or intermittent injection.
- For use along with other parenteral agents, usually narcotic analgesics, to supplement subpotent inhalational anesthetic agents (such as nitrous oxide in oxygen) for longer surgical procedures.
- As intravenousanesthesia for short surgical, diagnostic, or therapeutic procedures associated with minimal painful stimuli (SeeWARNINGS).
- As an agent for inducing a hypnotic state.
Methohexital Sodium for Injection can be used in
- For rectal or intramuscularinductionof anesthesia prior to the use of other general anesthetic agents.
- For rectal or intramuscularinductionof anesthesia and as an adjunct to subpotent inhalational anesthetic agents for short surgical procedures.
- As rectal or intramuscularanesthesia for short surgical, diagnostic, or therapeutic procedures associated with minimal painful stimuli.
Facilities for assisting ventilation and administering oxygen are necessary adjuncts for all routes of administration of anesthesia. Since cardiorespiratory arrest may occur, patients should be observed carefully during and after use of Methohexital sodium for injection. Age- and size- appropriate resuscitative equipment (i.e., intubation and cardioversion equipment, oxygen, suction, and a secure intravenous line) and personnel qualified in its use must be immediately available.
Preanesthetic medication is generally advisable. Methohexital Sodium for Injection may be used with any of the recognized preanesthetic medications.
FOLLOW DILUTION INSTRUCTIONS EXACTLY.
Freshly prepare solutions of Methohexital Sodium for Injection and use promptly. Reconstituted solutions of Methohexital Sodium for Injection are chemically stable at room temperature for 24 hours.
ONLY USE BACTERIOSTATIC-FREE DILUENT - Recommended diluents are based on route of administration (See
Incompatible diluents: Lactated Ringer's Injection
1% solutions (10 mg/mL) should be prepared for intermittent intravenous and rectal administration; 0.2% solutions (2 mg/mL) should be prepared for continuous intravenous drug administration; 5% solutions (50 mg/mL) should be prepared for intramuscular administration.
Contents of vials should be diluted as follows:
The preferred diluent for intermittent intravenous and rectal administration is Sterile Water for Injection. 5% Dextrose Injection, or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection are also acceptable diluents.
Strength | Amount of Diluent to Be Added to the Contents of the Methohexital Sodium for Injection Vial | For 1% methohexital solution (10 mg/mL) |
| 500 mg | 50 mL | no further dilution needed |
For continuous drip anesthesia, prepare a 0.2% solution by adding 500 mg of Methohexital Sodium for Injection to 250 mL of diluent. For this dilution, either 5% glucose solution or isotonic (0.9%) sodium chloride solution ONLY is recommended as the diluent instead of sterile water for injection in order to avoid extreme hypotonicity.
Strength | Amount of Diluent to Be Added to the Contents of the Methohexital Sodium for Injection Vial | For 0.2% methohexital solution (2 mg/mL) |
| 500 mg | 15 mL | add to 235 mL diluent for 250 mL total volume |
The preferred diluent for intramuscular administration is Sterile Water for Injection. 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection is also an acceptable diluent.
Strength | Amount of Diluent to Be Added to the Contents of the Methohexital Sodium for Injection Vial | For 5% methohexital solution (50 mg/mL) |
| 500 mg | 10 mL | no further dilution needed |
Dosage is highly individualized; the drug should be administered only by those completely familiar with its quantitative differences from other barbiturate anesthetics.
Methohexital Sodium for Injection is administered intravenously in a concentration of no higher than 1 %. Higher concentrations markedly increase the incidence of muscular movements and irregularities in respiration and blood pressure.
For induction of anesthesia, a 1% solution is administered at a rate of about 1 mL/5 seconds. Gaseous anesthetics and/or skeletal muscle relaxants may be administered concomitantly. The dose required for induction may range from 50 to 120 mg or more but averages about 70 mg. The usual dosage in adults ranges from 1 to 1.5 mg/kg. The induction dose usually provides anesthesia for 5 to 7 minutes
Maintenance of anesthesia may be accomplished by intermittent injections of the 1% solution or, more easily, by continuous intravenous drip of a 0.2% solution. Intermittent injections of about 20 to 40 mg (2 to 4 mL of a 1% solution) may be given as required, usually every 4 to 7 minutes. For continuous drip, the average rate of administration is about 3 mL of a 0.2% solution/minute (1 drop/second). The rate of flow must be individualized for each patient. For longer surgical procedures, gradual reduction in the rate of administration is recommended (See discussion of prolonged administration in
Methohexital Sodium for Injection is Administered intramuscularly in a 5% concentration and administered rectally as a 1% solution.
For the induction of anesthesia by the intramuscular route of administration, the usual dose ranges from 6.6 to 10 mg/kg of the 5% concentration. For rectal administration, the usual dose for induction is 25 mg/kg using the 1% solution.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Solutions of Methohexital Sodium for Injection should not be mixed in the same syringe or administered simultaneously during intravenous infusion through the same needle with acid solutions, such as atropine sulfate, metocurine iodide, and succinylcholine chloride. Alteration of pH may cause free barbituric acid to be precipitated. Solubility of the soluble sodium salts of barbiturates, including Methohexital Sodium, is maintained only at a relatively high (basic) pH.
Because of numerous requests from anesthesiologists for information regarding the chemical compatibility of these mixtures, the following chart contains information obtained from compatibility studies in which a 1 % solution of Methohexital Sodium for Injection was mixed with therapeutic amounts of agents whose solutions have a low (acid) pH.
Active Ingredient | Potentcy per mL | Volume Used | Immediate | 15 min | Physical Change 30 min | 1 h |
| Methohexital Sodium for Injection | 10 mg | 10 mL | CONTROL | |||
| Atropine Sulfate | 1/150 gr | 1 mL | None | Haze | ||
| Atropine Sulfate | 1/100 gr | 1 mL | None | Ppt | Ppt | |
| Succinylcholine chloride | 0.5 mg | 4 mL | None | None | Haze | |
| Succinylcholine chloride | 1 mg | 4 mL | None | None | Haze | |
| Metocurine Iodide | 0.5 mg | 4 mL | None | None | Ppt | |
| Metocurine Iodide | 1 mg | 4 mL | None | None | Ppt | |
| Scopolamine hydrobromide | 1/120 gr | 1 mL | None | None | None | Haze |
| Tubocurarine chloride | 3 mg | 4 mL | None | Haze |
Methohexital Sodium for Injection is contraindicated in patients in whom general anesthesia is contraindicated, in those with latent or manifest porphyria, or in patients with a known hypersensitivity to barbiturates.
Side effects associated with Methohexital Sodium for Injection are extensions of pharmacologic effects and include:
Circulatory depression, thrombophlebitis, hypotension, tachycardia, peripheral vascular collapse, and convulsions in association with cardiorespiratory arrest
Respiratory depression (including apnea), cardiorespiratory arrest, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, hiccups, and dyspnea
Skeletal muscle hyperactivity (twitching), injury to nerves adjacent to injection site, and seizures
Emergence delirium, restlessness, and anxiety may occur, especially in the presence of postoperative pain
Nausea, emesis, abdominal pain, and liver function tests abnormal
Erythema, pruritus, urticaria, and cases of anaphylaxis have been reported rarely
Other adverse reactions include pain at injection site, salivation, headache, and rhinitis
Methohexital Sodium for injection, is 2,4,6 (1H, 3H, 5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 1- methyl-5-(1-methyl-2-pentynyl)-5-(2-propenyl)-, (±)-, monosodium salt and has the empirical formula C14H17N2NaO3. Its molecular weight is 284.29.
The structural formula is as follows:
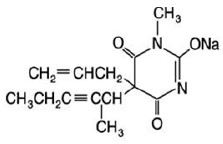
Methohexital sodium is a rapid, ultrashort-acting barbiturate anesthetic. Methohexital sodium for injection is a freeze-dried, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture of methohexital sodium with 6% anhydrous sodium carbonate added as a buffer. It contains not less than 90% and not more than 110% of the labeled amount of methohexital sodium. It occurs as a white, freeze-dried plug that is freely soluble in water.
This product is oxygen sensitive. The pH of the 1% solution is between 10 and 11; the pH of the 0.2% solution in 5% dextrose is between 9.5 and 10.5.
Methohexital sodium may be administered by direct intravenous injection or continuous intravenous drip, intramuscular or rectal routes (See