Metronidazole Prescribing Information
Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice and rats (see
In amebic liver abscess, metronidazole capsules 375 mg therapy does not obviate the need for aspiration or drainage of pus.
INTRA-ABDOMINAL INFECTIONS, including peritonitis, intra-abdominal abscess, and liver abscess, caused by
SKIN AND SKIN STRUCTURE INFECTIONS caused by
GYNECOLOGIC INFECTIONS, including endometritis, endomyometritis, tubo-ovarian abscess, and postsurgical vaginal cuff infection, caused by
BACTERIAL SEPTICEMIA caused by
BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONS (as adjunctive therapy) caused by
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) INFECTIONS, including meningitis and brain abscess, caused by
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS, including pneumonia, empyema, and lung abscess, caused by
ENDOCARDITIS caused by
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of metronidazole capsules 375 mg and other antibacterial drugs, metronidazole capsules 375 mg should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
In the Female: Seven-day course of treatment (375 mg two times daily for seven consecutive days).
A seven-day course of treatment may minimize reinfection by protecting the patient long enough for the sexual contacts to obtain treatment. Pregnant patients should not be treated during the first trimester (see
When repeat courses of the drug are required, it is recommended that an interval of four to six weeks elapse between courses and that the presence of the trichomonad be reconfirmed by appropriate laboratory measures. Total and differential leukocyte counts should be made before and after re-treatment.
In the Male: Treatment should be individualized as it is for the female.
Adults:
In the treatment of most serious anaerobic infections, intravenous metronidazole is usually administered initially.
The usual adult oral dosage is 7.5 mg/kg every 6 hours (approximately 500 mg for a 70 kg adult). A maximum of 4 g should not be exceeded during a 24-hour period.
The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 10 days; however, infections of the bone and joint, lower respiratory tract, and endocardium may require longer treatment.
For amebiasis patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment, pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation indicate that the metronidazole capsules 375 mg dose should be reduced by 50%. Therefore, the dosage regimen of metronidazole capsules 375 mg in Child Pugh C patients with amebiasis is 375 mg q8h for 5 to 10 days (see
For trichomoniasis patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment, pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation indicate that the frequency of metronidazole administration should be reduced from every 12 hours to every 24 hours. Therefore, the dosage regiment of metronidazole capsules 375 mg in Child Pugh C patients with trichomoniasis is 375 mg q24h for 7 days (see
Hemodialysis removes significant amounts of metronidazole and its metabolites from systemic circulation. The clearance of metronidazole will depend on the type of dialysis membrane used, the duration of the dialysis session, and other factors. If the administration of metronidazole cannot be separated from a hemodialysis session, supplementation of metronidazole dosage following the hemodialysis session should be considered, depending on the patient’s clinical situation (see
Metronidazole capsules 375 mg are contraindicated in patients with a prior history of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
In patients with trichomoniasis, metronidazole capsules 375 mg are contraindicated during the first trimester of pregnancy (see
Use of oral metronidazole is associated with psychotic reactions in alcoholic patients who were using disulfiram concurrently. Do not administer metronidazole to patients who have taken disulfiram within the last two weeks (see
Use of oral metronidazole is associated with a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol, including abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing. Discontinue consumption of alcohol or products containing propylene glycol during and for at least three days after therapy with metronidazole (see
Metronidazole capsules 375 mg are contraindicated in patients with Cockayne syndrome. Severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure with fatal outcomes have been reported after initiation of metronidazole in patients with Cockayne syndrome (see
The following reactions have been reported during treatment with metronidazole:
Patients with Crohn’s disease are known to have an increased incidence of gastrointestinal and certain extraintestinal cancers. There have been some reports in the medical literature of breast and colon cancer in Crohn’s disease patients who have been treated with metronidazole at high doses for extended periods of time. A cause and effect relationship has not been established. Crohn’s disease is not an approved indication for metronidazole capsules 375 mg.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited at 1-866-210-9797 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Metronidazole capsules USP 375 mg is an oral formulation of the synthetic nitroimidazole antimicrobial agent, 2-methyl-5-nitro-1
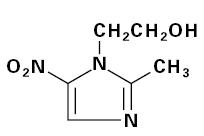
Metronidazole capsules USP 375 mg contain 375 mg of metronidazole USP. Inactive ingredients include corn starch, FD&C Yellow No. 5, gelatin, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate and titanium dioxide.