Movantik
(Naloxegol Oxalate)Dosage & Administration
The recommended MOVANTIK dosage is 25 mg once daily in the morning. If patients are not able to tolerate MOVANTIK, reduce the dosage to 12.5 mg once daily
The starting dosage for patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) <60 mL/min (i.e., patients with moderate, severe, or end-stage renal impairment) is 12.5 mg once daily. If this dosage is well tolerated but OIC symptoms continue, the dosage may be increased to 25 mg once daily taking into consideration the potential for markedly increased exposures in some patients with renal impairment and the increased risk of adverse reactions with higher exposures
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of MOVANTIK, 11% were 65 and over, while 2% were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
MOVANTIK exposure was higher in elderly healthy Japanese subjects compared to young subjects
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Movantik Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions
MOVANTIK
®is indicated for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation (OIC) in adult patients with chronic non-cancer pain, including patients with chronic pain related to prior cancer or its treatment who do not require frequent (e.g., weekly) opioid dosage escalation.
- Discontinue maintenance laxative therapy before starting MOVANTIK; may resume laxatives if patients have OIC symptoms after taking MOVANTIK for 3 days.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to starting MOVANTIK is not required.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- Take on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed and given orally or administered via nasogastric tube, see full prescribing information.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice.,
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
7.1) - Discontinue if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
2.1 Administration Instructions- Discontinue all maintenance laxative therapy prior to initiation of MOVANTIK. Laxative(s) can be used as needed if there is a suboptimal response to MOVANTIK after three days.
- Alteration in analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating MOVANTIK is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to MOVANTIK[see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Take MOVANTIK on an empty stomach at least 1 hour prior to the first meal of the day or 2 hours after the meal.
- For patients who are unable to swallow the MOVANTIK tablet whole, the tablet can be crushed to a powder, mixed with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, and drunk immediately. The glass should be refilled with 4 ounces (120 mL) of water, stirred and the contents drunk.
- MOVANTIK can also be administered via a nasogastric (NG) tube, as follows:
- Flush the NG tube with 1 ounce (30 mL) of water using a 60 mL syringe.
- Crush the tablet to a powder in a container and mix with approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water.
- Draw up the mixture using the 60 mL syringe and administer the syringe contents through the NG tube.
- Add approximately 2 ounces (60 mL) of water to the same container used to prepare the dose of MOVANTIK.
- Draw up the water using the same 60 mL syringe and use all the water to flush the NG tube and any remaining medicine from the NG tube into the stomach.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice during treatment with MOVANTIK.
- Discontinue MOVANTIK if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
- 25 mg once daily; if not tolerated, reduce to 12.5 mg once daily.
2.2 Adult DosageThe recommended MOVANTIK dosage is 25 mg once daily in the morning. If patients are not able to tolerate MOVANTIK, reduce the dosage to 12.5 mg once daily
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. - Renal Impairment (CLcr < 60 mL/min): 12.5 mg once daily; increase to 25 mg once daily if tolerated and monitor for adverse reactions.,
2.3 Dosage in Adult Patients with Renal ImpairmentThe starting dosage for patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) <60 mL/min (i.e., patients with moderate, severe, or end-stage renal impairment) is 12.5 mg once daily. If this dosage is well tolerated but OIC symptoms continue, the dosage may be increased to 25 mg once daily taking into consideration the potential for markedly increased exposures in some patients with renal impairment and the increased risk of adverse reactions with higher exposures
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].8.5 Geriatric UseOf the total number of subjects in clinical studies of MOVANTIK, 11% were 65 and over, while 2% were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
MOVANTIK exposure was higher in elderly healthy Japanese subjects compared to young subjects
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dosage adjustment is needed in elderly patients.
MOVANTIK (naloxegol) is available in two strengths:
- Tablets: 12.5 mg supplied as mauve, oval, biconvex, film-coated, intagliated with “nGL” on one side and “12.5” on the other side.
- Tablets: 25 mg supplied as mauve, oval, biconvex, film-coated, intagliated with “nGL” on one side and “25” on the other side.
- Pregnancy: May precipitate opioid withdrawal in pregnant women and the fetus.
8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryLimited available data with MOVANTIK use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. MOVANTIK may precipitate opioid withdrawal in the pregnant women and the fetus
(see Clinical Considerations).In animal development studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed following administration of naloxegol in pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 1452 times the human AUC (area under the plasma concentration-time curve) at the maximum recommended human dose. No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed following administration of naloxegol in pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 409 times the human AUC at the maximum recommended human dose.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically-recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical ConsiderationsMaternal and Fetal/Neonatal adverse reactionsThe use of MOVANTIK may be associated with opioid withdrawal in the pregnant woman and the fetus.
DataAnimal DataOral administration of up to 750 mg/kg/day naloxegol in rats (1452 times the human AUC at the maximum recommended human dose) and 450 mg/kg/day naloxegol in rabbits (409 times the human AUC at the maximum recommended human dose) during the period of organogenesis produced no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development. Oral administration of up to 500 mg/kg/day in rats (195 times the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis through lactation produced no adverse effects on parturition or the offspring.
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended.
8.2 LactationThere are no data on the presence of naloxegol in human milk, the effects in nursing infants, or the effects on milk production. Naloxegol is present in rat milk
(see Data). Because of the potential for adverse reactions, including opioid withdrawal in breastfed infants, advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with MOVANTIK.DataFollowing oral administration of naloxegol in lactating rats, concentrations of naloxegol in milk were approximately 3- to 4-fold higher than concentrations of naloxegol in maternal plasma. Naloxegol was detected in plasma from pups.
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid in severe impairment.
8.6 Renal ImpairmentSome subjects with creatinine clearance (CLcr) values <60 mL/minute (i.e., moderate, severe, or end-stage renal disease) were shown to exhibit markedly higher systemic exposure of naloxegol compared to subjects with normal renal function. The reason for these high exposures is not understood. However, as the risk of adverse reactions increases with systemic exposure, a lower starting dosage of 12.5 mg once daily is recommended. No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild renal impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
MOVANTIK is contraindicated in:
- Patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction and patients at risk of recurrent obstruction, due to the potential for gastrointestinal perforation[see
5.3 Gastrointestinal PerforationCases of gastrointestinal (GI) perforation have been reported with use of peripherally acting opioid antagonists, including MOVANTIK. Postmarketing cases of GI perforation, including fatal cases, were reported when MOVANTIK was used in patients at risk of GI perforation (e.g., infiltrative gastrointestinal tract malignancy, recent gastrointestinal tract surgery, diverticular disease including diverticulitis, ischemic colitis, or concomitantly treated with bevacizumab). MOVANTIK is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction or in patients at risk of recurrent obstruction[see Contraindications (4)]. Take into account the overall risk-benefit profile when using MOVANTIK in patients with these conditions or other conditions which might result in impaired integrity of the gastrointestinal tract wall (e.g., Crohn’s disease). Monitor for the development of severe, persistent or worsening abdominal pain; discontinue MOVANTIK in patients who develop this symptom.]. - Patients concomitantly using strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, ketoconazole) because these medications can significantly increase exposure to naloxegol which may precipitate opioid withdrawal symptoms such as hyperhidrosis, chills, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anxiety, irritability, and yawning[see
Drug Interactions (7.1)and12.3 PharmacokineticsAbsorptionFollowing oral administration, MOVANTIK is absorbed with peak concentrations (Cmax) achieved at less than 2 hours. In a majority of subjects, a secondary plasma concentration peak of naloxegol was observed approximately 0.4 to 3 hours after the first peak. Across the range of doses evaluated, peak plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) increased in a dose-proportional or almost dose-proportional manner. Accumulation was minimal following multiple daily doses of naloxegol.
MOVANTIK as a crushed tablet mixed in water, given orally or administered through a nasogastric tube into the stomach, provides systemic naloxegol concentrations that are comparable to the whole tablet, with a median tmaxof 0.75 and 1.5 hours (range 0.25 to 5 hours) for the crushed tablet given orally and the crushed tablet given via nasogastric (NG) tube, respectively
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].Food EffectsA high-fat meal increased the extent and rate of naloxegol absorption. The Cmaxand AUC were increased by approximately 30% and 45%, respectively. In clinical trials, naloxegol was dosed on an empty stomach approximately 1 hour prior to the first meal in the morning.
DistributionThe mean apparent volume of distribution during the terminal phase (Vz/F) in healthy volunteers ranged from 968 L to 2140 L across dosing groups and studies. Plasma protein binding of naloxegol in humans was low (~4.2%).
MetabolismNaloxegol is metabolized primarily by the CYP3A enzyme system. In a mass balance study in humans, a total of 6 metabolites were identified in plasma, urine, and feces. These metabolites were formed via N-dealkylation, O-demethylation, oxidation, and partial loss of the PEG chain. Human metabolism data suggests absence of major metabolites. The activity of the metabolites at the opioid receptor has not been determined.
ExcretionFollowing oral administration of radio-labeled naloxegol, 68% and 16% of total administered dose were recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Parent naloxegol excreted in the urine accounted for less than 6% of the total administered dose. Approximately 16% of radioactivity in feces was noted to be unchanged naloxegol, while the remaining was attributed to metabolites. Thus, renal excretion is a minor clearance pathway for naloxegol. In a clinical pharmacology study, the half-life of naloxegol at therapeutic doses ranged from 6 to 11 hours.
Specific PopulationsRenal Impairment:The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of a 25 mg single oral dose of MOVANTIK was studied in subjects with renal impairment (RI) classified as moderate (n=8), severe (n=4), or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) not yet on dialysis (n=4), and compared with healthy subjects (n=6). Most renal impairment (RI) subjects (6 out of 8 with moderate RI, 3 out of 4 with severe RI, and 3 out of 4 with ESRD) had plasma naloxegol pharmacokinetics comparable to those in healthy subjects. The remaining individuals with renal impairment demonstrated higher naloxegol exposures (up to 10-fold) compared to the control group. The reason for these high exposures is unknown.
This study also included 8 ESRD patients on hemodialysis. Plasma concentrations of naloxegol in these subjects were similar to healthy volunteers with normal renal function, when MOVANTIK was administered either pre- or post-hemodialysis
[seeDosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Overdosage (10)].Hepatic Impairment:Slight decreases in AUC of naloxegol were observed in subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Classes A and B; n=8 per group) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function (n=8), following administration of a single 25 mg oral dose of MOVANTIK. The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of naloxegol was not evaluated
[seeUse in Specific Populations (8.7)].Age:The mean Cmax,ssand AUCτ,ssvalues seen in elderly healthy Japanese subjects (n=6) were approximately 45% and 54% greater than those obtained in young healthy subjects (n=6) following multiple daily doses of naloxegol (25 mg).
Gender:There is no gender effect on the pharmacokinetics of naloxegol.
Race:When compared to Caucasian subjects, naloxegol AUC was approximately 20% lower in Blacks and Cmaxwas approximately 10% lower and 30% higher in Blacks and Asians, respectively.
Drug Interaction StudiesEffect of MOVANTIK on Other DrugsIn
in vitrostudies at clinically relevant concentrations, naloxegol did not show a significant inhibitory effect on the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4 or CYP2C19, nor a significant induction effect on the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4. Therefore, MOVANTIK is not expected to alter the metabolic clearance of co-administered drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes. Naloxegol is not a significant inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3.In healthy subjects receiving morphine 5 mg/70 kg intravenously, single doses of MOVANTIK ranging from 8 mg to 1000 mg were given concomitantly with 5 to 6 subjects per dose cohort. With increasing MOVANTIK dose, there was no increasing or decreasing trend in morphine exposure compared to morphine administered alone. An analysis of the pooled data indicated that MOVANTIK had no meaningful impact on the systemic exposure of morphine and its major circulating metabolites.
Effect of Other Drugs on MOVANTIKNaloxegol is metabolized mainly by CYP3A enzymes and is a substrate of P-gp transporter. The effects of co-administered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of naloxegol are summarized in Figure 1
[seeDrug Interactions (7.1)].The effects of once daily oral dosing of 400 mg ketoconazole, once daily oral dosing of 600 mg rifampicin and once daily oral dosing of 240 mg diltiazem (as an extended release formulation) on the pharmacokinetics of 25 mg MOVANTIK were studied following multiple dosing and at steady state exposure of the perpetrator drugs. The effects of 600 mg oral dosing of quinidine and intravenous morphine (5 mg/70 kg) on the pharmacokinetics of 25 mg MOVANTIK were studied following single dosing of the perpetrator drugs.
Figure 1: Effect of Co-administered Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Naloxegol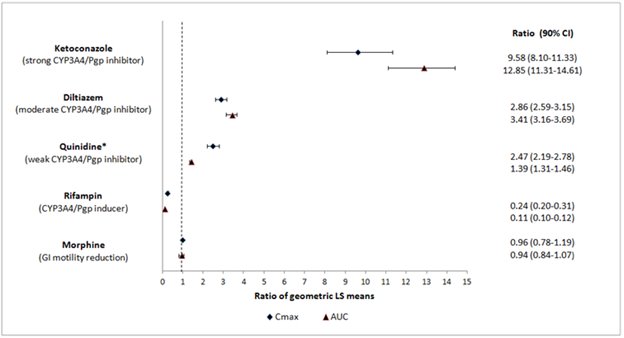
*Quinidine due to its effect on P-gp transporter increased naloxegol Cmaxby 2.5-fold; the AUC increased by 1.4-fold; no dosage adjustment is necessary.
No drug interaction studies have been conducted for MOVANTIK with drugs that alter gastric pH (e.g., antacids, proton-pump inhibitors).
Simulations using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling, suggested that naloxegol exposures after co-administration of a single oral 25 mg dose of MOVANTIK with a moderate CYP3A inducer efavirenz (400 mg once a day) are similar to those after 12.5 mg MOVANTIK alone.

Figure 1 ]. - Patients who have had a known serious or severe hypersensitivity reaction to MOVANTIK or any of its excipients[see.]
6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of MOVANTIK. Because reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions: angioedema, rash, and urticaria.Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal perforation[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].