Natazia prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Natazia patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
How to Take Natazia
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Natazia must be taken exactly as directed. Take one tablet by mouth at the same time every day. Tablets must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. Tablets should not be skipped or intake delayed by more than 12 hours. For patient instructions for missed pills, see FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
How to Start Natazia
Instruct the patient to begin taking Natazia on Day 1 of her menstrual cycle (that is, the first day of her menstrual bleeding). See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling . Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal contraceptive as back-up during the first 9 days.
For postpartum women who do not breastfeed or after a second trimester abortion, start Natazia no earlier than 4 weeks postpartum due to the increased risk of thromboembolism. If the patient starts on Natazia postpartum and has not yet had a period, evaluate for possible pregnancy, and instruct her to use an additional method of contraception until she has taken Natazia for 9 consecutive days. The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of medication should also be considered.
If the patient is switching from a combination hormonal method such as:
- Another pill
- Vaginal ring
- Patch
- Instruct her to take the first dark yellow pill on the first day of her withdrawal bleed. She should not continue taking the pills from her previous birth control pack. If she does not have a withdrawal bleed, rule out pregnancy before starting Natazia.
- If she previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch, she should start using Natazia on the day the ring or patch is removed.
- Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom or spermicide for the first 9 days.
If the patient is switching from a progestin-only method such as a:
- Progestin-only pill
- Implant
- Intrauterine system
- Injection
- Instruct her to take the first dark yellow pill on the day she would have taken her next progestin-only pill or on the day of removal of her implant or intrauterine system or on the day when she would have had her next injection.
- Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom or spermicide for the first 9 days.
Advice in case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
In case of severe vomiting or diarrhea, absorption may not be complete and additional contraceptive measures should be taken. If vomiting or diarrhea occurs within 3-4 hours after taking a colored tablet, this can be regarded as a missed tablet.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Natazia prescribing information
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combination oral contraceptives (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs should not be used by women who are over 35 years of age and smoke. [See Contraindications (4 ).]
Contraindications, Pregnancy (4) Removed 6/2024
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Natazia is a combination of dienogest , a progestin, and estradiol valerate, an estrogen, indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy. (1 )
- The efficacy of Natazia in females of reproductive potential with a body mass index (BMI) of >30 kg/m 2 has not been evaluated. (1 , 8.8 )
- Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in females of reproductive potential without organic pathology who choose to use an oral contraceptive as their method of contraception. (1.2 )
Oral Contraception
Natazia ® is indicated for use by women to prevent pregnancy.
The efficacy of Natazia in women with a body mass index (BMI) of > 30 kg/m 2 has not been evaluated.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Natazia is also indicated for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in women without organic pathology who choose to use an oral contraceptive as their method of contraception [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
How to Take Natazia
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Natazia must be taken exactly as directed. Take one tablet by mouth at the same time every day. Tablets must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. Tablets should not be skipped or intake delayed by more than 12 hours. For patient instructions for missed pills, see FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
How to Start Natazia
Instruct the patient to begin taking Natazia on Day 1 of her menstrual cycle (that is, the first day of her menstrual bleeding). See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling . Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal contraceptive as back-up during the first 9 days.
For postpartum women who do not breastfeed or after a second trimester abortion, start Natazia no earlier than 4 weeks postpartum due to the increased risk of thromboembolism. If the patient starts on Natazia postpartum and has not yet had a period, evaluate for possible pregnancy, and instruct her to use an additional method of contraception until she has taken Natazia for 9 consecutive days. The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of medication should also be considered.
If the patient is switching from a combination hormonal method such as:
- Another pill
- Vaginal ring
- Patch
- Instruct her to take the first dark yellow pill on the first day of her withdrawal bleed. She should not continue taking the pills from her previous birth control pack. If she does not have a withdrawal bleed, rule out pregnancy before starting Natazia.
- If she previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch, she should start using Natazia on the day the ring or patch is removed.
- Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom or spermicide for the first 9 days.
If the patient is switching from a progestin-only method such as a:
- Progestin-only pill
- Implant
- Intrauterine system
- Injection
- Instruct her to take the first dark yellow pill on the day she would have taken her next progestin-only pill or on the day of removal of her implant or intrauterine system or on the day when she would have had her next injection.
- Instruct the patient to use a non-hormonal back-up method such as a condom or spermicide for the first 9 days.
Advice in case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
In case of severe vomiting or diarrhea, absorption may not be complete and additional contraceptive measures should be taken. If vomiting or diarrhea occurs within 3-4 hours after taking a colored tablet, this can be regarded as a missed tablet.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest) tablets are available in blister packs.
Each blister pack contains 28 round, biconvex, film-coated tablets in the following order:
- 2 dark yellow tablets, with an embossed “DD” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets, with an embossed “DJ” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets, with an embossed “DH” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets, with an embossed “DN” in a regular hexagon on one side, each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert), with an embossed “DT” in a regular hexagon on one side
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There is no reason to use COCs in pregnancy Discontinue Natazia if pregnancy occurs. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or non-genital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs prior to conception or during early pregnancy.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4 percent and 15 to 20 percent, respectively.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Contraceptive hormones and/or metabolites are present in human milk. CHCs can reduce milk production in breastfeeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breastfeeding is well-established. When possible, advise the nursing female to use other forms of contraception until she discontinues breastfeeding. [See also Dosage and Administration (2.2 )]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Natazia and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from Natazia or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of Natazia have been established in women of reproductive age. Efficacy is expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents under the age of 18 and for users 18 years and older. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
Geriatric Use
Natazia has not been studied in postmenopausal women and is not indicated in this population.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Natazia has not been studied in subjects with renal impairment, but an effect requiring dose adjustment is unlikely to be present [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Natazia has not been studied in subjects with hepatic impairment. Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal. [See Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
Body Mass Index
The safety and efficacy of Natazia in women with a BMI of > 30 kg/m 2 has not been evaluated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Natazia is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include women who are known to:
- Smoke, if over age 35 [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, now or in the past [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have cerebrovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Have uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Have diabetes mellitus with vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or have migraine headaches with or without aura if over age 35 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )]
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone sensitive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.7 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ])].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Vascular risks : Stop Natazia if a thrombotic event occurs. Stop Natazia at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery. Start Natazia no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. (5.1 )
- Liver disease : Discontinue Natazia if jaundice occurs. (5.3 )
- High blood pressure : Do not prescribe Natazia for women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease. (5.4 )
- Carbohydrate and lipid metabolic effects : Monitor prediabetic and diabetic women taking Natazia. Consider an alternate contraceptive method for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia. (5.6 )
- Headache : Evaluate significant change in headaches and discontinue Natazia if indicated. (5.7 )
- Uterine bleeding : Evaluate irregular bleeding or amenorrhea. (5.8 )
- CYP3A4 induction : Women taking strong CYP3A4 inducers (for example, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, and St. John’s wort) should not choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive due to the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy. (5.13 , 7.1 )
Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
Stop Natazia if an arterial or venous thrombotic event (VTE) occurs.
The use of COCs increases the risk of venous thromboembolism. However, pregnancy increases the risk of venous thromboembolism as much or more than the use of COCs. The risk of VTE in women using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 per 10,000 woman-years. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of use. Data from a large, prospective cohort safety study of various COCs suggest that this increased risk, as compared to that in non-COC users, is greatest during the first 6 months of COC use. Data from this safety study indicate that the greatest risk of VTE is present after initially starting a COC or restarting (following a 4 week or greater pill-free interval) the same or a different COC.
Use of COCs also increases the risk of arterial thromboses such as strokes and myocardial infarctions, especially in women with other risk factors for these events.
The risk of thromboembolic disease due to oral contraceptives gradually disappears after COC use is discontinued.
If feasible, stop Natazia at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of thromboembolism.
Start Natazia no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum thromboembolism decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the risk of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
COCs have been shown to increase both the relative and attributable risks of cerebrovascular events (thrombotic and hemorrhagic strokes), although, in general, the risk is greatest among older (>35 years of age), hypertensive women who also smoke. COCs also increase the risk for stroke in women with other underlying risk factors.
Oral contraceptives must be used with caution in women with cardiovascular disease risk factors.
Stop Natazia if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions. Evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately. [See Adverse Reactions (6 ).]
Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
Natazia is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive [see Contraindications (4 )].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] .
Cervical Cancer
Some studies suggest that COCs are associated with an increase in the risk of cervical cancer or intraepithelial neoplasia. However, there is controversy about the extent to which these findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
Liver Disease
Discontinue Natazia if jaundice develops. Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded.
Hepatic adenomas are associated with COC use. An estimate of the attributable risk is 3.3 cases/100,000 COC users. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (> 8 years) COC users. However, the attributable risk of liver cancers in COC users is less than one case per million users.
Oral contraceptive-related cholestasis may occur in women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis. Women with a history of COC-related cholestasis may have the condition recur with subsequent COC use.
High Blood Pressure
For women with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop Natazia if blood pressure rises significantly. Women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease should not use COCs.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in women taking COCs, and this increase is more likely in older women and with extended duration of use. The incidence of hypertension increases with increasing concentration of progestin.
Gallbladder Disease
Studies suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among COC users.
Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Carefully monitor prediabetic and diabetic women who are taking Natazia. COCs may decrease glucose tolerance in a dose-related fashion.
Consider alternative contraception for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia. A small proportion of women will have adverse lipid changes while on COCs.
Women with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may be at an increased risk of pancreatitis when using COCs.
Headache
If a woman taking Natazia develops new headaches that are recurrent, persistent, or severe, evaluate the cause and discontinue Natazia if indicated.
An increase in frequency or severity of migraine during COC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event) may be a reason for immediate discontinuation of the COC.
Bleeding Irregularities
Breakthrough bleeding and spotting sometimes occur in patients on COCs, especially during the first three months of use. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, check for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy. If pathology and pregnancy are excluded, bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or with a change to a different COC.
Women who are not pregnant and use Natazia, may experience amenorrhea. Based on patient diaries, amenorrhea occurs in approximately 16% of cycles in women using Natazia. Pregnancy should be ruled out in the event of amenorrhea occurring in two or more consecutive cycles. Some women may encounter amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea after stopping COCs, especially when such a condition was pre-existent.
Based on patient diaries from three clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of Natazia for contraception, 10-23% of women experienced intracyclic bleeding per cycle.
Depression
Women with a history of depression should be carefully observed and Natazia discontinued if depression recurs to a serious degree .
Interference with Laboratory Tests
The use of COCs may change the results of some laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors, lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins. Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because serum concentrations of thyroid-binding globulin increase with use of COCs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Monitoring
A woman who is taking COCs should have a yearly visit with her healthcare provider for a blood pressure check and for other indicated healthcare.
Drug Interactions
Women who take medications that are strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inducers (for example, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, and St. John’s wort) should not choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive while using these inducers and for at least 28 days after discontinuation of these inducers due to the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Other Conditions
In women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of angioedema. Chloasma may occasionally occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma gravidarum. Women with a tendency to chloasma should avoid exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation while taking COCs.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Vascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
Adverse reactions commonly reported by COC users are:
- Irregular uterine bleeding
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Contraception and Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Studies
A total of 2,131 women, 18 to 54 years of age, who took at least one dose of Natazia were enrolled in four clinical phase 3 trials. A total of 1,867 subjects were included in two clinical phase 3 studies with a treatment duration up to 28 cycles with Natazia as an oral contraceptive and 264 subjects in the two phase 3 clinical trials with a treatment duration of 7 cycles evaluating Natazia in the treatment of heavy, prolonged, and/or frequent menstrual bleeding in women without organic pathology [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 )].
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation : 11.4% of the women discontinued from the clinical trials due to an adverse reaction; the most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were menstrual disorder (metrorrhagia, menorrhagia, menstruation irregular, genital hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding) (2.3%); mood changes (depression, mood swings, mood altered, depressed mood, dysthymic disorder, crying) (1.2%); acne (1.1%), headache (including migraines) (1.1%), and weight increased (0.7 %).
Common Adverse Reactions (≥ 2%): headache (including migraines) (12.7%), breast pain, discomfort or tenderness (7.0%), menstrual disorders (metrorrhagia, menstruation irregular, menorrhagia, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, genital hemorrhage, abnormal withdrawal bleeding, uterine hemorrhage) (6.9%), nausea or vomiting (6.0%), acne (3.9%), mood changes (depression, mood swings, depressed mood, mood altered, affect lability, dysthymic disorder, crying) (3.0%) and increased weight (2.9%).
Serious Adverse Reactions: myocardial infarction (2 cases), ruptured ovarian cyst (2 cases), deep vein thrombosis, focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver, uterine leiomyoma, acute cholecystitis, and chronic acalculous cholecystitis.
Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 1).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 1). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19–1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8–10 years of COC use.
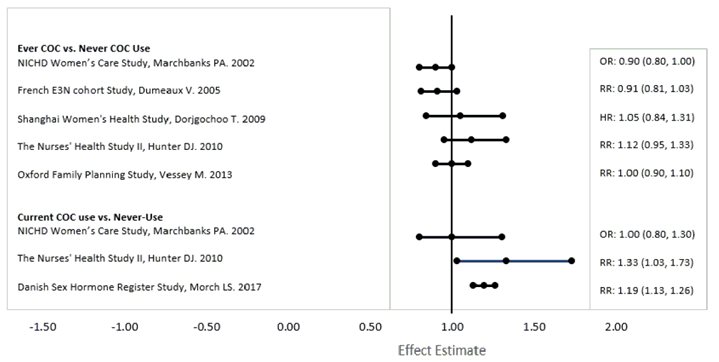
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Natazia. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Vascular disorders: Venous and arterial thromboembolic events (including pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis, cerebral thrombosis, myocardial infarction and stroke), hypertension
Hepatobiliary disorders: Gallbladder disease, hepatitis
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Fluid retention, hypertriglyceridemia
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Chloasma, angioedema, erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme
Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal symptoms (for example, abdominal pain)
Infections and infestations: Vulvovaginal candidiasis
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Consult the labeling of all concurrently-used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with hormonal contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations .
Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances diminishing the efficacy of COCs: Dienogest is a substrate of CYP3A4. Women who take medications that are strong CYP3A4 inducers should not choose Natazia as their oral contraceptive while using these inducers and for at least 28 days after discontinuation of these inducers due to the possibility of increased breakthrough bleeding and/or decreased contraceptive efficacy.
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4, may decrease the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, topiramate and products containing St. John’s wort. Interactions between oral contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or contraceptive failure. Counsel women to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with COCs, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
Multiple dose co-administration of the strong CYP3A4 inducer rifampin with estradiol valerate/dienogest tablets in healthy postmenopausal women led to a decrease in dienogest and estradiol systemic exposure at steady state. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).]
Substances Increasing the Systemic Exposure of COCs (enzyme inhibitors): Concomitant administration of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like azole antifungals (for example, ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole), verapamil, macrolides (for example, clarithromycin, erythromycin), diltiazem, and grapefruit increase the serum concentrations of both estradiol and dienogest.
In a multiple dose study investigating the effect of CYP3A4 inhibitors (ketoconazole and erythromycin) on Natazia, steady state estradiol and dienogest exposures were increased when co-administered with ketoconazole or erythromycin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)/Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Protease Inhibitors and Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors : Significant changes (increase and decrease) in plasma concentrations of estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibiotics : There have been reports of pregnancy while taking hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown consistent effects of antibiotics on plasma concentrations of synthetic steroids.
Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
COCs containing ethinyl estradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. COCs have been shown to significantly decrease plasma concentrations of lamotrigine, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary. Consult the labeling of the concurrently-used drug to obtain further information about interactions with COCs or the potential for enzyme alterations. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ).]
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because serum concentrations of thyroid-binding globulin increase with use of COCs.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
DESCRIPTION
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest) tablets provide an oral contraceptive regimen consisting of 26 active film-coated tablets that contain the active ingredients specified for each tablet below, followed by two inert film-coated tablets:
- 2 dark yellow tablets each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 medium red tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 light yellow tablets each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 dark red tablets each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white tablets (inert)
Natazia also contains the excipients lactose monohydrate, maize starch, maize starch pre-gelatinized, povidone 25, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide, and ferric oxide pigment, yellow, or ferric oxide pigment, red.
The empirical formula of estradiol valerate is C 23 H 32 O 3 and the chemical structure is:
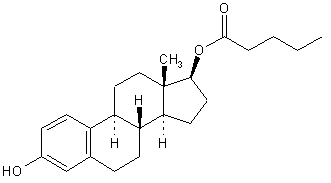
The chemical name of estradiol valerate is Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol(17ß)-,17-pentanoate.
The empirical formula of dienogest is C 20 H 25 NO 2 and the chemical structure is:
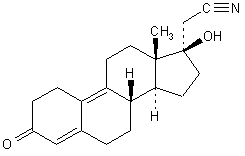
The chemical name of dienogest is (17α)-17-Hydroxy-3-oxo-19-norpregna-4,9-diene-21-nitrile.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
COCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation.
Pharmacodynamics
The estrogen in Natazia is estradiol valerate, a synthetic prodrug of 17ß-estradiol.
The progestin in Natazia is dienogest (DNG). DNG displays properties of 19-nortestosterone derivatives as well as properties associated with progesterone derivatives.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of Natazia on QT prolongation was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, positive (moxifloxacin 400 mg) and negative (placebo) controlled crossover study in healthy subjects. A total of 53 subjects were administered Natazia (containing 3 mg dienogest and 2 mg estradiol valerate), dienogest 10 mg, and placebo as once daily doses for 4 days, and moxifloxacin 400 mg as a single oral dose. The upper bound of the 90% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on Fridericia’s correction method (QTcF) was below 10 msec, the threshold for regulatory concern.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After oral administration of estradiol valerate, cleavage to 17β-estradiol and valeric acid takes place during absorption by the intestinal mucosa or in the course of the first liver passage. This gives rise to estradiol and its metabolites, estrone and other metabolites. Maximum serum estradiol concentrations of 73.3 pg/mL are reached at a median of approximately 6 hours (range: 1.5–12 hours) and the area under the estradiol concentration curve [AUC(0–24h)] was 1301 pg·h/mL after single ingestion of a tablet containing 3 mg estradiol valerate under fasted condition on Day 1 of the 28-day sequential regimen.
Bioavailability of dienogest is about 91%. Maximum serum dienogest concentrations of 91.7 ng/mL are reached at a median of approximately 1 hour (range: 0.5–1.5 hour) and the area under the dienogest concentration curve [AUC(0–24h)] was 964 ng/mL after single oral administration of Natazia tablet containing 2 mg estradiol valerate/3 mg dienogest under fasted condition. The pharmacokinetics of dienogest are dose-proportional within the dose range of 1–8 mg. Steady state is reached after 4 days of the same dosage of 2 mg dienogest. The mean accumulation ratio for AUC (0–24h) is approximately 1.24.
The mean plasma pharmacokinetic parameters at steady state following repeated oral doses of a 2 mg estradiol valerate/3 mg dienogest combination tablet in fertile women under fasted condition are reported in Table 1.
Parameter | Dienogest | Estradiol | Estrone |
C max C max = Maximum serum concentration | 85.2 (19.7) ng/ml | 70.5 (25.9) pg/ml | 483 (198) pg/ml |
T max Tmax = Time to reach maximum concentration (h) Median (range) for T max | 1.5 (1–2) | 3 (1.5–12) | 4 (3–12) |
AUC AUC(0-24h) = Area under the concentration-time curve from 0 h data point up to 48 h post-administration (0–24h) | 828 (187) ng·h/ml | 1323 (480) pg·h/ml | 7562 (3403) pg·h/ml |
t ½ (h) | 12.3 (1.4) | NA NA: Data not available | NA |
Food Effect
Concomitant food intake in women resulted in a 28% decrease for dienogest C max and 23% increase of estradiol C max while the exposure (AUC) of both dienogest and estradiol did not change.
Distribution
In serum, 38% of estradiol is bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), 60% to albumin and 2–3% circulates in free form. An apparent volume of distribution of approximately 1.2 L/kg was determined after intravenous (IV) administration.
A relatively high fraction (10%) of circulating dienogest is present in the free form, with approximately 90% being bound non-specifically to albumin. Dienogest does not bind to SHBG and corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG). The volume of distribution at steady state (V d,ss ) of dienogest is 46 L after the IV administration of 85 mcg 3 H-dienogest.
Metabolism
After oral administration of estradiol valerate, approximately 3% of the dose is directly bioavailable as estradiol. Estradiol undergoes an extensive first-pass effect and a considerable part of the dose administered is already metabolized in the gastrointestinal mucosa. The CYP 3A family is known to play the most important role in human estradiol metabolism. Together with the pre-systemic metabolism in the liver, about 95% of the orally administered dose becomes metabolized before entering the systemic circulation. The main metabolites are estrone and its sulfate or glucuronide conjugates.
Dienogest is extensively metabolized by the known pathways of steroid metabolism (hydroxylation, conjugation), with the formation of endocrinologically mostly inactive metabolites. CYP3A4 was identified as a predominant enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of dienogest.
Excretion
Estradiol and its metabolites are mainly excreted in urine, with about 10% being excreted in the feces. The terminal half-life of estradiol is approximately 14 hours.
Dienogest is mainly excreted renally in the form of metabolites and unchanged dienogest is the dominating fraction in plasma. The terminal half-life of dienogest is approximately 11 hours.
Use in Specific Populations
Pediatric Use: Safety and efficacy of Natazia has been established in women of reproductive age. Efficacy is expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents under the age of 18 and for users 18 years and older. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
Geriatric Use : Natazia has not been studied in postmenopausal women and is not indicated in this population.
Renal Impairment : The pharmacokinetics of Natazia has not been studied in subjects with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment : The pharmacokinetics of Natazia has not been studied in subjects with hepatic impairment. Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ).]
Body Mass Index : The efficacy of Natazia in women with a BMI of > 30 kg/m 2 has not been evaluated.
Drug Interactions
Consult the labeling of all concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with oral contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations.
Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances diminishing the efficacy of COCs: Dienogest is a substrate of CYP3A4. Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4, may decrease the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding.
The effect of the CYP3A4 inducer rifampin was studied in an open-label, non-randomized, single center study in 16 healthy postmenopausal women. All volunteers received a treatment regimen of 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest combination tablets, dosed once daily over 17 days, and of rifampin, which was administered once daily in an oral dose of 600 mg on Days 12 to 16. Twenty-four-hour (24h) pharmacokinetics of estradiol and dienogest on Days 11 and 17 were compared. Co-administration of rifampin with estradiol valerate/dienogest tablets led to a 52 % and 83% decrease in the mean Cmax and AUC(0–24h), respectively, for dienogest and a 25% and 44% decrease in Cmax and AUC(0–24h), respectively, for estradiol at steady state.
Substances Increasing the Systemic Exposure of COCs (enzyme inhibitors): The effect of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, ketoconazole, on dienogest and estradiol exposure was studied in an open-label, one-sequence, one-way crossover study in healthy postmenopausal Caucasian women. One tablet of 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest was administered orally once a day for 14 days. Twelve volunteers received an oral dose of 400 mg ketoconazole (that is, 2 tablets containing 200 mg ketoconazole) once daily for 7 days (Days 8–14). Twenty-four hour pharmacokinetics of estradiol and dienogest on Days 7 and 14 were compared. Co-administration with the strong inhibitor ketoconazole increased the AUC (0–24h) at steady state for dienogest and estradiol by 2.86 and 1.57-fold, respectively. There was also a 1.94 and 1.65-fold increase of Cmax at steady state for dienogest and estradiol when co-administered with ketoconazole.
The effect of a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, erythromycin, on dienogest and estradiol exposure was studied in an open-label, one-sequence, one-way crossover study in healthy postmenopausal Caucasian women. One tablet of 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest was administered orally once a day for 14 days. Twelve volunteers received an oral dose of 500 mg erythromycin three times a day for 7 days (Days 8–14). Twenty-four hour pharmacokinetics of estradiol and dienogest on Days 7 and 14 were compared. When co-administered with the moderate inhibitor erythromycin, the AUC (0–24h) of dienogest and estradiol at steady state were increased by 1.62 and 1.33-fold, respectively. There was also a 1.33 and 1.51-fold increase of Cmax at steady state for dienogest and estradiol, respectively, when co-administered with erythromycin.
HIV/HCV Protease Inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma concentrations of the estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibiotics: There have been reports of pregnancy while taking hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown consistent effects of antibiotics on plasma concentrations of synthetic steroids.
Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
COCs containing ethinyl estradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. COCs have been shown to significantly decrease plasma concentrations of lamotrigine, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary. Consult the labeling of the concurrently-used drug to obtain further information about interactions with COCs or the potential for enzyme alterations.
In vitro studies with human CYP enzymes did not indicate an inhibitory potential of dienogest at clinically relevant concentrations.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because serum concentration of thyroid-binding globulin increases with use of COCs.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 24-month carcinogenicity study in mice dosed orally with dienogest by gavage with doses of 5, 15 and 50 mg/kg/day (males) and 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg/day (females), the systemic exposures in the females were 1.1, 3.5, and 10.6 times the exposure (AUC of dienogest) of women taking a 3 mg dose. A statistically significantly higher incidence of stromal polyps of the uterus was observed in females given 100 mg/kg. In a similar study in rats given 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg for 104 weeks, 0.2, 1.4, and 6.1 times the exposure of women taking a 3 mg dose, there were no statistically significant drug-related neoplasms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3 )] .
Dienogest was not mutagenic in in vitro reverse mutation tests in bacteria, in chromosome aberration tests in human peripheral lymphocytes, mouse lymphoma cells, and Chinese hamster lung cells, and tests of unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) in rat and human liver cells. Dienogest was also negative in an in vivo mouse micronucleus test, a rat liver initiation-promotion model, and an in vitro/in vivo UDS test in female rats.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Oral Contraceptive Clinical Trials
The study conducted in North America (U.S. and Canada) was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm, unintended pregnancy study. There were 490 healthy subjects between 18 and 35 years of age (mean age: 25.1 years) who were treated for up to 28 cycles of 28 days each. The racial demographic of enrolled women was: Caucasian (76%), Hispanic (13%), African-American (7%), Asian (3%), and Other (1%). The weight range for treated women was 40 to 100 kg (mean weight: 62.5 kg) and the BMI range was 14 to 30 kg/m 2 (mean BMI: 23.3 kg/m 2 ). Of treated women, 15% discontinued the study treatment due to an adverse event, 13% were lost to follow up, 10% withdrew their consent, 8% discontinued due to other reason, 1% discontinued due to protocol deviation, and 1% discontinued due to pregnancy.
The study conducted in Europe (Germany, Austria and Spain) was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm contraceptive reliability study. There were 1,377 healthy subjects between 18 and 50 years of age (mean age: 30.3 years) who were treated for 20 cycles of 28 days each. The racial demographic of enrolled women was predominantly Caucasian (99.2%). The weight range for treated women was 38 to 98 kg (mean weight: 63.8 kg) and the BMI range was 15 to 31.8 kg/m 2 (mean BMI: 22.8 kg/m 2 ). Of treated women, 10% discontinued the study treatment due to an adverse event, 5% discontinued due to other reason, 2% were lost to follow up, 2% discontinued due to protocol deviation, 2% withdrew their consent, and 1% discontinued due to pregnancy.
The Pearl Index (PI) was the primary efficacy endpoint used to assess contraceptive reliability and was assessed in each of the two studies, assuming all subjects were at risk of pregnancy in all medication cycles unless back-up contraception was documented. The PI is based on pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment and within 7 days after the last pill intake. Cycles in which conception did not occur, but which included the use of back-up contraception, were not included in the calculation of the PI. The PI also includes patients who did not take the drug correctly. The estimated PI for the North American study is 1.64 and the estimated PI for the European study is 1.04. The Kaplan-Meier method was also used to calculate the contraceptive failure rate.
The summary of the Pearl Indexes and cumulative contraceptive failure rates are provided in Table 2:
Study | Age Group | Relative Treatment Exposure Cycles Total treatment exposure time without back-up contraception | Number of Pregnancies within 13 Cycles and 7 Days after Last Treatment | Pearl Index | Upper Limit of 95% CI | Contraceptive Failure Rate at the End of First Year |
North America | 18–35 | 3,969 | 5 | 1.64 | 3.82 | 0.016 |
Europe | 18–35 | 11,275 | 9 | 1.04 | 1.97 | 0.010 |
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of Natazia were evaluated in two multi-regional, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Study 308960 was performed in the United States and Canada and Study 308961 was performed in Australia and 9 European countries. The studies were identical in design. The studies enrolled women, 18 years of age or older, with a diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding characterized as heavy, prolonged and/or frequent bleeding without organic pathology. Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) was defined as menstrual blood loss of 80 mL or more in at least 2 bleeding episodes. The diagnosis of HMB was documented through the collection of used sanitary protection (pads and tampons) to quantify blood loss assessed by the alkaline hematin method. Overall, about 85% of the subjects qualified for the study because they had heavy menstrual bleeding symptoms.
A total of 421 women with a mean age of 38.2 and a mean BMI of 25.5 were randomized to the two clinical studies, for a total of 269 women in the Natazia group and 152 women in the placebo group, and treated for seven 28-day cycles. Approximately 81% were Caucasian, 13% were Black, and 6% were Hispanic or Asian or Other.
The primary efficacy variable was the proportion of subjects who were completely relieved of symptoms, which was defined by the number of subjects with the absence of any dysfunctional bleeding symptom and who met up to 8 strictly defined criteria for success during the 90-day efficacy assessment phase. In Study 308960, the proportion of the intent-to-treat subjects with complete symptom relief was 29.2% in the Natazia group compared to 2.9% in the placebo group. In Study 308961, the proportion of the intent-to-treat subjects with complete symptom relief was 29.5% in the Natazia group compared to 1.2% in the placebo group.
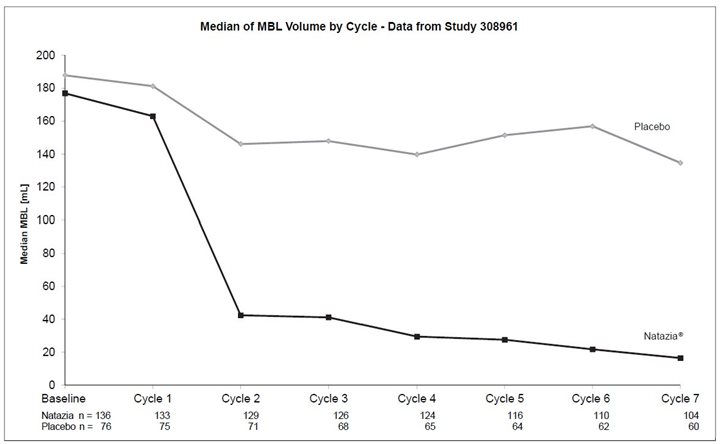
In both studies, Natazia was effective in treating the symptoms of HMB in the subset of women who entered the study with symptoms specific to HMB. Among patients with HMB, menstrual blood loss (MBL) was statistically significantly reduced in the group treated with Natazia compared with placebo (p<0.0001 for both studies). Evaluating data based on 28-day cycles, the median menstrual blood volume at Cycle 7 was reduced from the baseline median by 90% in one trial and 87% in the other. For women treated with placebo, the median menstrual blood volume at Cycle 7 was reduced from the baseline median by 14% and 32% in the two trials, respectively. Figures 2 and 3 display the MBL volume by cycle and by study.
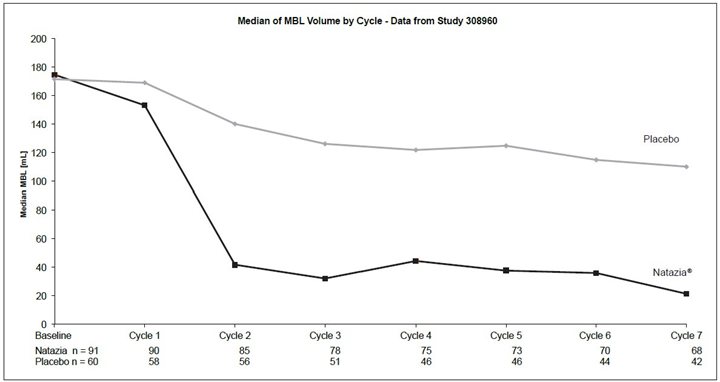
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Natazia (estradiol valerate and estradiol valerate/dienogest) tablets are available in packages of three blister packs (NDC 50419-409-03).
The active and inert film-coated tablets are rounded with biconvex faces, one side is embossed with a regular hexagon shape with the letters DD or DJ or DH or DN or DT.
Each blister pack (28 film-coated tablets) contains in the following order:
- 2 round biconvex dark yellow film-coated tablets with embossed “DD” in a regular hexagon on one side each containing 3 mg estradiol valerate
- 5 round biconvex medium red film-coated tablets with embossed “DJ” in a regular hexagon on one side each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 2 mg dienogest
- 17 round biconvex light yellow film-coated tablets with embossed “DH” in a regular hexagon on one side each containing 2 mg estradiol valerate and 3 mg dienogest
- 2 round biconvex dark red film-coated tablets with embossed “DN” in a regular hexagon on one side each containing 1 mg estradiol valerate
- 2 white round biconvex white film-coated tablets with embossed “DT” in a regular hexagon on one side (inert)
Storage
Store at 25º C (77º F); excursions permitted to 15–30 o C (59–86 o F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
Mechanism of Action
COCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation.