Get your patient on Neupro (Rotigotine)
Neupro prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Neupro patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Parkinson's disease: Initially, 2 mg/24 hours for early-stage disease or 4 mg/24 hours for advanced-stage disease. The dose may be increased as needed by 2 mg/24 hours at weekly intervals, up to 6 mg/24 hours for early-stage disease and up to 8 mg/24 hours for advanced-stage disease. (2.1 )
- Restless Legs Syndrome: Initially, 1 mg/24 hours, increased as needed by 1 mg/24 hours at weekly intervals, up to 3 mg/24 hours. (2.2 )
- Apply once a day to the skin; press firmly in place for 30 seconds. Do not place NEUPRO on oily, irritated, or damaged skin, or where it will be rubbed by tight clothing. Do not use the same site more than once every 14 days. The prescribed dose may be achieved using single or multiple patches. (2.3 )
- To discontinue treatment, reduce the dose gradually until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO. (2.4 )
Dosage in Parkinson's Disease
Early-Stage Parkinson's Disease
In patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 2 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 2 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The lowest effective dose is 4 mg/24 hours. The maximum recommended dose for early-stage Parkinson's disease is 6 mg/24 hours.
Advanced-Stage Parkinson's Disease
In patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 4 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 2 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The maximum recommended dose for advanced-stage Parkinson's disease is 8 mg/24 hours.
Dosage in Restless Legs Syndrome
In patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 1 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 1 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The lowest effective dose is 1 mg/24 hours. The maximum recommended dose is 3 mg/24 hours.
Administration Information
NEUPRO is applied once a day. The adhesive side of the transdermal system should be applied to clean, dry, intact healthy skin on the front of the abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, or upper arm. The transdermal system should be applied at approximately the same time every day, at a convenient time for the patient.
Because NEUPRO is administered transdermally, food is not expected to affect absorption and it can be applied irrespective of the timing of meals. The application site for NEUPRO should be moved on a daily basis (for example, from the right side to the left side and from the upper body to the lower body). NEUPRO should not be applied to the same application site more than once every 14 days and should not be placed on skin that is oily, irritated, or damaged, or where it will be rubbed by tight clothing. If it is necessary to apply NEUPRO to a hairy area, the area should be shaved at least 3 days prior to NEUPRO application. The system should be applied immediately after opening the pouch and removing the protective liner. The system should be pressed firmly in place for 30 seconds, making sure there is good contact, especially around the edges. If the patient forgets to replace NEUPRO, or if the transdermal system becomes dislodged, another transdermal system should be applied for the remainder of the day. The prescribed dose may be achieved using single or multiple patches [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ].
Discontinuation of NEUPRO
For discontinuation of NEUPRO in patients with Parkinson's disease, reduce the daily dose by a maximum of 2 mg every 24 hours preferably every other day, until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO is achieved.
For discontinuation of NEUPRO in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, reduce the daily dose by 1 mg every 24 hours preferably every other day, until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO is achieved.
Coverage
See specific coverage requirements, including prior authorization and step therapies.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Neupro prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NEUPRO is a dopamine agonist indicated for the treatment of:
Parkinson's Disease (PD)
NEUPRO is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
NEUPRO is indicated for the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary Restless Legs Syndrome.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Parkinson's disease: Initially, 2 mg/24 hours for early-stage disease or 4 mg/24 hours for advanced-stage disease. The dose may be increased as needed by 2 mg/24 hours at weekly intervals, up to 6 mg/24 hours for early-stage disease and up to 8 mg/24 hours for advanced-stage disease. (2.1 )
- Restless Legs Syndrome: Initially, 1 mg/24 hours, increased as needed by 1 mg/24 hours at weekly intervals, up to 3 mg/24 hours. (2.2 )
- Apply once a day to the skin; press firmly in place for 30 seconds. Do not place NEUPRO on oily, irritated, or damaged skin, or where it will be rubbed by tight clothing. Do not use the same site more than once every 14 days. The prescribed dose may be achieved using single or multiple patches. (2.3 )
- To discontinue treatment, reduce the dose gradually until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO. (2.4 )
Dosage in Parkinson's Disease
Early-Stage Parkinson's Disease
In patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 2 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 2 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The lowest effective dose is 4 mg/24 hours. The maximum recommended dose for early-stage Parkinson's disease is 6 mg/24 hours.
Advanced-Stage Parkinson's Disease
In patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 4 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 2 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The maximum recommended dose for advanced-stage Parkinson's disease is 8 mg/24 hours.
Dosage in Restless Legs Syndrome
In patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, the recommended starting dose for NEUPRO is 1 mg/24 hours. Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, NEUPRO dosage may be increased weekly by 1 mg/24 hours if additional therapeutic effect is needed. The lowest effective dose is 1 mg/24 hours. The maximum recommended dose is 3 mg/24 hours.
Administration Information
NEUPRO is applied once a day. The adhesive side of the transdermal system should be applied to clean, dry, intact healthy skin on the front of the abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, or upper arm. The transdermal system should be applied at approximately the same time every day, at a convenient time for the patient.
Because NEUPRO is administered transdermally, food is not expected to affect absorption and it can be applied irrespective of the timing of meals. The application site for NEUPRO should be moved on a daily basis (for example, from the right side to the left side and from the upper body to the lower body). NEUPRO should not be applied to the same application site more than once every 14 days and should not be placed on skin that is oily, irritated, or damaged, or where it will be rubbed by tight clothing. If it is necessary to apply NEUPRO to a hairy area, the area should be shaved at least 3 days prior to NEUPRO application. The system should be applied immediately after opening the pouch and removing the protective liner. The system should be pressed firmly in place for 30 seconds, making sure there is good contact, especially around the edges. If the patient forgets to replace NEUPRO, or if the transdermal system becomes dislodged, another transdermal system should be applied for the remainder of the day. The prescribed dose may be achieved using single or multiple patches [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ].
Discontinuation of NEUPRO
For discontinuation of NEUPRO in patients with Parkinson's disease, reduce the daily dose by a maximum of 2 mg every 24 hours preferably every other day, until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO is achieved.
For discontinuation of NEUPRO in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, reduce the daily dose by 1 mg every 24 hours preferably every other day, until complete withdrawal of NEUPRO is achieved.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Transdermal System: 1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, 3 mg/24 hours, 4 mg/24 hours, 6 mg/24 hours, and 8 mg/24 hours of rotigotine.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of NEUPRO in pregnant women. In animal studies, rotigotine was shown to have adverse effects on embryofetal development when administered during pregnancy at doses similar to or lower than those used clinically [ see Data ].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Rotigotine administered subcutaneously (0, 10, 30, or 90 mg/kg/day) to pregnant mice during organogenesis (gestation days 6 through 15) resulted in increased incidences of delayed skeletal ossification and decreased fetal body weights at the two highest doses and an increase in embryofetal death at the high dose. The no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity in mice is approximately 6 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for Parkinson's disease (8 mg/24 hours) on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis. Rotigotine administered subcutaneously (0, 0.5, 1.5, or 5 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats during organogenesis (gestation days 6 through 17) resulted in increased embryofetal death at all doses. The lowest effect dose is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis. This effect in rats is thought to be due to the prolactin-lowering effect of rotigotine. When rotigotine was administered subcutaneously (0, 5, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis (gestation days 7 through 19), an increase in embryofetal death occurred at the two highest doses tested. The no-effect dose is 12 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
In a study in which rotigotine was administered subcutaneously (0, 0.1, 0.3, or 1 mg/kg/day) to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation (gestation day 6 through postnatal day 21), impaired growth and development during lactation and long-term neurobehavioral abnormalities were observed in the offspring at the highest dose tested; when those offspring were mated, growth and survival of the next generation were adversely affected. The no- effect dose for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity (0.3 mg/kg/day) is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of rotigotine in human milk, the effects of rotigotine on the breastfed infant, or the effects of rotigotine on milk production. However, inhibition of lactation may occur because rotigotine decreases secretion of prolactin in humans. Studies have shown that rotigotine and/or its metabolite(s) are excreted in rat milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for NEUPRO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from NEUPRO or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients for any indication have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of patients receiving NEUPRO in clinical studies for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, approximately 50% were age 65 and over, and approximately 11% were age 75 and over. Among patients receiving NEUPRO in clinical studies for the treatment of RLS, 26% were age 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
No overall differences in plasma levels of rotigotine were observed between patients who were 65 to 80 years old compared with younger patients receiving the same rotigotine doses.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NEUPRO is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to rotigotine or the components of the transdermal system.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Contains sodium metabisulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions in those with sulfite sensitivity. (5.1 )
- Falling asleep during activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, and somnolence may occur. (5.2 )
- Hallucinations/psychosis and dyskinesia may occur. (5.3 , 5.9 )
- Symptomatic postural hypotension and syncope may occur, especially during dose escalation. (5.4 , 5.5 )
- Consider dose reduction or stopping NEUPRO if patient develops compulsive behaviors. (5.6 )
- Elevation of blood pressure and heart rate may occur. (5.7 )
- Application site reactions can occur and may be severe. (5.10 )
- Hyperpyrexia and confusion may occur with sudden discontinuation or dose reduction. (5.14 )
Sulfite Sensitivity
NEUPRO contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic people.
Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
Patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and with Restless Legs Syndrome treated with NEUPRO have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents. Although many of these patients reported somnolence while on NEUPRO, some did not perceive warning signs, such as excessive drowsiness, and believed that they were alert immediately prior to the event. Some of these events have been reported as late as one year after initiation of treatment. In clinical trials in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, 2% of patients treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose (3 mg/24 hours) reported sleep attacks compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients.
It has been reported that falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living always occurs in a setting of pre-existing somnolence, although patients may not give such a history. For this reason, prescribers should reassess patients for drowsiness or sleepiness especially since some of the events occur well after the start of treatment.
Somnolence is a common occurrence in patients receiving NEUPRO. In patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, there was an increased risk of somnolence for early-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 19%, placebo 3%), for advanced-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 32%, placebo 28%), and for Restless Legs Syndrome (NEUPRO 10%, placebo 4%). Prescribers should also be aware that patients may not acknowledge drowsiness or sleepiness until directly questioned about drowsiness or sleepiness during specific activities. Patients should be advised to exercise caution while driving, operating machines, or working at heights during treatment with NEUPRO. Patients who have already experienced somnolence and/or an episode of sudden sleep onset should not participate in these activities while taking NEUPRO.
Before initiating treatment with NEUPRO, patients should be advised of the potential to develop drowsiness and specifically asked about factors that may increase this risk with NEUPRO such as concomitant sedating medications and the presence of sleep disorders. If a patient develops daytime sleepiness or episodes of falling asleep during activities that require active participation (e.g., conversations, eating, etc.), NEUPRO should ordinarily be discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
If a decision is made to continue NEUPRO, patients should be advised not to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities. There is insufficient information to establish whether dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living.
Hallucinations/Psychosis
There was an increased risk for hallucinations in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease treated with NEUPRO. In patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, the incidence of hallucinations was 7% for NEUPRO and 3% for placebo, and this treatment difference increased with increasing dose.
Hallucinations were of sufficient severity to cause discontinuation of treatment (mainly during the dose escalation/titration period) in 3% of advanced-stage Parkinson's disease patients treated with the maximum recommended dose of NEUPRO compared with 1% of placebo-treated patients. Hallucinations have also been reported in post-marketing reports.
Post-marketing reports indicate that patients with Parkinson's disease or RLS may experience new or worsening mental status and behavioral changes, which may be severe, including psychotic behavior during NEUPRO treatment or after starting or increasing the dose of NEUPRO. Other drugs prescribed to improve the symptoms of Parkinson's disease or RLS can have similar effects on thinking and behavior. This abnormal thinking and behavior may consist of one or more of the following: paranoid ideation, delusions, hallucinations, confusion, symptoms of mania (e.g., insomnia, psychomotor agitation), disorientation, aggressive behavior, agitation, and delirium. These various manifestations of psychotic behavior were also observed during the clinical development of NEUPRO for early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and Restless Legs Syndrome.
Patients with a major psychotic disorder should ordinarily not be treated with NEUPRO because of the risk of exacerbating psychosis. In addition, certain medications used to treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and may decrease the effectiveness of NEUPRO [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Symptomatic Hypotension
Dopaminergic agonists, in clinical studies and clinical experience, appear to impair the systemic regulation of blood pressure, resulting in postural/orthostatic hypotension, especially during dose escalation. Parkinson's disease patients, in addition, appear to have an impaired capacity to respond to a postural challenge. For these reasons, both Parkinson's and Restless Legs Syndrome patients being treated with dopaminergic agonists ordinarily (1) require careful monitoring for signs and symptoms of postural hypotension, especially during dose escalation, and (2) should be informed of this risk.
An increased risk for decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure were observed when supine, standing, and changing from supine to standing position in patients treated with NEUPRO. In patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, orthostatic (change from supine to standing) decreases in systolic blood pressure (at least 20 mm Hg or greater) was 16% for NEUPRO and 14% for placebo in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, 32% for NEUPRO and 27% for placebo in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, and 13% for NEUPRO and 11% for placebo in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome.
More severe decreases in systolic blood pressure (40 mm Hg or greater) and in diastolic blood pressure (20 mm Hg or greater) also occurred more frequently (NEUPRO incidence at least 2% greater than placebo) in patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease during measurements when supine, standing, or changing from supine to standing position. Patients experienced dose-related decreases in blood pressure at different times throughout the trial including the final visit.
An analysis using a variety of adverse reaction terms suggestive of orthostatic hypotension, including dizziness/postural dizziness and others, showed an increased risk for all patients treated with NEUPRO. For the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, the incidence of adverse reactions suggestive of hypotension/orthostatic hypotension was 29% for NEUPRO and 11% for placebo in early-stage Parkinson's disease, 27% for NEUPRO and 23% for placebo in advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, and 8% for NEUPRO and 7% for placebo in Restless Legs Syndrome.
This increased risk for symptomatic hypotension and decreases in blood pressure was observed in a setting in which patients were very carefully titrated, and patients with clinically relevant cardiovascular disease or symptomatic orthostatic hypotension at baseline had been excluded from this study. The increased risk for significant decreases in blood pressure or orthostatic hypotension occurred especially in the dose escalation/titration period.
Syncope
Syncope has been reported in patients using dopamine agonists, and for this reason patients should be alerted to the possibility of syncope. Because the studies of NEUPRO excluded patients with clinically relevant cardiovascular disease, patients with severe cardiovascular disease should be asked about symptoms of syncope and pre-syncope.
Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Patients may experience intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge eating, and/or other intense urges, and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications, including NEUPRO, that increase central dopaminergic tone. In some cases, although not all, these urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or the medication was discontinued. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending, or other urges while being treated with NEUPRO for Parkinson's disease or RLS. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome, the repeated use of more NEUPRO than as prescribed to manage their symptoms of Parkinson's disease or RLS, was observed in some patients during treatment with NEUPRO. Physicians should consider dose reduction or stopping the medication if a patient develops such urges while taking NEUPRO .
Elevation of Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Some patients treated with NEUPRO exhibited increases in systolic blood pressure (greater than 180 mm Hg) and/or diastolic blood pressure (greater than 105 mm Hg) while supine or standing. In patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, this increased risk for systolic blood pressure greater than 180 mm Hg was 5% for NEUPRO and 3% for placebo and for diastolic blood pressure greater than 105 mm Hg was 4% for NEUPRO and 0% for placebo. In patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, this increased risk for diastolic blood pressure greater than 105 mm Hg was 8% for NEUPRO and 4% for placebo.
Increases in systolic blood pressure (at least 20 mm Hg or more) and in diastolic blood pressure (at least 10 mm Hg or more) occurred more frequently (incidence at least 5% greater than placebo) in all patients (i.e., early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and Restless Legs Syndrome) taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose. These increases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure were observed when supine, standing, and changing from supine to standing position. More severe increases in systolic blood pressure (40 mm Hg or more) and in diastolic blood pressure (20 mm Hg or more) also occurred more frequently (incidence at least 2% greater than placebo) in NEUPRO-treated patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and with Restless Legs Syndrome during measurements when supine, standing, and/or changing from supine to standing position.
In the placebo-controlled trials, there was an increased risk for hypertension as an adverse reaction with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 3% vs. placebo 0%) and Restless Legs Syndrome (NEUPRO 4% vs. placebo 0%).
Some patients treated with NEUPRO exhibited increased pulse (greater than 100 beats per minute) while supine and/or standing. In patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, there was an increased risk (at least 2% greater than placebo) of increased pulse for patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose. In patients with Restless Legs Syndrome, there was an increased risk (at least 5% greater than placebo) of increased pulse for patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose.
These findings of blood pressure and heart rate elevations should be considered when treating patients with cardiovascular disease.
Weight Gain and Fluid Retention
Patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose for early-stage Parkinson's disease had a higher incidence (2%) of substantial weight gain (more than 10% of baseline weight) than patients taking placebo (0%). In advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, the incidence of weight gain more than 10% of baseline weight was 9% in NEUPRO-treated patients (for the maximum recommended dose) and 1% in placebo-treated patients. This weight gain was frequently associated with the development of peripheral edema in patients with Parkinson's disease, suggesting that NEUPRO may cause fluid retention in some Parkinson's patients. In patients taking the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, the incidence of peripheral edema was 3% for NEUPRO and 2% for placebo in early-stage Parkinson's disease and 9% for NEUPRO and 1% for placebo in advanced-stage Parkinson's disease. These treatment differences increased further with treatment at NEUPRO dosing above the maximum recommended doses. Monitor for weight gain and fluid retention when treating patients with concomitant illnesses such as congestive heart failure or renal insufficiency.
Dyskinesia
NEUPRO may potentiate the dopaminergic side effects of levodopa and may cause or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia. For the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, the incidence of dyskinesia was increased for NEUPRO (NEUPRO 14% vs. placebo 7%) in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, and this incidence increased with increasing dose. Patients treated with the maximum recommended dose of NEUPRO also had an increased risk (NEUPRO 3% vs. placebo 0%) for early discontinuation from the study because of dyskinesia.
Application Site Reactions
Application site reactions (ASRs) occurred at a greater frequency in the NEUPRO-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients in the double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response studies with NEUPRO. For the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose, the incidence of application site reactions was 32% for NEUPRO and 19% for placebo in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, 36% for NEUPRO and 13% for placebo in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, and 43% for NEUPRO and 4% for placebo in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome. ASRs exhibited a dose-dependent relationship for all doses for patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and Restless Legs Syndrome. ASRs were also of sufficient severity to cause study discontinuation for patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 3% vs. placebo 0%), advanced-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 2% vs. placebo 0%), and Restless Legs Syndrome (NEUPRO 12% vs. placebo 0%) who were treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose.
The signs and symptoms of these reactions generally were localized erythema, edema, or pruritus limited to the patch area and usually did not lead to dose reduction. Generalized skin reactions (e.g., allergic rash, including erythematous, macular-papular rash, or pruritus) have been reported at lower rates than ASRs during the development of NEUPRO.
In a clinical study designed to investigate the cumulative skin irritation of NEUPRO, daily rotation of NEUPRO application sites has been shown to reduce the incidence of ASRs in comparison to repetitive application to the same site. In a clinical study investigating the skin sensitizing potential of NEUPRO in 221 healthy subjects, no case of contact sensitization was observed. Localized sensitization reactions were observed in a study with healthy subjects by continuously rotating a 0.5 mg/24 hours transdermal system, after induction of maximal irritational stress was achieved by repetitive transdermal system application to the same site.
If a patient reports a persistent application site reaction (of more than a few days), reports an increase in severity, or reports a skin reaction spreading outside the application site, an assessment of the risk and benefits for the individual patient should be conducted. If a generalized skin reaction associated with the use of NEUPRO is observed, NEUPRO should be discontinued.
Augmentation and Rebound in RLS
Augmentation is a worsening of RLS symptoms during treatment, leading to an increase in overall symptom severity or earlier time of symptom onset each day compared to before initiation of treatment. Use of dopaminergic medications, including NEUPRO, may result in augmentation.
Rebound, an exacerbation of RLS symptoms, is considered to be an end of dose effect, related to the half-life of the therapeutic agent. Reports in the published literature indicate discontinuation or wearing off of dopaminergic medications can result in rebound.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cardioversion
The backing layer of NEUPRO contains aluminum. To avoid skin burns, NEUPRO should be removed prior to magnetic resonance imaging or cardioversion.
Heat Application
The effect of application of heat to the transdermal system has not been studied. However, heat application has been shown to increase absorption several fold with other transdermal products. Patients should be advised to avoid exposing the NEUPRO application site to external sources of direct heat, such as heating pads or electric blankets, heat lamps, saunas, hot tubs, heated water beds, and prolonged direct sunlight.
Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
A symptom complex resembling the neuroleptic malignant syndrome (characterized by elevated temperature, muscular rigidity, altered consciousness, rhabdomyolysis, and/or autonomic instability), with no other obvious etiology, has been reported in association with rapid dose reduction, withdrawal of, or changes in anti- Parkinsonian therapy. Therefore, it is recommended that the dose be tapered at the end of NEUPRO treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Withdrawal Symptoms
Symptoms including apathy, anxiety, depression, fatigue, insomnia, sweating and pain have been reported during taper or after discontinuation of dopamine agonists, including NEUPRO. These symptoms generally do not respond to levodopa.
Prior to discontinuation, patients should be informed about potential withdrawal symptoms, and monitored during and after discontinuation. In case of severe withdrawal symptoms, a trial re-administration of a dopamine agonist at the lowest effective dose may be considered.
Fibrotic Complications
Cases of retroperitoneal fibrosis, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusion, pleural thickening, pericarditis, and cardiac valvulopathy have been reported in some patients treated with ergot-derived dopaminergic agents. While these complications may resolve when the drug is discontinued, complete resolution does not always occur.
Although these adverse events are believed to be related to the ergoline structure of these compounds, whether other, nonergot-derived dopamine agonists can cause them is unknown.
Binding to Melanin
As has been reported with other dopamine agonists, binding to melanin-containing tissues (i.e., eyes) in the pigmented rat and monkey was evident after a single dose of rotigotine, but was slowly cleared over the 14-day observation period.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Sulfite Sensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Hallucinations/Psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Symptomatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Elevation of Blood Pressure and Heart Rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Weight Gain and Fluid Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Application Site Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Augmentation and Rebound in RLS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Hyperpyrexia and Confusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ]
- Withdrawal Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ]
- Fibrotic Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the incidence of adverse reactions (number of unique patients experiencing an adverse reaction associated with treatment/total number of patients treated) observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to incidence of adverse reactions in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the incidence of adverse reactions observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Early-Stage Parkinson's Disease
The safety of NEUPRO was evaluated in a total of 649 early-stage Parkinson's disease patients who participated in three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with durations of 3 to 9 months. Additional safety information was collected in short-term studies and two open-label extension studies in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease.
In the double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, the most common adverse reactions (at least 5% greater than placebo) for the maximum recommended dose of NEUPRO (6 mg/24 hours) were nausea, vomiting, somnolence, application site reactions, dizziness, anorexia, disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep, hyperhidrosis, and visual disturbance.
In this trial, 12% of patients treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose (6 mg/24 hours) discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions, compared with 6% of patients who received placebo.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in greater than 2% of NEUPRO-treated patients and more frequent than in placebo-treated patients in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease. Incidences for the non-recommended 8 mg/24 hours dose are also shown.
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo N=64 % | NEUPRO Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg/24h N=67 % | 4 mg/24h N=63 % | 6 mg/24h N=65 % | 8 mg/24h N=70 % | ||
| Nausea | 13 | 34 | 38 | 48 | 41 |
| Vomiting | 3 | 10 | 16 | 20 | 11 |
| Somnolence | 3 | 12 | 14 | 19 | 20 |
| Application and instillation site reactions | 19 | 21 | 19 | 32 | 43 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 21 | 14 | 22 | 20 |
| Anorexia | 0 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 4 |
| Disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep | 6 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 11 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 3 | 3 | 3 | 11 | 3 |
| Visual disturbance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3 |
| Abnormal dreams | 0 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| Abnormal Electrocardiogram T wave | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Balance disorder | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 3 | 8 | 18 | 6 | 13 |
| Tinnitus | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Constipation | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
| Erythema | 3 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| Hallucinations | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Muscle spasms | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Paresthesia | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| White blood cells urine positive | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
The incidence of certain adverse reactions with NEUPRO was notably increased compared to placebo treatment (i.e., at least 5% greater than placebo) in either the titration or maintenance phases of the dose-response trial.
During the titration phase, this increased incidence of a treatment difference was observed for nausea, somnolence, vomiting, application site reactions (ASRs), dizziness, sweating increased, anorexia, and visual disturbance. During the maintenance phase, an increased incidence was observed for nausea and ASRs. Some adverse reactions developing in the titration phase persisted (at least 7 days) into the maintenance phase. These "persistent" adverse reactions included ASRs, anorexia, somnolence, and nausea.
Adverse Reactions in Advanced-Stage Parkinson's Disease
The safety evaluation of NEUPRO was based on a total of 672 NEUPRO-treated patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease who participated in three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (two fixed-dose trials and one flexible-dose trial) with durations of 3 to 7 months. Patients received concomitant levodopa in these studies. Additional safety information was collected in earlier short-term studies and two open-label extension studies in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease.
In the dose-response, placebo-controlled trial for advanced-stage Parkinson's disease, the most common adverse reactions (at least 5% greater than placebo) for the maximum recommended dose of NEUPRO (8 mg/24 hours) were application site reactions, nausea, peripheral edema, dizziness, and dyskinesia.
In this trial, approximately 15% of patients treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose (8 mg/24 hours) discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions, compared with 9% of patients who received placebo.
Table 2 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in greater than 2% of NEUPRO-treated patients and more frequent than in placebo-treated patients in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease. Incidences for the non-recommended 12 mg/24 hours dose are also shown.
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo N=120 % | NEUPRO Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mg/24h N=118 % | 12 mg/24h N=111 % | ||
| Application and instillation site reactions | 13 | 36 | 46 |
| Nausea | 19 | 28 | 22 |
| Peripheral edema | 1 | 9 | 14 |
| Dizziness | 15 | 23 | 14 |
| Dyskinesia | 7 | 14 | 17 |
| Somnolence | 28 | 32 | 32 |
| Vomiting | 6 | 10 | 8 |
| Arthralgia | 7 | 11 | 8 |
| Hallucinations | 3 | 7 | 13 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| Sinus congestion | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| Constipation | 6 | 9 | 5 |
| Disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep | 6 | 9 | 14 |
| First degree atrioventricular block | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Herpes simplex | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| Influenza | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| Nasal congestion | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Headache | 8 | 10 | 8 |
| Diarrhea | 5 | 7 | 5 |
| Basal cell carcinoma | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Cough | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Dyspepsia | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Erythema | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Hot flush | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Paresthesias | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Tremor | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Hypoaesthesia | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Nightmare | 2 | 3 | 5 |
The incidence of certain adverse reactions with NEUPRO was notably increased compared to placebo treatment (i.e., at least 5% greater than placebo) in either the titration or maintenance phases of the dose-response trial.
During the titration phase, an increased incidence was observed for application site reactions (ASRs), nausea, hallucinations, constipation, dyskinesia, and dizziness. During the maintenance phase, an increased incidence was observed for ASRs and peripheral edema. Some adverse reactions developing in the titration phase persisted (at least 7 days) into the maintenance phase. A notably "persistent" adverse reaction was ASRs.
Adverse Reactions in Restless Legs Syndrome
The safety evaluation of NEUPRO was based on 745 NEUPRO-treated patients with Restless Legs Syndrome who participated in two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with maintenance durations of 6 months.
Additional safety information was collected in earlier short-term studies and three open-label extension studies in patients with RLS.
In the two double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trials for RLS, the most common adverse reactions (at least 5% greater than placebo) for the maximum recommended dose of NEUPRO (3 mg/24 hours) were application site reactions, nausea, disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep, somnolence, and headache.
In the two fixed-dose, placebo-controlled trials, 24% of patients treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose (3 mg/24 hours) discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions, compared with 3% of patients who received placebo.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of NEUPRO-treated patients and more frequent than in placebo-treated patients in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trials in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome.
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo N=217 % | NEUPRO Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 mg/24h N=99 % | 1 mg/24h N=215 % | 2 mg/24h N=211 % | 3 mg/24h N=220 % | ||
| Application and instillation site reactions | 4 | 23 | 27 | 38 | 43 |
| Nausea | 10 | 18 | 15 | 23 | 21 |
| Disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 10 |
| Headache | 11 | 21 | 15 | 18 | 16 |
| Asthenic conditions Asthenic conditions is a high-level term for the following preferred terms: asthenia, malaise, and fatigue. | 8 | 11 | 7 | 14 | 12 |
| Somnolence | 4 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 10 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Pruritus | 3 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| Dry mouth | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| Vomiting | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Dizziness | 6 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 6 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| Abnormal dreams | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Irritability | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Muscle spasms | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Hot flush | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Menstrual disorder | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Sleep disorder | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Viral gastroenteritis | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Sleep attacks | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Sexual desire disorder | 3 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Depression | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Decreased serum ferritin | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Vertigo | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Constipation | 3 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Erythema | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Sinusitis | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Diarrhea | 4 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Increased weight | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 7 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 8 |
The incidence of certain adverse reactions with NEUPRO treatment was increased compared to placebo (i.e., at least 5% greater than placebo) in either the titration or maintenance phases of the dose-response trials. During the titration phase, an increased incidence was observed for application site reactions (ASRs), nausea, headache, asthenic conditions, and disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep. During the maintenance phase, an increased incidence was observed for ASRs. Some adverse reactions developing in the titration phase persisted (at least 7 days) into the maintenance phase. These "persistent" adverse reactions were ASRs, nausea, and disturbances in initiating and maintaining sleep.
Laboratory Changes
Some clinical laboratory analytes were abnormal in patients treated with the maximum recommended NEUPRO dose in the fixed-dose, placebo-controlled, dose-response trials for patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease and with RLS.
Patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO had an increased risk for low hemoglobin below the normal reference range (NEUPRO 8% vs. placebo 2%) and for decreased hematocrit below the normal reference range (NEUPRO 8% vs. placebo 5%). Patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO had an increased risk for a low hemoglobin below the normal reference range (NEUPRO 15% vs. placebo 11%) and for decreased hematocrit below the normal reference range (NEUPRO 17% vs. placebo 14%). Patients with RLS receiving NEUPRO had an increased risk for a decreased hemoglobin below the normal reference range (NEUPRO 15% vs. placebo 12%). There was also an increased risk for markedly decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit (NEUPRO 2% vs. placebo 0%) in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO and for markedly decreased hematocrit (NEUPRO 1% vs. placebo 0%) in patients with RLS receiving NEUPRO.
Patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO had an increased risk for elevated serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) above the normal reference range (NEUPRO 11% vs. placebo 2%). There was also an increased risk for markedly elevated serum BUN (NEUPRO 3% vs. placebo 2%) in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO.
There was an increased risk for low serum glucose below the normal reference range in patients with early- stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO (NEUPRO 15% vs. placebo 6%) and in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease (NEUPRO 10% vs. placebo 7%). There was also an increased risk for markedly decreased serum glucose (NEUPRO 1% vs. placebo 0%) in patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease receiving NEUPRO.
Serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) was elevated in Japanese patients taking NEUPRO for early- or advanced-stage Parkinson's disease in placebo-controlled, flexible-dose studies conducted in Japan. The frequency of CPK elevation observed in patients receiving NEUPRO for early-stage Parkinson's disease was 40% (35/88) in the NEUPRO group compared to 17% (15/89) in the placebo group. The frequency of CPK elevation observed in patients receiving NEUPRO for advanced-stage Parkinson's disease was 39% (99/253) in the NEUPRO group compared to 20% (34/171) in the placebo group using pooled data from two studies.
Increased CPK occurred at any time during the respective studies, and in some instances increased CPK was observed at two or more consecutive visits. The total daily dose of NEUPRO taken by patients with early- and advanced-stage Parkinson's disease ranged between 2 mg/24 hours to 16 mg/24 hours. Studies of NEUPRO conducted outside of Japan did not include assessments of serum CPK in patients treated for Parkinson's disease . Increased CPK was also reported in postmarketing data.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reaction has been identified during post-approval use of NEUPRO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions : withdrawal symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ]
Nervous System Disorders : Dropped head syndrome
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Rhabdomyolysis
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Dopamine Antagonists
Dopamine antagonists, such as antipsychotics or metoclopramide, may diminish the effectiveness of NEUPRO [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DESCRIPTION
NEUPRO is a transdermal system that provides continuous delivery of rotigotine, a non-ergoline dopamine agonist, for 24 hours following application to intact skin.
NEUPRO is available in six strengths as shown in Table 4.
| NEUPRO Nominal Dose | Rotigotine Content per System | NEUPRO System Size |
|---|---|---|
| 1 mg/24 hours | 2.25 mg | 5 cm 2 |
| 2 mg/24 hours | 4.5 mg | 10 cm 2 |
| 3 mg/24 hours | 6.75 mg | 15 cm 2 |
| 4 mg/24 hours | 9 mg | 20 cm 2 |
| 6 mg/24 hours | 13.5 mg | 30 cm 2 |
| 8 mg/24 hours | 18 mg | 40 cm 2 |
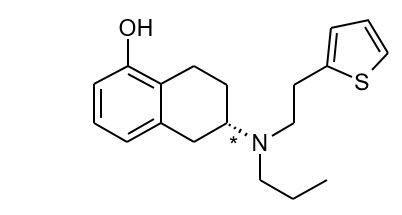
The chemical name of rotigotine is (6S)-6-{propyl[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]amino}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenol. The empirical formula is C 19 H 25 NOS. The molecular weight is 315.48. The structural formula for rotigotine is:
| The asterisk designates the chiral center. |
|
System Components and Structure
NEUPRO is a thin, matrix-type transdermal system composed of three layers as shown in Figure 1:
| Backing film Drug matrix Protective liner |
| Figure 1: System Schematic | |
- A flexible, tan-colored backing film, consisting of an aluminized polyester film coated with a pigment-layer on the outer side. The backing provides structural support and protection of the drug-loaded adhesive layer from the environment.
- A self-adhesive drug matrix layer, consisting of the active component rotigotine and the following inactive components: ascorbyl palmitate, povidone, silicone adhesive, sodium metabisulfite, and dl-alpha-tocopherol.
- A protective liner, consisting of a transparent fluoropolymer-coated polyester film. This liner protects the adhesive layer during storage and is removed just prior to application.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Rotigotine is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. The precise mechanism of action of rotigotine as a treatment for Parkinson's disease is unknown, although it is thought to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors within the caudate-putamen in the brain. The precise mechanism of action of rotigotine as a treatment for Restless Legs Syndrome is unknown but is thought to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
There is no indication of a QT/QTc prolonging effect of NEUPRO in doses up to 24 mg/24 hours. The effects of NEUPRO at doses up to 24 mg/24 hours (supratherapeutic doses) on the QT/QTc interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg IV, single dose), parallel-group trial with an overall treatment period of 52 days in male and female patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease. Assay sensitivity was confirmed by significant QTc prolongation by moxifloxacin.
Pharmacokinetics
On average, approximately 45% of the rotigotine from the patch is released within 24 hours (0.2 mg/cm 2 ). Rotigotine is primarily eliminated in the urine as inactive conjugates. After removal of the patch, plasma levels decreased with a terminal half-life of 5 to 7 hours. The pharmacokinetic profile showed a biphasic elimination with an initial half-life of 3 hours.
Absorption and Bioavailability
When single doses of 8 mg/24 hours are applied to the trunk, there is an average lag time of approximately 3 hours until drug is detected in plasma (range 1 to 8 hours). T max typically occurs between 15 to 18 hours post dose but can occur from 4 to 27 hours post dose. However, there is no characteristic peak concentration observed. Rotigotine displays dose-proportionality over a daily dose range of 1 mg/24 hours to 24 mg/24 hours. In the clinical studies of rotigotine effectiveness, the transdermal system application site was rotated from day to day (abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, or upper arm) and the mean measured plasma concentrations of rotigotine were stable over the 6 months of maintenance treatment. Relative bioavailability for the different application sites at steady-state was evaluated in subjects with Parkinson's disease. In a single trial conducted in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease, differences in bioavailability ranged from less than 1% (abdomen vs. hip) to 46% (shoulder vs. thigh) with shoulder application showing higher bioavailability.
Because rotigotine is administered transdermally, food should not affect absorption.
In a 14-day clinical study with rotigotine administered to healthy subjects, steady-state plasma concentrations were achieved within 2 to 3 days of daily dosing.
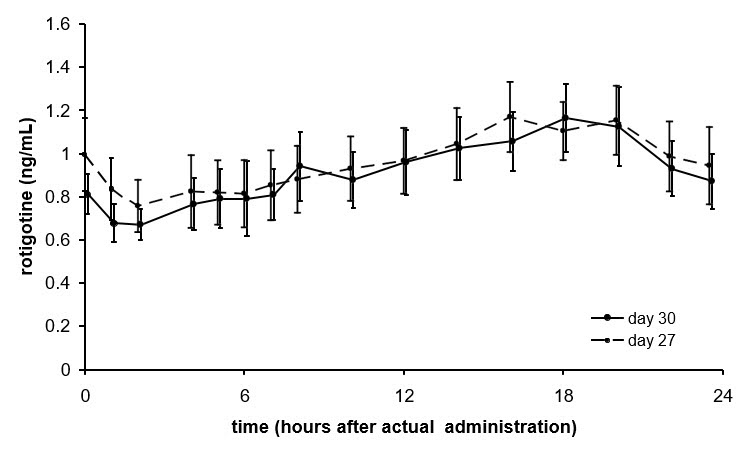
Average NEUPRO plasma concentrations (±95% CI) in patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease are shown in Figure 2 after application of a 8 mg/24 hours transdermal system to 1 of 6 application sites (shoulder, upper arm, flank, hip, abdomen, or thigh) on 2 different days during the maintenance phase.
 |
Distribution
The weight normalized apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) in humans is approximately 84 L/kg after repeated dose administration.
The binding of rotigotine to human plasma proteins is approximately 92% in vitro and 89.5% in vivo .
Metabolism and Elimination
Rotigotine is extensively metabolized by conjugation and N-dealkylation. After intravenous dosing the predominant metabolites in human plasma are sulfate conjugates of rotigotine, glucuronide conjugates of rotigotine, sulfate conjugates of the N-despropyl-rotigotine and conjugates of N-desthienylethyl-rotigotine. Multiple CYP isoenzymes, sulfotransferases and two UDP-glucuronosyltransferases catalyze the metabolism of rotigotine.
After removal of the patch, plasma levels decreased with a terminal half-life of 5 to 7 hours. The pharmacokinetic profile showed a biphasic elimination with an initial half-life of 3 hours.
Rotigotine is primarily excreted in urine (approximately 71%) as inactive conjugates of the parent compound and N-desalkyl metabolites. A smaller proportion is excreted in feces (approximately 23%). The major metabolites found in urine were rotigotine sulfate (16% to 22% of the absorbed dose), rotigotine glucuronide (11% to 15%), and N-despropyl-rotigotine sulfate metabolite (14% to 20%) and N-desthienylethyl-rotigotine sulfate metabolite (10% to 21%). Approximately 11% is renally eliminated as other metabolites. A small amount of unconjugated rotigotine is renally eliminated (less than 1% of the absorbed dose).
Drug Interaction Studies
CYP Interactions
In vitro studies indicate that multiple CYP-isoforms are capable of catalyzing the metabolism of rotigotine. In human liver microsomes, no extensive inhibition of the metabolism of rotigotine was observed when co-incubated with CYP isoform specific inhibitors. If an individual CYP isoform is inhibited, other isoforms can catalyze rotigotine metabolism.
Rotigotine, the 5-O-glucuronide and its desalkyl and monohydroxy metabolites were analyzed for interactions with the human CYP isoenzymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 in vitro . Based on these results, no risk for inhibition of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 catalyzed metabolism of other drugs is predicted at therapeutic rotigotine concentrations. There is a low risk of inhibition of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 catalyzed metabolism of other drugs at therapeutic concentrations.
In human hepatocytes in vitro , there was no indication for induction of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4.
Rotigotine is metabolized by multiple sulfotransferases and two UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT1A9 and UGT2B15). These multiple pathways make it unlikely that inhibition of any one pathway would alter rotigotine concentrations significantly.
Protein Displacement, Warfarin
In vitro , no potential for displacement of warfarin by rotigotine (and vice versa) from their respective human serum albumin binding sites was detected.
Digoxin
The effect of rotigotine on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin has been investigated in vitro in Caco-2 cells. Rotigotine did not influence the P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of digoxin. Therefore, rotigotine would not be expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of digoxin.
Cimetidine
Co-administration of rotigotine (up to 4 mg/24 hours) with cimetidine (400 mg twice daily), an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, did not alter the steady-state pharmacokinetics of rotigotine in healthy subjects.
Levodopa/Carbidopa
Co-administration of levodopa/carbidopa (100/25 mg twice daily) with rotigotine (4 mg/24 hours) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of rotigotine; rotigotine had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of levodopa/carbidopa.
Oral Contraception
Co-administration of rotigotine (3 mg/24 hours) did not affect the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of oral contraceptives (0.03 mg ethinylestradiol, 0.15 mg levonorgestrel).
Omeprazole
Co-administration of the CYP2C19 selective inhibitor omeprazole (40 mg/day) had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of rotigotine (4 mg/24 hours).
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of impaired hepatic function on the pharmacokinetics of rotigotine has been studied in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classification – Grade B). There were no relevant changes in rotigotine plasma concentrations. No information is available on subjects with severe impairment of hepatic function.
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal function on rotigotine pharmacokinetics has been studied in subjects with mild to severe impairment of renal function including subjects requiring dialysis compared to healthy subjects. There were no relevant changes in rotigotine plasma concentrations (up to end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis). In subjects with severe renal impairment not on dialysis (i.e., creatinine clearance 15 to less than 30 ml/min), exposure to conjugated rotigotine metabolites was doubled.
Gender
Female and male subjects and patients had similar plasma concentrations (body weight normalized).
Geriatric Patients
Plasma concentrations of rotigotine in patients 65 to 80 years of age were similar to those in younger patients, approximately 40 to 64 years of age. Although not studied, exposures in older subjects (more than 80 years) may be higher due to skin changes with aging.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of rotigotine in subjects below the age of 18 years has not been established.
Race
The pharmacokinetic profile was similar in Caucasians, Blacks, and Japanese.
Adhesion
Adhesion was examined in subjects with Parkinson's disease when patches were applied to rotating sites. Similar results were observed for the 4 mg/24 hours (20 cm 2 ), 6 mg/24 hours (30 cm 2 ), and 8 mg/24 hours (40 cm 2 ) patches. An adherence of 90% or more of the patch surface was observed in 71% to 82% of cases. A partial detachment of more than 10% was observed in 15% to 24% of cases. A complete detachment of the patch was observed in 3% to 5% of cases.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Two-year carcinogenicity studies of rotigotine were conducted in mice at doses of 0, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg and in rats at doses of 0, 0.3, 1, and 3 mg/kg; in both studies rotigotine was administered subcutaneously once every 48 hours. No significant increases in tumors occurred in mice at doses up to 9 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) in Parkinson's disease (8 mg/24 hours).
In rats, there were increases in Leydig cell tumors and in uterine tumors (adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas) at all doses. The endocrine mechanisms believed to be involved in the production of these tumors in rats are not considered relevant to humans. Therefore, there were no tumor findings considered relevant to humans at plasma exposures (AUC) up to 4 to 6 times that in humans at the MRHD.
Mutagenesis
Rotigotine was negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) and in the in vivo micronucleus assays. Rotigotine was mutagenic and clastogenic in the in vivo mouse lymphoma tk assay.
Infertility
When rotigotine was administered subcutaneously (0, 1.5, 5, or 15 mg/kg/day) to female rats prior to and during mating and continuing through gestation day 7, an absence of implantation was observed at all doses. The lowest dose tested is 2 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis. In male rats treated from 70 days prior to and during mating, there was no effect on fertility; however, a decrease in epididymal sperm motility was observed at the highest dose tested. The no-effect dose (5 mg/kg/day) is 6 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis. When rotigotine was administered subcutaneously to female mice at doses of 0, 10, 30, and 90 mg/kg/day from 2 weeks until 4 days before mating and then at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (all groups) (approximately 4 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis) from 3 days before mating until gestation day 7, a markedly reduced (low dose) or complete absence of implantation (mid and high doses) was observed. The effects on implantation in rodents are thought to be due to the prolactin-lowering effect of rotigotine. In humans, chorionic gonadotropin, not prolactin, is essential for implantation.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Retinal Pathology: Albino rats
Retinal degeneration was observed in albino rats in a 6-month toxicity study at the highest dose of rotigotine (plasma exposure [AUC] at least 15 times that in humans at the MRHD). Retinal degeneration was not observed in the 2-year carcinogenicity studies in albino rat (plasma AUCs up to 4-6 times that in humans at the MRHD) or albino mouse, or in monkeys treated for 1 year. The potential significance of this effect in humans has not been established, but cannot be disregarded because disruption of a mechanism that is universally present in vertebrates (i.e., disk shedding) may be involved.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Parkinson's Disease
The effectiveness of NEUPRO in the treatment of the signs and symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's disease was established in five parallel-group, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials conducted in the U.S. and abroad. Three of these five trials enrolled patients with early-stage Parkinson's disease (not receiving levodopa), and two enrolled patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease who were receiving levodopa. Depending on trial design, patients underwent a weekly titration of NEUPRO in 2 mg/24 hours increments to either the randomized dose or optimal dose. Back titrations by 2 mg/24 hours decrement of NEUPRO were permitted for intolerable adverse events. Patch application sites were changed on a daily basis.
Change from baseline in the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), Parts II + III, served as the primary outcome assessment measure in the early-stage studies. The UPDRS is a four-part multi-item rating scale intended to evaluate mentation (Part I), Activities of Daily Living (ADL) (Part II), motor performance (Part III), and complications of therapy (Part IV). Part II of the UPDRS contains 13 questions relating to ADL, which are scored from 0 (normal) to 4 (maximal severity) for a maximum (worst) score of 52. Part III of the UPDRS contains 27 questions (for 14 items) and is scored as described for Part II. Part III is designed to assess the severity of the cardinal motor findings in patients with Parkinson's disease (e.g., tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, etc.), scored for different body regions, and has a maximum (worst) score of 108.
Change from baseline in time spent "off" (hours) based on daily diaries was the primary outcome assessment in the two trials of advanced-stage Parkinson's disease (with levodopa).
Studies in Patients with Early-Stage Parkinson's Disease
Patients (N=649) in the three trials of early-stage Parkinson's disease had limited or no prior exposure to levodopa (off levodopa for at least 28 days prior to baseline or levodopa use for no more than 6 months). Patients were excluded from the studies if they had a history of pallidotomy, thalamotomy, deep brain stimulation, or fetal tissue transplant. Patients receiving selegiline, anticholinergic agents, or amantadine must have been on a stable dose and able to maintain that dose for the duration of the study.
PD-1
This trial was a multicenter, multinational, dose-response study in which 316 early-stage Parkinson's disease patients were titrated over 4 weeks to their randomized treatment with either placebo or one of four fixed doses of NEUPRO (2 mg/24 hours, 4 mg/24 hours, 6 mg/24 hours, or 8 mg/24 hours). The patches were applied to the upper abdomen and the sites of application were rotated on a daily basis.
Patients underwent a weekly titration (increasing the number of 2 mg/24 hours patches or placebo patches at weekly intervals) over 4 weeks such that the target doses of NEUPRO were achieved for all groups by the end of 3 weeks and were administered over the fourth week of the titration phase. Patients then continued on treatment for a 7-week maintenance phase followed by a down titration during the last week. Two back titrations by a single patch (i.e., 2 mg/24 hours decrement of NEUPRO or placebo) at a time were permitted for intolerable adverse events. The mean age of patients was approximately 60 years (range 33-83 years; approximately 36% were 65 years or older) and the study enrolled more men (62%) than women (39%). Most patients (85%) were Caucasian and most randomized patients (≥88%) completed the full treatment period.
Mean baseline combined UPDRS (Parts II + III) scores were similar among all treatment groups, between 27.1 and 28.5 for all groups. The mean change from baseline and difference from placebo for each treatment group is shown in Table 5. Statistically significant mean changes reflecting dose-related improvement were observed at the three highest doses, and the 6 mg/24 hours and 8 mg/24 hours doses had a similar effect.
| Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | -1.4 | NA |
| NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours | -3.5 | -2.1 |
| NEUPRO 4 mg/24 hours | -4.5 | -3.1 |
| NEUPRO 6 mg/24 hours | -6.3 | -4.9 |
| NEUPRO 8 mg/24 hours | -6.3 | -5.0 |
PD-2
This trial was a multinational, randomized, double-blind, flexible NEUPRO dose (2 mg/24 hours, 4 mg/24 hours, or 6 mg/24 hours), parallel-group study in which 277 early-stage Parkinson's disease patients were assigned (2: 1 ratio) to treatment with NEUPRO or placebo for a period up to about 28 weeks. This trial was conducted in 47 sites in North America (U.S. and Canada). Patches were applied to different body parts including upper or lower abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, and/or upper arm and patch application sites were to be rotated on a daily basis. Patients underwent a weekly titration (consisting of 2 mg/24 hours increments at weekly intervals) over 3 weeks to a maximal dose of 6 mg/24 hours depending on efficacy and tolerability, and then received treatment over a 24-week maintenance phase followed by a de-escalation over a period up to 4 days. Back/down titration by a single patch (i.e., 2 mg/24 hours decrement of NEUPRO or placebo) was permitted during the titration phase for intolerable adverse events but was not permitted during the maintenance phase (i.e., patients with intolerable adverse events had to leave the study). Primary efficacy data were collected after a treatment period of up to approximately 27 weeks.
The mean age of patients was approximately 63 years (range 32-86 years; approximately 45% were 65 years or older), approximately two-thirds of all patients were men, and nearly all patients were Caucasian.
Approximately 90% of patients randomized to NEUPRO achieved a maximal daily dose of 6 mg/24 hours; 70% maintained this dose for most (more than 20 weeks) of the maintenance phase. Most enrolled patients (≥81%) completed the full treatment period.
Mean baseline combined UPDRS (Parts II + III) was similar in both groups (29.9 NEUPRO group, 30.0 placebo). NEUPRO-treated patients experienced a mean change in the combined UPDRS (Parts II + III) from baseline to end of treatment (end of treatment week 27 or last visit for patients discontinuing early) of -4.0 (Table 6), and the difference from placebo was statistically significant.
| Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | +1.3 | NA |
| NEUPRO up to 6 mg/24 hours | -4.0 | -5.3 |
PD-3
This study was a multinational, randomized, double-blind, flexible-dose (NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours, 4 mg/24 hours, 6 mg/24 hours, or 8 mg/24 hours), three-arm, parallel-group study using a double-dummy treatment in which 561 early-stage Parkinson's disease patients were assigned to treatment with either placebo or NEUPRO or active oral comparator in a ratio of 1: 2: 2 for a period up to about 39 weeks. This study was conducted in up to 81 sites in many countries outside of North America. Patches were applied to different body parts including upper or lower abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, and/or upper arm and patch application sites were to be rotated on a daily basis. Treatment with a patch and placebo was given to all patients in a double-blinded manner such that no one would know the actual treatment (i.e., NEUPRO, comparator, or placebo). Patients underwent a weekly dose escalation/titration of patch (consisting of 2 mg/24 hours increments of NEUPRO or placebo) and a dose escalation of capsules of comparator or placebo over 13 weeks (13-week titration was planned for the comparator treatment) up to a maximal dose of 8 mg/24 hours of NEUPRO depending on achieving optimal efficacy or intolerability at a lower dose. Patients randomized to NEUPRO achieved the maximal dose of 8 mg/24 hours after a 4-week titration if maximal efficacy and intolerability had not occurred over a 4-week titration period. Patients then received treatment over a 24-week maintenance phase followed by a de-escalation over a period up to 12 days. A single back titration by a single patch (i.e., 2 mg/24 hours decrement of NEUPRO or placebo) or capsule was permitted during the titration phase for intolerable adverse events but was not permitted during the maintenance phase (i.e., patients with intolerable adverse events had to discontinue from this study). Primary efficacy data were collected after a treatment period of up to approximately 37 weeks of randomized treatment.
The mean age of patients was approximately 61 years (range 30-86 years; approximately 41% were 65 years or older), nearly 60% of all patients were men, and nearly all patients were Caucasian. About 73% of patients completed the full treatment period. The mean daily dose of NEUPRO was just less than 8 mg/24 hours and approximately 90% of patients achieved the maximal daily dose of 8 mg/24 hours.
Mean baseline combined UPDRS (Parts II + III) was similar across all groups (33.2 NEUPRO, 31.3 placebo, 32.2 comparator). NEUPRO-treated patients experienced a mean change in the combined UPDRS (Parts II + III) from baseline to end of treatment (end of treatment week 37 or last visit for patients discontinuing early) of -6.8, and the difference from placebo-treated patients showed a mean change from baseline of -2.3 (see Table 7 ), a difference that was statistically significant.
| Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | -2.3 | NA |
| NEUPRO up to 8 mg/24 hours | -6.8 | -4.5 |
Studies in Patients with Advanced-Stage Parkinson's Disease
Patients (N=658) in the three trials of NEUPRO in advanced-stage Parkinson's disease had to be experiencing "on-off" periods at baseline, despite treatment with optimal doses of levodopa. Patients continued concomitant levodopa during the trial; however, reductions in the dosage of levodopa were allowed if patients experienced adverse events that the investigator considered related to dopaminergic therapy. Patients were excluded from the studies if they had a history of pallidotomy, thalamotomy, deep brain stimulation, or fetal tissue transplant.
Patients receiving selegiline, anticholinergic agents, or amantadine must have been on a stable dose and able to maintain that dose for the duration of the study. In the North American trial, COMT-inhibitors were not permitted.
PD-4
This trial was a multinational, three-arm, parallel-group study in which 351 advanced-stage Parkinson's disease patients were titrated over 5 weeks to treatment with either placebo or NEUPRO (8 mg/24 hours or 12 mg/24 hours) and maintained treatment for 24 weeks followed by a down titration over the last week. This study was conducted in 55 sites in North America (U.S. and Canada).
Mean baseline "off" times were similar among all treatment groups (6.4, 6.8, and 6.3 hours for the placebo, NEUPRO 8 mg/24 hours and 12 mg/24 hours treatment groups, respectively). NEUPRO-treated patients experienced a mean change in "off" time from baseline to end of treatment of -2.7 hours for the 8 mg/24 hours treatment arm and -2.1 hours for the 12 mg/24 hours treatment arm (Table 8), and the difference from placebo was statistically significant for both NEUPRO doses (8 mg/24 hours, 12 mg/24 hours). Onset of treatment benefit began as early as the first week of treatment.
| Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | -0.9 | NA |
| NEUPRO 8 mg/24 hours | -2.7 | -1.8 |
| NEUPRO 12 mg/24 hours | -2.1 | -1.2 |
PD-5
This trial was a multinational, flexible-dose, three-arm, parallel-group study using a double-dummy treatment in which 506 advanced-stage Parkinson's disease patients were titrated over 7 weeks to treatment with either NEUPRO from a minimum dose of 4 mg/24 hours up to an optimal dose not exceeding 16 mg/24 hours, active oral comparator, or placebo and maintained treatment for 16 weeks followed by a down titration over 6 days.
This study was conducted in 77 sites in many countries outside of North America.
Mean baseline "off" times were similar among all treatment groups (6.6, 6.2, and 6.0 hours for the placebo, NEUPRO, and comparator treatment groups, respectively). NEUPRO-treated patients experienced a mean 2.5 hour decrease change in "off" time from baseline to end of treatment (Table 9), and the difference from placebo was statistically significant. Onset of treatment benefit began as early as the first week of treatment. The optimal NEUPRO dose was established as 4 mg/24 hours for 2% of patients, 6 mg/24 hours for 6%, 8 mg/24 hours for 8%, 10 mg/24 hours for 9%, 12 mg/24 hours for 16%, 14 mg/24 hours for 11% and 16 mg/24 hours for 44%.
| Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | -0.9 | NA |
| NEUPRO up to 16 mg/24 hours | -2.5 | -1.6 |
Restless Legs Syndrome
The clinical program included 1309 patients with moderate-to-severe RLS. The efficacy of NEUPRO in the treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) was primarily evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trials with maintenance periods of 6 months duration. Patients received NEUPRO doses ranging from 0.5 mg/24 hours to 3 mg/24 hours or placebo once daily. In these two trials, the mean duration of RLS was 2.1 to 3.1 years, mean age was approximately 55 years (range 19-78 years), approximately 68% were women, and 97% were Caucasian. In both trials, patches were applied to different application sites including the abdomen, thigh, hip, flank, shoulder, and/or upper arm and patch application sites were rotated on a daily basis.
The two outcome measures used to assess the effect of treatment as co-primary efficacy endpoints were the International RLS Rating Scale (IRLS Scale) and a Clinical Global Impression - Improvement (CGI-I) assessment. The IRLS Scale contains 10 items designed to assess the severity of sensory and motor symptoms, sleep disturbance, daytime somnolence, and impact on activities of daily living and mood associated with RLS. The range of scores is 0 to 40, with 0 being absence of RLS symptoms and 40 the most severe symptoms. The CGI-I is designed to assess clinical progress (global improvement) on a 7-point scale.
RLS-1
This trial was a multicenter, five-arm, parallel-group, fixed-dose trial of NEUPRO in subjects with moderate-to-severe RLS. A total of 505 subjects were randomized in this trial, participating at approximately 50 sites in the U.S. Subjects received placebo or NEUPRO (0.5 mg/24 hours, 1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, 3 mg/24 hours). Subjects began treatment at a daily dosage of 0.5 mg/24 hours NEUPRO and were titrated over a 4-week period to their assigned daily dose followed by a 6-month maintenance period and 7-day down titration period.
Mean baseline IRLS sum score were similar among all treatment groups (23.5, 23.1, 23.2, 23.3, and 23.6 for the placebo, NEUPRO 0.5 mg/24 hours, 1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, and 3 mg/24 hours groups, respectively).
Patients experienced a mean change in the IRLS sum score from baseline to the end of treatment for each of the four NEUPRO dose groups. The mean changes from baseline and differences from placebo in IRLS sum score and CGI Item 1 are shown for each treatment group in Table 10. The difference between the two highest treatment groups (2 mg/24 hours and 3 mg/24 hours) and placebo were statistically significant. Of the NEUPRO-treated patients, 23% had an IRLS score of 0 compared to 9.1% of placebo patients at the end of the maintenance period. Onset of treatment benefit was seen with the 1 mg/24 hours dose.
| Variable | Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRLS sum score | Placebo | -9.0 | NA |
| NEUPRO 0.5 mg/24 hours | -11.1 | -2.2 | |
| NEUPRO 1 mg/24 hours | -11.2 | -2.3 | |
| NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours | -13.5 | -4.5 | |
| NEUPRO 3 mg/24 hours | -14.2 | -5.2 | |
| CGI Item 1 | Placebo | -1.4 | NA |
| NEUPRO 0.5 mg/24 hours | -1.8 | -0.35 | |
| NEUPRO 1 mg/24 hours | -1.7 | -0.32 | |
| NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours | -2.1 | -0.65 | |
| NEUPRO 3 mg/24 hours | -2.3 | -0.90 |
RLS-2
This trial was a multicenter, four-arm, parallel-group trial of NEUPRO in subjects with moderate-to-severe RLS. A total of 458 subjects were randomized in this trial, participating at approximately 50 sites in 8 European countries. Patients received placebo or NEUPRO (1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, 3 mg/24 hours). Patients began treatment at a daily dosage of 1 mg/24 hours NEUPRO and were titrated over a 3-week period to their assigned daily dose followed by a 6-month maintenance period and 7-day down-titration period.
Mean baseline IRLS sum score were similar among all treatment groups (28.1, 28.1, 28.2, and 28.0 for the placebo, NEUPRO 1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, and 3 mg/24 hours groups, respectively). Patients experienced a mean change in the IRLS sum score from baseline to the end of treatment for each of the three NEUPRO dose groups. The mean changes from baseline and differences from placebo in IRLS sum score and CGI Item 1 are shown for each treatment group in Table 11. The difference between all three treatment groups (1 mg/24 hours, 2 mg/24 hours, and 3 mg/24 hours) and placebo were statistically significant. Of the NEUPRO-treated patients, 24% had an IRLS score of 0 compared to 12% of placebo patients at the end of the maintenance period. Onset of treatment benefit was seen with the 1 mg/24 hours dose.
| Variable | Treatment | Mean Change from Baseline | Difference from Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRLS sum score | Placebo | -8.6 | NA |
| NEUPRO 1 mg/24 hours | -13.7 | -5.1 | |
| NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours | -16.2 | -7.5 | |
| NEUPRO 3 mg/24 hours | -16.8 | -8.2 | |
| CGI Item 1 | Placebo | -1.3 | NA |
| NEUPRO 1 mg/24 hours | -2.0 | -0.76 | |
| NEUPRO 2 mg/24 hours | -2.4 | -1.07 | |
| NEUPRO 3 mg/24 hours | -2.5 | -1.21 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each transdermal system is packaged in a separate pouch.
Each strength is available in cartons of 30 transdermal systems.
| 1 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-801-03 |
| 2 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-802-03 |
| 3 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-803-03 |
| 4 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-804-03 |
| 6 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-805-03 |
| 8 mg/24 hours | 30 transdermal systems | NDC #50474-806-03 |
Store at 20º - 25ºC (68º - 77ºF); excursions permitted between 15º - 30ºC (59º - 86ºF). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]
NEUPRO should be stored in the original pouch. Do not store outside of pouch.
Apply the transdermal system immediately upon removal from the pouch. Discard used systems in household trash in a manner that prevents accidental application or ingestion by children, pets, or others.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE NEUPRO ® [NU pro] (rotigotine transdermal system)
When to apply NEUPRO:
Each NEUPRO patch is sealed in a pouch that protects it until you are ready to apply it. See Figure A .

- NEUPRO should be applied right away after removing it from the protective pouch. Do not damage or cut your NEUPRO patch into smaller pieces.
- Choose the time of day or night that works best for you to apply your NEUPRO patch. Apply your NEUPRO patch at the same time each day.
- Wear your NEUPRO patch for 24 hours.
- After 24 hours, remove your NEUPRO patch and apply a new one right away to a different area of your skin.
Where to apply NEUPRO:
- Choose an area of clean, dry, and healthy skin on the stomach, thigh, hip, side of the body between the ribs and the pelvis (flank), shoulder, or upper arm. See Figure B .
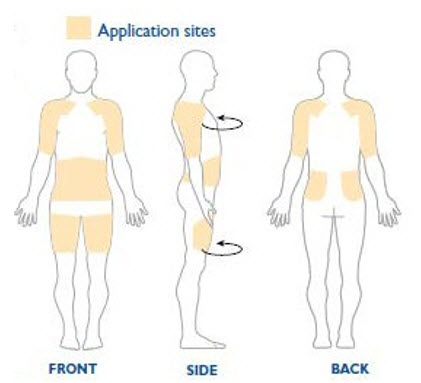
- Apply your NEUPRO patch to a different place on your skin each day, for example, from the right side to the left side and from the upper body to the lower body. Your NEUPRO patch should not be applied to the same area of your skin more than 1 time every 14 days. Apply NEUPRO to a different area of skin (only one of the shaded areas in Figure B) each day to reduce the chance of getting skin irritation.
- If you need to apply your NEUPRO patch to a hairy area, the area should be shaved at least 3 days before applying the patch.
- Avoid applying your NEUPRO patch to areas where it could be rubbed by tight clothing or under a waistband.
- Avoid applying your NEUPRO patch on skin folds.
- Do not apply your NEUPRO patch to skin that is red, irritated, or injured.
- Avoid applying creams, lotions, ointments, oils, and powders to the skin area where your NEUPRO patch will be placed.
How to apply NEUPRO:
| Step 1 . | Grasp the two sides of the pouch and pull apart. See Figures C and D . |
 |  |
| Step 2 . | Remove your NEUPRO patch from the pouch. See Figure E . |
| Step 3 . | Hold your NEUPRO patch with both hands, with the protective liner on top. See Figure F . |
| Step 4 . | Bend the edges of your NEUPRO patch away from you so that the S-shaped cut in the liner opens up. See Figure G . |
| Step 5. | Peel off one half of the protective liner. Do not touch the sticky surface of your NEUPRO patch because the medicine could come off on your fingers. See Figure H . |
| Step 6. | Apply the sticky half of your NEUPRO patch to a clean area of your skin and remove the remaining liner. See Figures I and J . |
 |  |
| Step 7. | Press your NEUPRO patch firmly with the palm of your hand for 30 seconds to make sure there is good contact with your skin, especially around the edges. The warmth of your hand helps the adhesive on the patch to stick to your skin. Make sure that your NEUPRO patch is flat against your skin. There should be no bumps or folds in your NEUPRO patch. See Figure K . |
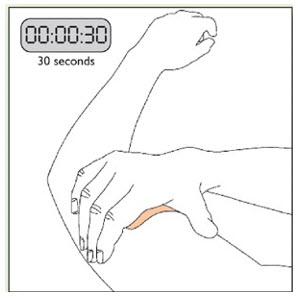
| Step 8 . | Wash your hands with soap and water right after handling your NEUPRO patch to remove any medicine that may have gotten on them. Do not touch your eyes until after you have washed your hands. |
How to remove NEUPRO:
- Slowly and carefully peel off your used NEUPRO patch. Carefully fold it in half (sticky sides together) and throw away the folded patch so that children and pets cannot reach it. Your NEUPRO patch still contains some medicine and could harm a child or pet.
- Gently wash the area with warm water and mild soap to remove any sticky material (adhesive) that stays on your skin.
- Baby or mineral oil may also be used to remove any adhesive. Avoid using alcohol or other solvents, such as nail polish remover. They may cause your skin to become irritated.
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- You may see mild redness at the site when a patch is removed like when you remove an adhesive bandage. This redness should go away over time. If irritation or itchiness continues, tell your doctor.
This Patient Package Insert and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for: UCB, Inc., Smyrna, GA 30080
Neupro ® is a registered trademark of the UCB Group of Companies. ©2021 UCB, Inc., Smyrna, GA 30080. All rights reserved.
Rev. 7/2021
Mechanism of Action
Rotigotine is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. The precise mechanism of action of rotigotine as a treatment for Parkinson's disease is unknown, although it is thought to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors within the caudate-putamen in the brain. The precise mechanism of action of rotigotine as a treatment for Restless Legs Syndrome is unknown but is thought to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors.