Odomzo prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Odomzo patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended dosage: 200 mg orally once daily taken on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. (2.2 )
Important Safety Information
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ODOMZO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ODOMZO is 200 mg taken orally once daily on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal, administered until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Obtain serum creatine kinase (CK) levels and renal function tests prior to initiating ODOMZO in all patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
If a dose of ODOMZO is missed, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Interrupt ODOMZO for
- Severe or intolerable musculoskeletal adverse reactions.
- First occurrence of serum CK elevation between 2.5 and 10 times upper limit of normal (ULN).
- Recurrent serum CK elevation between 2.5 and 5 times ULN.
Resume ODOMZO at 200 mg daily upon resolution of clinical signs and symptoms.
Permanently discontinue ODOMZO for
- Serum CK elevation greater than 2.5 times ULN with worsening renal function.
- Serum CK elevation greater than 10 times ULN.
- Recurrent serum CK elevation greater than 5 times ULN.
- Recurrent severe or intolerable musculoskeletal adverse reactions.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Odomzo prescribing information
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
- ODOMZO can cause embryo-fetal death or severe birth defects when administered to a pregnant woman. ODOMZO is embryotoxic, fetotoxic, and teratogenic in animals [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1) andUse in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
- Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating therapy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 20 months after the last dose [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1) andUse in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
- Advise males of the potential risk of exposure through semen and to use condoms with a pregnant partner or a female partner of reproductive potential during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 8 months after the last dose [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1) andUse in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ODOMZO (sonidegib) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) that has recurred following surgery or radiation therapy, or those who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended dosage: 200 mg orally once daily taken on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. (2.2 )
Important Safety Information
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ODOMZO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ODOMZO is 200 mg taken orally once daily on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal, administered until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Obtain serum creatine kinase (CK) levels and renal function tests prior to initiating ODOMZO in all patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
If a dose of ODOMZO is missed, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Interrupt ODOMZO for
- Severe or intolerable musculoskeletal adverse reactions.
- First occurrence of serum CK elevation between 2.5 and 10 times upper limit of normal (ULN).
- Recurrent serum CK elevation between 2.5 and 5 times ULN.
Resume ODOMZO at 200 mg daily upon resolution of clinical signs and symptoms.
Permanently discontinue ODOMZO for
- Serum CK elevation greater than 2.5 times ULN with worsening renal function.
- Serum CK elevation greater than 10 times ULN.
- Recurrent serum CK elevation greater than 5 times ULN.
- Recurrent severe or intolerable musculoskeletal adverse reactions.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 200 mg, opaque pink colored with ‘SONIDEGIB 200MG’ printed on the body and ‘NVR’ printed on the cap in black ink (equivalent to 281 mg of diphosphate salt of sonidegib).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action and data from animal reproduction studies, ODOMZO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ]. There are no available data on the use of ODOMZO in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of sonidegib during organogenesis at doses below the recommended human dose of 200 mg resulted in embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rabbits (see Data). Teratogenic effects observed included severe midline defects, missing digits, and other irreversible malformations. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Report pregnancies to Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-406-7984.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 15-20%.
Data
Animal Data
Daily oral administration of sonidegib to pregnant rabbits resulted in abortion, complete resorption of fetuses, or severe malformations at ≥ 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.05 times the recommended human dose based on AUC). Teratogenic effects included vertebral, distal limb and digit malformations, severe craniofacial malformations, and other severe midline defects. Skeletal variations were observed when maternal exposure to sonidegib was below the limit of detection.
Lactation
No data are available regarding the presence of sonidegib in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ODOMZO and for 20 months after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on its mechanism of action and animal data, ODOMZO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ODOMZO treatment.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 20 months after the last dose.
Males
It is not known if sonidegib is present in semen. Advise male patients to use condoms, even after a vasectomy, to avoid potential drug exposure to pregnant partners and female partners of reproductive potential during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 8 months after the last dose.
Advise males not to donate semen during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 8 months after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings from animal studies, female fertility may be compromised with ODOMZO [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ODOMZO have not been established in pediatric patients.
Epiphyseal disorders, including premature fusion of the epiphyses, have been reported in pediatric patients exposed to ODOMZO in a clinical trial. In some cases, pediatric patients treated with other Hh pathway inhibitors have experienced progression of epiphyseal fusion despite discontinuation of the Hh pathway inhibitor.
Juvenile Animal Data
In a 5-week juvenile rat toxicology study, effects of sonidegib were observed in bone, teeth, reproductive tissues, and nerves at doses ≥10 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on AUC). Bone findings included thinning/closure of bone growth plate, decreased bone length and width, and hyperostosis. Findings in teeth included missing or fractured teeth, and atrophy. Reproductive tissue toxicity was evidenced by atrophy of testes, ovaries, and uterus, partial development of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles, and inflammation and aspermia of the epididymis. Nerve degeneration was also noted.
Geriatric Use
Of the 229 patients who received ODOMZO (79 patients receiving 200 mg daily and 150 patients receiving 800 mg daily) in BOLT, 54% were 65 years and older, while 28% were 75 years and older. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients. There was a higher incidence of serious adverse reactions, Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions, and adverse reactions requiring dose interruption or discontinuation in patients ≥65 years compared with younger patients; this was not attributable to an increase in any specific adverse event.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Advise patients not to donate blood or blood products during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 20 months after the last dose. (5.1 )
- Musculoskeletal Adverse Reactions: Obtain serum creatine kinase (CK) and creatinine levels prior to initiating therapy, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Temporary dose interruption or discontinuation of ODOMZO may be required based on the severity of musculoskeletal adverse reactions. (2.2 , 5.2 )
- Premature fusion of the epiphyses (5.3 , 8.4 )
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
ODOMZO can cause embryo-fetal death or severe birth defects when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, sonidegib was embryotoxic, fetotoxic, and teratogenic at maternal exposures below the recommended human dose of 200 mg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Females of Reproductive Potential
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ODOMZO treatment. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to use effective contraception during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 20 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
Males
Advise male patients with female partners to use condoms, even after a vasectomy, during treatment with ODOMZO and for at least 8 months after the last dose to avoid potential drug exposure in pregnant females or females of reproductive potential [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
Blood Donation
Advise patients not to donate blood or blood products while taking ODOMZO and for at least 20 months after the last dose of ODOMZO, because their blood or blood products might be given to a female of reproductive potential.
Musculoskeletal Adverse Reactions
Musculoskeletal adverse reactions, which may be accompanied by serum creatine kinase (CK) elevations, occur with ODOMZO and other drugs which inhibit the hedgehog (Hh) pathway.
In a pooled safety analysis of 12 clinical studies involving 571 patients with various advanced cancers treated with ODOMZO at doses ranging from 100 mg to 3000 mg, rhabdomyolysis (defined as serum CK increase of more than ten times the baseline value with a concurrent 1.5-fold or greater increase in serum creatinine above baseline value) occurred in one patient (0.2%) treated with ODOMZO 800 mg.
In the BOLT study, musculoskeletal adverse reactions occurred in 68% (54/79) of patients treated with ODOMZO 200 mg daily with 9% (7/79) reported as Grade 3 or 4. The most frequent manifestations of musculoskeletal adverse reactions reported as an adverse event were muscle spasms (54%), musculoskeletal pain (32%), and myalgia (19%). Increased serum CK laboratory values occurred in 61% (48/79) of patients with 8% (6/79) of patients having Grade 3 or 4 serum CK elevations. Musculoskeletal pain and myalgia usually preceded serum CK elevation. Among patients with Grade 2 or higher CK elevations, the median time to onset was 12.9 weeks (range: 2 to 39 weeks) and the median time to resolution (to ≤ Grade 1) was 12 days (95% CI: 8 to 14 days). ODOMZO was temporarily interrupted in 8% of patients or permanently discontinued in 8% of patients for musculoskeletal adverse reactions. The incidence of musculoskeletal adverse reactions requiring medical intervention (magnesium supplementation, muscle relaxants, and analgesics or narcotics) was 29%, including four patients (5%) who received intravenous hydration or were hospitalized.
Obtain baseline serum CK and creatinine levels prior to initiating ODOMZO, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated (e.g., if muscle symptoms are reported). Obtain serum creatinine and CK levels at least weekly in patients with musculoskeletal adverse reactions with concurrent serum CK elevation greater than 2.5 times ULN until resolution of clinical signs and symptoms. Depending on the severity of symptoms, temporary dose interruption or discontinuation may be required for musculoskeletal adverse reactions or serum CK elevation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] . Advise patients starting therapy with ODOMZO of the risk of muscle-related adverse reactions. Advise patients to report promptly any new unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness occurring during treatment or that persists after discontinuing ODOMZO.
Premature Fusion of the Epiphyses
Premature fusion of the epiphyses has been reported in pediatric patients exposed to ODOMZO and other Hh pathway inhibitors. Despite discontinuation of drug, cases of progressive of epiphyseal fusion have been reported in pediatric patients receiving other Hh pathway inhibitors. ODOMZO is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Musculoskeletal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of ODOMZO was evaluated in BOLT, a randomized, double-blind, multiple cohort trial in which 229 patients received ODOMZO at either 200 mg (n=79) or 800 mg (n=150) daily. The frequency of common adverse reactions including muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, fatigue, nausea, decreased weight, decreased appetite, myalgia, pain, and vomiting was greater in patients treated with ODOMZO 800 mg as compared to 200 mg.
The data described below reflect exposure to ODOMZO 200 mg daily in 79 patients with locally advanced BCC (laBCC; n=66) or metastatic BCC (mBCC; n=13) enrolled in BOLT. Patients were followed for at least 18 months unless discontinued earlier. The median duration of treatment with ODOMZO was 11.0 months (range 1.3 to 33.5 months).
The study population characteristics were: median age of 67 years (range 25 to 92; 59% were ≥65 years), 61% male, and 90% white. The majority of patients had prior surgery (75%), radiotherapy (24%), systemic chemotherapy (4%), or topical or photodynamic therapies (18%) for treatment of BCC. No patient had prior exposure to a Hh pathway inhibitor.
ODOMZO was permanently discontinued in 34% of patients or temporarily interrupted in 20% of patients for adverse reactions. Adverse reactions reported in at least two patients that led to discontinuation of the drug were: muscle spasms, and dysgeusia (each 5%), asthenia, increased lipase, and nausea (each 4%), fatigue, decreased appetite, alopecia, and decreased weight (each 3%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥10% of patients treated with ODOMZO 200 mg were muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, fatigue, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, decreased weight, decreased appetite, myalgia, abdominal pain, headache, pain, vomiting, and pruritus (Table 1).
The key laboratory abnormalities are described in Table 2.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥10% of Patients in BOLT
Adverse Reaction | ODOMZO 200 mg (N=79) | |
a No Grade 4 adverse reactions were reported. | ||
All Grades a % | Grade 3 % | |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||
Muscle spasms | 54 | 3 |
Musculoskeletal pain | 32 | 1 |
Myalgia | 19 | 0 |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
Alopecia | 53 | 0 |
Pruritus | 10 | 0 |
Nervous system | ||
Dysgeusia | 46 | 0 |
Headache | 15 | 1 |
General | ||
Fatigue | 41 | 4 |
Pain | 14 | 1 |
Gastrointestinal | ||
Nausea | 39 | 1 |
Diarrhea | 32 | 1 |
Abdominal pain | 18 | 0 |
Vomiting | 11 | 1 |
Investigations | ||
Decreased weight | 30 | 3 |
Metabolism and nutrition | ||
Decreased appetite | 23 | 1 |
Table 2: Key Laboratory Abnormalities a in BOLT
Laboratory Test | ODOMZO 200 mg (N=79) | |
a Based on worst post-treatment laboratory value regardless of baseline; grading by CTCAE v4.03. b The serum creatinine level remained within normal range in 76% (60/79) of patients. | ||
All Grades % | Grades 3-4 % | |
Chemistry | ||
Increased serum creatinine | 92 b | 0 |
Increased serum creatine kinase (CK) | 61 | 8 |
Hyperglycemia | 51 | 4 |
Increased lipase | 43 | 13 |
Increased alanine aminotransferase | 19 | 4 |
Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 19 | 4 |
Increased amylase | 16 | 1 |
Hematology | ||
Anemia | 32 | 0 |
Lymphopenia | 28 | 3 |
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea lasting for at least 18 months occurred in two of 14 pre-menopausal women treated with ODOMZO 200 mg or 800 mg once daily.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of Other Drugs on ODOMZO
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant administration of ODOMZO with strong CYP3A inhibitors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Avoid concomitant administration of ODOMZO with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If a moderate CYP3A inhibitor must be used, administer the moderate CYP3A inhibitor for less than 14 days and monitor closely for adverse reactions particularly musculoskeletal adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Avoid concomitant administration of ODOMZO with strong and moderate CYP3A inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
DESCRIPTION
Sonidegib is a Hh pathway inhibitor. The molecular formula for sonidegib phosphate is C 26 H 26 F 3 N 3 O 3 • 2H 3 PO 4 . The molecular weight is 681.49 daltons. The chemical name is N-[6-(cis-2,6-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl)pyridine-3-yl]-2-methyl-4’-(trifluoromethoxy) [1,1’-biphenyl]-3-carboxamide diphosphate. The molecular structure is shown below:
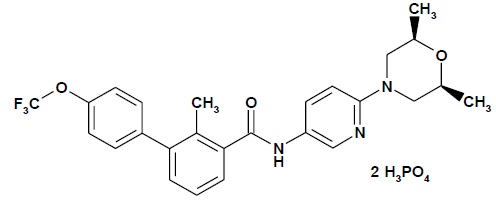
Sonidegib phosphate is a white to off-white powder. Sonidegib freebase is practically insoluble.
ODOMZO (sonidegib) capsules for oral use contain 200 mg of sonidegib as the freebase (equivalent to 281 mg of diphosphate salt of sonidegib) and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, poloxamer and sodium lauryl sulfate. The opaque pink hard gelatin capsule shell contains gelatin, red iron oxide, and titanium dioxide. The black printing ink contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sonidegib is an inhibitor of the Hh pathway. Sonidegib binds to and inhibits Smoothened, a transmembrane protein involved in Hh signal transduction.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose of 800 mg once daily, sonidegib does not prolong the QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
Sonidegib exhibited dose-proportional increases in the area under the curve (AUC) and the maximal concentration (C max ) over the dose range of 100 mg to 400 mg, but less than dose-proportional increases at doses greater than 400 mg. Steady-state was reached approximately 4 months after starting ODOMZO and the estimated accumulation at steady-state was 19-fold. Following a dose of 200 mg once daily, the estimated mean steady-state C max is 1030 ng/mL, AUC 0-24h is 22 μg•h/mL and minimal concentration (C min ) is 890 ng/mL.
Absorption
Less than 10% of an oral dose of ODOMZO is absorbed. Following the administration of a single ODOMZO dose (100 mg to 3000 mg) under fasted conditions in patients with cancer, the median time-to-peak concentration (T max ) was 2 to 4 hours.
Effect of Food
A high-fat meal (approximately 1000 calories with 50% of calories from fat) increased exposure to sonidegib (geometric mean AUC inf and C max ) by 7.4- to 7.8-fold [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Distribution
The estimated apparent steady-state volume of distribution (V ss /F) was 9,166 L. Sonidegib was greater than 97% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro and the binding was concentration independent. In vitro studies suggested that sonidegib is not a substrate of P-glycoprotein, MRP2 or BCRP.
Elimination
The elimination half-life (t 1/2 ) of sonidegib estimated from population pharmacokinetic (PK) modeling was approximately 28 days.
Metabolism
Sonidegib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A. The main circulating compound was unchanged sonidegib (36% of circulating radioactivity).
Excretion
Sonidegib and its metabolites are eliminated primarily by the hepatic route. Of the absorbed dose, approximately 70% was eliminated in the feces and 30% was eliminated in the urine. Unchanged sonidegib was not detectable in the urine.
Specific Populations
Age, body weight, hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A, B and C), mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to 89 mL/min) and sex had no clinically meaningful effect on sonidegib steady-state exposure.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
A cross study comparison suggests that geometric mean AUC inf of sonidegib is 1.7-fold higher in Japanese healthy subjects compared to Western healthy subjects (Whites and Blacks) following a single 200 mg dose of ODOMZO.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effects of CYP3A Inhibitors on Sonidegib
Strong CYP3A inhibitor: The geometric mean sonidegib AUC 0-10d increased by 2.2-fold and the C max increased by 1.5-fold when ODOMZO at a dose of 800 mg was taken with ketoconazole compared to ODOMZO alone [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . The geometric mean sonidegib steady-state AUC 0-24h would similarly increase in cancer patients taking ODOMZO 200 mg once daily when coadministered with a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 14 days.
Moderate CYP3A inhibitor: The geometric mean sonidegib steady-state AUC 0-24h would increase 1.8-fold when ODOMZO 200 mg once daily is coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor (erythromycin) for 14 days and would increase 2.8-fold when ODOMZO 200 mg once daily is coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor (erythromycin) for 4 months.
Effects of CYP3A Inducers on Sonidegib
Strong CYP3A inducer: The geometric mean sonidegib AUC 0-10d decreased by 72% and the C max decreased by 54% when ODOMZO at a dose of 800 mg was taken with rifampicin compared to ODOMZO alone [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Moderate CYP3A inducer: The geometric mean sonidegib steady-state AUC 0-24h would decrease 56% in cancer patients taking ODOMZO 200 mg once daily when coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inducer (efavirenz) for 14 days and would decrease 69% when coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inducer (efavirenz) for 4 months [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Effect of Sonidegib on Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Transporters
In vitro studies suggested that sonidegib inhibits CYP2B6 and CYP2C9 and it does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A expression or activity.
In vitro studies suggested that sonidegib inhibits BCRP, but not P-glycoprotein, MRP2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1 or OCT2.
Effects of Acid Reducing Agents on Sonidegib
No clinically meaningful effect on sonidegib exposure was observed when ODOMZO at dose of 200 mg was coadministered with esomeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies were performed in mice and rats. No carcinogenic potential was identified in either species.
Sonidegib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic or aneugenic in the in vitro human chromosome aberration assay or in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Sonidegib resulted in a lack of fertility when administered to female rats at ≥20 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.3 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area (BSA). A reduction of the number of pregnant females, an increase in the number of early resorptions, and a decrease in the number of viable fetuses was also noted at 2 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.12 times the recommended human dose based on BSA). In addition, in a 6 month repeat-dose toxicology study in rats, effects on female reproductive organs included atrophy of the uterus and ovaries at doses of 10 mg/kg (approximately ≥2 times the exposure in humans at the recommended dose of 200 mg based on AUC). No adverse effects on fertility were noted when male rats were administered sonidegib at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Body tremors along with significant increases in creatine kinase were observed in rats administered oral sonidegib for 13 weeks or longer at ≥10 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥2 times the recommended human dose based on AUC).
CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and effectiveness of ODOMZO were evaluated in a single, multicenter, double-blind, multiple cohort clinical trial conducted in patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (laBCC) (n=194) or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (mBCC) (n=36) (BOLT, NCT01327053). Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either ODOMZO 800 mg or 200 mg orally, once daily, until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Randomization was stratified by stage of disease (locally advanced or metastatic), laBCC disease histology (aggressive vs. non-aggressive), and geographic region. Patients with laBCC were required to have lesions for which radiotherapy was contraindicated or inappropriate (e.g., Gorlin syndrome or limitations because of location of tumor), that had recurred after radiotherapy, that were unresectable or for which surgical resection would result in substantial deformity, or that had recurred after prior surgical resection.
The major efficacy outcome measure of the trial was objective response rate (ORR) as determined by blinded central review according to modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) for patients with laBCC or RECIST version 1.1 for patients with mBCC. Duration of response (DoR), determined by blinded central review, was a key secondary outcome measure.
For patients with laBCC, the evaluation of tumor response was based on a composite assessment that integrated tumor measurements obtained by radiographic assessments of target lesions (per RECIST 1.1), digital clinical photography, and histopathology assessments (via punch biopsies). All modalities used must have demonstrated absence of tumor to achieve a composite assessment of complete response (CR). Response by digital clinical photography was evaluated by World Health Organization (WHO) adapted criteria [partial response (PR): ≥50% decrease in the sum of the product of perpendicular diameters (SPD) of the lesions, CR: disappearance of all lesions, progressive disease (PD): ≥25% increase in the SPD of the lesions]. Multiple punch biopsies of target lesions were performed to confirm a CR or when a response assessment was confounded by presence of lesion ulceration, cyst, and or scarring/fibrosis.
A total of 66 patients randomized to ODOMZO 200 mg daily had laBCC. Three of these patients had a diagnosis of Gorlin Syndrome. The demographic characteristics of the 66 patients with laBCC were: median age of 67 years (range: 25 to 92 years; 58% were ≥65 years); 58% male, 89% white, and ECOG performance status of 0 (67%). Seventy-six percent of patients had prior therapy for treatment of BCC; this included surgery (73%), radiotherapy (18%), and topical/photodynamic therapies (21%). Approximately half of these patients (56%) had aggressive histology.
Patients with laBCC randomized to receive ODOMZO 200 mg daily were followed for at least 30 months unless discontinued earlier. The ORR was 56% (95% confidence interval: 43, 68), consisting of 3 (5%) complete responses and 34 (52%) partial responses. A pre-specified sensitivity analysis using an alternative definition for complete response, defined as at least a PR according to MRI and/or photography and no evidence of tumor on biopsy of the residual lesion, yielded a CR rate of 21%. The median duration of response was 26.1 months (95% CI:10.1, not reached).
A total of 128 patients randomized to ODOMZO 800 mg daily had laBCC. Twelve of these patients had a diagnosis of Gorlin Syndrome. There was no evidence of better antitumor activity (ORR) among patients with laBCC randomized to receive ODOMZO 800 mg daily and followed for at least 30 months unless discontinued earlier.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each ODOMZO capsule has an opaque pink color with ‘SONIDEGIB 200MG’ printed on the capsule body and ‘NVR’ printed on the cap in black ink. ODOMZO capsules are supplied as follows:
Bottle of 30 capsules NDC 47335-303-83
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
Sonidegib is an inhibitor of the Hh pathway. Sonidegib binds to and inhibits Smoothened, a transmembrane protein involved in Hh signal transduction.