Opsumit prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Opsumit patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 10 mg once daily . Doses higher than 10 mg once daily have not been studied in patients with PAH and are not recommended (2.1 ).
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of OPSUMIT is 10 mg once daily for oral administration. Doses higher than 10 mg once daily have not been studied in patients with PAH and are not recommended.
Pregnancy Testing in Females of Reproductive Potential
Exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment with OPSUMIT in females of reproductive potential [see Boxed Warning , Contraindications (4.1) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Opsumit prescribing information
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
OPSUMIT is contraindicated for use during pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm based on animal data [see Contraindications (4.1) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Therefore, for females of reproductive potential, exclude pregnancy before the start of treatment with OPSUMIT. Advise use of effective contraception before the initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after stopping treatment with OPSUMIT [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ]. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue OPSUMIT as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Boxed Warning | 4/2025 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) | 4/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) | 4/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2) | Removal 4/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
OPSUMIT is an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, WHO Group I) in adults to reduce the risks of disease progression and hospitalization for PAH (1.1 ).
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
OPSUMIT is an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, WHO Group I) in adults to reduce the risks of disease progression and hospitalization for PAH.
Effectiveness was established in a long-term study in PAH patients with predominantly WHO Functional Class II–III symptoms treated for an average of 2 years. Patients had idiopathic and heritable PAH (57%), PAH caused by connective tissue disorders (31%), and PAH caused by congenital heart disease with repaired shunts (8%) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 10 mg once daily . Doses higher than 10 mg once daily have not been studied in patients with PAH and are not recommended (2.1 ).
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of OPSUMIT is 10 mg once daily for oral administration. Doses higher than 10 mg once daily have not been studied in patients with PAH and are not recommended.
Pregnancy Testing in Females of Reproductive Potential
Exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment with OPSUMIT in females of reproductive potential [see Boxed Warning , Contraindications (4.1) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 10 mg, bi-convex film-coated, round, white, and debossed with "10" on both sides.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on data from animal reproduction studies, OPSUMIT may cause embryo-fetal toxicity, including birth defects and fetal death, when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. There are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension in pregnancy [see Clinical Considerations ] . Available data from postmarketing reports and published literature over decades of use with ERAs in the same class as OPSUMIT have not identified an increased risk of major birth defects; however, these data are limited. Methodological limitations of these postmarketing reports and published literature include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and missing data. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal ERA use. Macitentan was teratogenic in rabbits and rats at all doses tested. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, advise the patient of the risk to a fetus [see Contraindications (4.1) ] .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
In patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension, pregnancy is associated with an increased rate of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, including spontaneous abortion, intrauterine growth restriction and premature labor.
Data
Animal Data
In both rabbits and rats, there were cardiovascular and mandibular arch fusion abnormalities. Administration of macitentan to female rats from late pregnancy through lactation caused reduced pup survival and impairment of the male fertility of the offspring at all dose levels tested.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of macitentan in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effect on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from OPSUMIT advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with OPSUMIT.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on data from animal reproductive toxicity studies, OPSUMIT can cause fetal harm, including birth defects and fetal death, when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify that patients who can become pregnant are not pregnant prior to initiating OPSUMIT. The patient should contact their physician immediately for pregnancy testing if onset of menses is delayed or pregnancy is suspected. If the pregnancy test is positive, the physician and patient should discuss the risks to the pregnancy, and the fetus.
Contraception
Patients who can become pregnant who are using OPSUMIT should use an effective method of contraception prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with OPSUMIT to prevent pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Infertility
Based on findings in animals, OPSUMIT may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether effects on fertility would be reversible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of OPSUMIT in pediatric patients have not been established for the treatment of PAH.
OPSUMIT was evaluated in 148 pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age with PAH in a single open-label, randomized trial with an extension period in which all patients received treatment. The trial did not demonstrate a clinical benefit of OPSUMIT compared with standard of care in the treatment of PAH. It cannot be ruled out that a trial with a different design would demonstrate a clinical benefit in this patient population. Adverse reactions observed in the trial were similar in nature to those reported in clinical trials in adults.
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in the clinical study of OPSUMIT for PAH, 14% were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
OPSUMIT may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. OPSUMIT is contraindicated in females who are pregnant. OPSUMIT was consistently shown to have teratogenic effects when administered to animals. If OPSUMIT is used during pregnancy, advise the patient of the potential risk to a fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Hypersensitivity
OPSUMIT is contraindicated in patients with a history of a hypersensitivity reaction to macitentan or any component of the product [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- ERAs cause hepatotoxicity and liver failure. Obtain baseline liver enzymes and monitor as clinically indicated (5.2 ).
- Fluid retention may require intervention (5.3 ).
- Decreases in hemoglobin (5.4 ).
- Pulmonary edema in patients with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. If confirmed, discontinue treatment (5.5 ).
- Decreases in sperm count have been observed in patients taking ERAs (5.6 ).
Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal reproduction studies, OPSUMIT may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy. The available human data for ERAs do not establish the presence or absence of major birth defects related to the use of OPSUMIT. Advise patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Obtain a pregnancy test prior to initiation of therapy with OPSUMIT. Advise patients who can become pregnant to use effective contraceptive methods prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with OPSUMIT. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue use as soon as possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Contraindications (4.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
Hepatotoxicity
ERAs have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. The incidence of elevated aminotransferases in the study of OPSUMIT in PAH is shown in Table 1.
| OPSUMIT 10 mg (N=242) | Placebo (N=249) | |
|---|---|---|
| >3 × ULN | 3.4% | 4.5% |
| >8 × ULN | 2.1% | 0.4% |
In the placebo-controlled study of OPSUMIT, discontinuations for hepatic adverse events were 3.3% in the OPSUMIT 10 mg group vs. 1.6% for placebo.
Obtain liver enzyme tests prior to initiation of OPSUMIT and repeat during treatment as clinically indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
Advise patients to report symptoms suggesting hepatic injury (nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, fatigue, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, fever, or itching). If clinically relevant aminotransferase elevations occur, or if elevations are accompanied by an increase in bilirubin >2 × ULN, or by clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity, discontinue OPSUMIT. Consider re-initiation of OPSUMIT when hepatic enzyme levels normalize in patients who have not experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity.
Fluid Retention
Peripheral edema and fluid retention are known clinical consequences of PAH and known effects of ERAs. In the placebo-controlled study of OPSUMIT in PAH, the incidence of edema was 21.9% in the OPSUMIT 10 mg group and 20.5% in the placebo group.
Patients with underlying left ventricular dysfunction may be at particular risk for developing significant fluid retention after initiation of ERA treatment. In a small study of OPSUMIT in patients with pulmonary hypertension because of left ventricular dysfunction, more patients in the OPSUMIT group developed significant fluid retention and had more hospitalizations because of worsening heart failure compared to those randomized to placebo. Postmarketing cases of edema and fluid retention occurring within weeks of starting OPSUMIT, some requiring intervention with a diuretic or hospitalization for decompensated heart failure, have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
Monitor for signs of fluid retention after OPSUMIT initiation. If clinically significant fluid retention develops, evaluate the patient to determine the cause, such as OPSUMIT or underlying heart failure, and the possible need to discontinue OPSUMIT.
Hemoglobin Decrease
Decreases in hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit have occurred following administration of other ERAs and were observed in clinical studies with OPSUMIT. These decreases occurred early and stabilized thereafter. In the placebo-controlled study of OPSUMIT in PAH, OPSUMIT 10 mg caused a mean decrease in hemoglobin from baseline to up to 18 months of about 1.0 g/dL compared to no change in the placebo group. A decrease in hemoglobin to below 10.0 g/dL was reported in 8.7% of the OPSUMIT 10 mg group and in 3.4% of the placebo group. Decreases in hemoglobin seldom require transfusion. Initiation of OPSUMIT is not recommended in patients with severe anemia. Measure hemoglobin prior to initiation of treatment and repeat during treatment as clinically indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Pulmonary Edema with Pulmonary Veno-occlusive Disease (PVOD)
Should signs of pulmonary edema occur, consider the possibility of associated PVOD. If confirmed, discontinue OPSUMIT.
Decreased Sperm Counts
OPSUMIT, like other ERAs, may have an adverse effect on spermatogenesis. Counsel men about potential effects on fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinically significant adverse reactions that appear in other sections of the labeling include:
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Fluid Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Decrease in Hemoglobin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Safety data for OPSUMIT were obtained primarily from one placebo-controlled clinical study in 742 patients with PAH (SERAPHIN study) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
The exposure to OPSUMIT in this trial was up to 3.6 years with a median exposure of about 2 years (N=542 for 1 year; N=429 for 2 years; and N=98 for more than 3 years). The overall incidence of treatment discontinuations because of adverse events was similar across OPSUMIT 10 mg and placebo treatment groups (approximately 11%).
Table 2 presents adverse reactions more frequent on OPSUMIT than on placebo by ≥3%.
| Adverse Reaction | OPSUMIT 10 mg (N=242) (%) | Placebo (N=249) (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia | 13 | 3 |
| Nasopharyngitis/pharyngitis | 20 | 13 |
| Bronchitis | 12 | 6 |
| Headache | 14 | 9 |
| Influenza | 6 | 2 |
| Urinary tract infection | 9 | 6 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of OPSUMIT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions (angioedema, pruritus and rash)
Vascular disorders : flushing
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: nasal congestion
Gastrointestinal disorders: Elevations of liver aminotransferases (ALT, AST) and liver injury have been reported with OPSUMIT use; in most cases alternative causes could be identified (heart failure, hepatic congestion, autoimmune hepatitis). Endothelin receptor antagonists have been associated with elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and cases of liver failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
General disorders and administration site conditions: edema/fluid retention. Cases of edema and fluid retention occurred within weeks of starting OPSUMIT, some requiring intervention with a diuretic, fluid management or hospitalization for decompensated heart failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Cardiac disorders: symptomatic hypotension
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A4 inducers (rifampin) reduce exposure to macitentan: avoid co-administration with OPSUMIT (7.1 , 12.3 ).
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (ketoconazole, ritonavir) increase exposure to macitentan: avoid co-administration with OPSUMIT (7.2 , 12.3 ) .
- Moderate dual CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 inhibitors (fluconazole, amiodarone) or use of combined CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 inhibitors may increase exposure to macitentan: avoid co-administration with OPSUMIT (7.3 , 12.3 ).
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Strong inducers of CYP3A4 such as rifampin significantly reduce macitentan exposure. Concomitant use of OPSUMIT with strong CYP3A4 inducers should be avoided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole approximately double macitentan exposure. Many HIV drugs like ritonavir are strong inhibitors of CYP3A4. Avoid concomitant use of OPSUMIT with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Use other PAH treatment options when strong CYP3A4 inhibitors are needed as part of HIV treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Moderate Dual or Combined CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 Inhibitors
Concomitant use of moderate dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 such as fluconazole is predicted to increase macitentan exposure approximately 4-fold based on physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling. Avoid concomitant use of OPSUMIT with moderate dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 (such as fluconazole and amiodarone) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Concomitant treatment of both a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and moderate CYP2C9 inhibitor with OPSUMIT should also be avoided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
DESCRIPTION
OPSUMIT ® (macitentan) is an endothelin receptor antagonist. The chemical name of macitentan is N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N'-propylsulfamide. It has a molecular formula of C 19 H 20 Br 2 N 6 O 4 S and a molecular weight of 588.27. Macitentan is achiral and has the following structural formula:
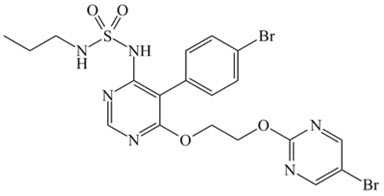
Macitentan is a crystalline powder that is insoluble in water. In the solid state macitentan is very stable, is not hygroscopic, and is not light sensitive.
OPSUMIT is available as a 10 mg film-coated tablet for once daily oral administration. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate Type A. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyvinyl alcohol, soya lecithin, talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Endothelin (ET)-1 and its receptors (ET A and ET B ) mediate a variety of deleterious effects, such as vasoconstriction, fibrosis, proliferation, hypertrophy, and inflammation. In disease conditions such as PAH, the local ET system is upregulated and is involved in vascular hypertrophy and in organ damage.
Macitentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist that inhibits the binding of ET-1 to both ET A and ET B receptors. Macitentan displays high affinity and sustained occupancy of the ET receptors in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. One of the metabolites of macitentan is also pharmacologically active at the ET receptors and is estimated to be about 20% as potent as the parent drug in vitro . The clinical impact of dual endothelin blockage is unknown.
Pharmacodynamics
Pulmonary Hemodynamics
The clinical efficacy study in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension assessed hemodynamic parameters in a subset of patients after 6 months of treatment. Patients treated with OPSUMIT 10 mg (N=57) achieved a median reduction of 37% (95% CI 22–49) in pulmonary vascular resistance and an increase of 0.6 L/min/m 2 (95% CI 0.3–0.9) in cardiac index compared to placebo (N=67).
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a randomized, placebo-controlled four-way crossover study with a positive control in healthy subjects, repeated doses of macitentan 10 and 30 mg (3 times the recommended dosage) had no significant effect on the QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of macitentan and its active metabolite have been studied primarily in healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of macitentan are dose proportional over a range from 1 mg to 30 mg after once daily administration.
A cross study comparison shows that the exposures to macitentan and its active metabolite in patients with PAH are similar to those observed in healthy subjects.
Absorption and Distribution
The maximum plasma concentration of macitentan is achieved about 8 hours after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability after oral administration is not known. In a study in healthy subjects, the exposure to macitentan and its active metabolite were unchanged after a high fat breakfast. Macitentan may therefore be taken with or without food.
Macitentan and its active metabolite are highly bound to plasma proteins (>99%), primarily to albumin and to a lesser extent to alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. The apparent volumes of distribution (Vss/F) of macitentan and its active metabolite were about 50 L and 40 L respectively in healthy subjects.
Metabolism and Elimination
Following oral administration, the apparent elimination half-lives of macitentan and its active metabolite are approximately 16 hours and 48 hours, respectively. Macitentan is metabolized primarily by oxidative depropylation of the sulfamide to form the pharmacologically active metabolite. This reaction is dependent on the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, mainly CYP3A4 with minor contributions of CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. At steady state in PAH patients, the systemic exposure to the active metabolite is 3-times the exposure to macitentan and is expected to contribute approximately 40% of the total pharmacologic activity. In a study in healthy subjects with radiolabeled macitentan, approximately 50% of radioactive drug material was eliminated in urine but none was in the form of unchanged drug or the active metabolite. About 24% of the radioactive drug material was recovered from feces.
Special Populations
There are no clinically relevant effects of age, sex, or race on the pharmacokinetics of macitentan and its active metabolite.
Renal Impairment
Exposure to macitentan and its active metabolite in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 15–29 mL/min) compared to healthy subjects was increased by 30% and 60%, respectively. This increase is not considered clinically relevant.
Hepatic Impairment
Exposure to macitentan was decreased by 21%, 34%, and 6% and exposure to the active metabolite was decreased by 20%, 25%, and 25% in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, and C), respectively. This decrease is not considered clinically relevant.
Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies
At plasma levels obtained with dosing at 10 mg once daily, macitentan has no relevant inhibitory or inducing effects on CYP enzymes. Macitentan is not a substrate or inhibitor of multi-drug resistance protein (P-gp, MDR-1). The active metabolite of macitentan also is not an inhibitor of P-gp/MDR-1 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Macitentan and its active metabolite are not expected to have significant interaction with drug transporters such as organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP1B1, OATP1B3), multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE-1, MATE-2K), bile salt export pump (BSEP), sodium-taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP), organic cation transporter (OCT-1, OCT-3), organic anion transporter (OAT-1, OAT-3) or BCRP transporter at clinically relevant plasma concentrations.
In Vivo Studies
Effect of other drugs on macitentan
The effect of other drugs on macitentan and its active metabolite are studied in healthy subjects and are shown in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1
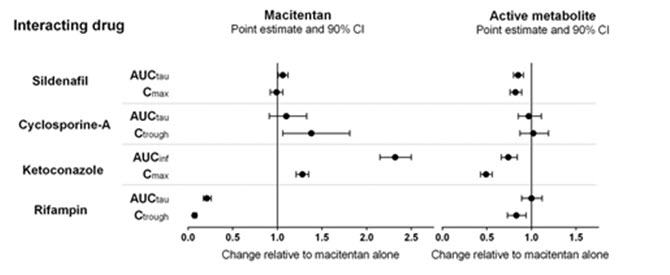
Effects of other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ritonavir on macitentan were not studied, but are likely to result in an increase in macitentan exposure at steady state similar to that seen with ketoconazole [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
PBPK modeling and simulations based analysis showed that a moderate dual inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 such as fluconazole (400 mg once daily) is predicted to increase macitentan exposure approximately 4-fold without relevant effect on the exposure to its active metabolite [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ] .
Effect of macitentan on other drugs
Warfarin : Macitentan once daily dosing did not alter the exposure to R- and S-warfarin or their effect on international normalized ratio (INR).
Sildenafil : At steady-state, the exposure to sildenafil 20 mg t.i.d. increased by 15% during concomitant administration of macitentan 10 mg once daily. This change is not considered clinically relevant.
Hormonal contraceptives : Macitentan 10 mg once daily did not affect the pharmacokinetics of an oral contraceptive (norethisterone 1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 35 µg).
BCRP Substrate drugs : Macitentan 10 mg once daily did not affect the pharmacokinetics of concomitant use of a BCRP substrate drug (riociguat 1 mg and rosuvastatin 10 mg).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of 2 years' duration did not reveal any carcinogenic potential at exposures 75-fold and 140-fold the human exposure (based on AUC) in male and female mice, respectively, and 8.3- and 42-fold in male and female rats, respectively.
Mutagenesis
Macitentan was not genotoxic in a standard battery of in vitro and in vivo assays that included a bacterial reverse mutation assay, an assay for gene mutations in mouse lymphoma cells, a chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, and an in vivo micronucleus test in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Reversible testicular tubular dilatation was observed in chronic toxicity studies at exposures greater than 7-fold and 23-fold the human exposure in rats and dogs, respectively. After 2 years of treatment, tubular atrophy was seen in rats at 4-fold the human exposure. Macitentan did not affect male or female fertility at exposures ranging from 19- to 44-fold the human exposure, respectively, and had no effect on sperm count, motility, and morphology in male rats. No testicular findings were noted in mice after treatment up to 2 years.
Animal Toxicology
In dogs, macitentan decreased blood pressure at exposures similar to the therapeutic human exposure. Intimal thickening of coronary arteries was observed at 17-fold the human exposure after 4 to 39 weeks of treatment. Due to the species-specific sensitivity and the safety margin, this finding is considered not relevant for humans.
There were no adverse liver findings in long-term studies conducted in mice, rats, and dogs at exposures of 12- to 116-fold the human exposure.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
The effect of macitentan on progression of PAH was demonstrated in a multi-center, long-term (average duration of exposure approximately 2 years), placebo-controlled study in 742 patients with symptomatic [WHO functional class (FC) II–IV] PAH who were randomized to placebo (n=250), 3 mg macitentan (n=250), or 10 mg macitentan (n=242) once daily. Patients were treated with OPSUMIT monotherapy or in combination with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.
The primary study endpoint was time to the first occurrence of death, a significant morbidity event, defined as atrial septostomy, lung transplantation, initiation of IV or subcutaneous (SC) prostanoids, or "other worsening of PAH" during double-blind treatment plus 7 days. Other worsening was defined as all of the following: 1) a sustained ≥15% decrease from baseline in 6 minute walk distance (6MWD), 2) worsening of PAH symptoms (worsening of WHO FC), and 3) need for additional treatment for PAH. All of these other worsening events were confirmed by an independent adjudication committee, blinded to treatment allocation. A critical secondary endpoint was time to PAH death or PAH hospitalization.
The mean patient age was 46 years (14% were age 65 or above). Most patients were white (55%) or Asian (29%) and female (77%). Approximately 52%, 46%, and 2% of patients were in WHO FC II, III, and IV, respectively.
Idiopathic or heritable PAH was the most common etiology in the study population (57%) followed by PAH caused by connective tissue disorders (31%), PAH caused by congenital heart disease with repaired shunts (8%), and PAH caused by other etiologies [drugs and toxins (3%) and HIV (1%)].
At baseline, the majority of enrolled patients (64%) were being treated with a stable dose of specific therapy for PAH, either oral phosphodiesterase inhibitors (61%) and/or inhaled/oral prostanoids (6%).
Study results are described for the placebo and OPSUMIT 10 mg groups. The median treatment durations were 101 and 118 weeks in the placebo and OPSUMIT 10 mg groups, respectively, up to a maximum of 188 weeks.
Treatment with OPSUMIT 10 mg resulted in a 45% reduction (HR 0.55, 97.5% CI 0.39–0.76; logrank p<0.0001) in the occurrence of the primary endpoint up to end of double-blind treatment compared to placebo (Table 3 and Figure 2). The beneficial effect of OPSUMIT 10 mg was primarily attributable to a reduction in clinical worsening events (deterioration in 6MWD and worsening of PAH symptoms and need for additional PAH treatment).
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier Estimates of the Occurrence of the Primary Endpoint Event in the SERAPHIN Study
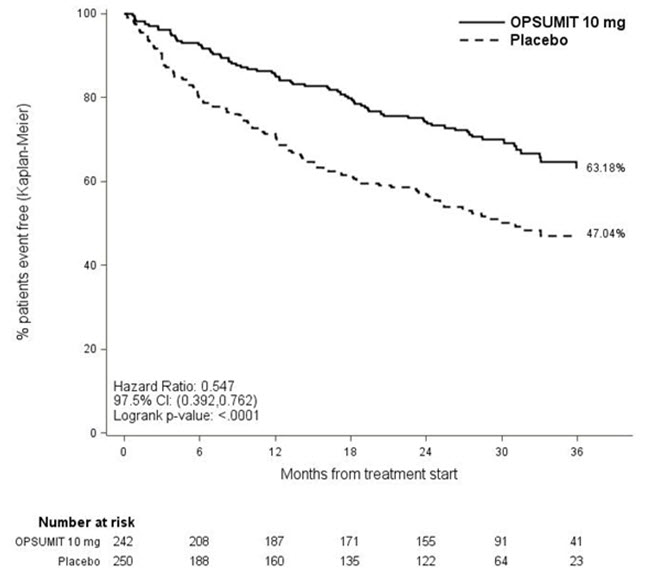
| Placebo N=250 n (%) | OPSUMIT 10 mg N=242 n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with a primary endpoint event No patients experienced an event of lung transplantation or atrial septostomy in the placebo or OPSUMIT 10 mg treatment groups. | 116 (46.4) | 76 (31.4) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Worsening PAH | 93 (37.2) | 59 (24.4) |
| Death | 17 (6.8) | 16 (6.6) |
| IV/SC prostanoid | 6 (2.4) | 1 (0.4) |
Subgroup analyses were performed to examine their influence on outcome as shown in Figure 3. Consistent efficacy of OPSUMIT 10 mg on the primary endpoint was seen across subgroups of age, sex, race, etiology, by monotherapy or in combination with another PAH therapy, baseline 6MWD, and baseline WHO FC.
Figure 3 Subgroup Analysis of the SERAPHIN Study
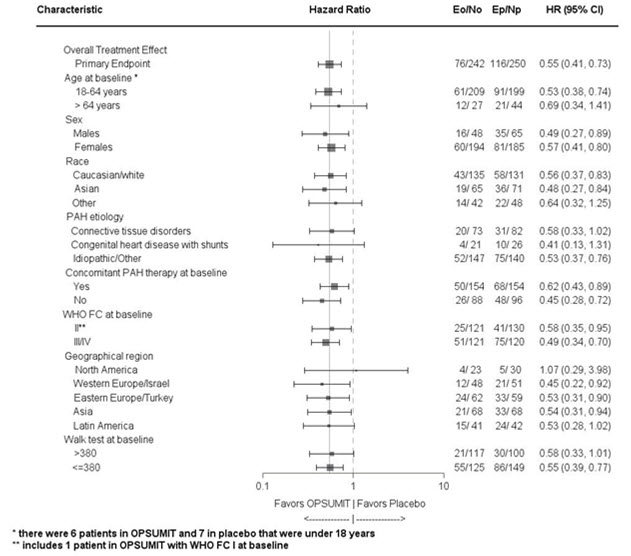
Eo = Number of events OPSUMIT 10 mg; No = Number of patients randomized to OPSUMIT 10 mg Ep = Number of events placebo; Np = Number of patients randomized to placebo
PAH related death or hospitalization for PAH was assessed as a secondary endpoint. The risk of PAH related death or hospitalization for PAH was reduced by 50% in patients receiving OPSUMIT 10 mg compared to placebo (HR 0.50, 97.5% CI 0.34–0.75; logrank p<0.0001) (Table 4 and Figure 4).
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier Estimates of the Occurrence of Death due to PAH or Hospitalization for PAH in SERAPHIN
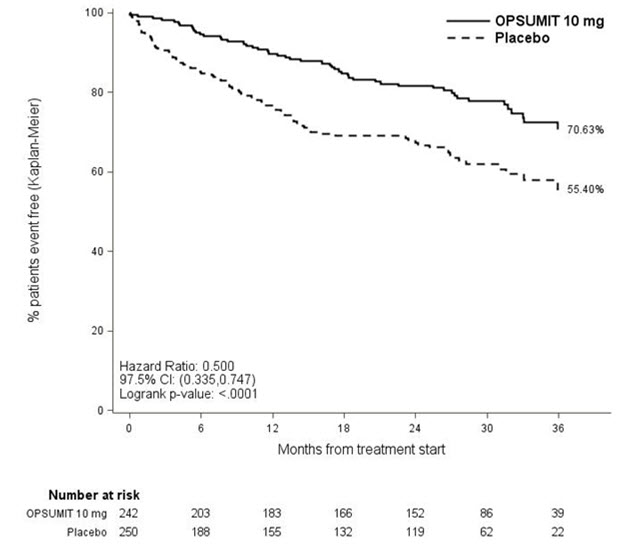
| Placebo (N=250) n (%) | OPSUMIT 10 mg (N=242) n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Death due to PAH or hospitalization for PAH | 84 (33.6) | 50 (20.7) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Death due to PAH | 5 (2.0) | 5 (2.1) |
| Hospitalization for PAH | 79 (31.6) | 45 (18.6) |
Treatment with OPSUMIT 10 mg resulted in a placebo-corrected mean increase in 6MWD of 22 meters at Month 6 (97.5% CI 3–41; p=0.0078), with significant improvement in 6MWD by Month 3. 6MWD increased more in patients with worse baseline WHO Functional Class (37 meters and 12 meters placebo-corrected mean increase in WHO FC III/IV and FC I/II, respectively). The increase in 6MWD achieved with OPSUMIT was maintained for the duration of the study.
Treatment with OPSUMIT 10 mg led to an improvement of at least one WHO Functional Class at Month 6 in 22% of patients compared to 13% of patients treated with placebo.
Long-Term Treatment of PAH
In long-term follow-up of patients who were treated with OPSUMIT 10 mg in the placebo-controlled study (N=242) and the open-label extension study, Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival at 1, 2, 5, and 7 years were 95%, 89%, 73%, and 63% respectively. The median exposure to OPSUMIT was 4.6 years. These uncontrolled observations do not allow comparison with a group not given OPSUMIT and cannot be used to determine the long term-effect of OPSUMIT on mortality.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
OPSUMIT ® (macitentan) tablets are 10 mg white, film-coated, bi-convex debossed with "10" on both sides and supplied as follows:
15 count /PVC/ PE/PVDC aluminum foil blisters in carton (NDC 66215-501-15)
30 count white high-density polyethylene bottle in carton (NDC 66215-501-30)
Store at 20 ºC to 25 ºC (68 ºF to 77 ºF). Excursions are permitted between 15 °C and 30 °C (59 °F and 86 °F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
Keep out of reach of children.
Mechanism of Action
Endothelin (ET)-1 and its receptors (ET A and ET B ) mediate a variety of deleterious effects, such as vasoconstriction, fibrosis, proliferation, hypertrophy, and inflammation. In disease conditions such as PAH, the local ET system is upregulated and is involved in vascular hypertrophy and in organ damage.
Macitentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist that inhibits the binding of ET-1 to both ET A and ET B receptors. Macitentan displays high affinity and sustained occupancy of the ET receptors in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. One of the metabolites of macitentan is also pharmacologically active at the ET receptors and is estimated to be about 20% as potent as the parent drug in vitro . The clinical impact of dual endothelin blockage is unknown.